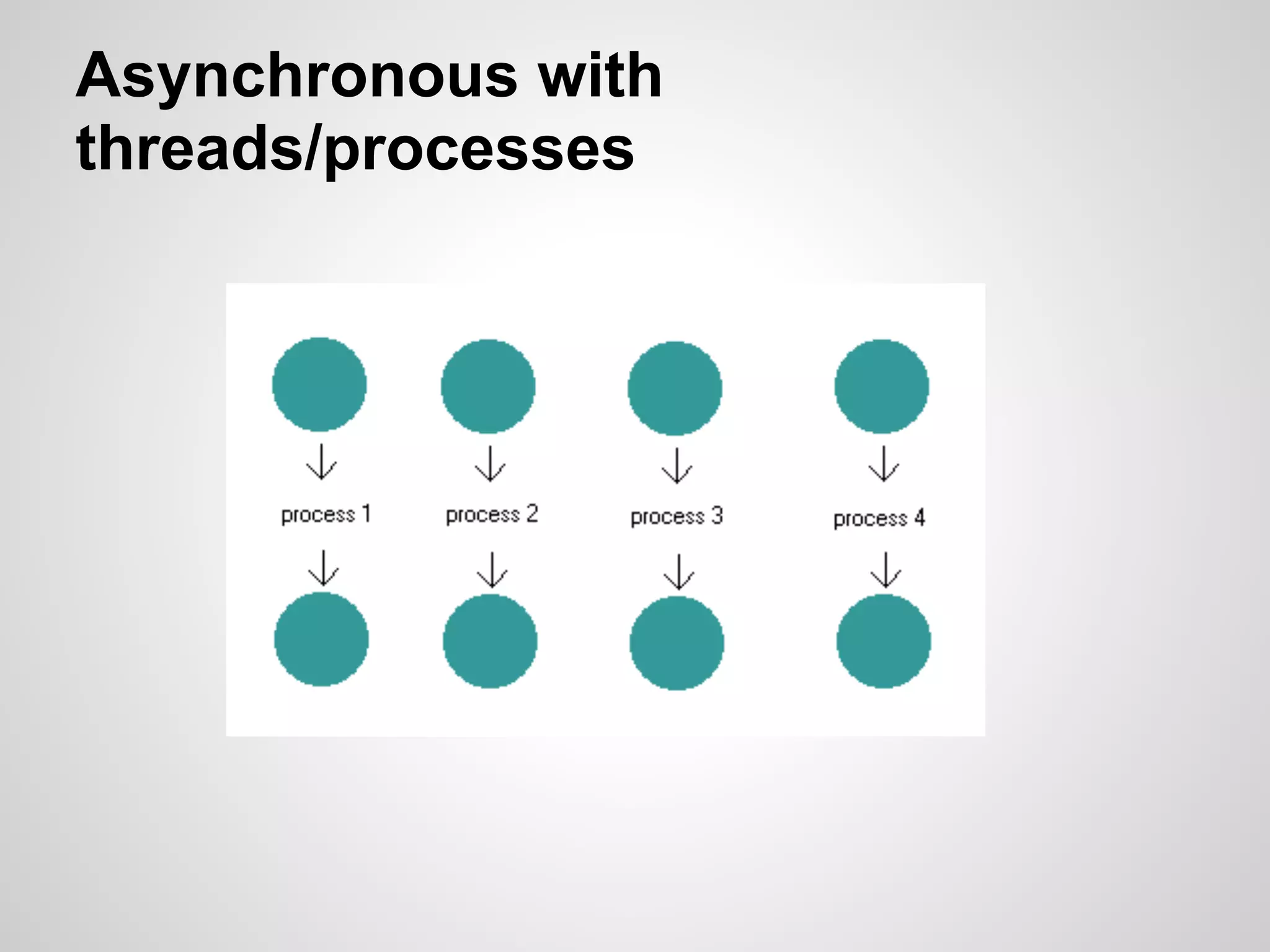
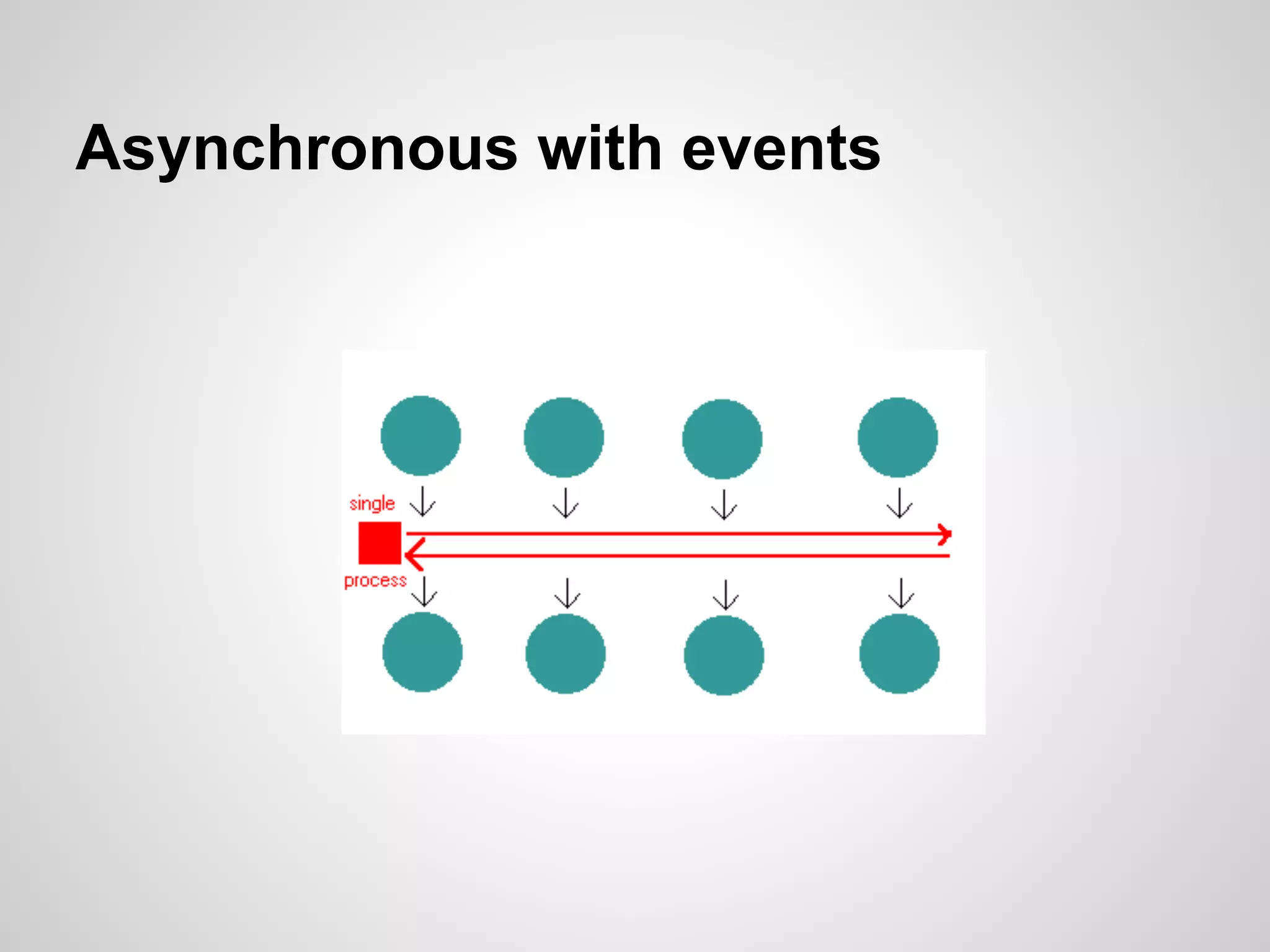
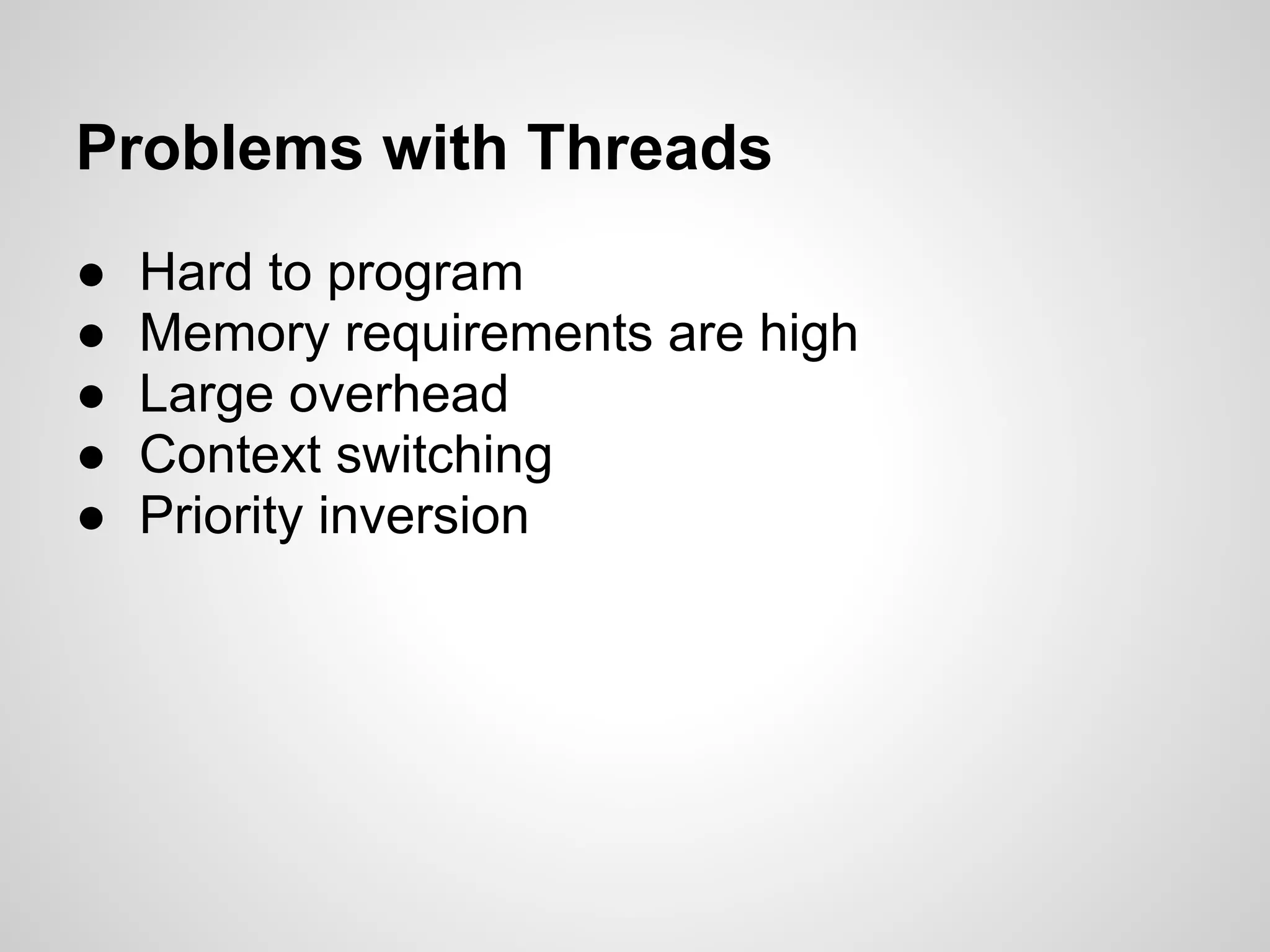
