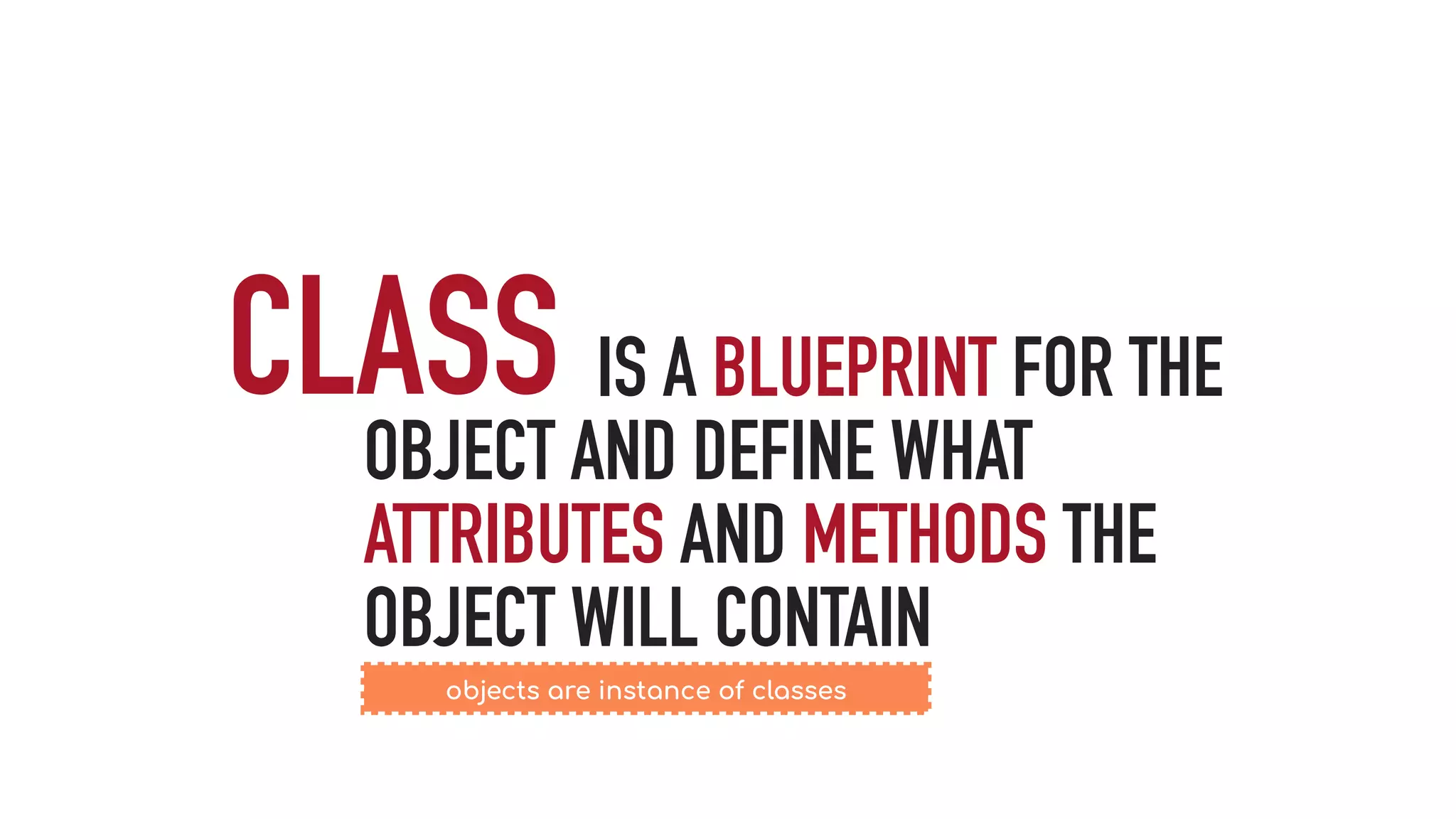
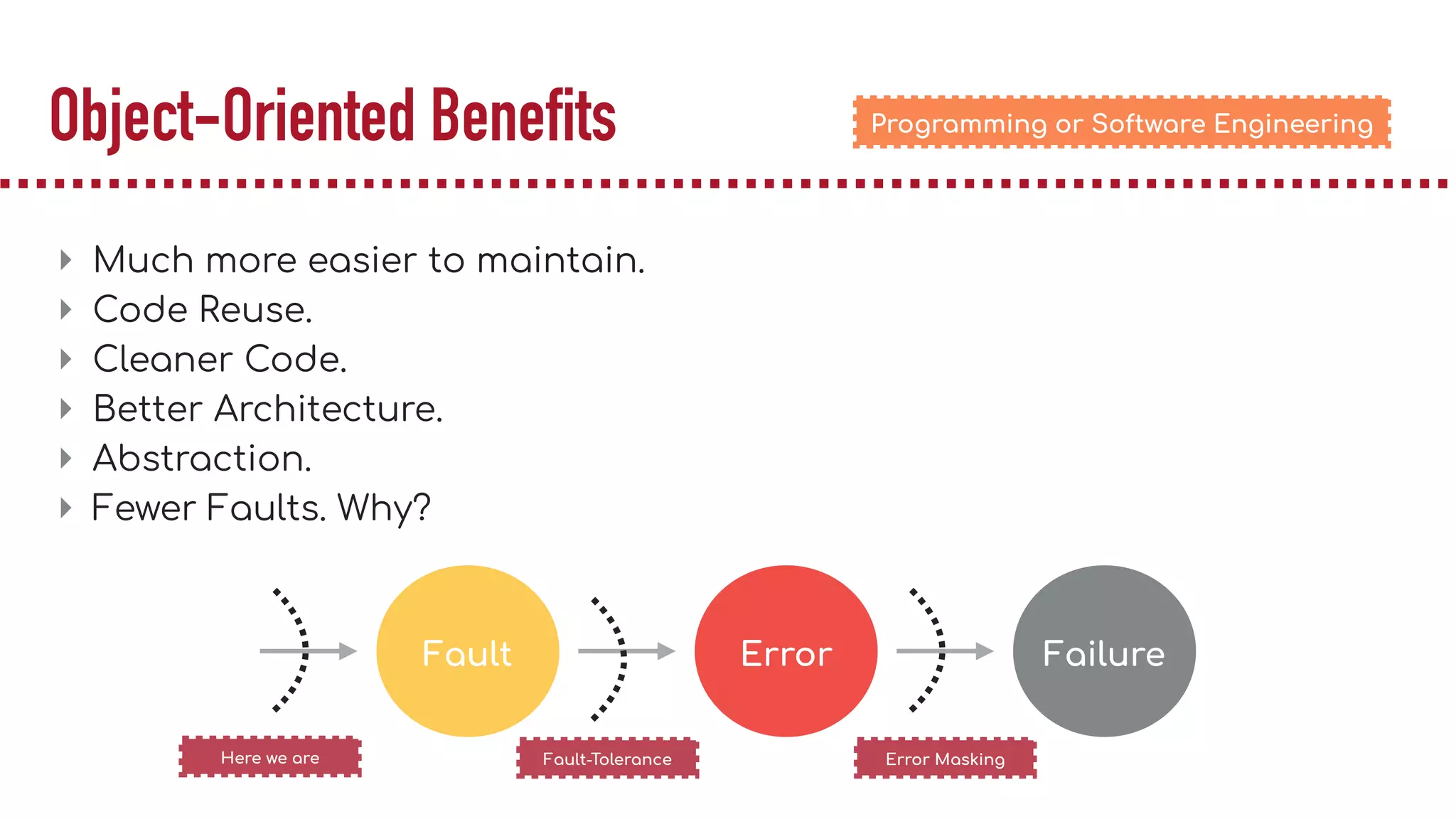
