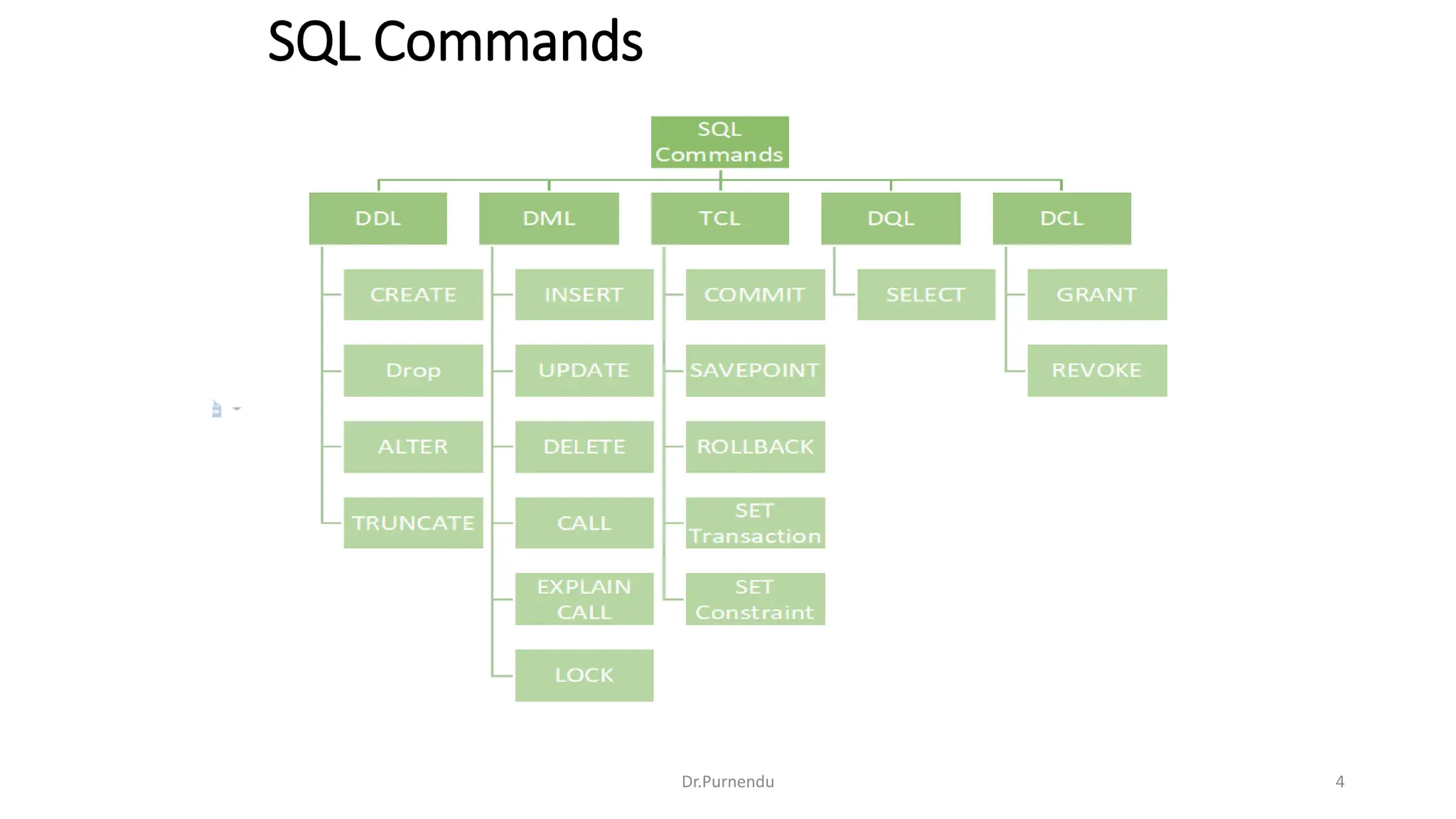
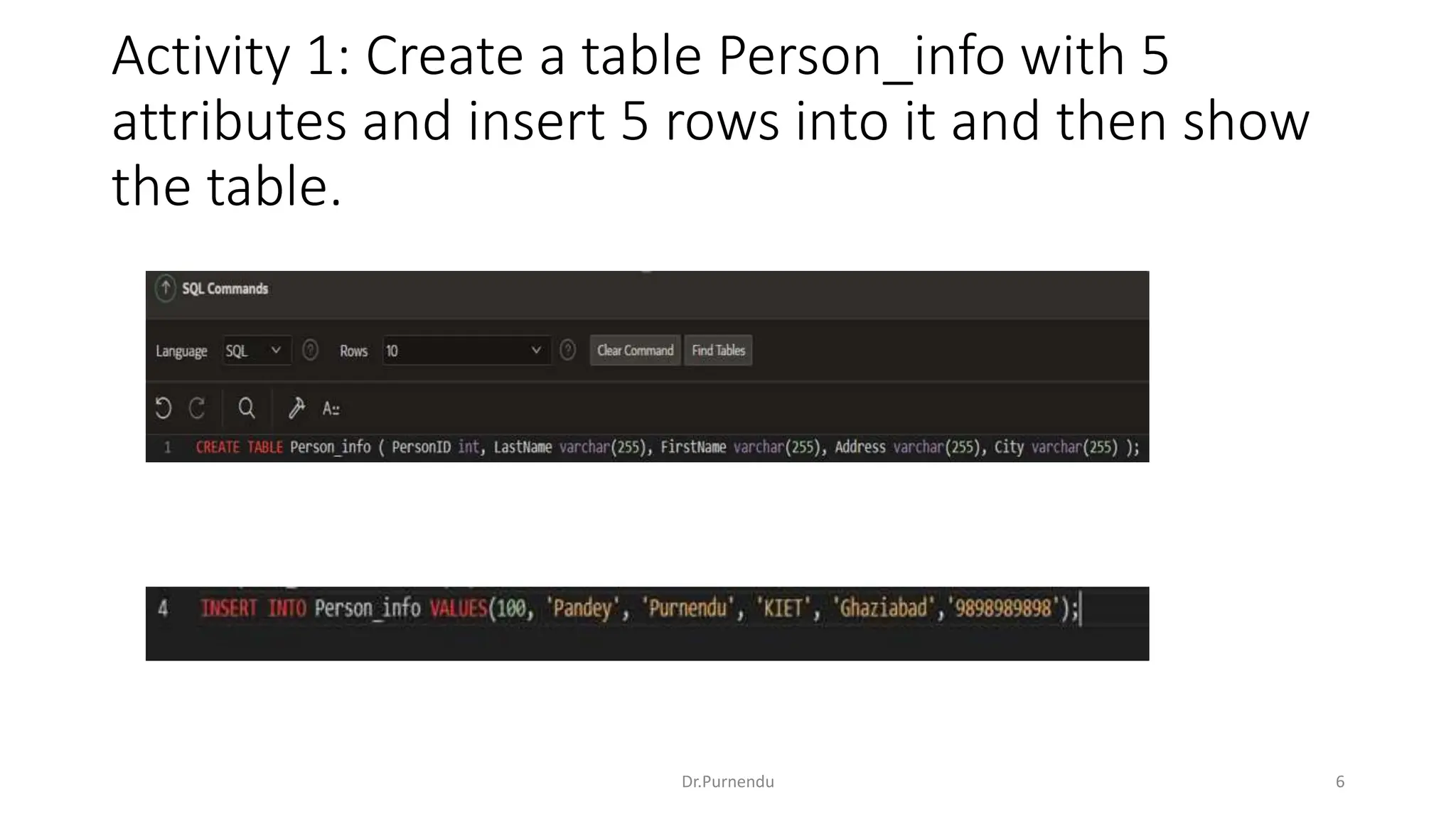
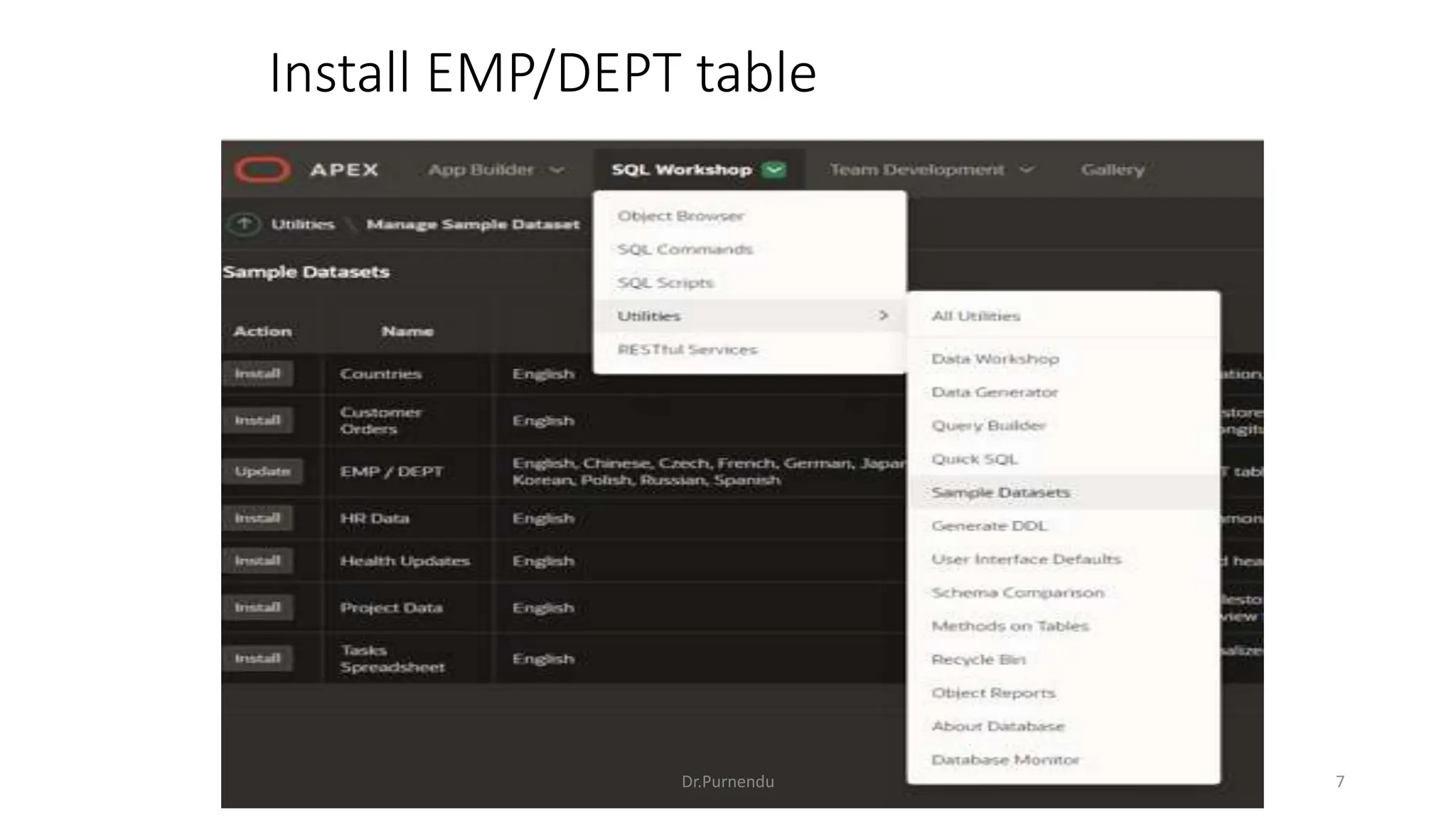
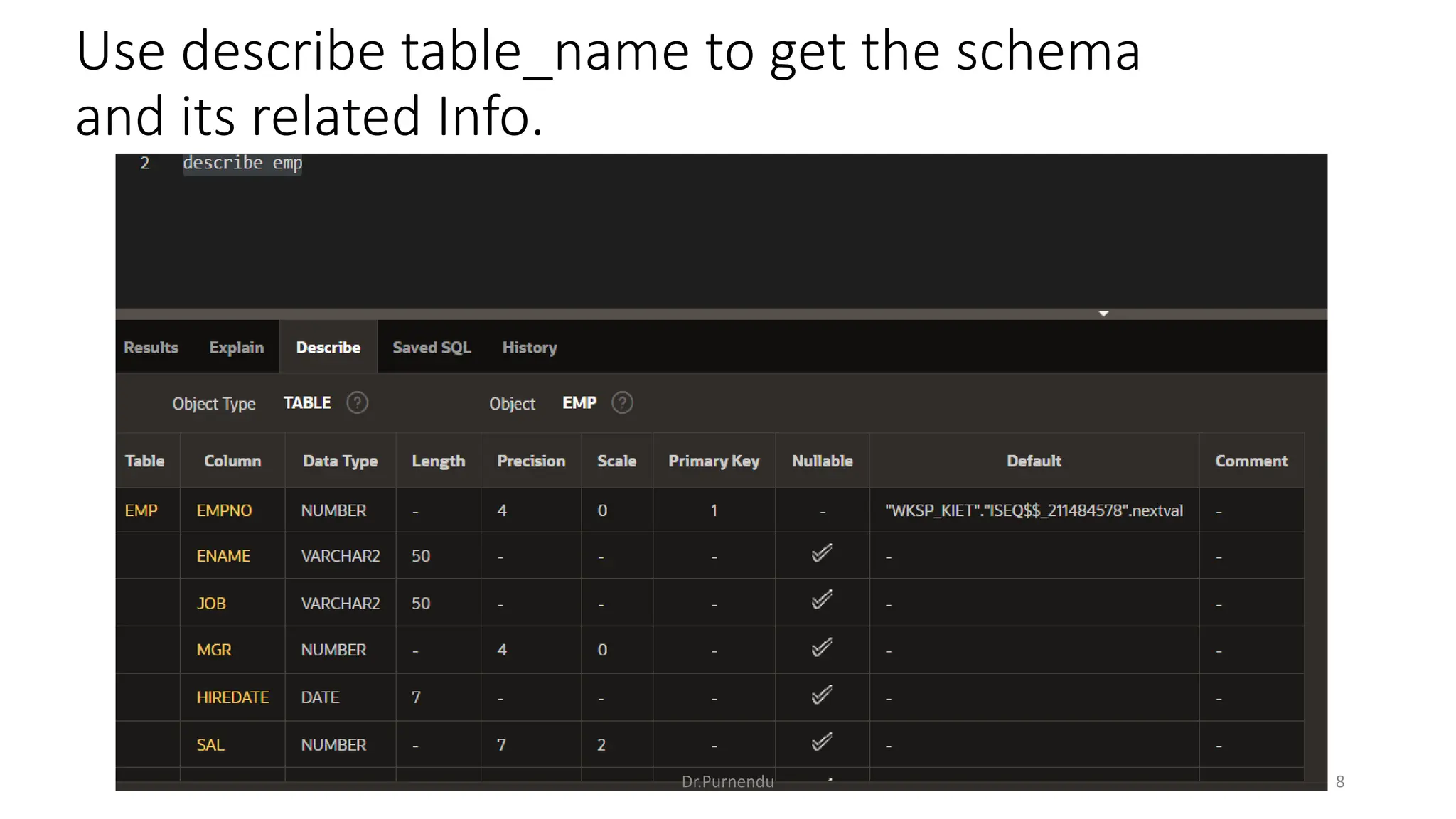
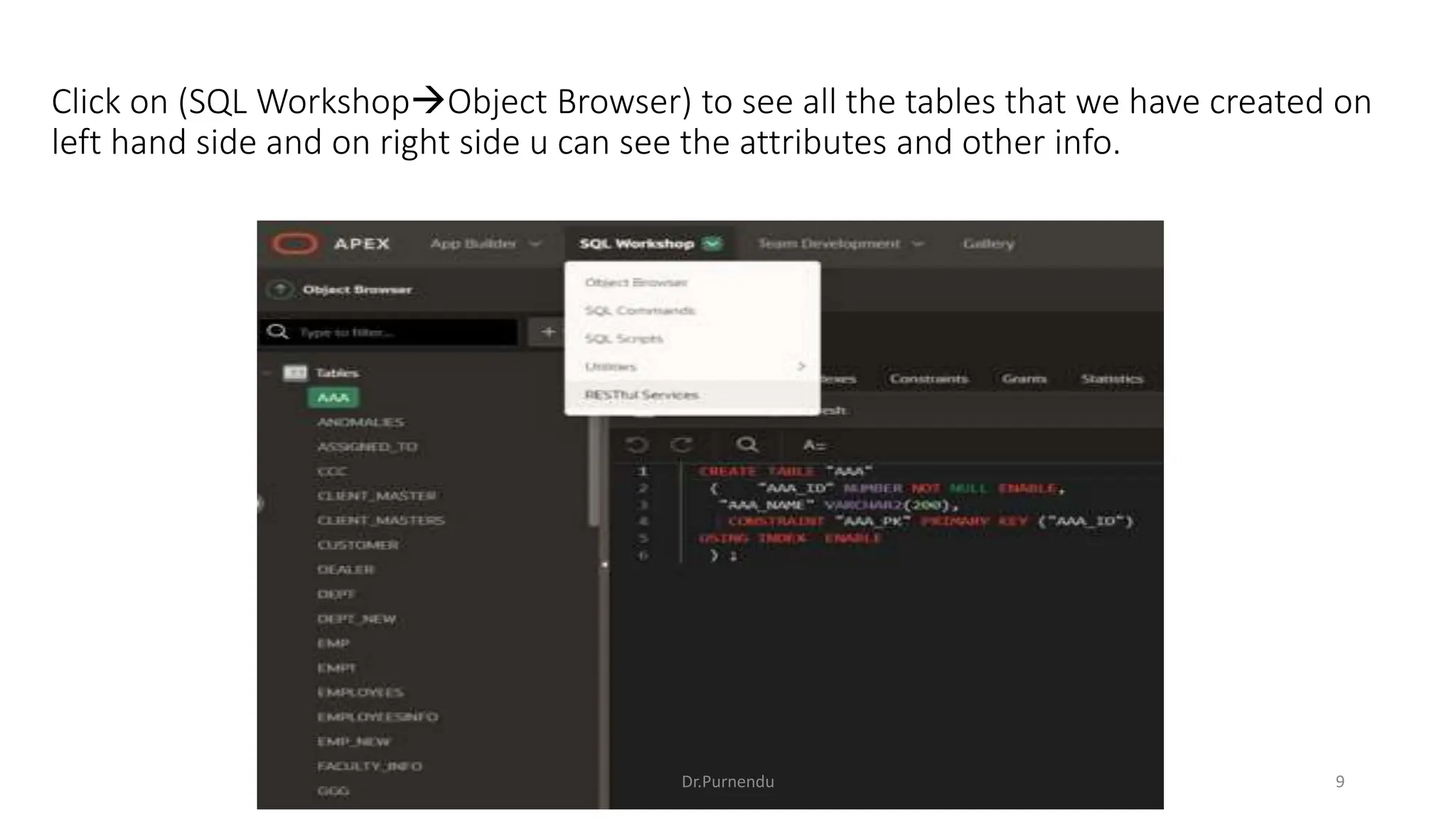
