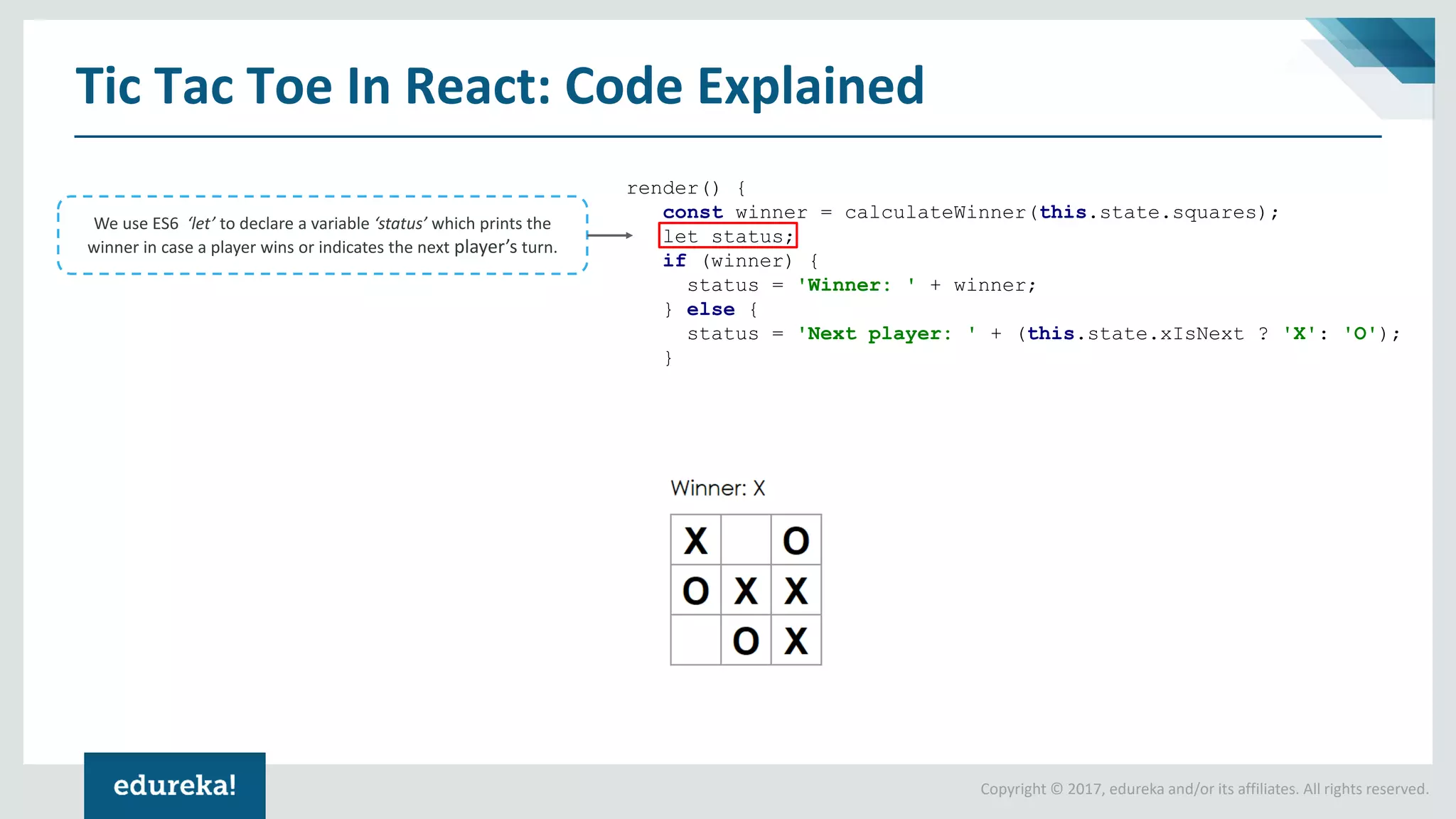
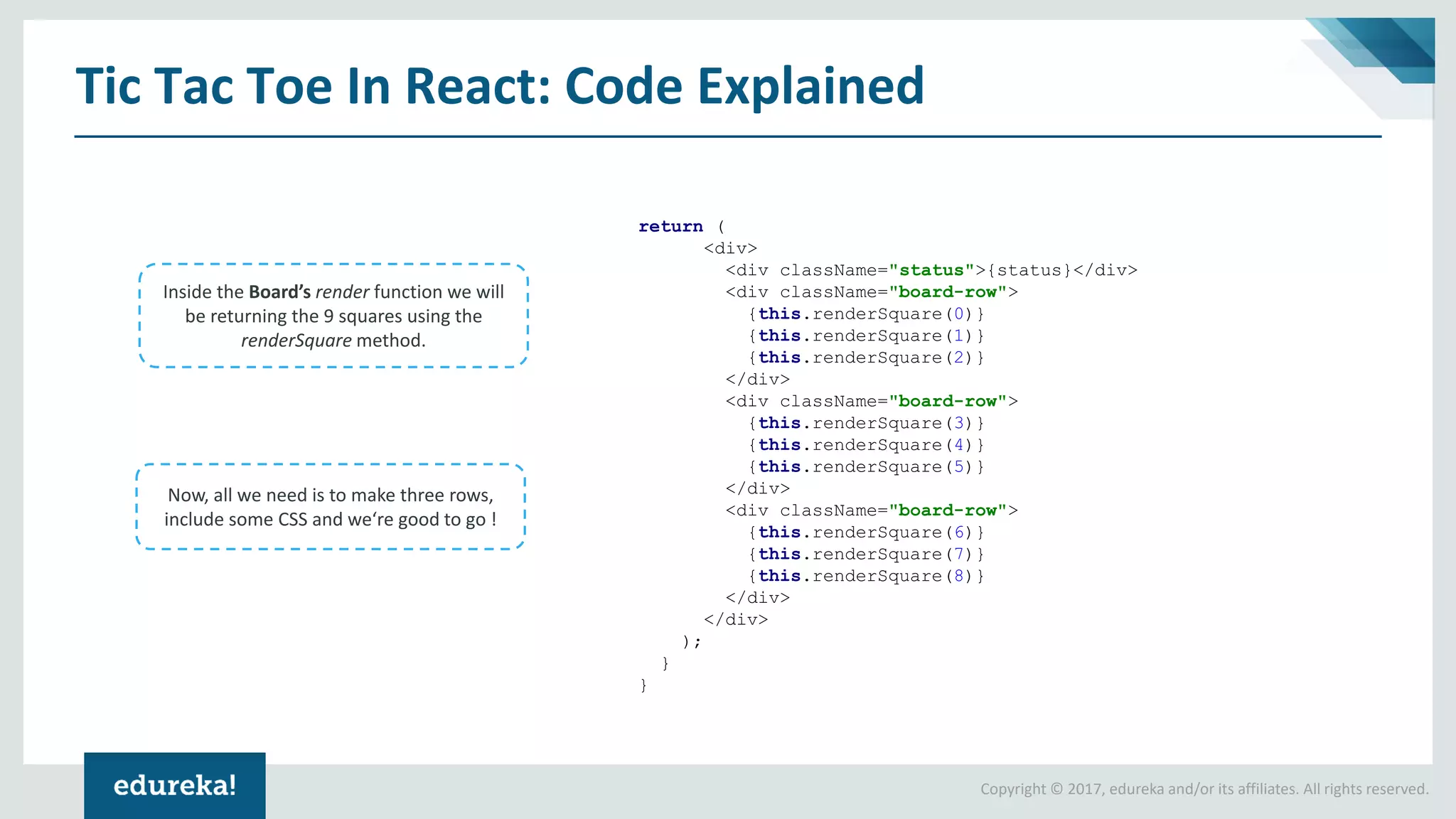
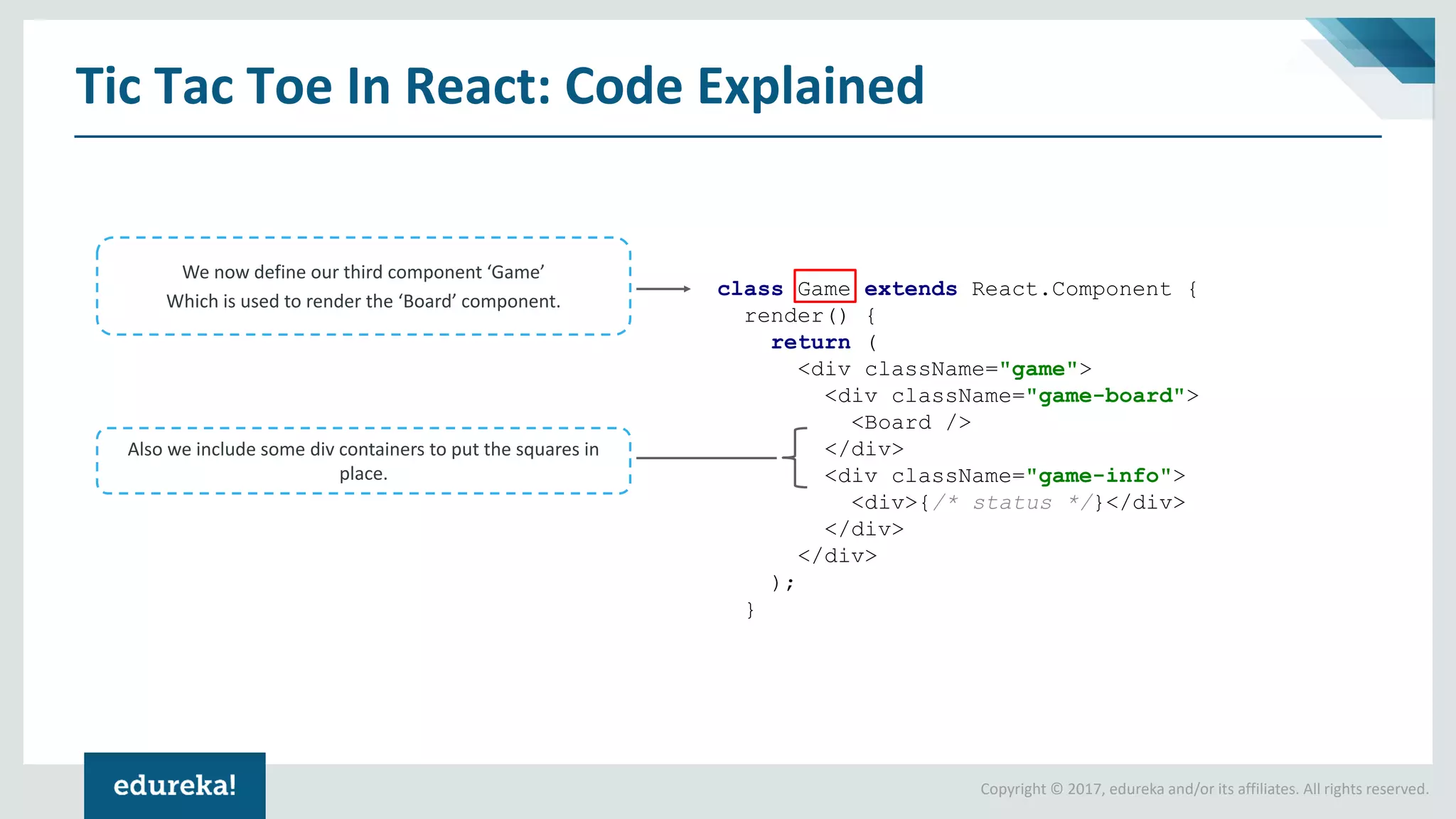
