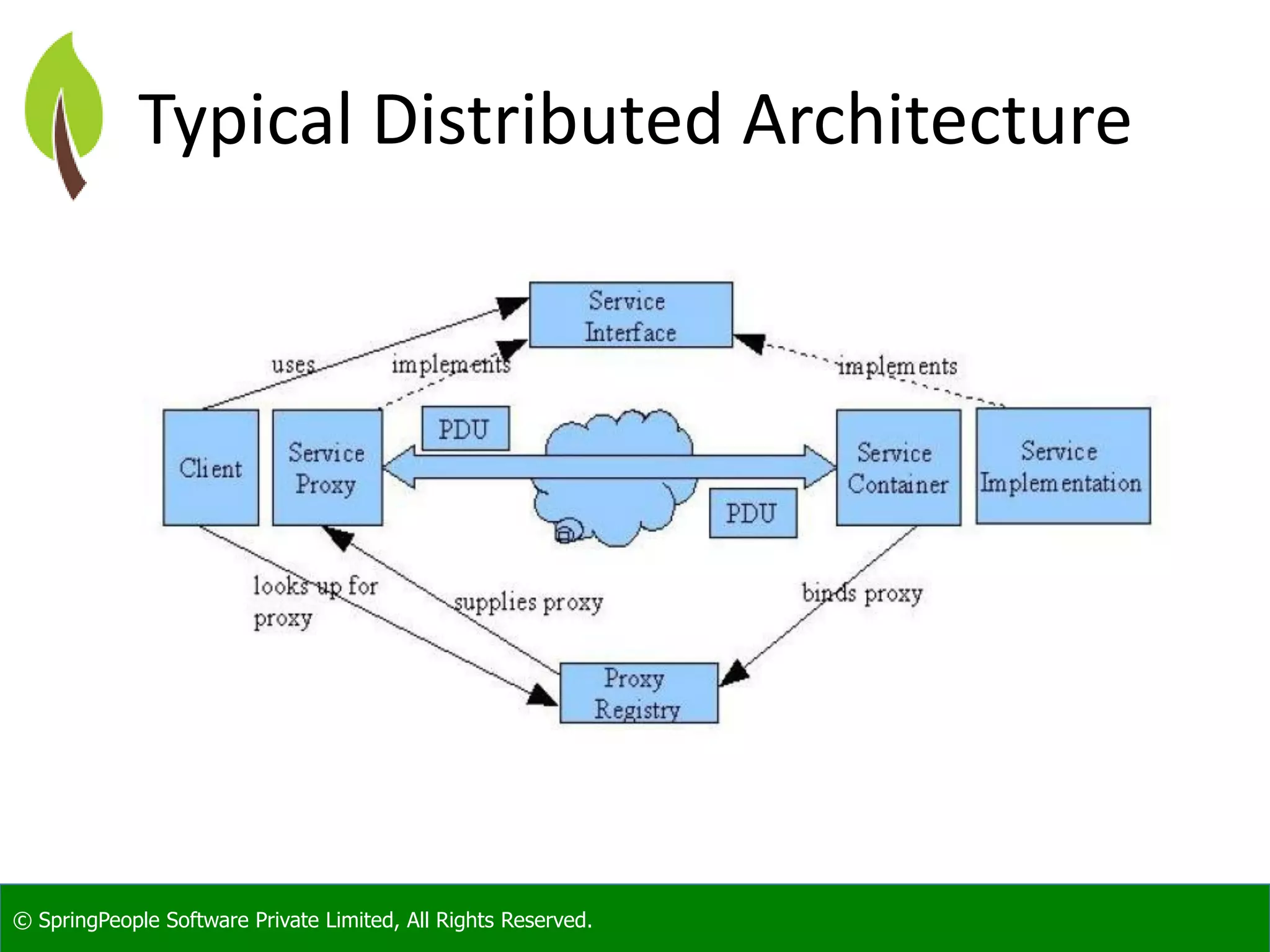
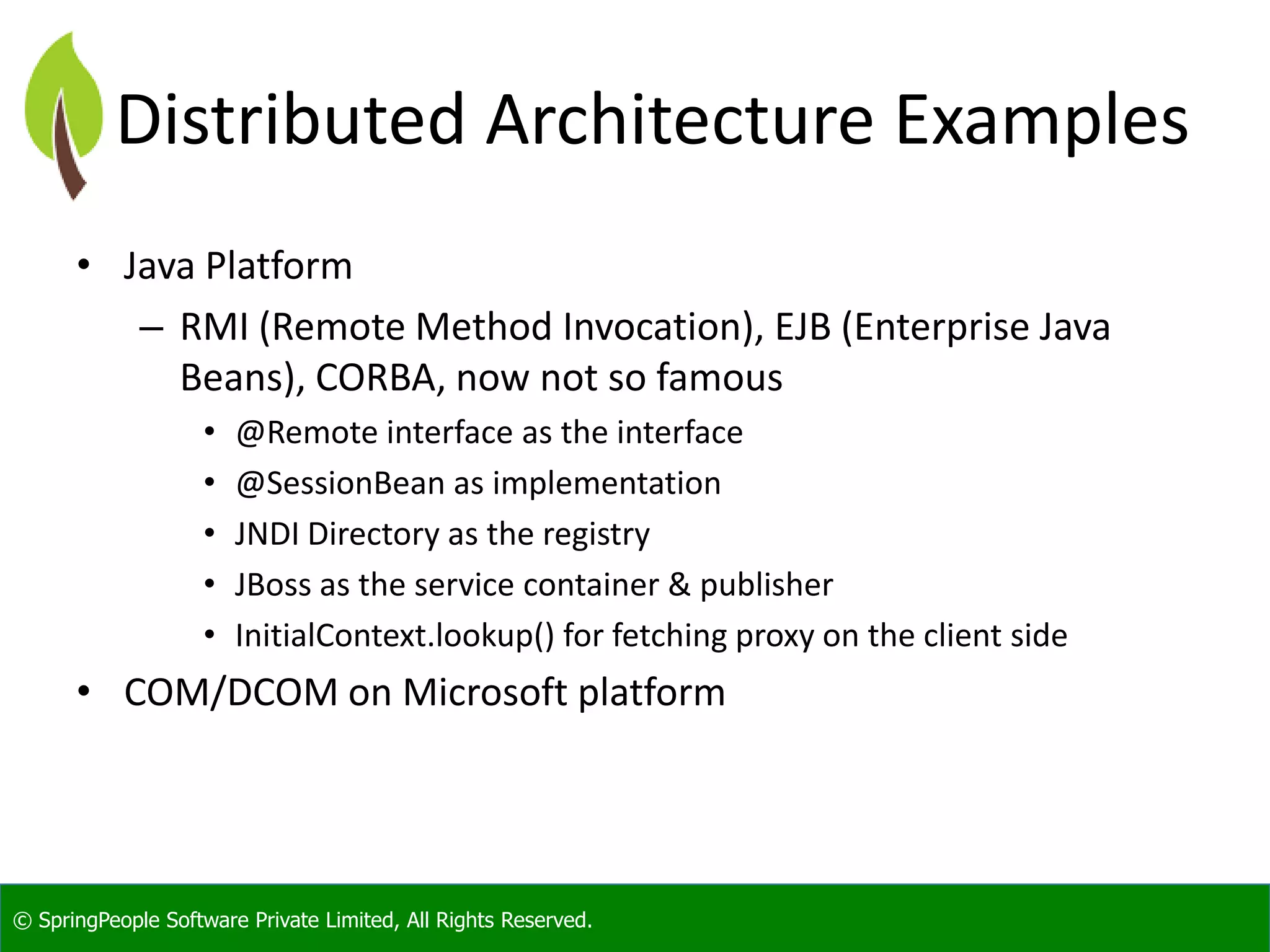
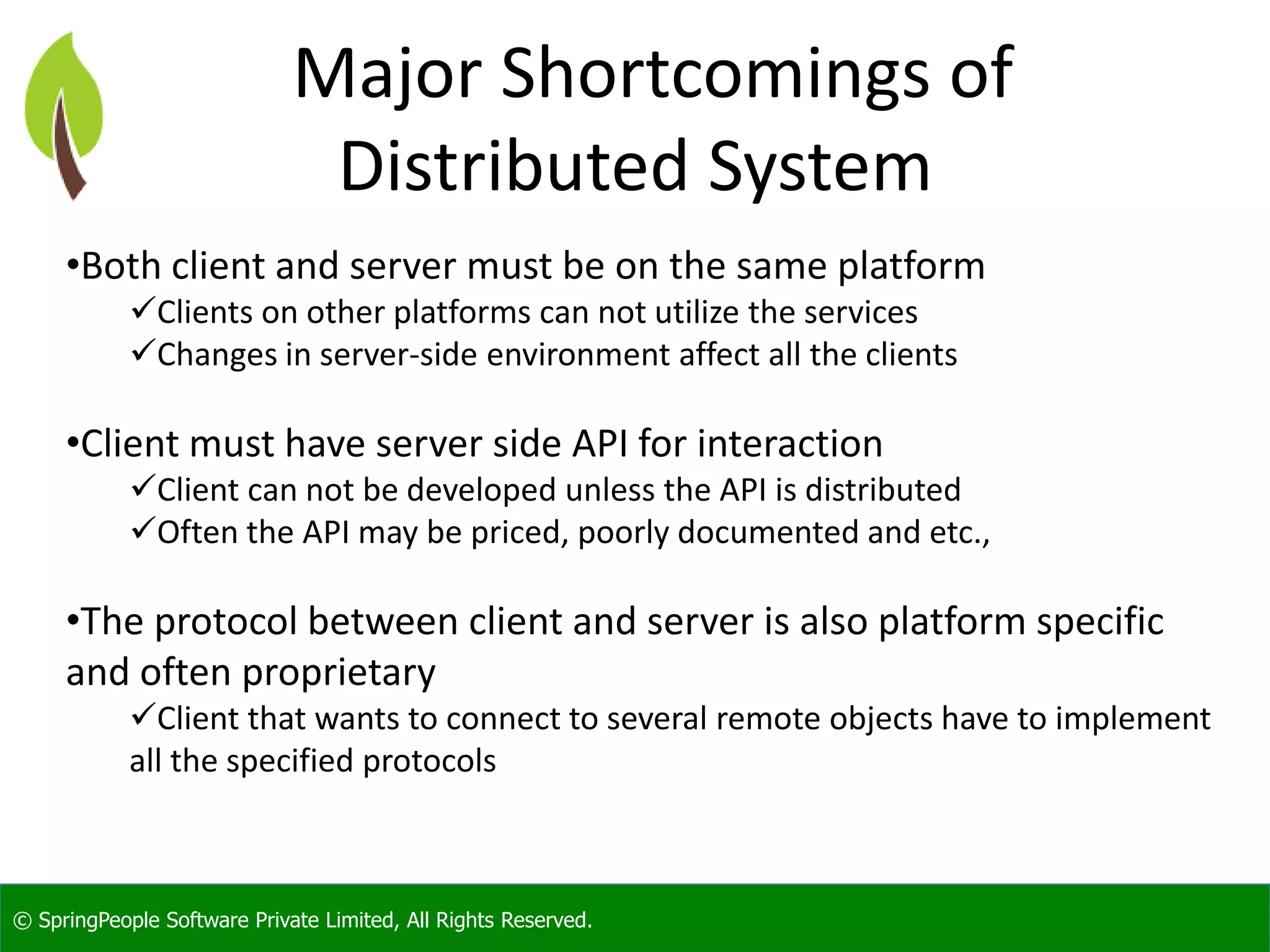