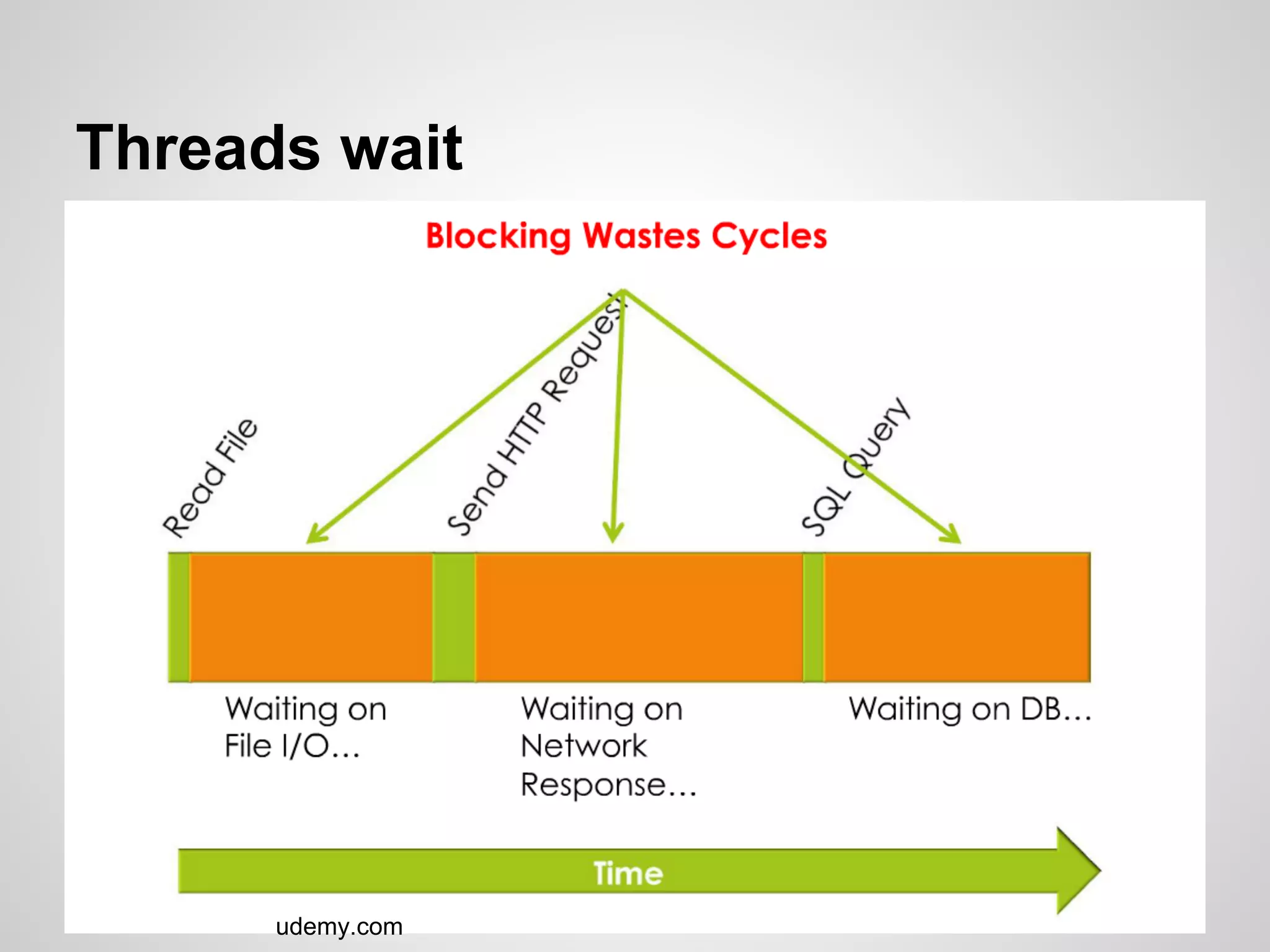
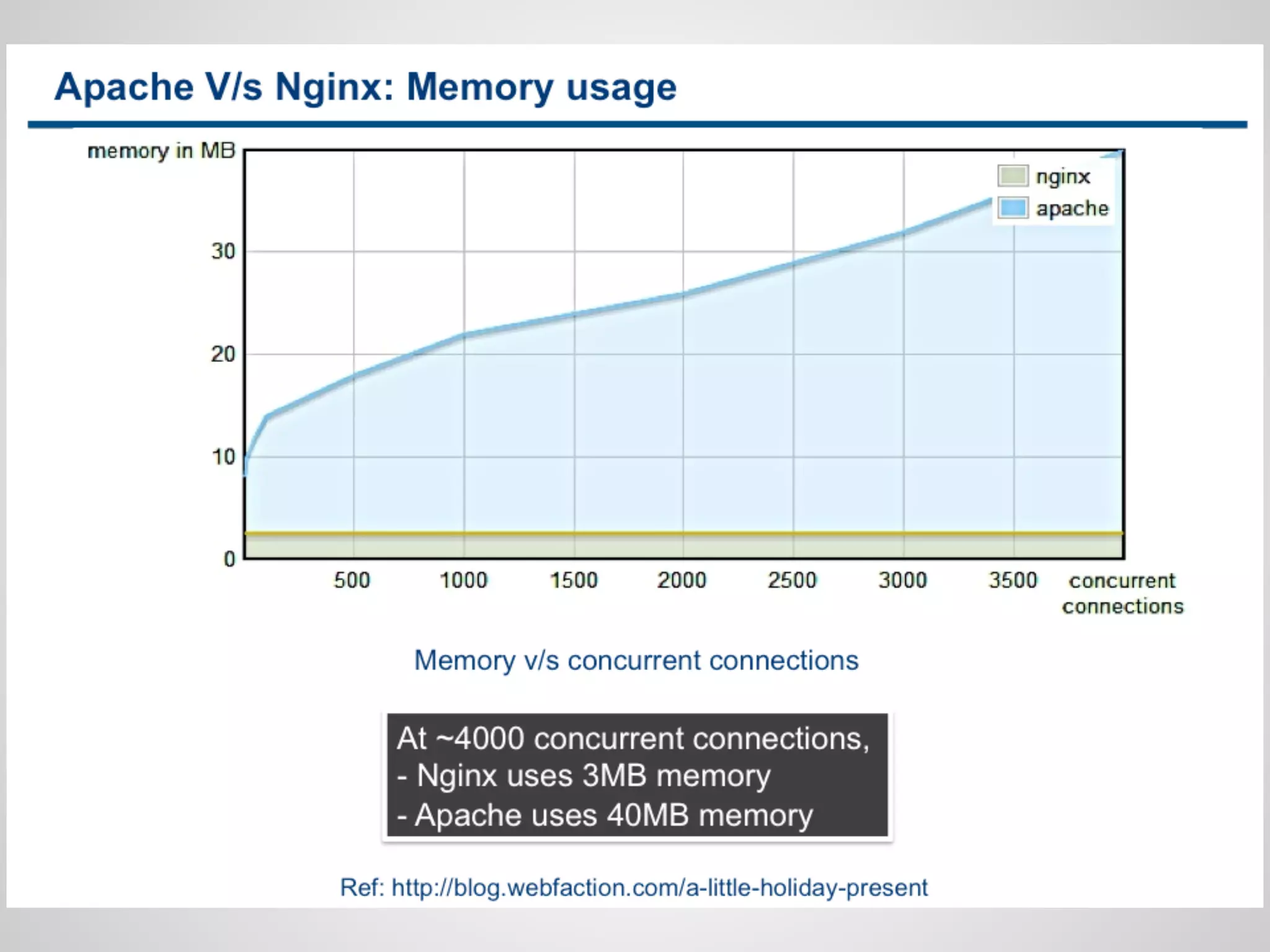