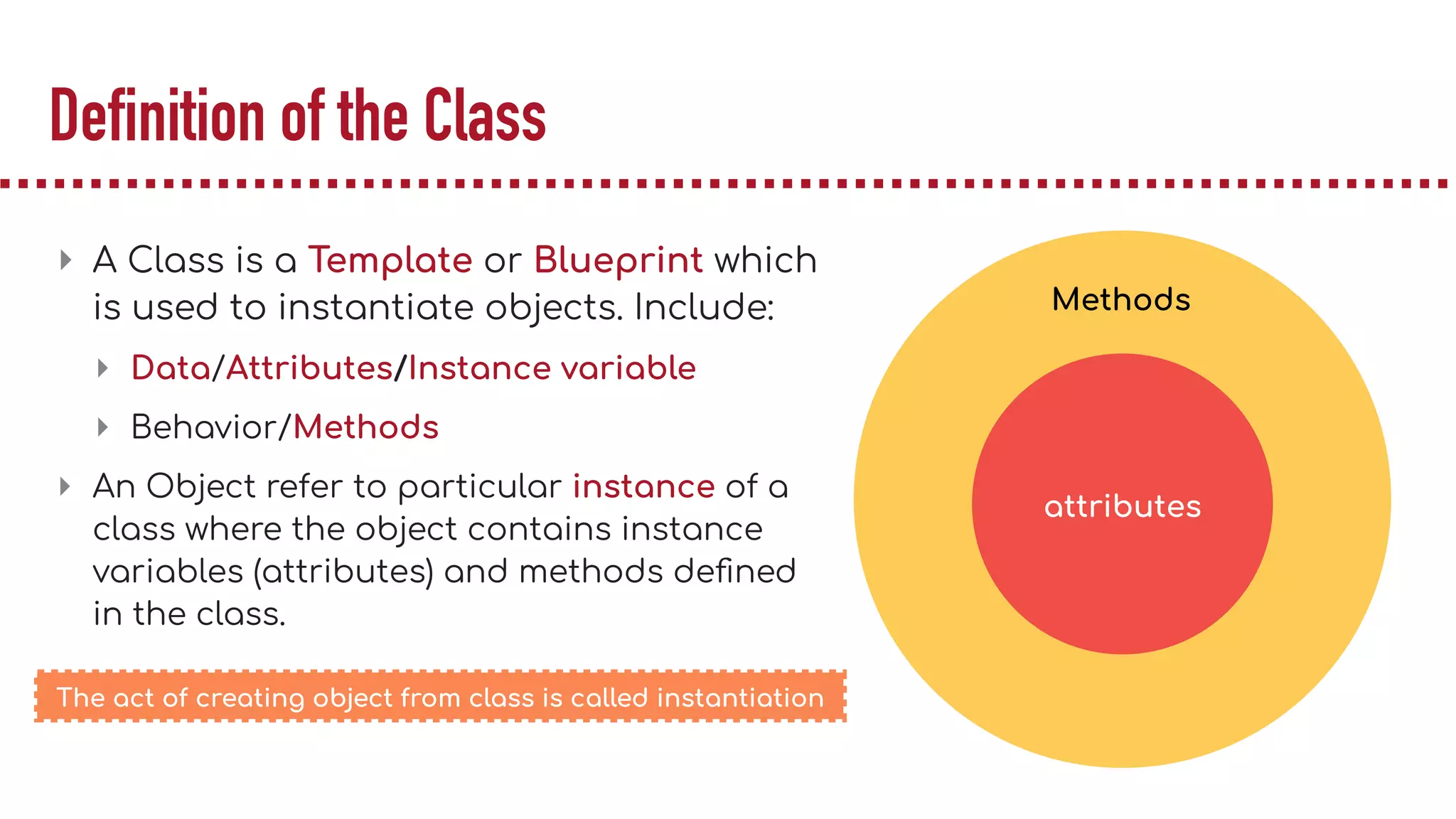
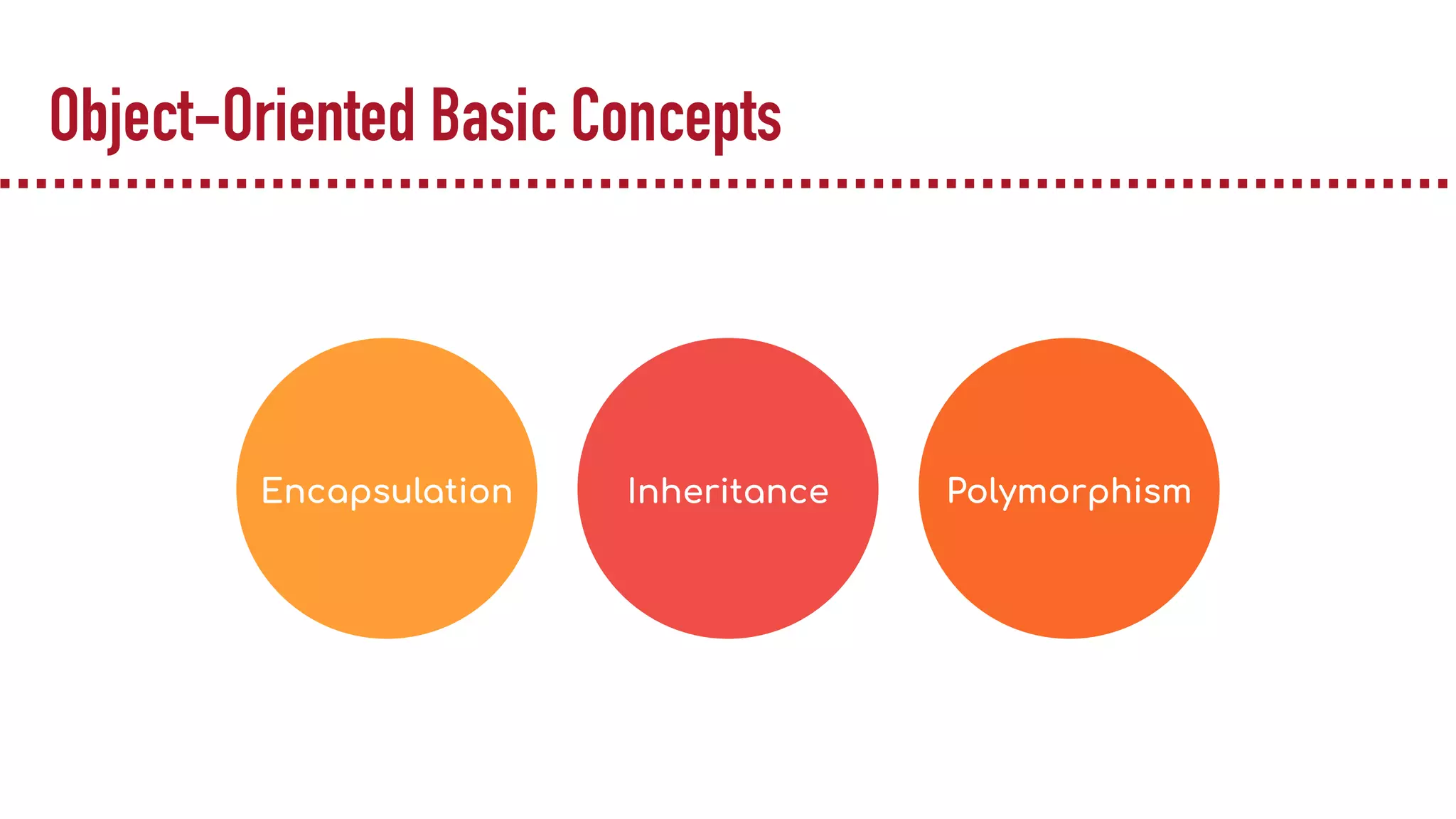