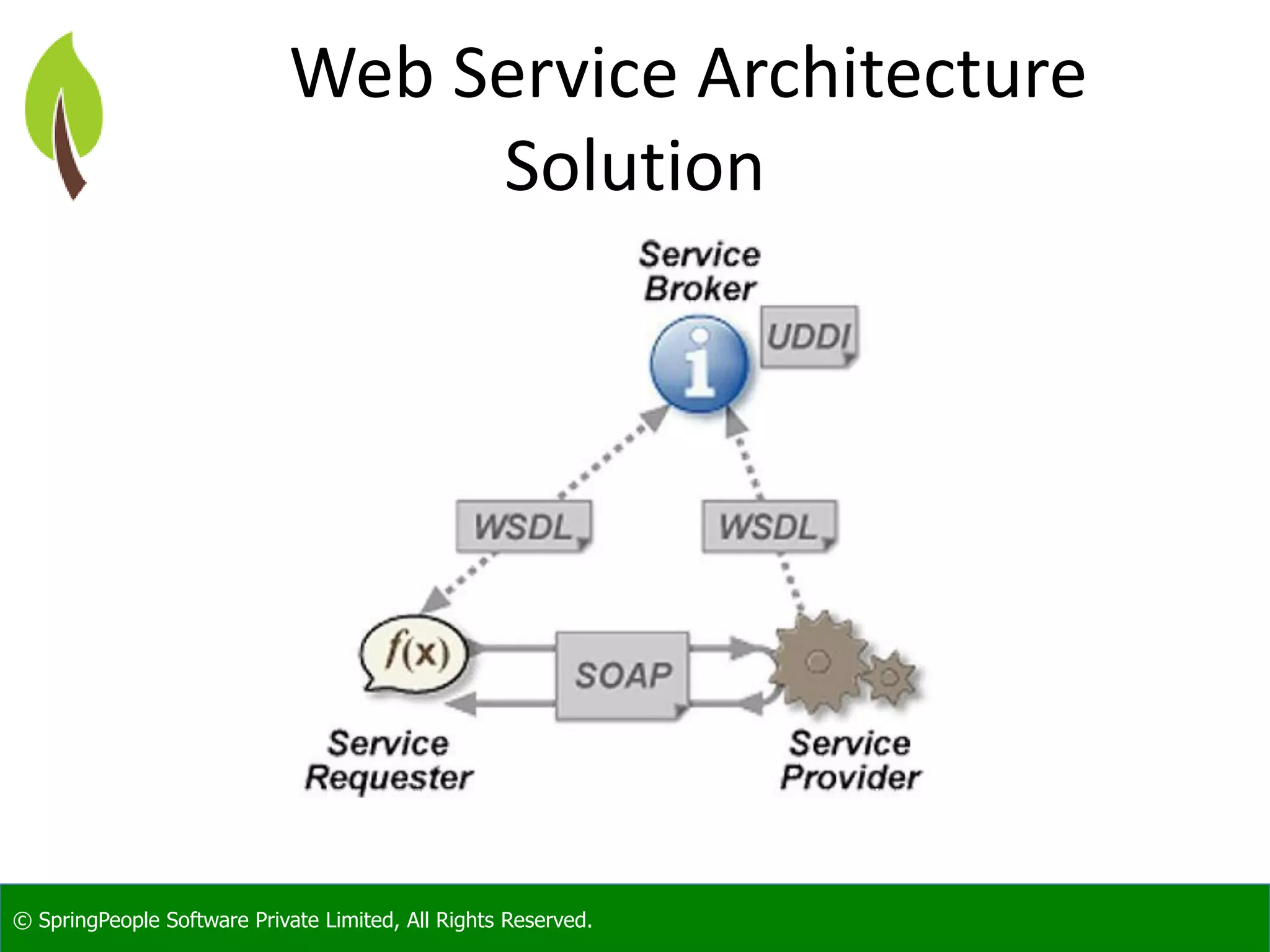
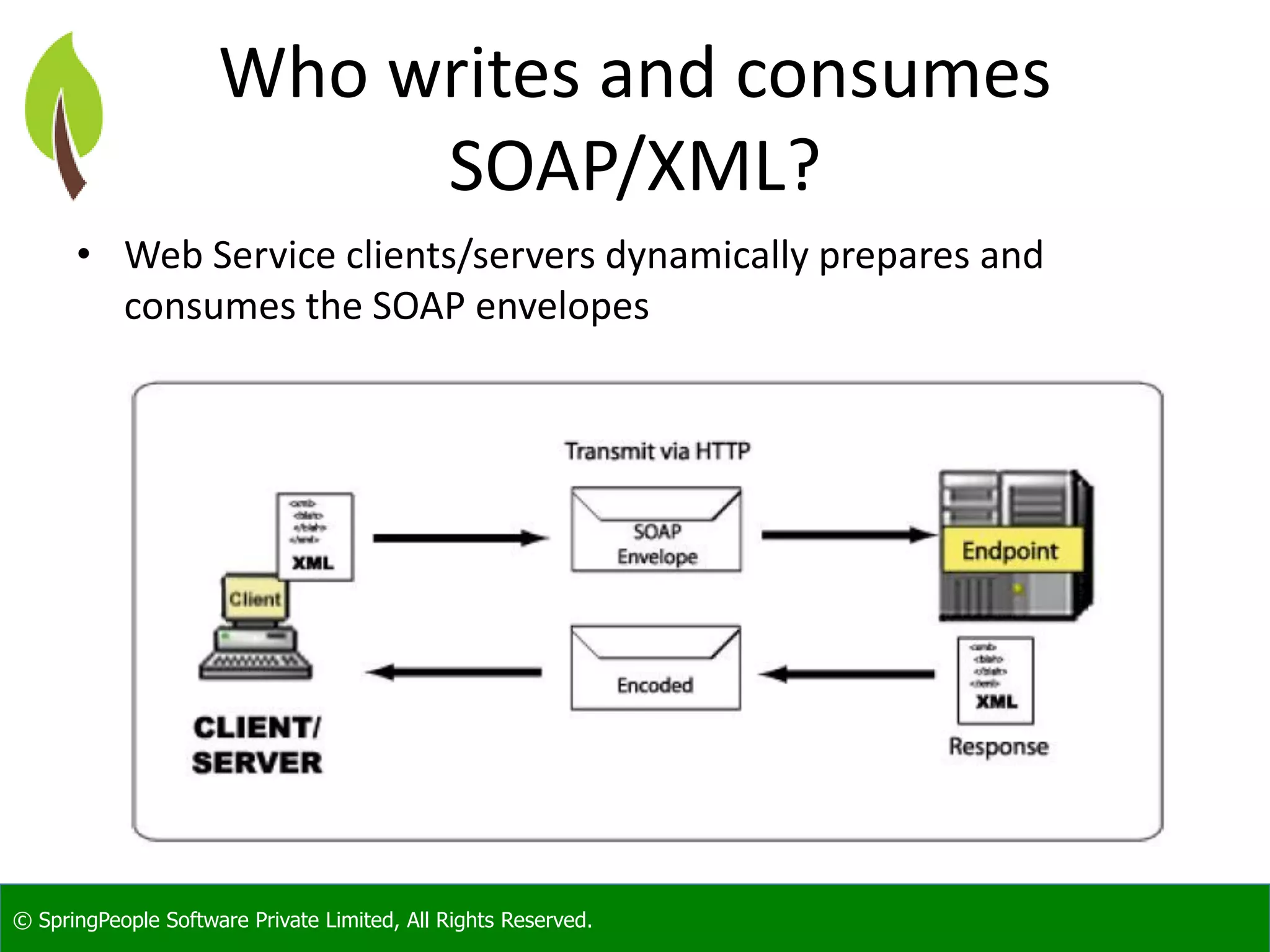