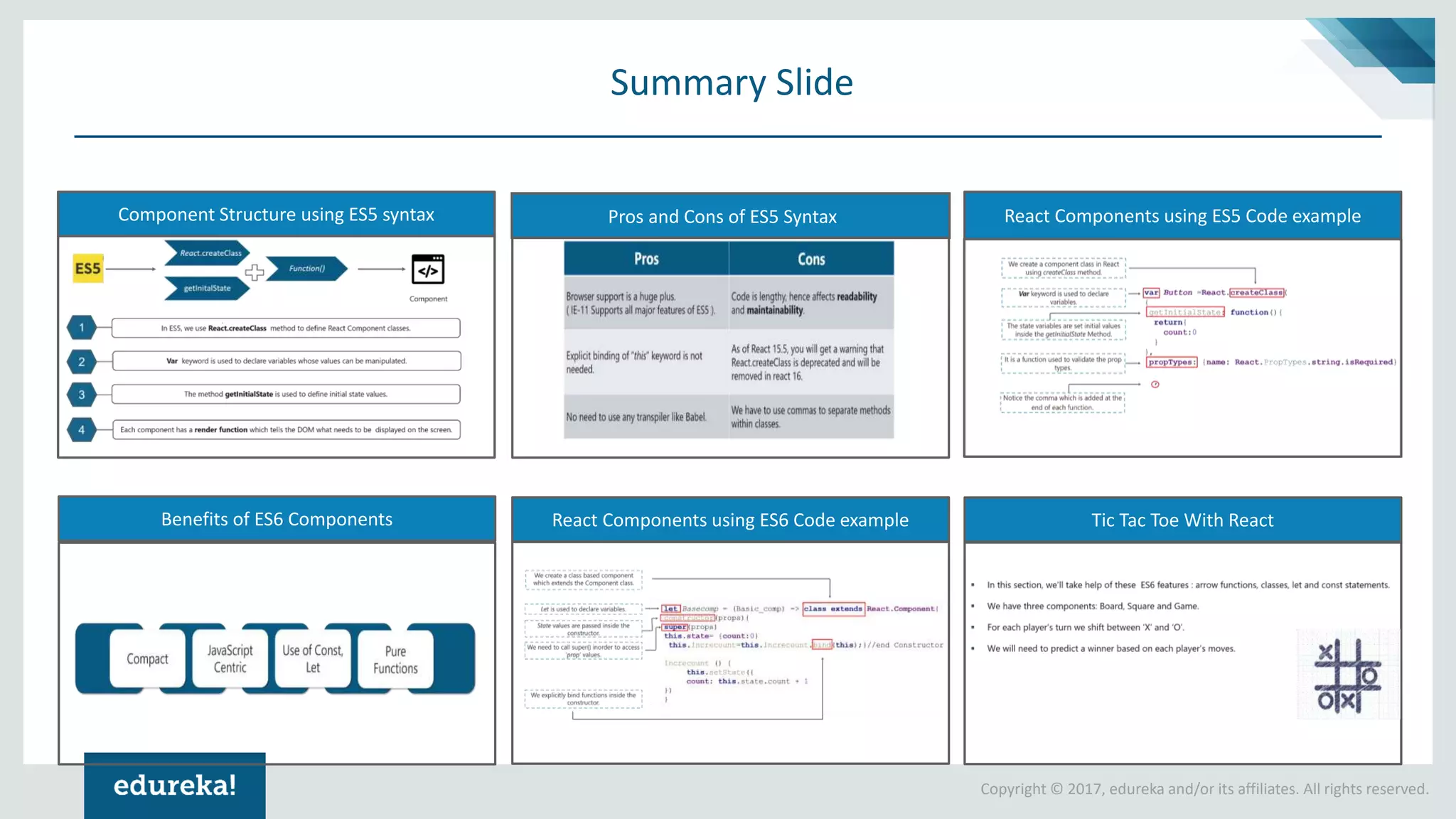
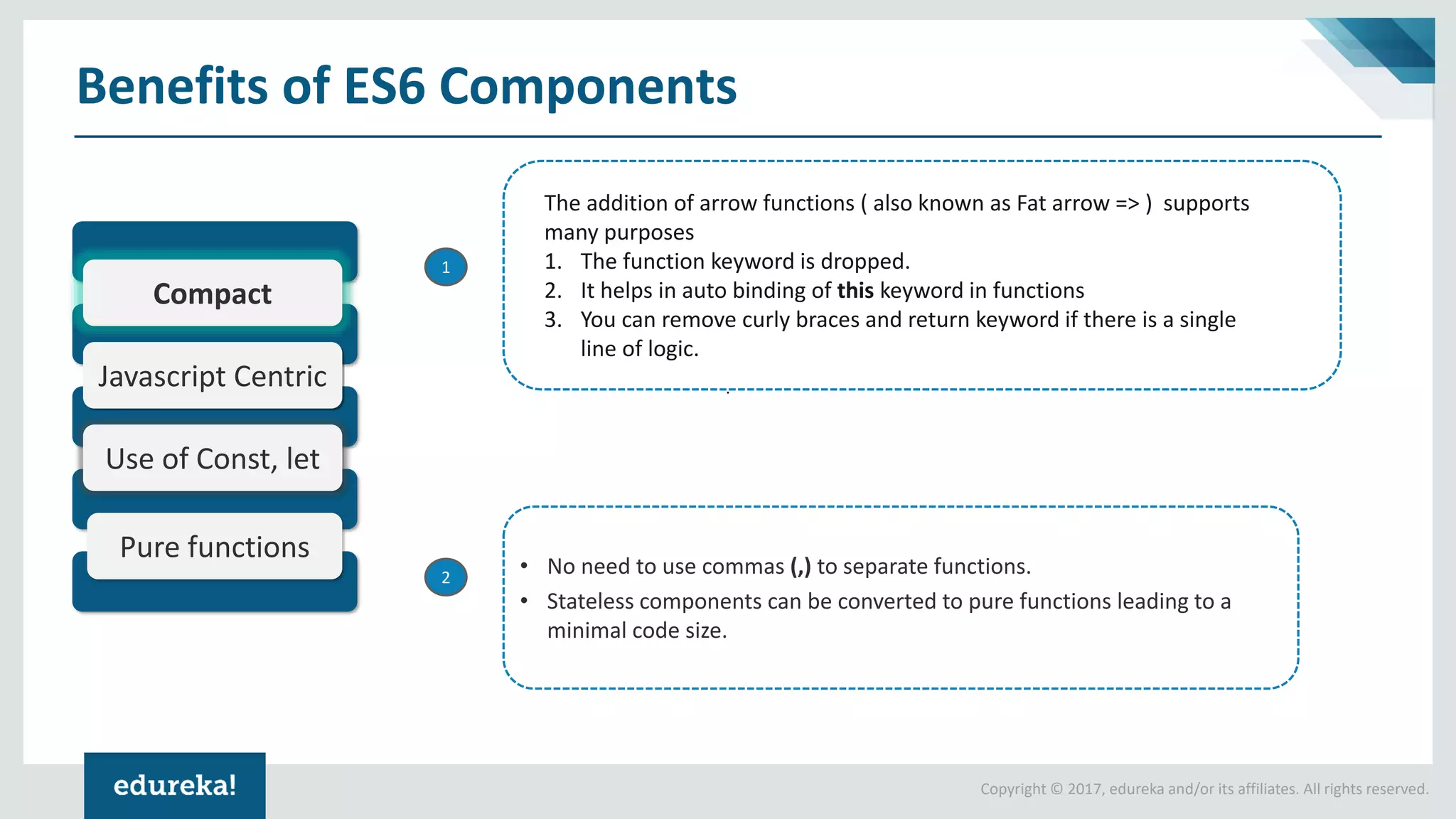
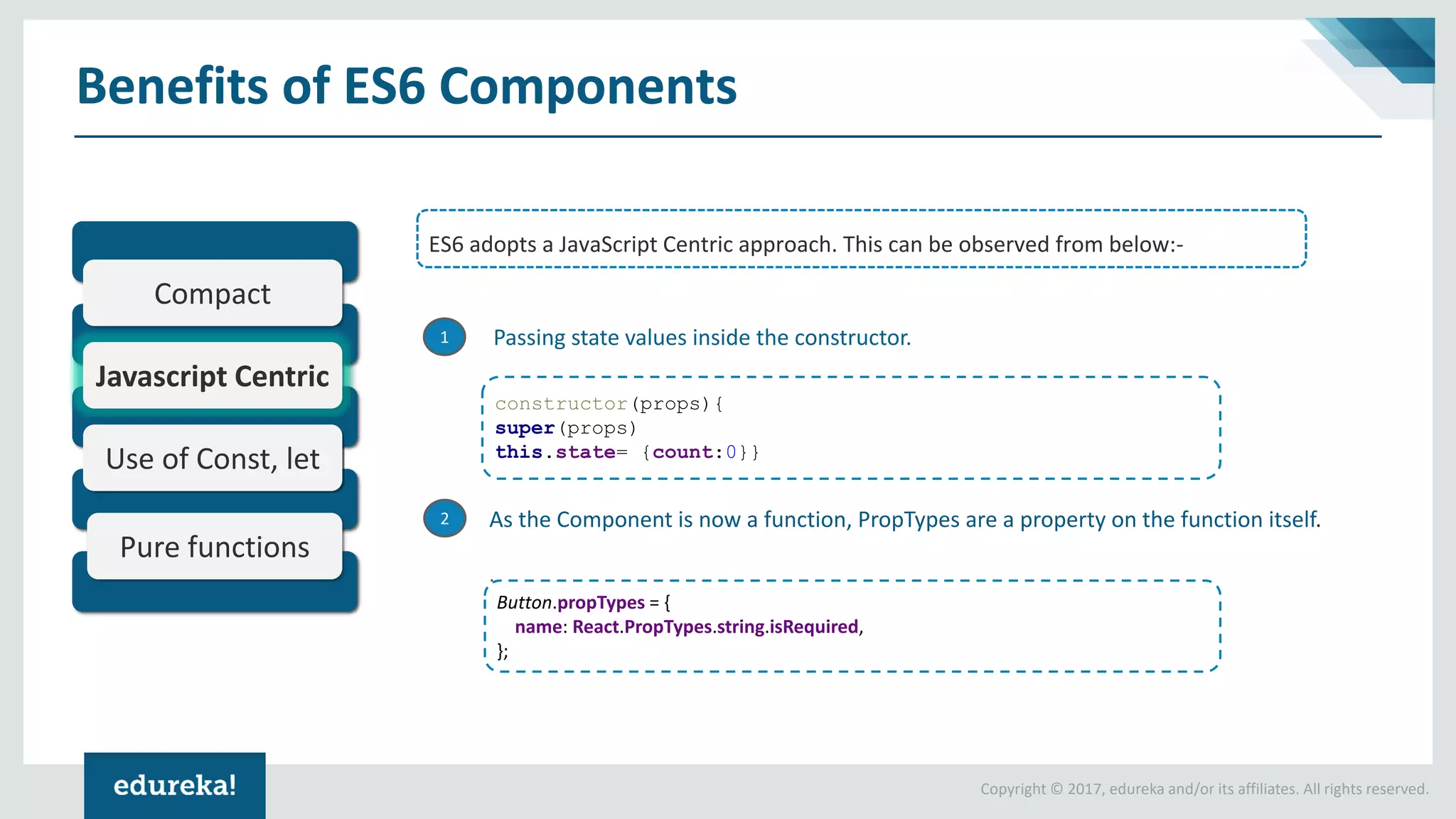
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to React components, exploring both ES5 and ES6 syntax for building applications. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each syntax, illustrates concepts through code examples, and culminates in a demonstration of building a Tic Tac Toe game using ES6 features. Key highlights include modular design, state management, and the transition from ES5 to ES6 for improved code readability and functionality.

