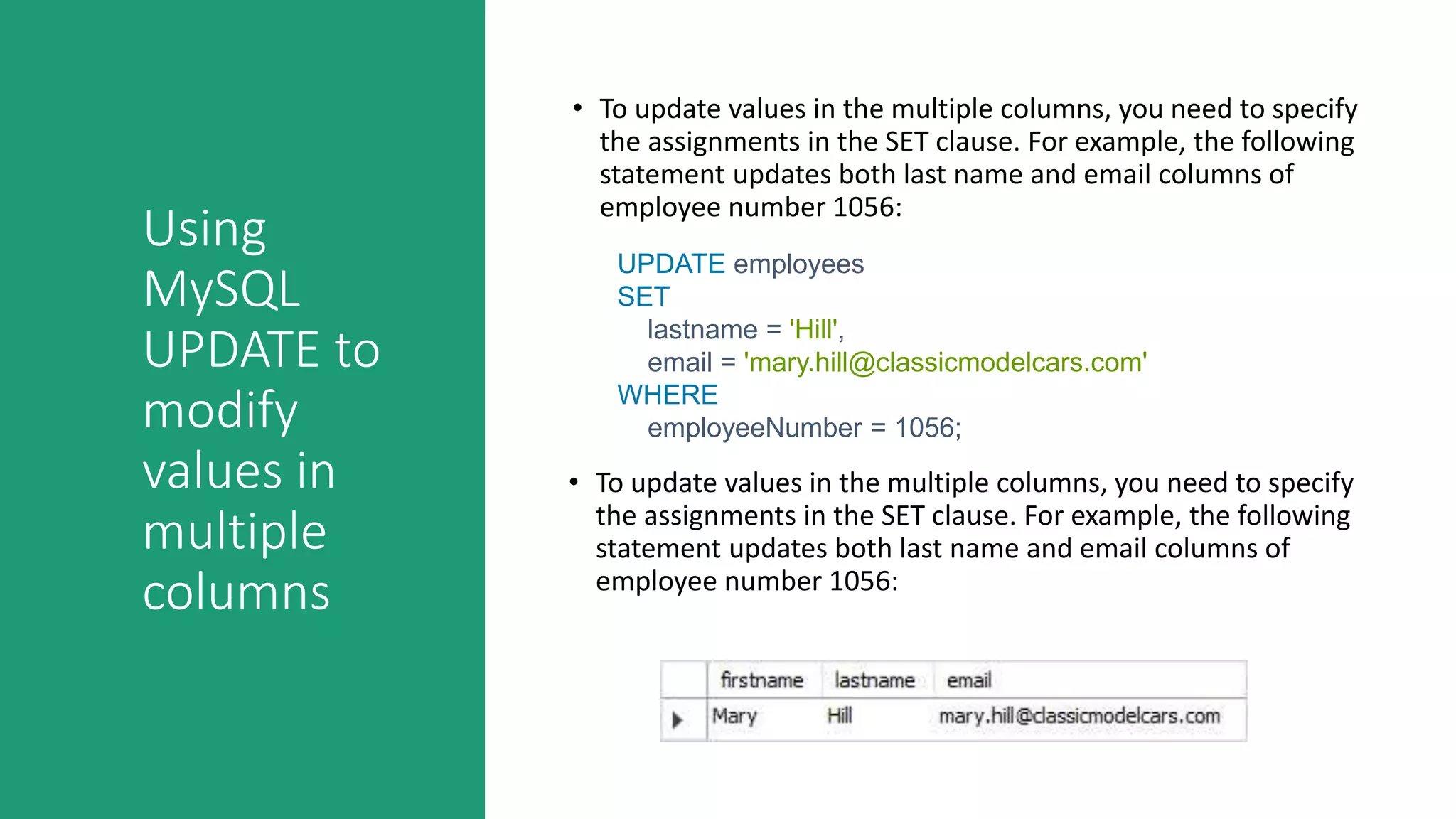
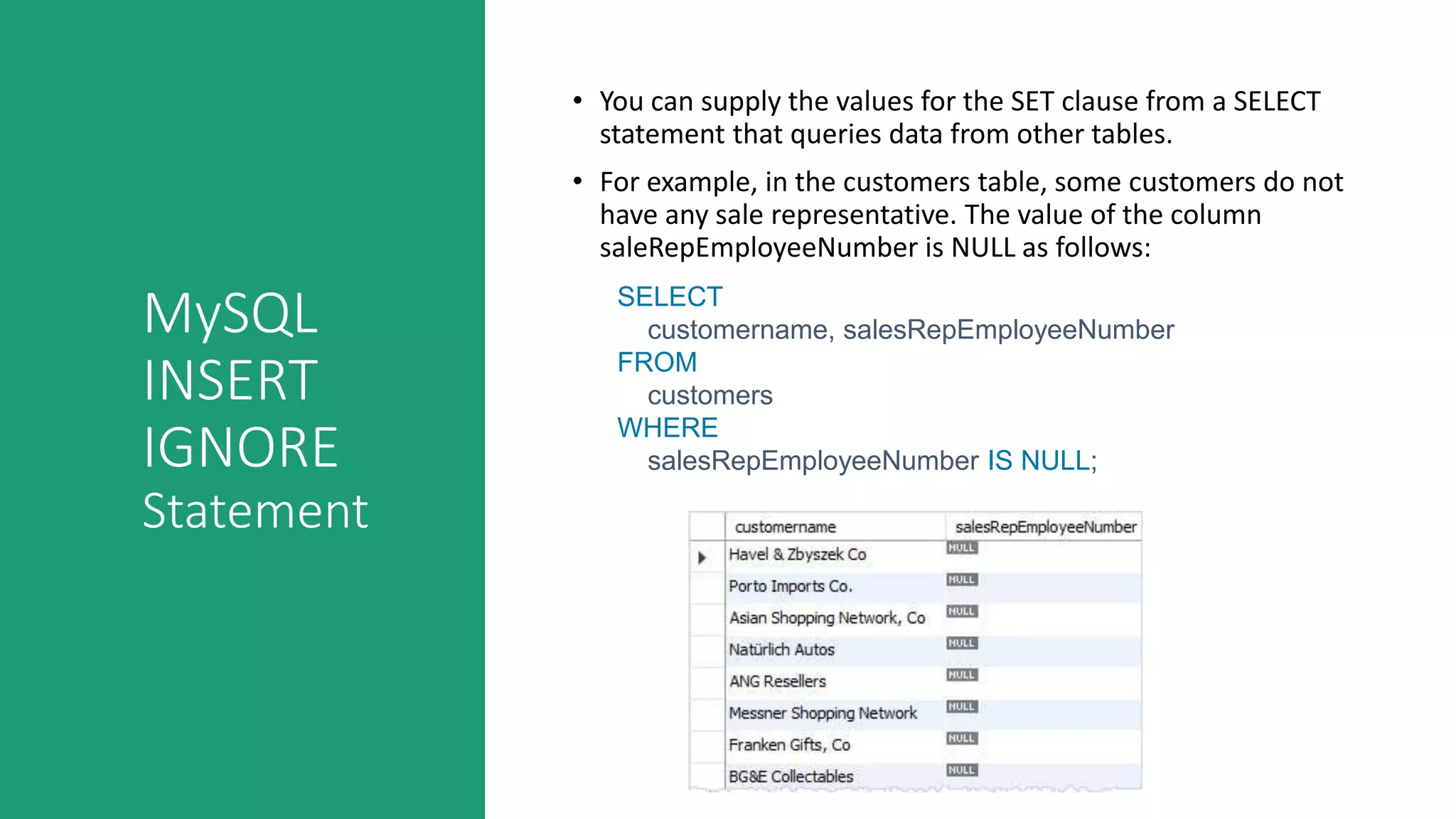
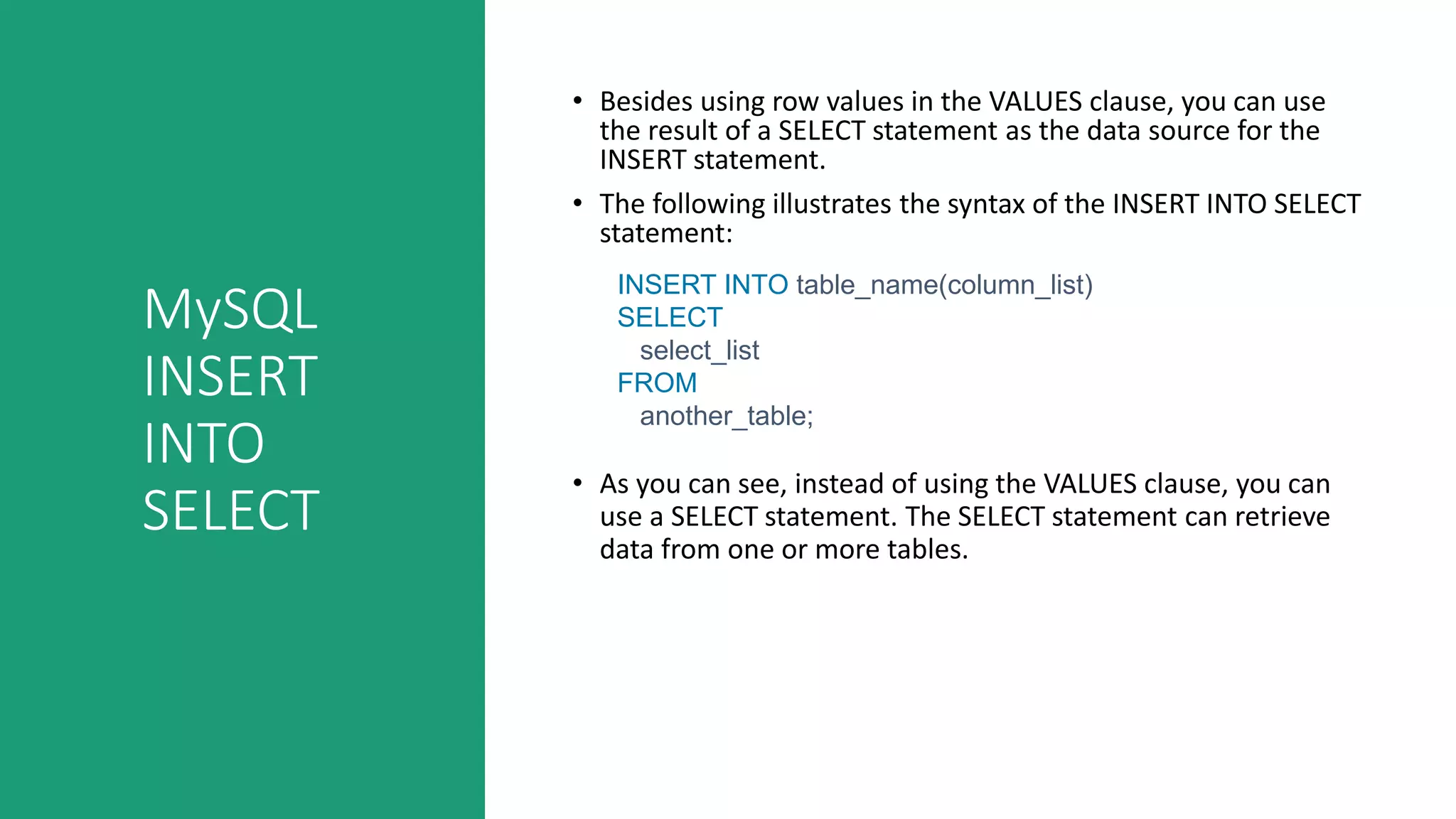
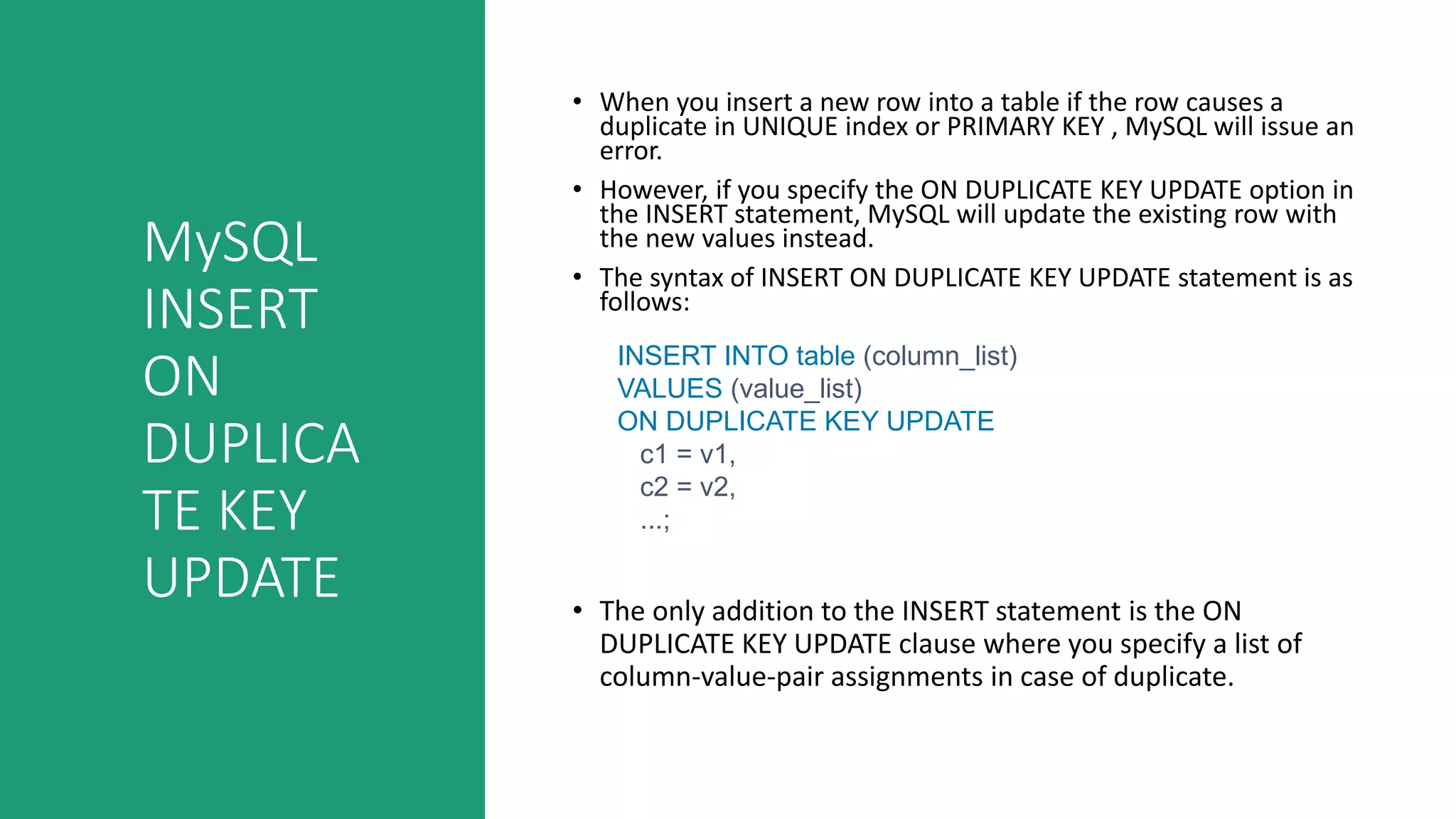
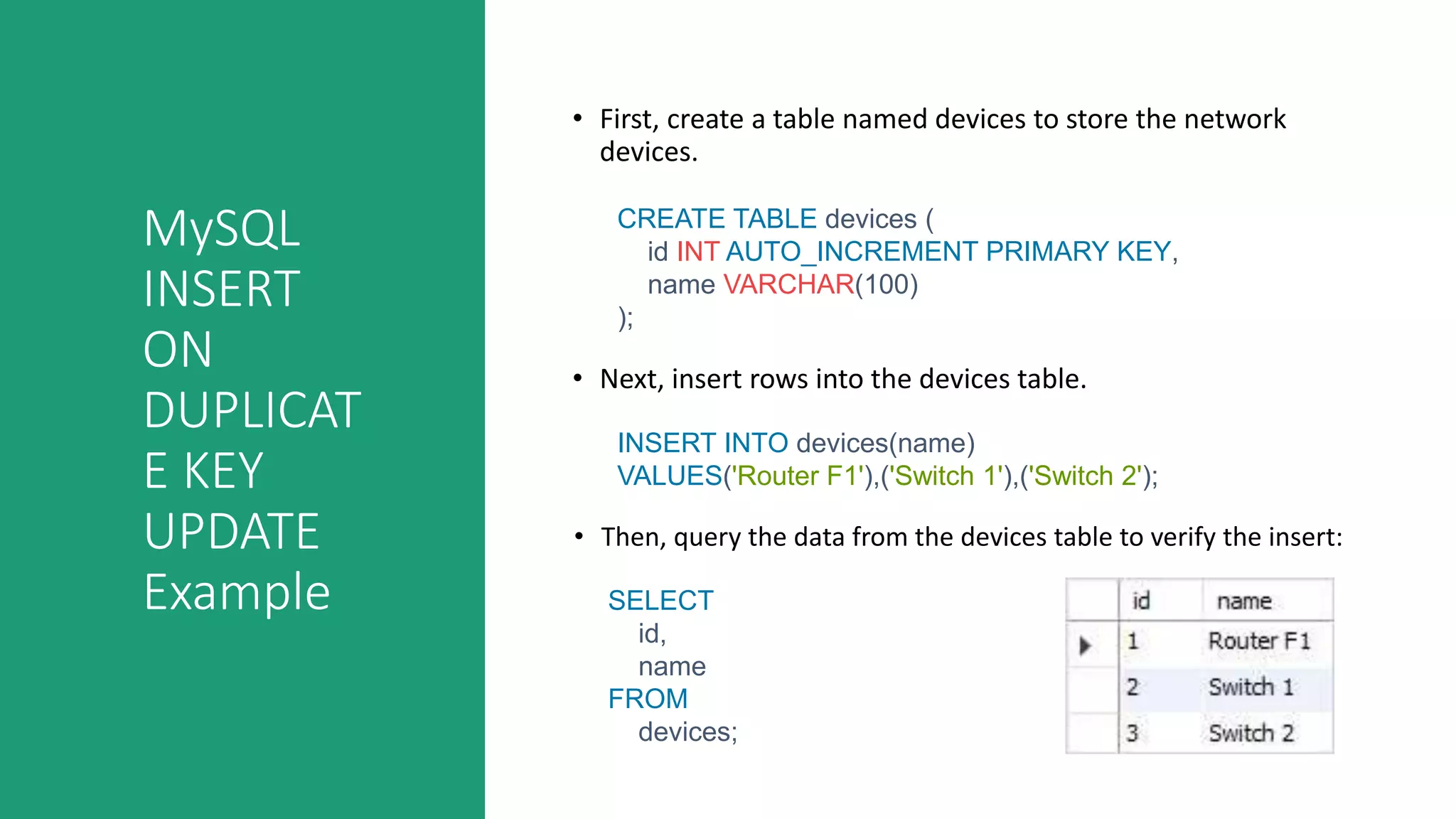