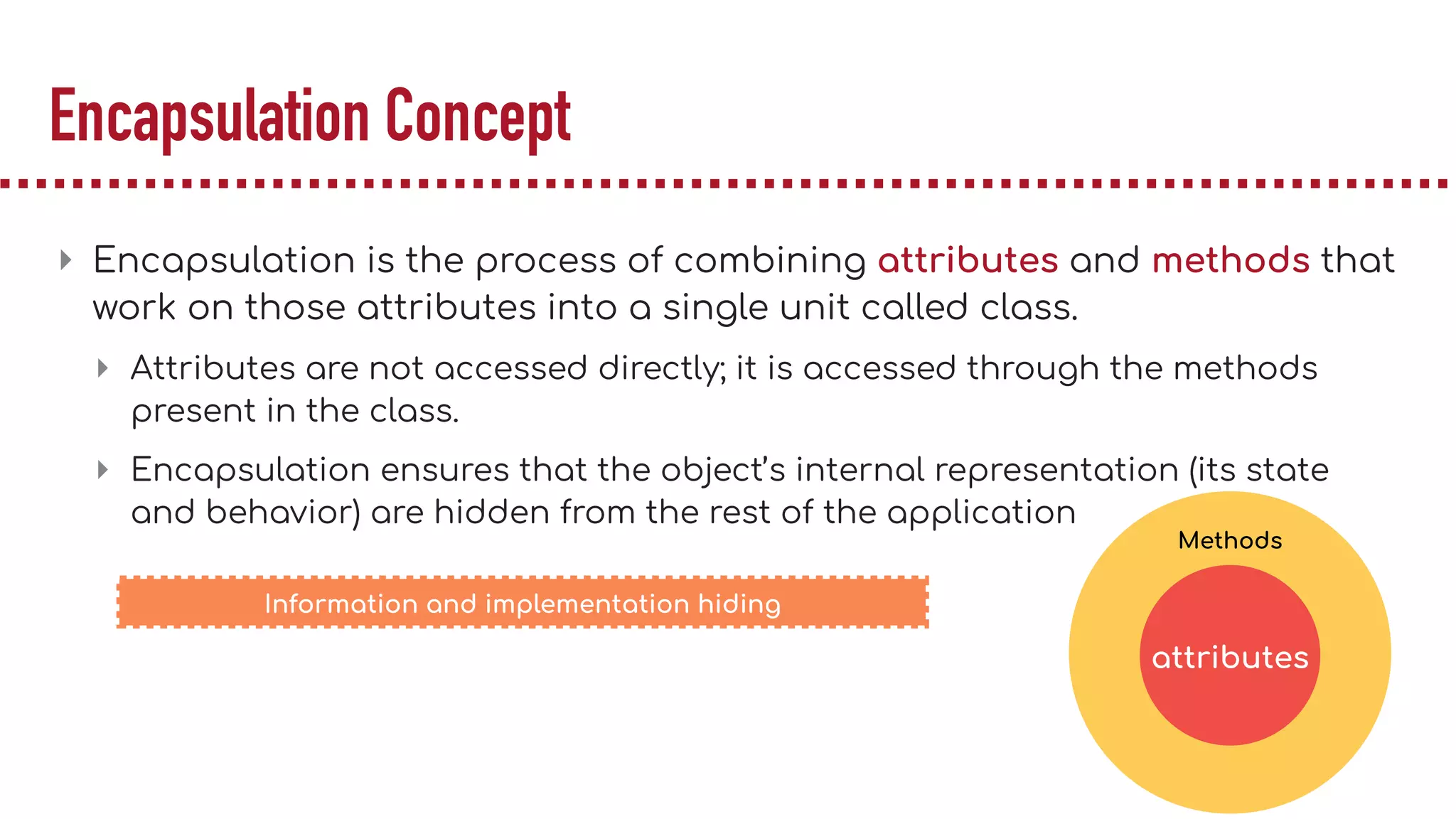
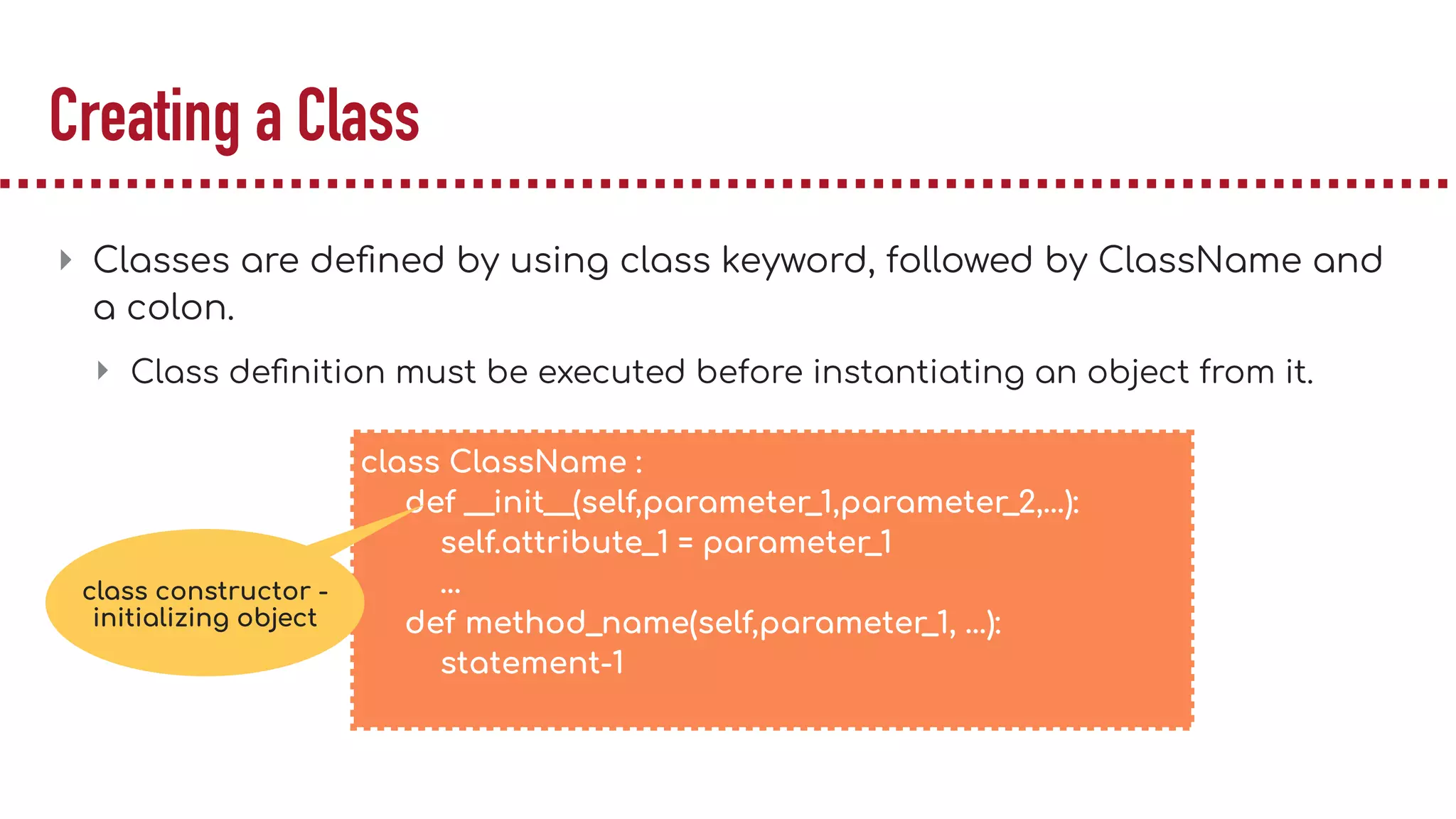