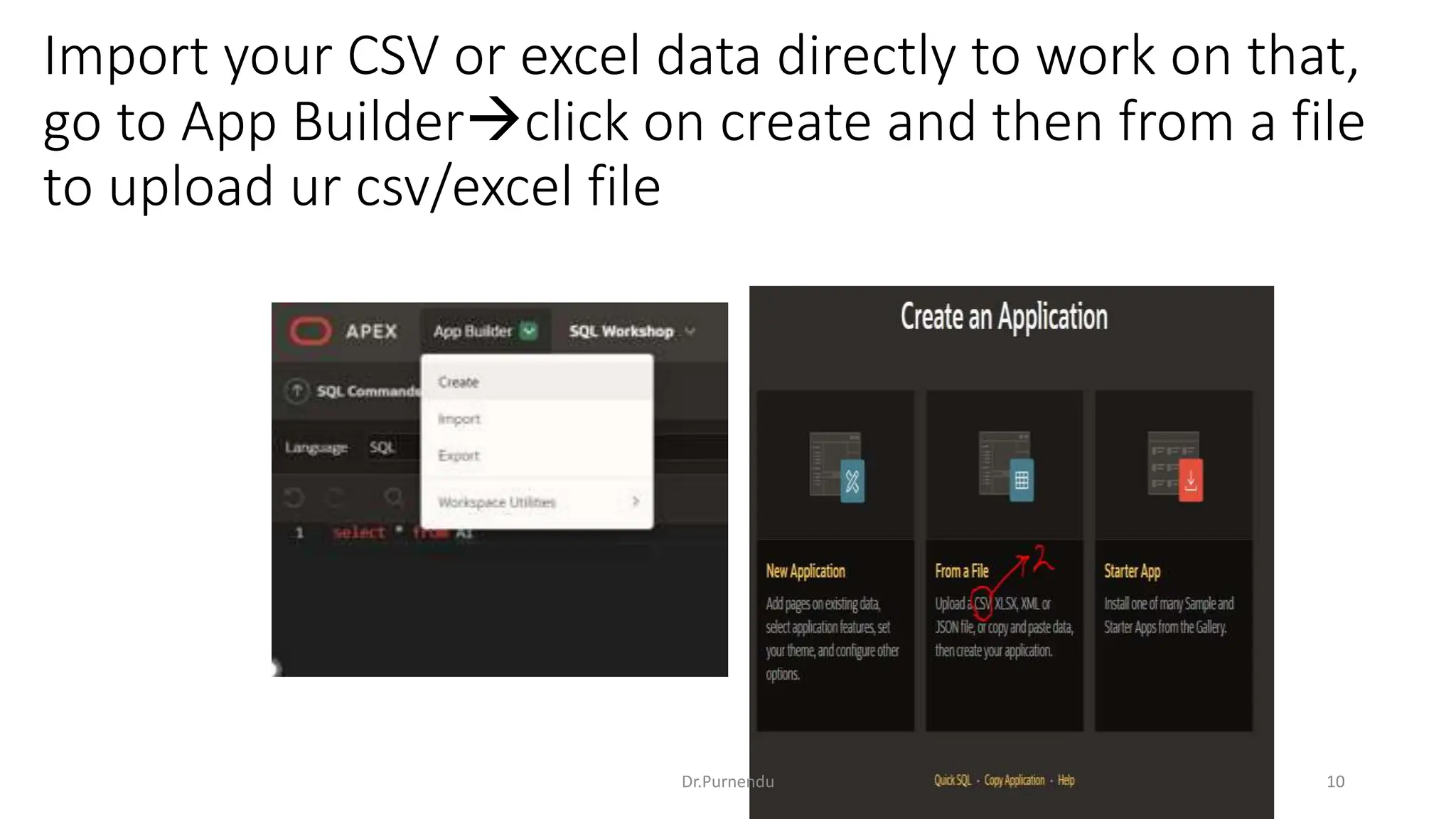
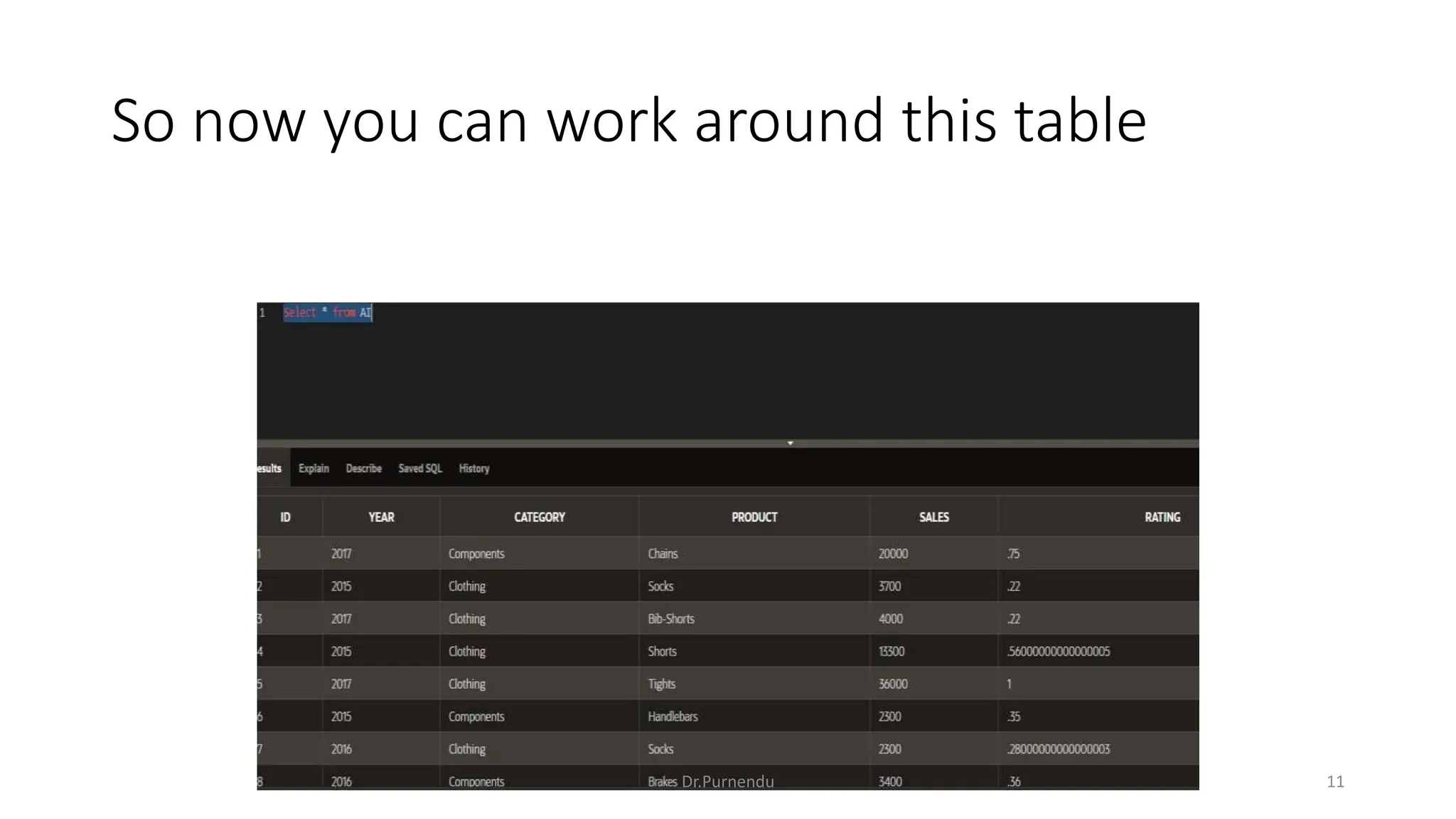
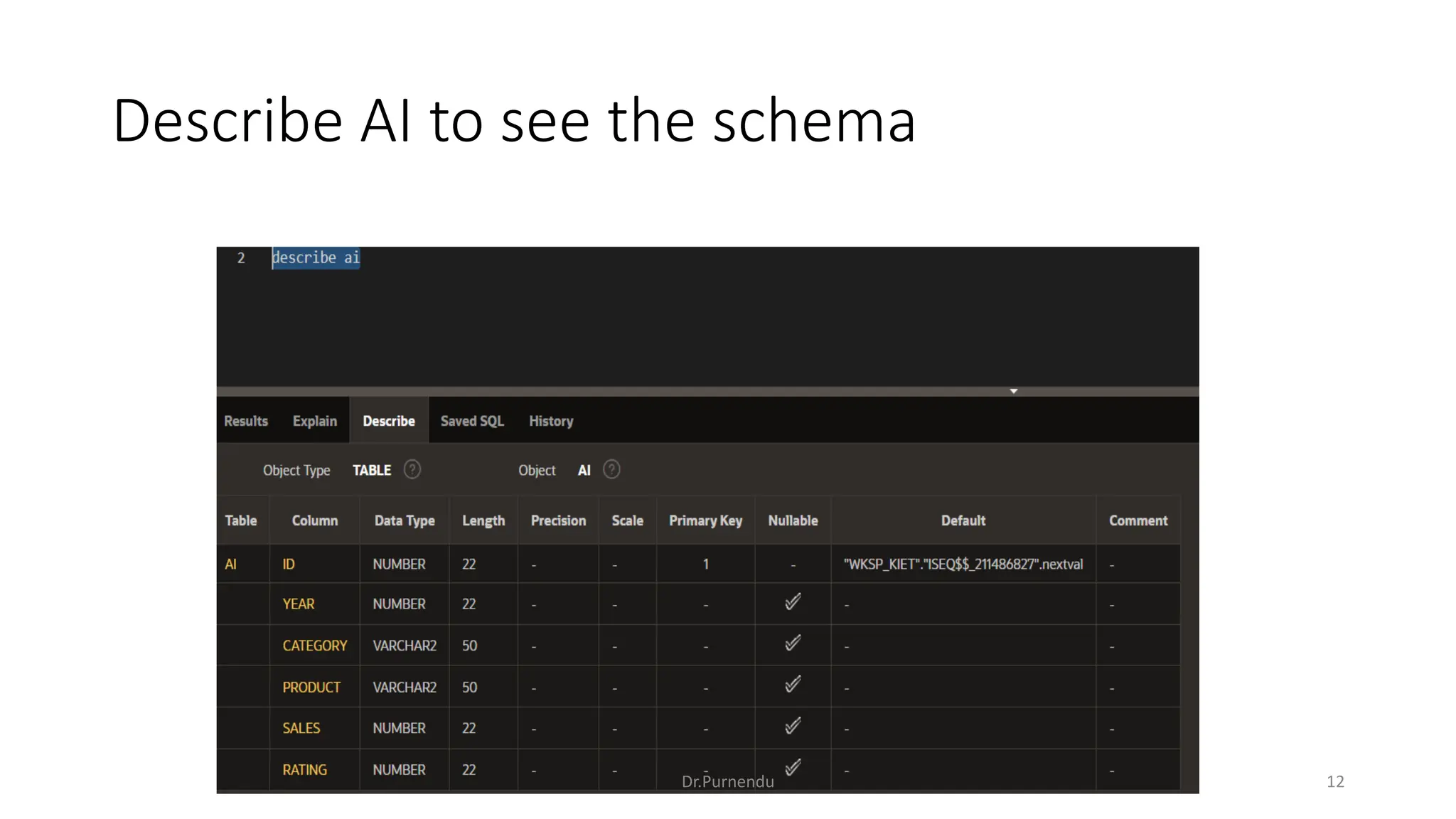
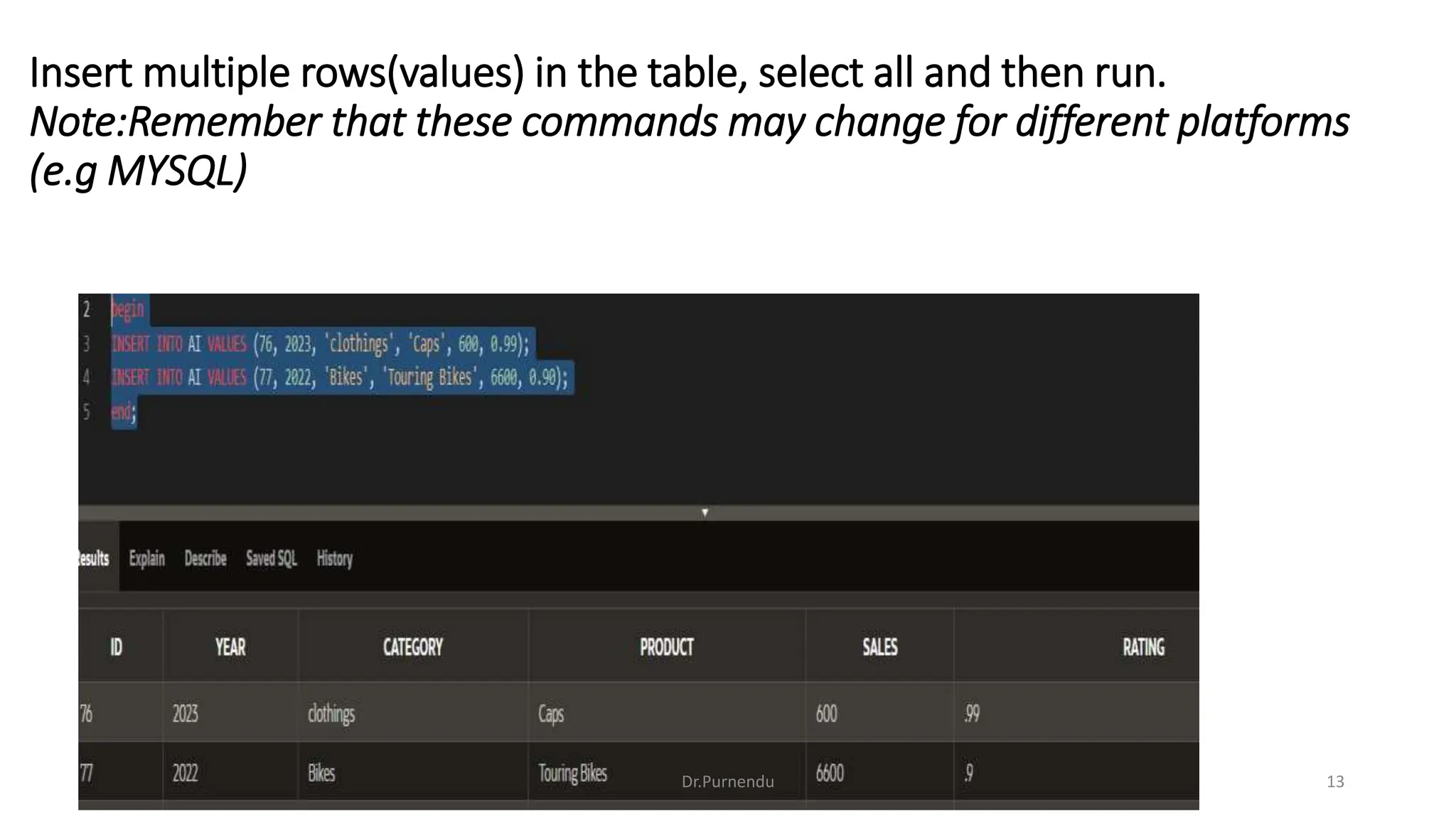