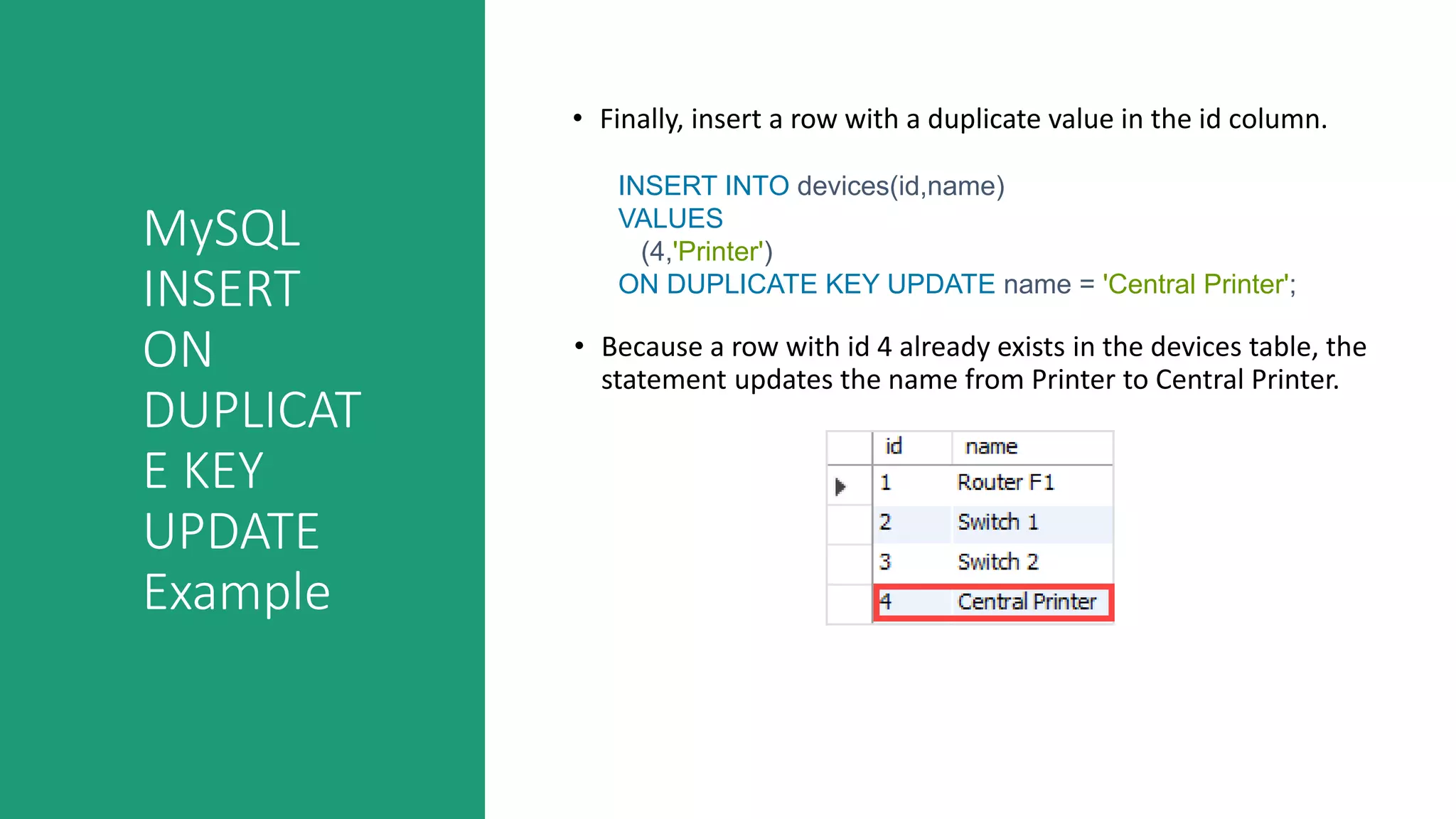
This document discusses various MySQL INSERT statements: - INSERT inserts one or more rows into a table and its syntax. - INSERT INTO SELECT inserts rows selected from another table. - INSERT ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE inserts a row and updates it if a duplicate key occurs. - INSERT IGNORE ignores errors on duplicate keys and inserts valid rows. It also covers the MySQL UPDATE statement for modifying data in tables and provides examples of their usage.




















![MySQL INSERT IGNORE Statement • You use the UPDATE statement to update existing data in a table. you can also use the UPDATE statement to change column values of a single row, a group of rows, or all rows in a table. • The following illustrates the syntax of the MySQL UPDATE statement: UPDATE [LOW_PRIORITY] [IGNORE] table_name SET column_name1 = expr1, column_name2 = expr2, ... [WHERE condition];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlmodifyingdatainmysqlparti-190404111459/75/Sql-modifying-data-MYSQL-part-I-25-2048.jpg)