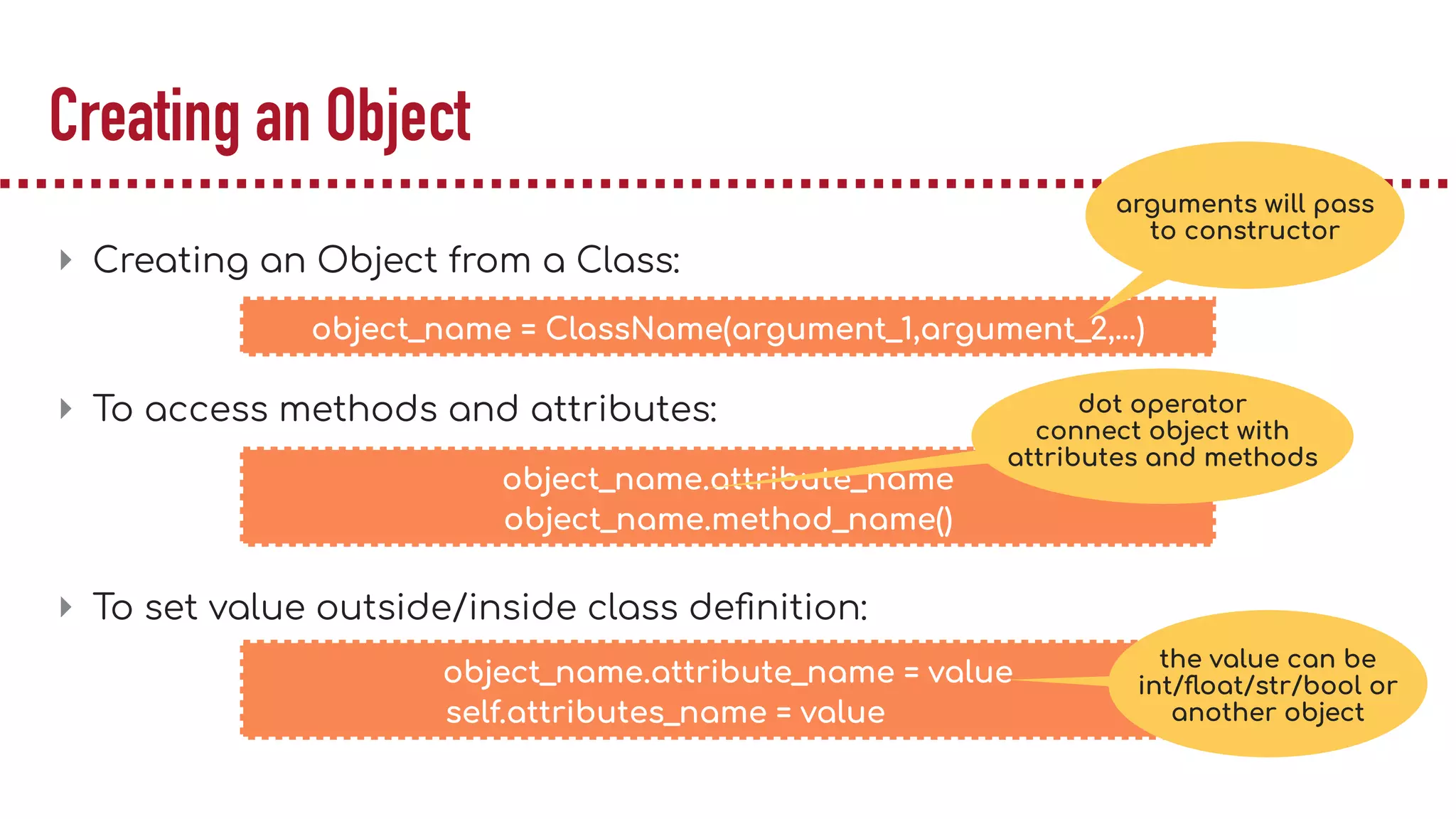
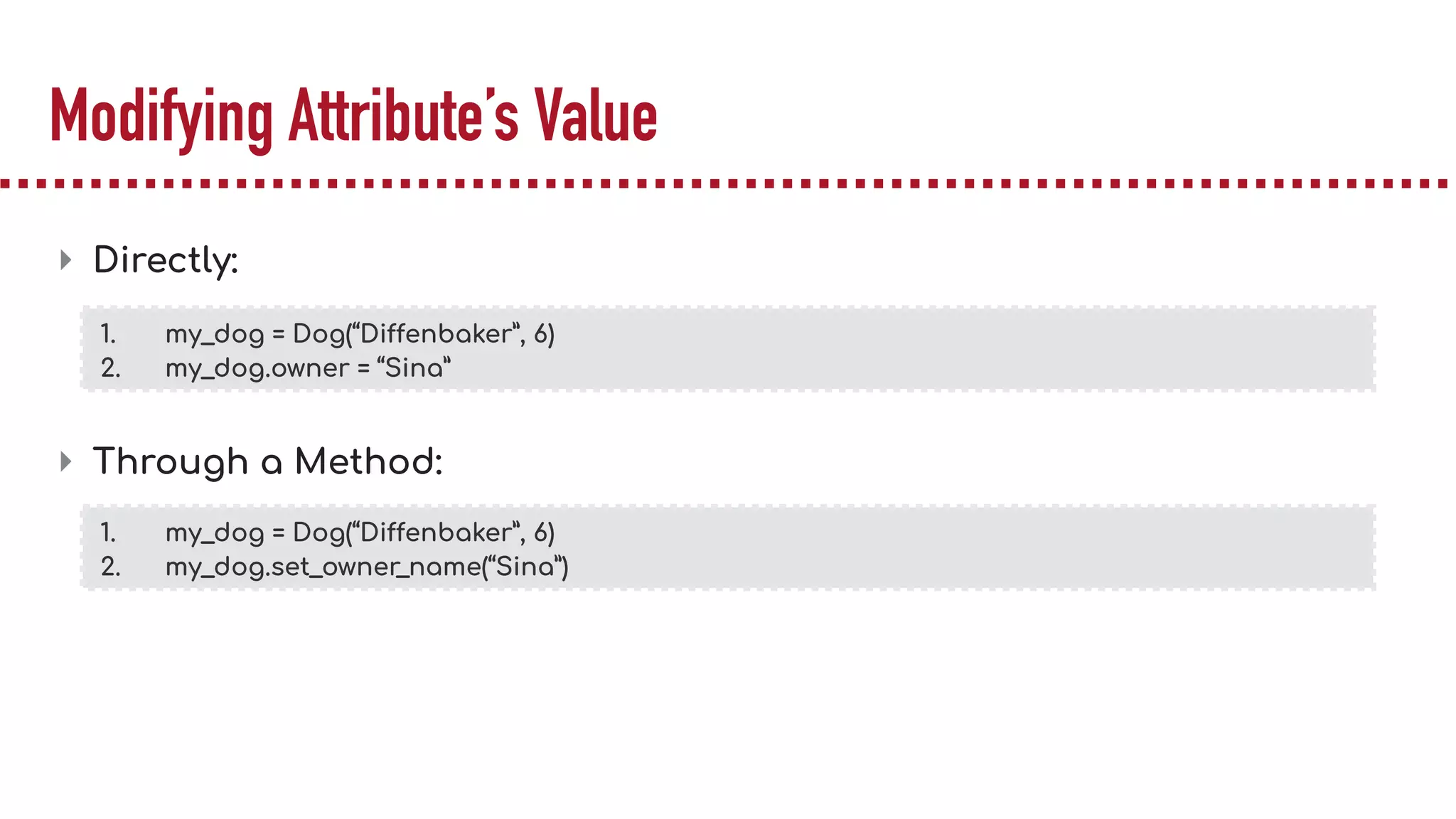
