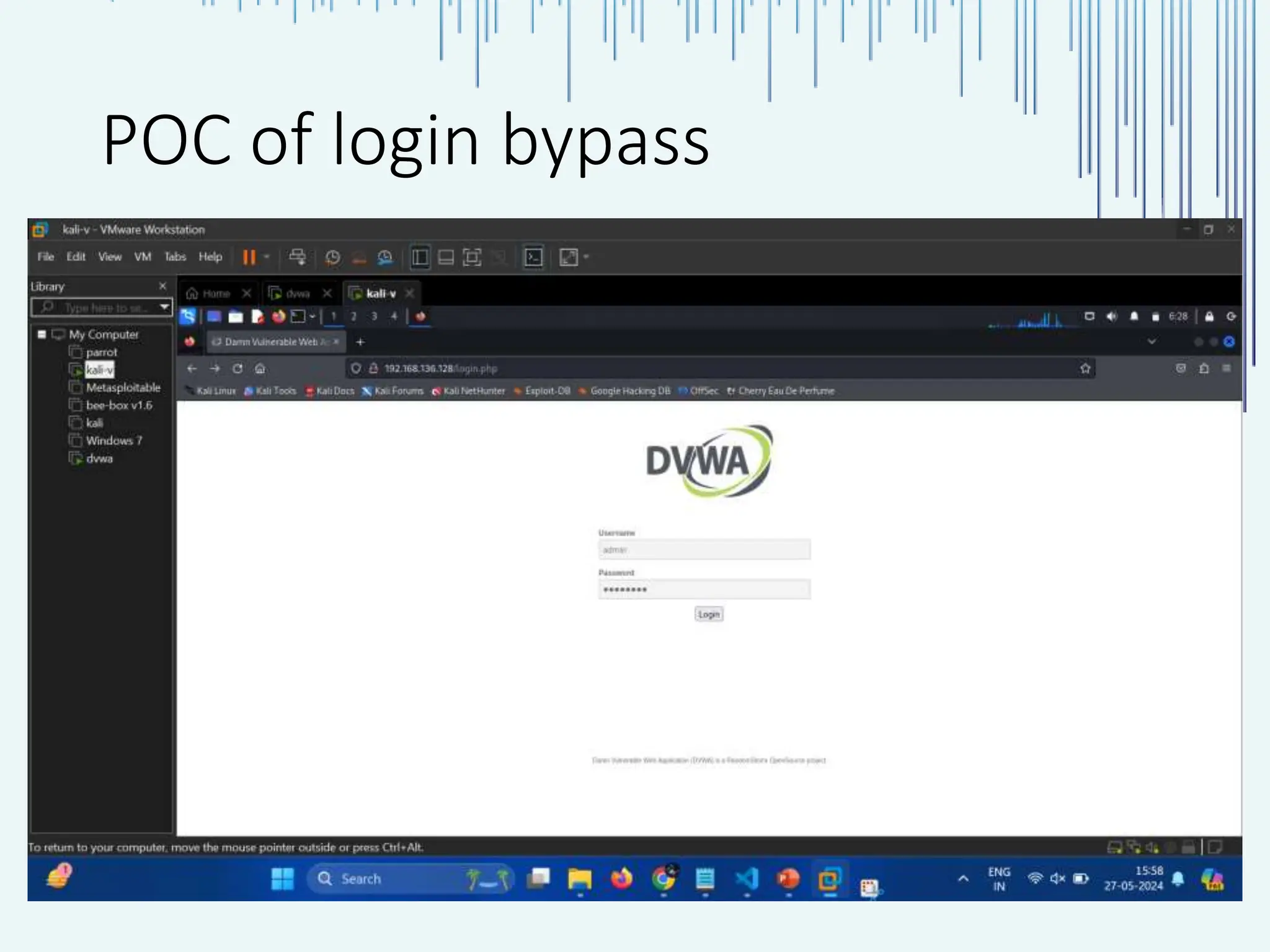
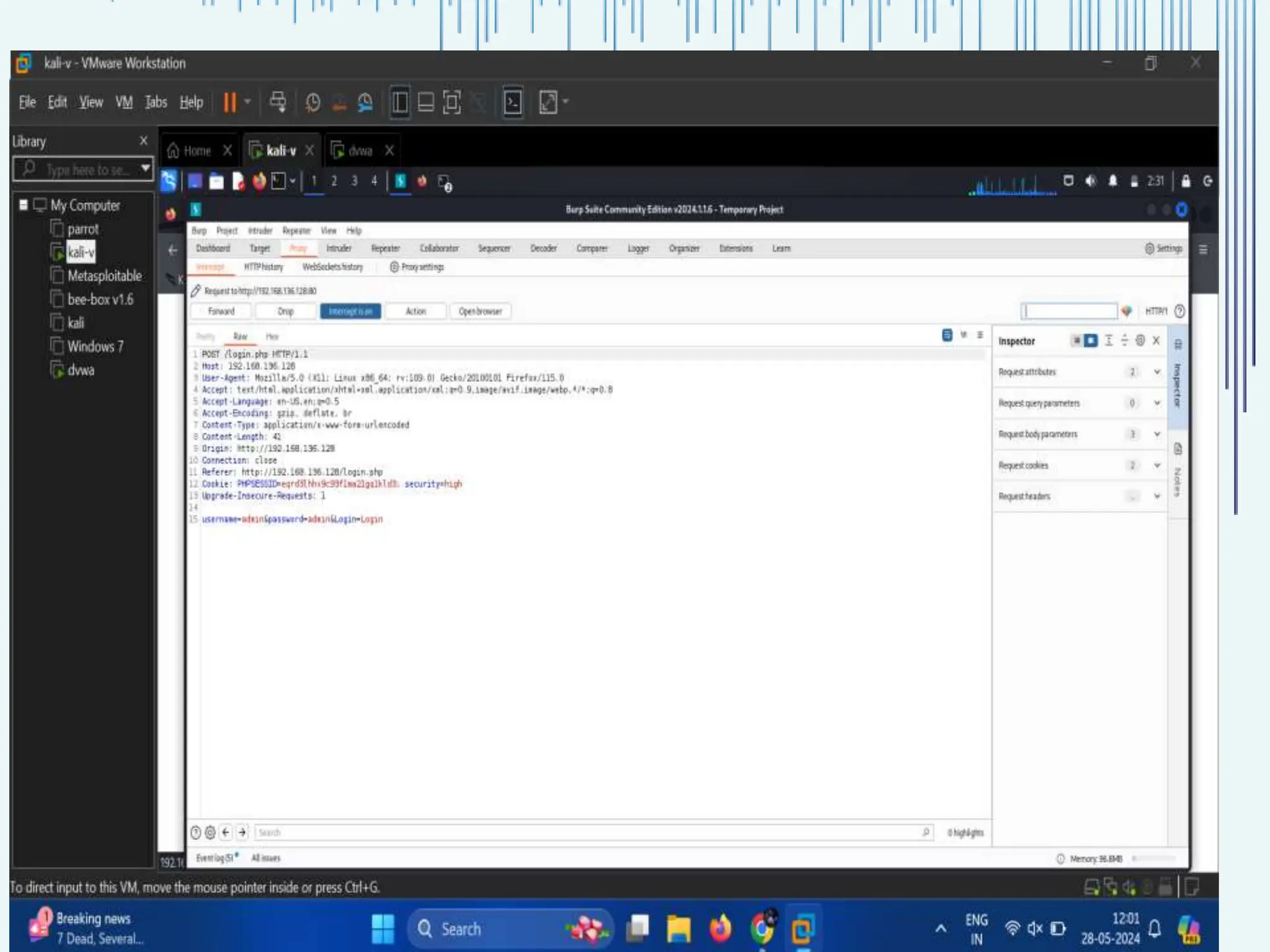
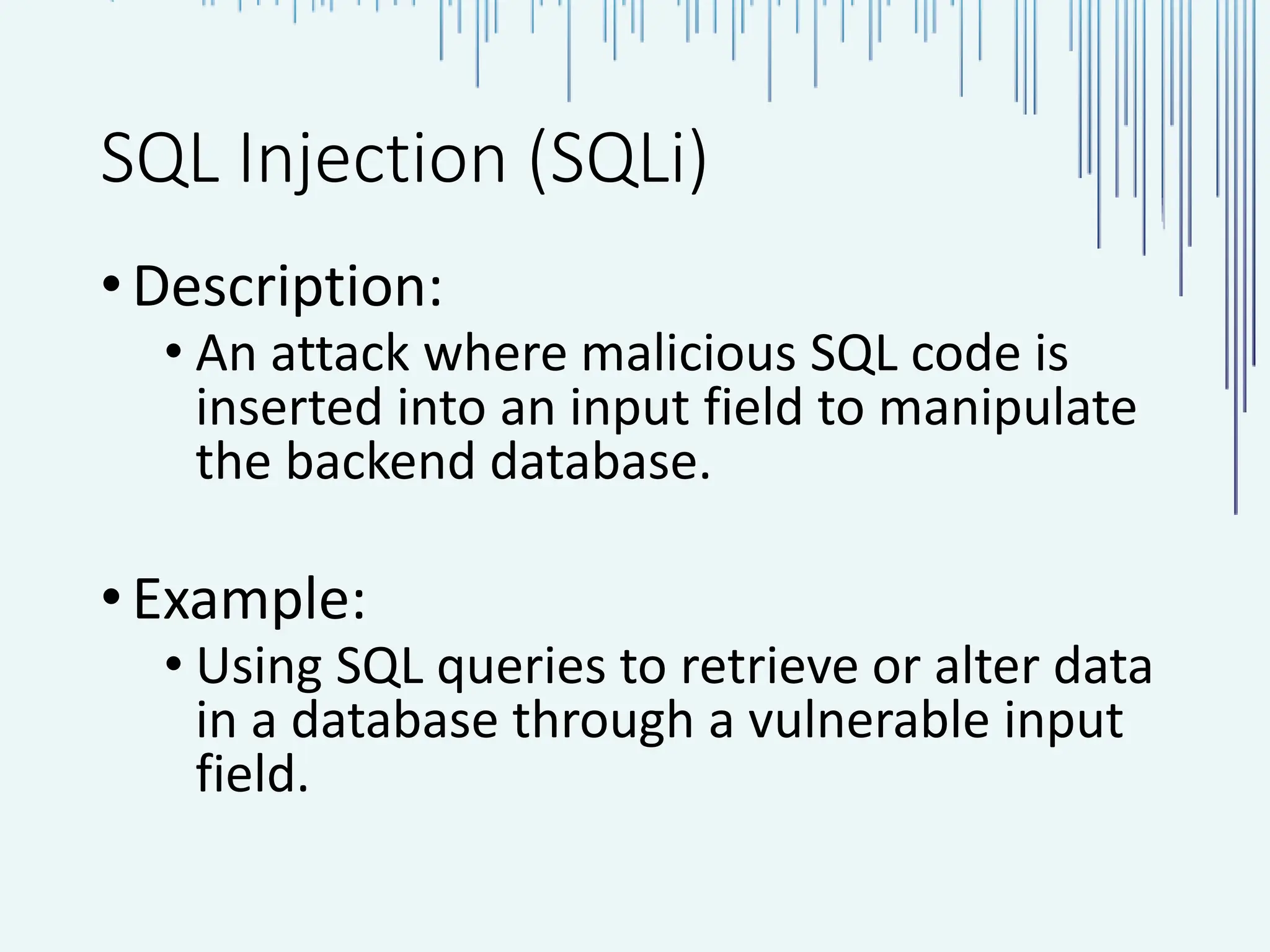
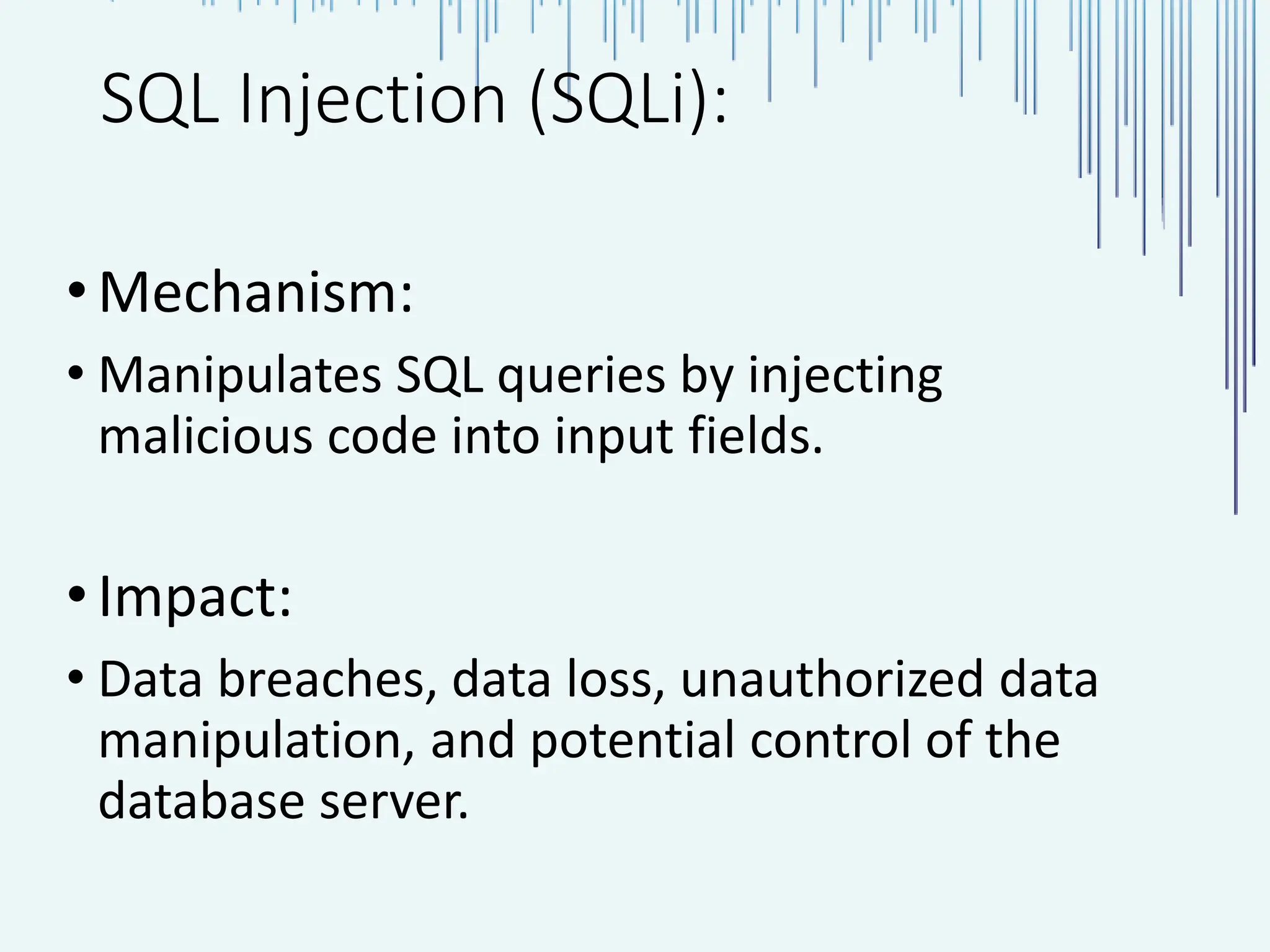
