The document discusses the integration of SQL with NoSQL databases and the role of Apache Calcite in optimizing queries across different data storage systems. It highlights the challenges posed by diverse data models and the need for unified query languages in mixed data environments. The presentation outlines how Calcite serves as a framework to facilitate SQL interfaces and query optimizations for various NoSQL technologies.





![“Standard” Data Process/Query Language? 7 • Functional - Unified Programming Model • Apache {Beam, Spark, Flink, Apex, Crunch}, Cascading • Converging around Apache Beam • Declarative - SQL • Adopted by many NoSQL Vendors • Most Hadoop tasks: Hive and SQL-on-Hadoop • Spark SQL - most used production component for 2016 • Google F1 pcollection.apply(Read.from(”in.txt")) .apply(FlatMapElements.via((String word) -> asList(word.split("[^a-zA-Z']+"))) .apply(Filter.by((String word)->!word.isEmpty())) .apply(Count.<String>perElement()) SELECT b."totalPrice", c."firstName” FROM "BookOrder" as b INNER JOIN "Customer" as c ON b."customerNumber" = c."customerNumber” WHERE b."totalPrice" > 0; Batch & Streaming, OLTP OLAP, EDW, Exploration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fosdem2017christiantzolov-170206202927/75/SQL-for-NoSQL-and-how-Apache-Calcite-can-help-7-2048.jpg)


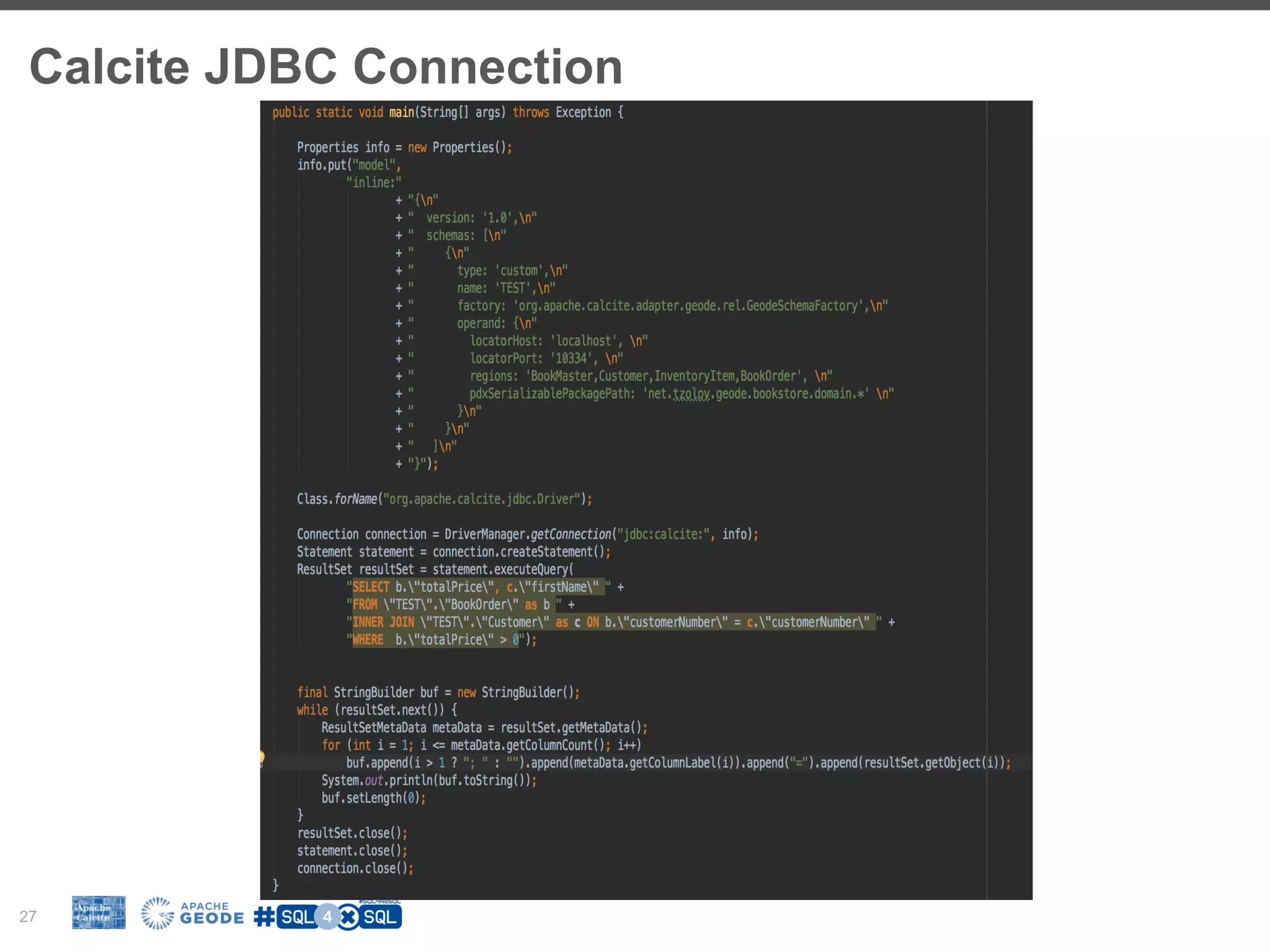
![Simple SQL Adapter 16 <<SchemaFactory>> MySchemaFactory +create(operands):Schema <<create>> <<ScannableTable>> MyTable +getRowType(RelDataTypeFactor) +scan(ctx):Ennumerator<Object[]> <<Schema>> MySchema +getTableMap():Map<String, Table>) <<on scan() create>> <<Enummerator>> MyEnummerator +moveNext() +convert(Object):E My NoSQL <<create>> <<Get all Data>> defaultSchema: 'MyNoSQL', schemas: [{ name: ’MyNoSQLAdapter, factory: MySchemaFactory’, operand: { myNoSqlUrl: …, } }] !connect jdbc:calcite:model=path-to-model.json Returns an