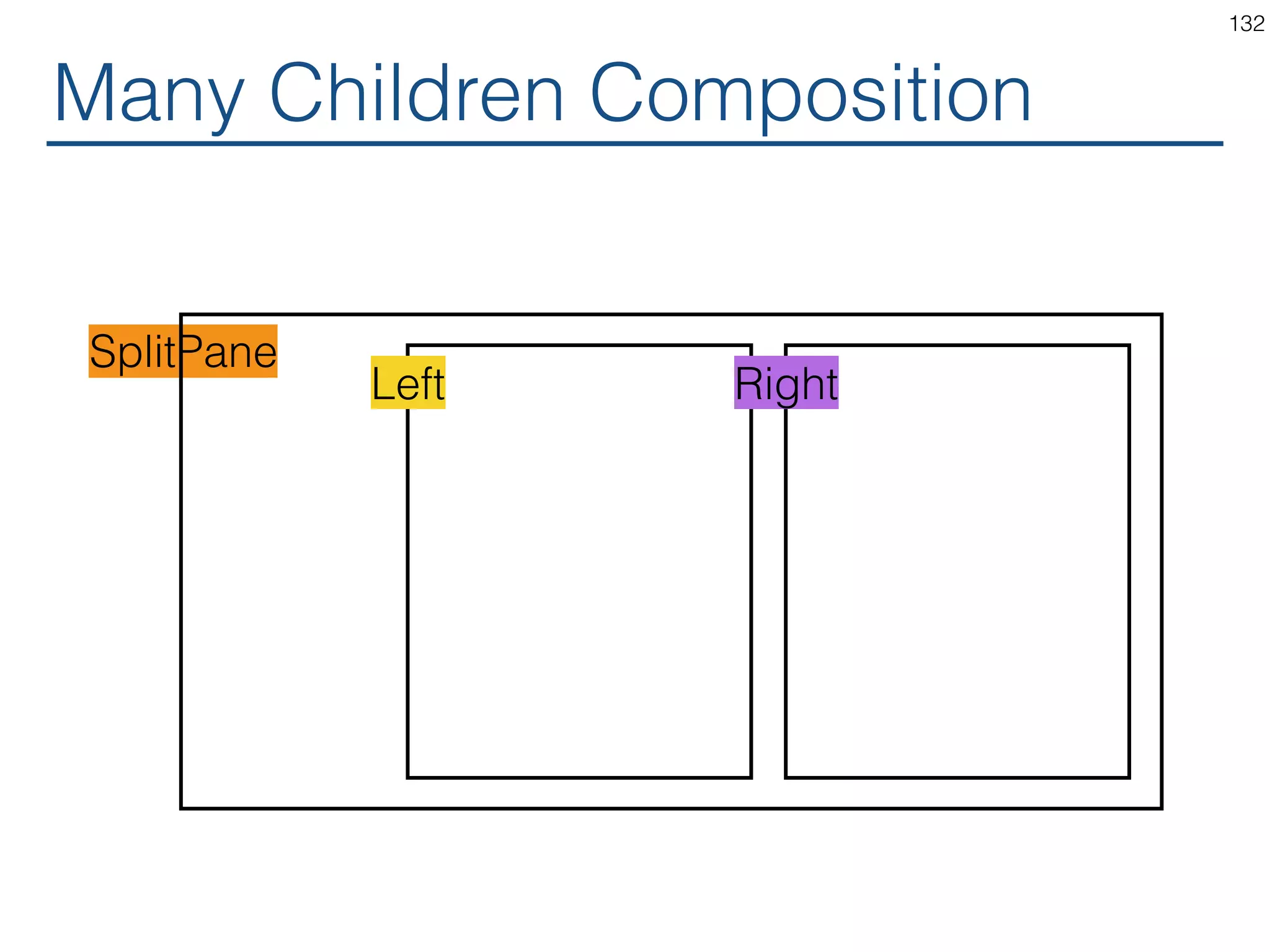
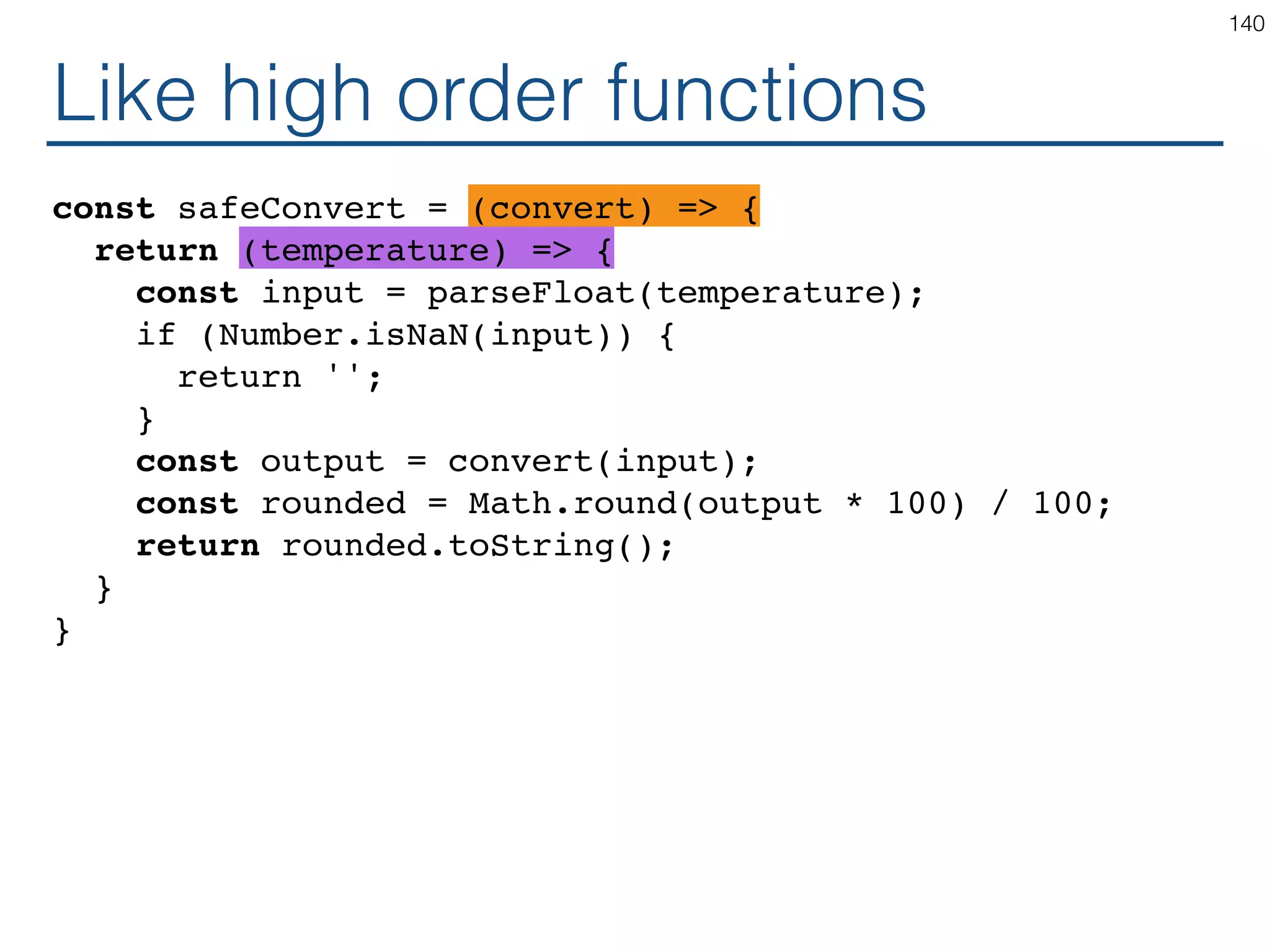
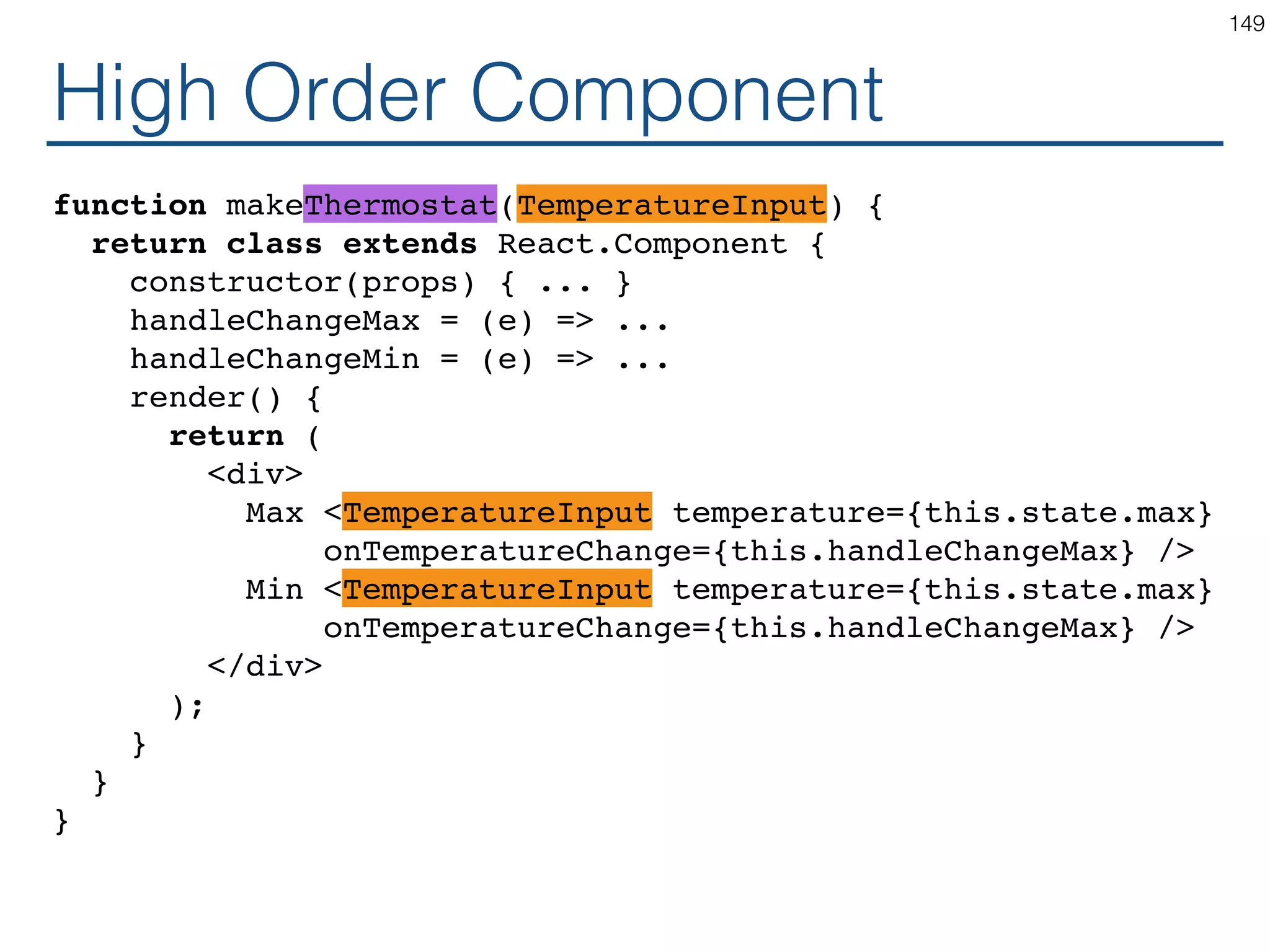
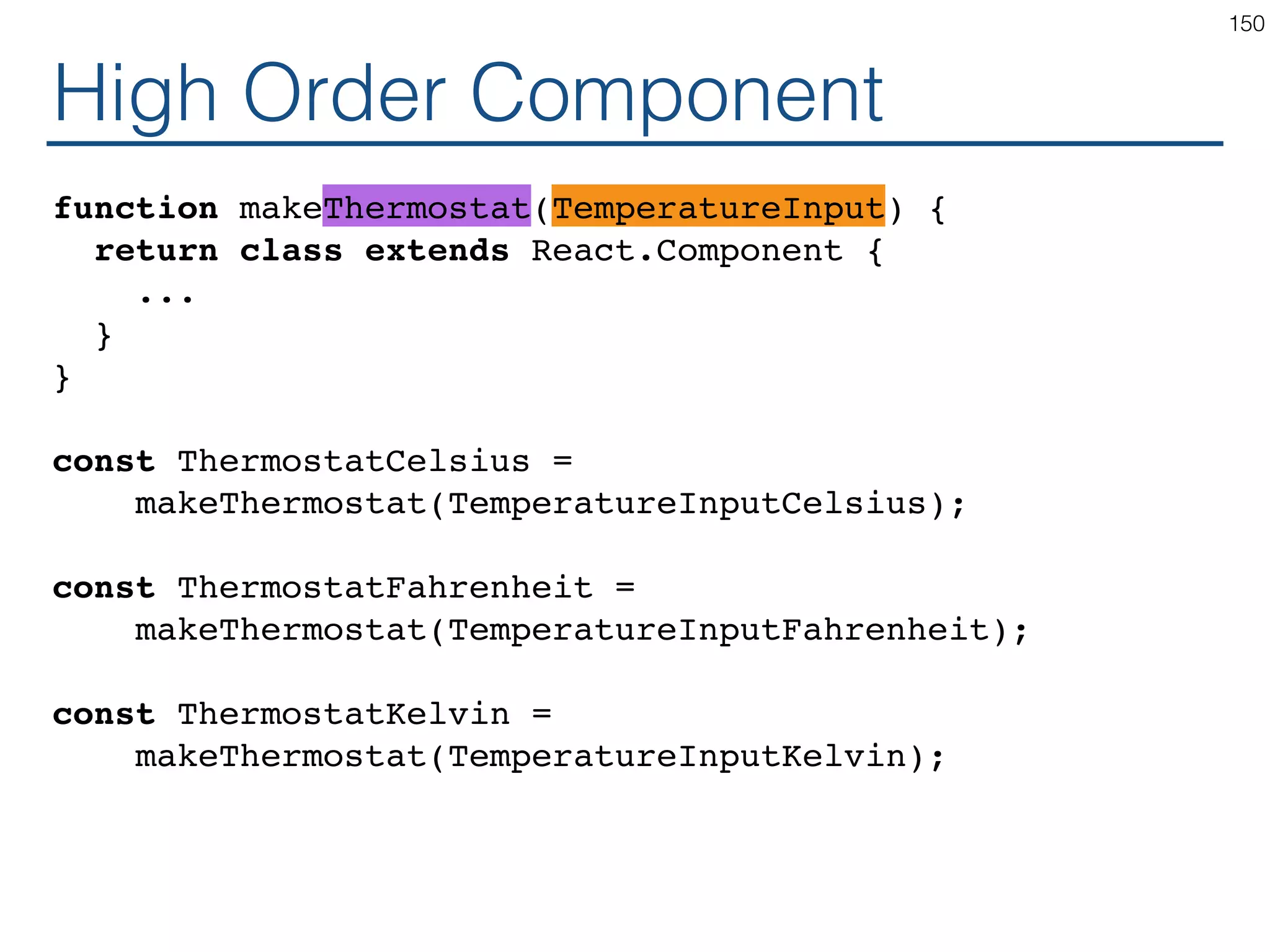
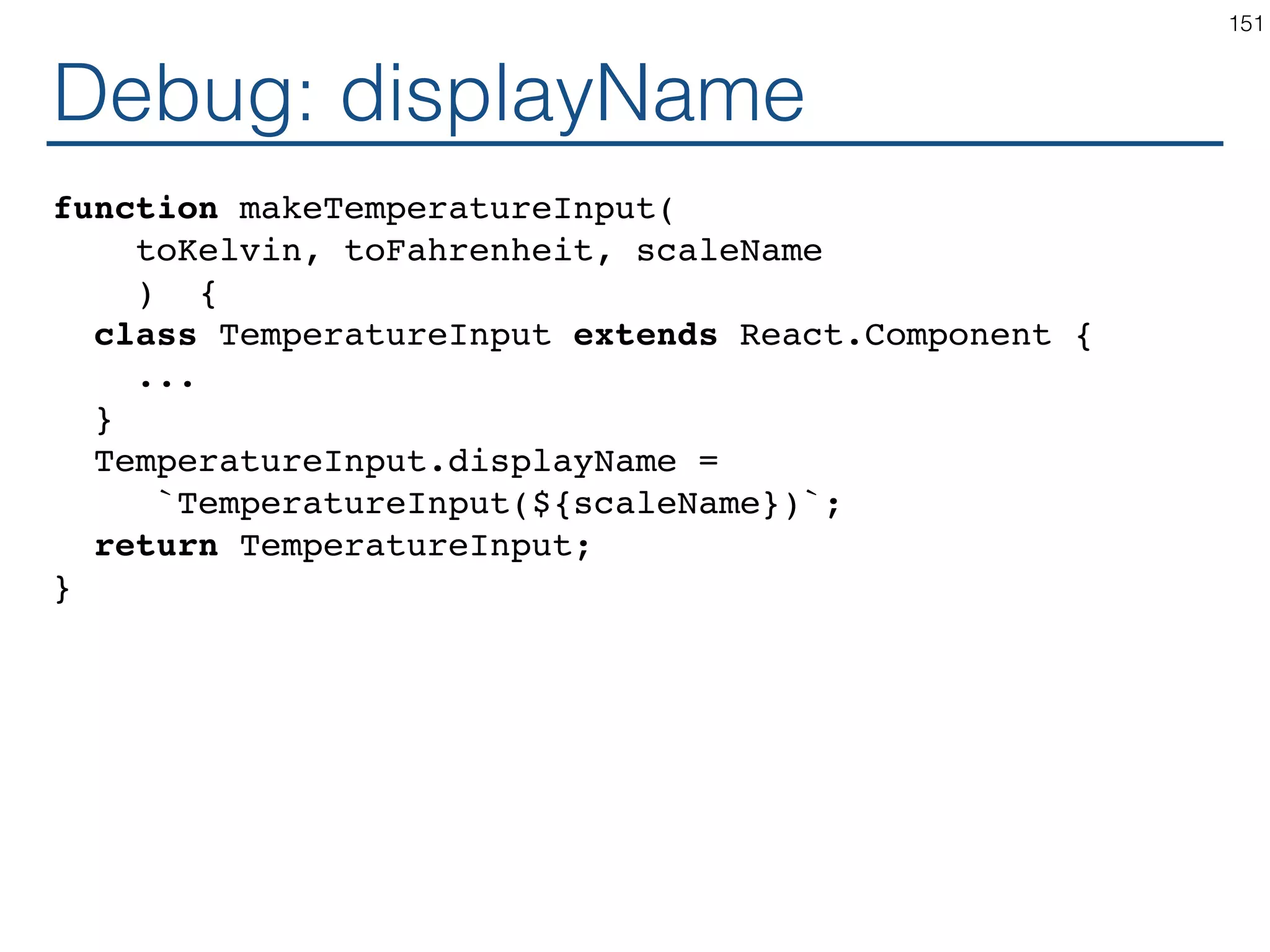
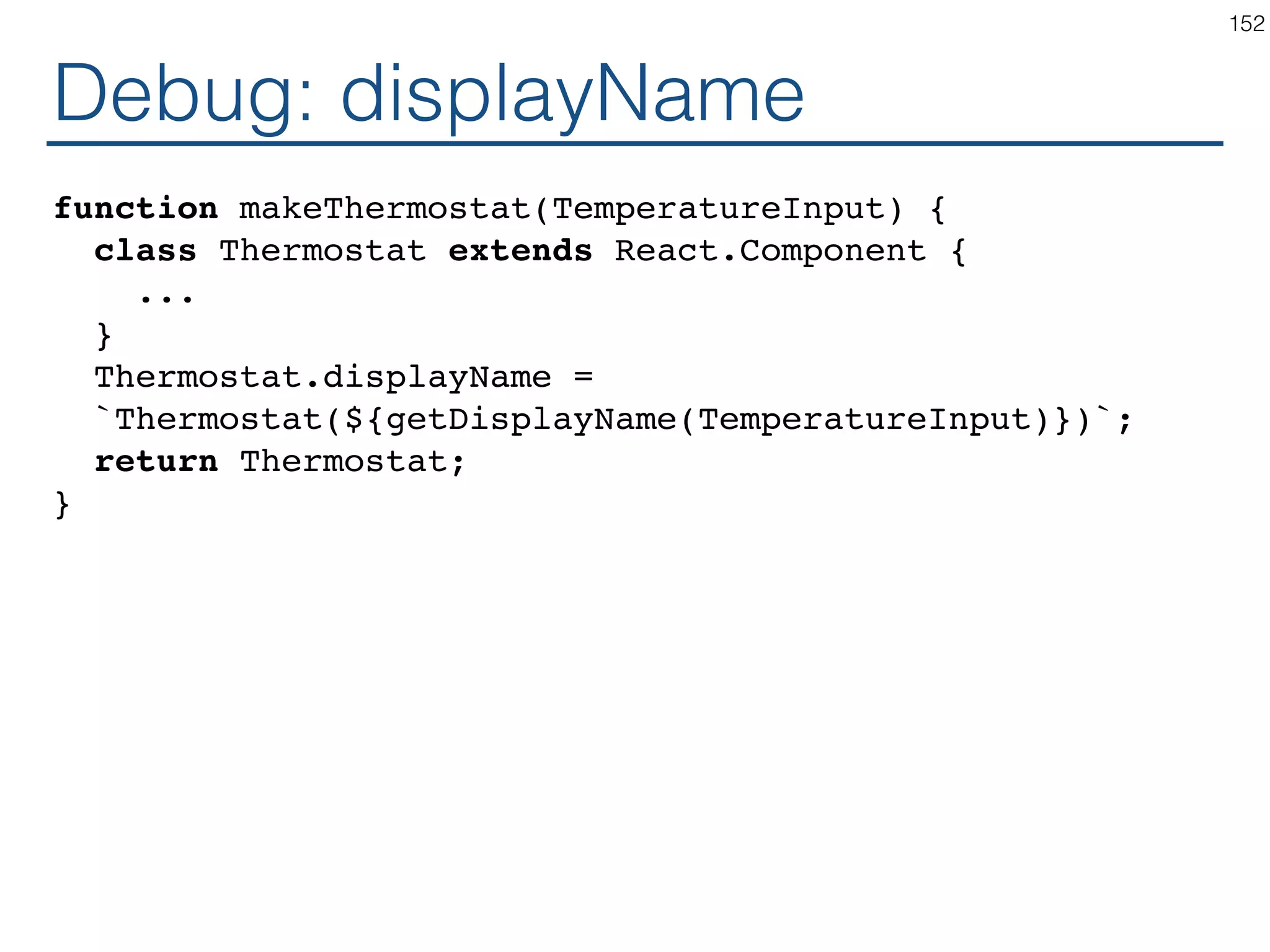
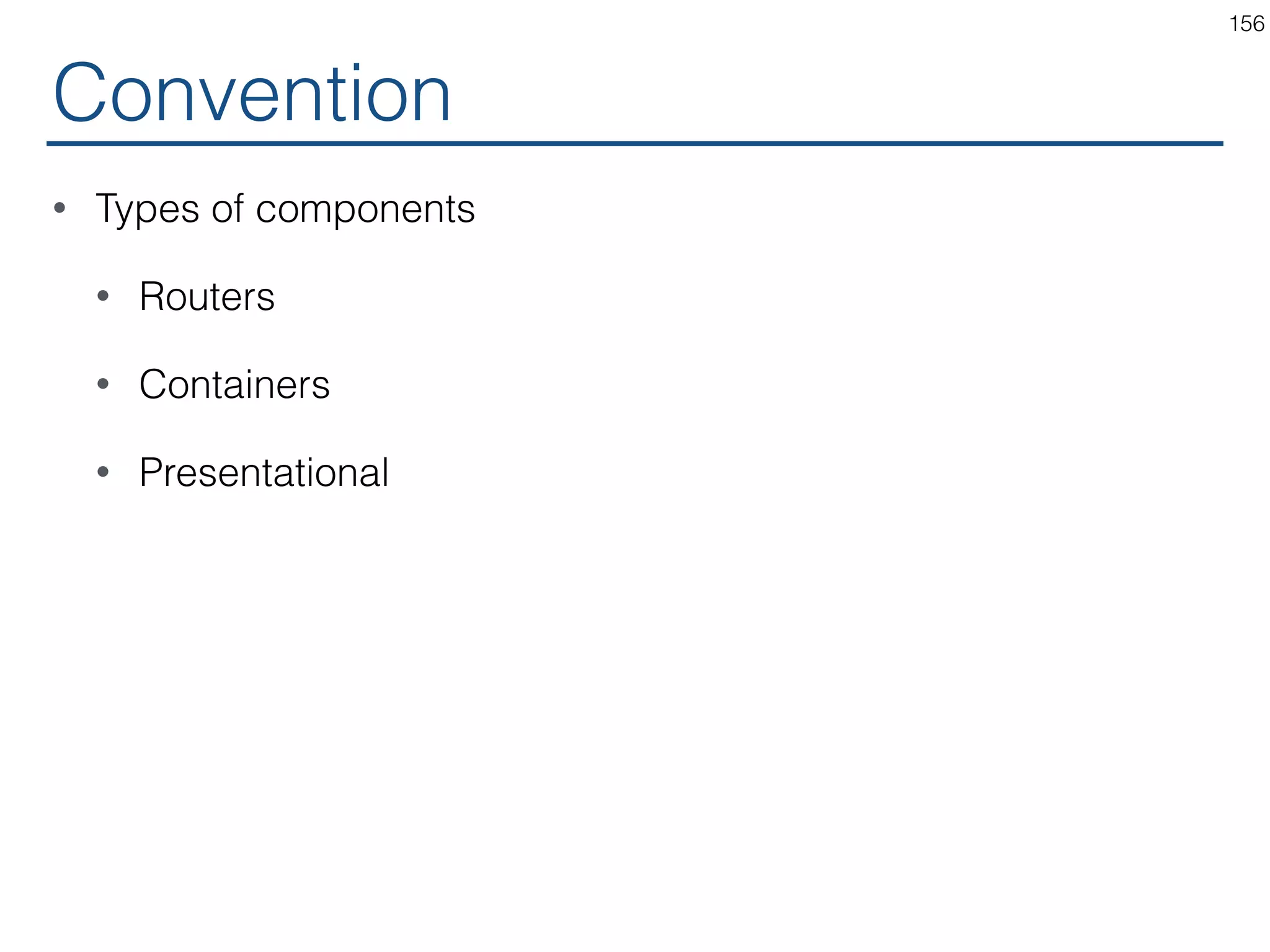
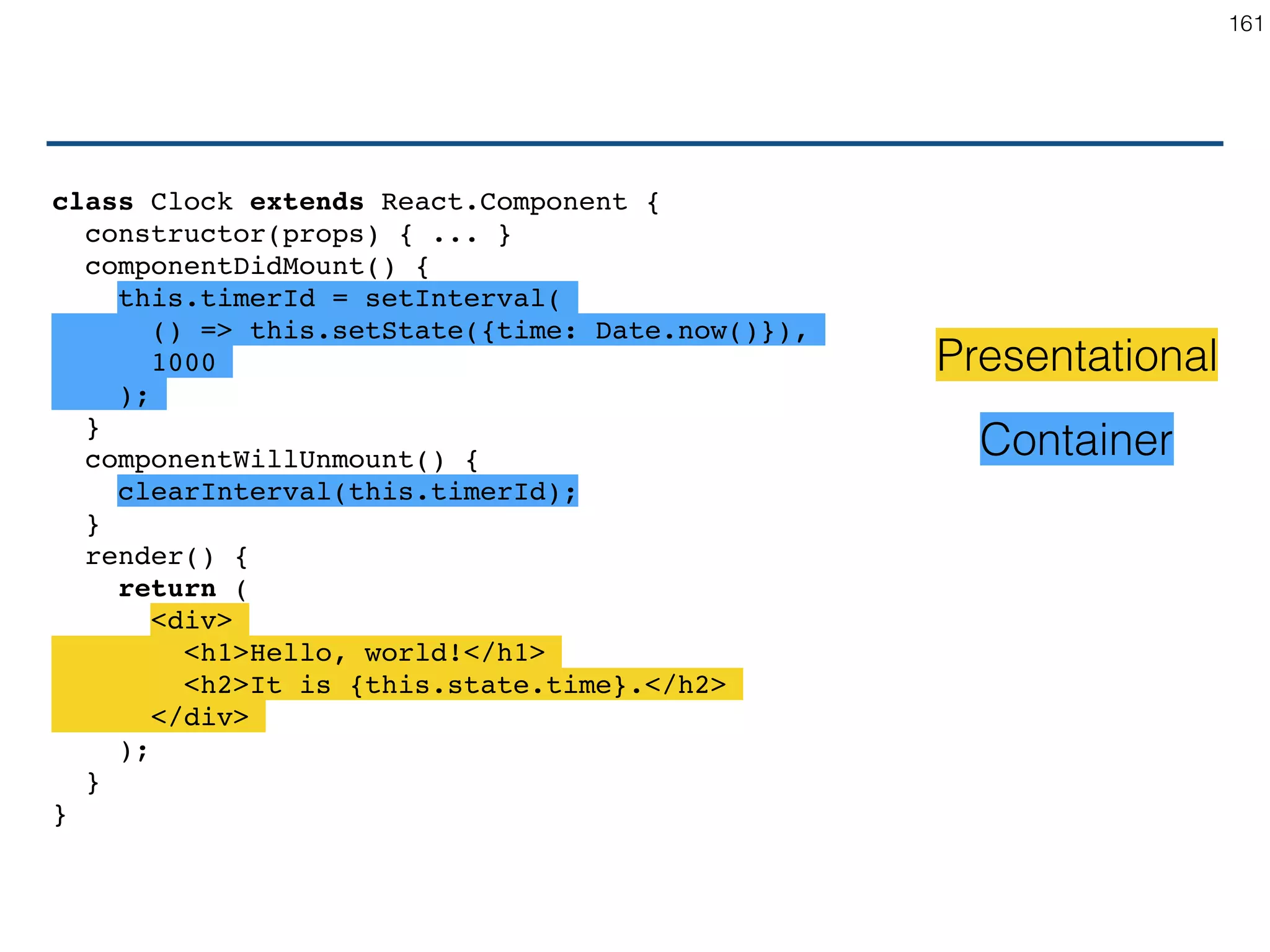
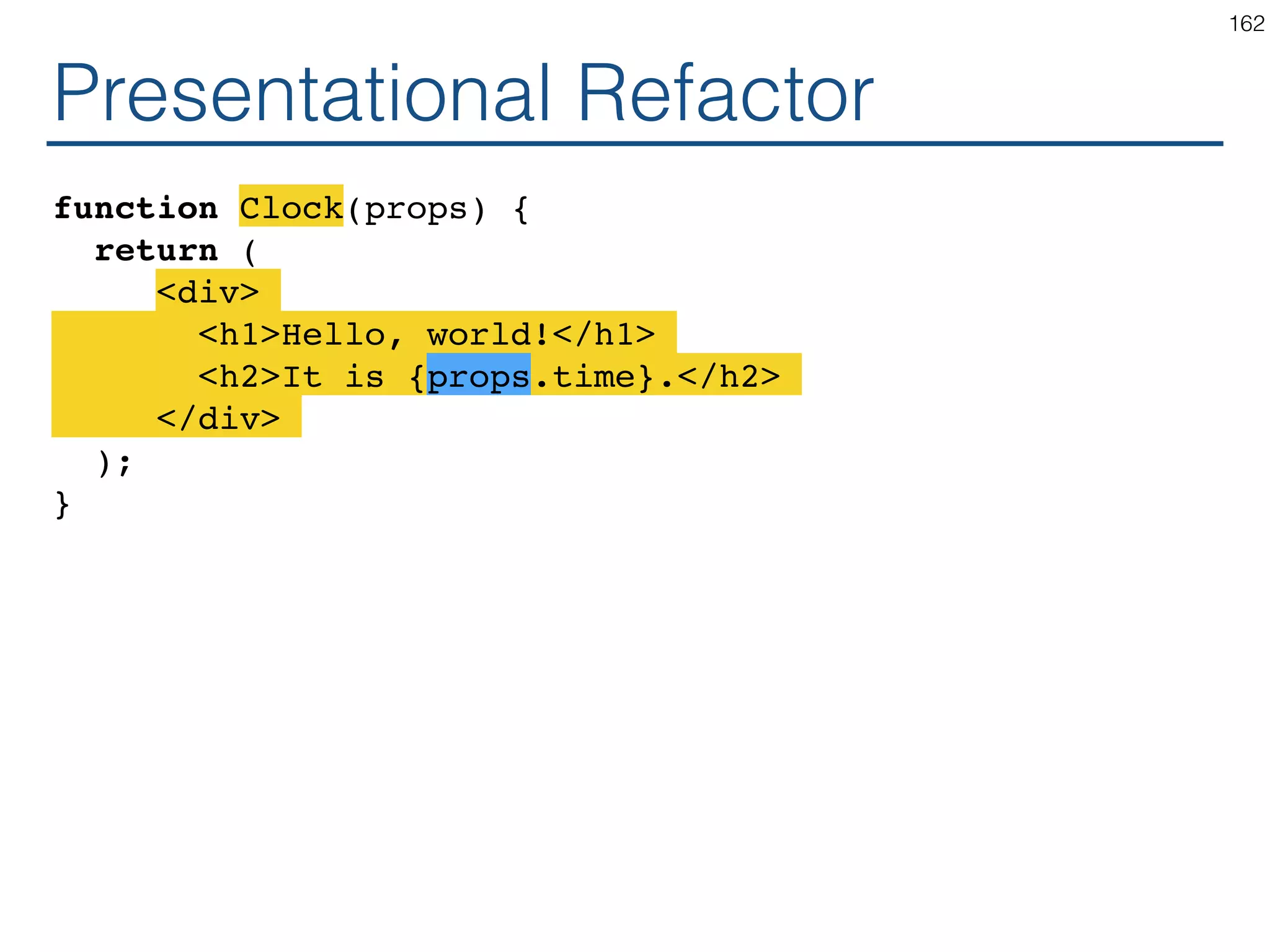
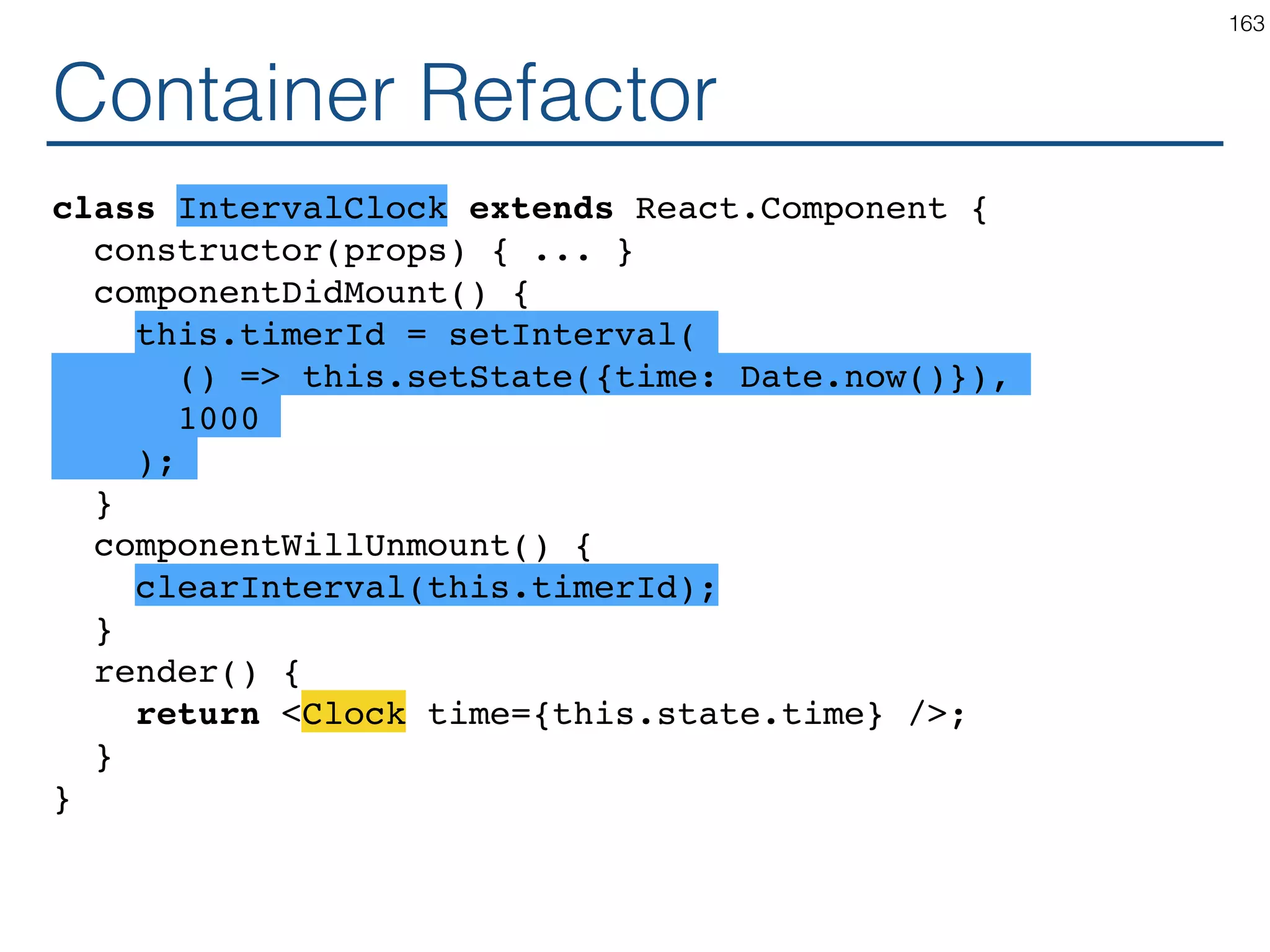
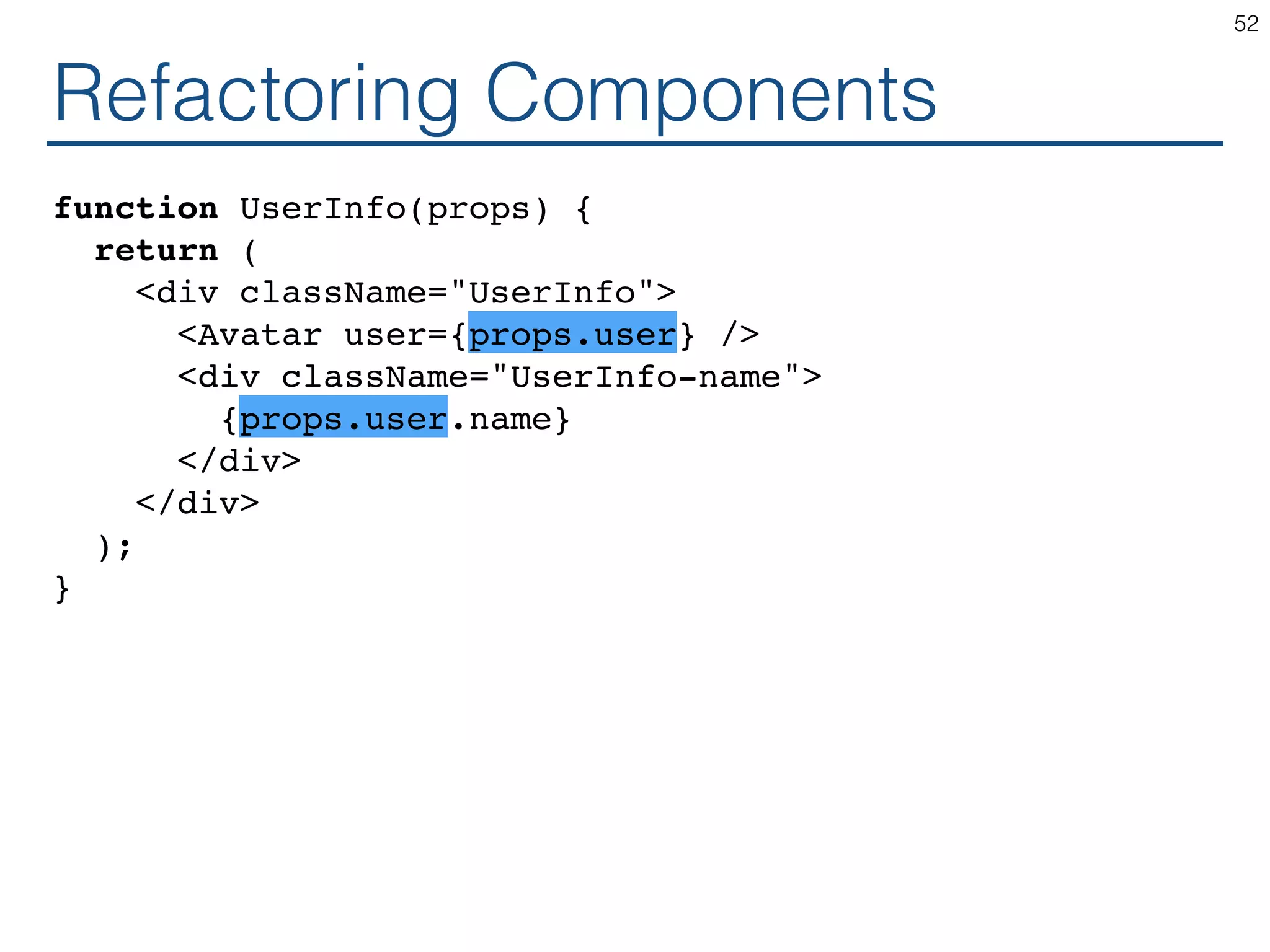
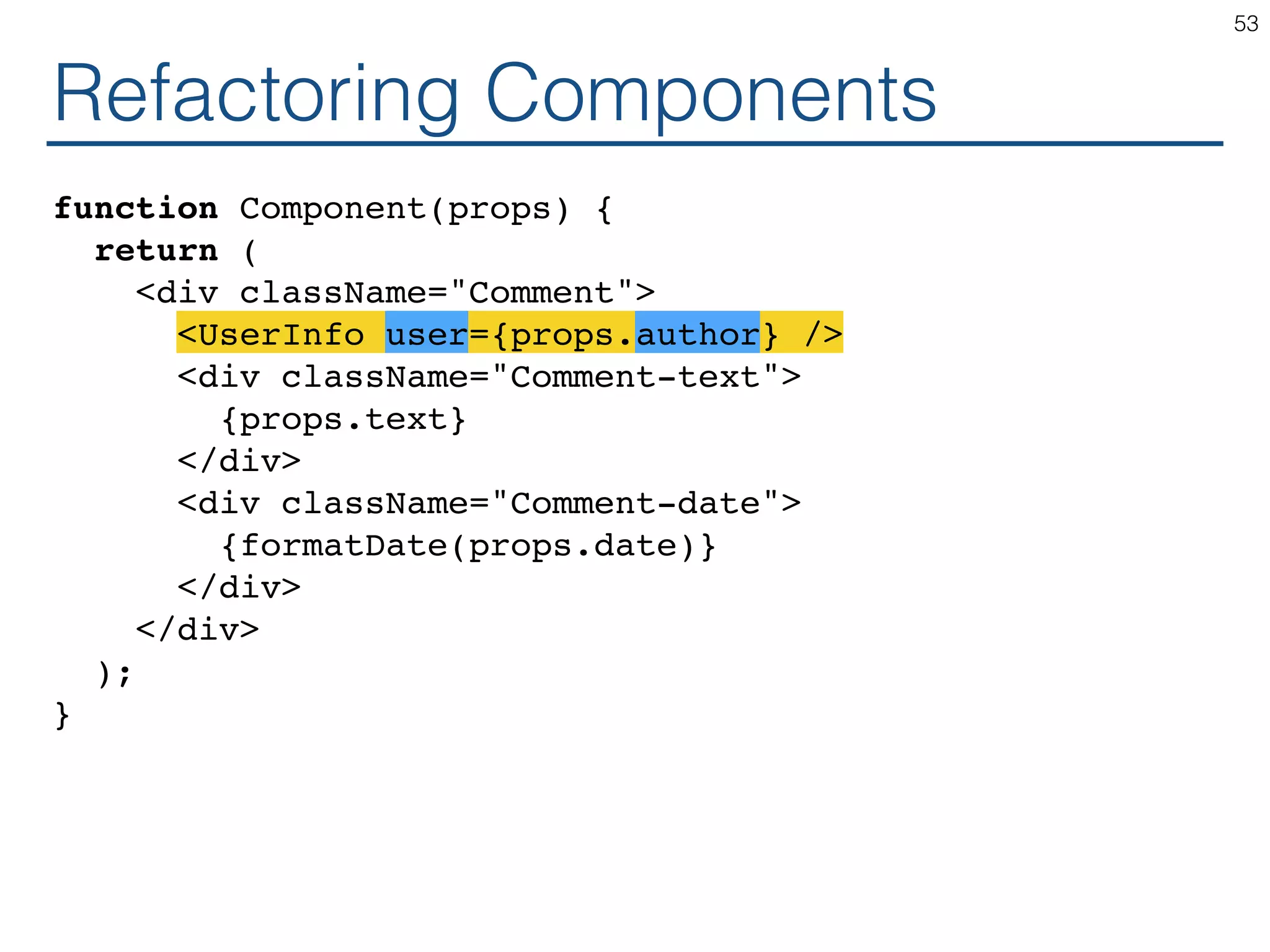
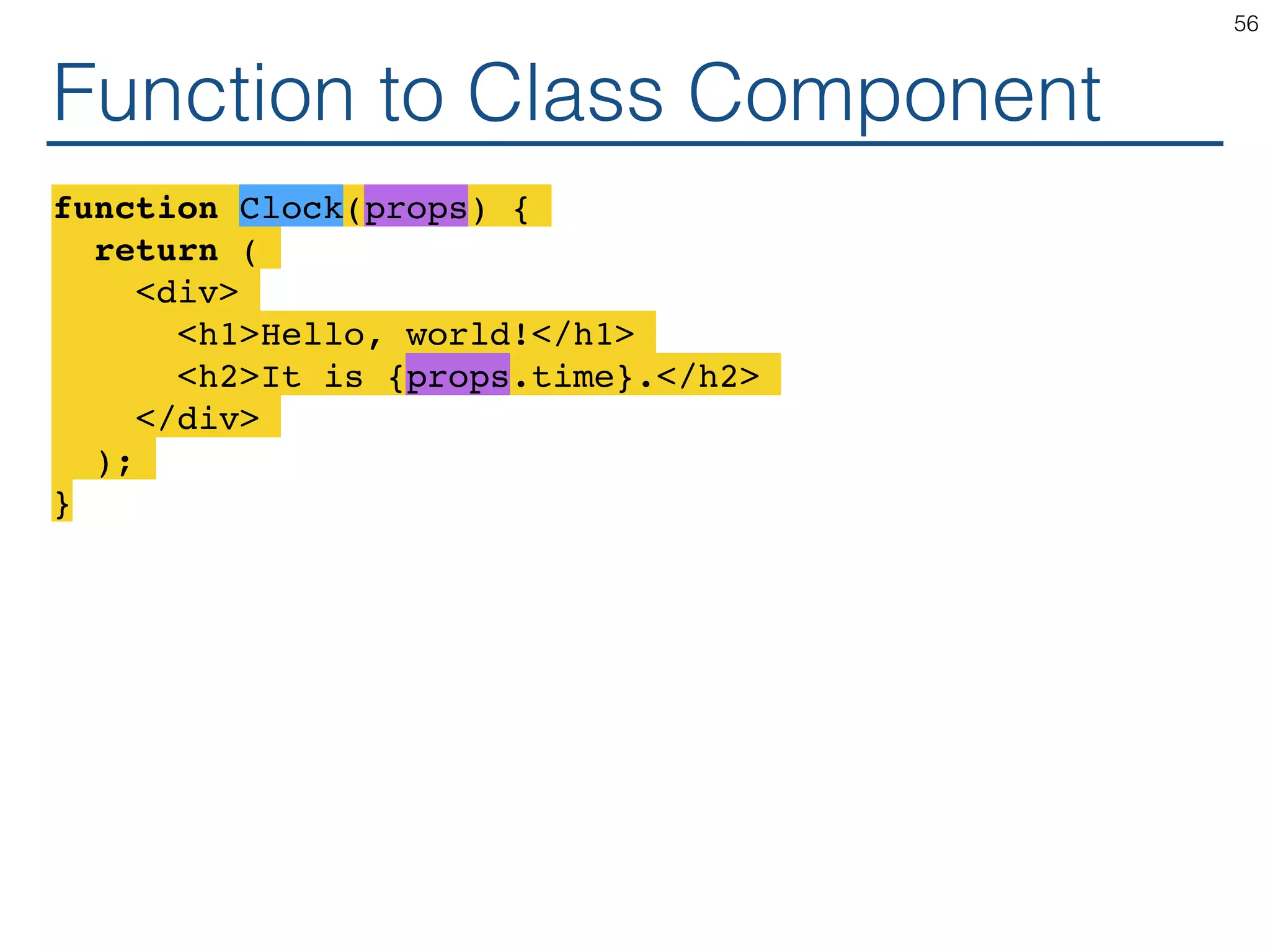
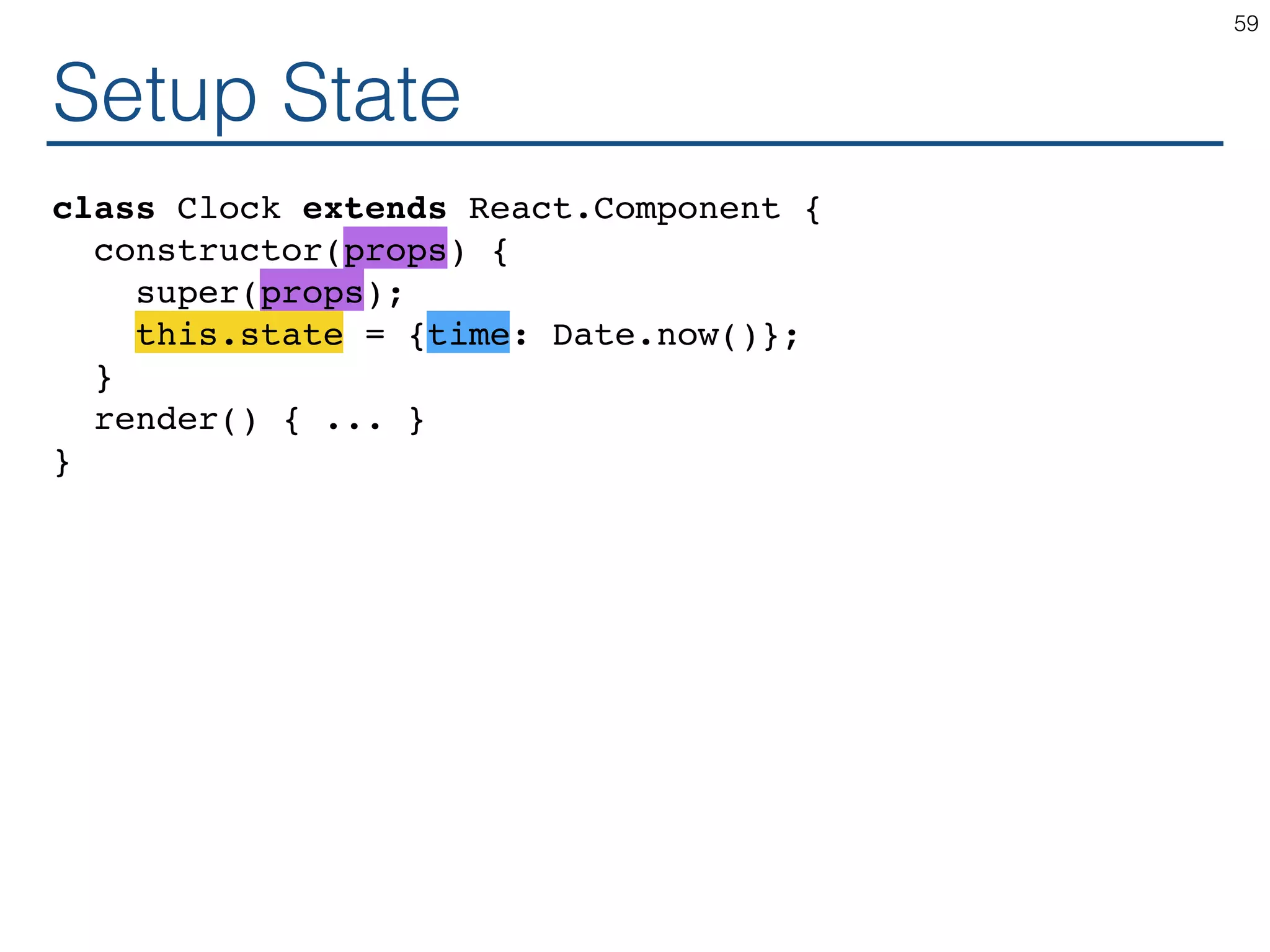
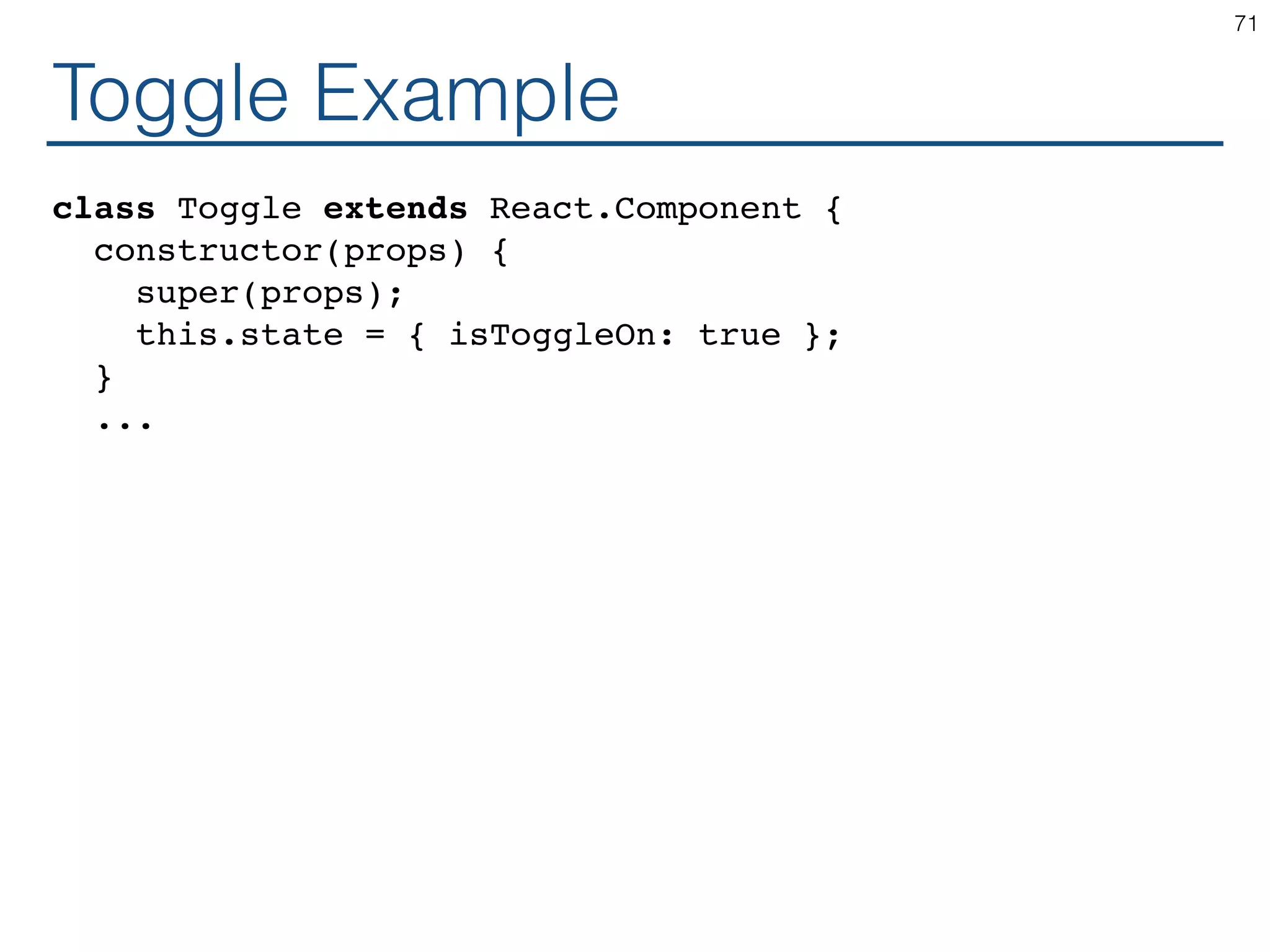
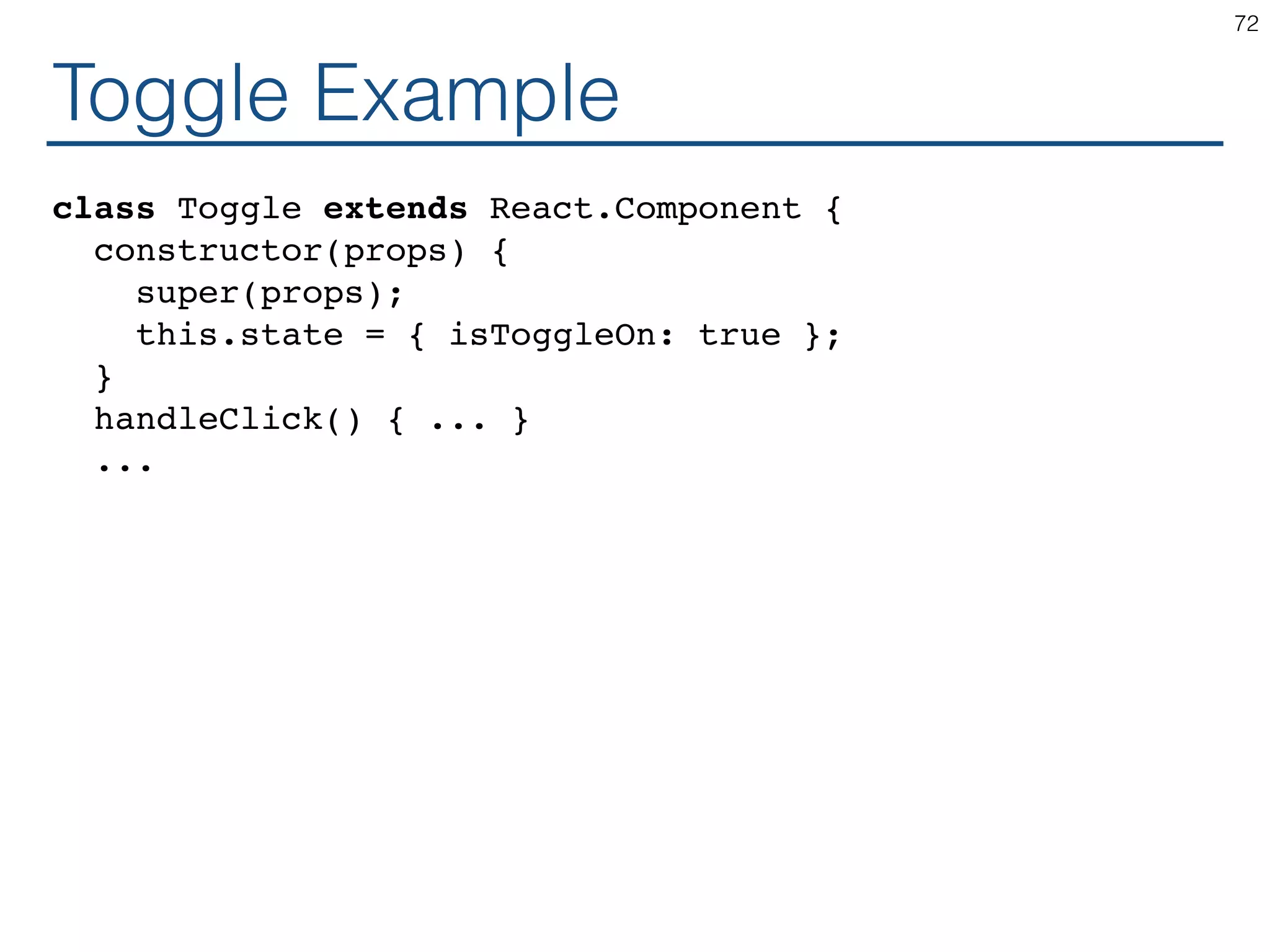
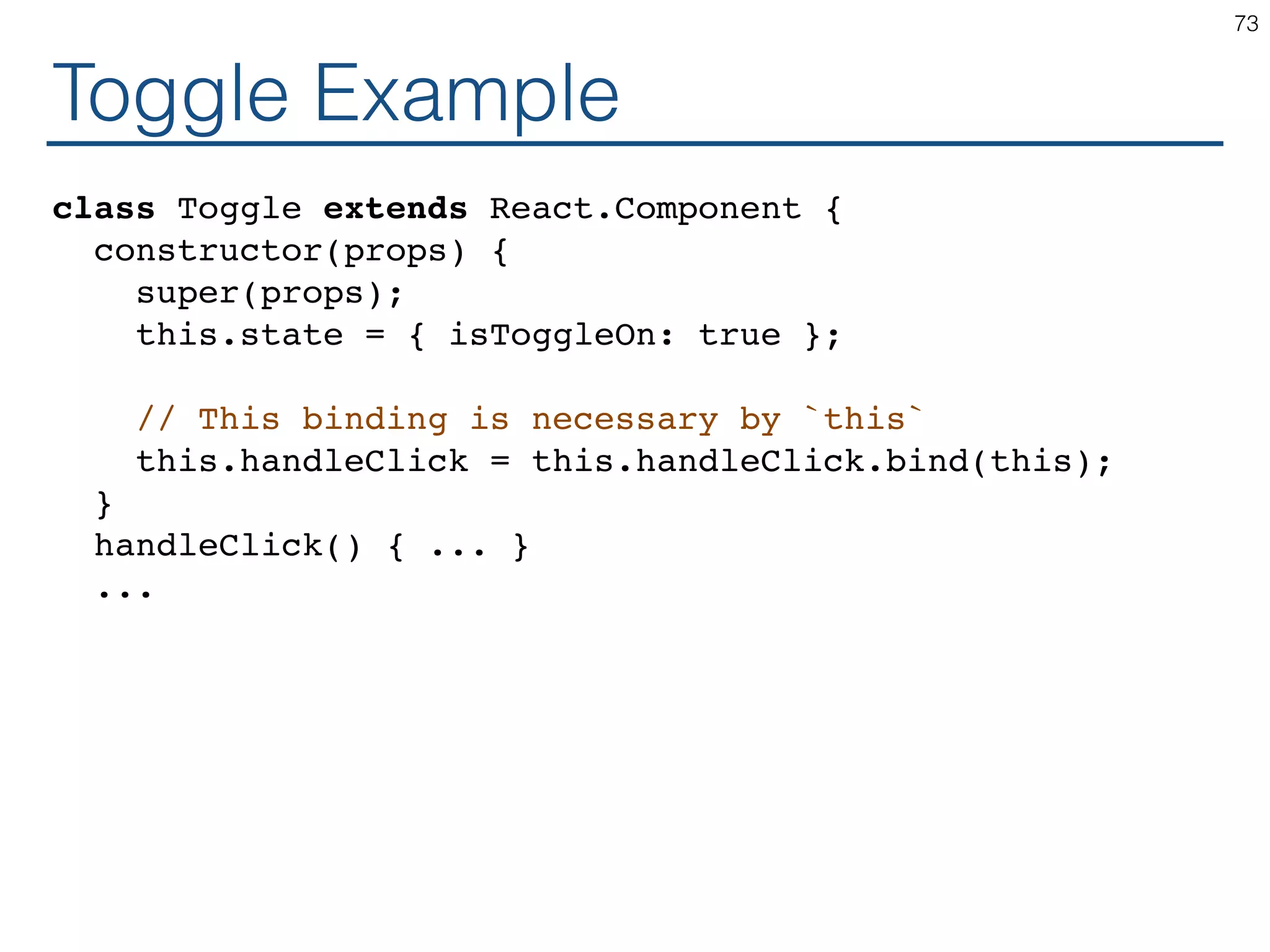
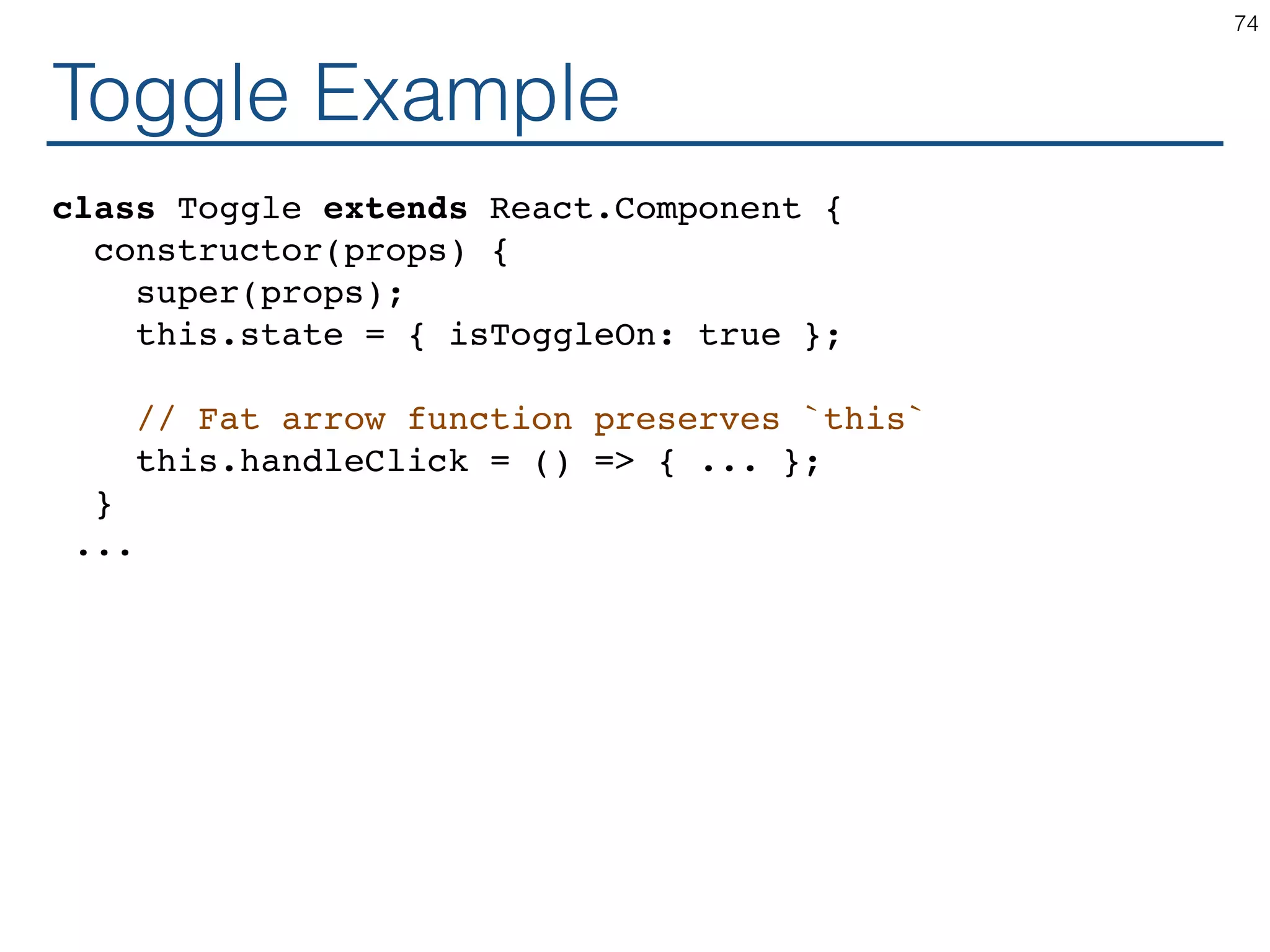
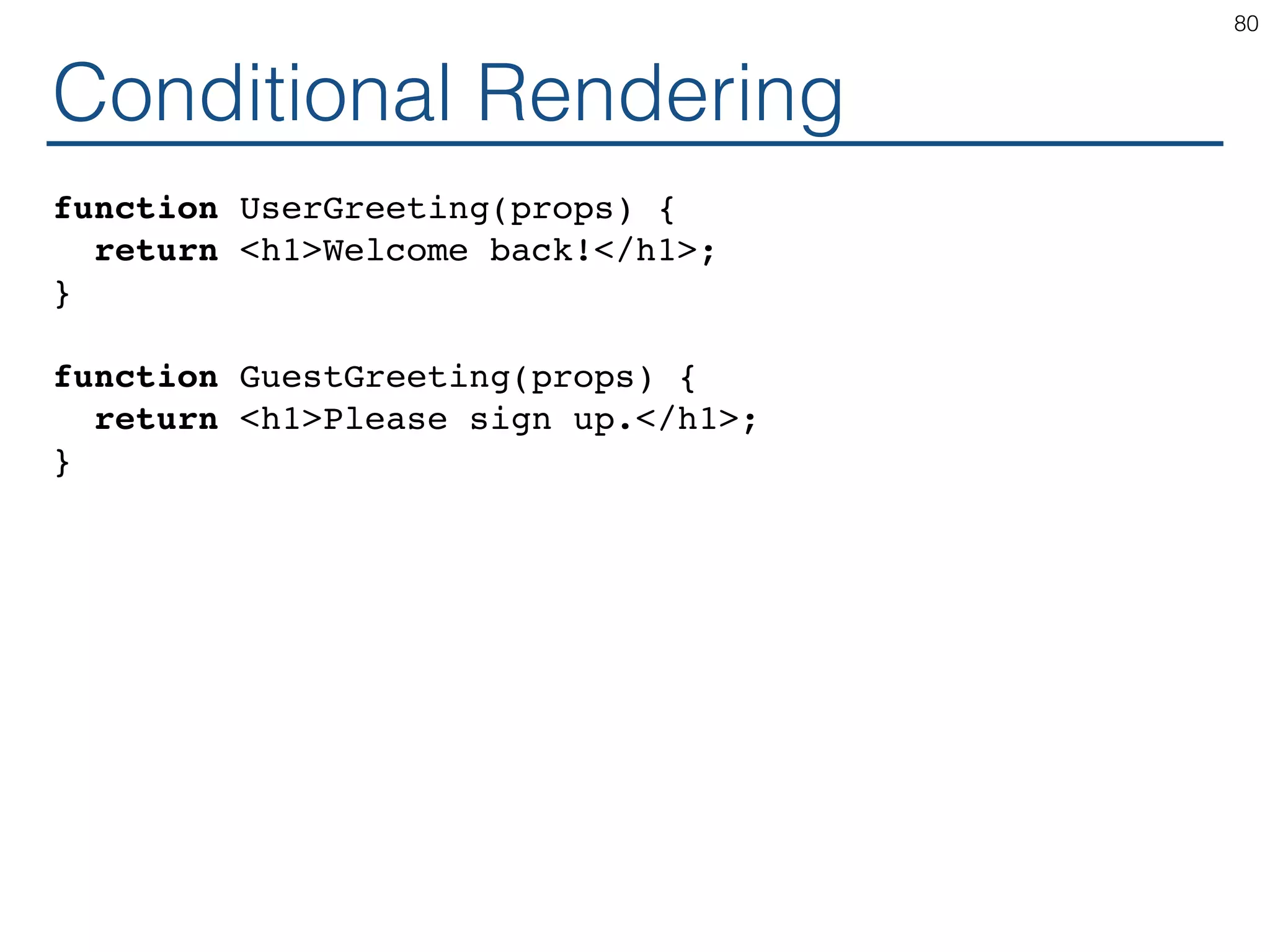
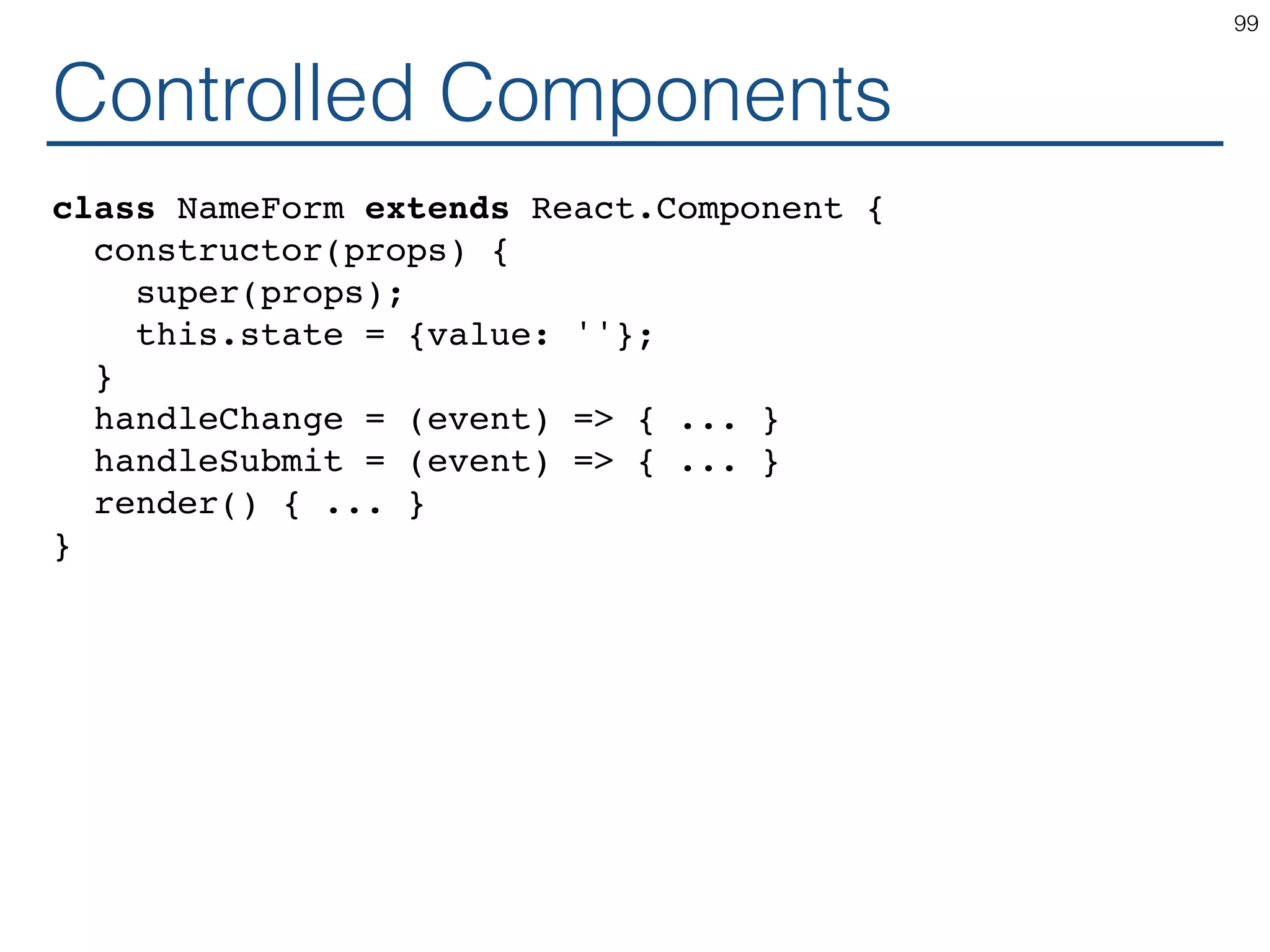