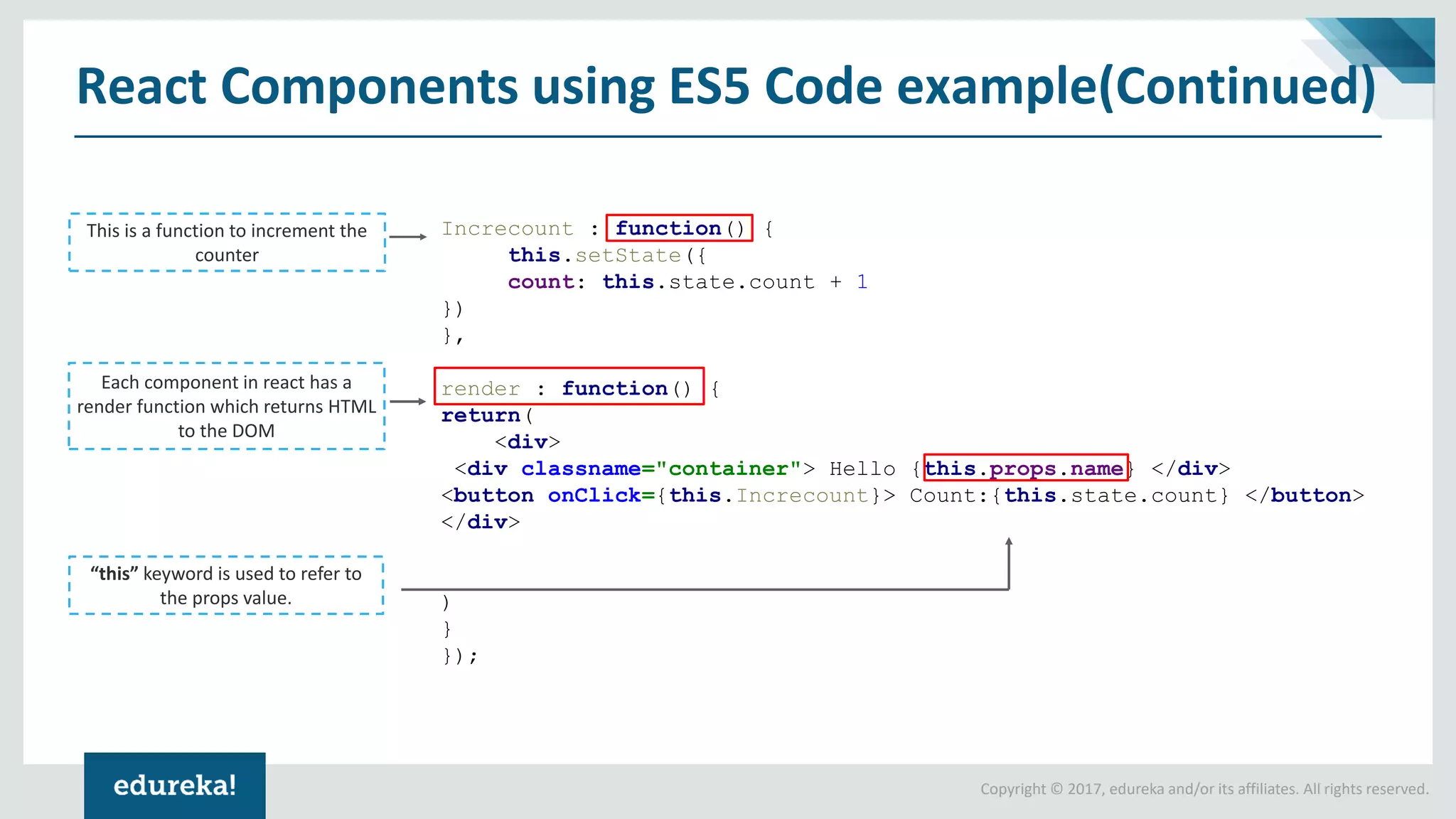


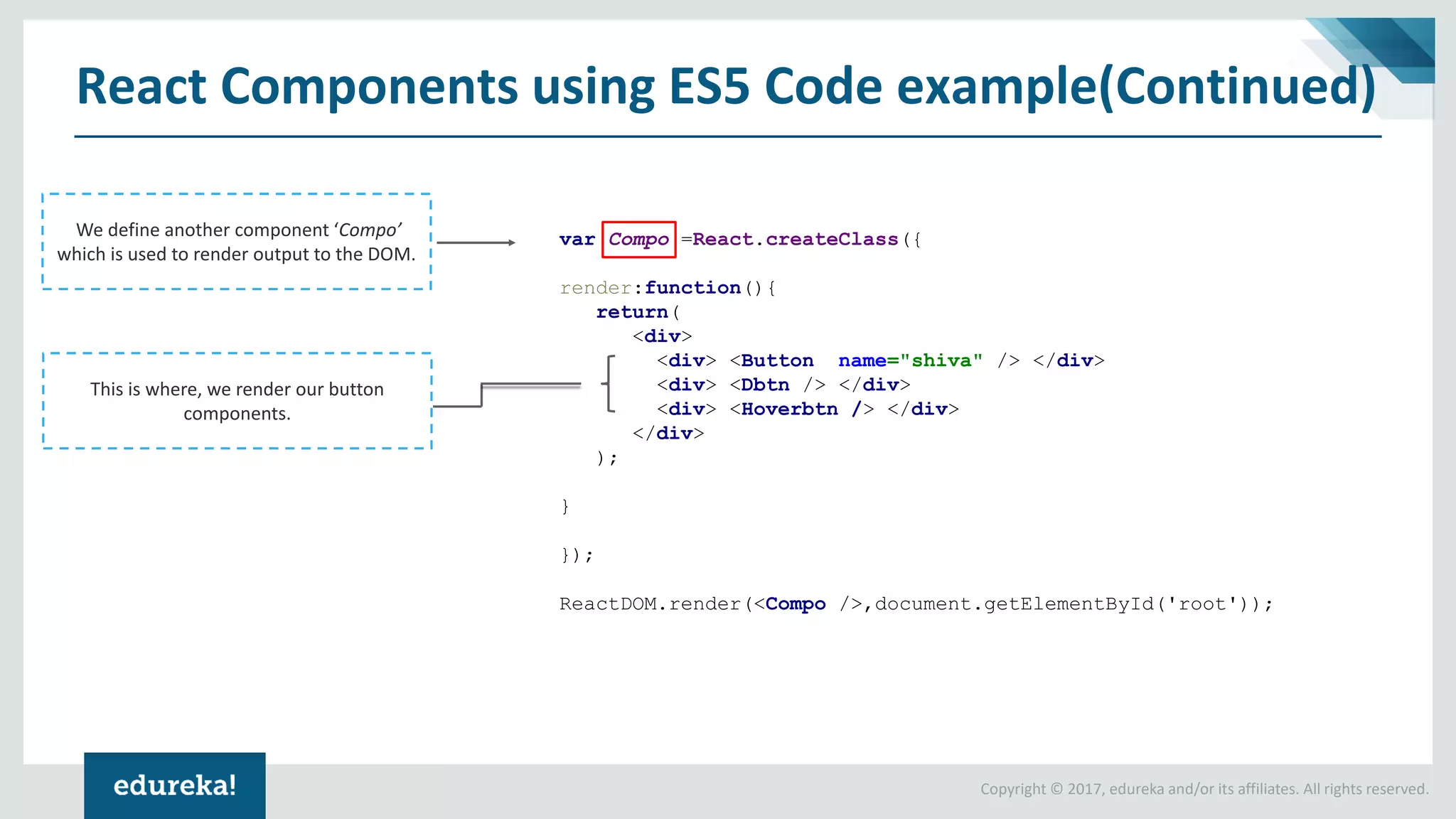





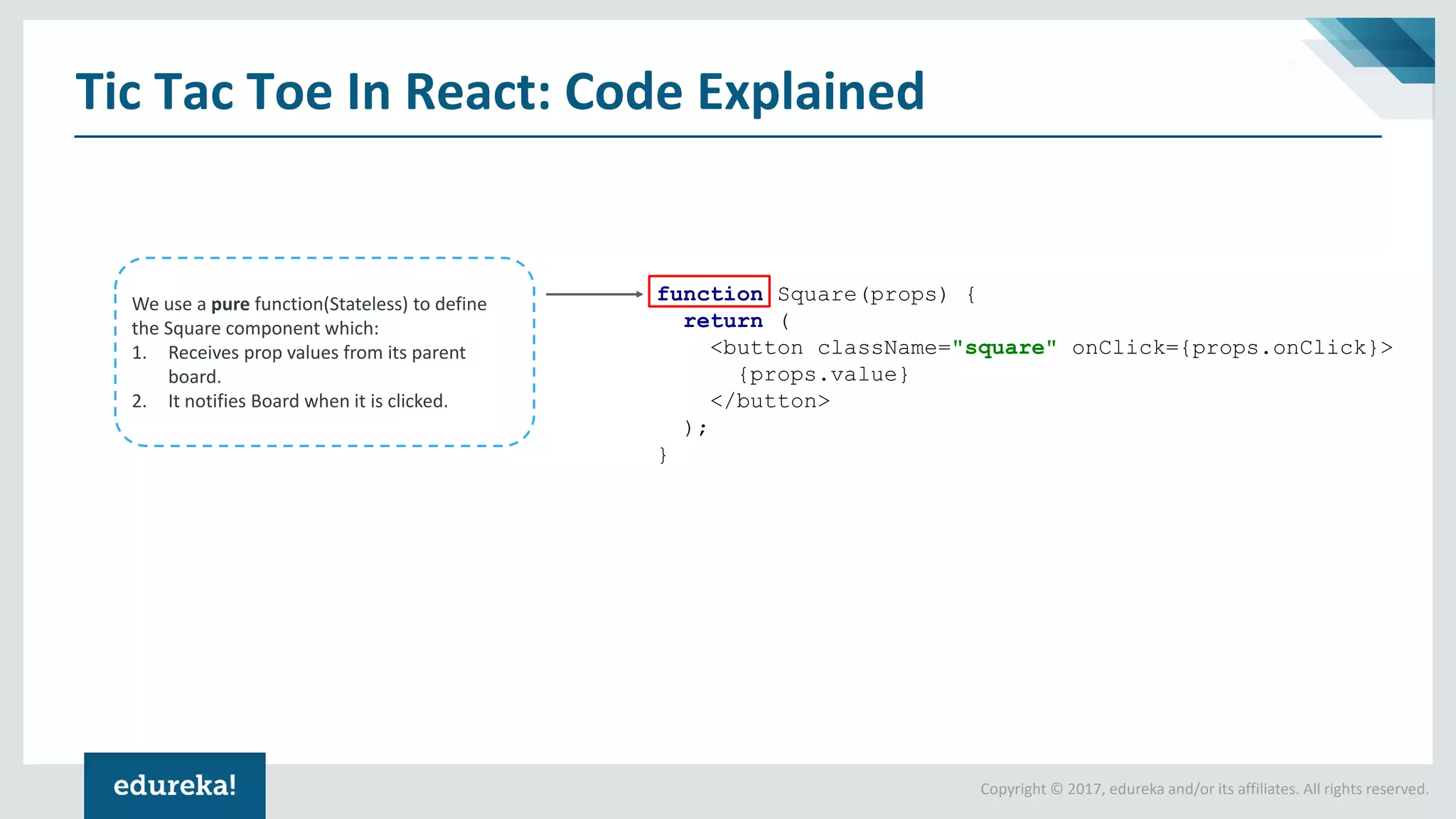
![Copyright © 2017, edureka and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Tic Tac Toe In React: Code Explained class Board extends React.Component { constructor() { super(); this.state = { squares: Array(9).fill(null), xIsNext: true, }; } We push state up into the Board component and fill the squares with null values for beginning. This is a Boolean value which is a pointer to switch between players renderSquare(i) { return ( <Square value={this.state.squares[i]} onClick={() => this.handleClick(i)} /> ); } Now we're passing down two props from Board to Square: value and onClick. The Board component can tell each Square what to display, this is why state should reside within Board component.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactes5es6-180808150300/75/React-ES5-to-ES6-React-ES5-vs-ES6-React-Tutorial-for-Beginners-React-online-Training-Edureka-27-2048.jpg)
