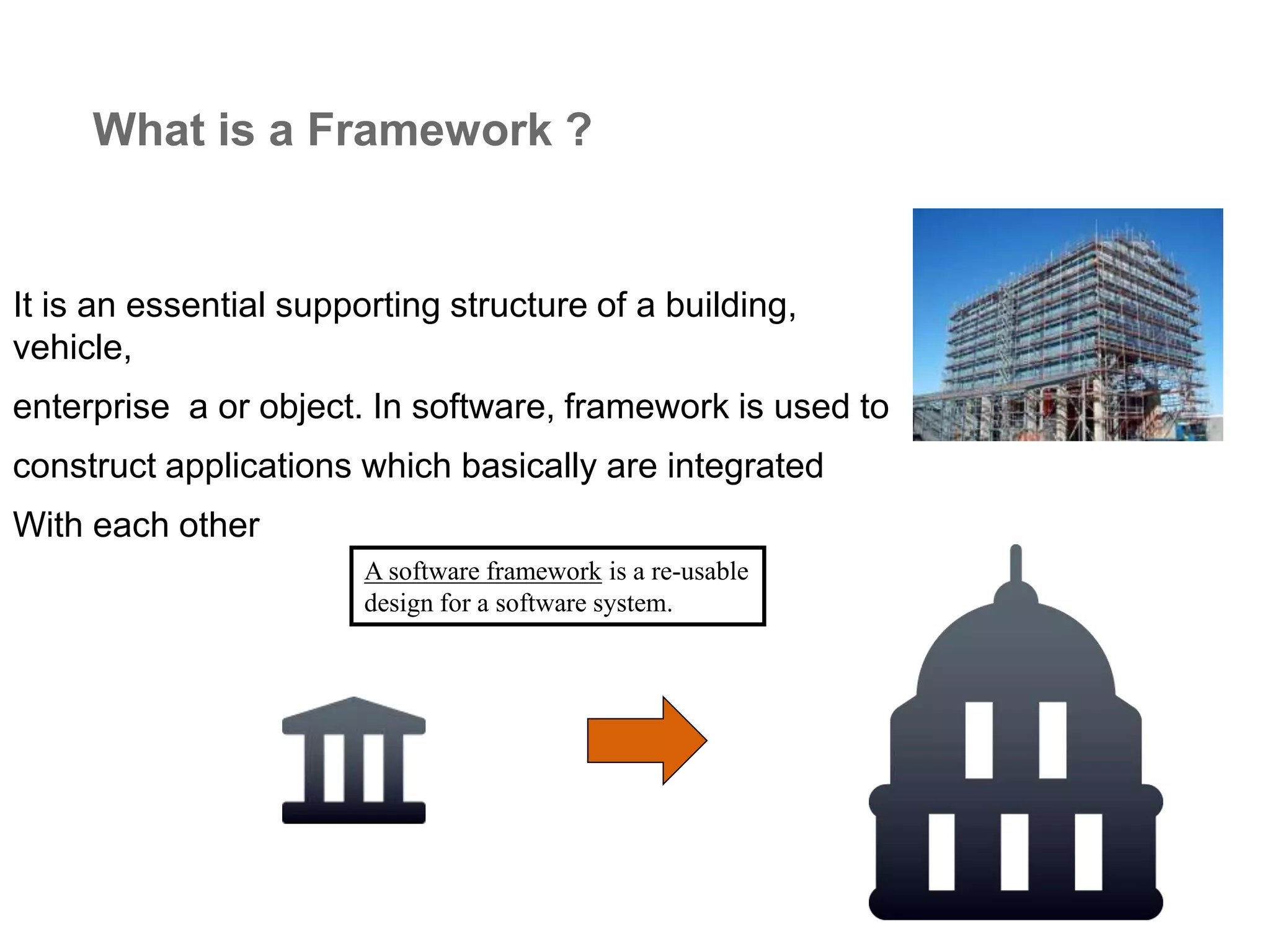
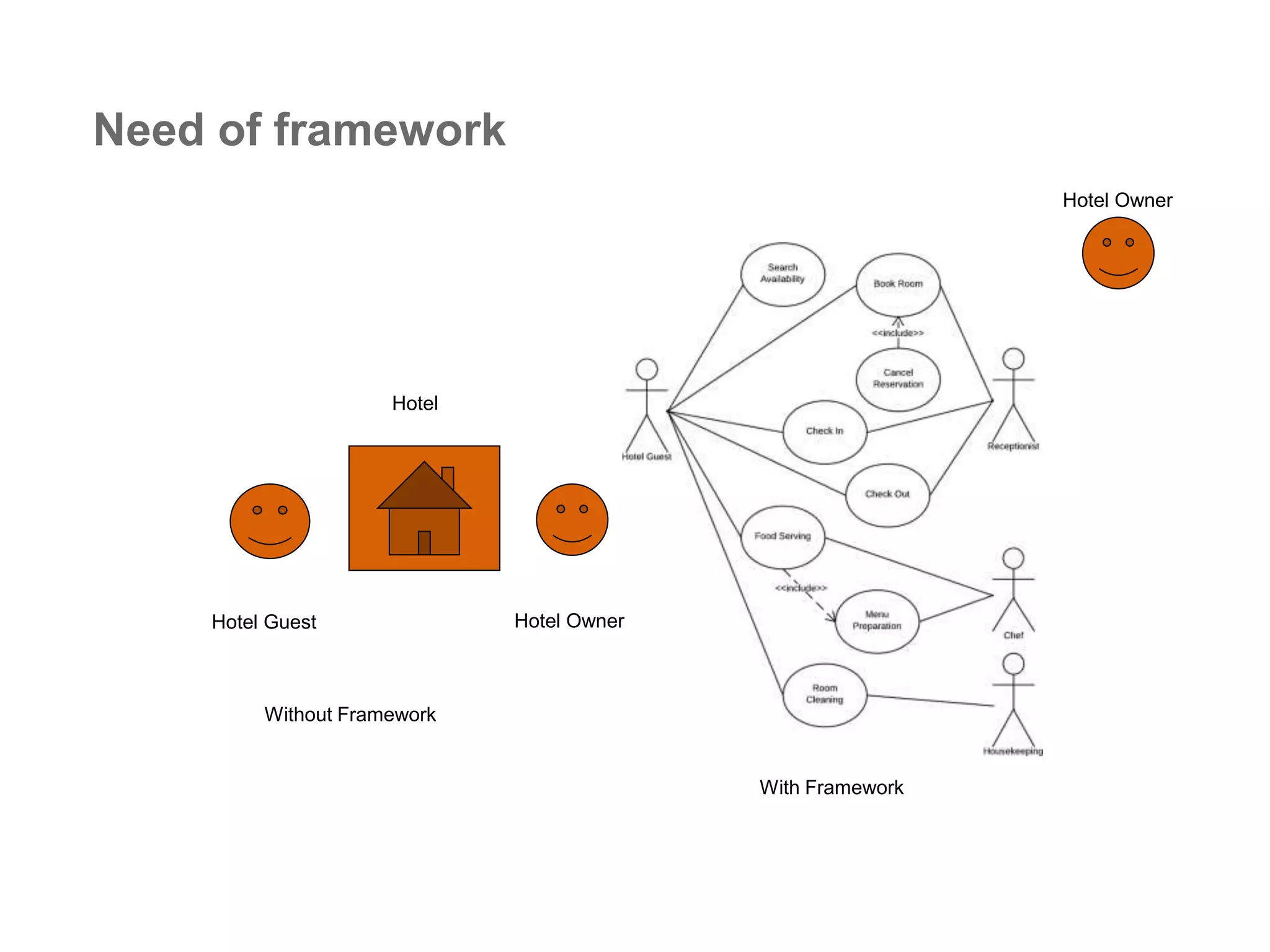
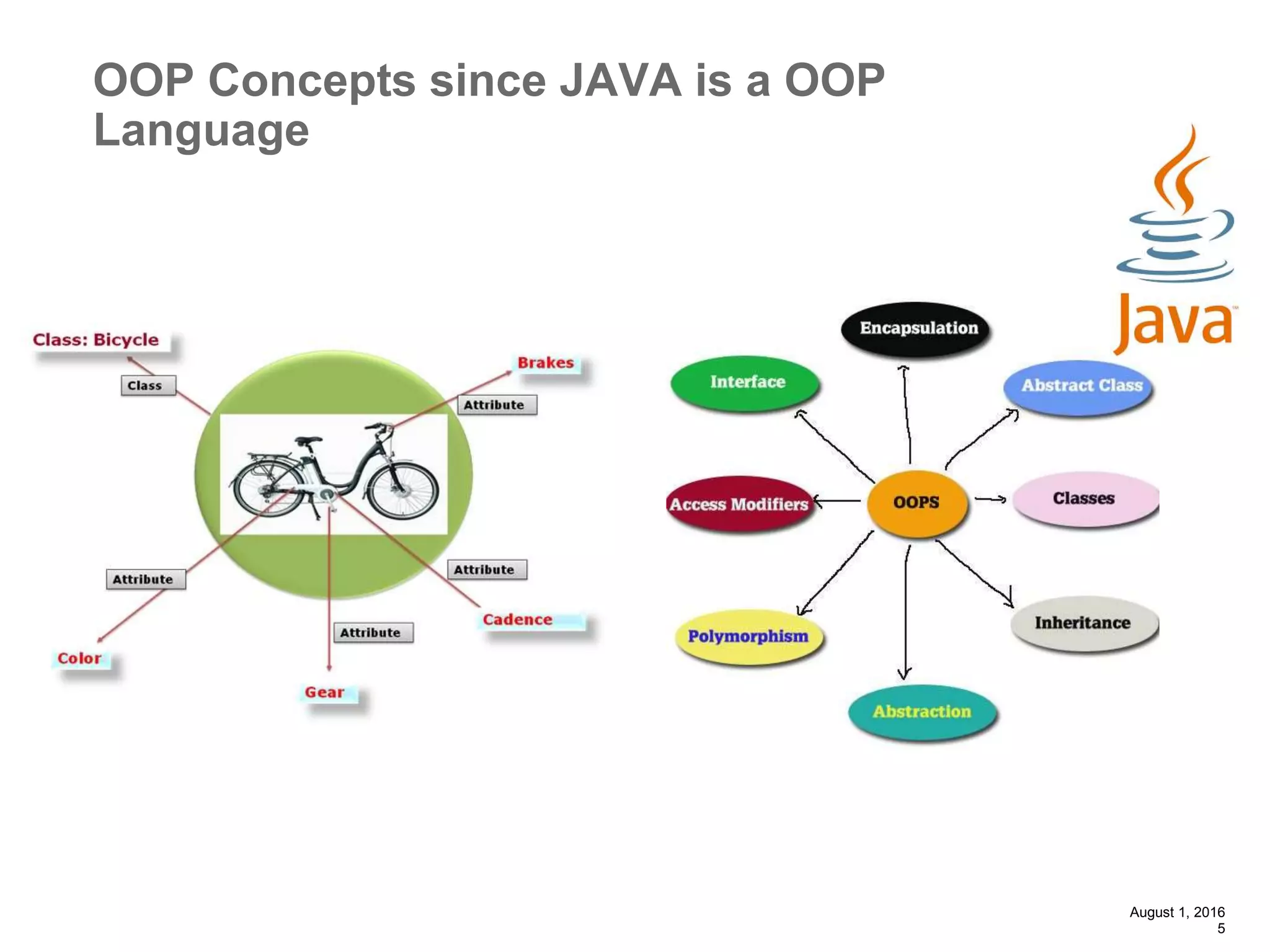