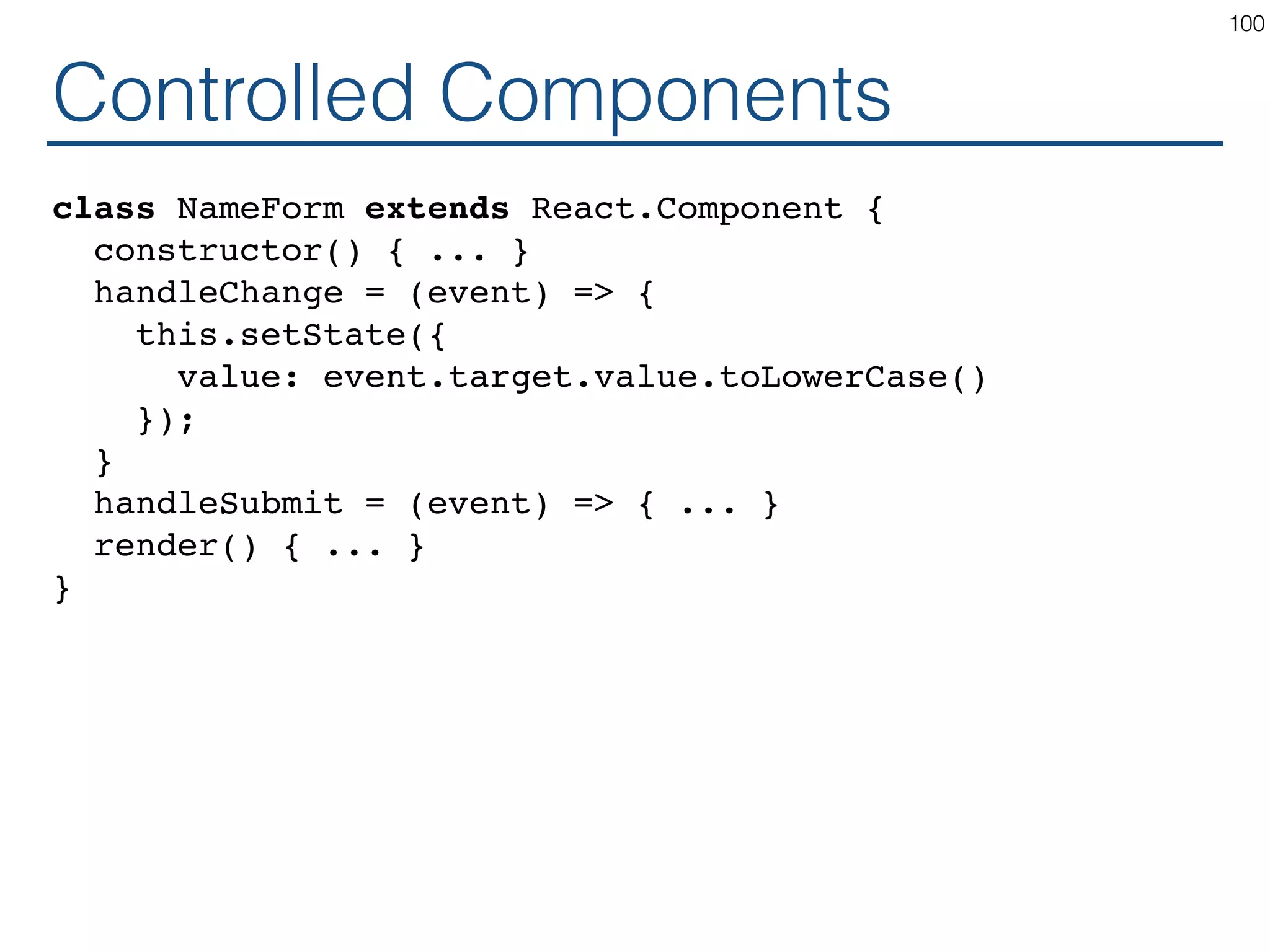
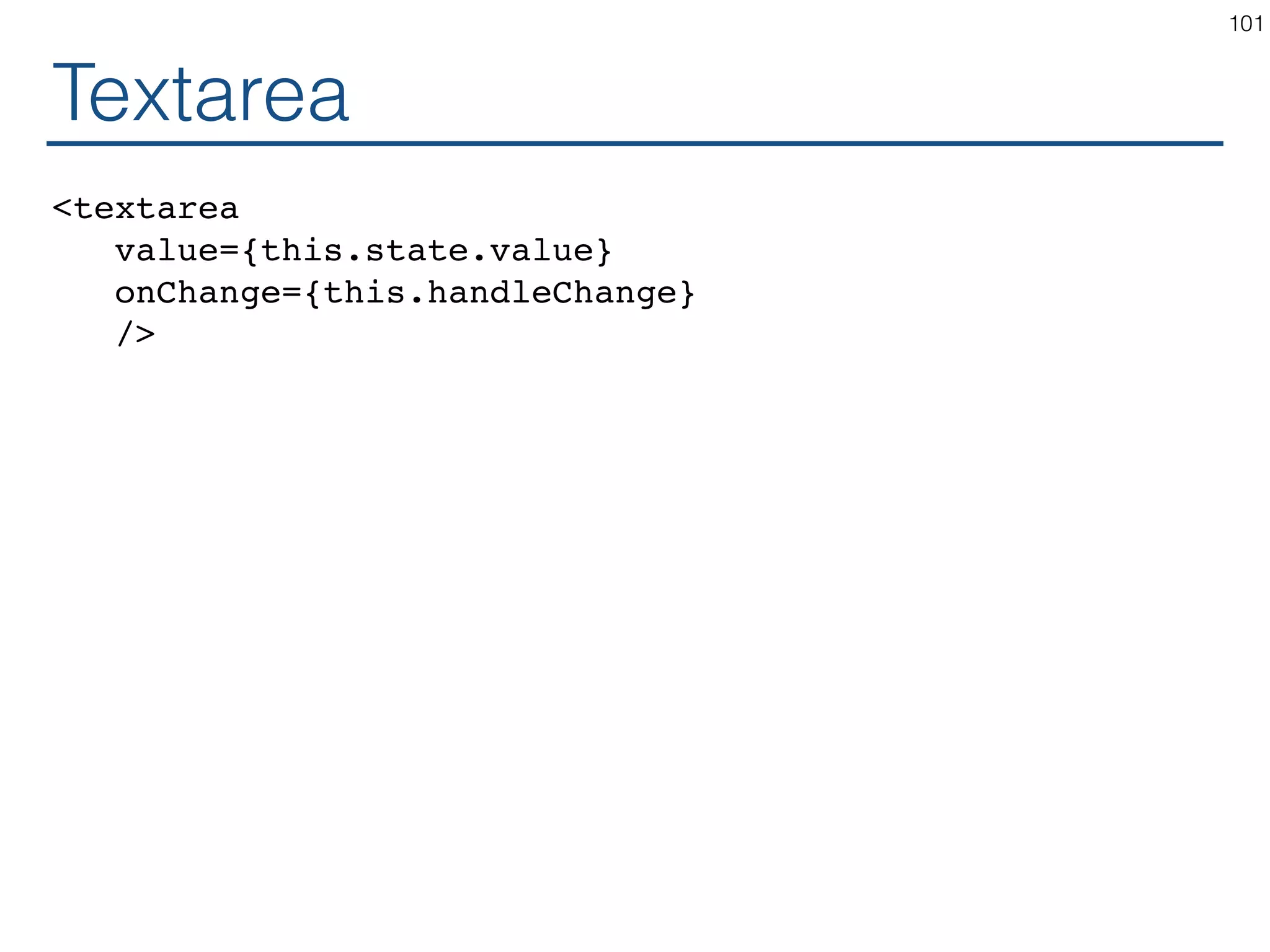
The document outlines an introductory guide to ReactJS, detailing concepts such as the virtual DOM, JSX syntax, components, props, state management, and event handling. It illustrates examples and best practices in using React for developing web applications, addressing challenges like code fragility and performance. Overall, the document serves as a practical resource for programmers to learn ReactJS fundamentals.


![FB about Chat 5 “Let’s see a real good example: FB chat” “How we get to the point, so we were annoying our users so much the just they wanted us to fix chat?” “The problems here were: • The code has no structure • It was very imperative, that makes it fragile • It loose a lot of the original intend behind it, its hard to tell