![Copyright © 2017, edureka and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Tic Tac Toe In React: Code Explained function calculateWinner(squares) { const lines = [ [0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8], [0, 3, 6], [1, 4, 7], [2, 5, 8], [0, 4, 8], [2, 4, 6], ]; for (let i = 0; i < lines.length; i++) { const [a, b, c] = lines[i]; if (squares[a] && squares[a] === squares[b] && squares[a] === squares[c]) { return squares[a]; } } return null; } We need a function to find a winner We pass all the square combinations in an array. We use a for loop to identify matching squares We return null if any condition fails else we return ‘X’ or ‘O’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactes5es6-180808150300/75/React-ES5-to-ES6-React-ES5-vs-ES6-React-Tutorial-for-Beginners-React-online-Training-Edureka-28-2048.jpg)
![Copyright © 2017, edureka and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Tic Tac Toe In React: Code Explained handleClick(i) { const squares = this.state.squares.slice(); if (calculateWinner(squares) || squares[i]) { return; } squares[i] = this.state.xIsNext ? 'X' : 'O'; this.setState({ squares: squares, xIsNext: !this.state.xIsNext, }); } handleclick() returns either the winner or the next player. We manipulate state variable XIsNext to Return the player. • Now that we have seen the ‘CalculateWinner Function()’, lets get back to the board component where we define handleClick event handler. • Board passed onClick={() => this.handleClick(i)} to Square, so, when called, it runs this.handleClick(i) on the Board.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactes5es6-180808150300/75/React-ES5-to-ES6-React-ES5-vs-ES6-React-Tutorial-for-Beginners-React-online-Training-Edureka-29-2048.jpg)