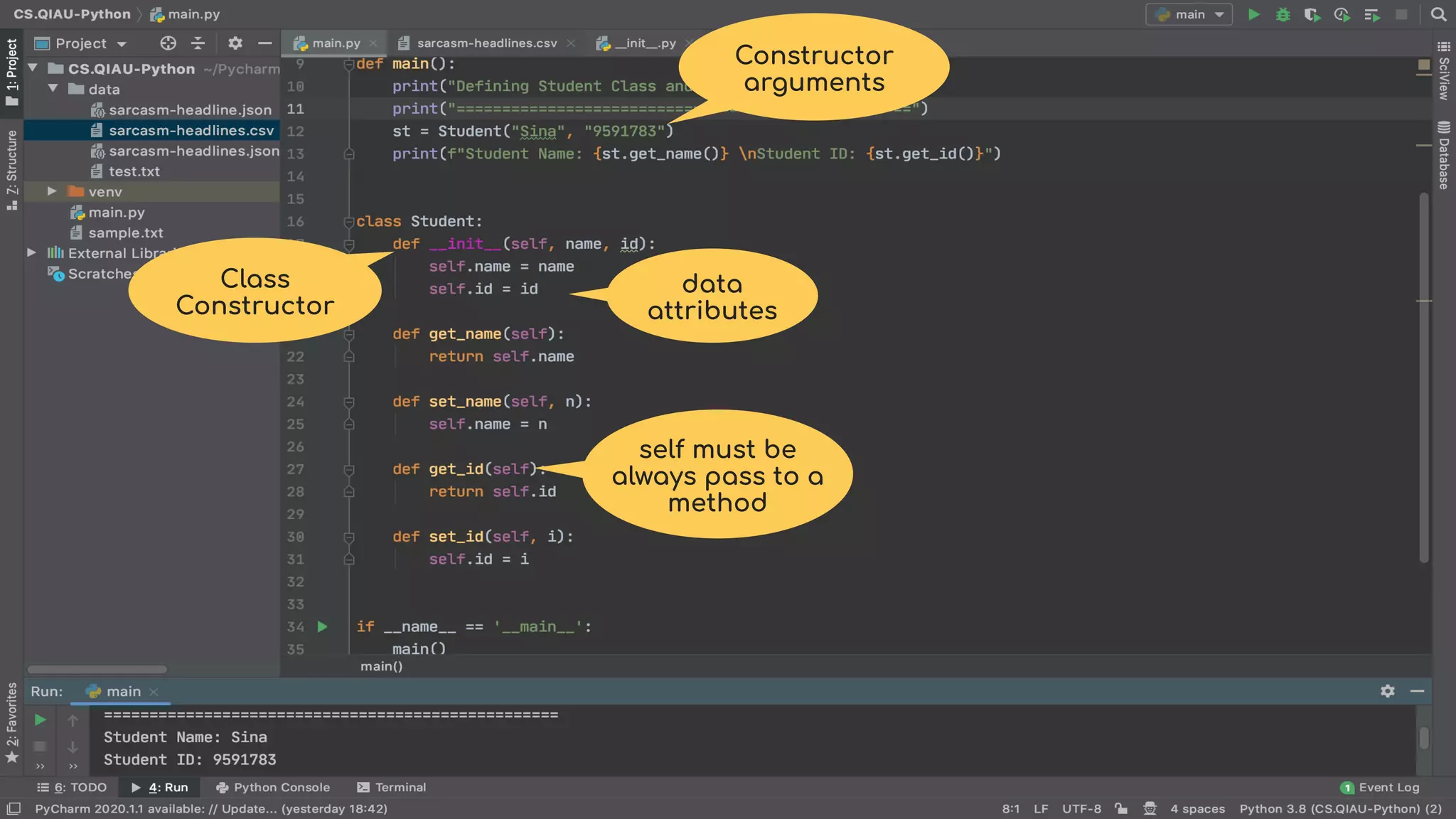