what it tries [to do] • Add more features only gets this code larger • We had our most annoying chat bug happen over and over • We were always fixing some pretty good edge case, the whole system was fragile • … • This code becomes more fragile with the time. • No member of the team wanted to touch it, they wanted to jump to any other bug.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-5-2048.jpg)







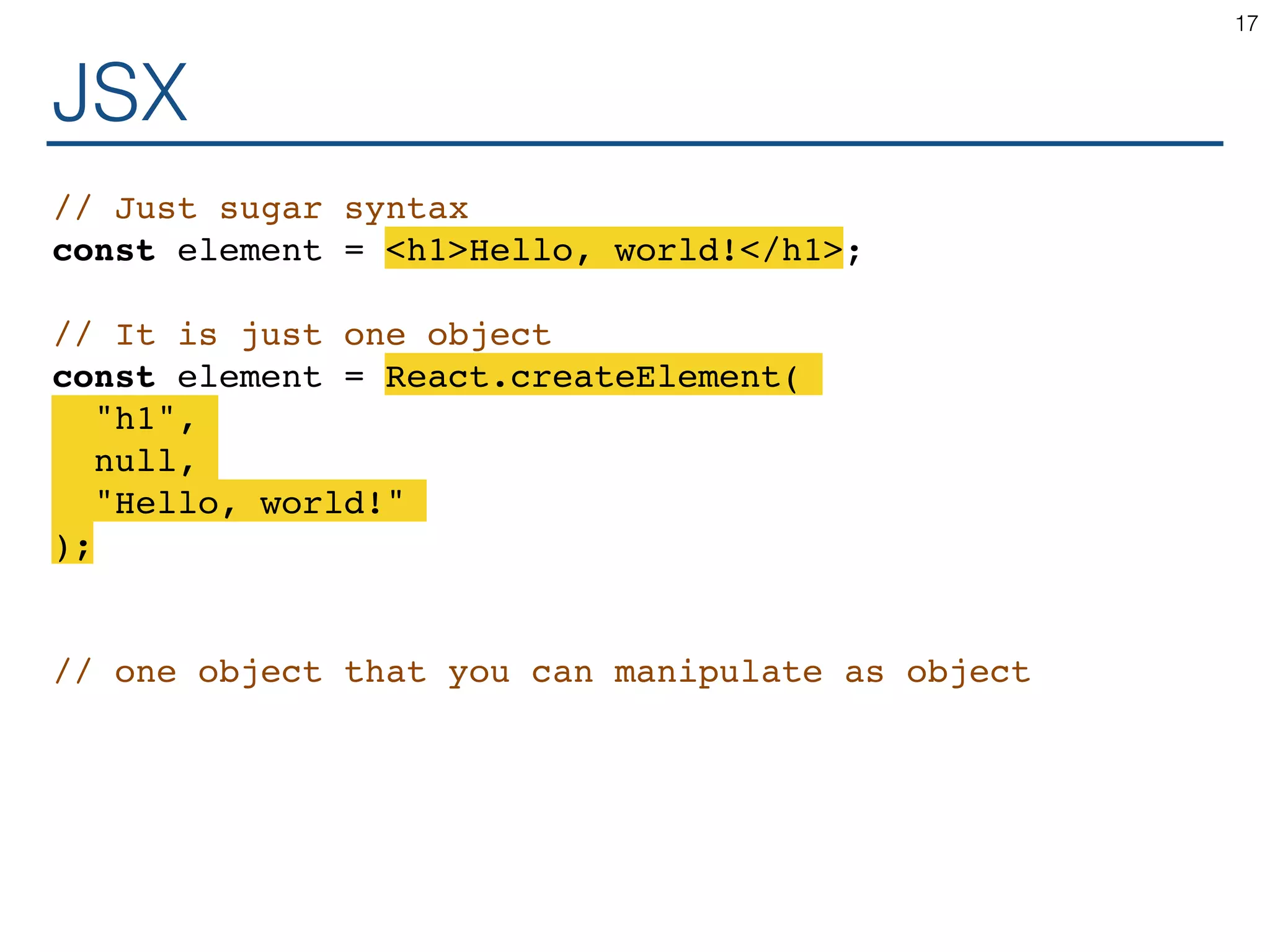
![JSX // May I? console.log(<h1>Hello!</h1>); console.log(<h1>Hello!</h1>.toString()); console.log([<h1>Hello!</h1>]); console.log({hello: <h1>Hello!</h1>}); console.log((() => <h1>Hello!</h1>)()); const salute = (what) => <h1>{what}!</h1>; console.log(salute('Hello')); 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-18-2048.jpg)






