Enumeration over the entire target data store Uses reflection to builds RelDataType from your value’s class type Converts MyNoSQL value response into Calcite row data Defined in the Linq4j sub-project ScannableTable, FilterableTable, ProjectableFilterableTable Initialize Query SELECT b."totalPrice” FROM "BookOrder" as b WHERE b."totalPrice" > 0;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fosdem2017christiantzolov-170206202927/75/SQL-for-NoSQL-and-how-Apache-Calcite-can-help-16-2048.jpg)
![Non-Relational Tables (Simple) 17 Scanned without intermediate relational expression. • ScannableTable - can be scanned • FilterableTable - can be scanned, applying supplied filter expressions • ProjectableFilterableTable - can be scanned, applying supplied filter expressions and projecting a given list of columns Enumerable<Object[]> scan(DataContext root, List<RexNode> filters, int[] projects); Enumerable<Object[]> scan(DataContext root, List<RexNode> filters); Enumerable<Object[]> scan(DataContext root);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fosdem2017christiantzolov-170206202927/75/SQL-for-NoSQL-and-how-Apache-Calcite-can-help-17-2048.jpg)
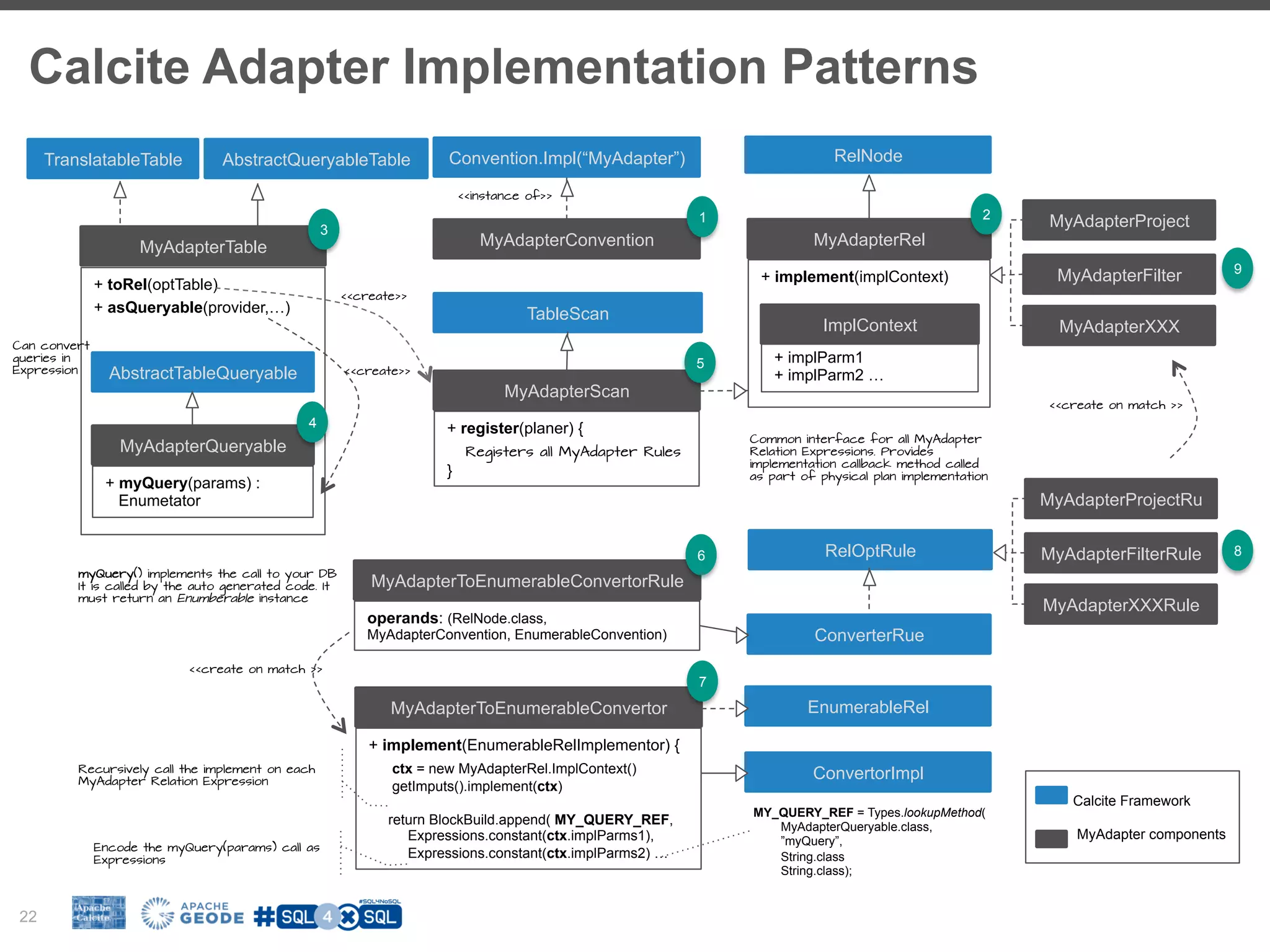
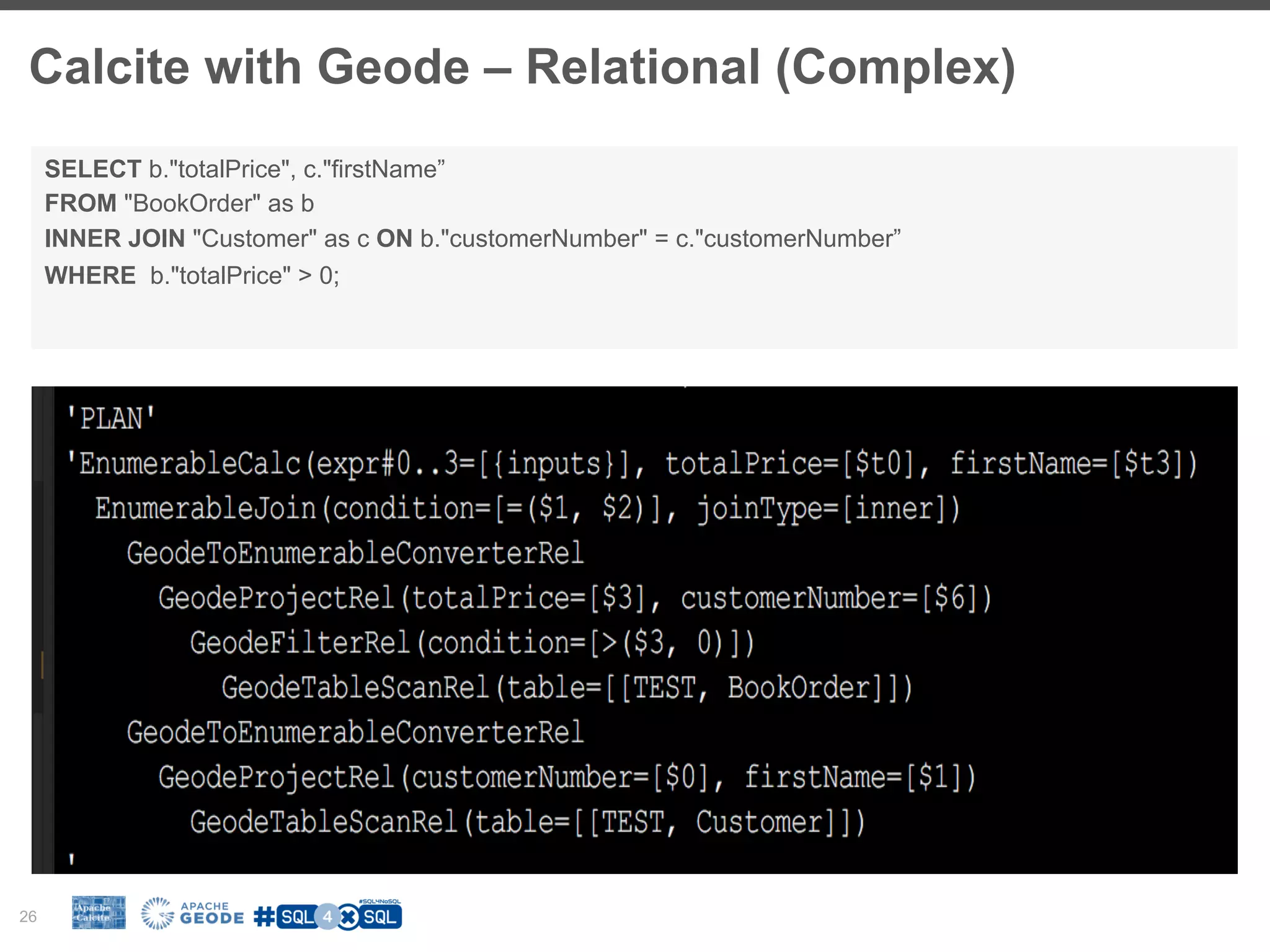
![Relational Algebra 23 Scan Scan Join Filter Project Customer [c] BookOrder [b] (on customerNumber) (b.totalPrice > 0) (c.firstName, b.totalPrice) SELECT b."totalPrice", c."firstName” FROM "BookOrder" as b INNER JOIN "Customer" as c ON b."customerNumber" = c."customerNumber” WHERE b."totalPrice" > 0; Scan Scan Join Project Customer [c] BookOrder [b] (on customerNumber) (totalPrice > 0) (c.firstName, b.totalPrice) Project(firstName, customerNumber) Filter (totalPrice, customerNumber)Project optimize](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fosdem2017christiantzolov-170206202927/75/SQL-for-NoSQL-and-how-Apache-Calcite-can-help-23-2048.jpg)