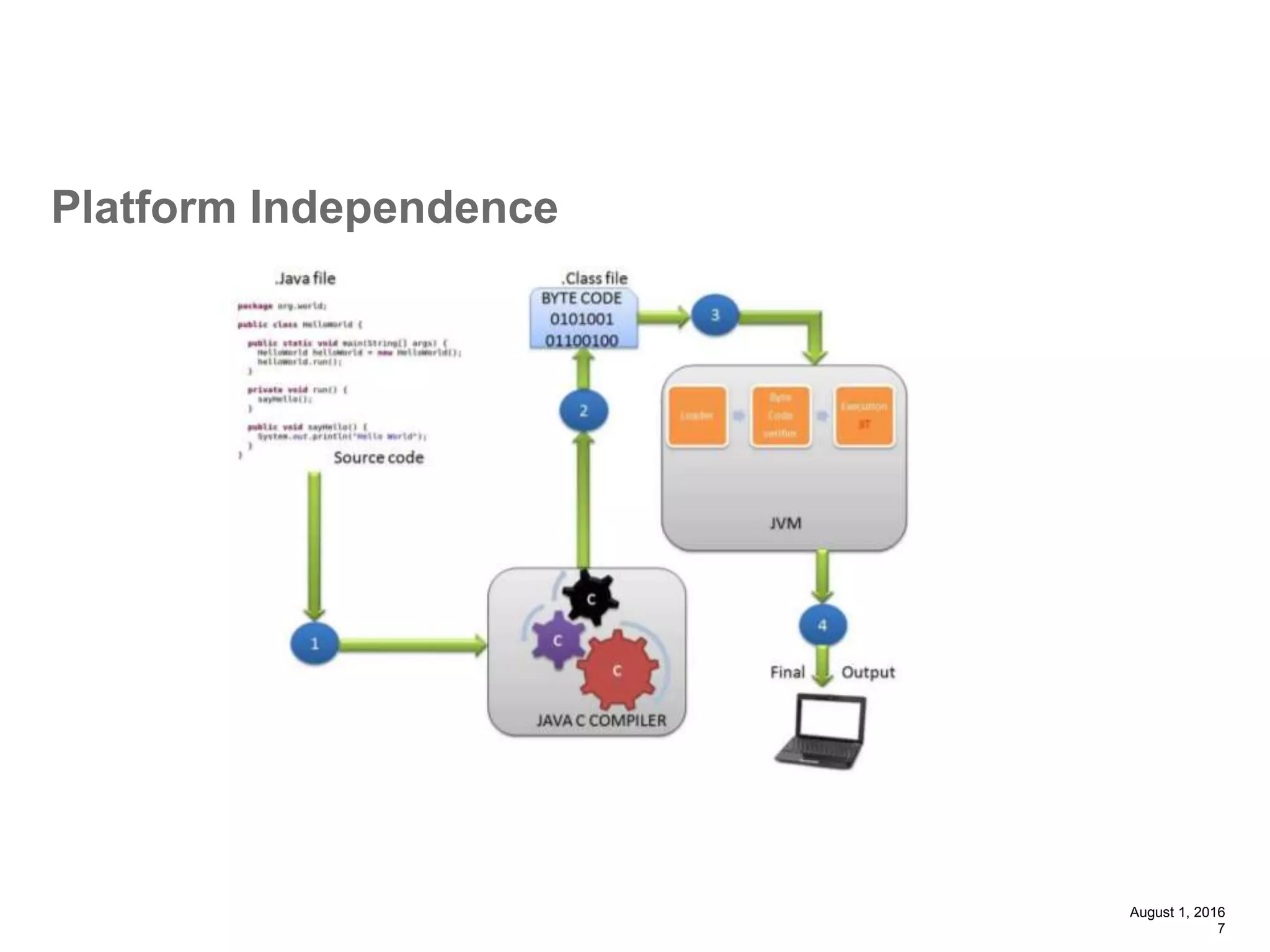
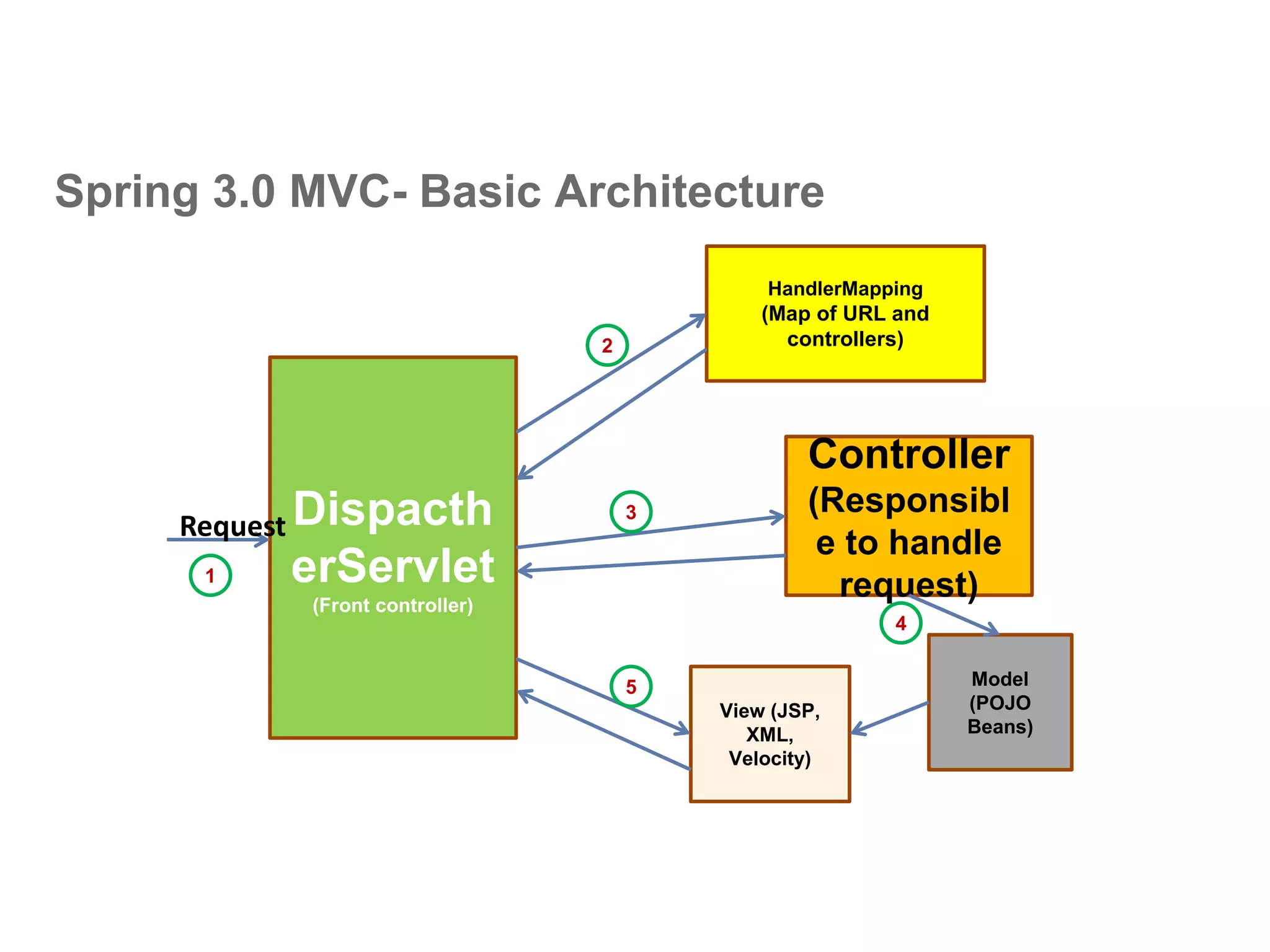
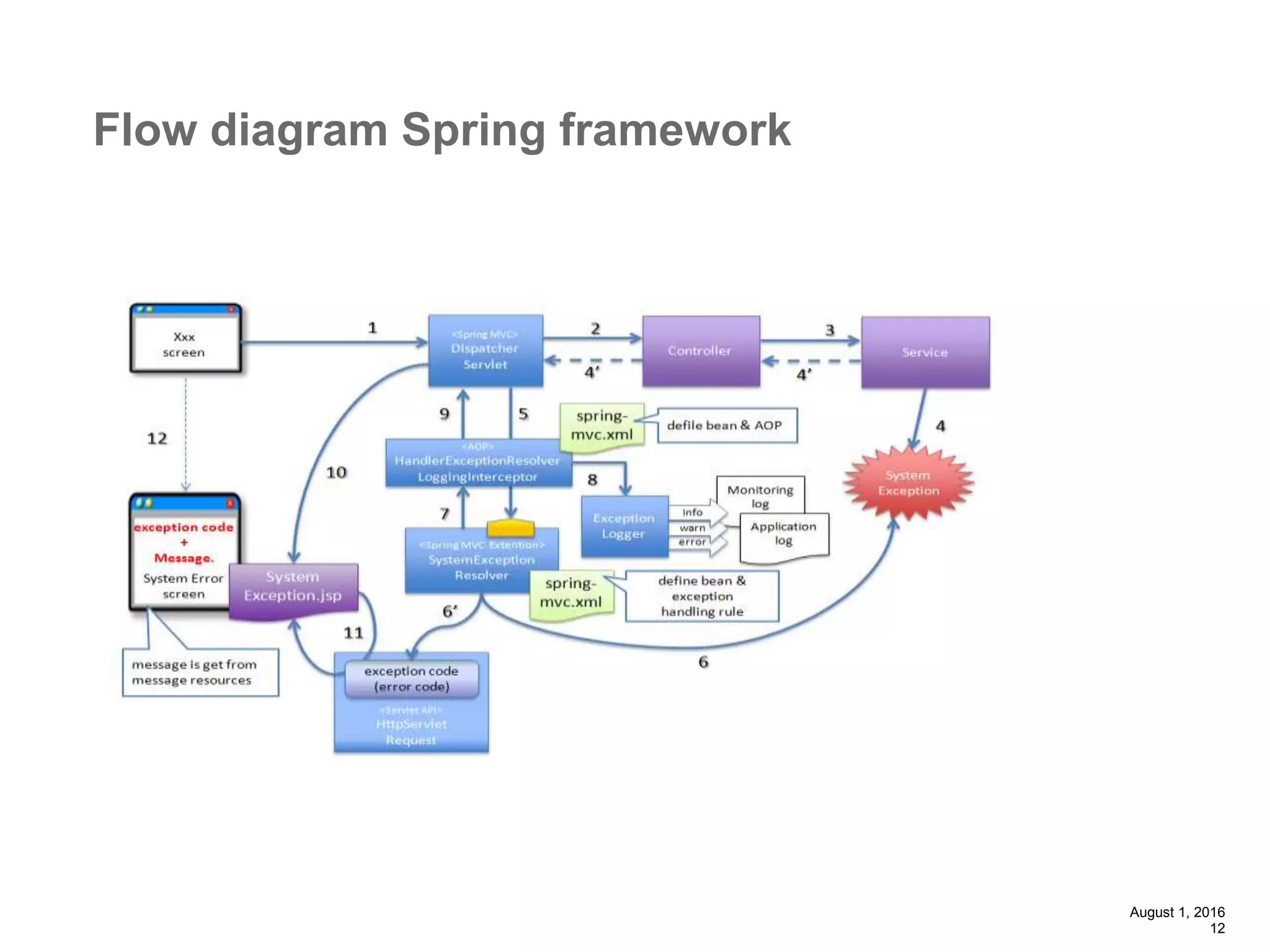
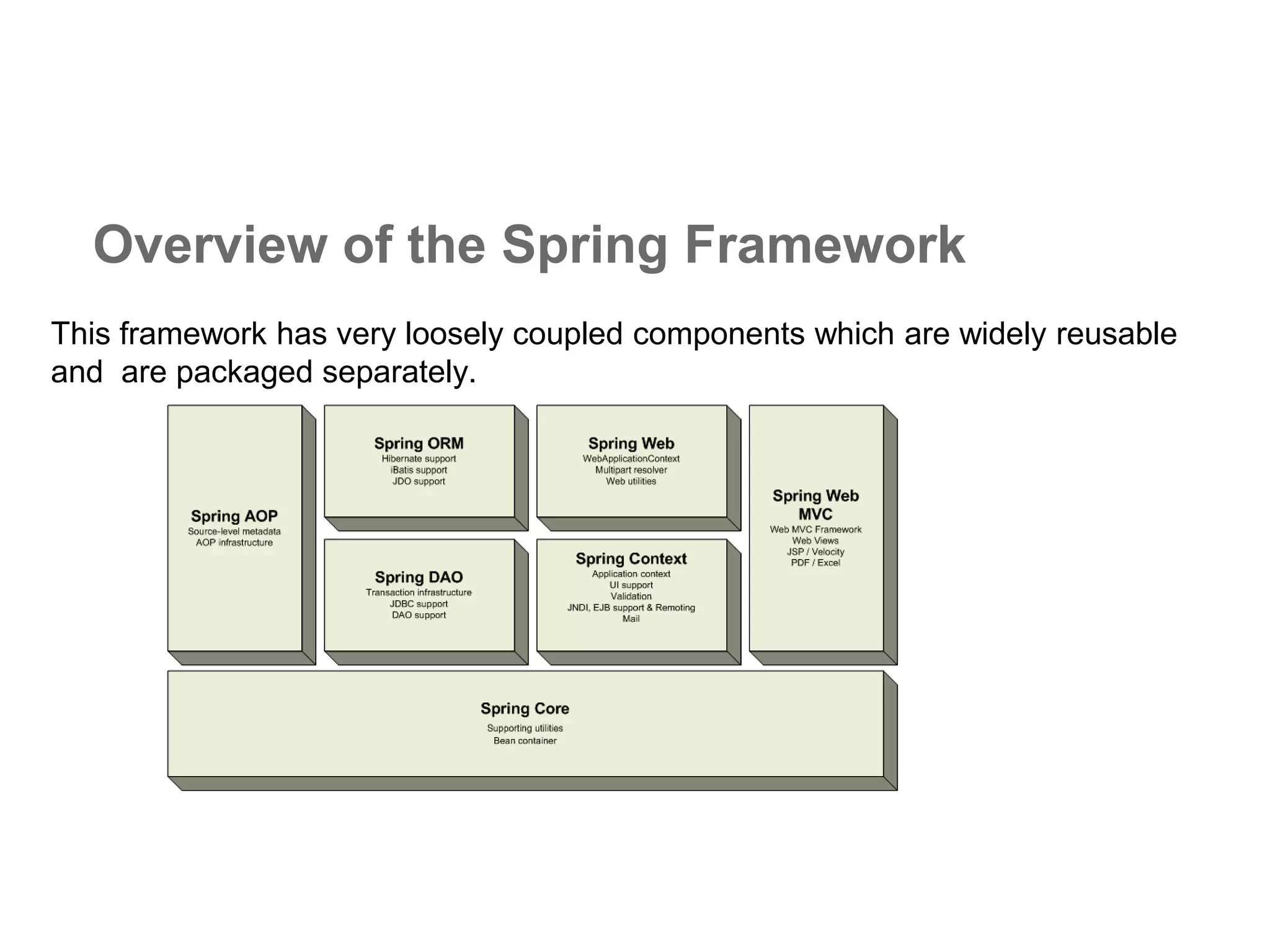