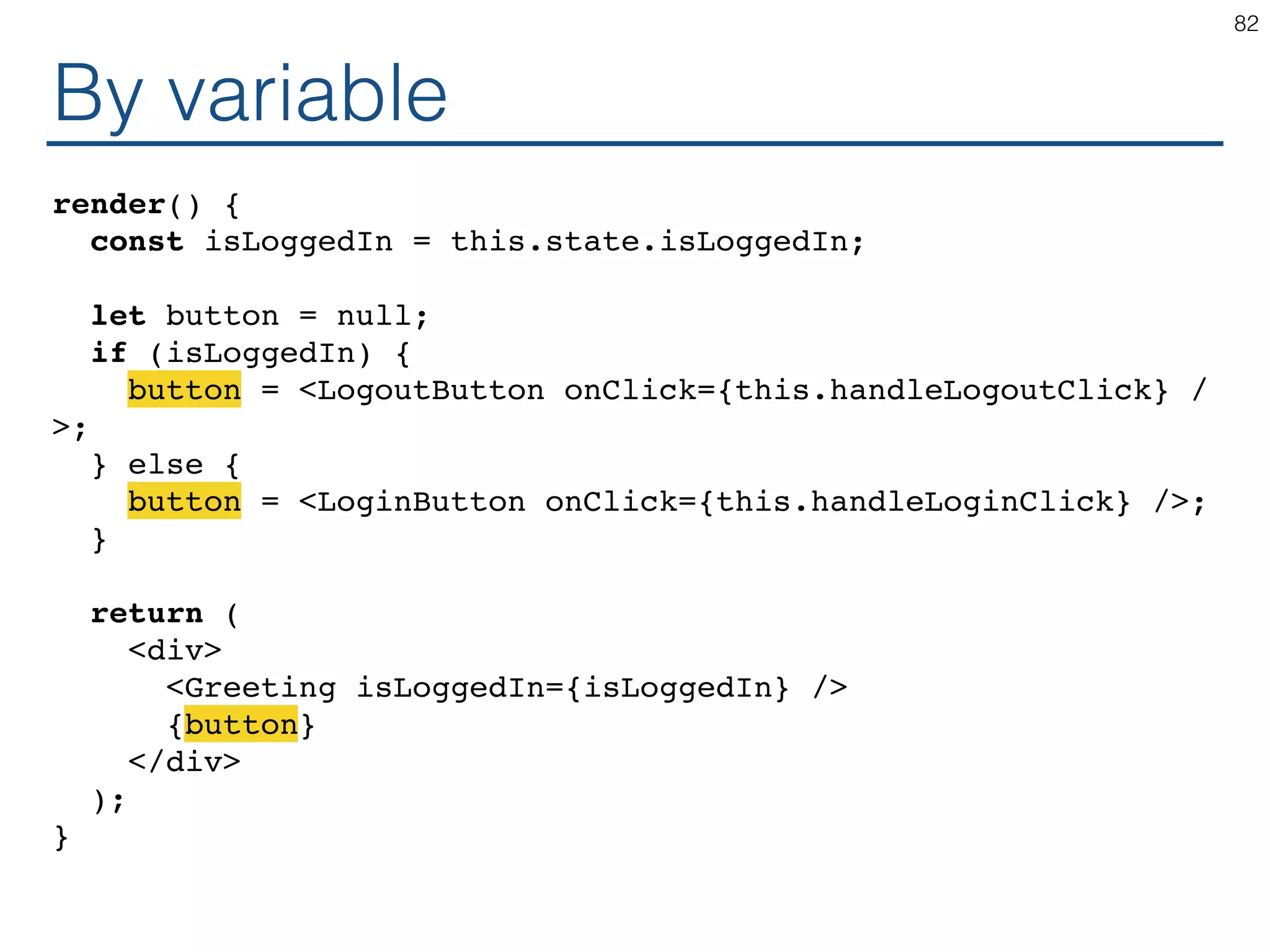
![States are Merged constructor() { this.state = {posts: [], users: []}; } componentDidMount() { getPosts((posts) => this.setState({posts})); getUsers((users) => this.setState({users})); } 65](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-65-2048.jpg)











![Remember... const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; const doubled = numbers.map((n) => n * 2); console.log(doubled); // [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] 87](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-87-2048.jpg)
![Render Multiple // Render a reactElements array const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; const listItems = numbers.map((number) => <li>{number}</li> ); ReactDOM.render( <ul>{listItems}</ul>, document.getElementById('root') ); 88](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-88-2048.jpg)