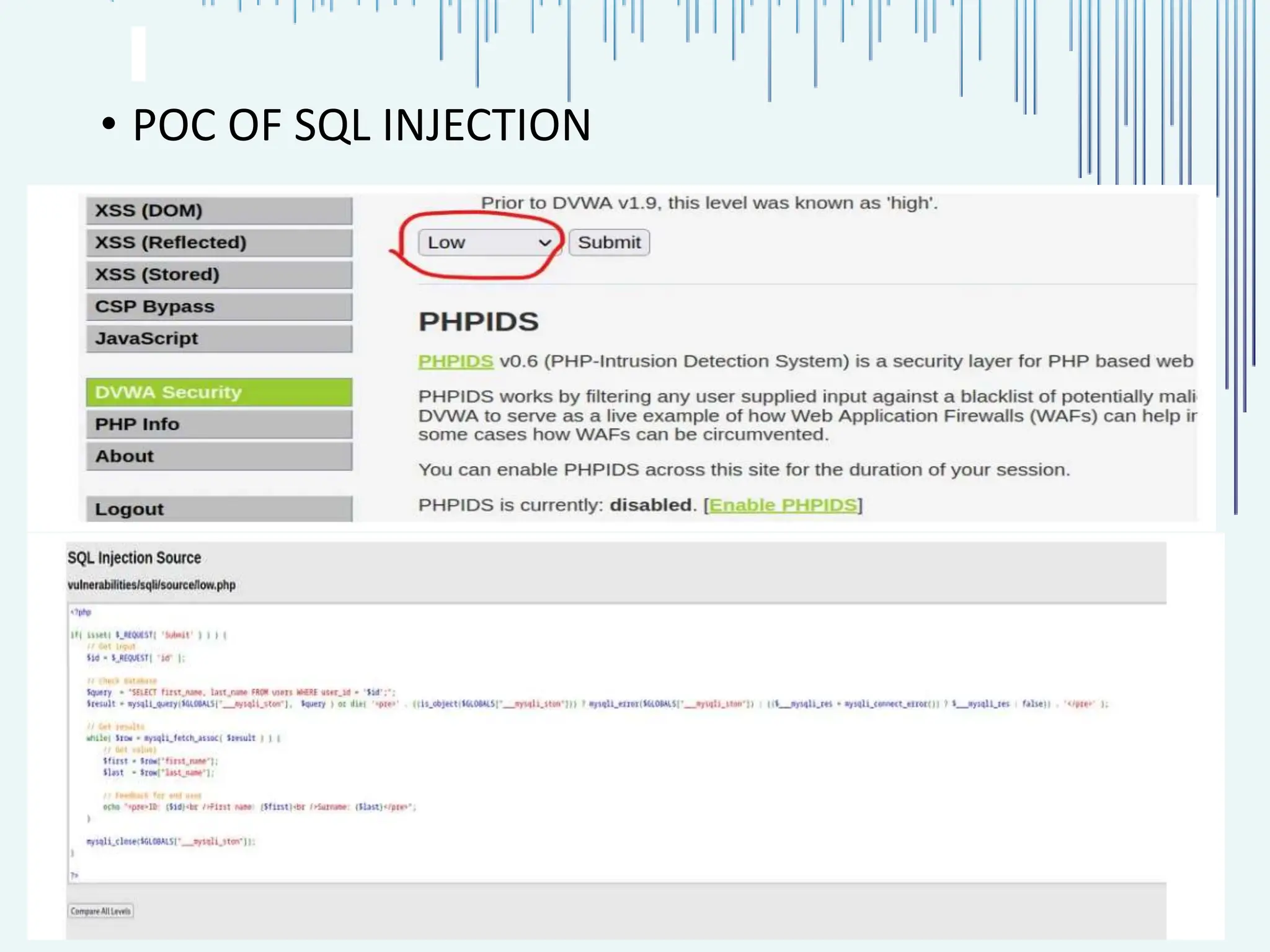
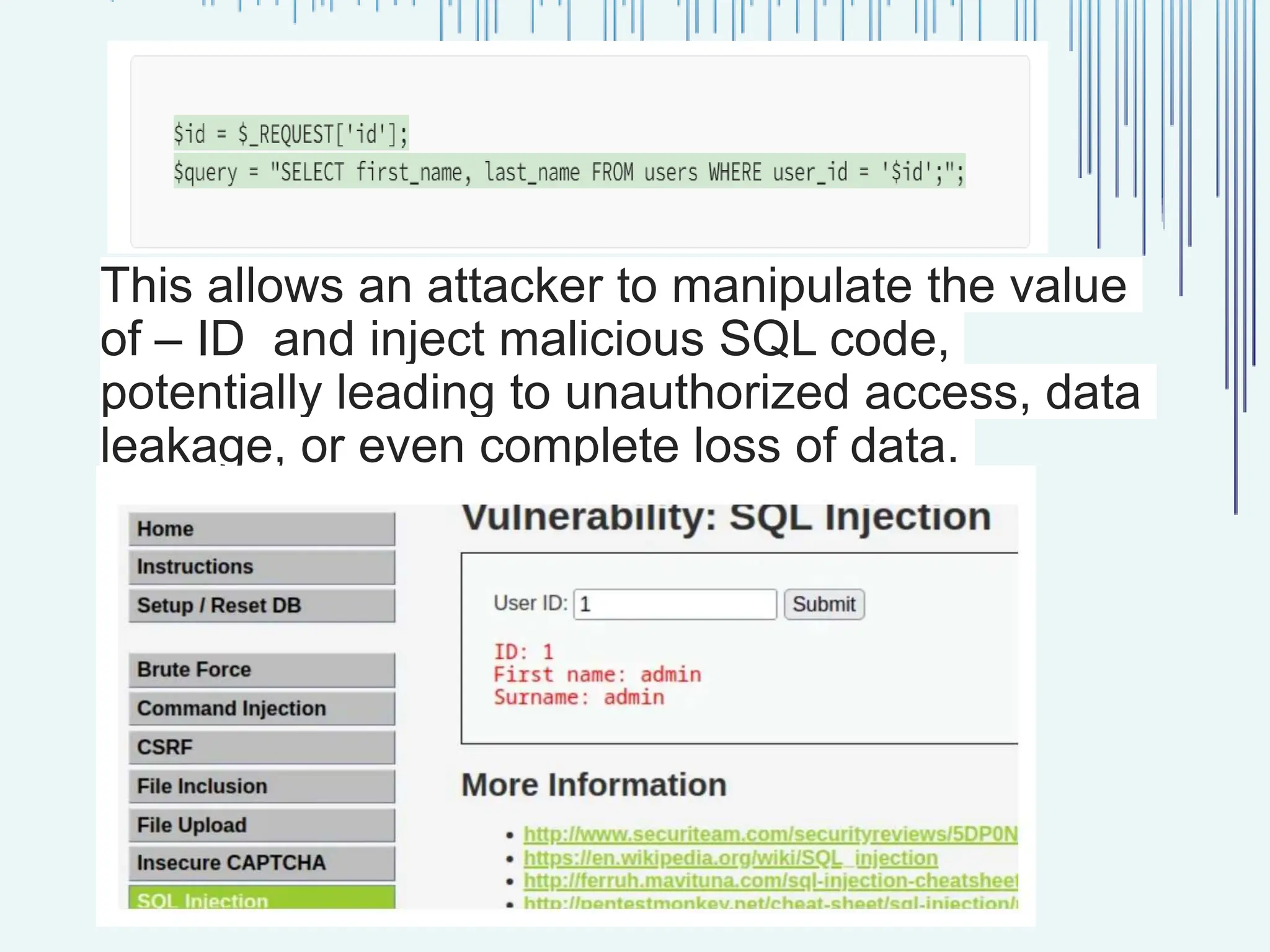
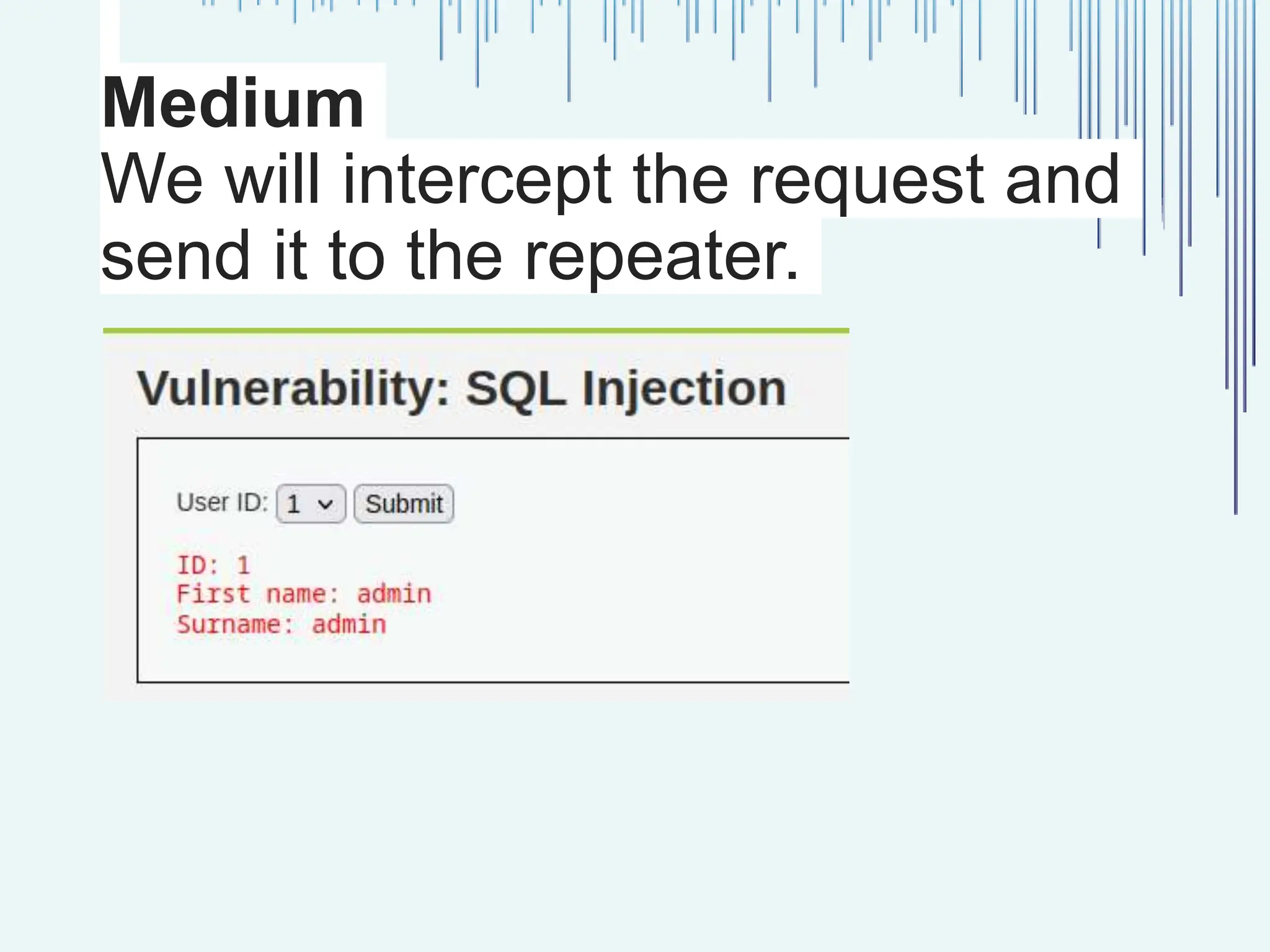
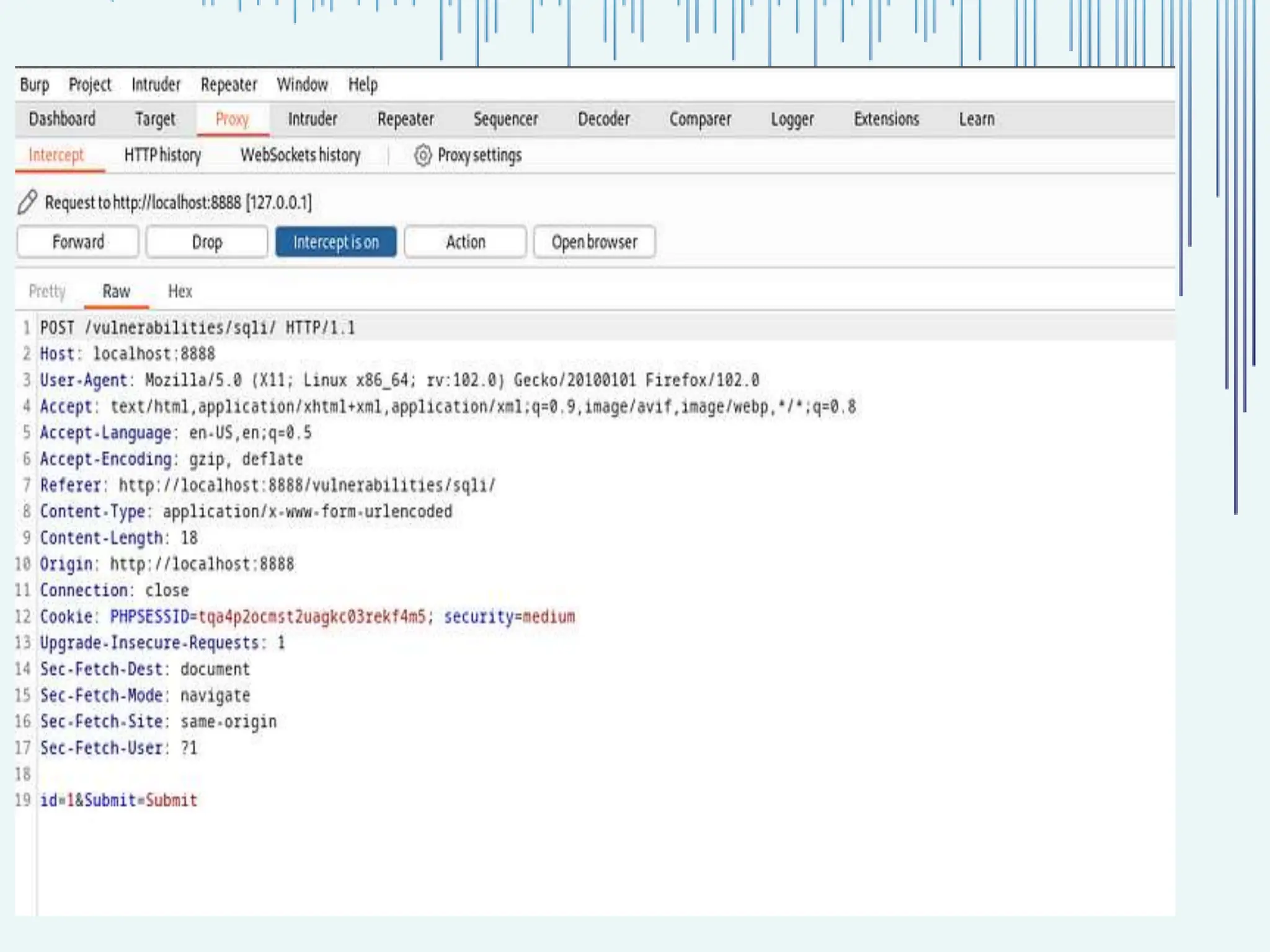