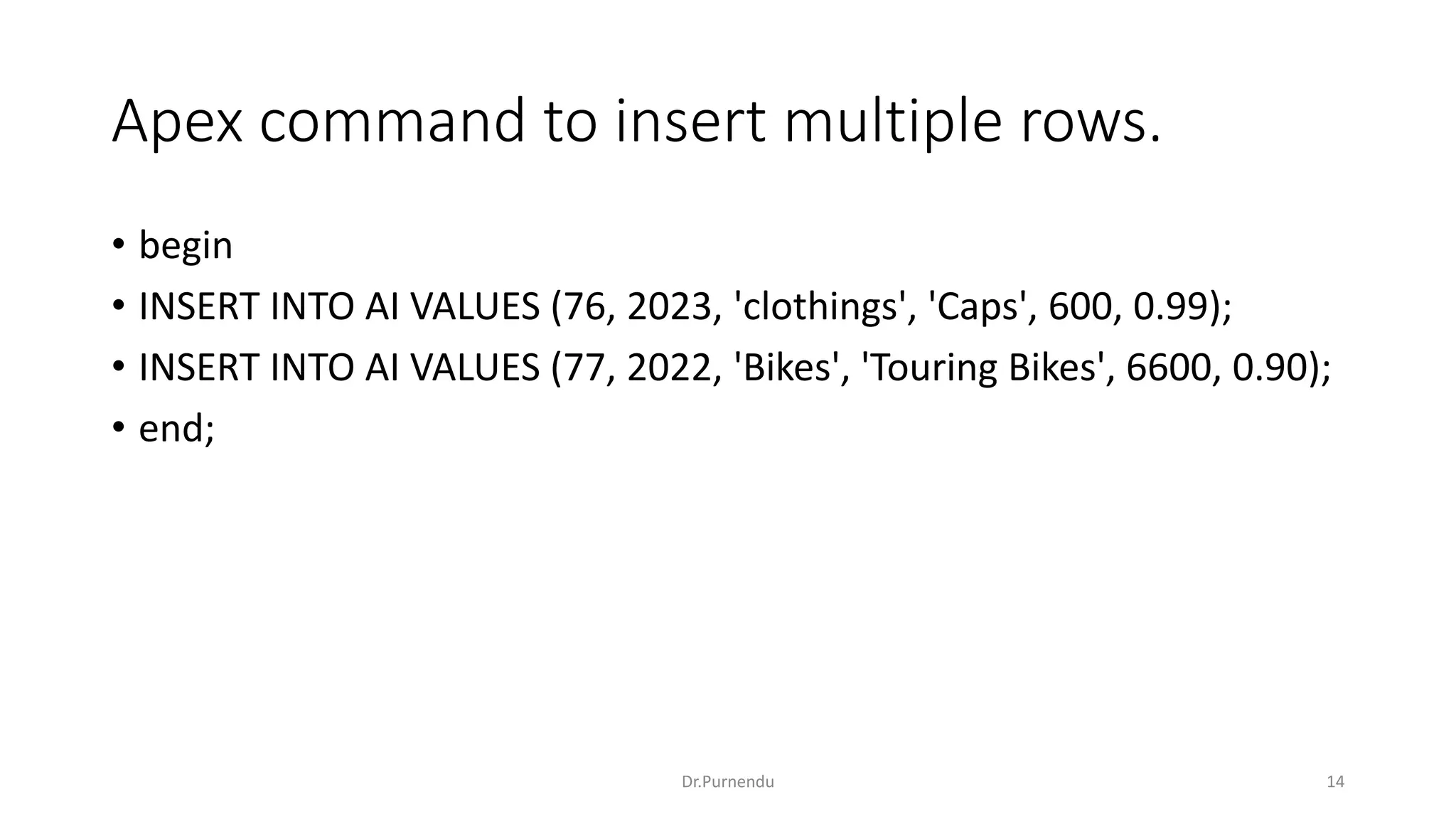
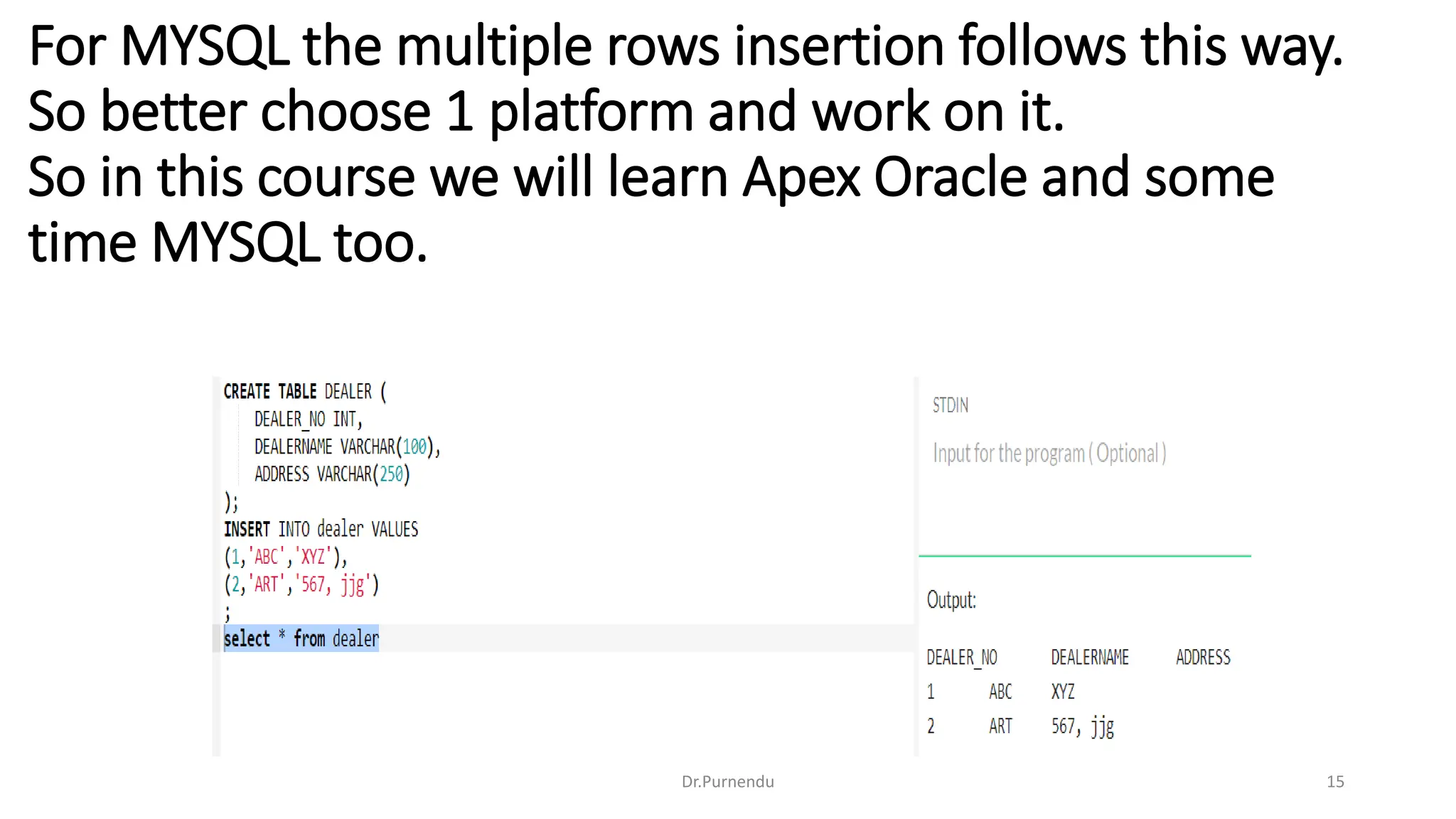
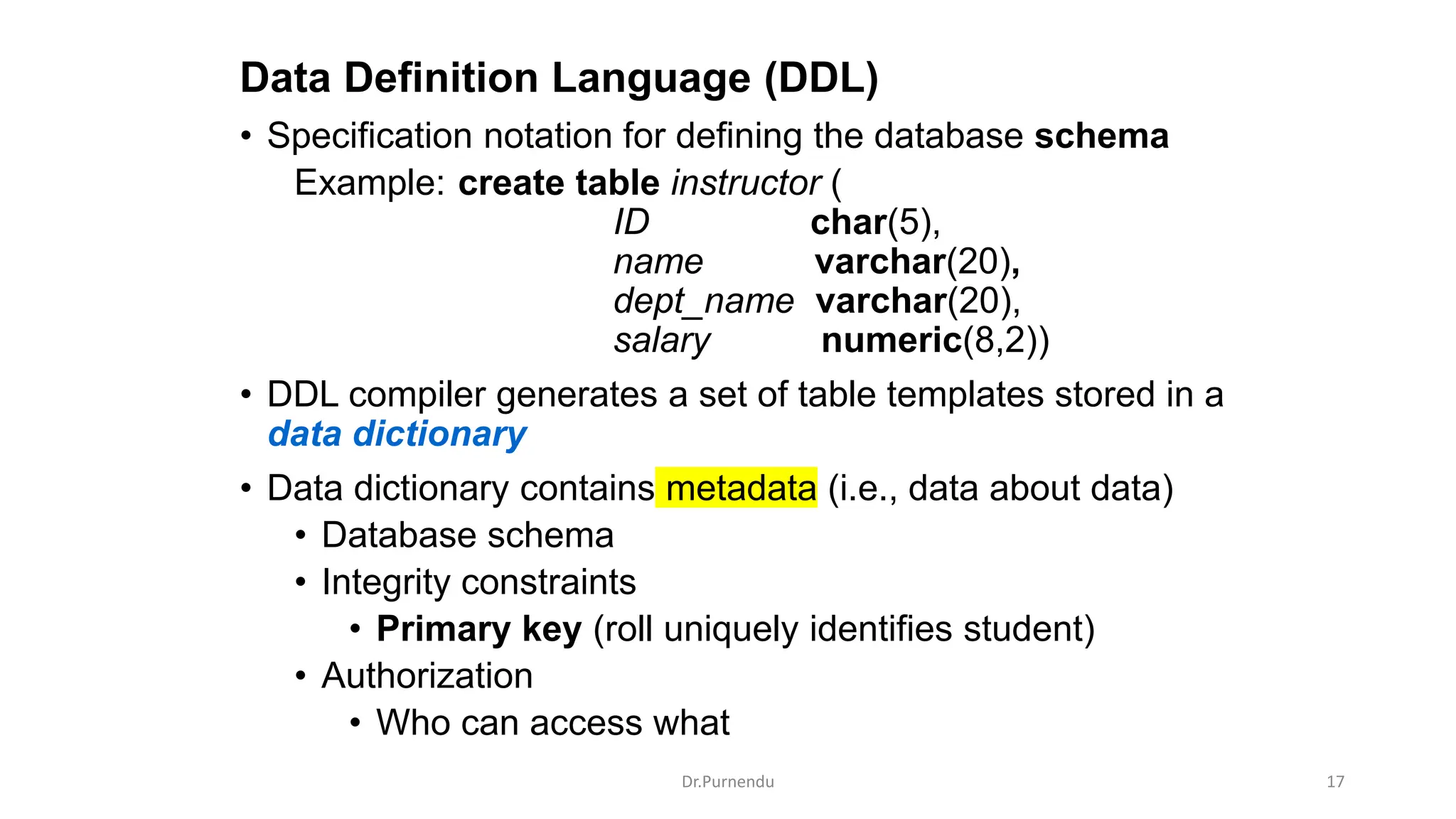
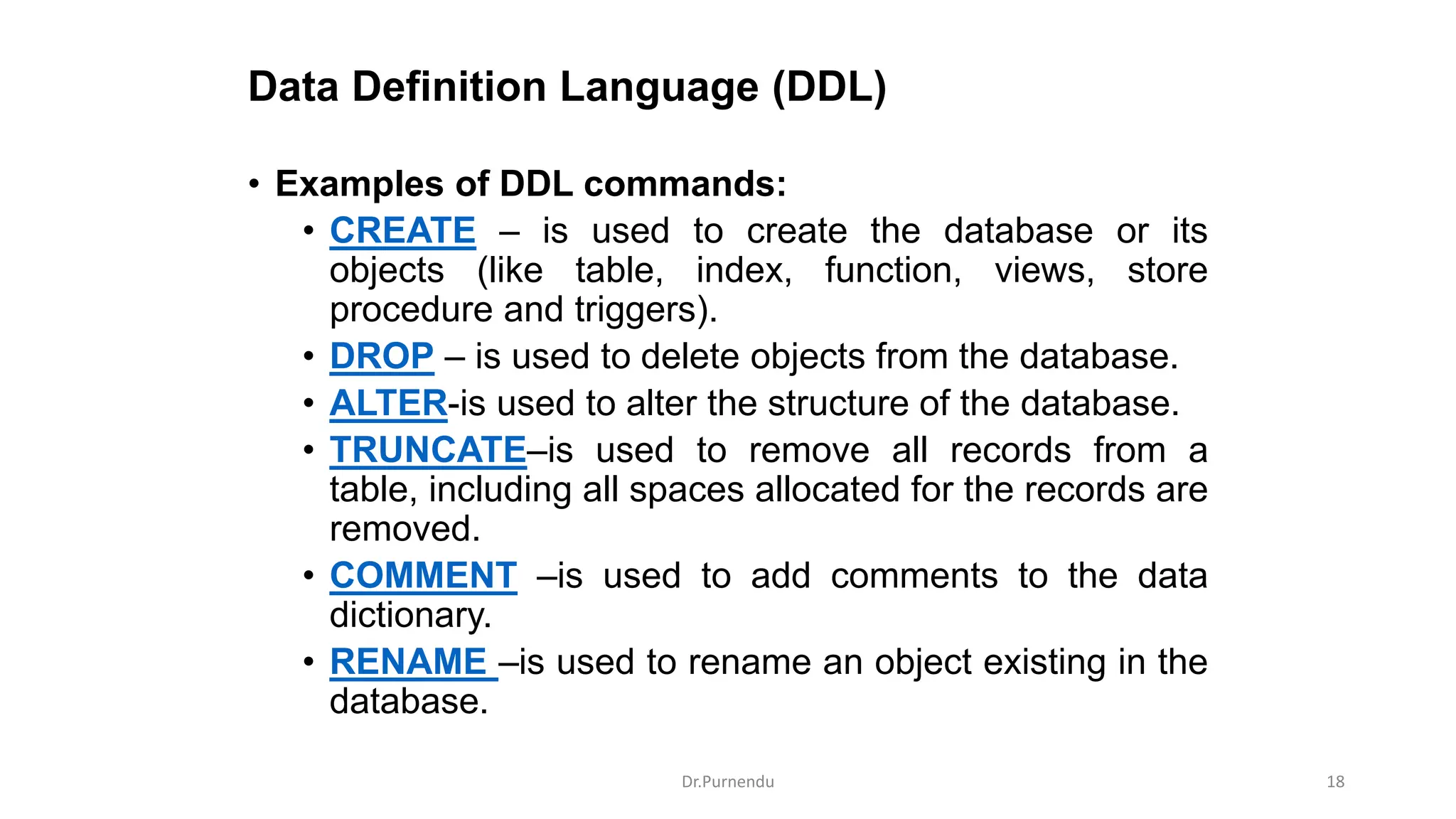
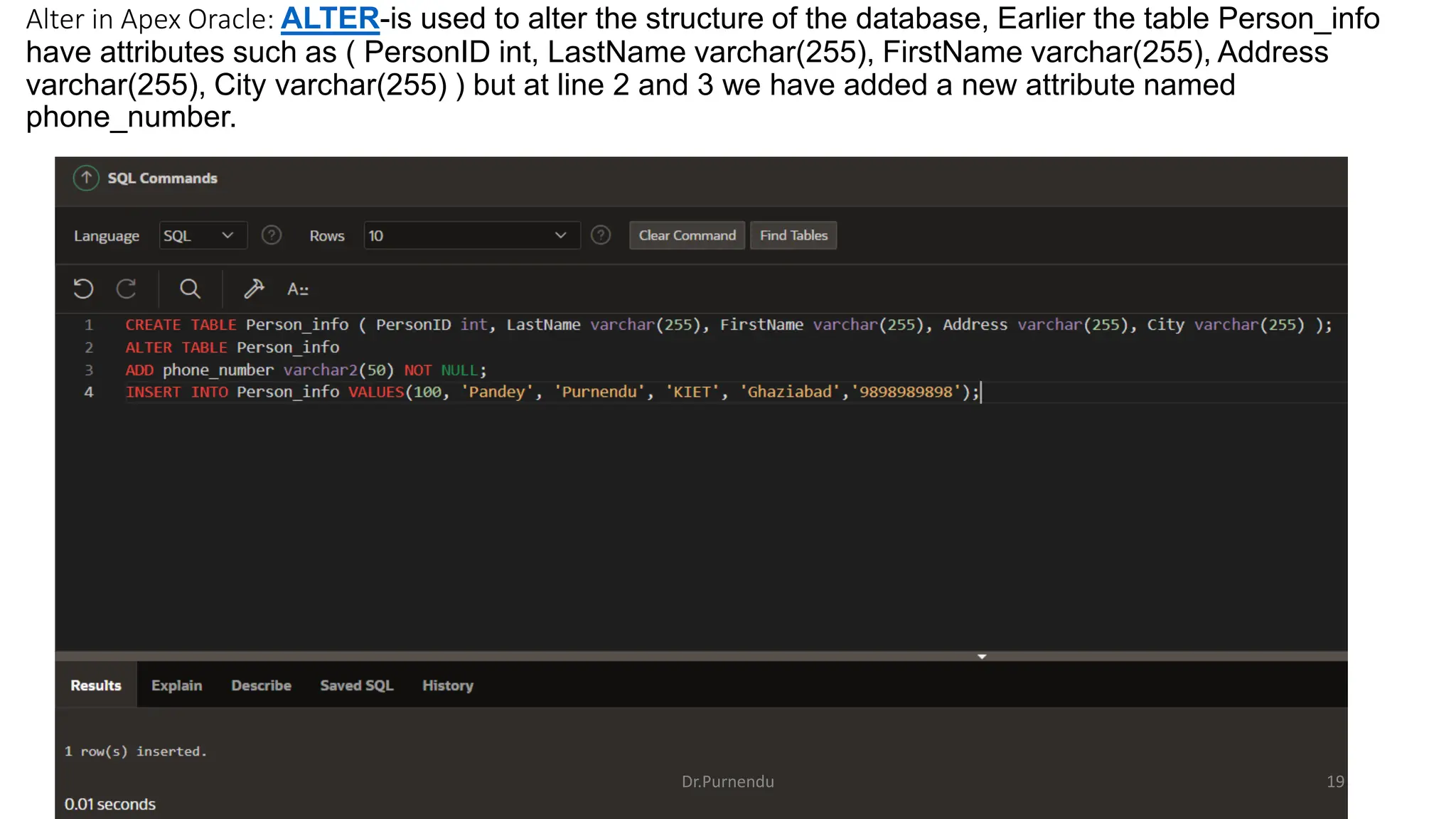