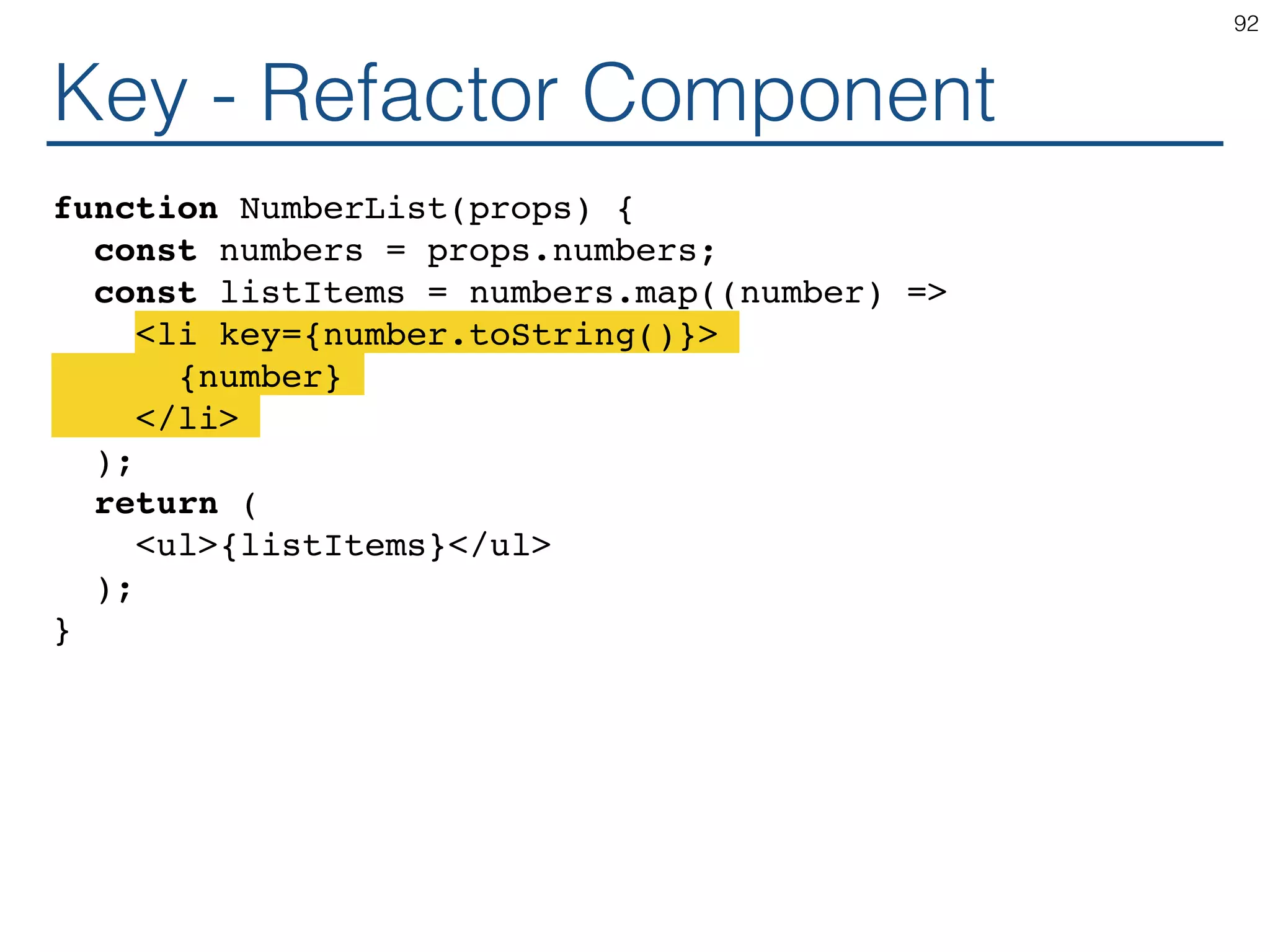
![Render Multiple // Refactor into component function NumberList(props) { const numbers = props.numbers; const listItems = numbers.map((number) => <li>{number}</li> ); return ( <ul>{listItems}</ul> ); } const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; ReactDOM.render( <NumberList numbers={numbers} />, document.getElementById('root') ); 89](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-89-2048.jpg)









![Multiple Inputs handleInputChange(event) { const target = event.target; const value = target.type === 'checkbox' ? target.checked : target.value; const name = target.name; this.setState({ [name]: value }); } 104](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-104-2048.jpg)