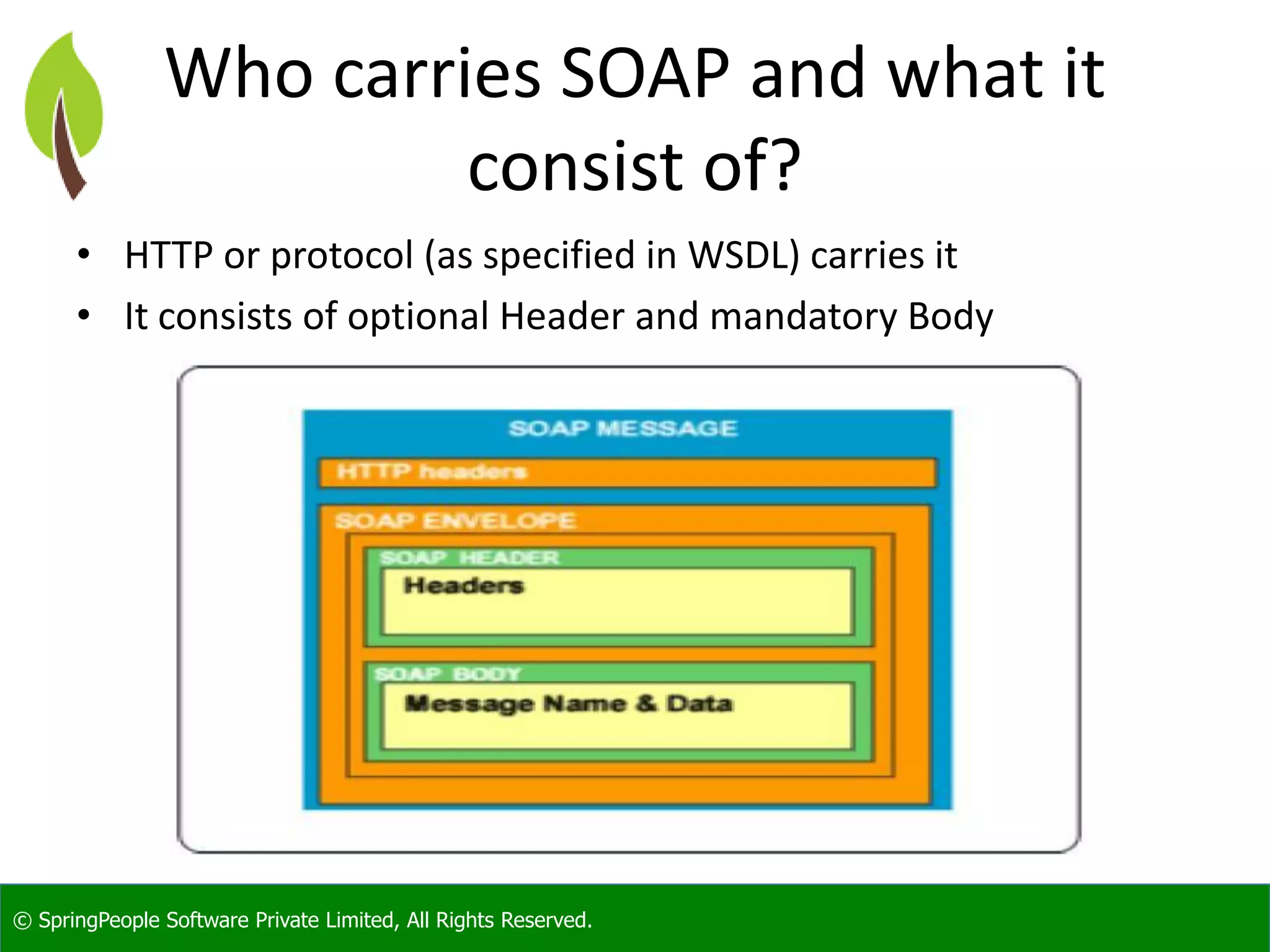
The document provides an introduction to Java web services, outlining their role in enabling interoperable distributed services across various platforms and programming languages. It details web service architecture, foundational standards, including WSDL and SOAP, and the major shortcomings of distributed systems. Additionally, it promotes a workshop for developers to gain expertise in building these services.