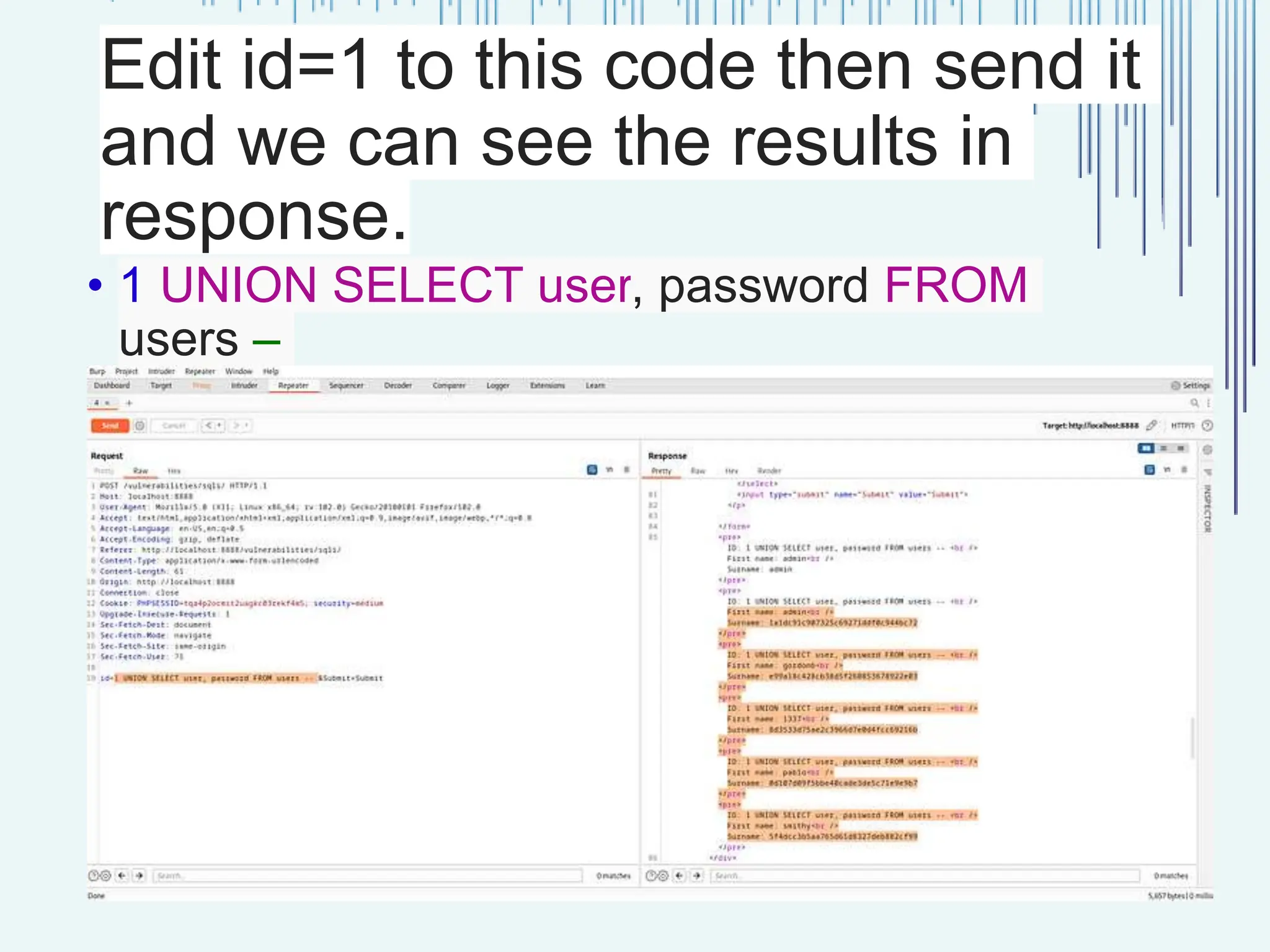
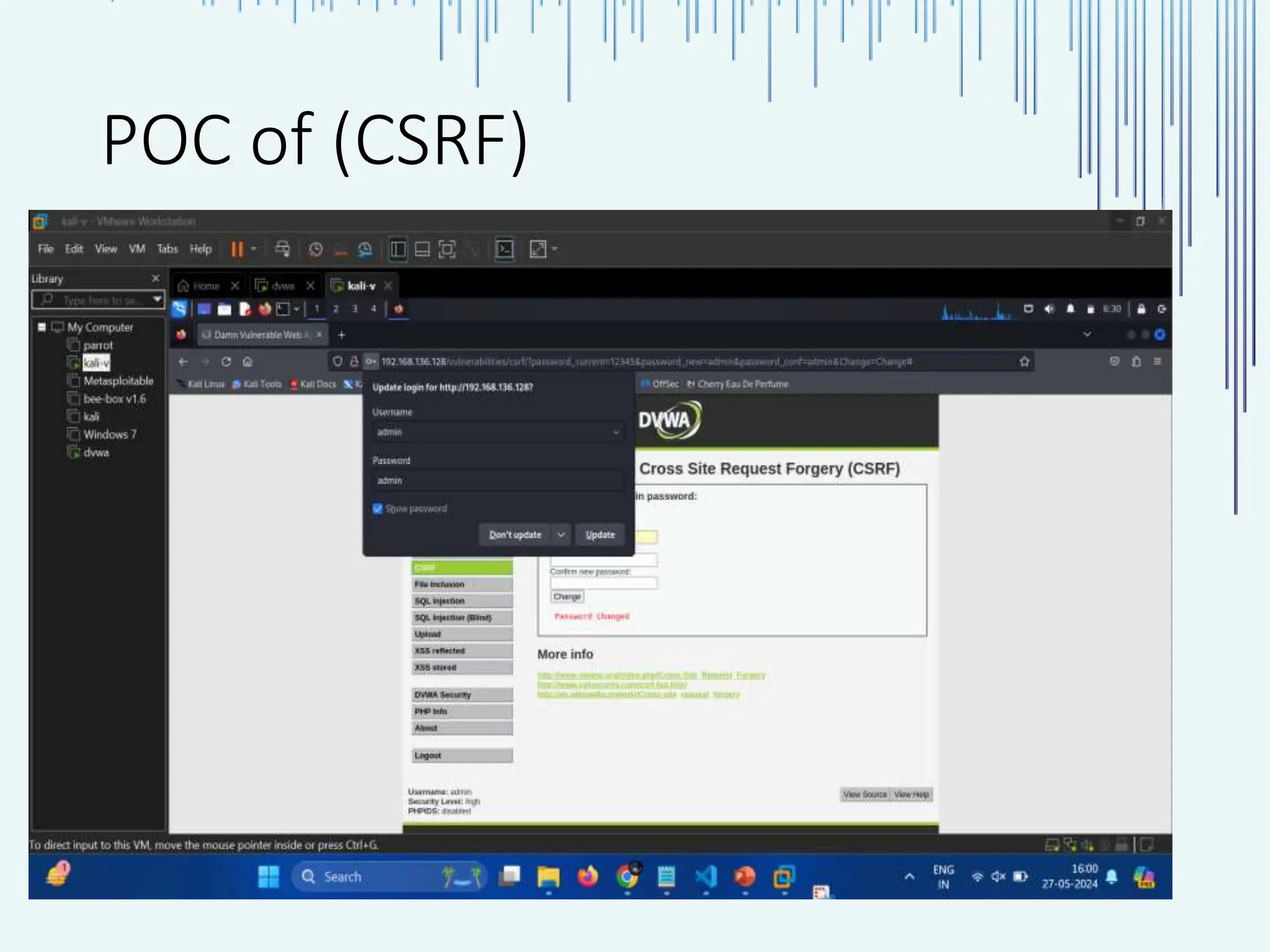
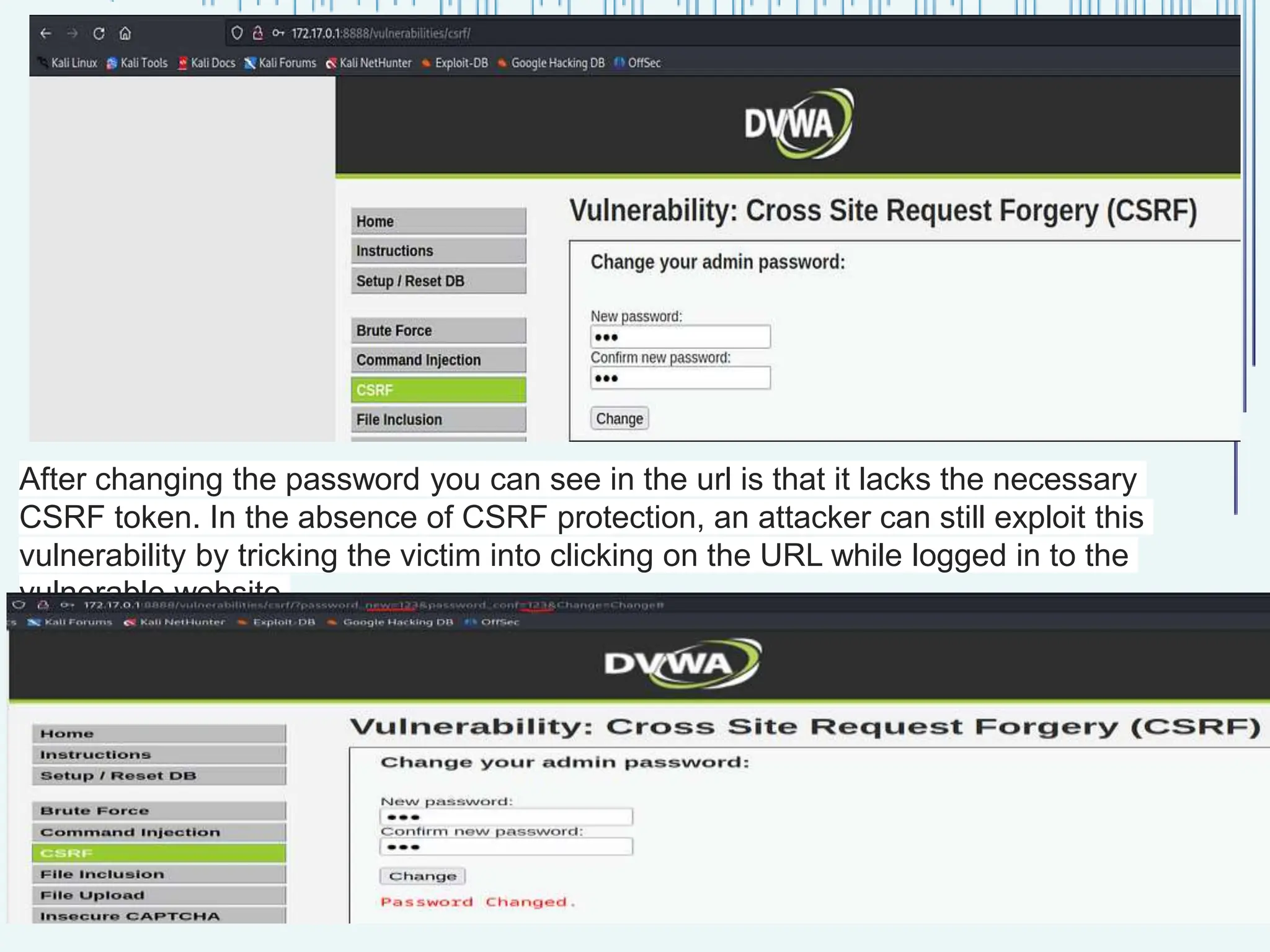
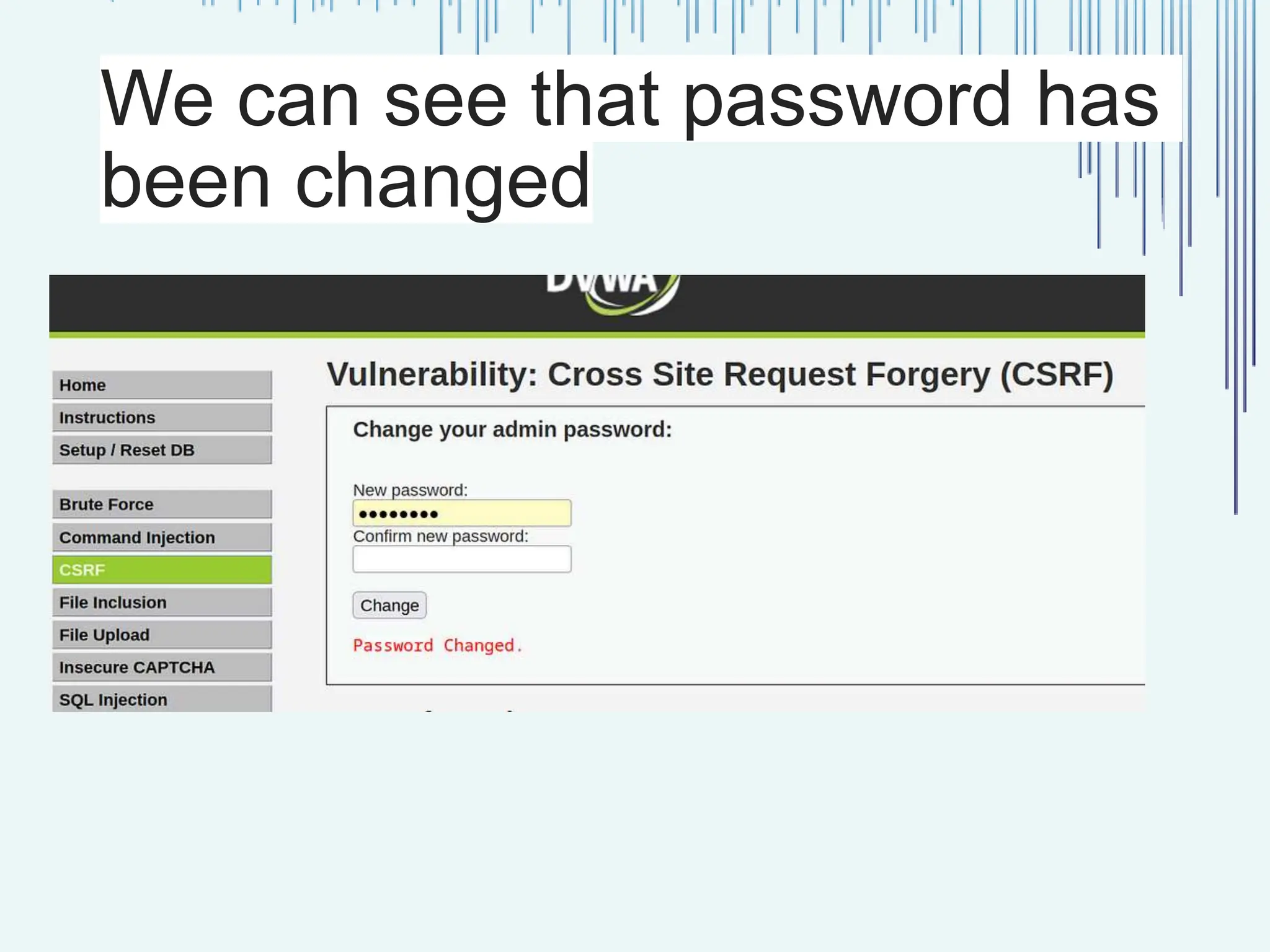