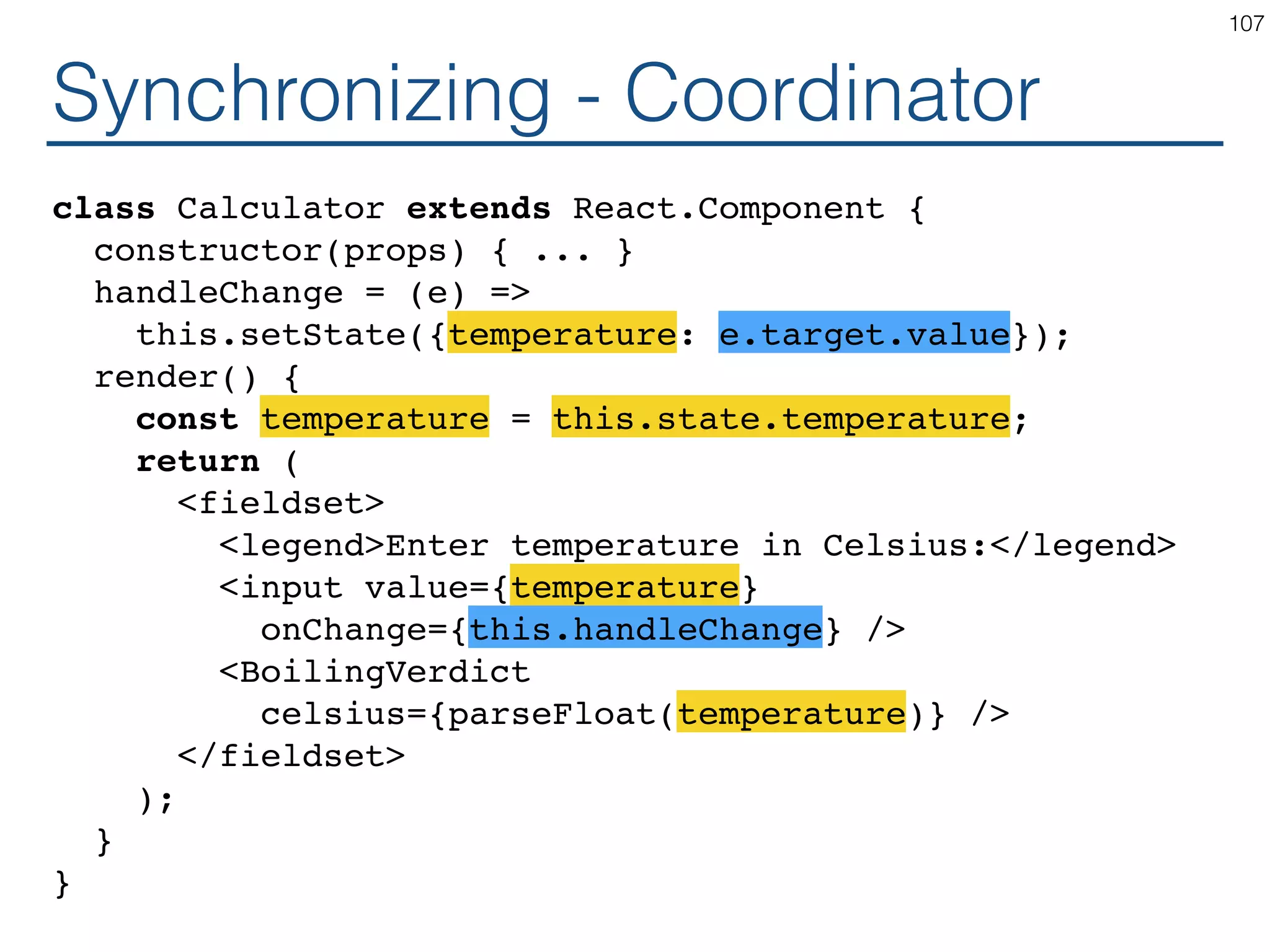
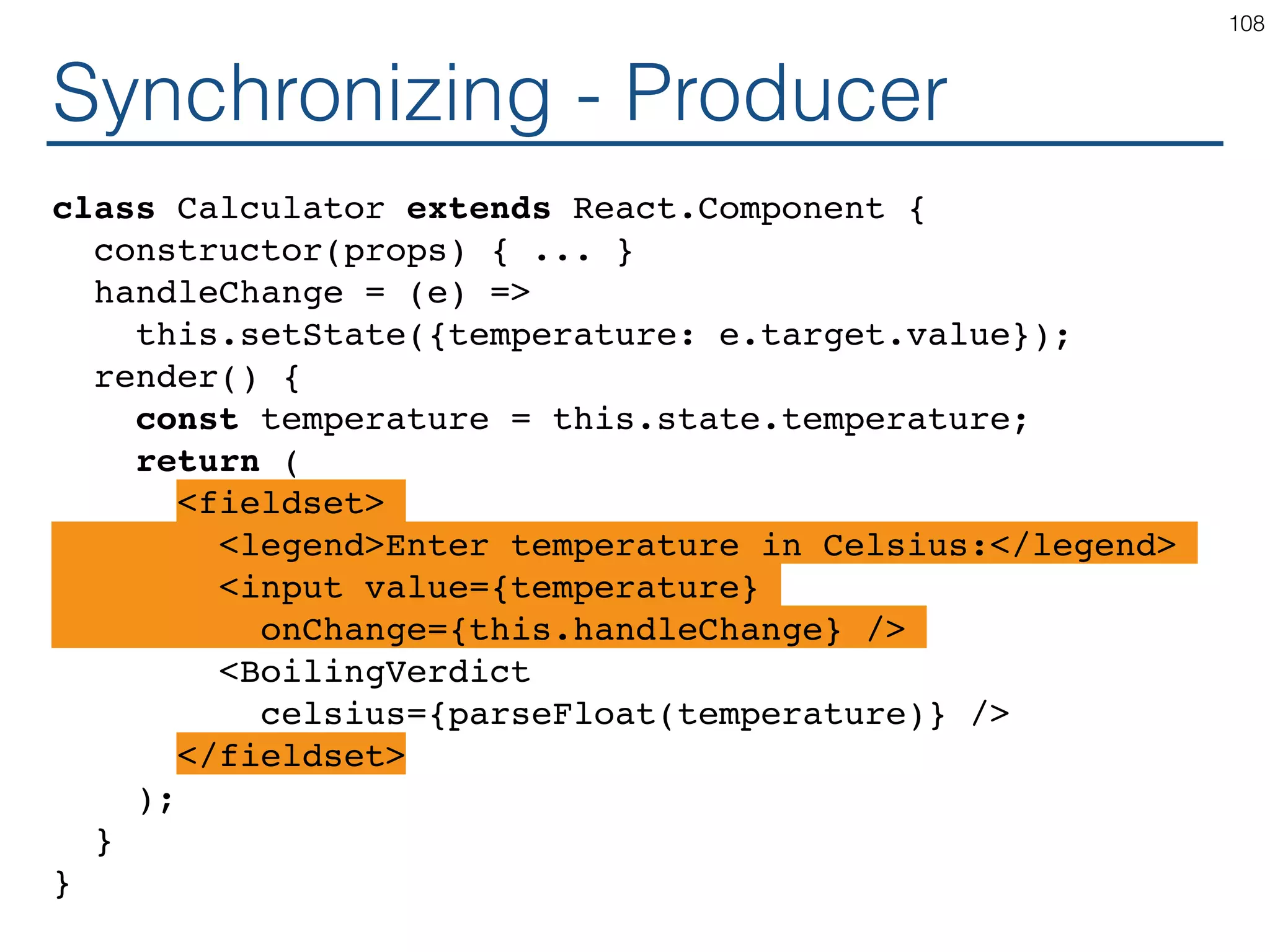
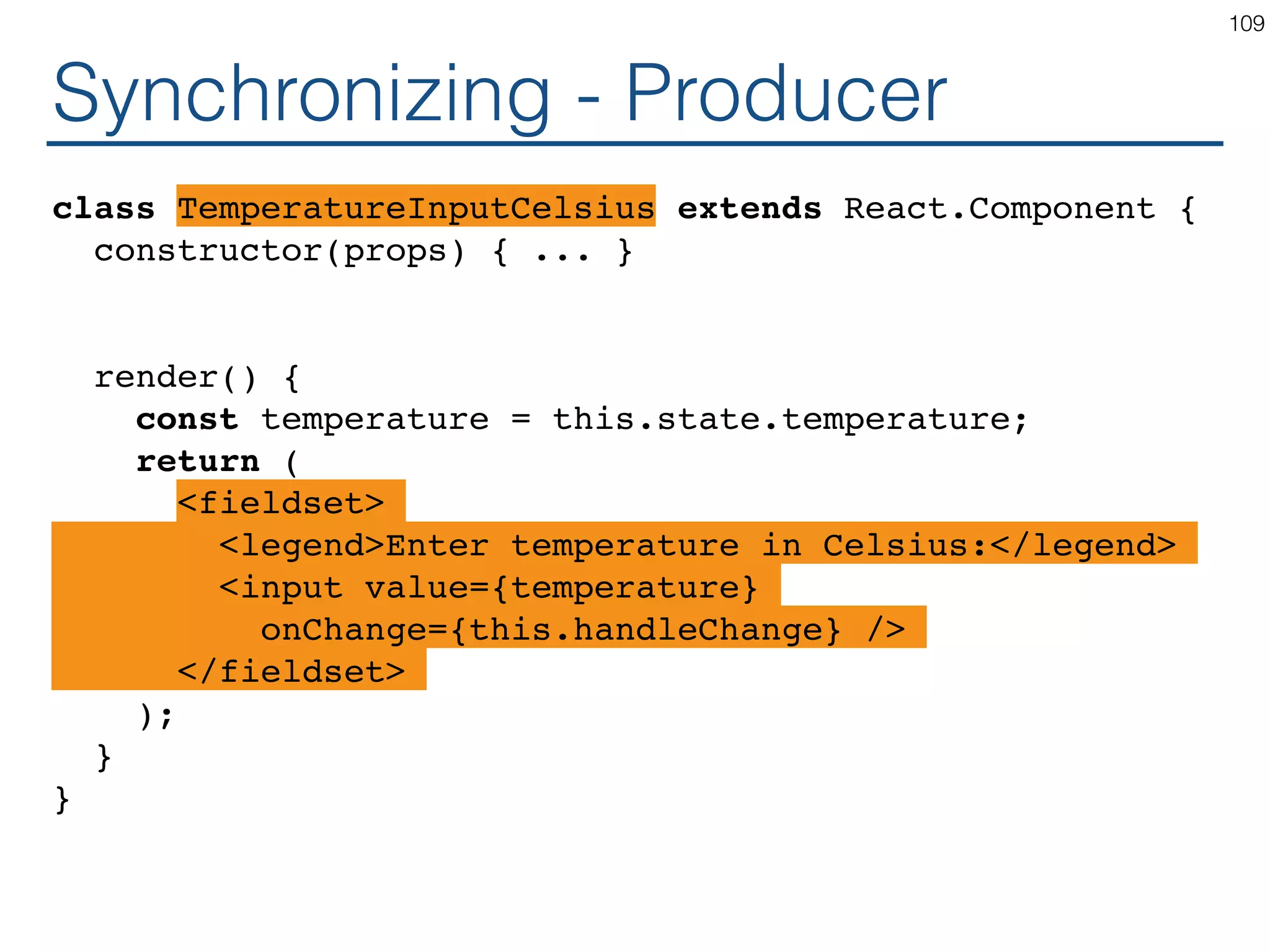
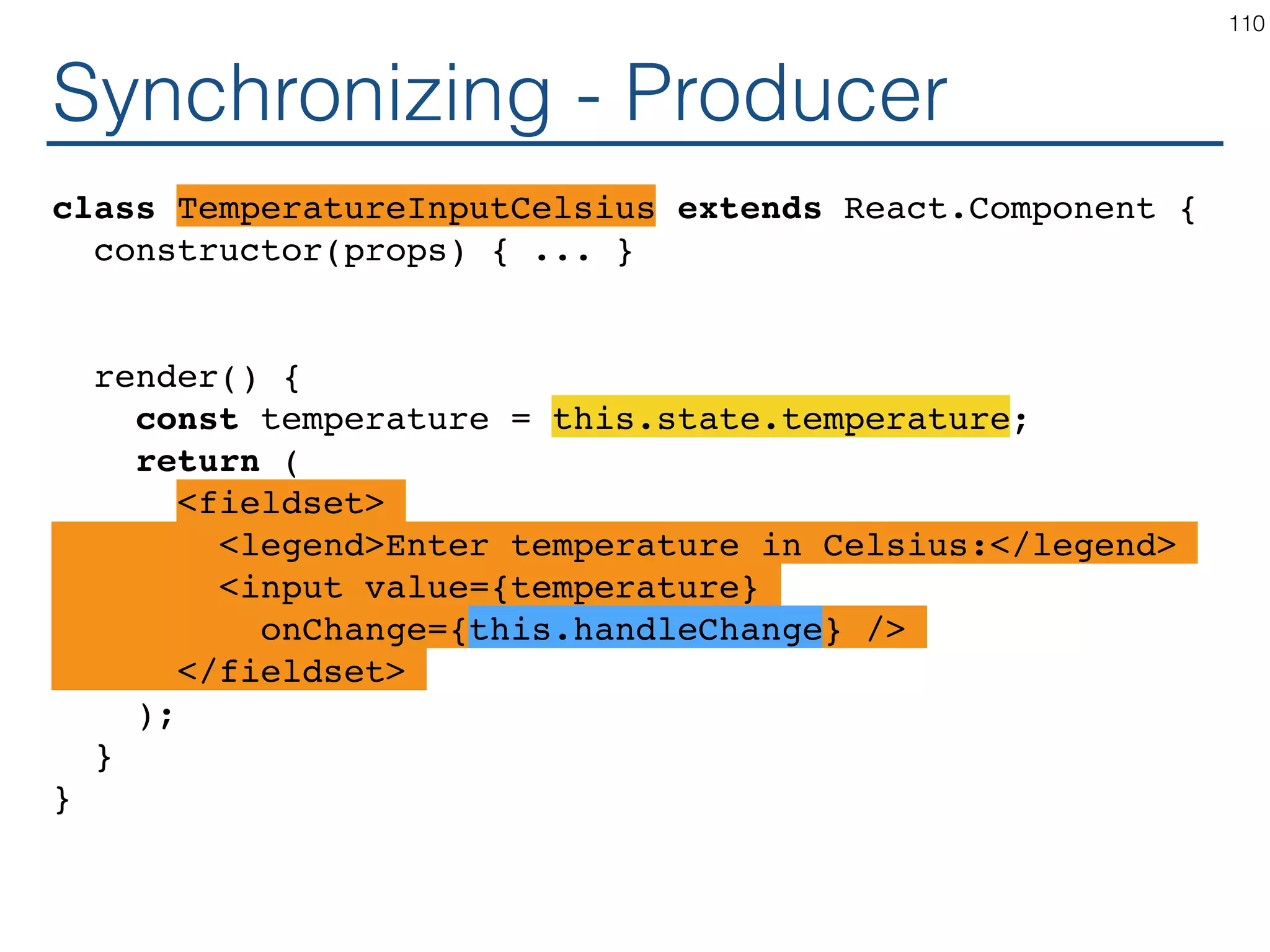
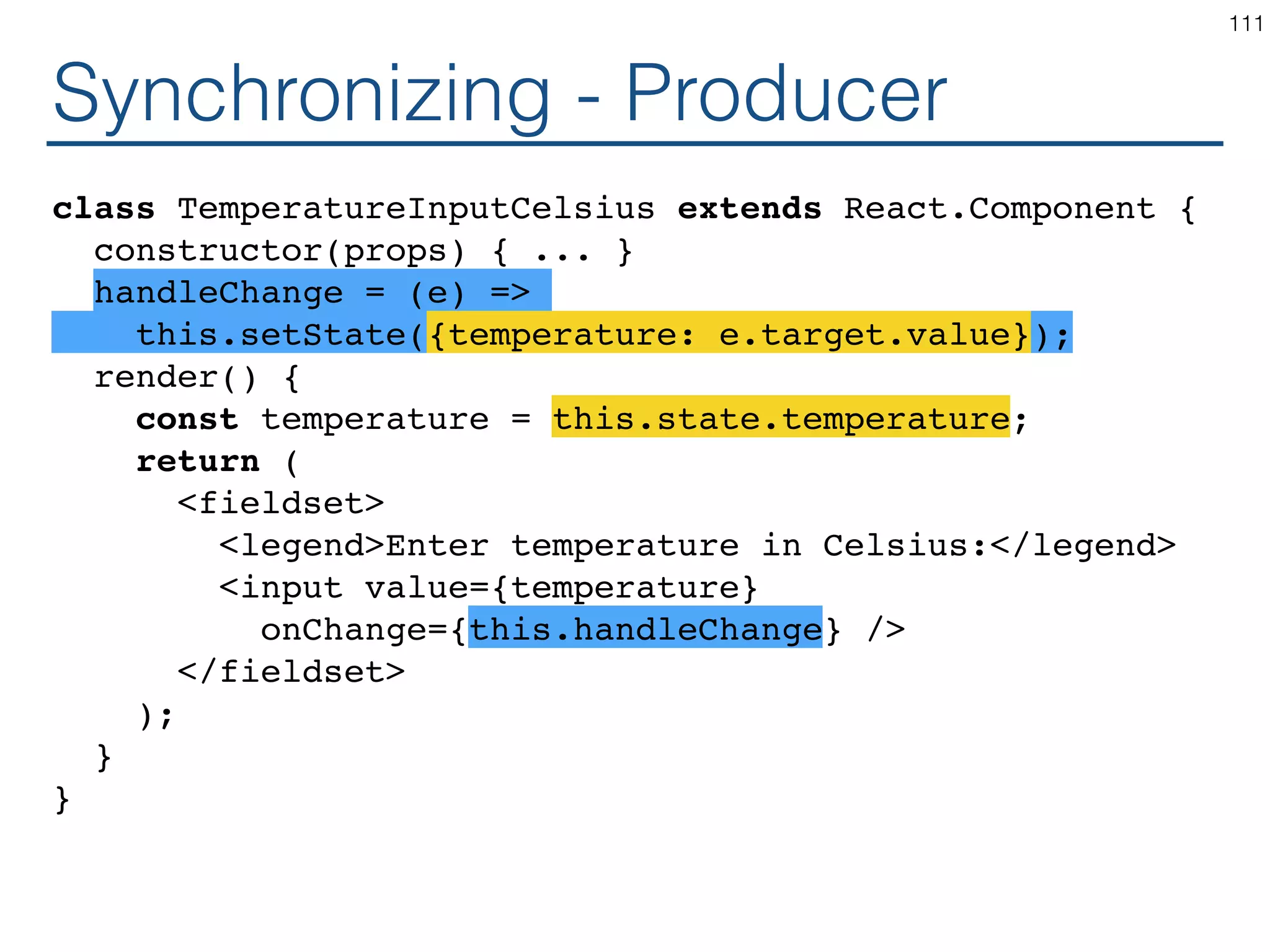
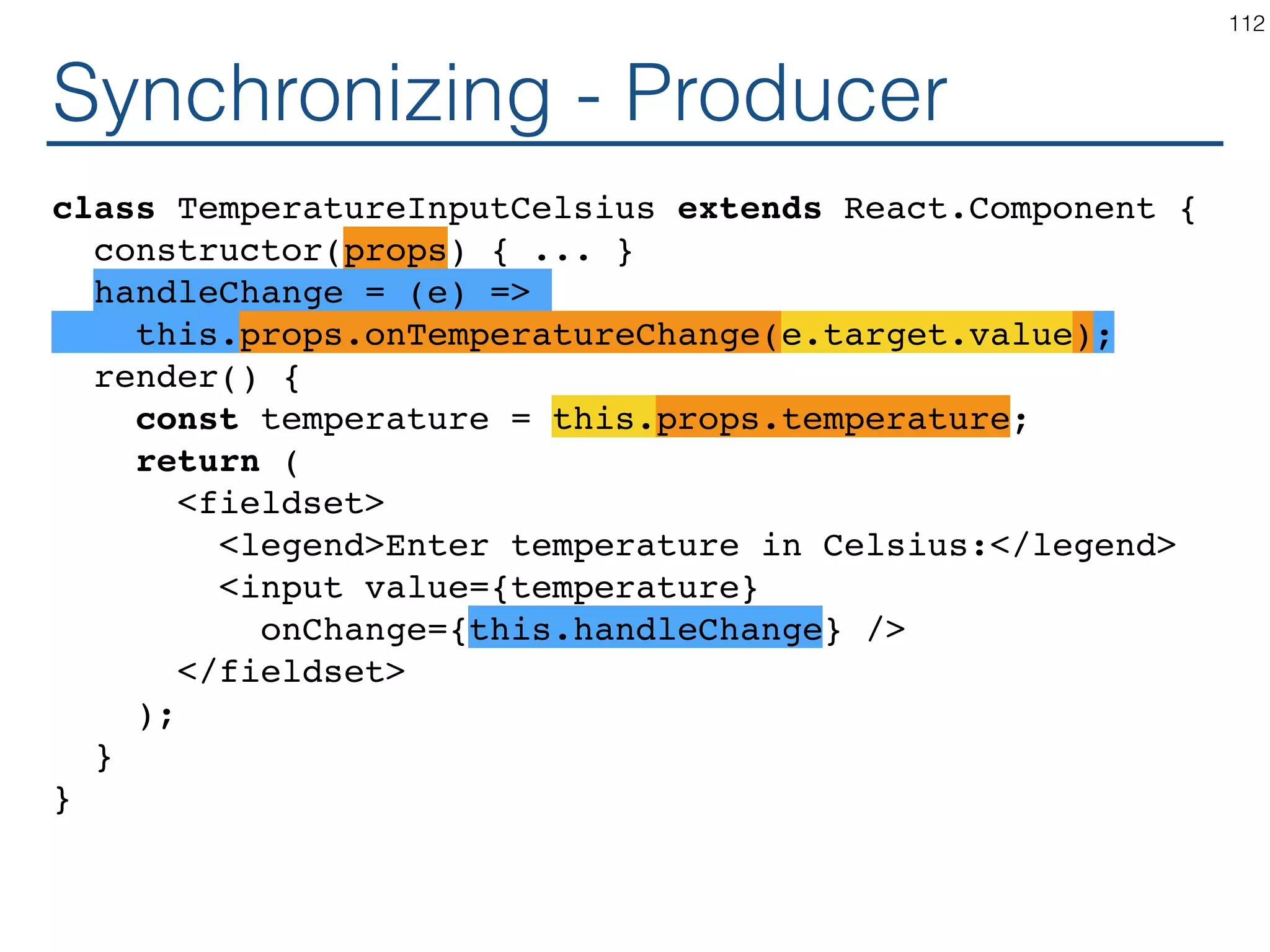
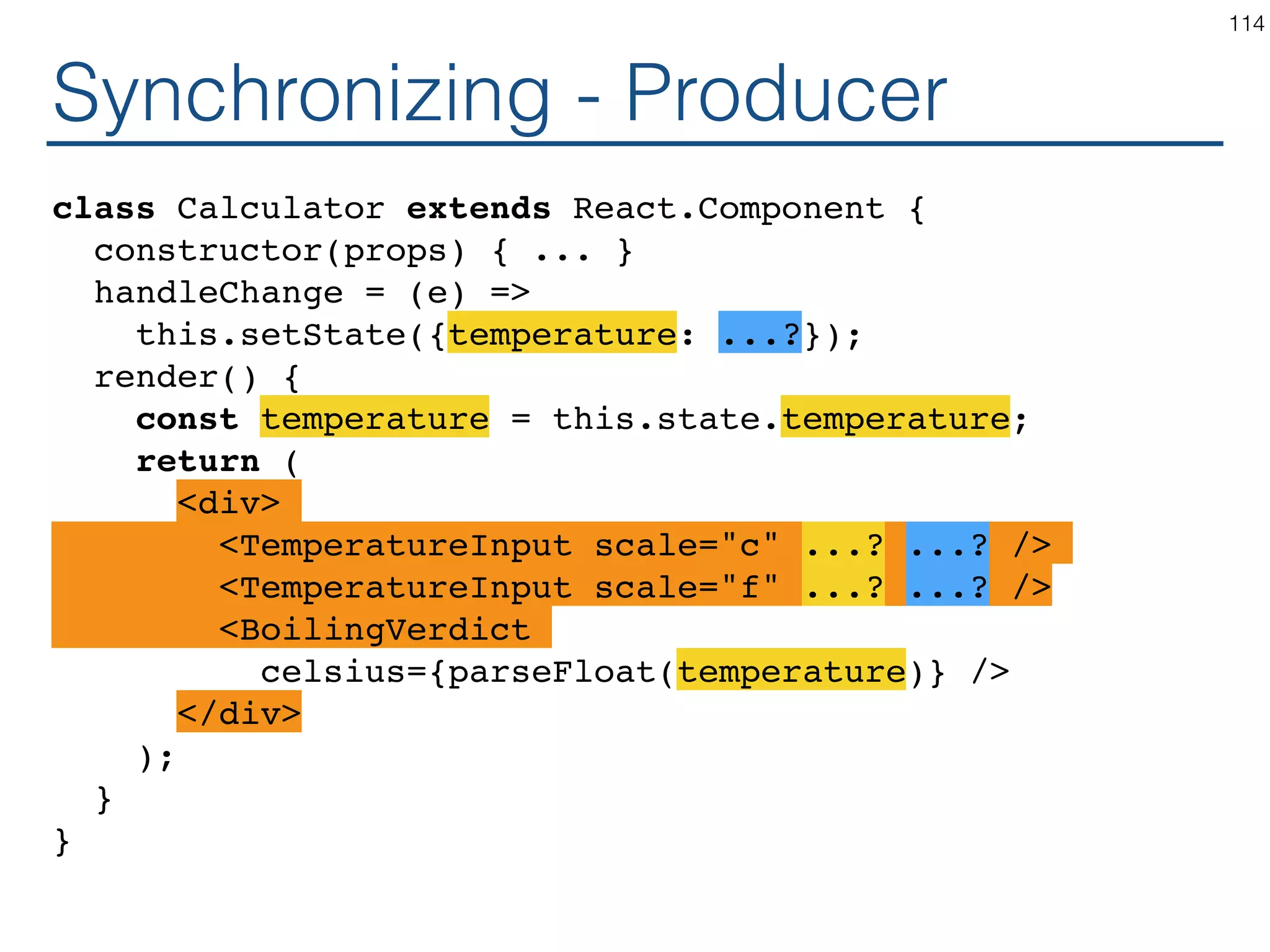
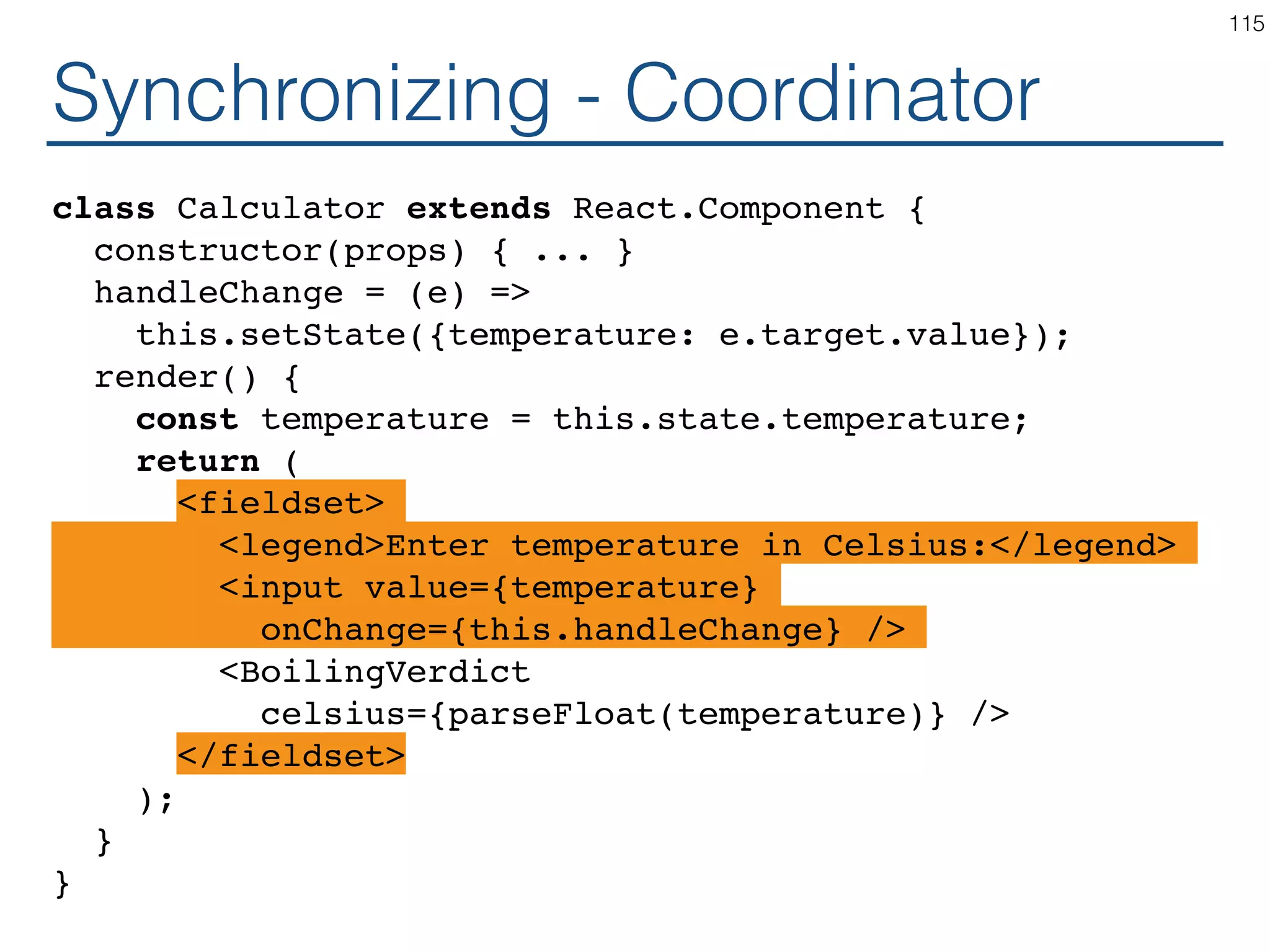
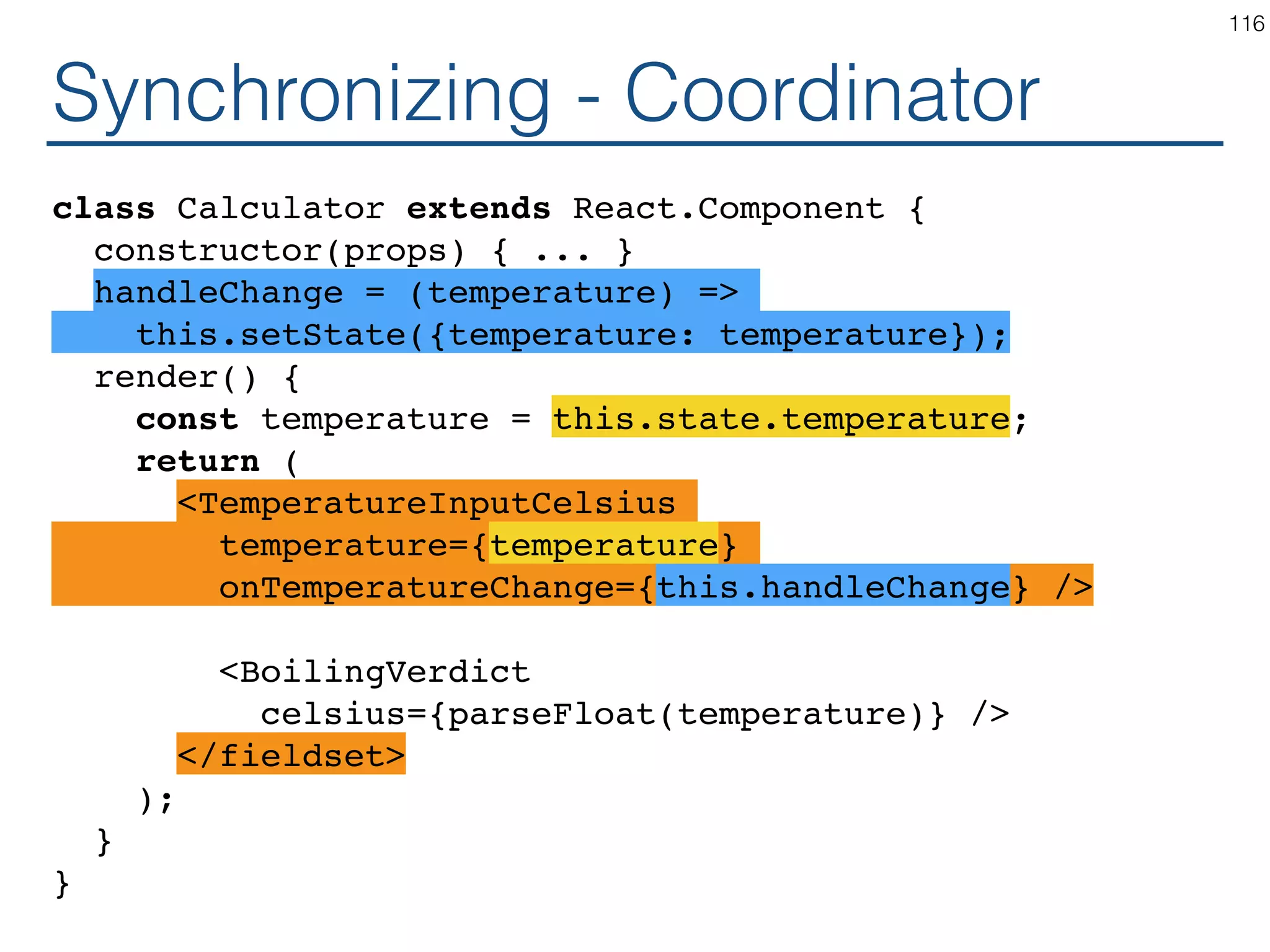
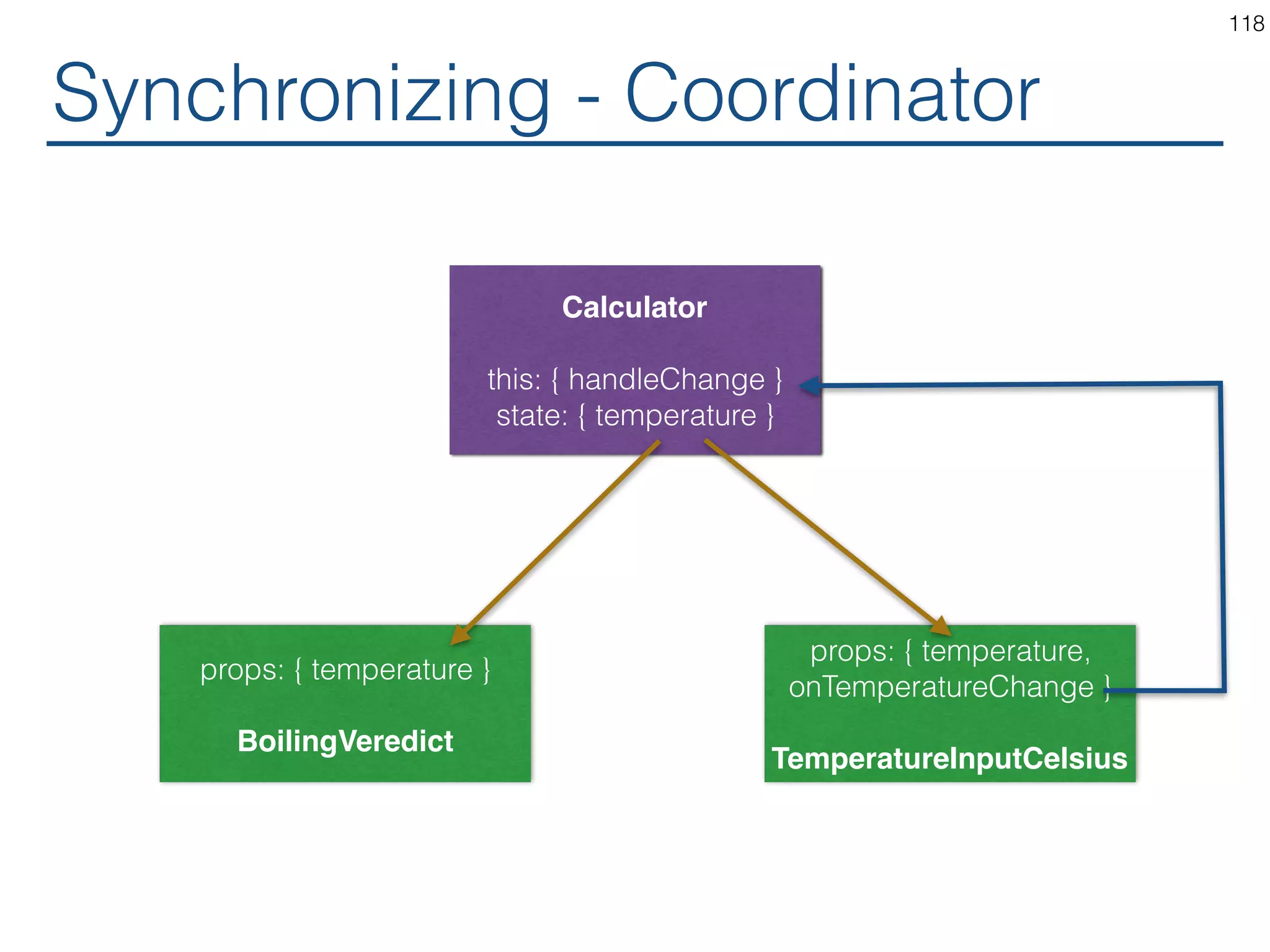
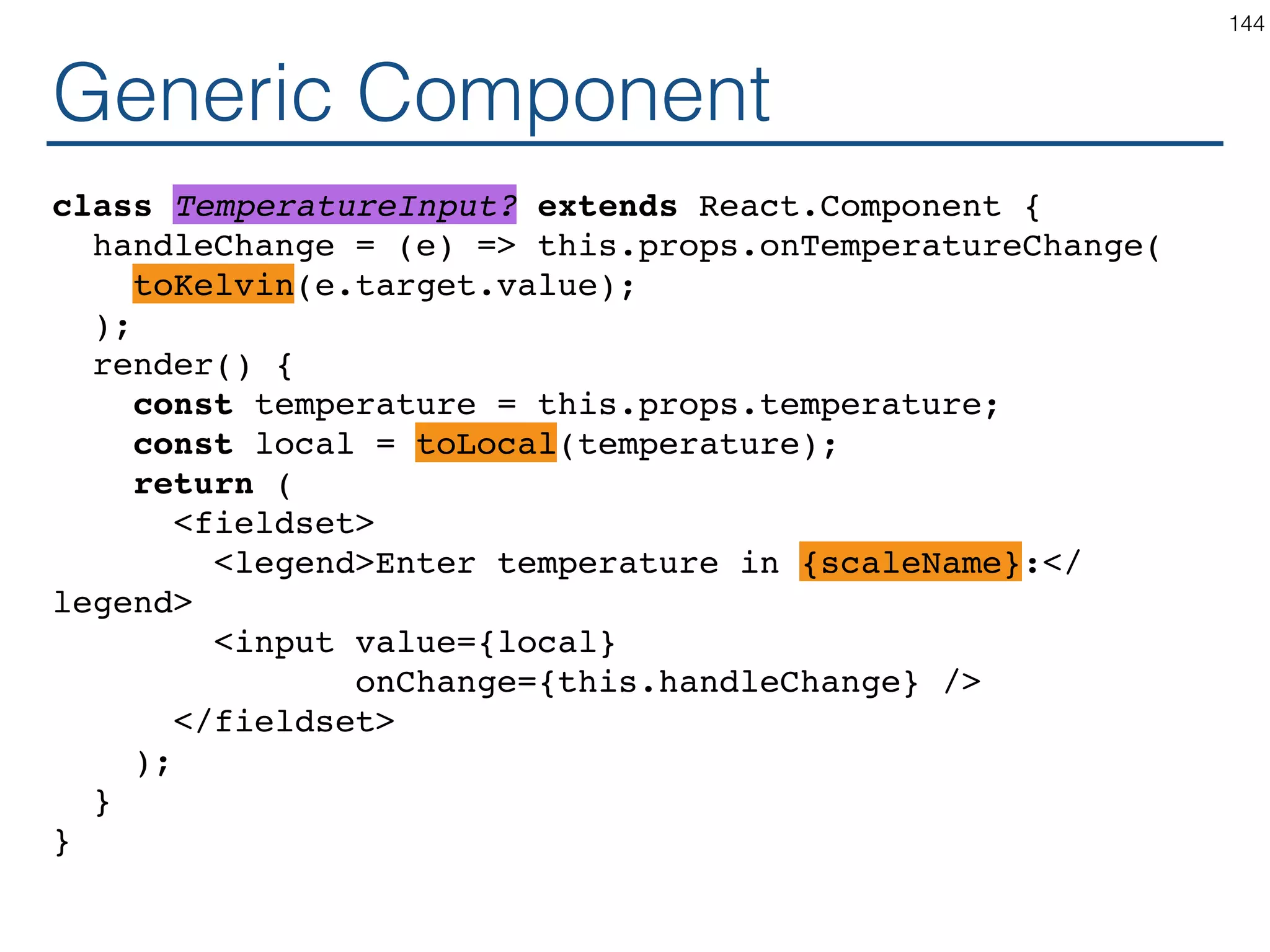
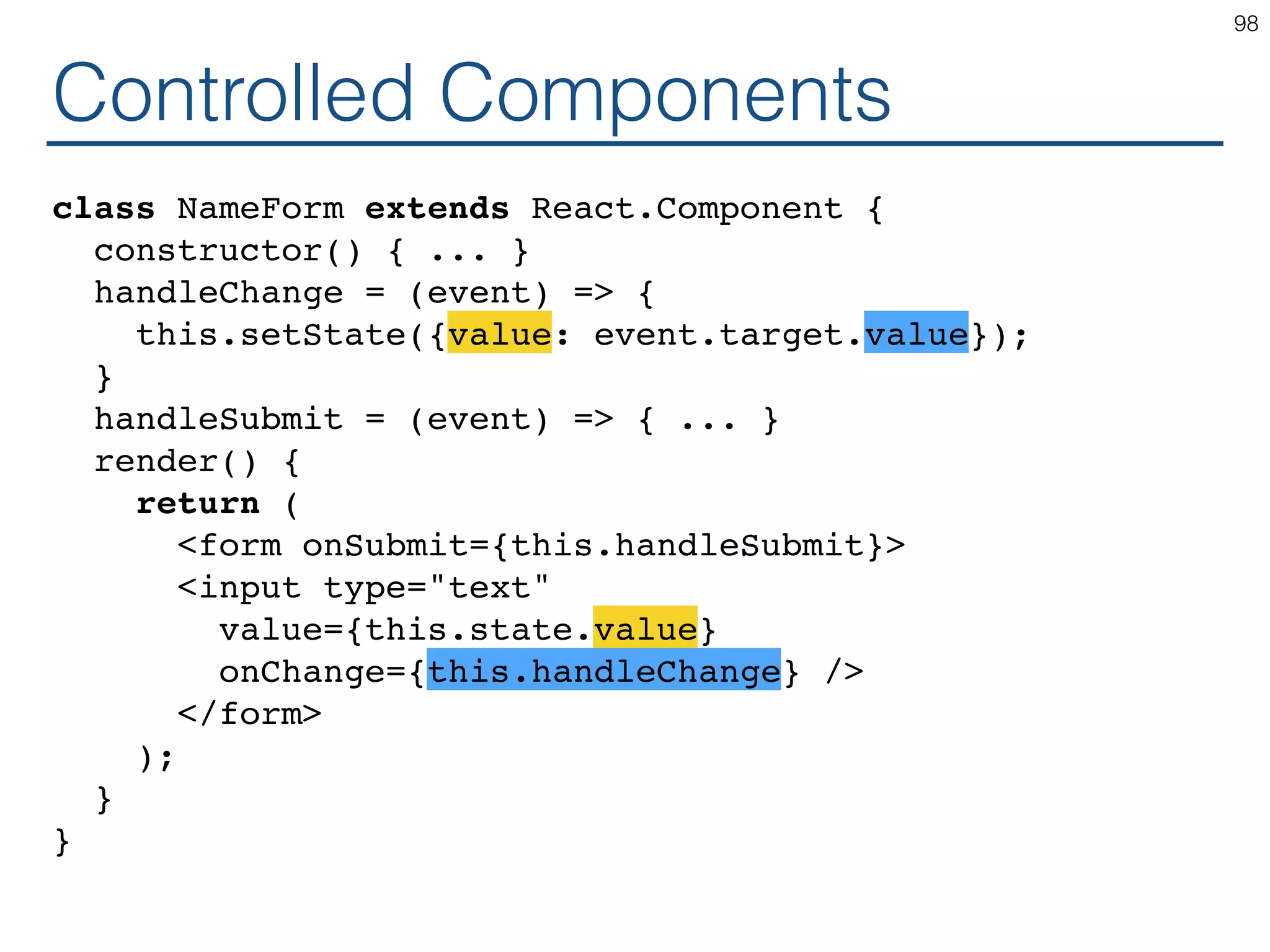
![Synchronizing - Producer class TemperatureInput extends React.Component { constructor(props) { ... } handleChange = (e) => this.setState({temperature: e.target.value}); render() { const temperature = this.state.temperature; const scaleName = scaleNames[this.props.scale]; return ( <fieldset> <legend>Enter temperature in {scaleName}:</ legend> <input value={temperature} onChange={this.handleChange} /> </fieldset> ); } } 119](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-119-2048.jpg)
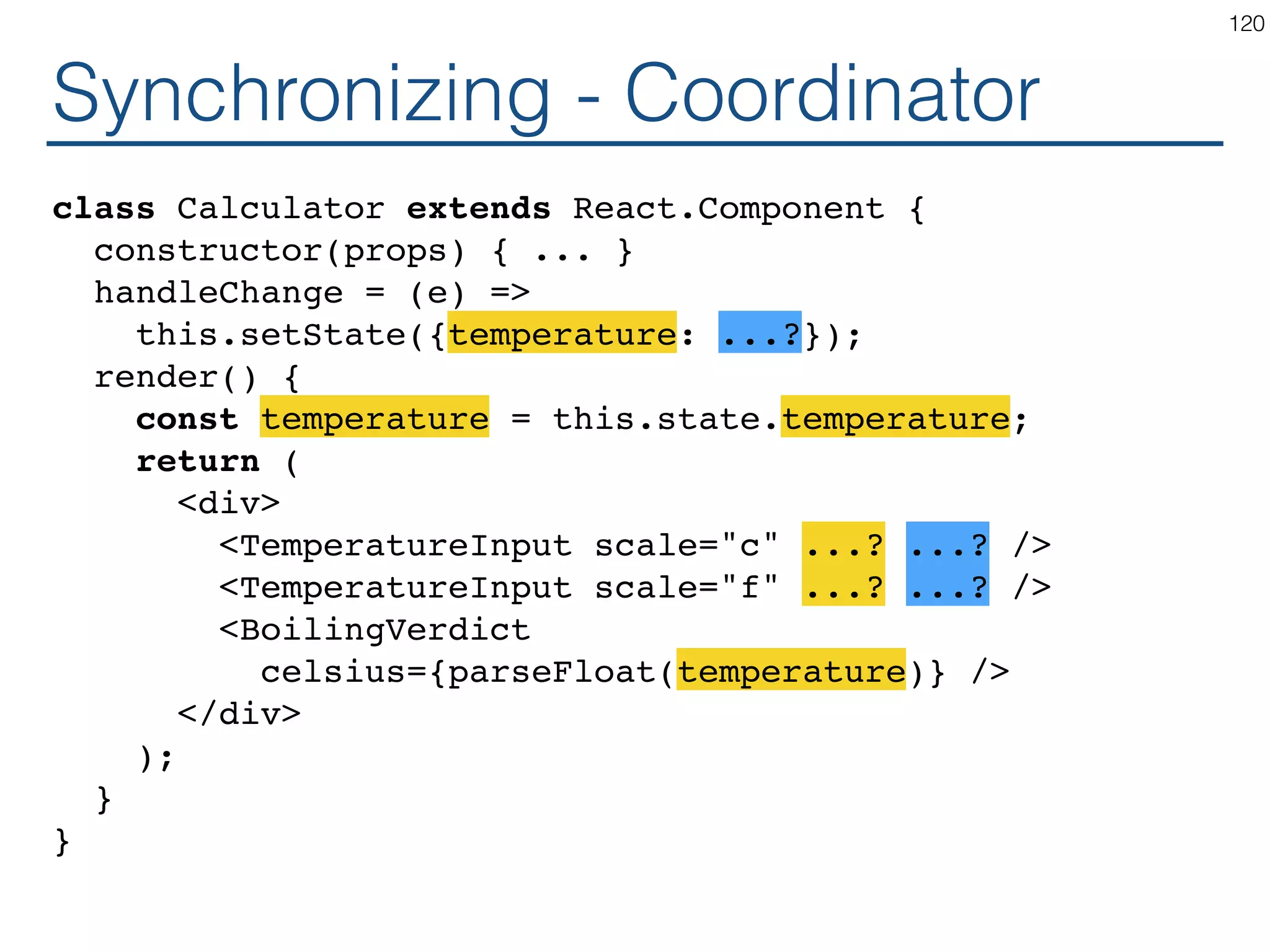
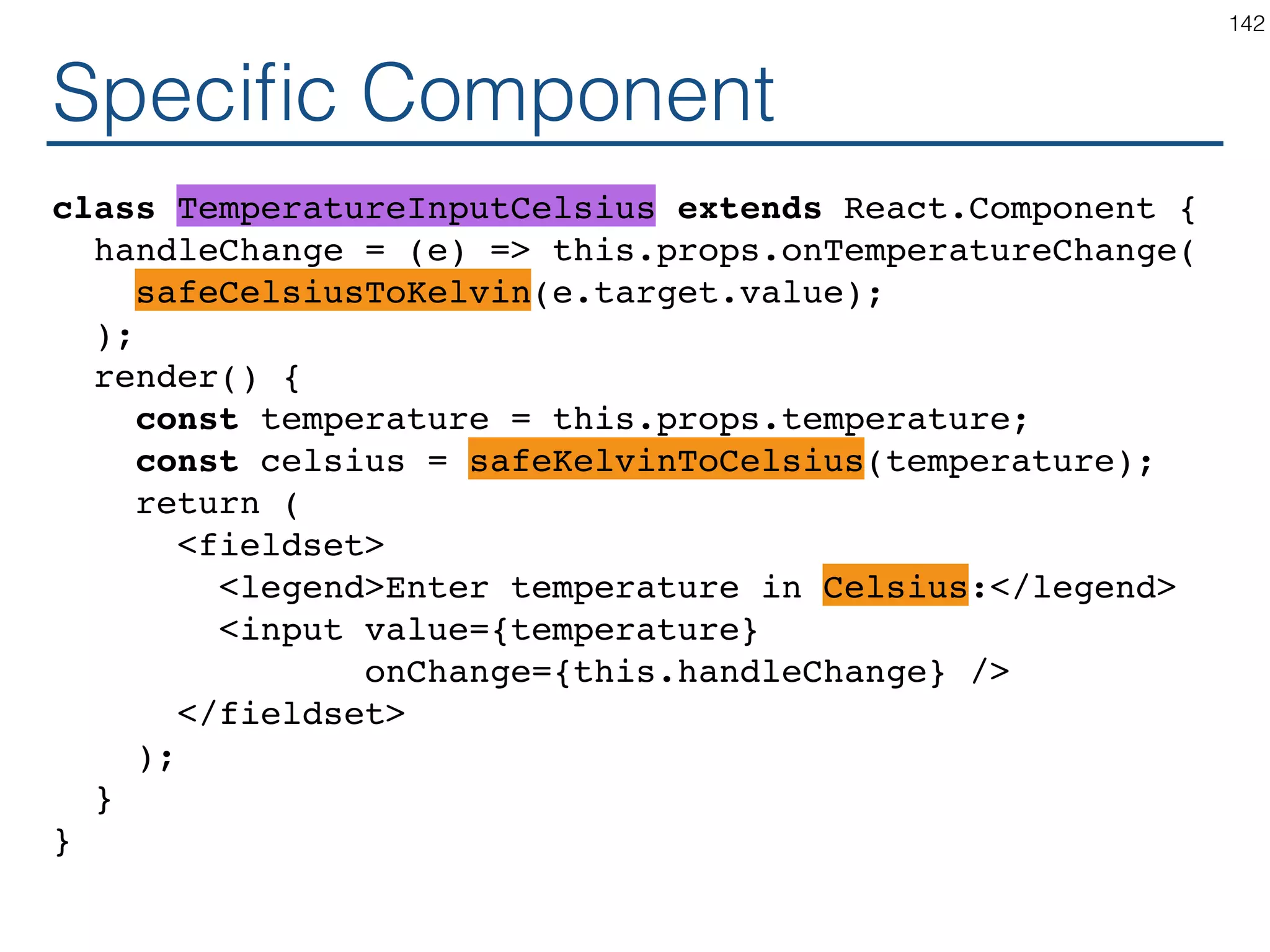
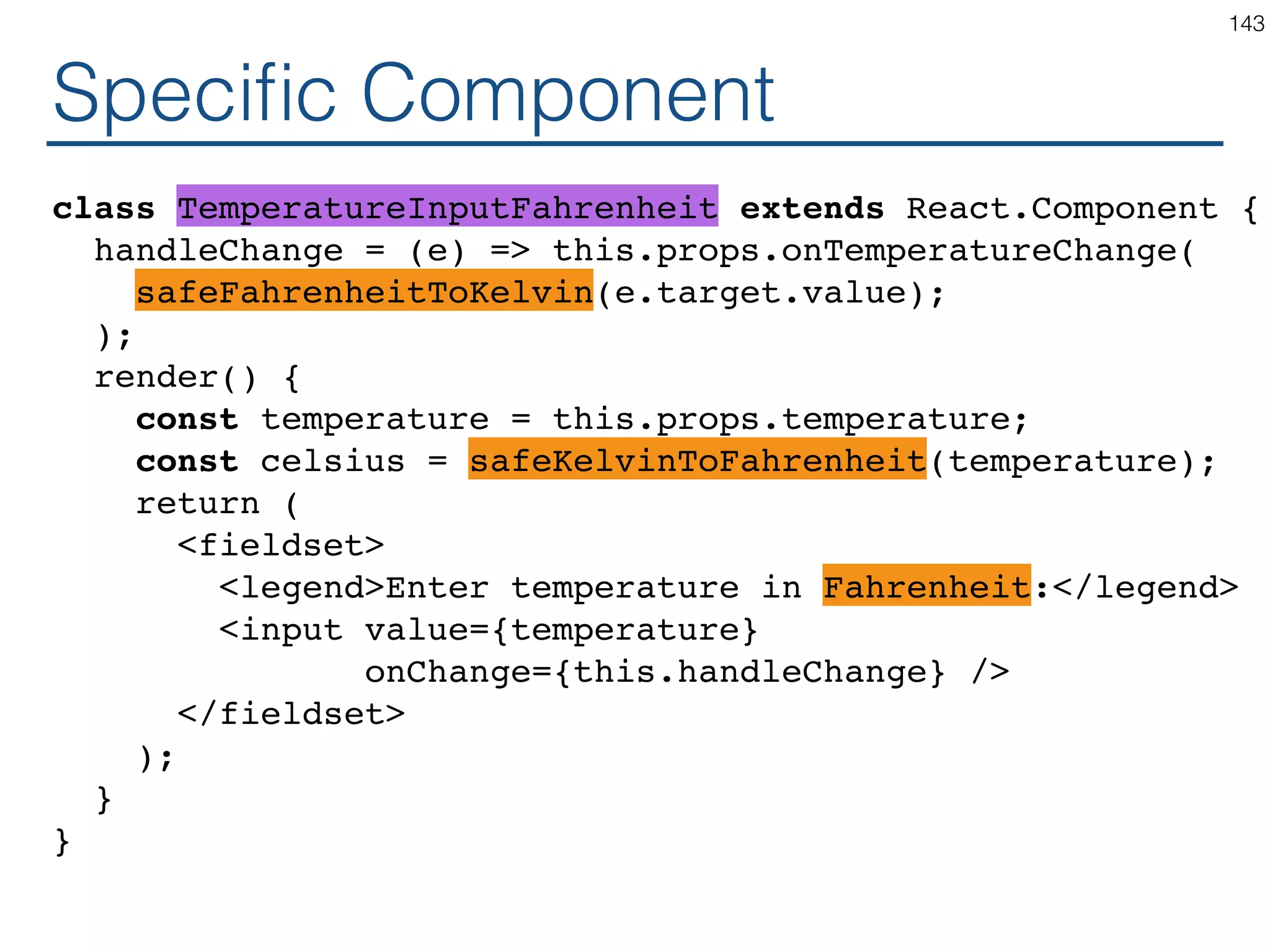
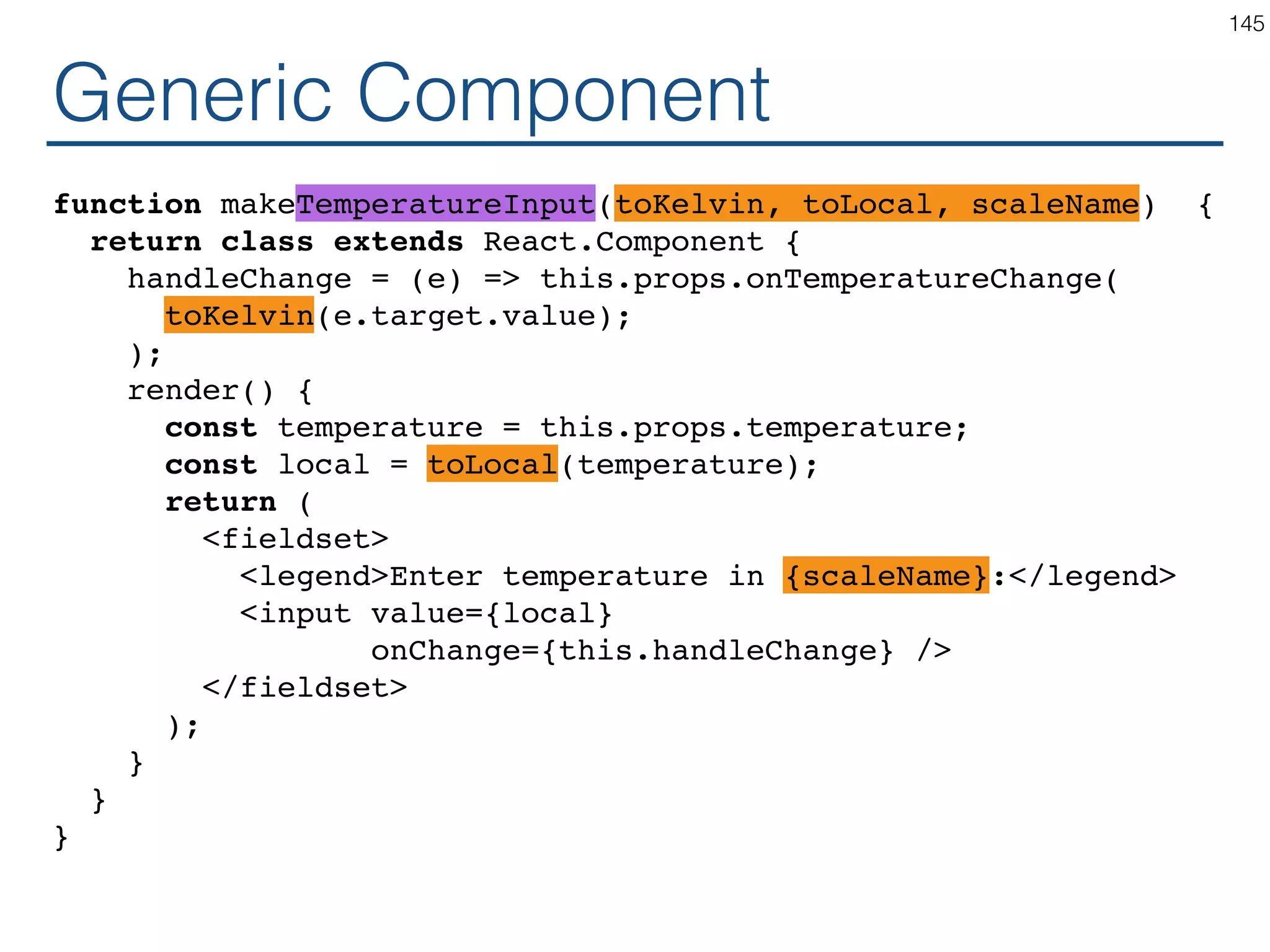
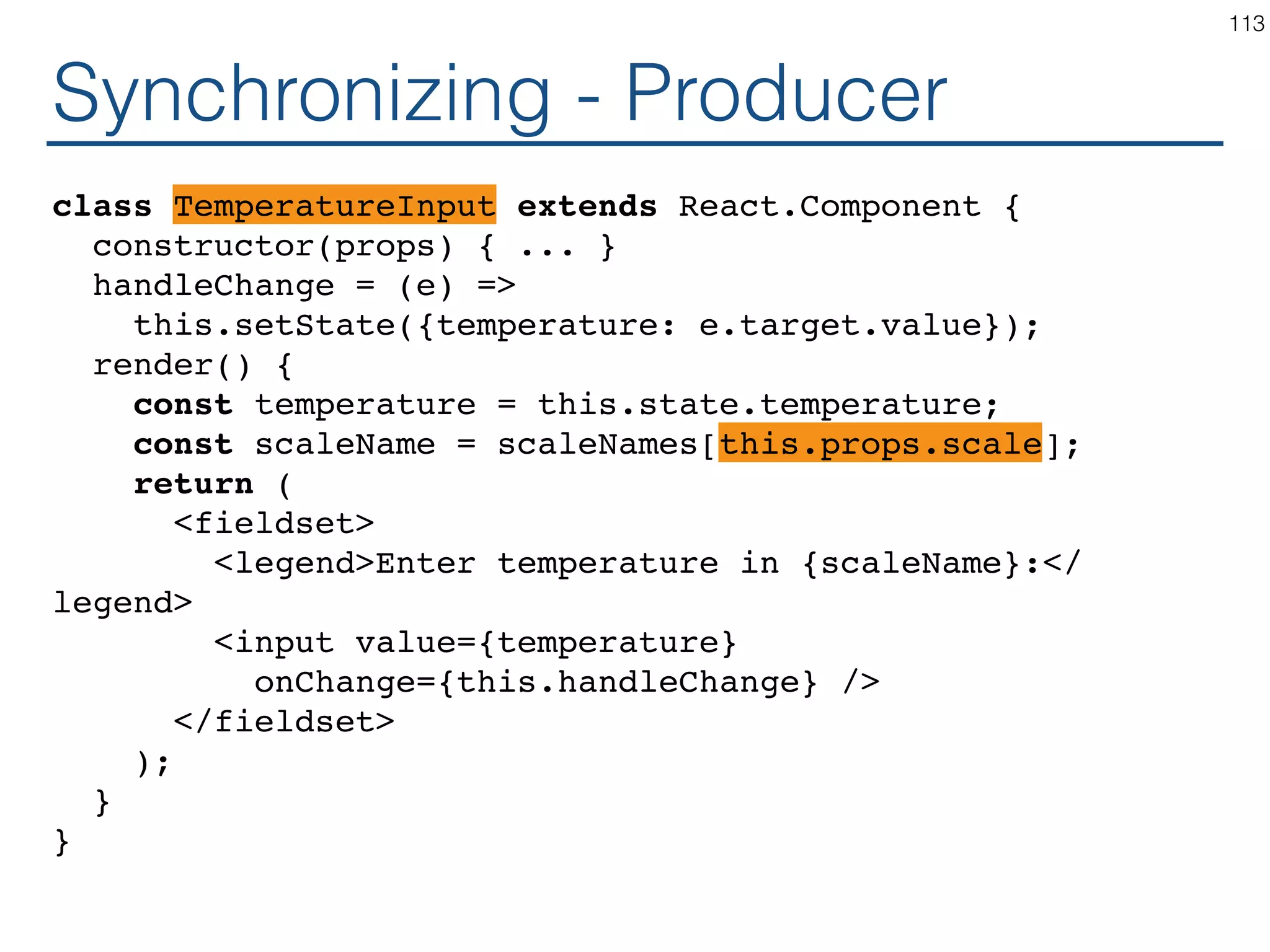
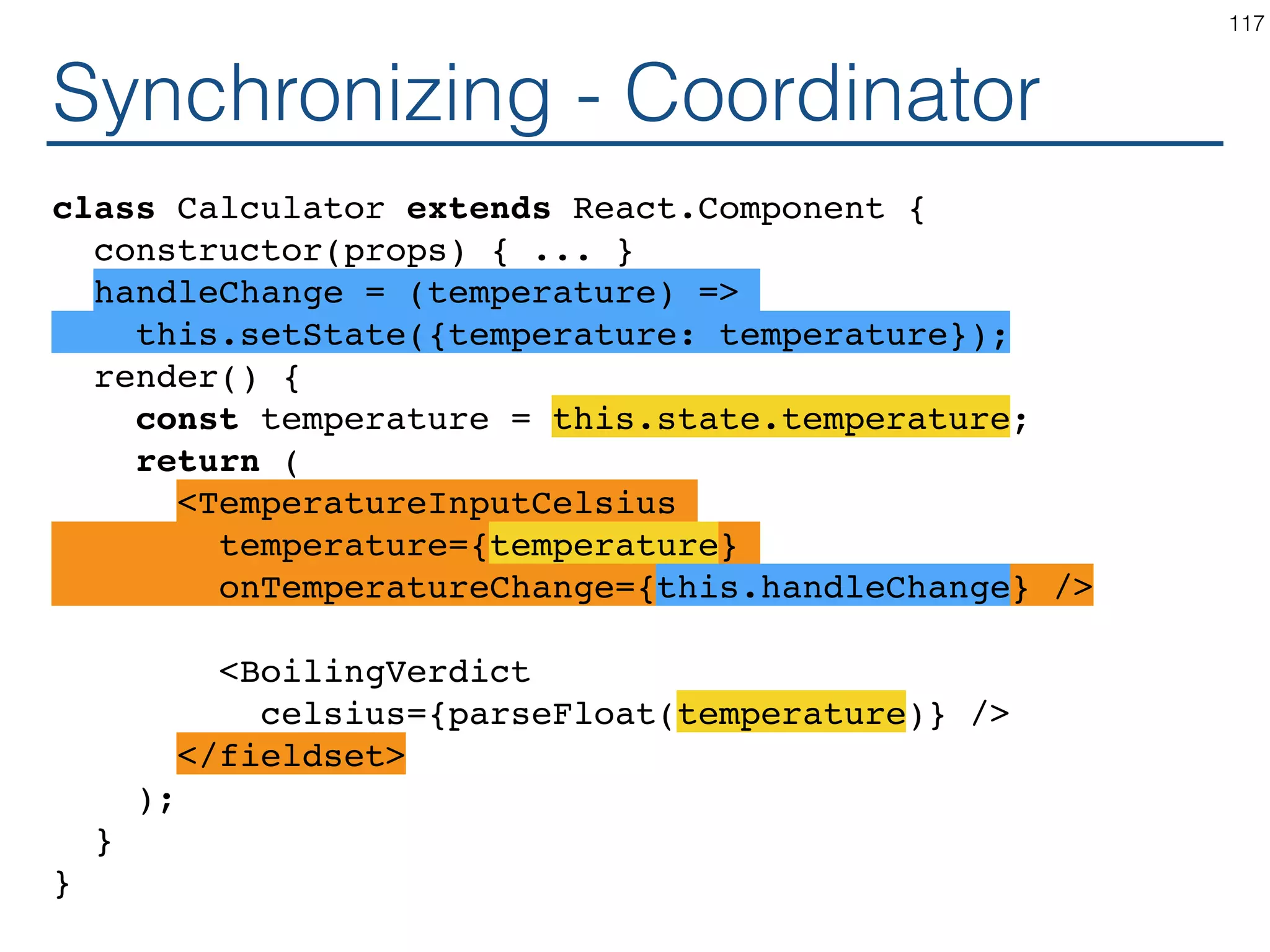
![Synchronizing - Producer class TemperatureInput extends React.Component { constructor(props) { ... } handleChange = (e) => this.props.onTemperatureChange(e.target.value); render() { const temperature = this.props.temperature; const scaleName = scaleNames[this.props.scale]; return ( <fieldset> <legend>Enter temperature in {scaleName}:</ legend> <input value={temperature} onChange={this.handleChange} /> </fieldset> ); } } 121](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-121-2048.jpg)