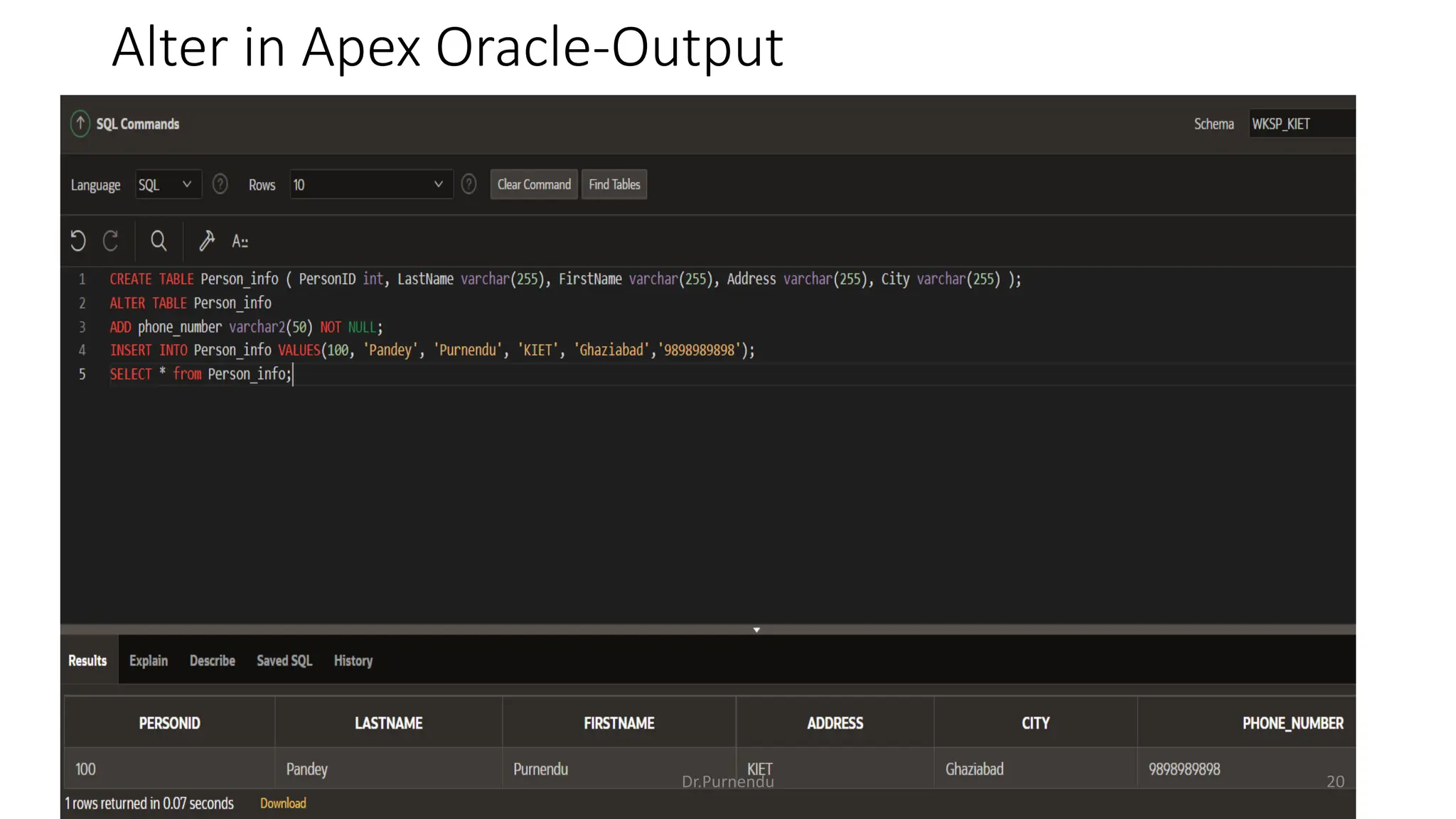
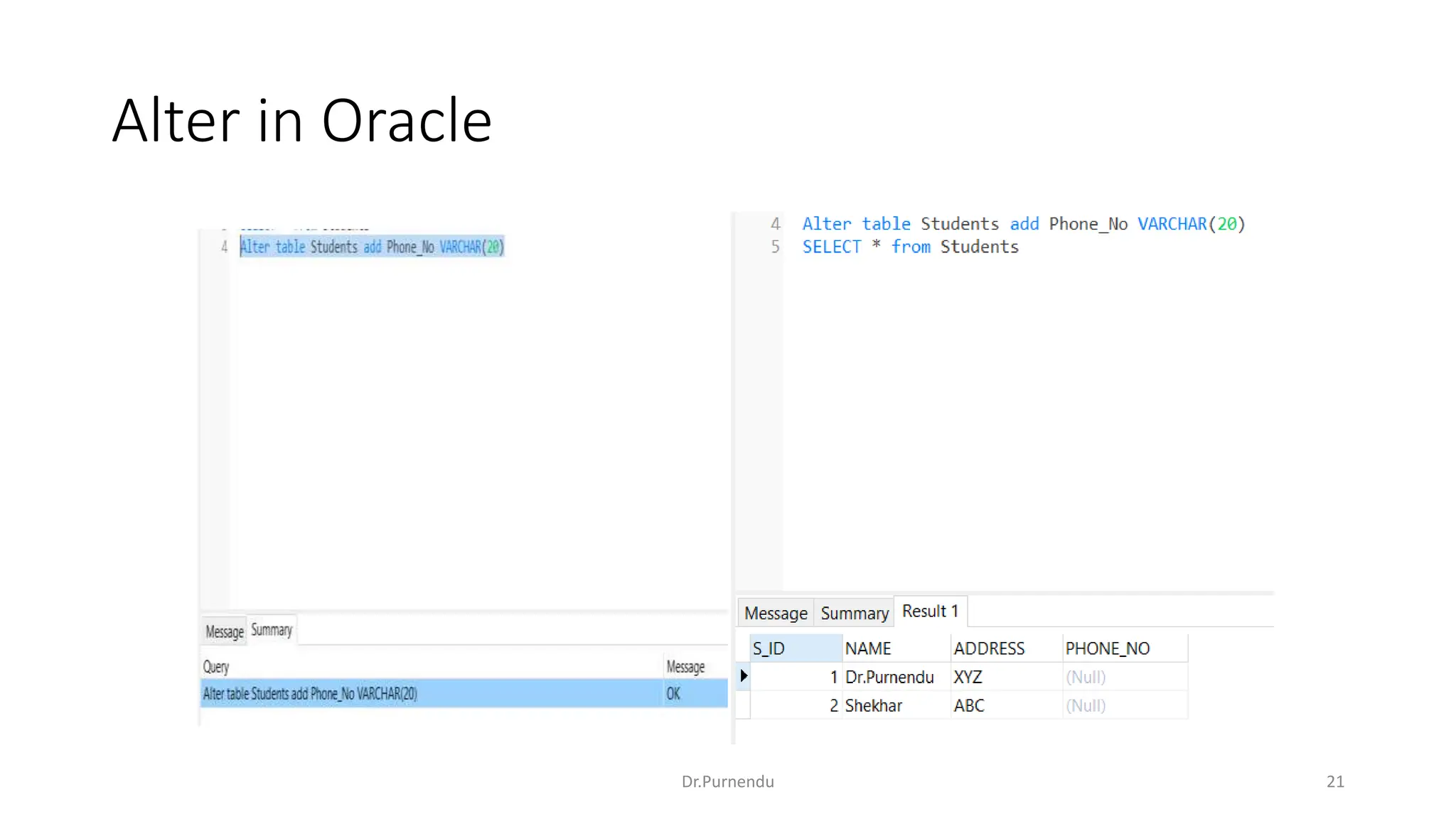
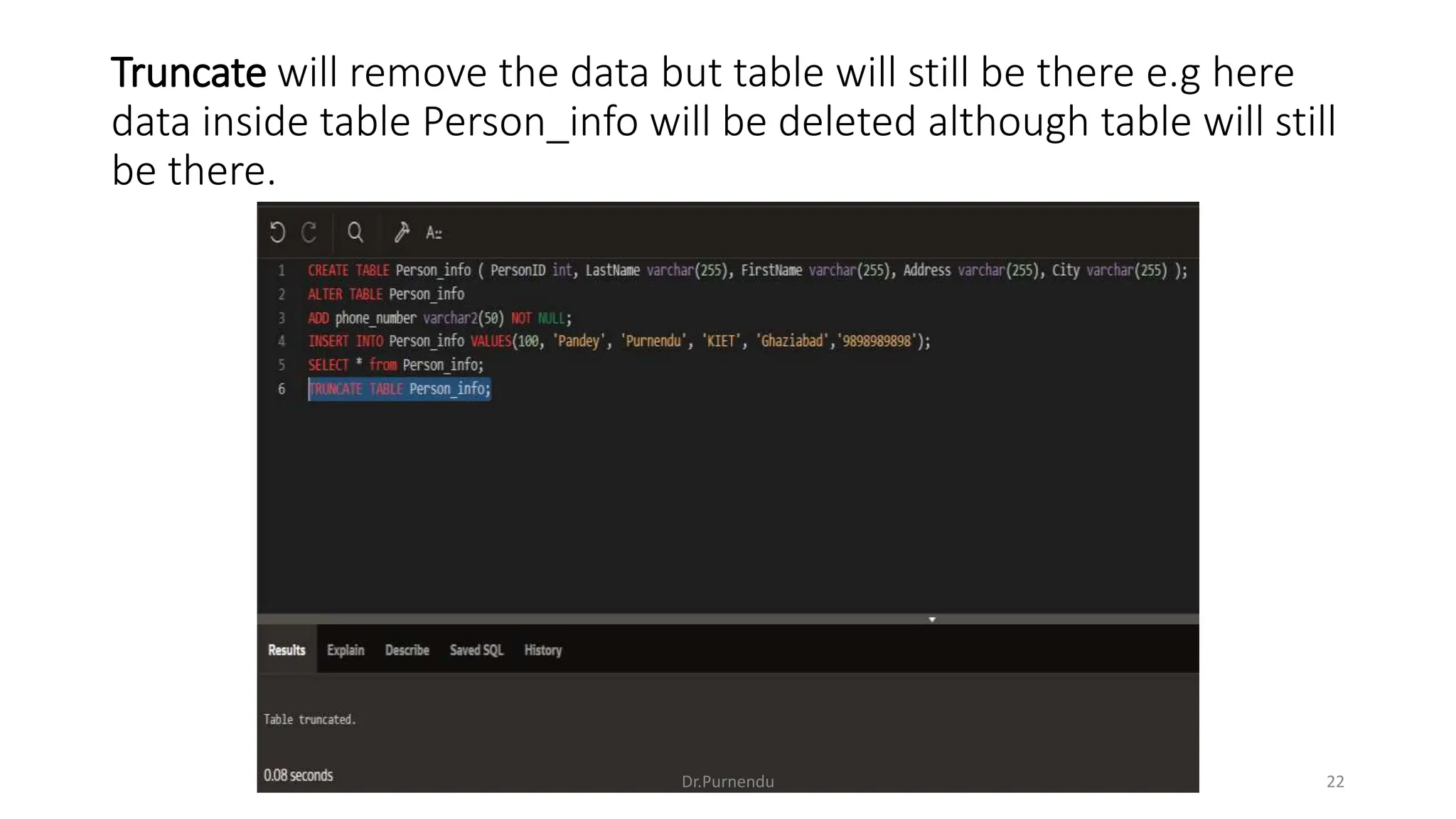
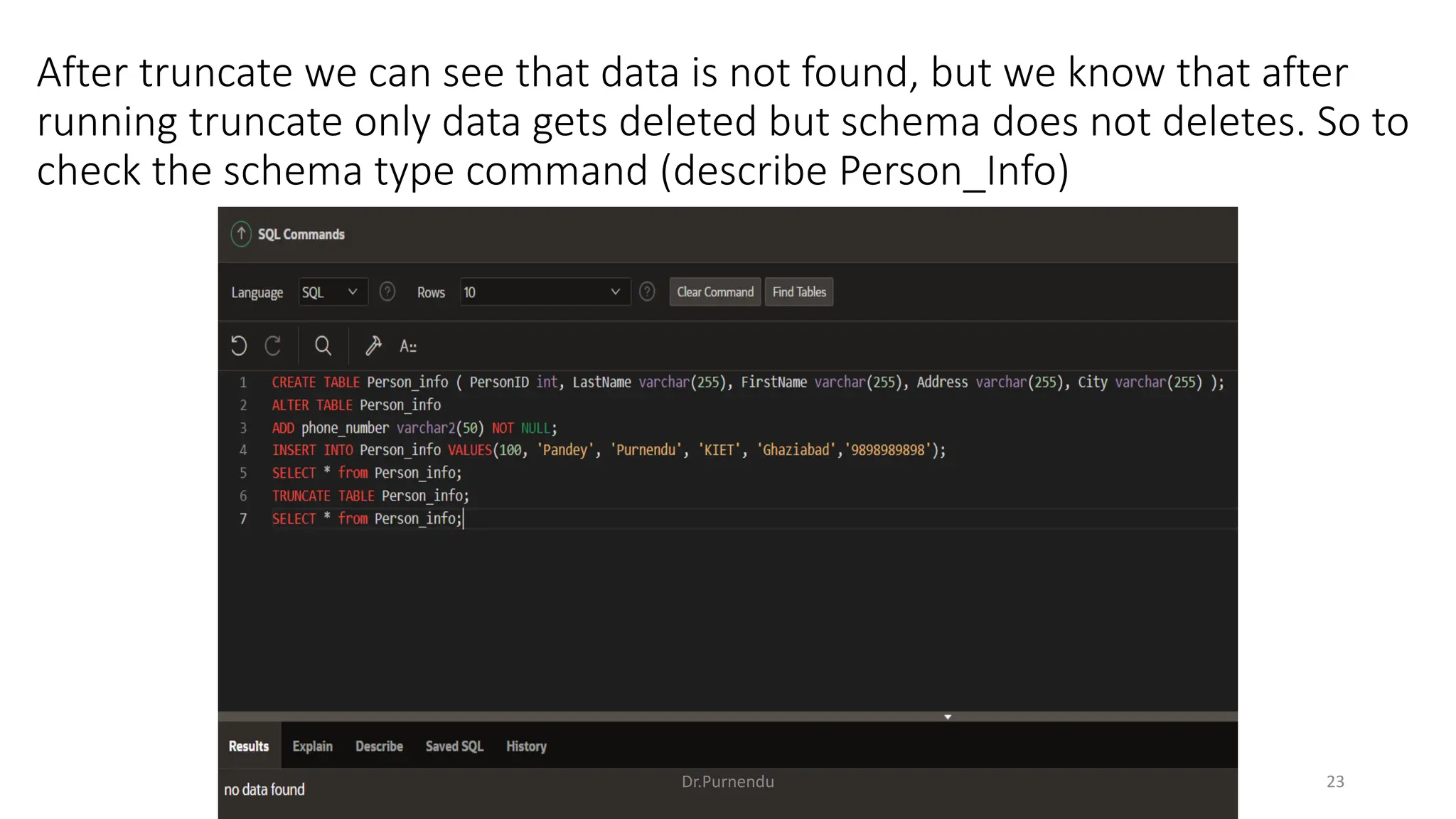
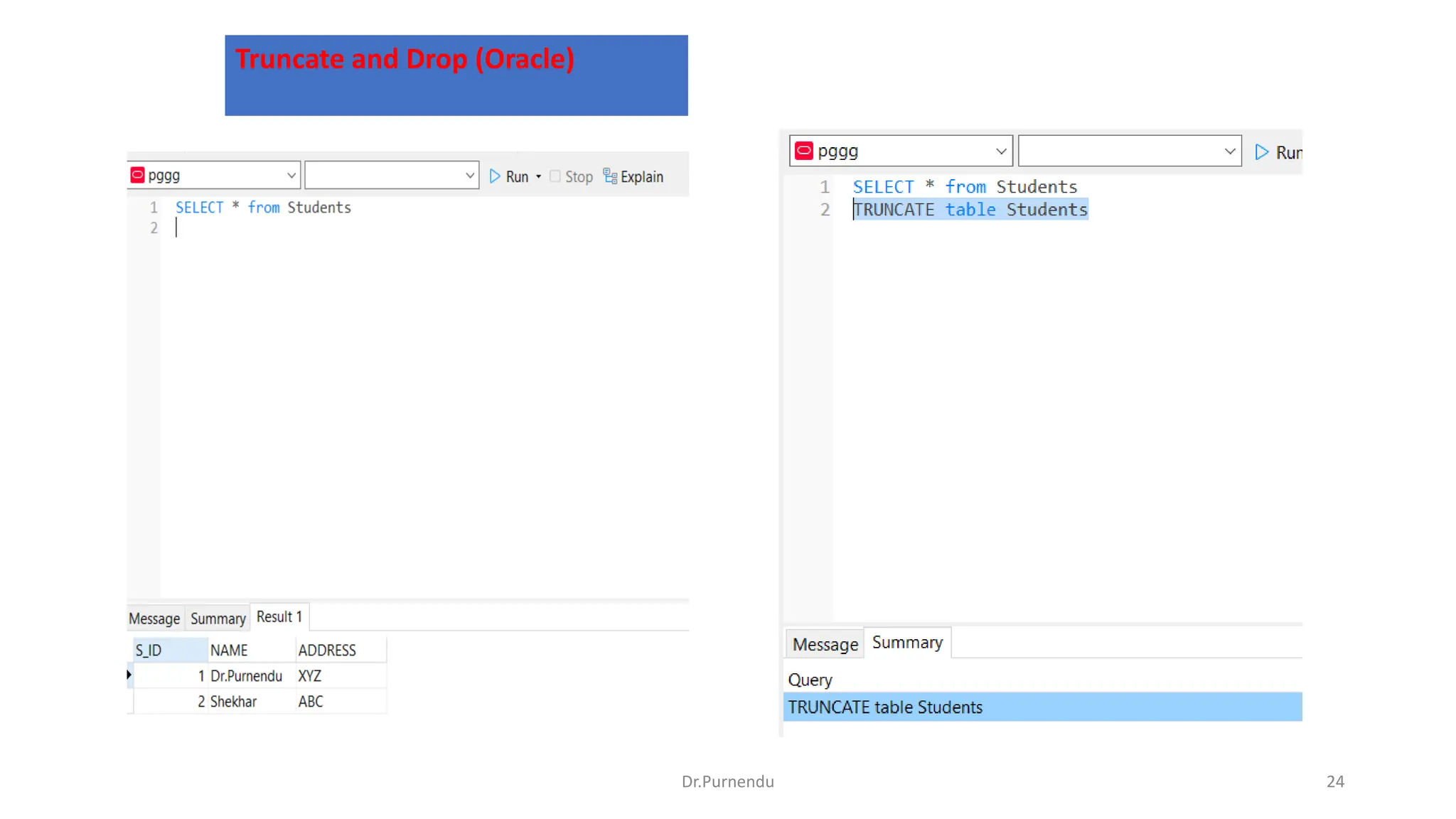