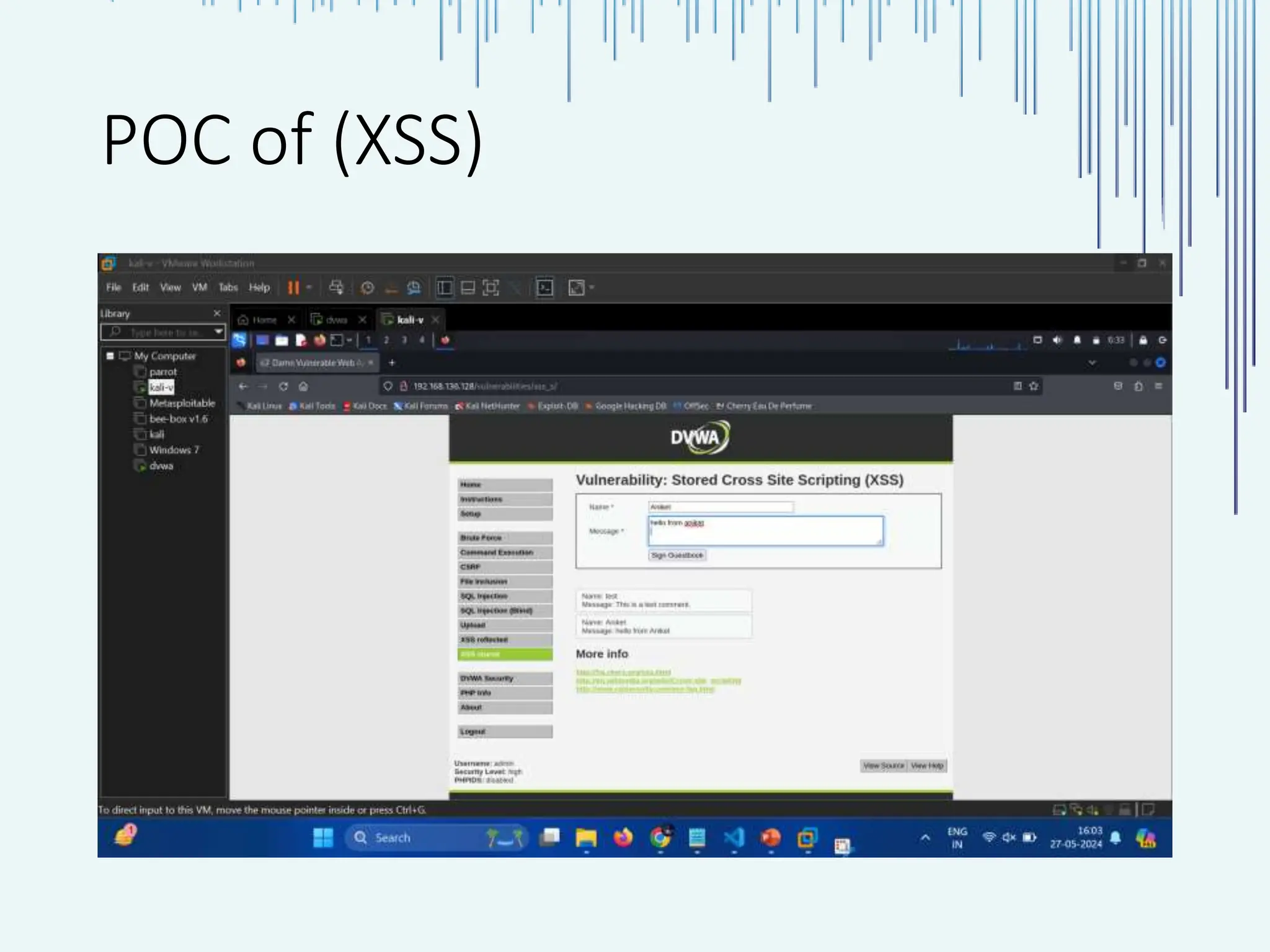
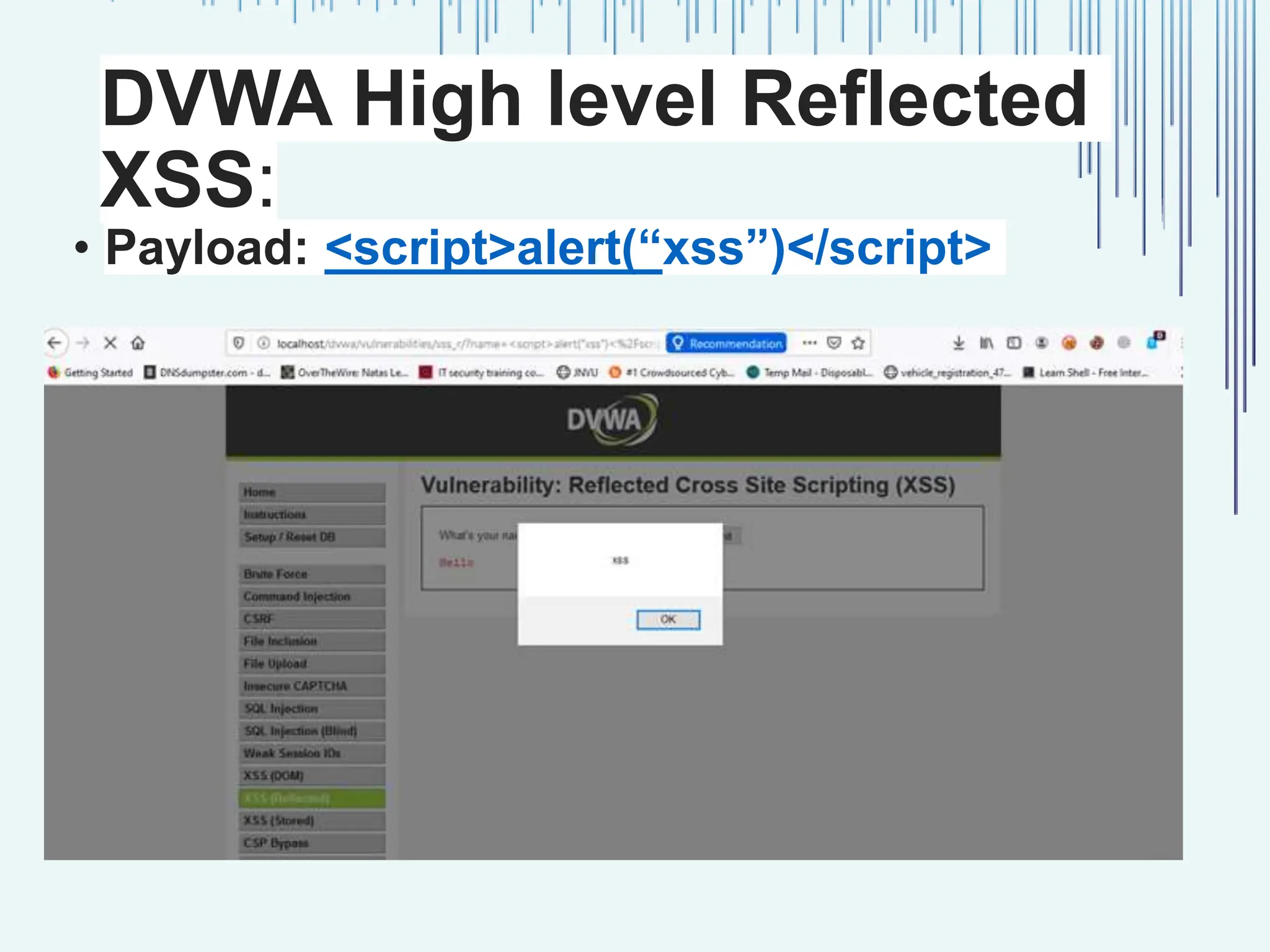
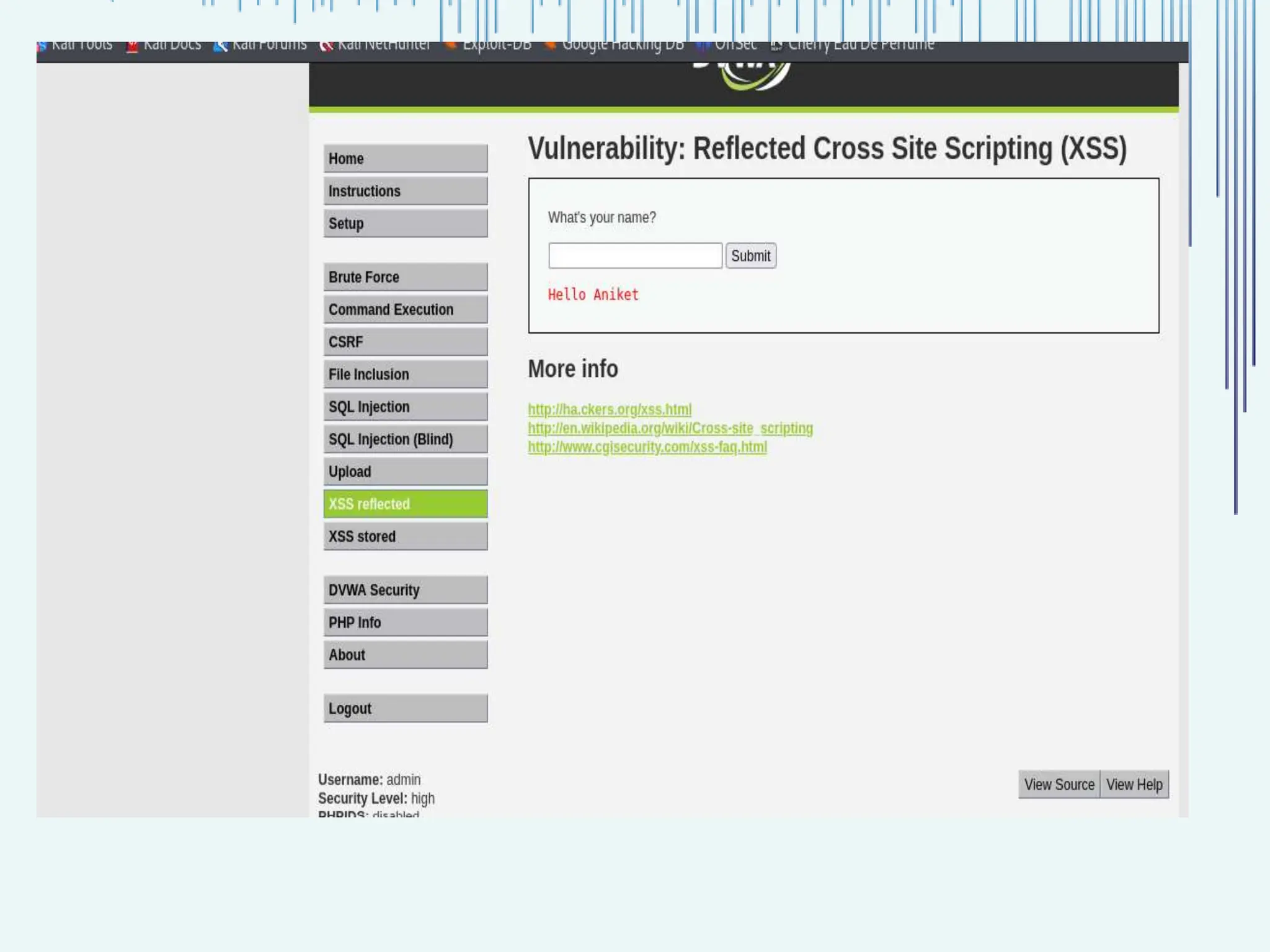
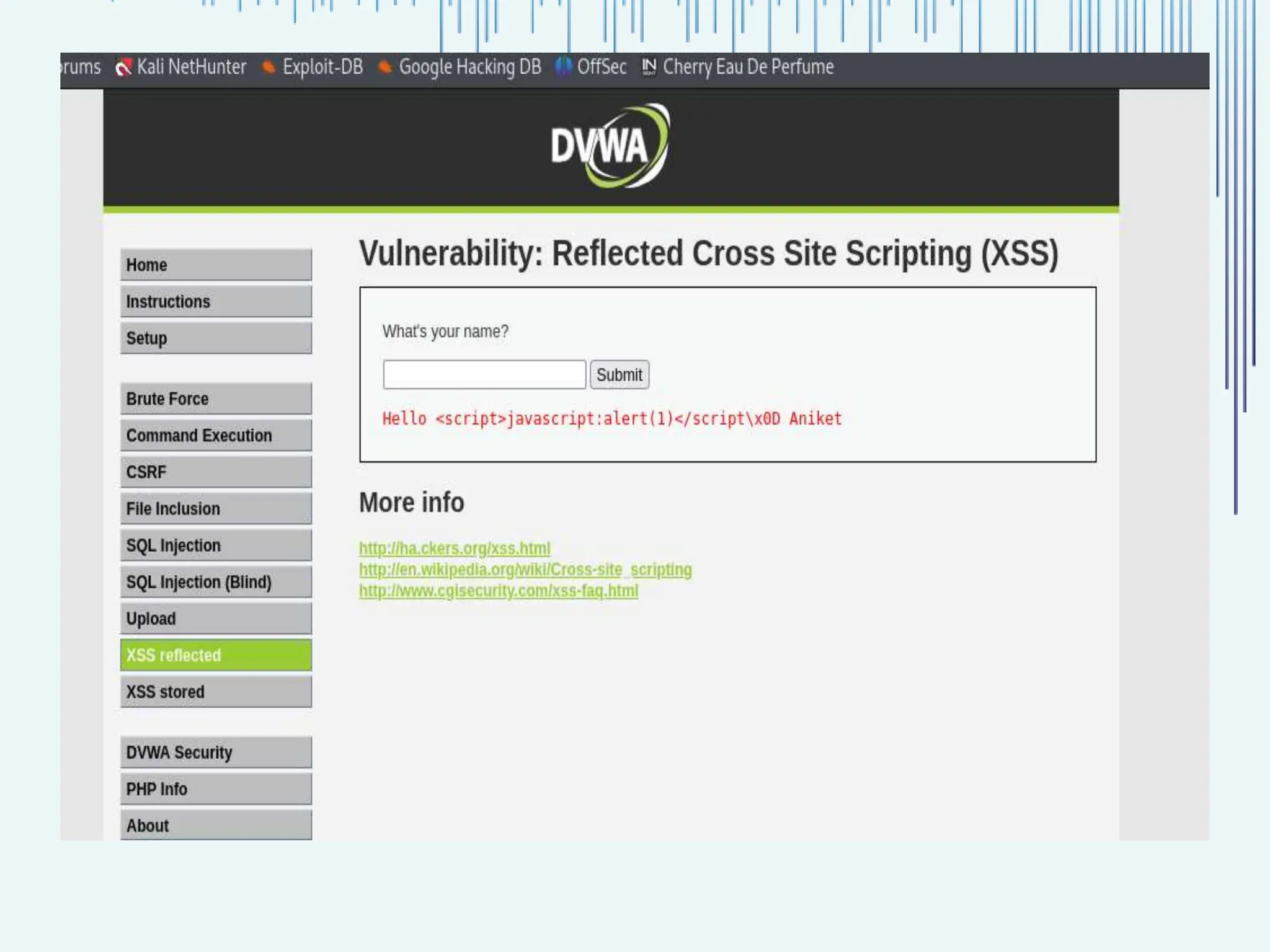