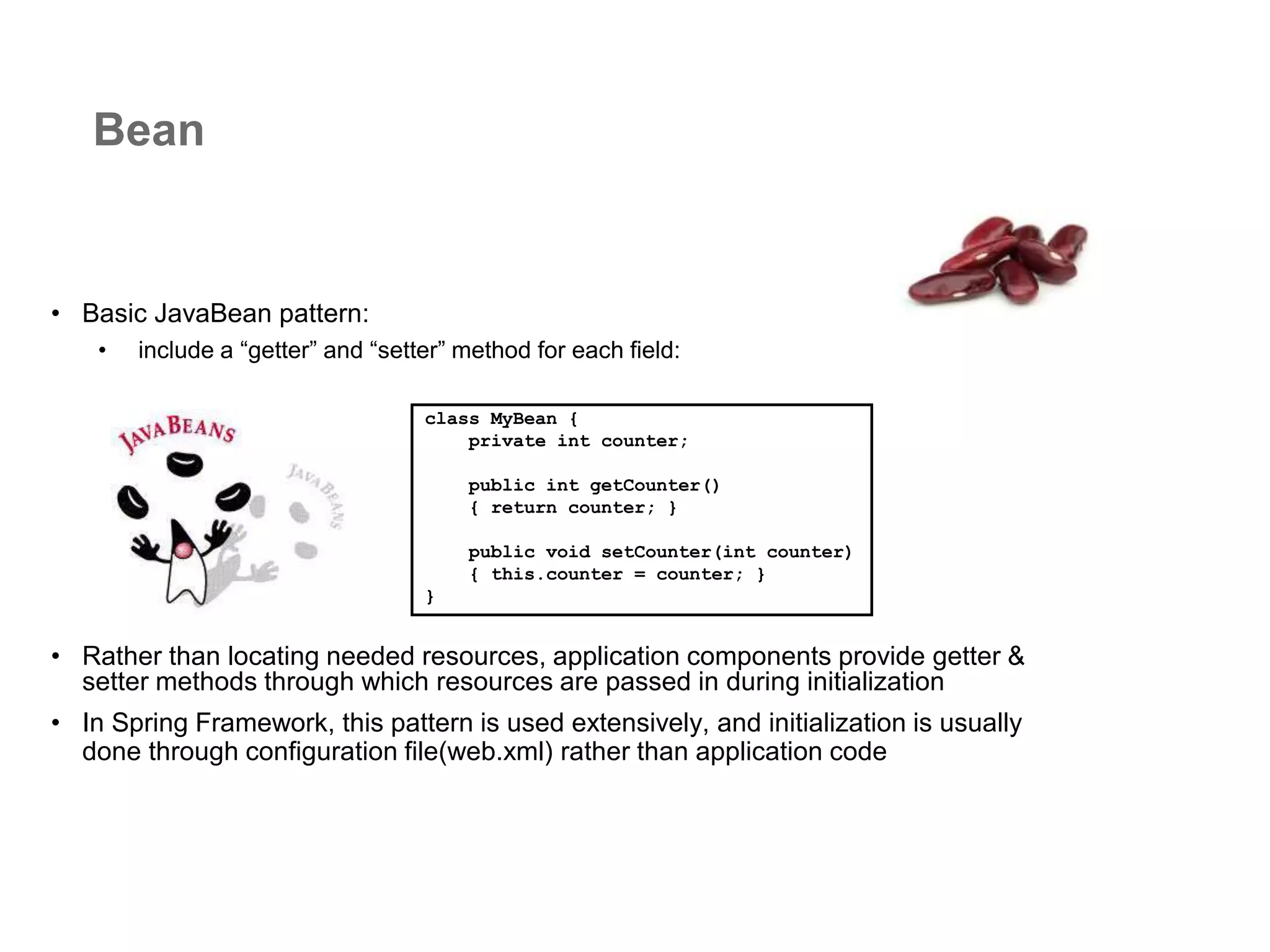
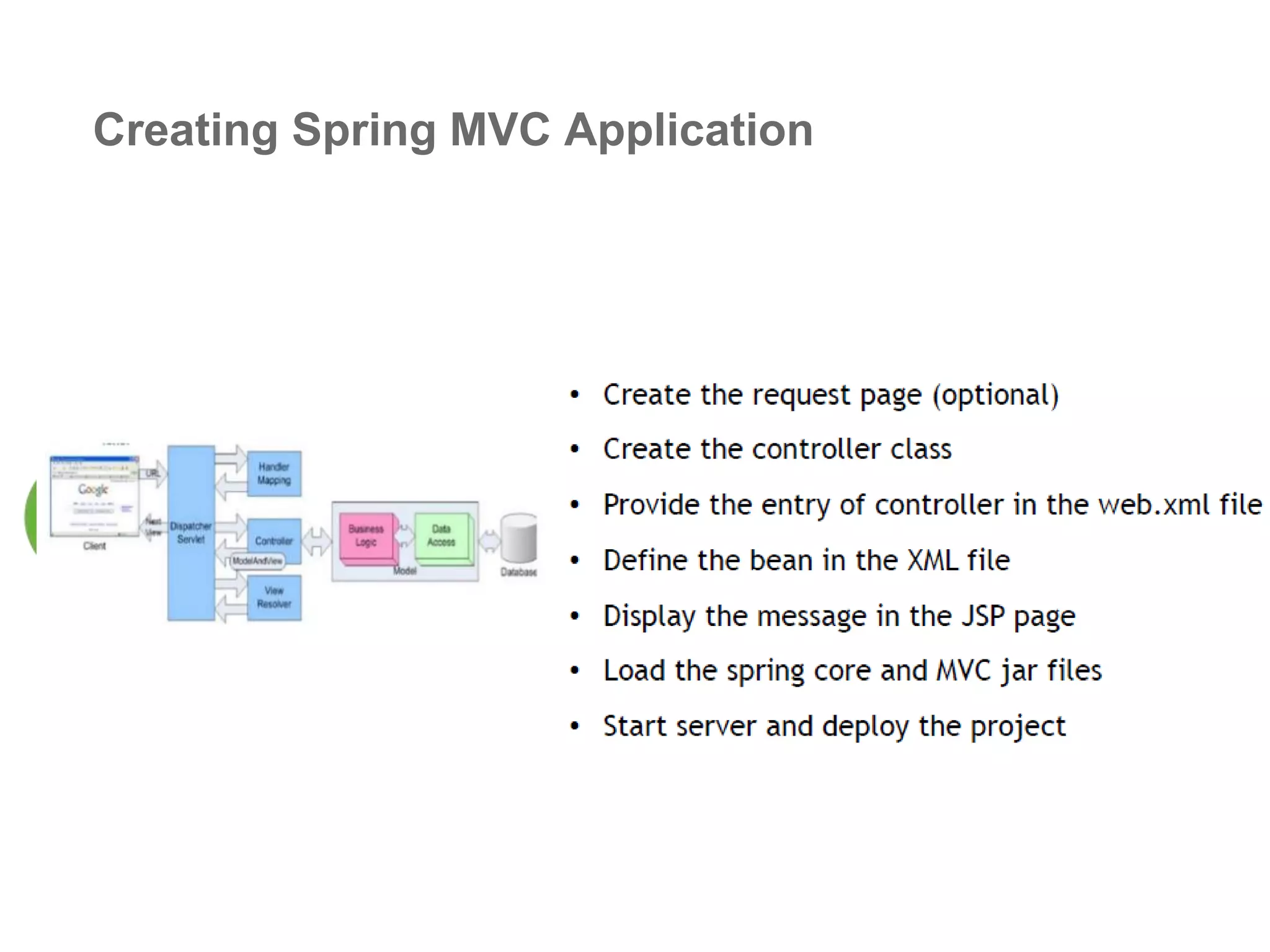
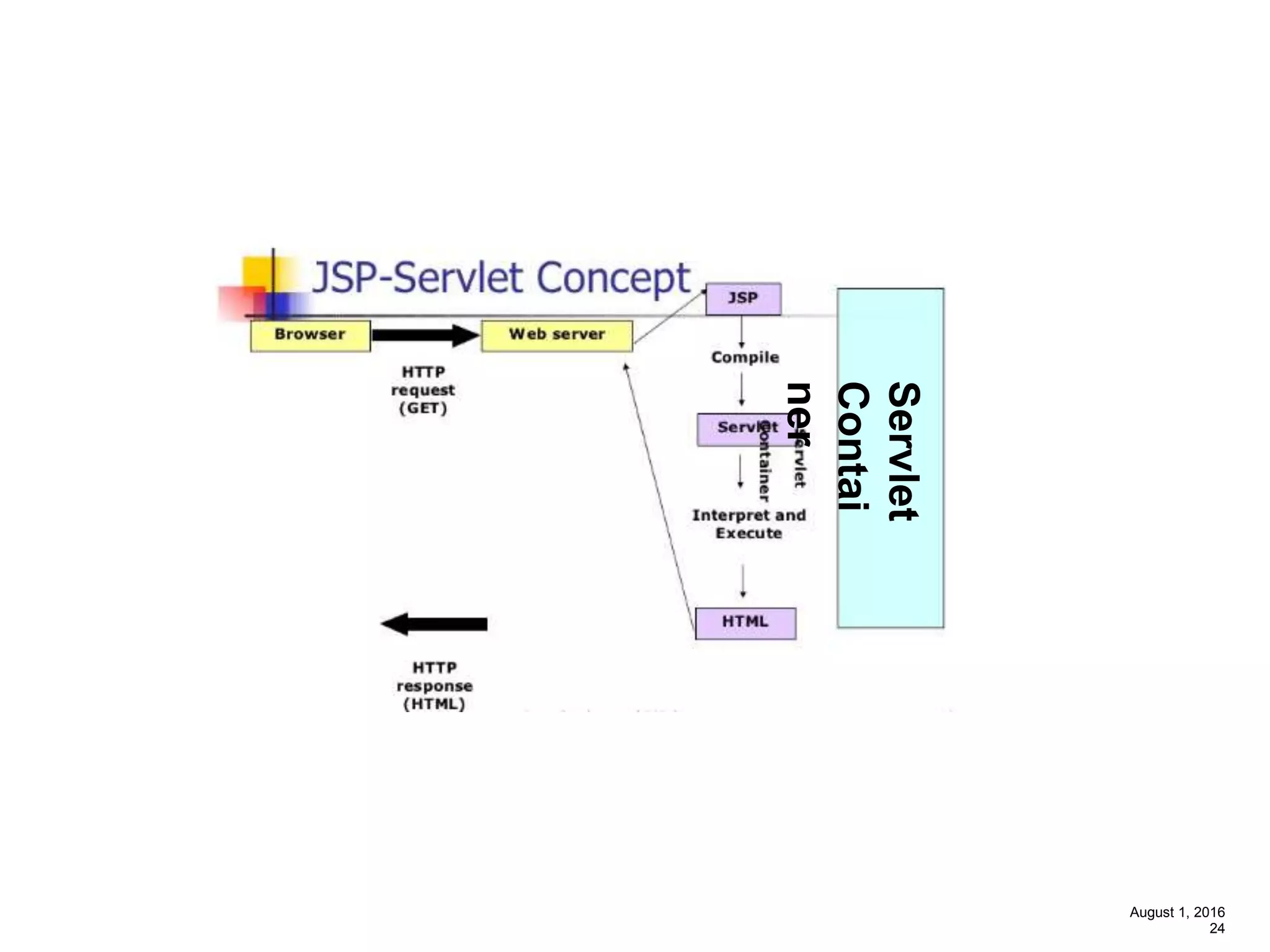