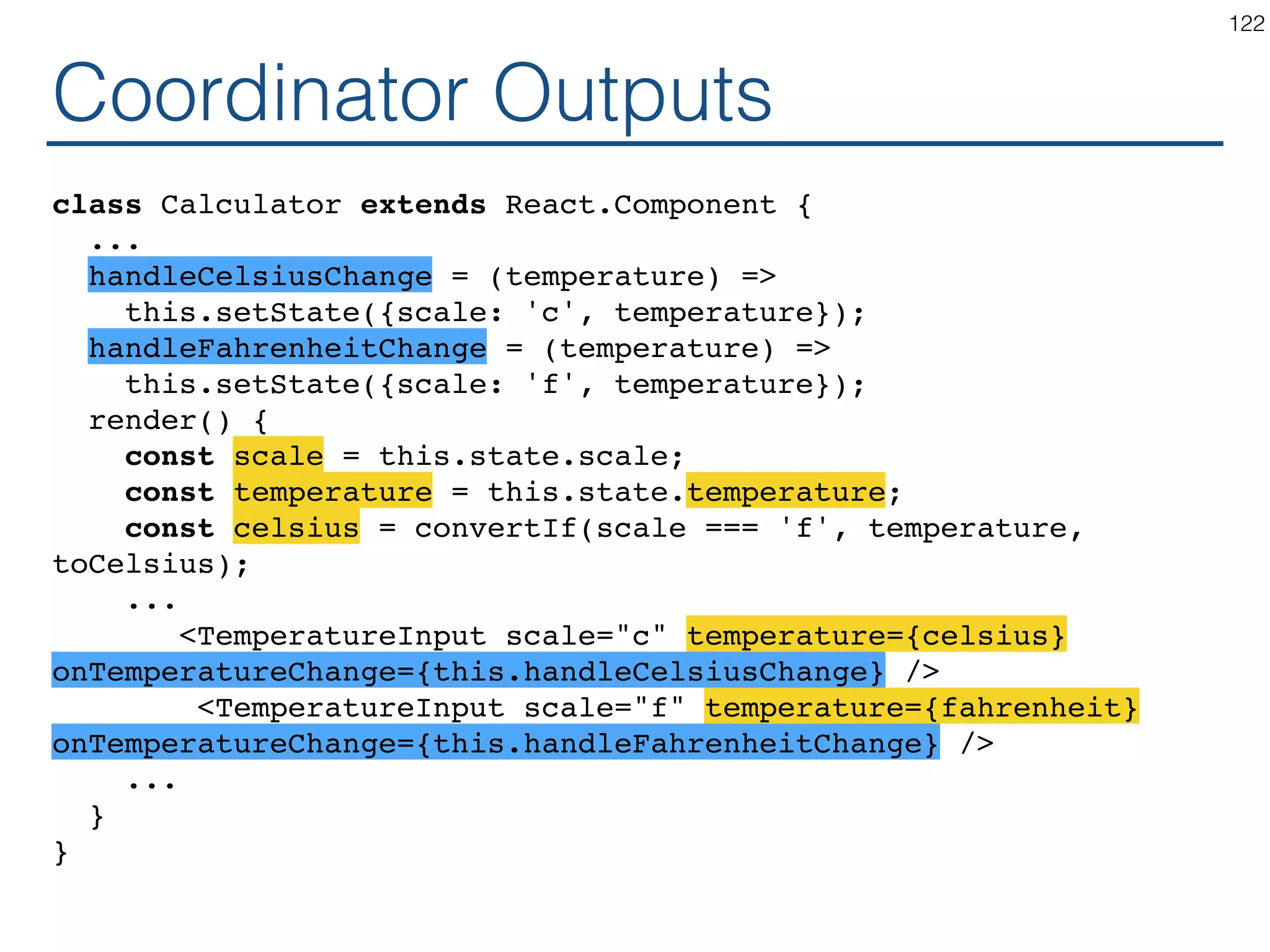
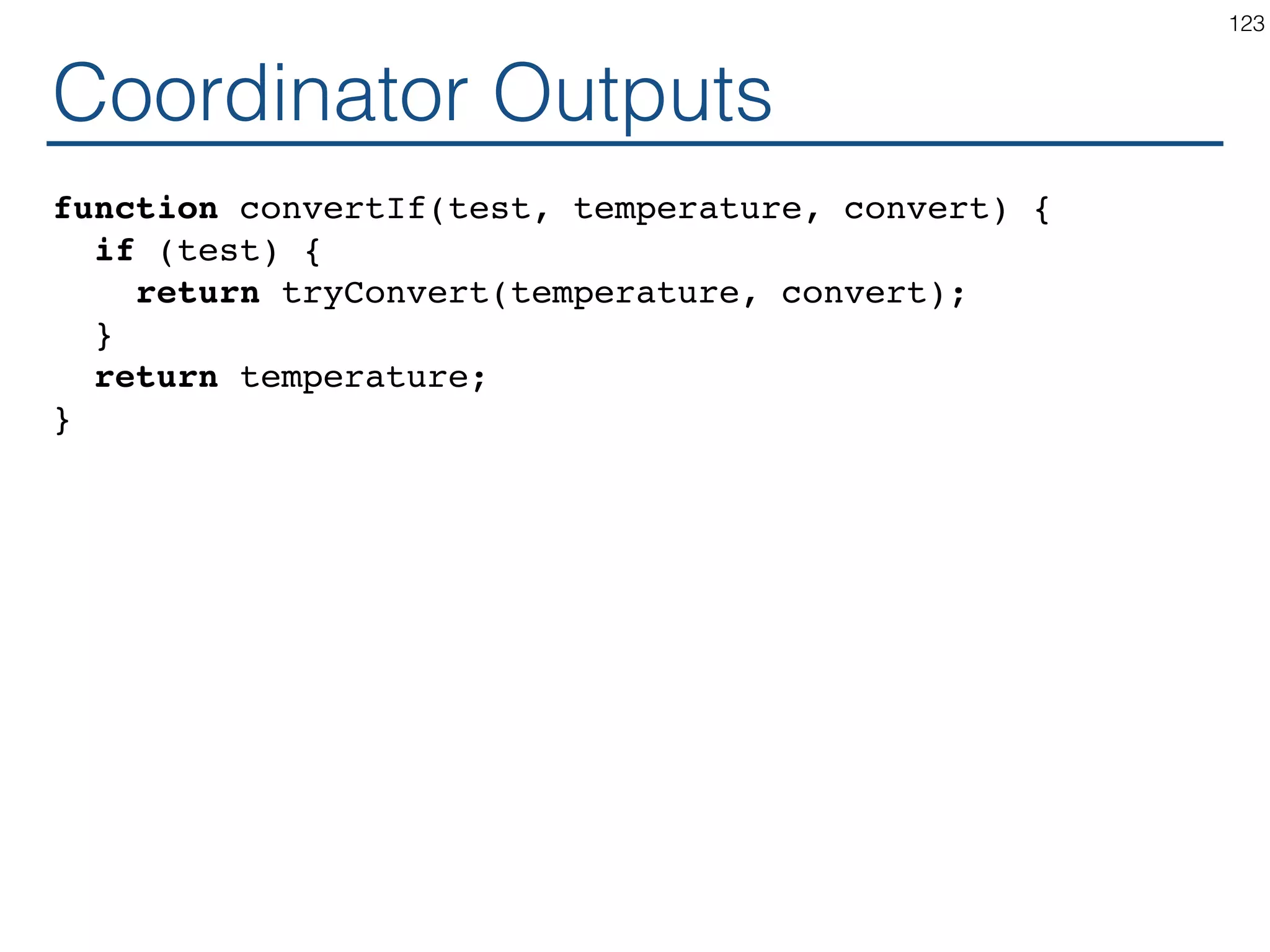


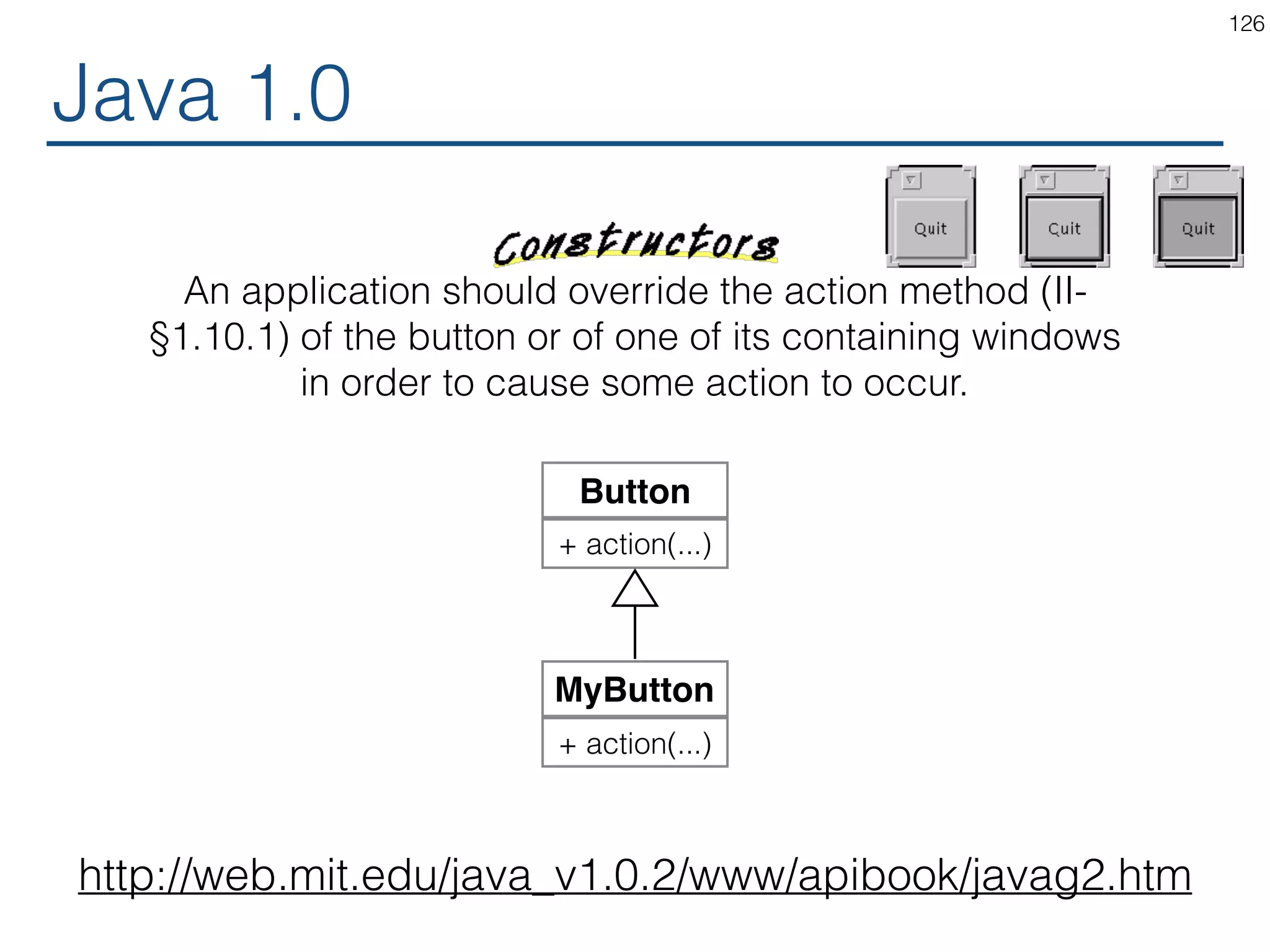
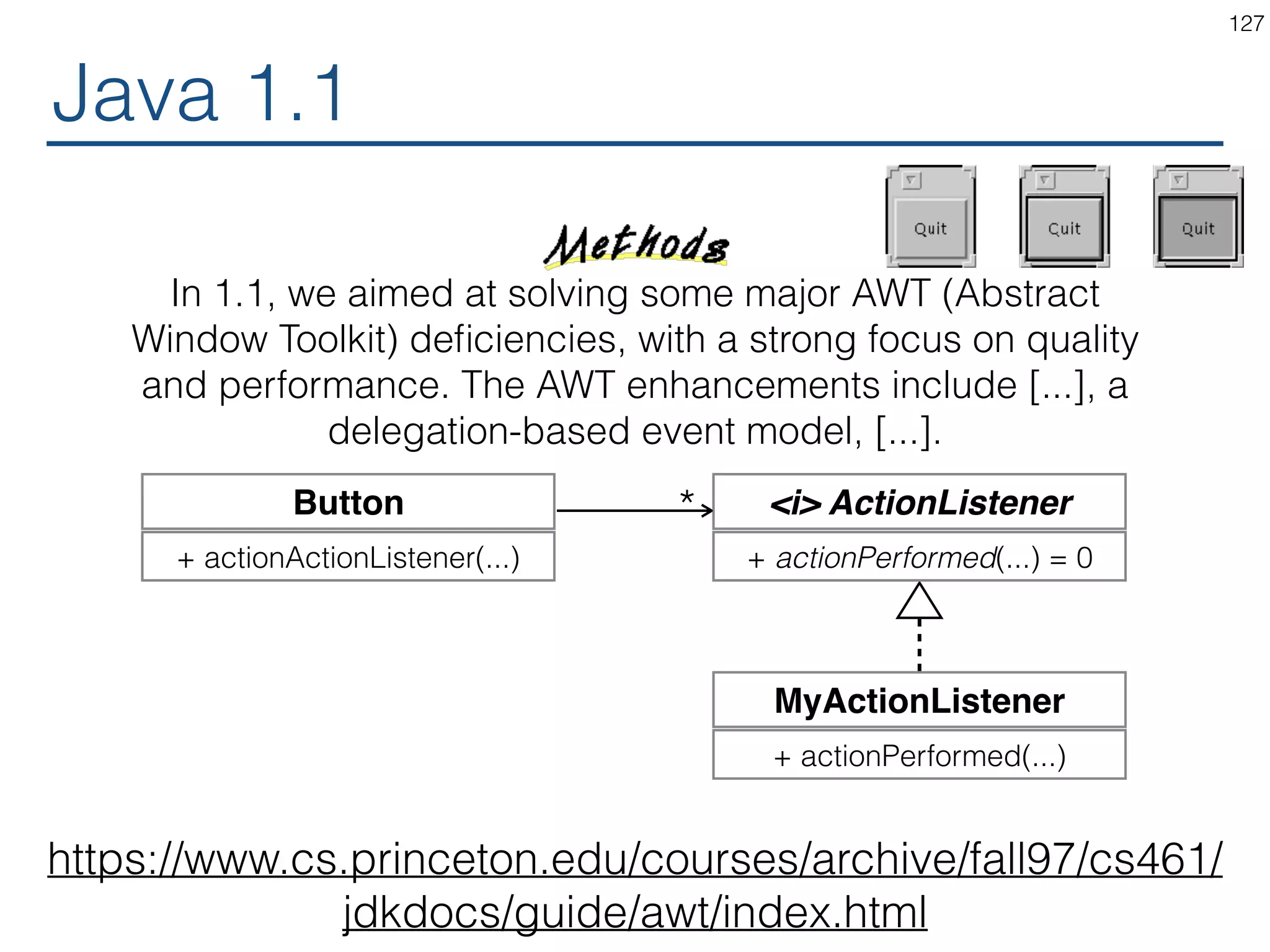

![Java 1.1 129 In 1.1, we aimed at solving some major AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) deficiencies, with a strong focus on quality and performance. The AWT enhancements include [...], a delegation-based event model, [...]. Button + actionActionListener(...) https://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/fall97/cs461/ jdkdocs/guide/awt/index.html <i> ActionListener + actionPerformed(...) = 0 MyActionListener + actionPerformed(...) *](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/react-170717163302/75/ReactJS-for-Programmers-129-2048.jpg)