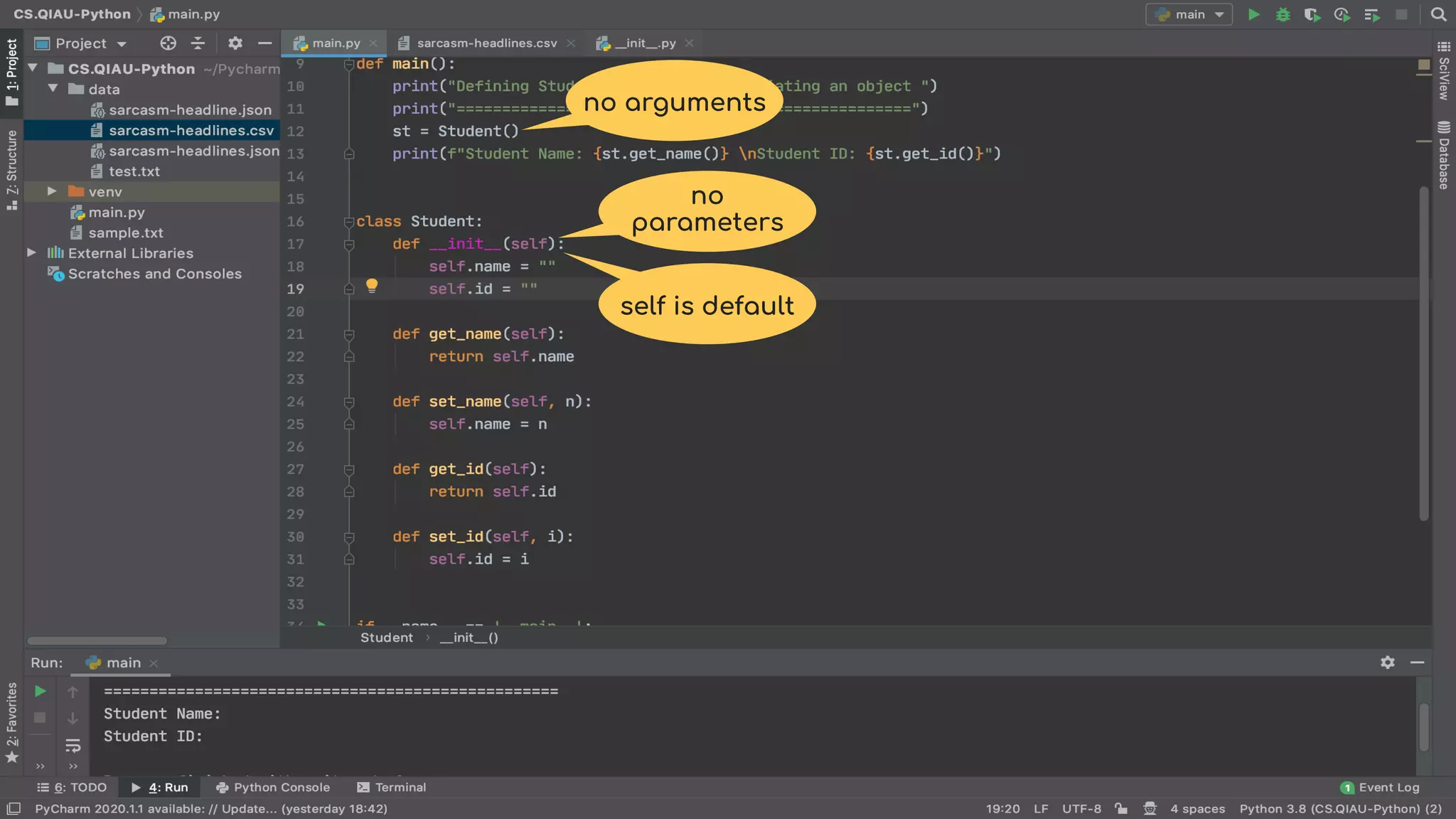
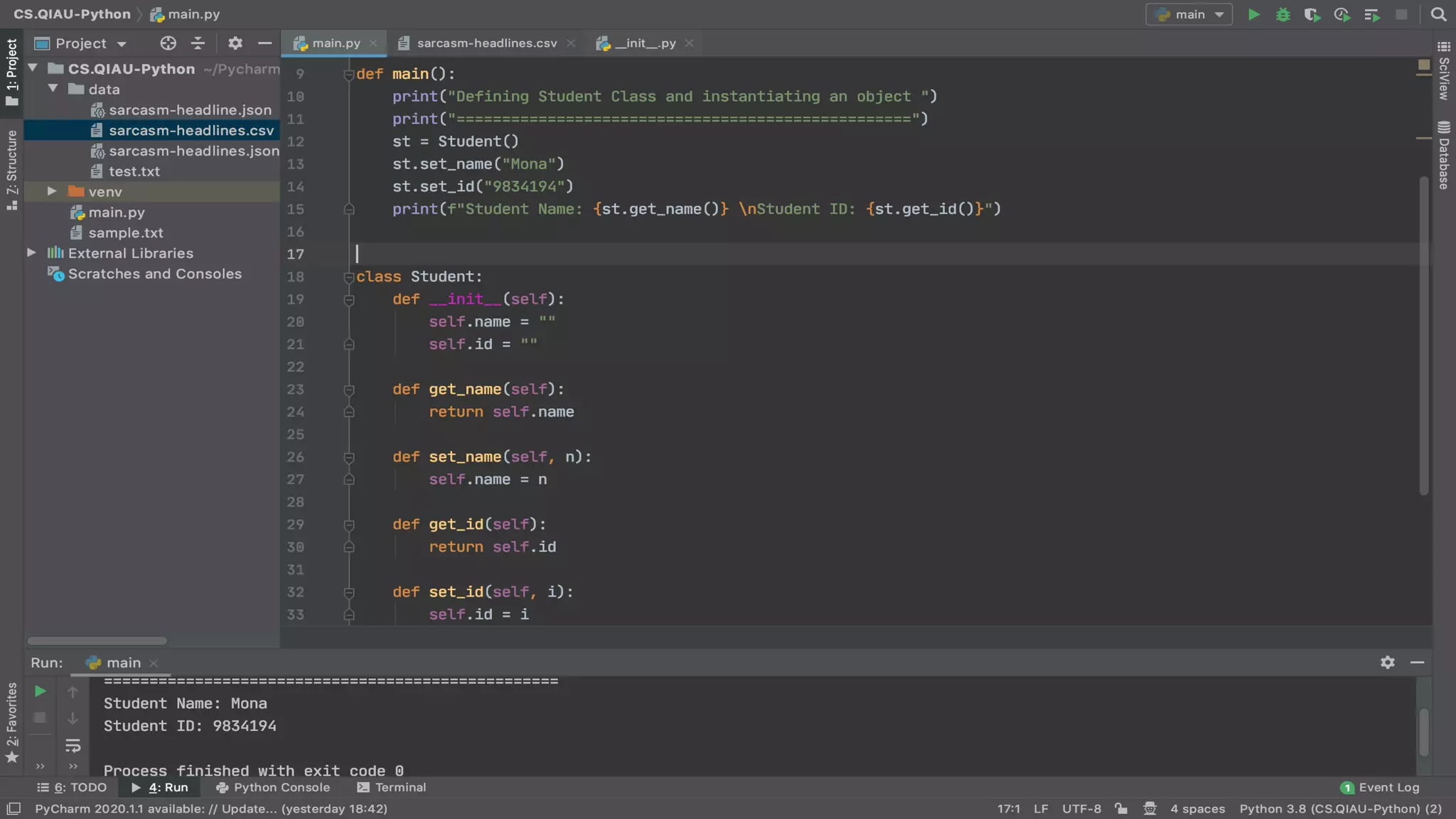