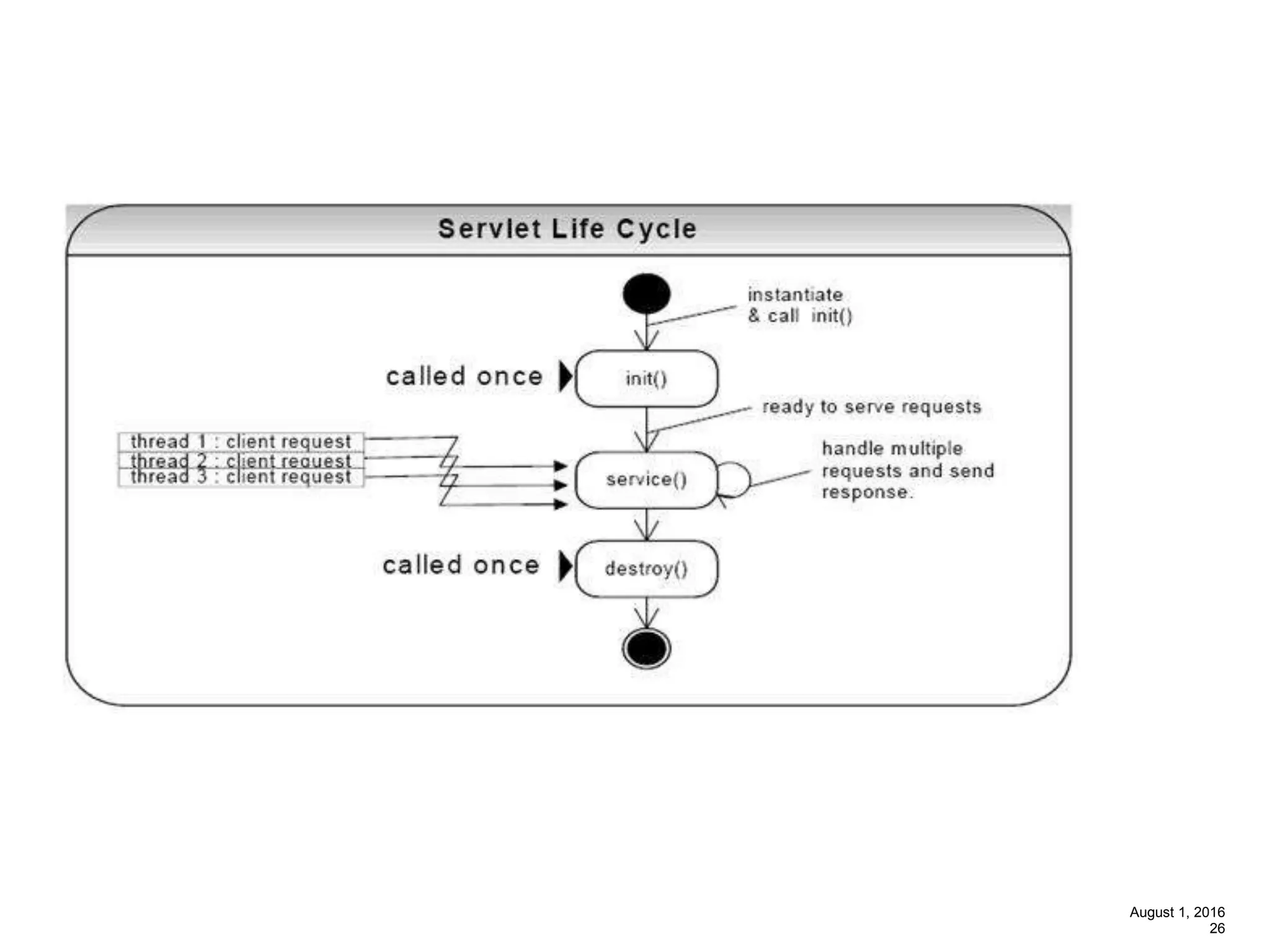
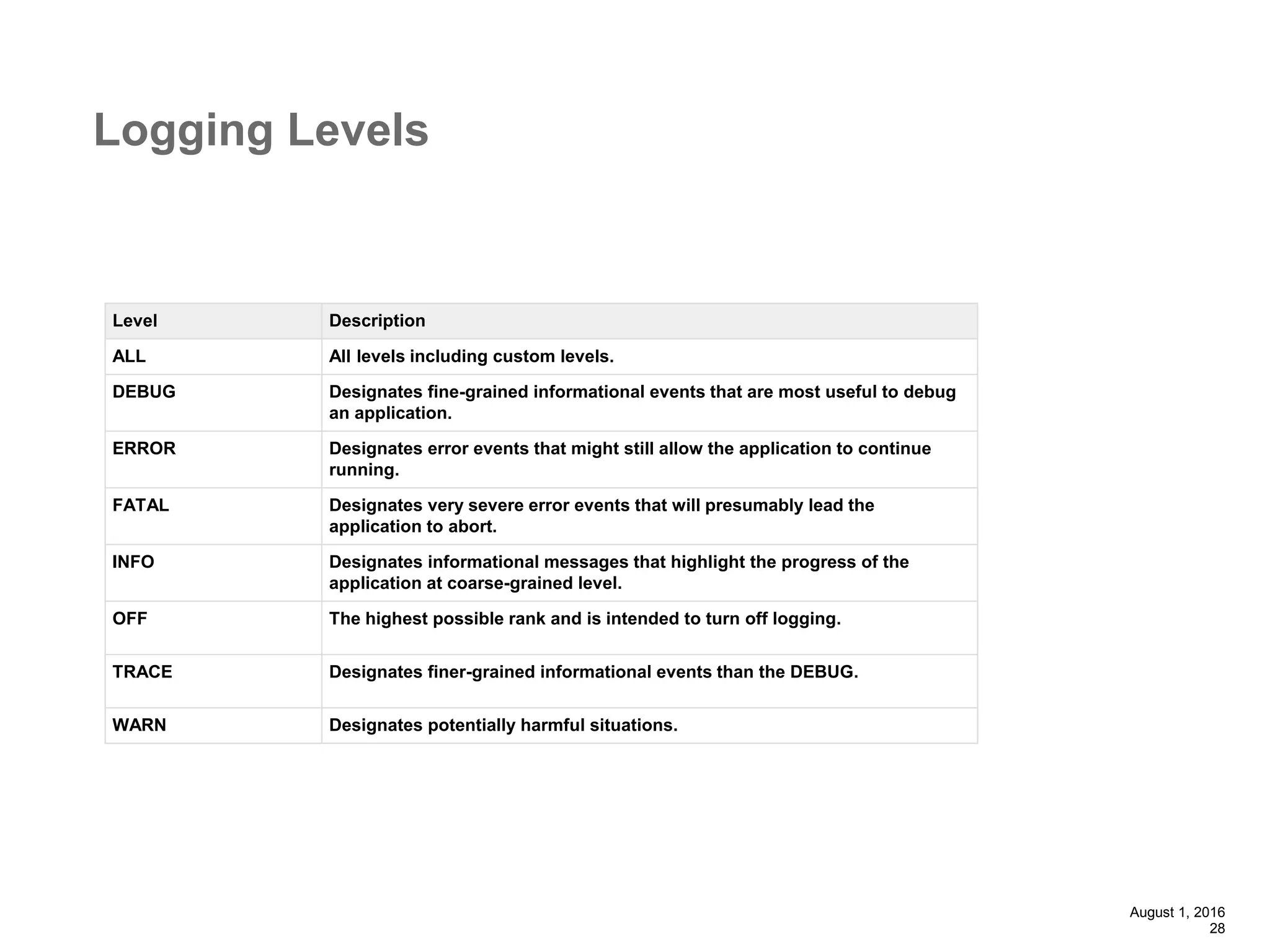
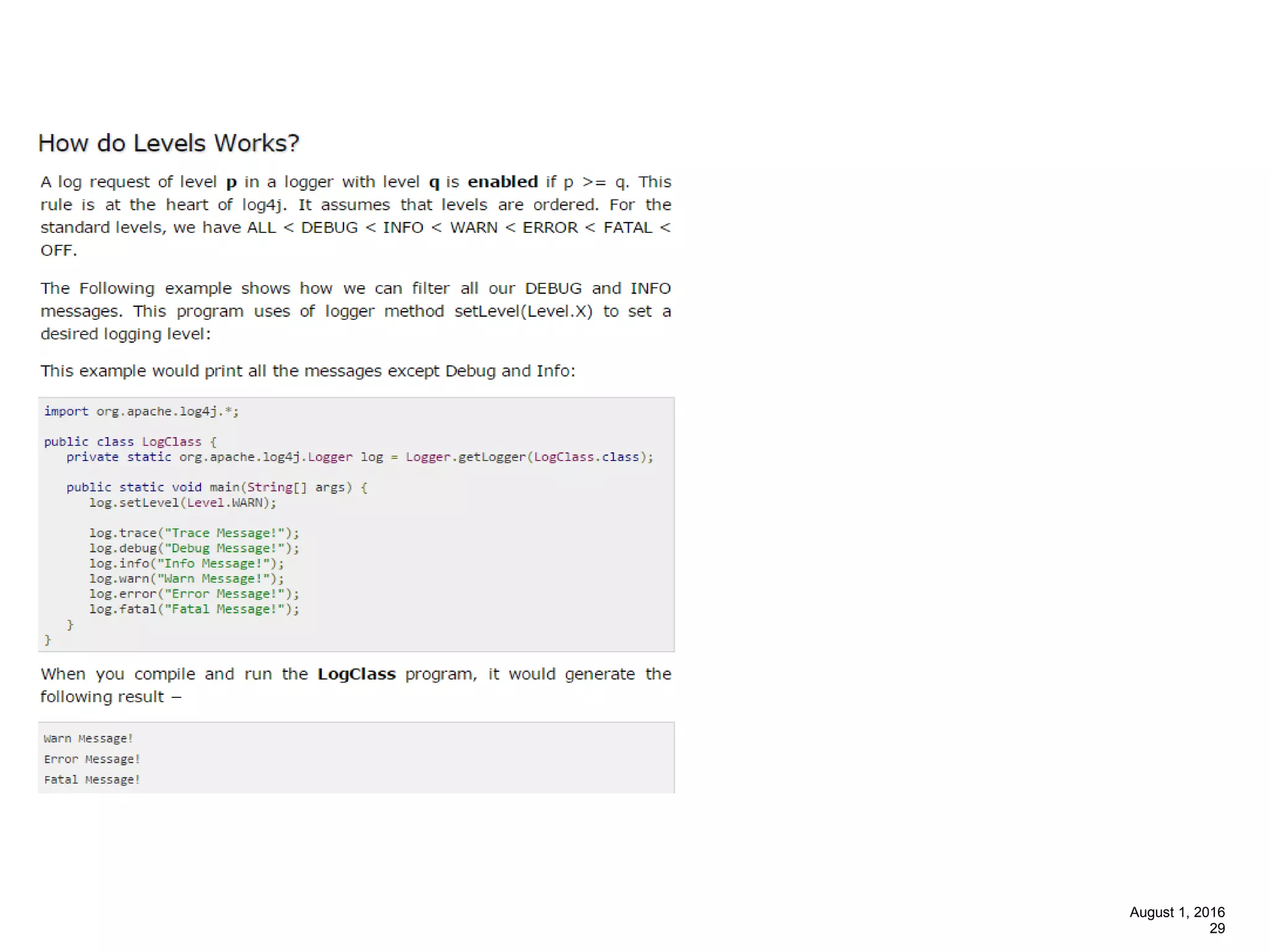
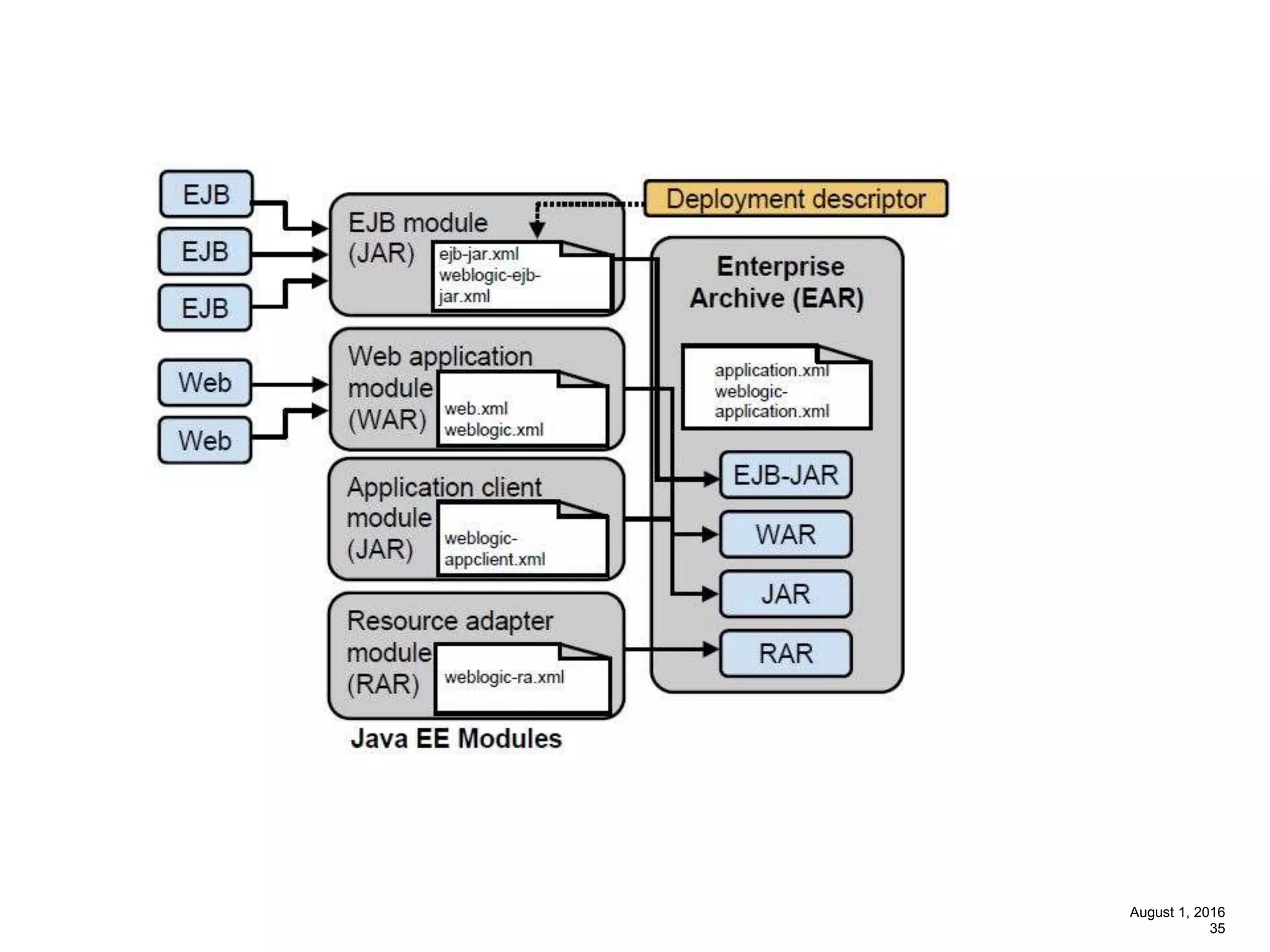
