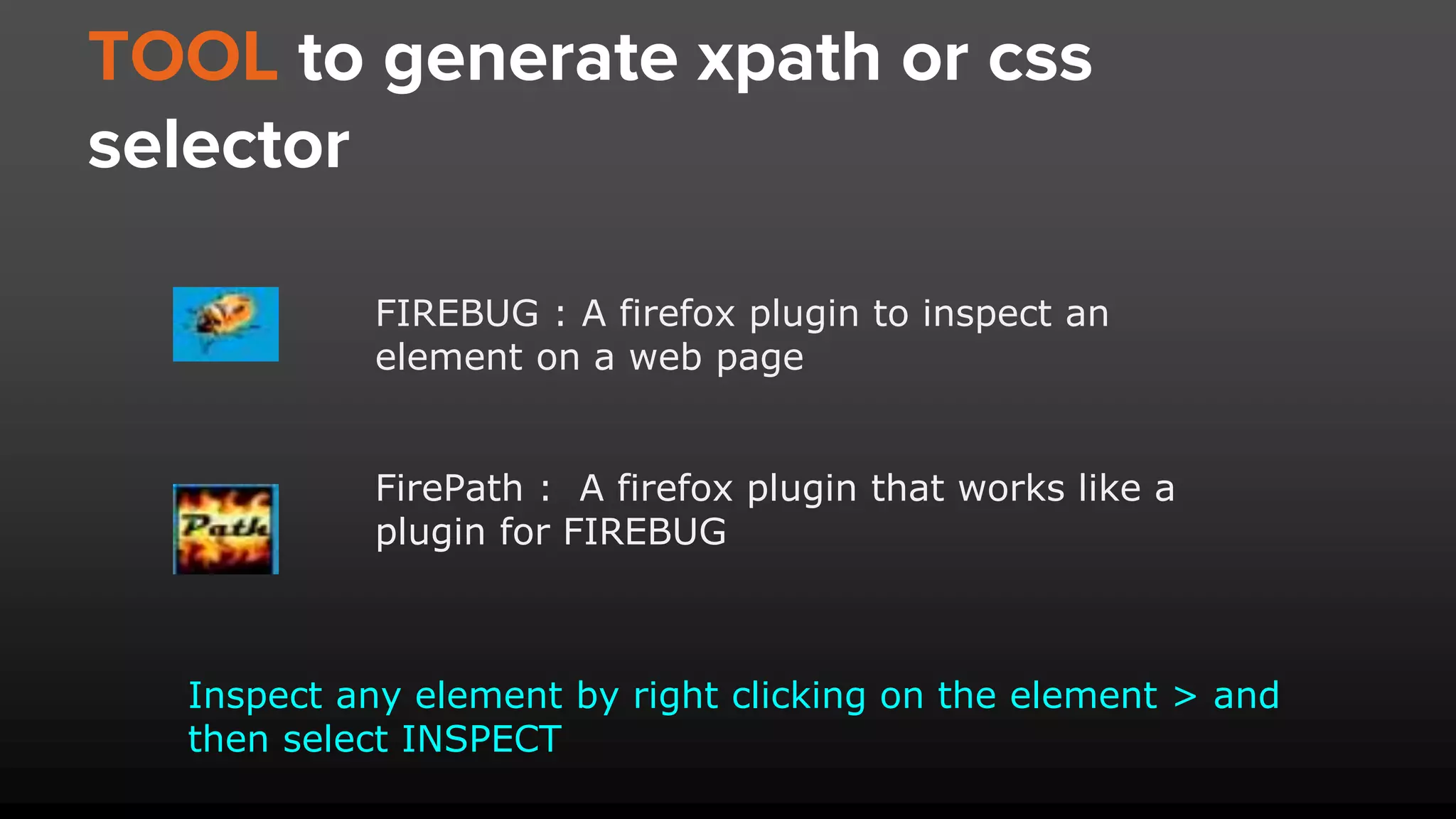
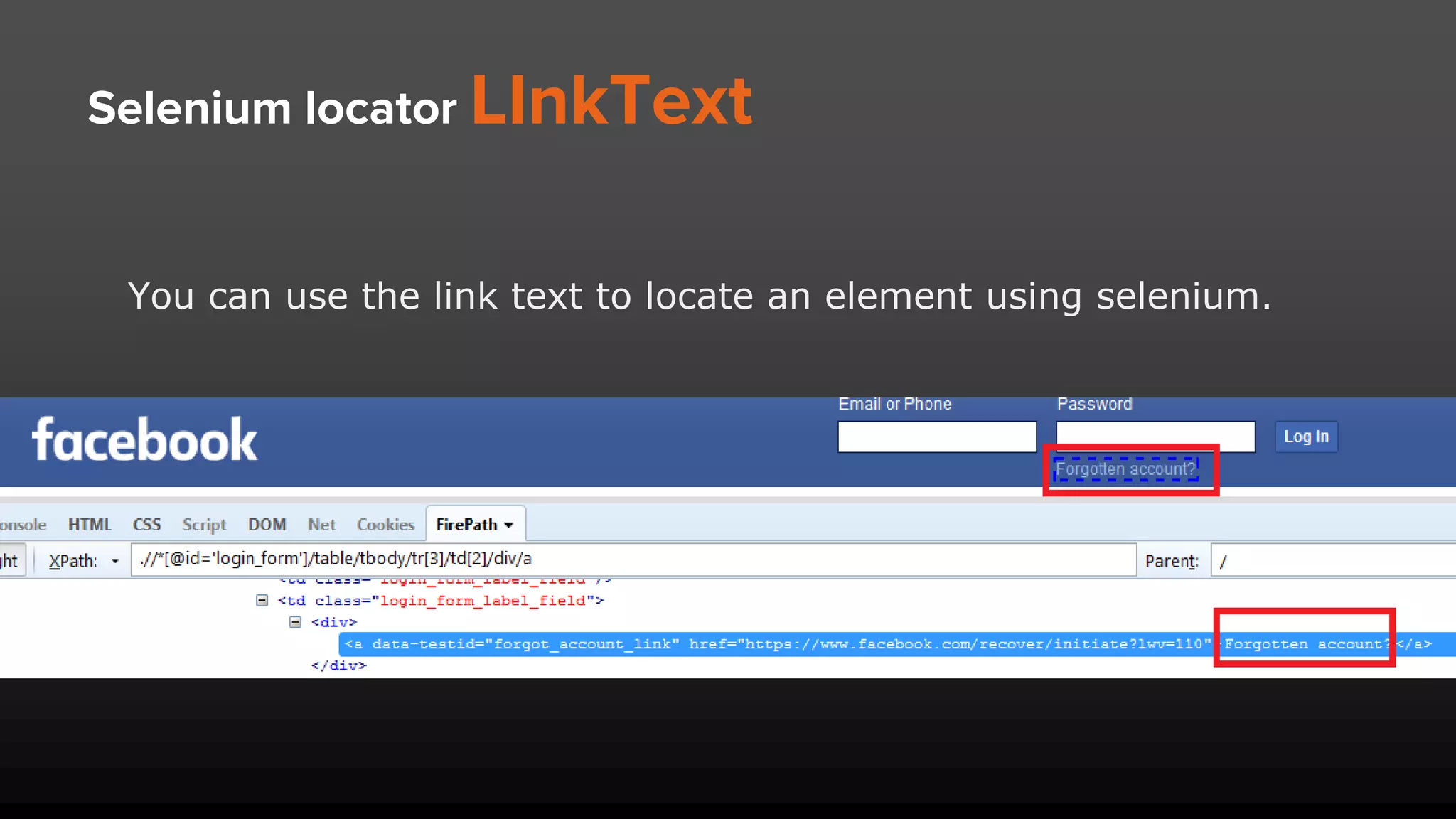
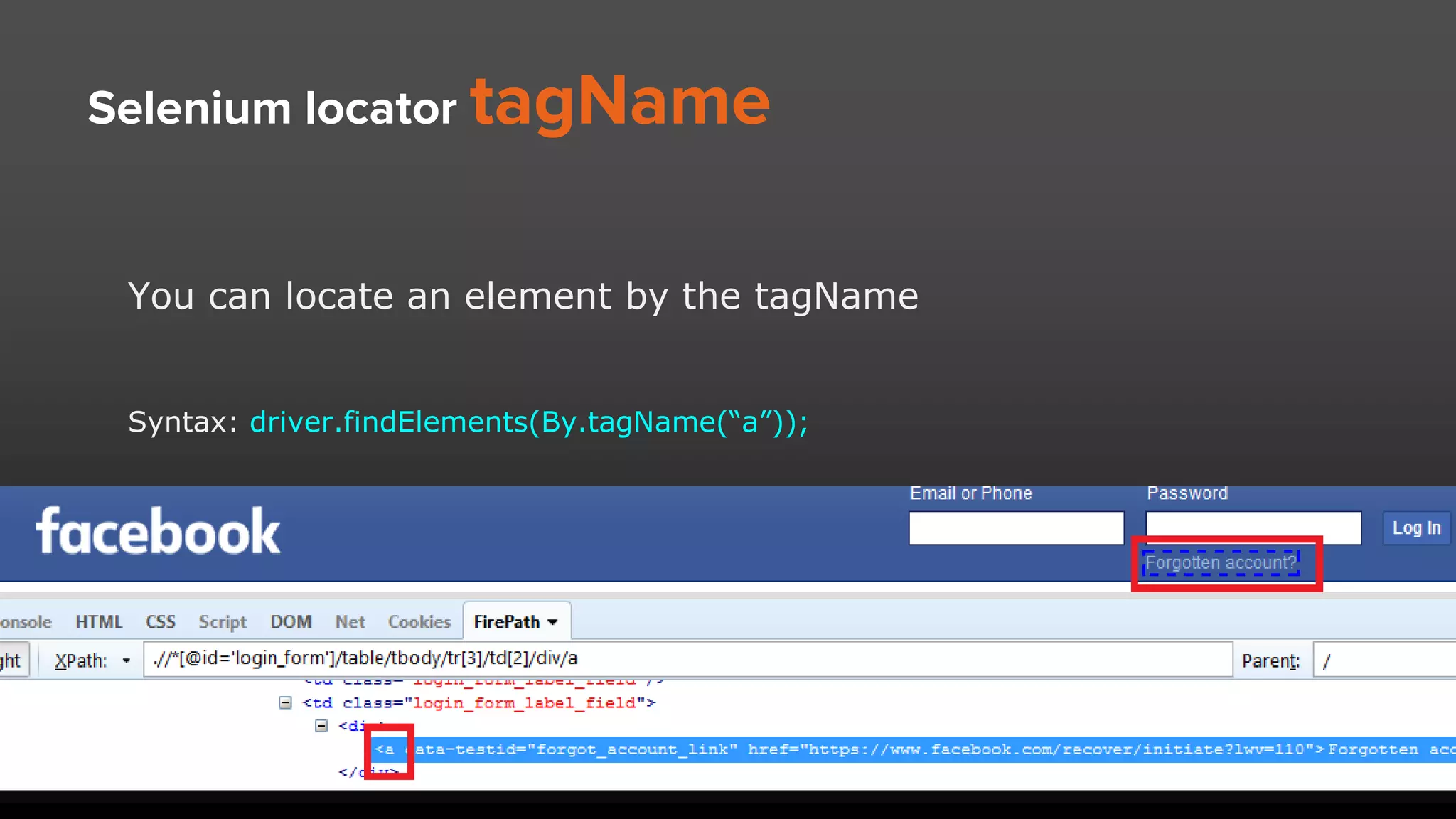
The document provides an overview of Selenium locators, essential for identifying web elements to perform actions in automated testing. It details types of locators such as ID, name, class name, CSS selector, and XPath, with specific syntax and pros/cons for each. Various methods and tools for generating XPath and CSS selectors are also discussed, including advantages of using ID locators for efficiency.








![Selenium locator xPath.. ● xPath stands for XML path ● XPath is the language used for locating nodes in an XML document ● It’s most flexible to derive xPath to identify web elements ● You can use any node attribute to create xPath of an element, but that attribute value should be unique in DOM xPath Syntax: //*[@attributeName=’attributeValue’][@attribute2=’value’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumlocators-170829070006/75/Selenium-locators-ID-Name-xpath-CSS-Selector-advance-methods-12-2048.jpg)