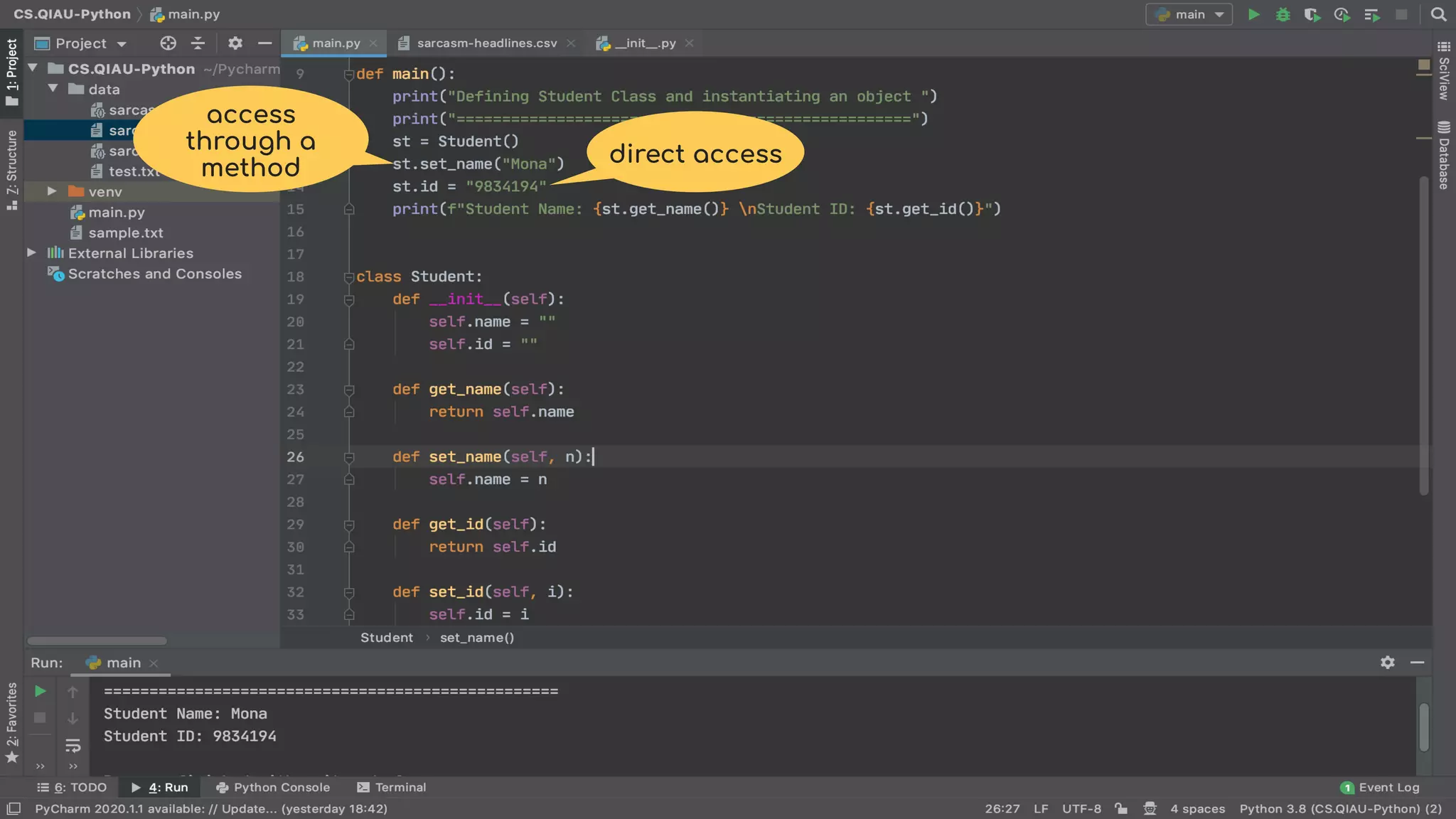
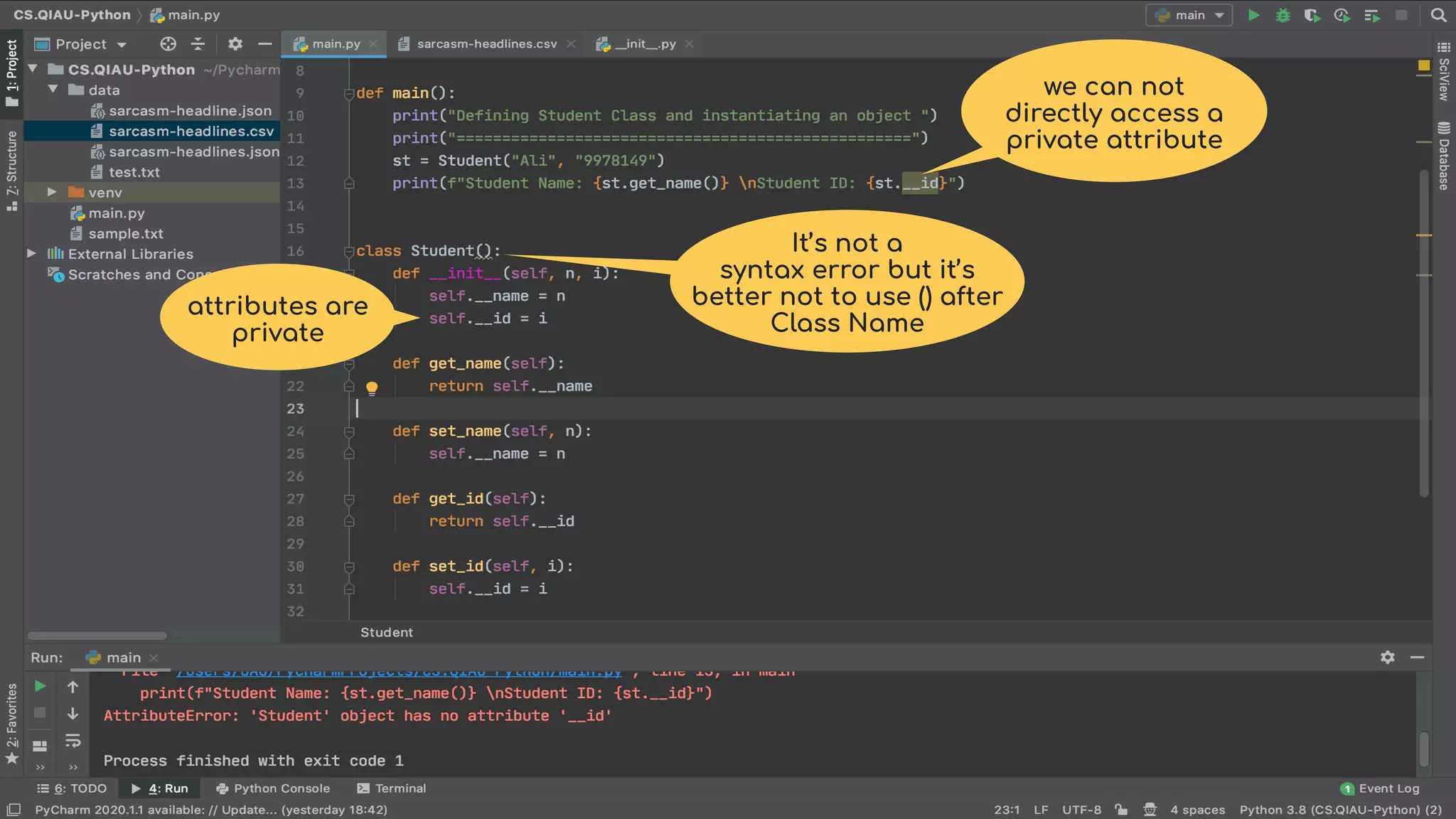
