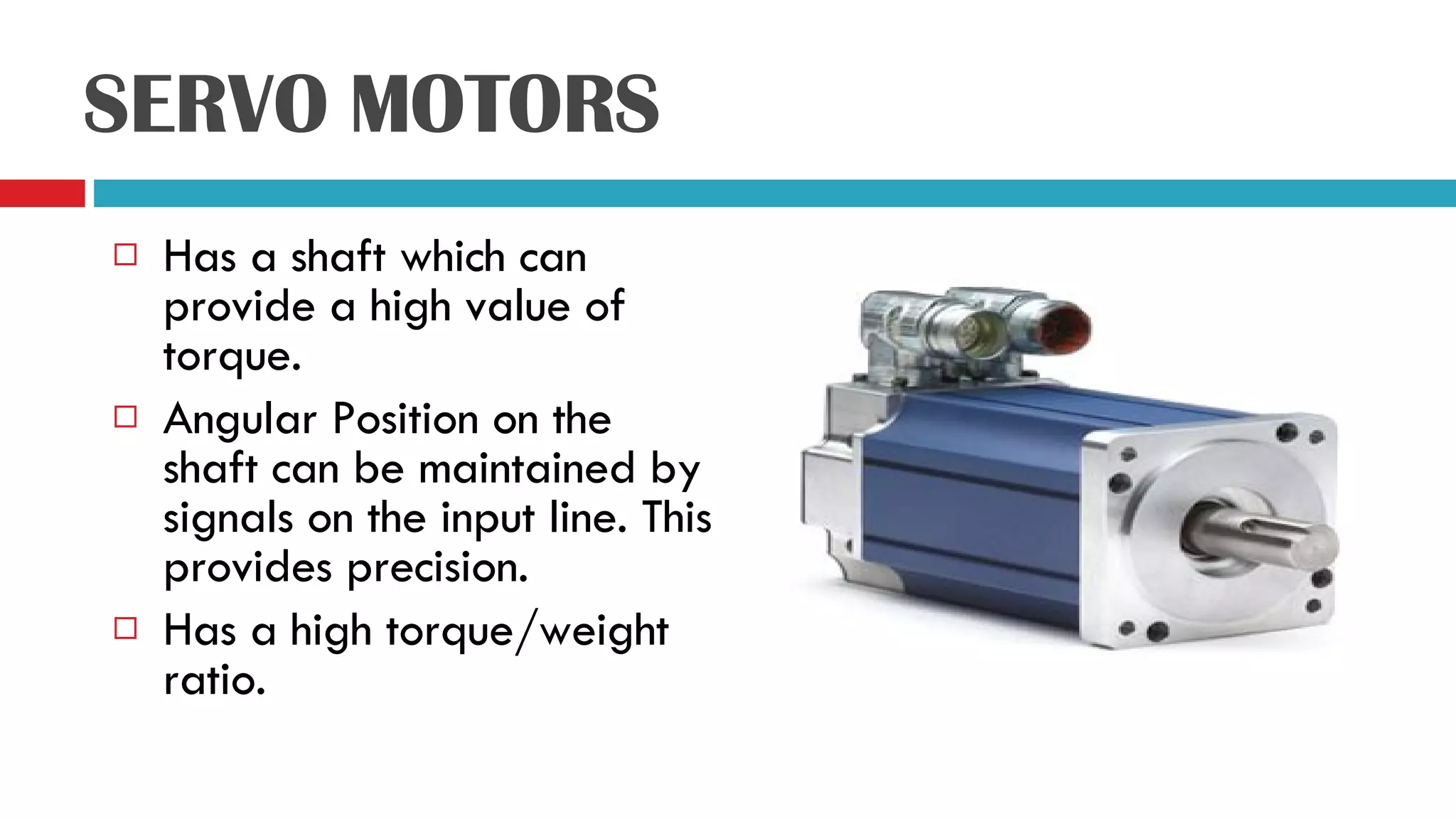
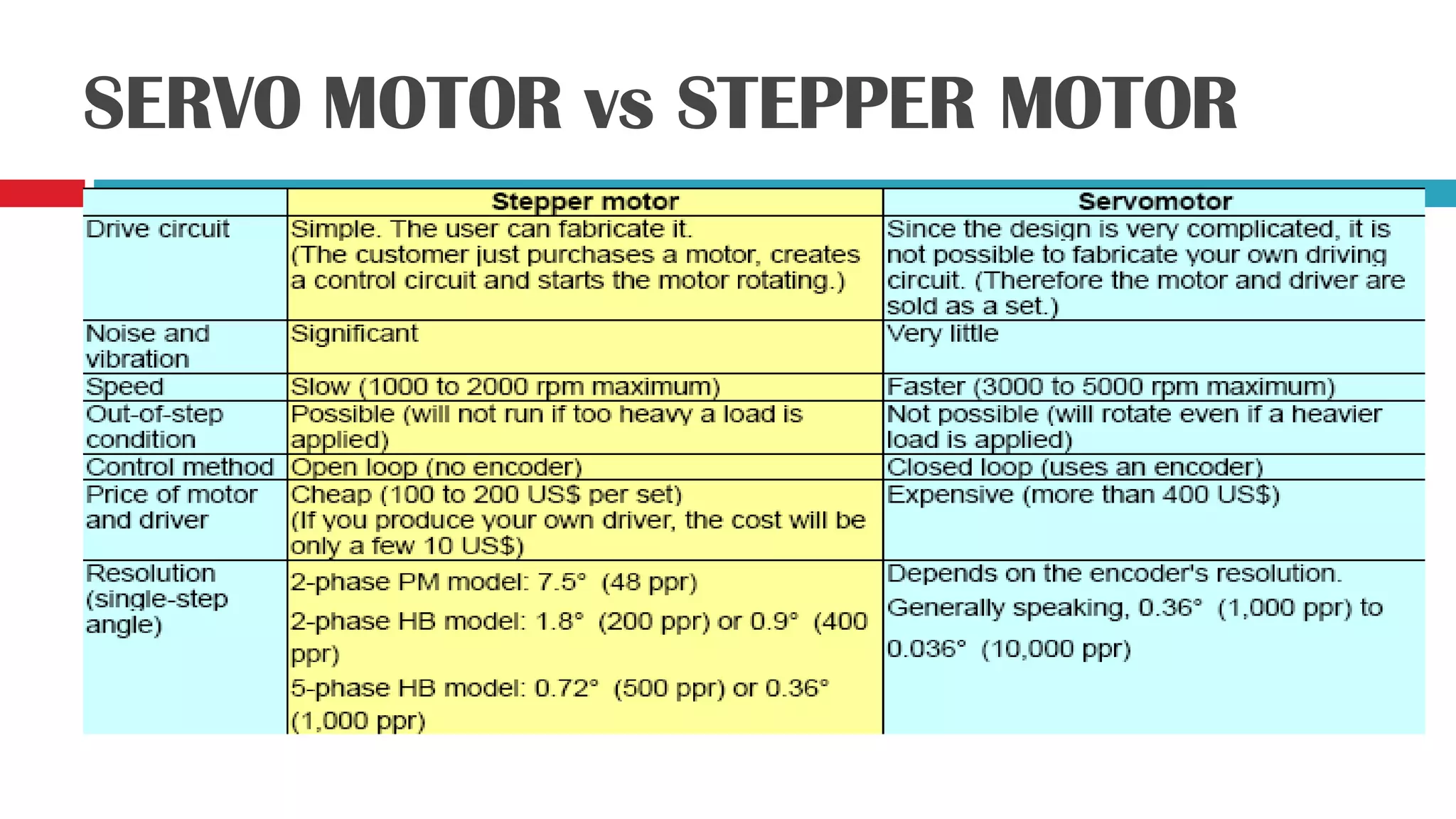
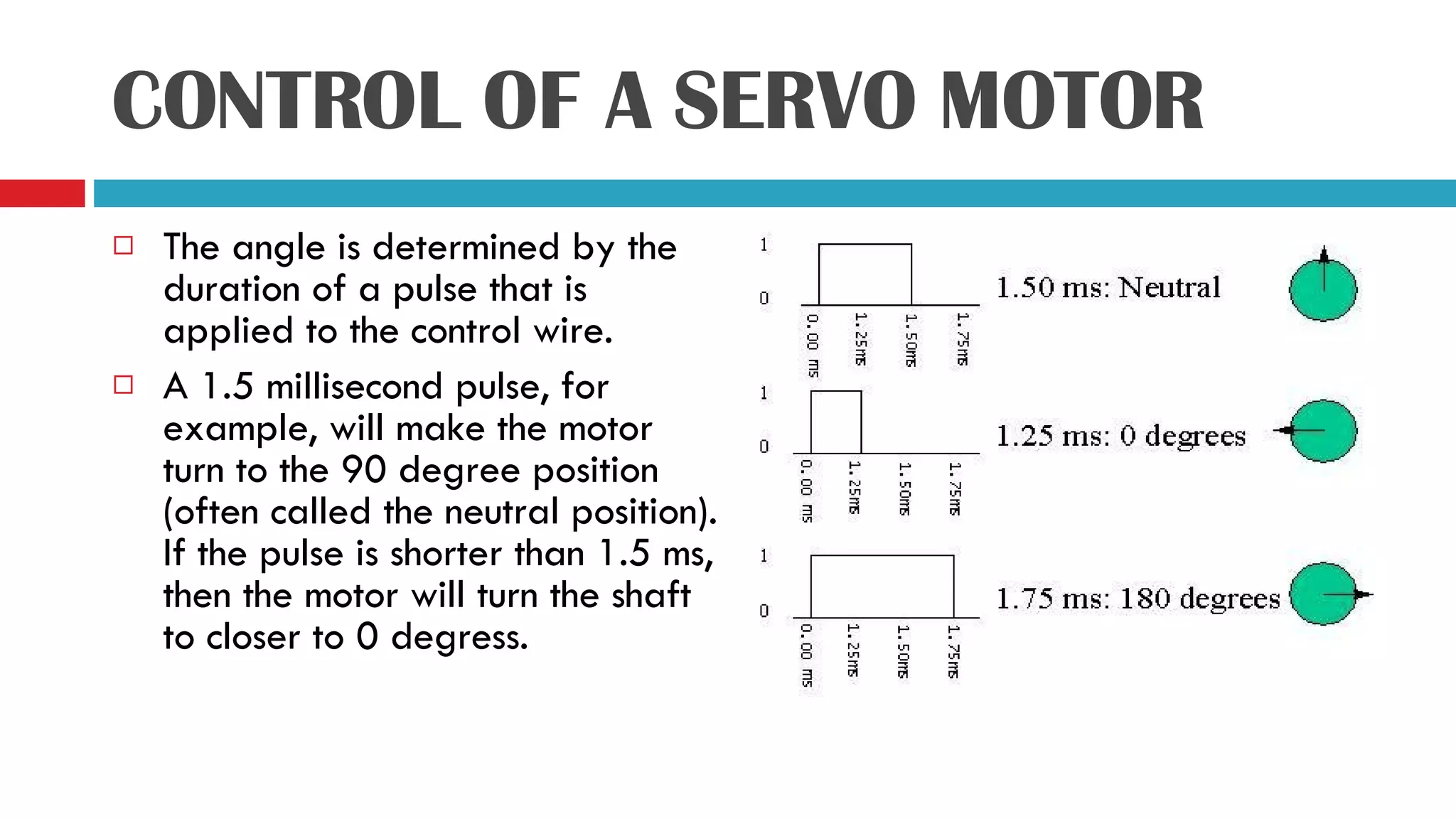
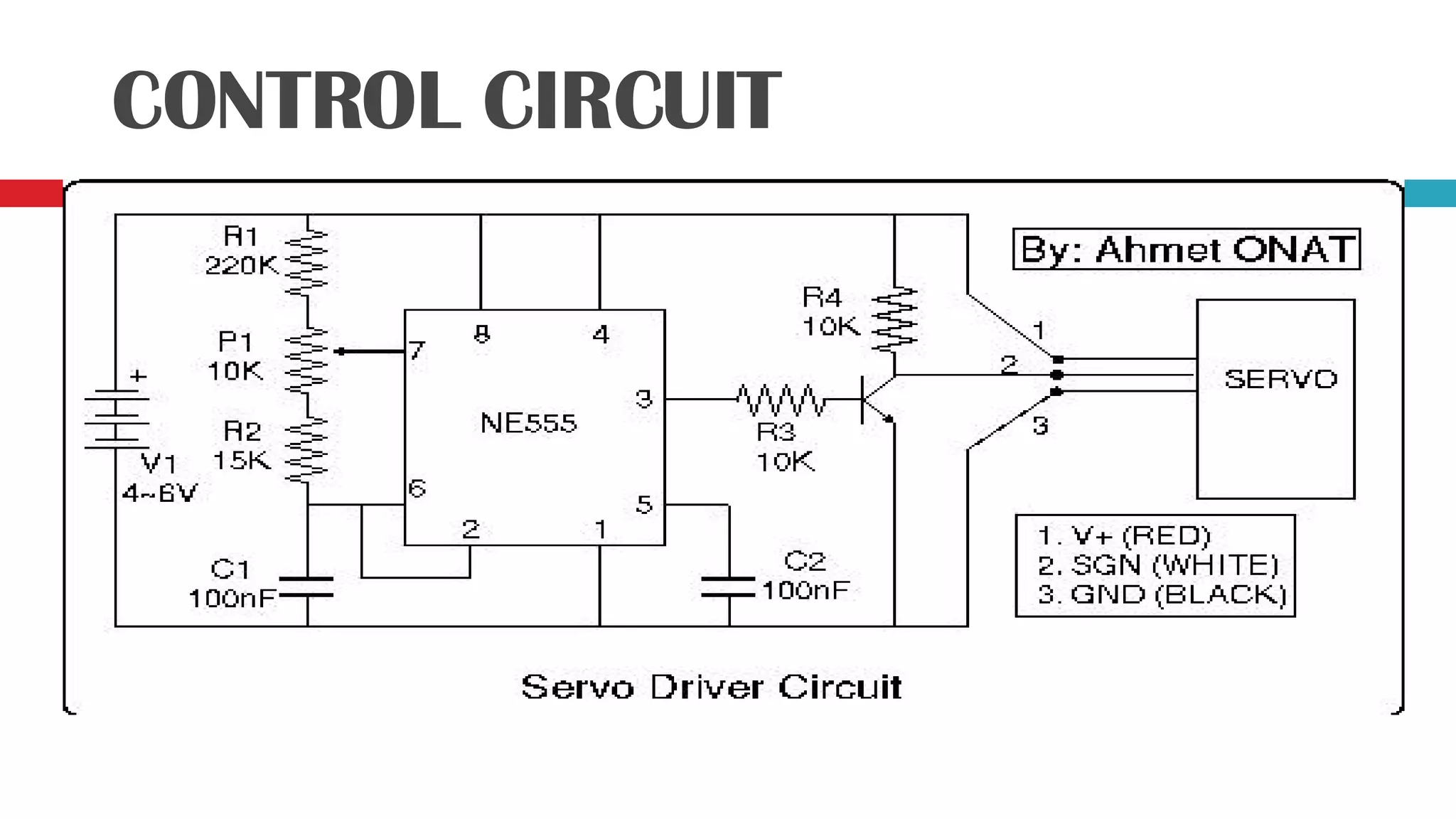
Servo motors can precisely control the angular position of a shaft through signals received on the input line. They have a high torque to weight ratio and consist of amplifiers, a gear reduction system, motor, and feedback potentiometer enclosed in a small case. The angle of the servo motor is determined by the duration of a control pulse applied to the input wire, with longer pulses rotating the shaft closer to 90 degrees and shorter pulses closer to 0 degrees. An example shows a 1.59ms pulse will rotate the shaft to 30 degrees. The circuit uses a NE555 timer IC to generate repeated pulses to control the servo motor position. While servo motors provide precise control, they have higher costs than stepper motors due to the motor and