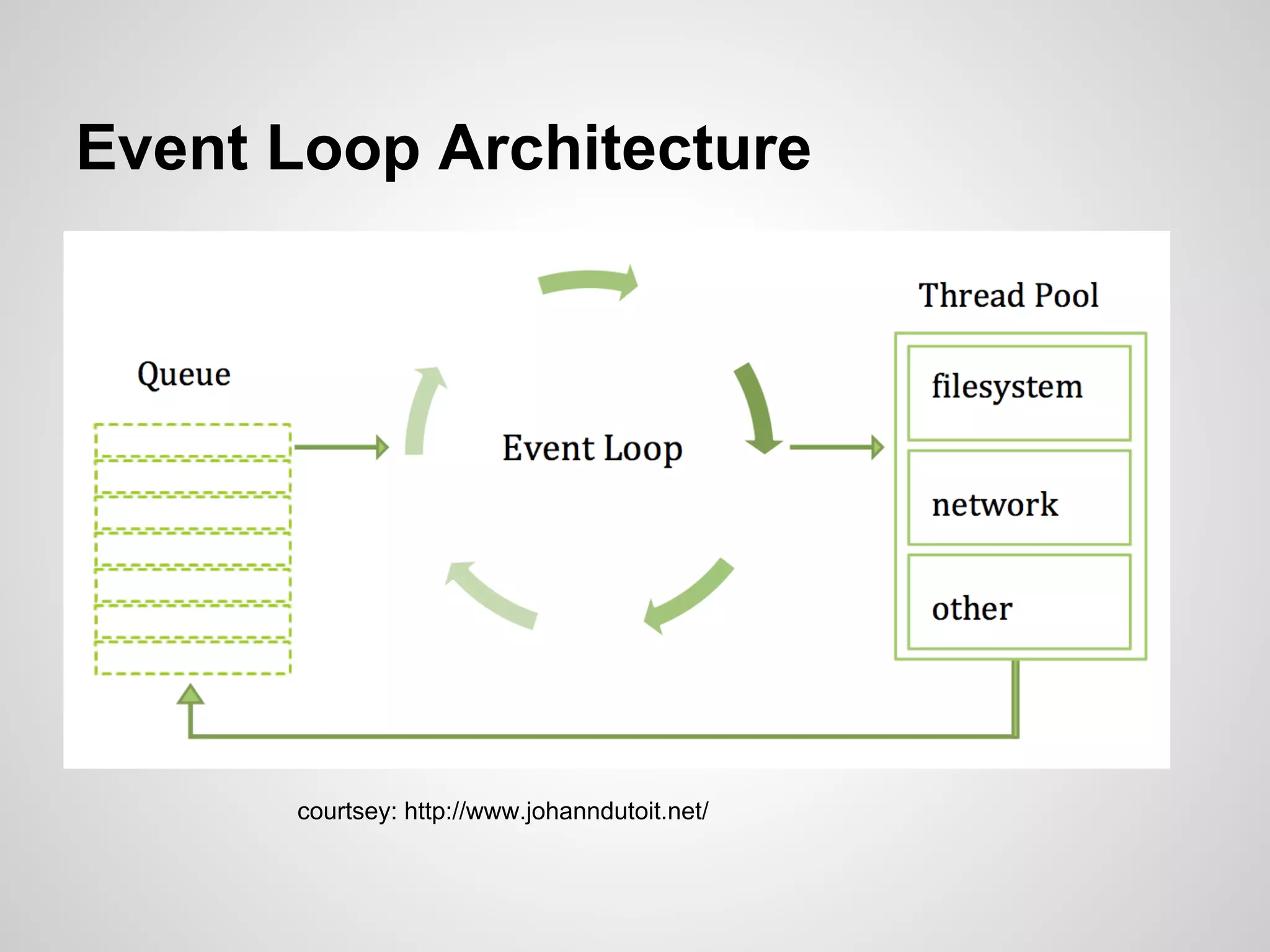
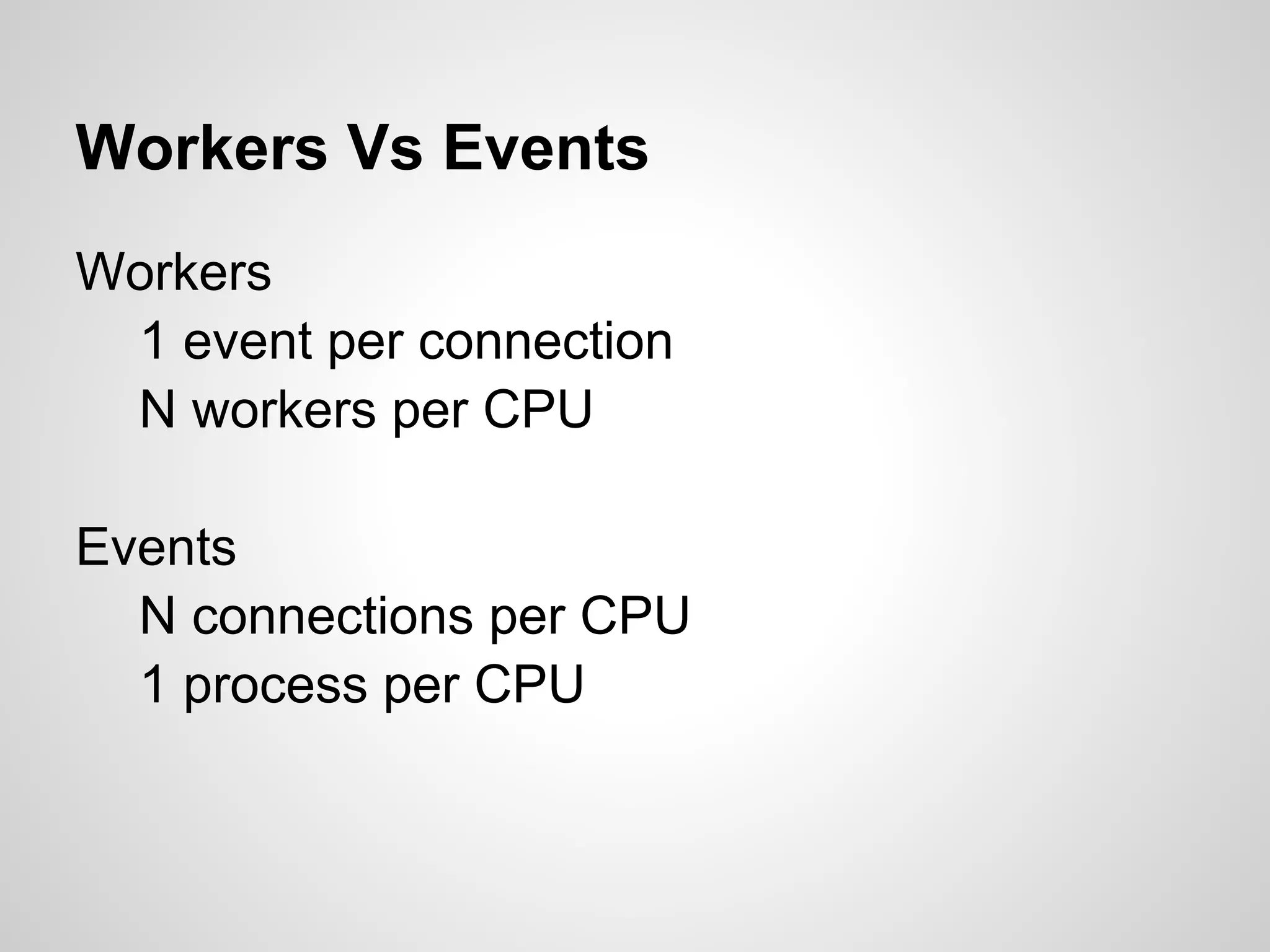
This document discusses server-side event-driven programming using Node.js. It covers how Node.js uses an event loop and asynchronous non-blocking I/O to handle many connections concurrently with high performance. Common Node.js concepts are explained like first-class functions, callbacks, and event emitters. Node.js is compared to traditional threaded programming and shown to have advantages in scalability and efficiency. Example Node.js applications and APIs are provided.