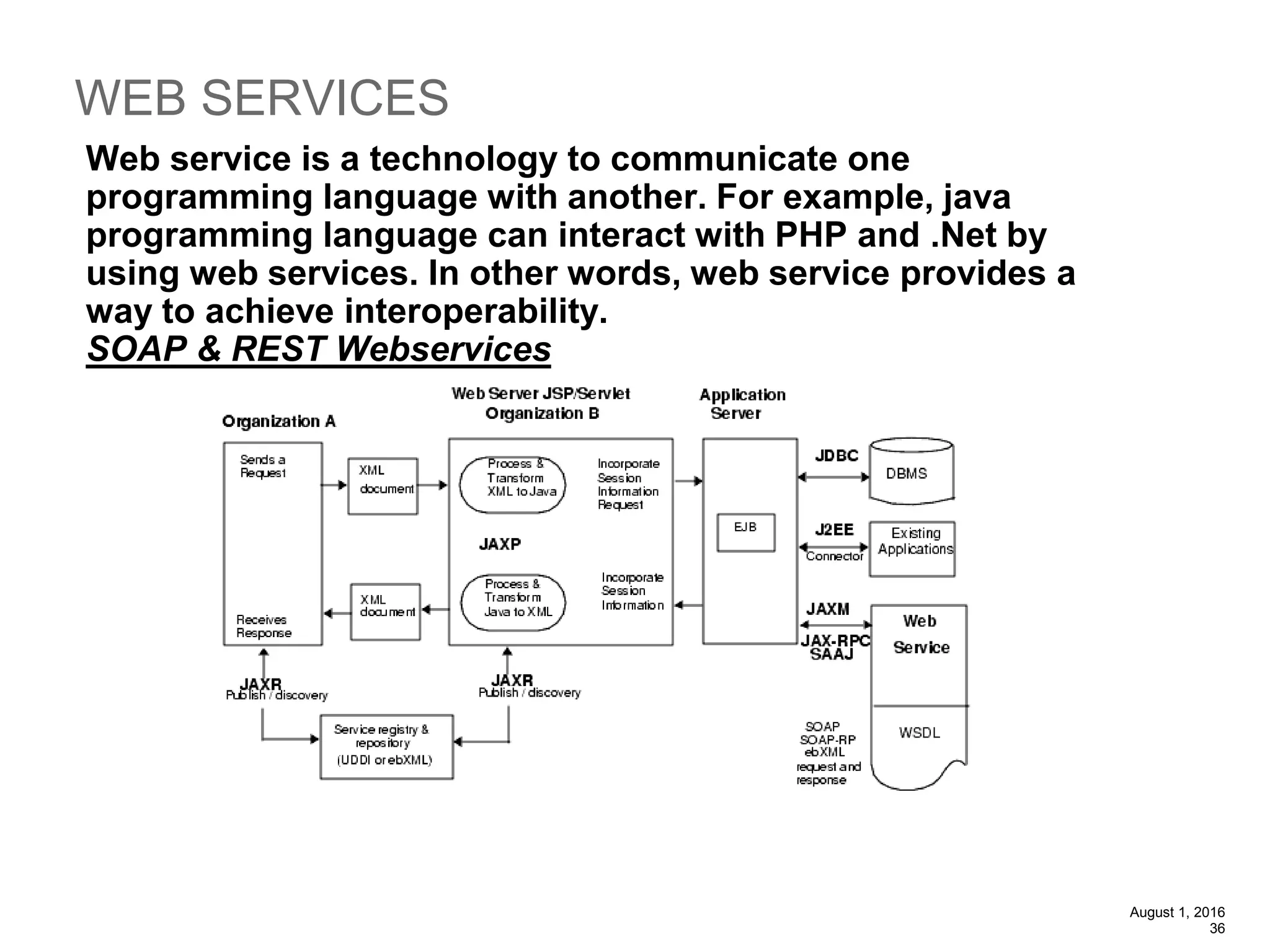
The document provides an overview of the Spring MVC framework, explaining its components, architecture, and the role of dependency injection and inversion of control. It discusses various aspects of the framework such as lightweight application development, logging with Log4j, and build automation using Apache Ant. Additionally, it highlights the structure of web services and the advantages of using the MVC architecture, emphasizing the framework's capability to facilitate scalable application design.