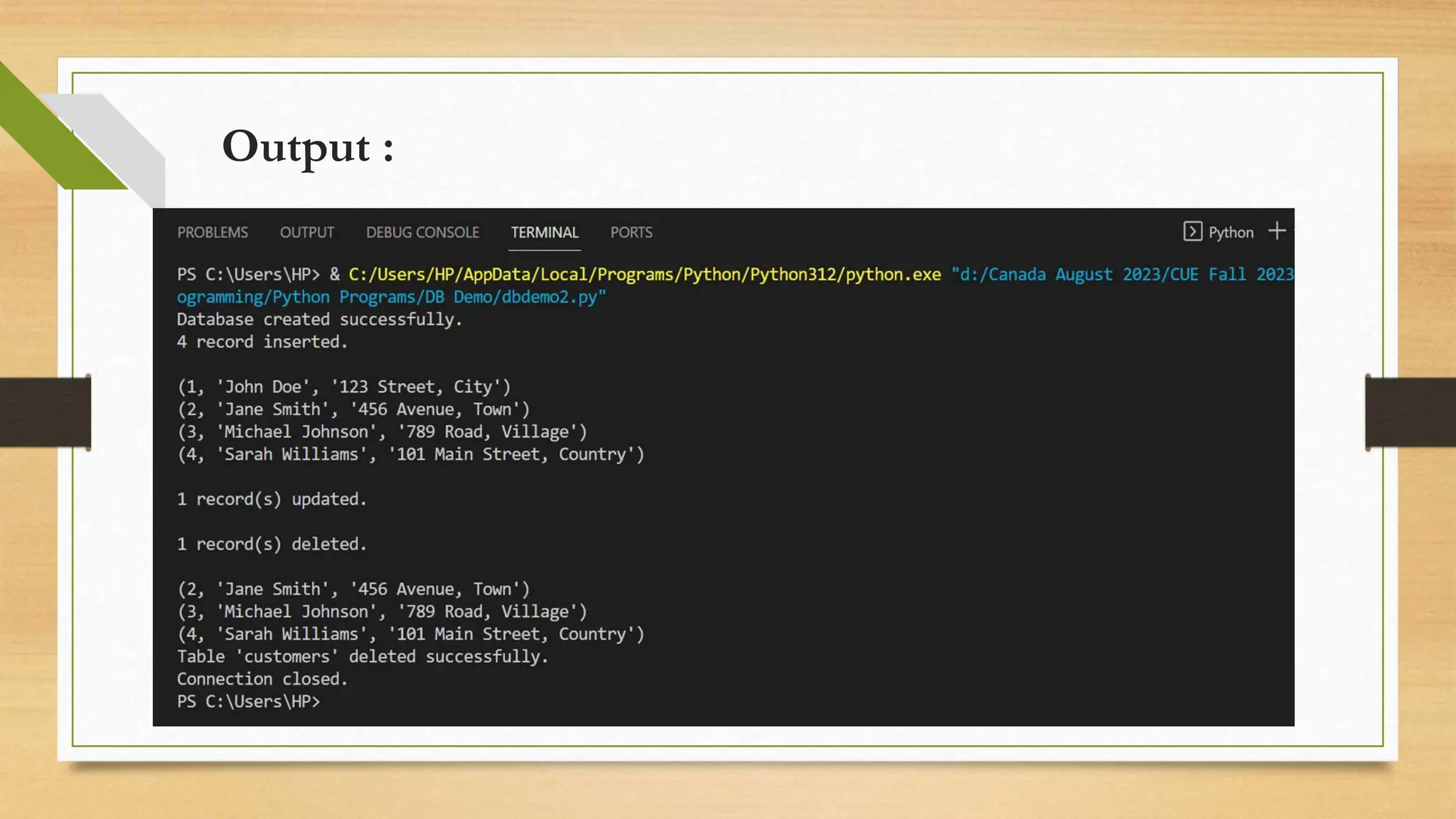
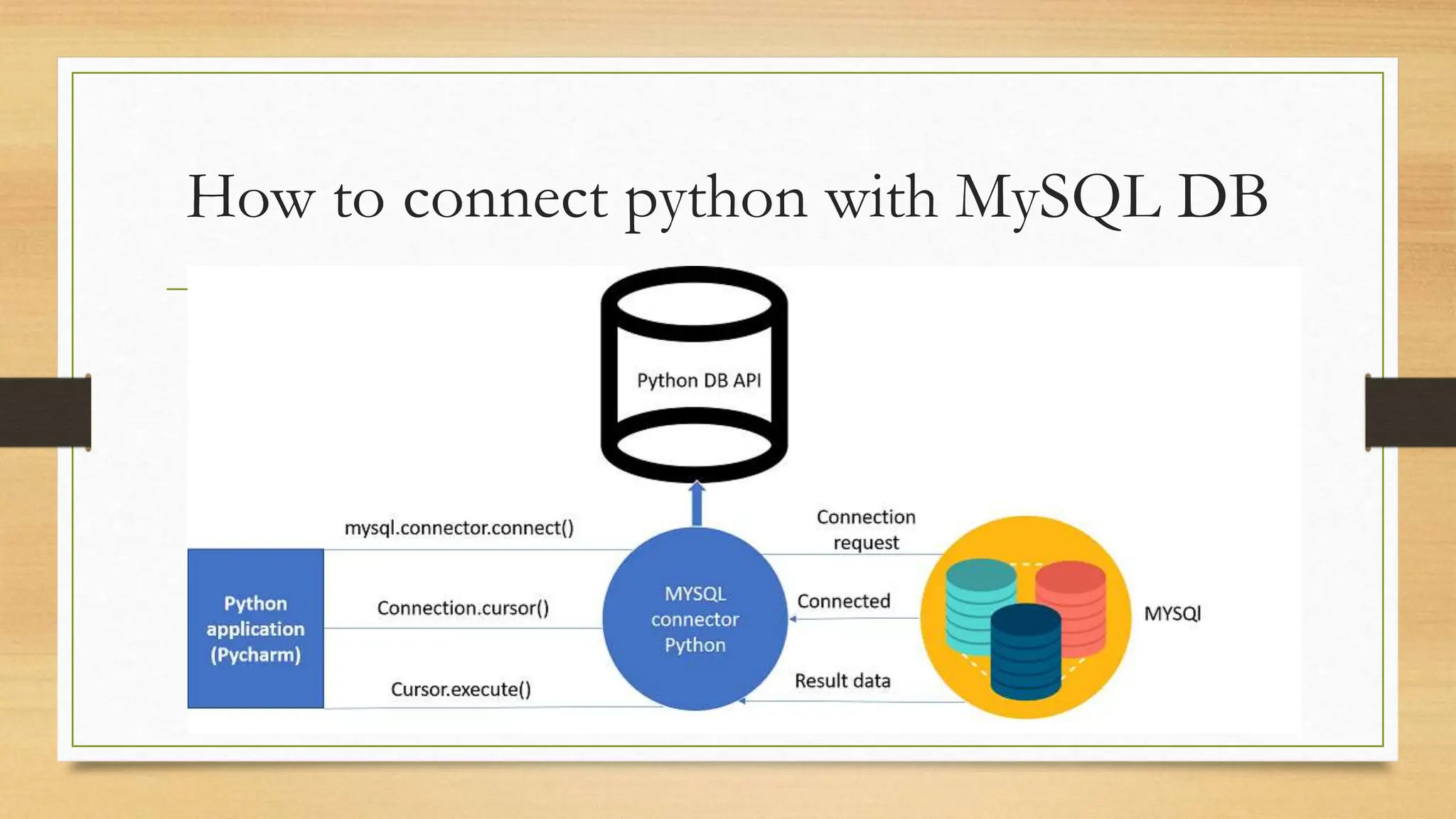
Python DB API allows Python applications to interact with relational databases in a uniform way. It supports various databases including SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server. The document discusses connecting Python to MySQL, executing SQL queries, and fetching data. It provides code to connect to a MySQL database, create a table, insert sample data, run queries, and display results.












![Execute SOL query • Executes an SQL. command against all parameter sequences or mappings found in the sequence sq sql = "INSERT INTO customer (name, address) VALUES (%s, %s)" val = [ ("John Doe", "123 Street, City"), ("Jane Smith", "456 Avenue, Town"), ("Michael Johnson", "789 Road, Village"), ("Sarah Williams", "101 Main Street, Country") ] mycursor.executemany(sql, val)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythondbapi-240205133434-c4d46639/75/PythonDatabaseAPI-Presentation-for-Database-17-2048.jpg)





![Demo Program CONTINUE.. # Creating a table mycursor.execute("CREATE TABLE if not exists customers (id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255), address VARCHAR(255))") # Inserting data into the table sql = "INSERT INTO customers (name, address) VALUES (%s, %s)" val = [ ("John Doe", "123 Street, City"), ("Jane Smith", "456 Avenue, Town"), ("Michael Johnson", "789 Road, Village"), ("Sarah Williams", "101 Main Street, Country") ] mycursor.executemany(sql, val) # Committing the changes mydb.commit() print(mycursor.rowcount, "record inserted.")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythondbapi-240205133434-c4d46639/75/PythonDatabaseAPI-Presentation-for-Database-23-2048.jpg)