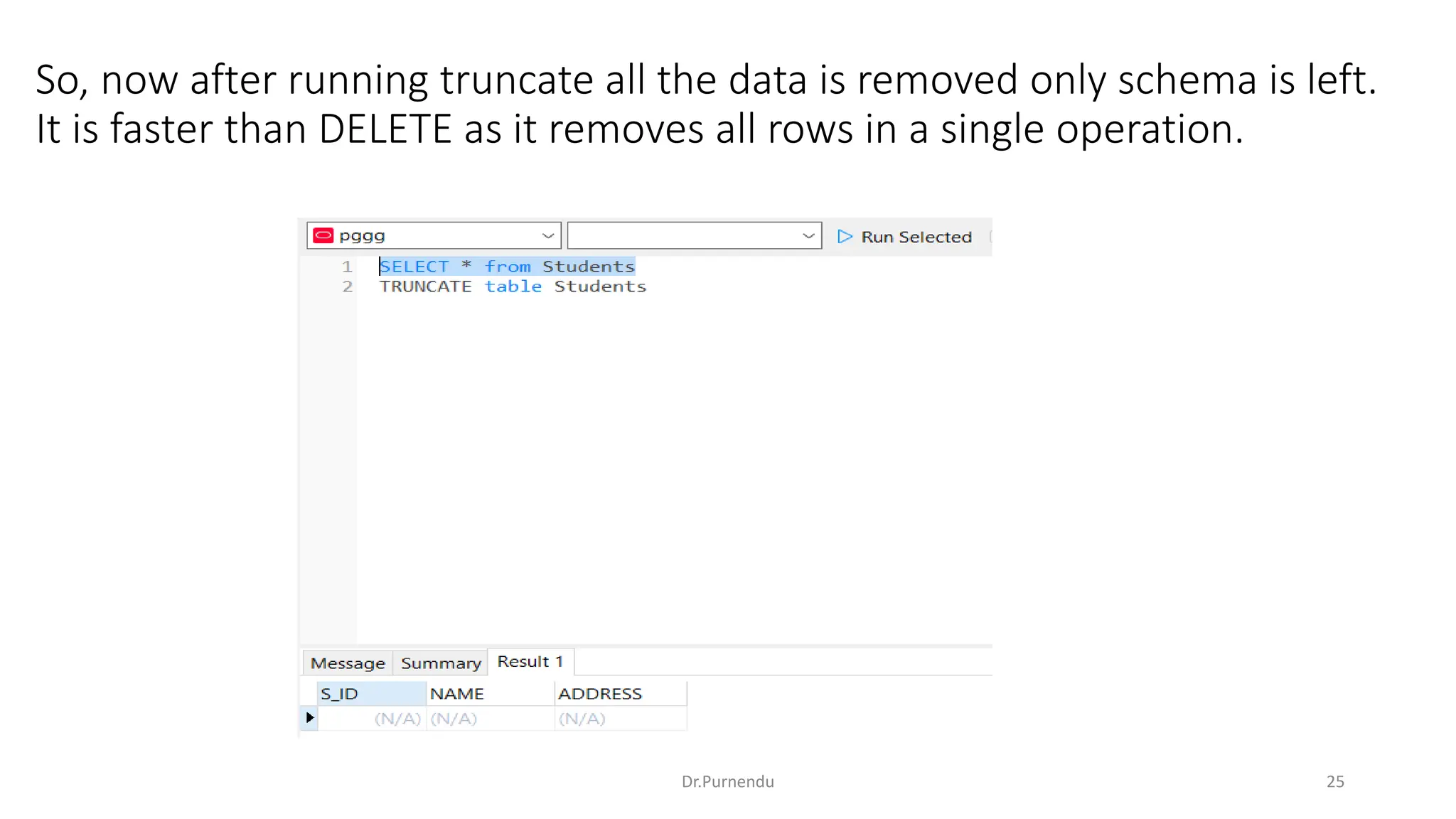
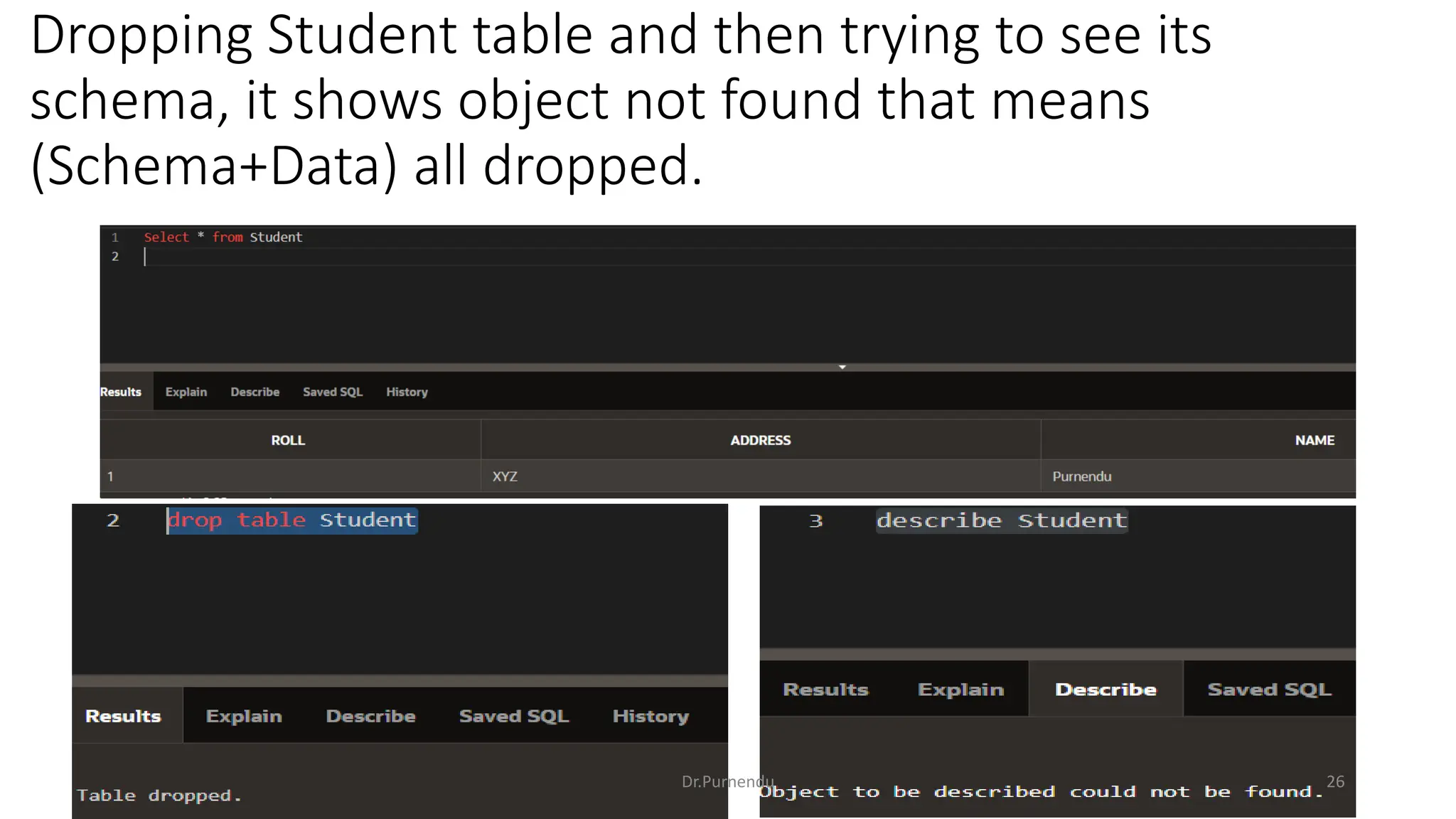
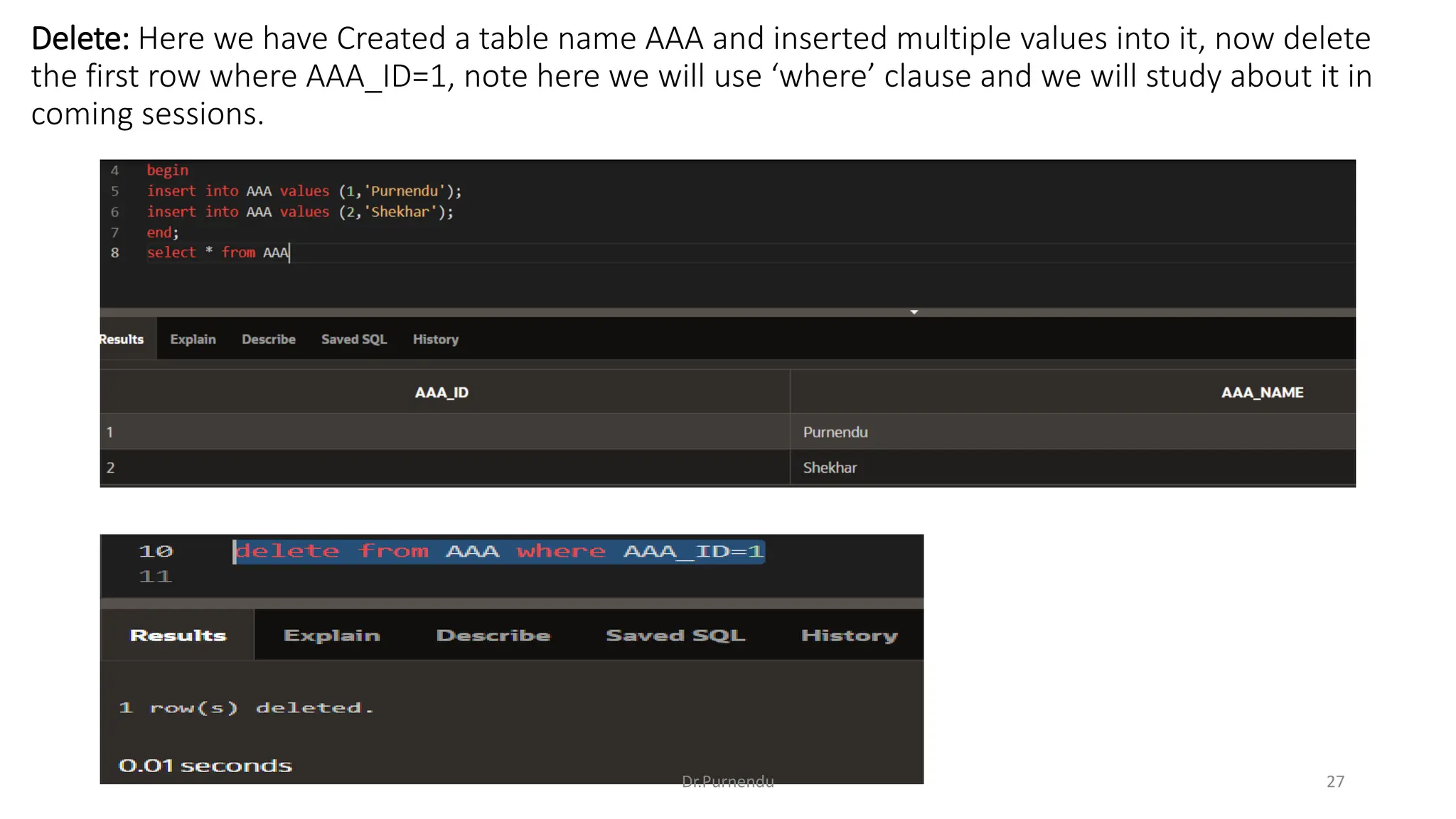
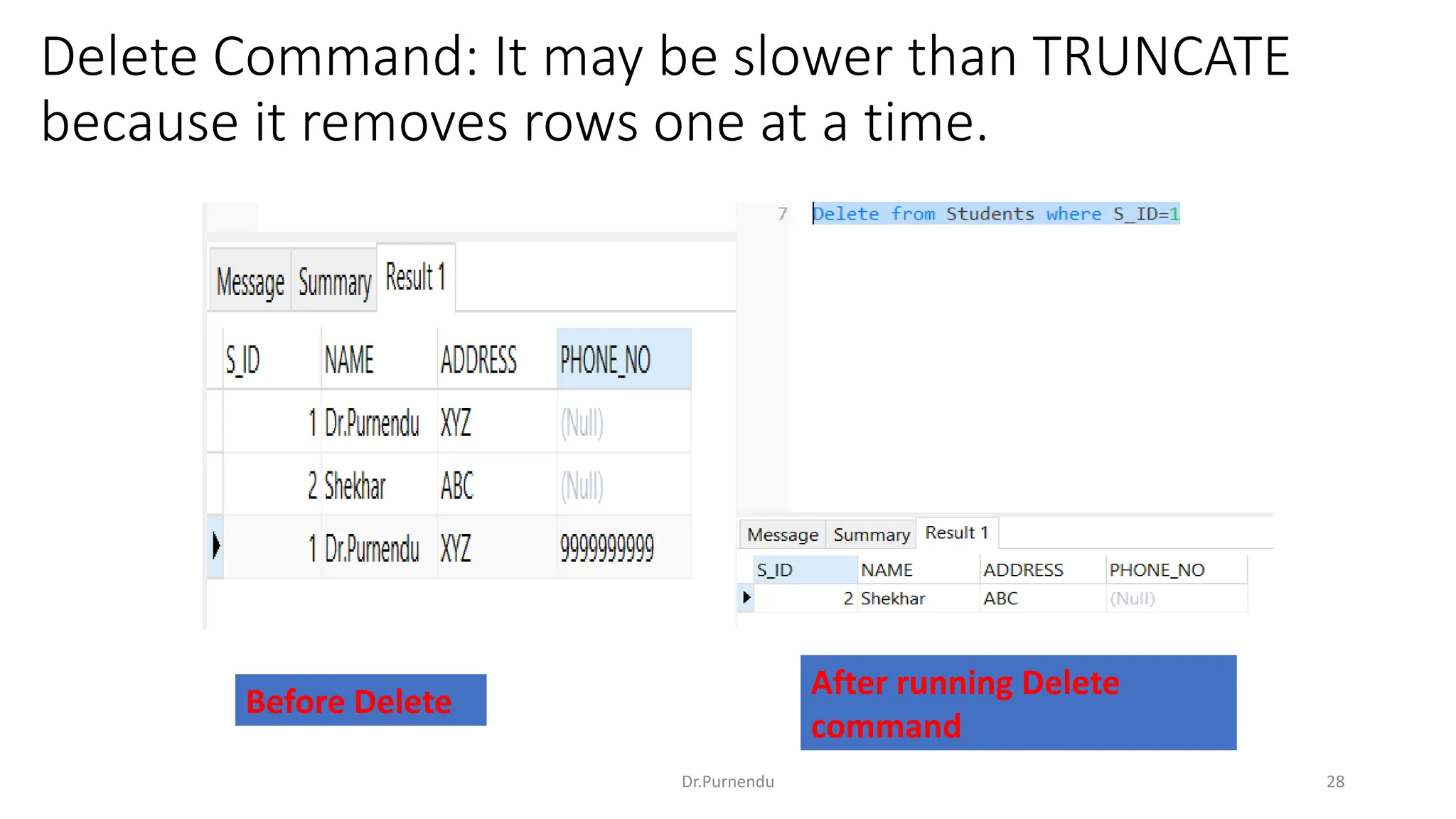
The document discusses various SQL commands categorized into DDL, DML, DQL, and DCL. It provides examples and explanations of each category. DDL commands like CREATE, ALTER, DROP are used to define and modify database schemas. DML commands like INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE manipulate the data. DQL commands mainly refers to SELECT which is used to query data. DCL commands like GRANT, REVOKE control access privileges to the database. The document also provides examples of using various SQL commands to create tables, insert data, delete rows, and alter table schemas.