![Types of xPath.. Absolute xPath Syntax: /html/body/form/div/span/span Relative xPath: Syntax: //Input[@AttributeName=’value’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumlocators-170829070006/75/Selenium-locators-ID-Name-xpath-CSS-Selector-advance-methods-13-2048.jpg)
![xPath Methods.. ● Contains() Syntax: //*[contains(text(),'Email')] ● Starts-with() Syntax: //*[starts-with(text(),'Pass')] ● text() Syntax: //*[text()='Password']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumlocators-170829070006/75/Selenium-locators-ID-Name-xpath-CSS-Selector-advance-methods-14-2048.jpg)
![xPath Advance.. ● parent() Syntax: //*[text()='Password']/parent::parentTagName[1] ● ancestor() Syntax: //*[text()='Password']/ancestor::table ● descendant() Syntax: .//*[@id='value']/descendant::h1 ● preceding/following sibling() Syntax: .//*[@class='_li']/div[1]/following-sibling::div](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumlocators-170829070006/75/Selenium-locators-ID-Name-xpath-CSS-Selector-advance-methods-15-2048.jpg)
![Selenium locator css Selector path (1/3) ● is the cascading stylesheet path ● Is a pattern to find an element in web page syntax : [attribute-Name=’value’][attribute2=’value’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumlocators-170829070006/75/Selenium-locators-ID-Name-xpath-CSS-Selector-advance-methods-16-2048.jpg)

![How to create a css Selector path (3/3) syntax : [attribute-Name=’value’][attribute2=’value’] ● Starts with = ^ Syntax: [attribute-Name^=’value’] ● Ends with = $ Syntax: [attribute-Name$=’value’] ● Contains = * Syntax: [attribute-Name*=’value’]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seleniumlocators-170829070006/75/Selenium-locators-ID-Name-xpath-CSS-Selector-advance-methods-18-2048.jpg)