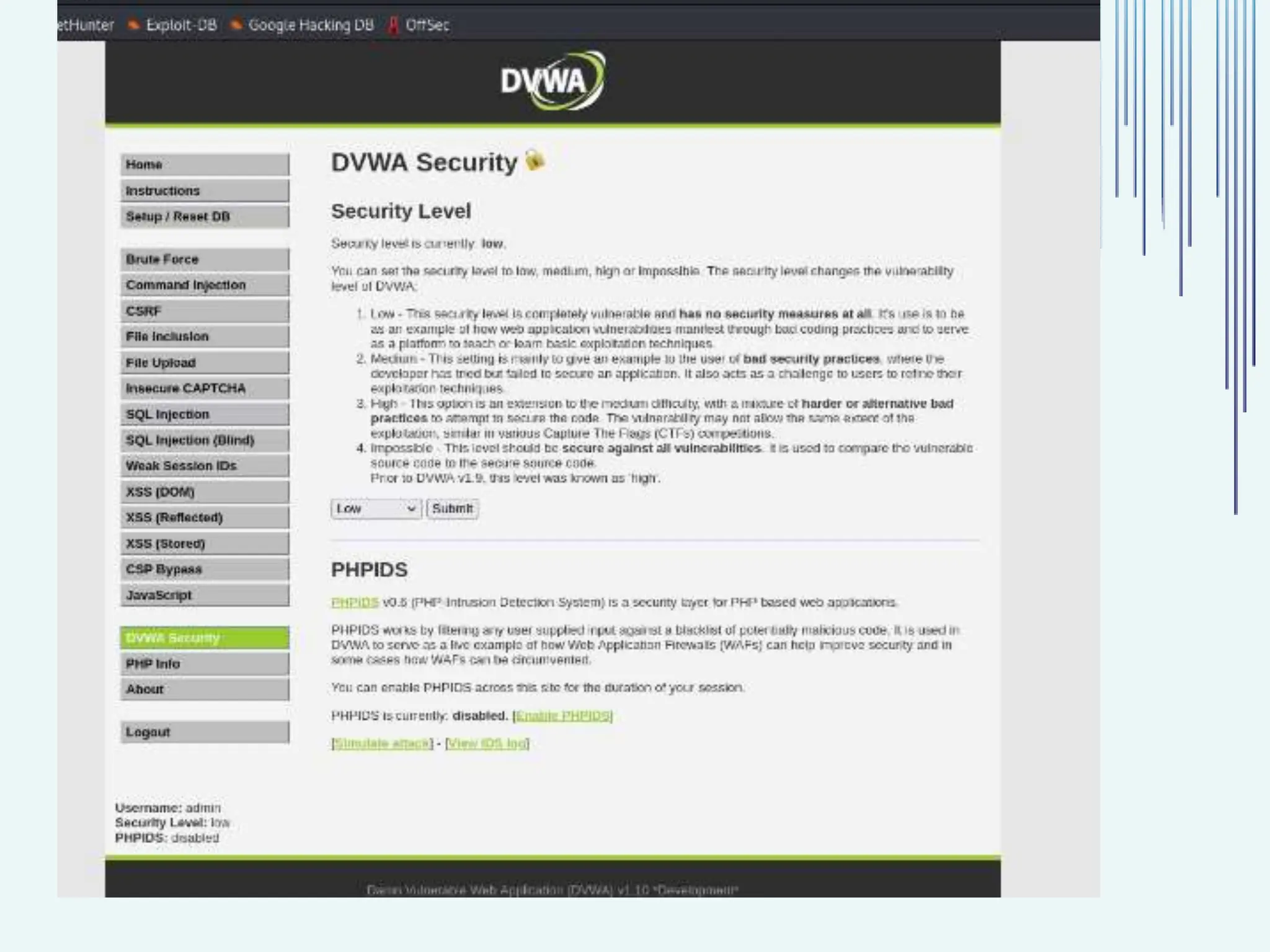
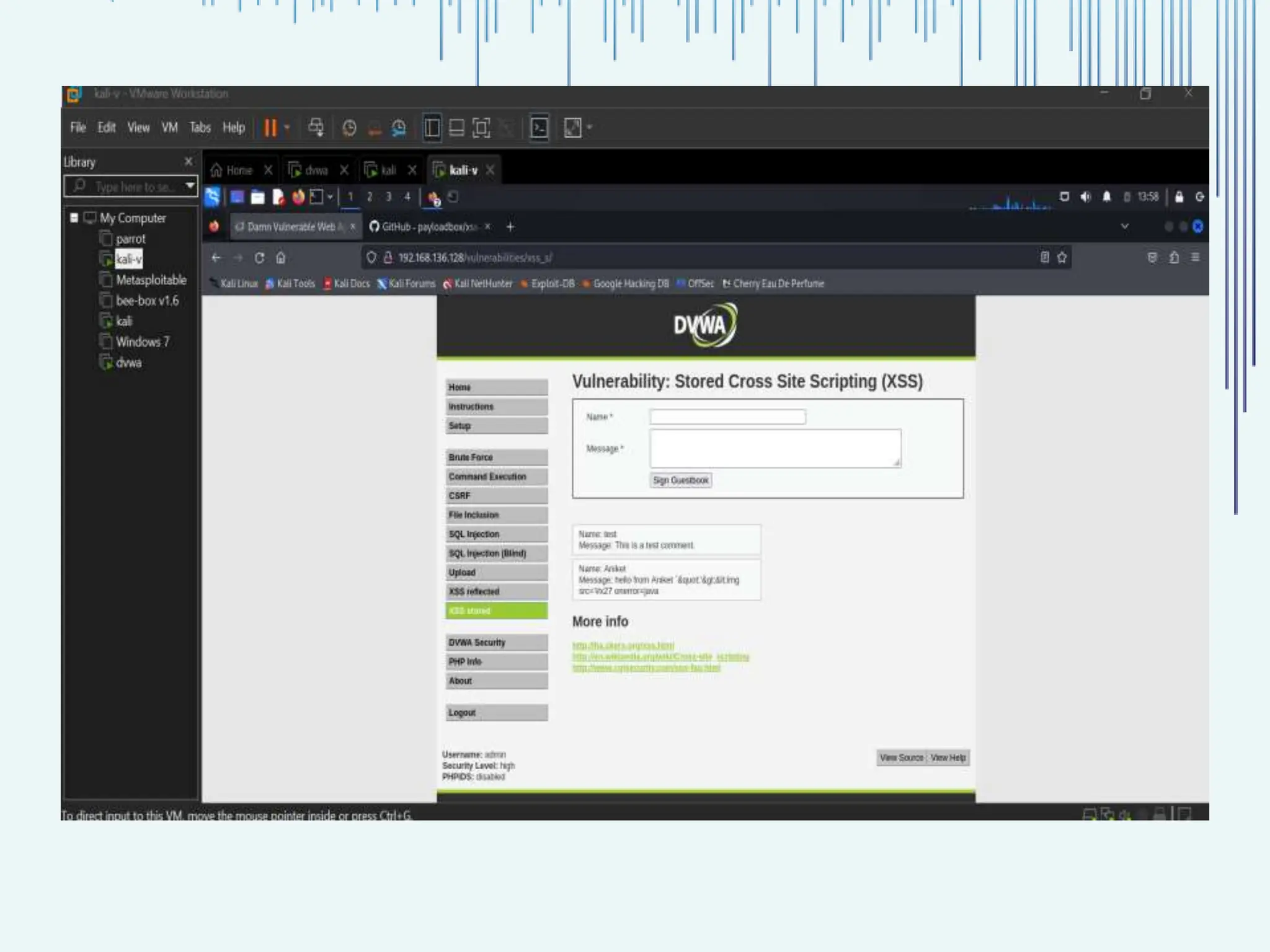
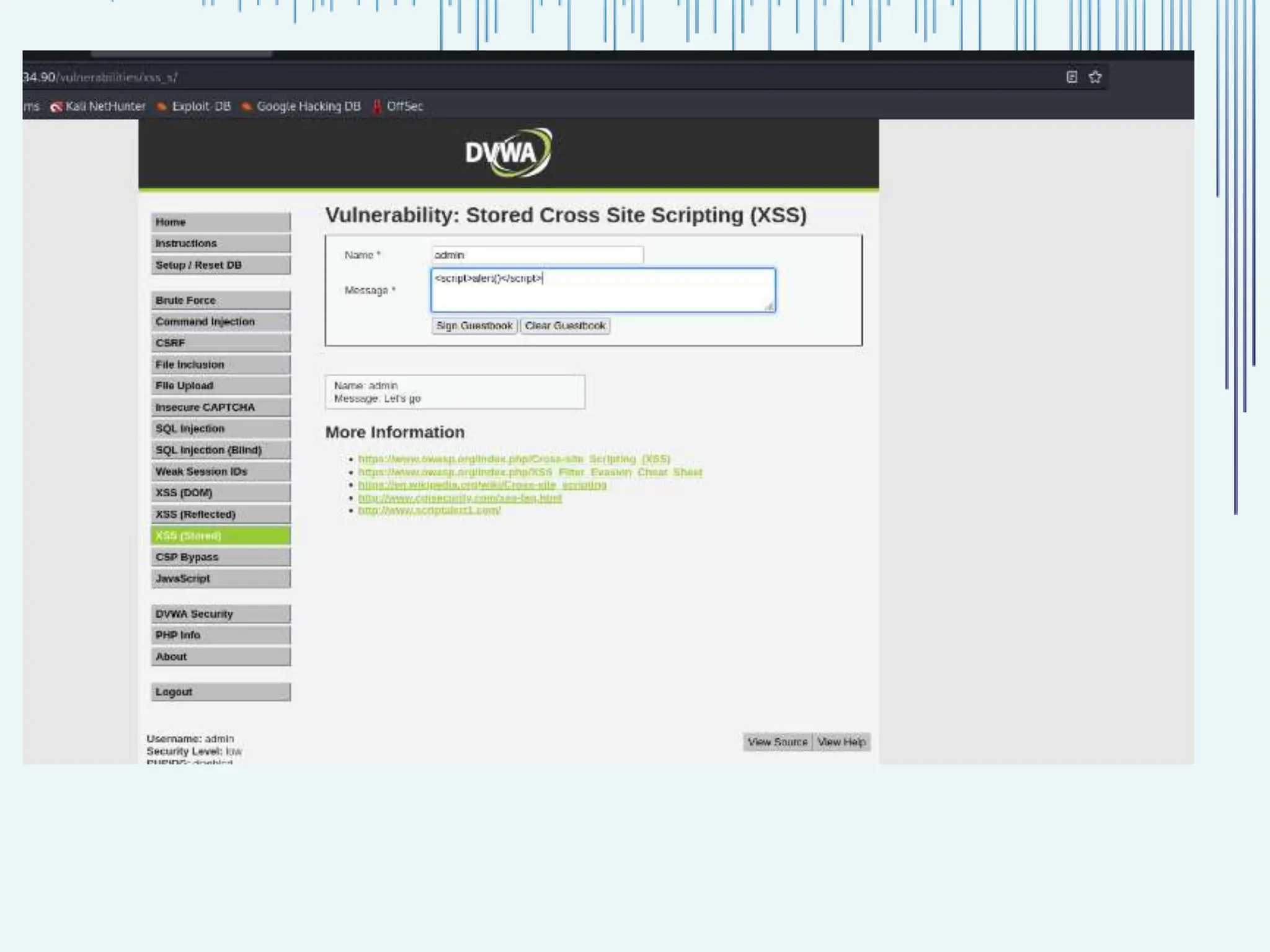
The document outlines common web vulnerabilities such as login bypass, SQL injection (SQLi), Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF), and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), detailing their mechanisms and impacts. It emphasizes the importance of securing web applications to protect sensitive data, maintain user trust, and prevent financial losses. The conclusion stresses that understanding and mitigating these vulnerabilities is essential for enhancing web application security.