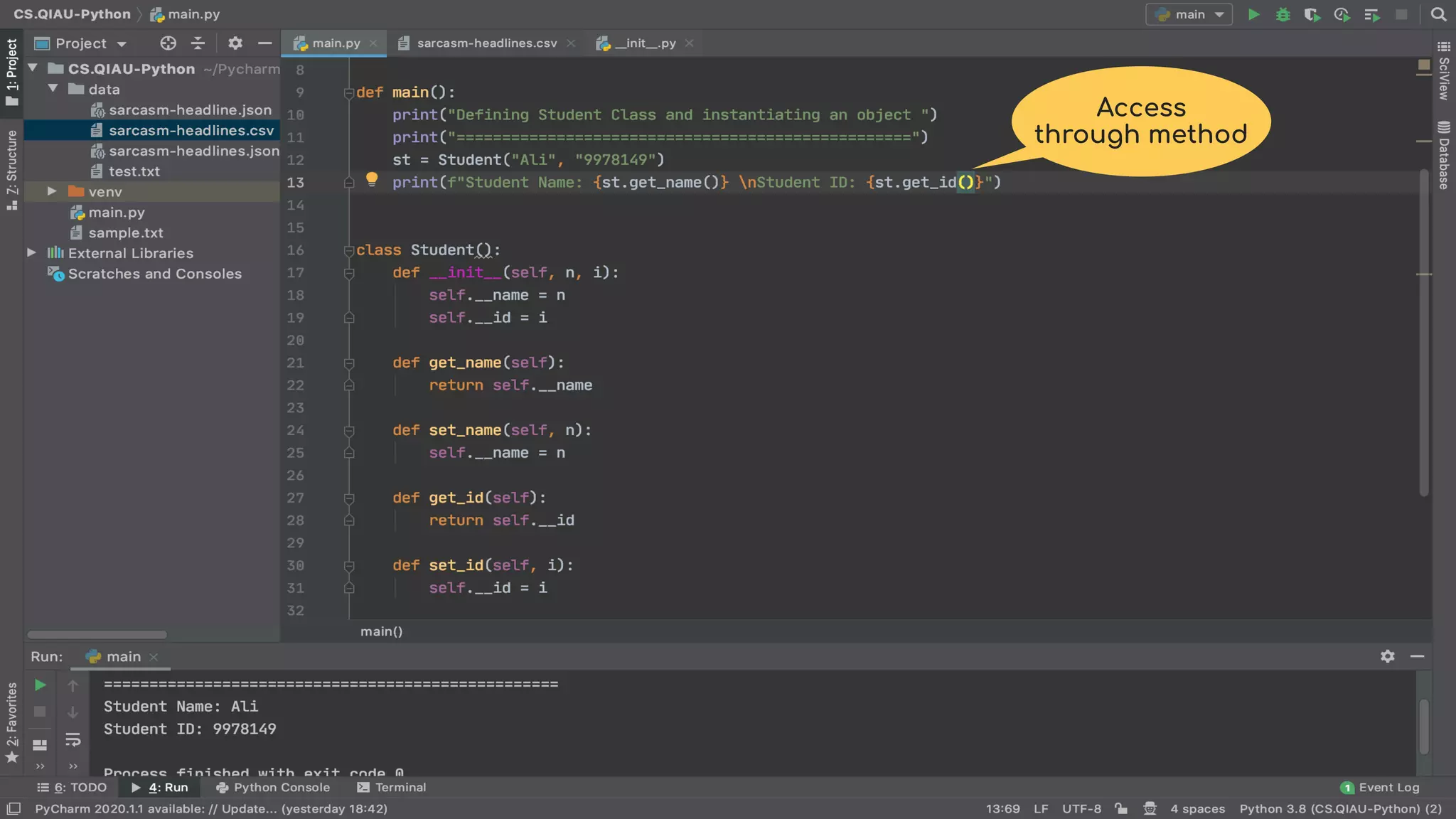
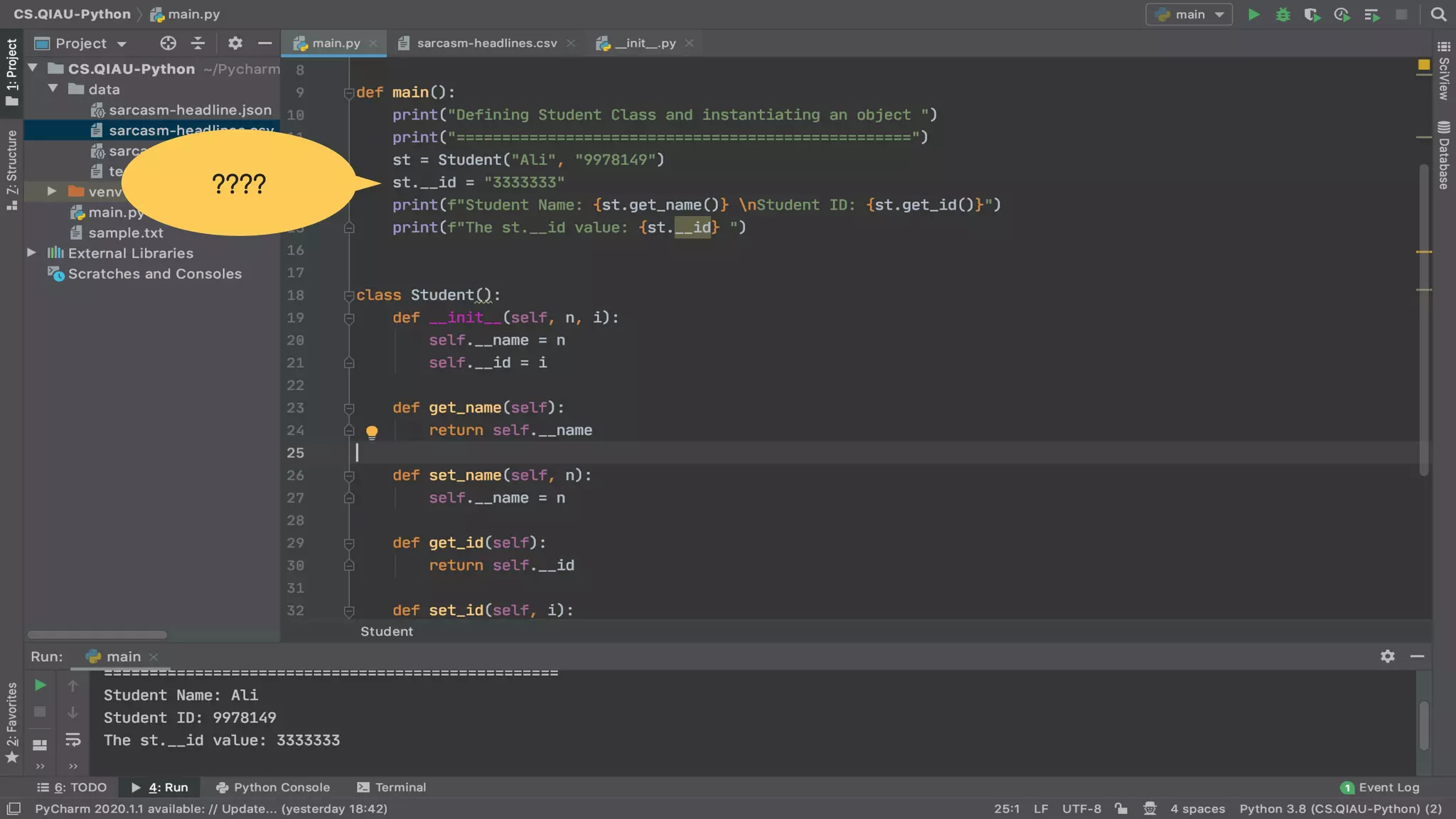
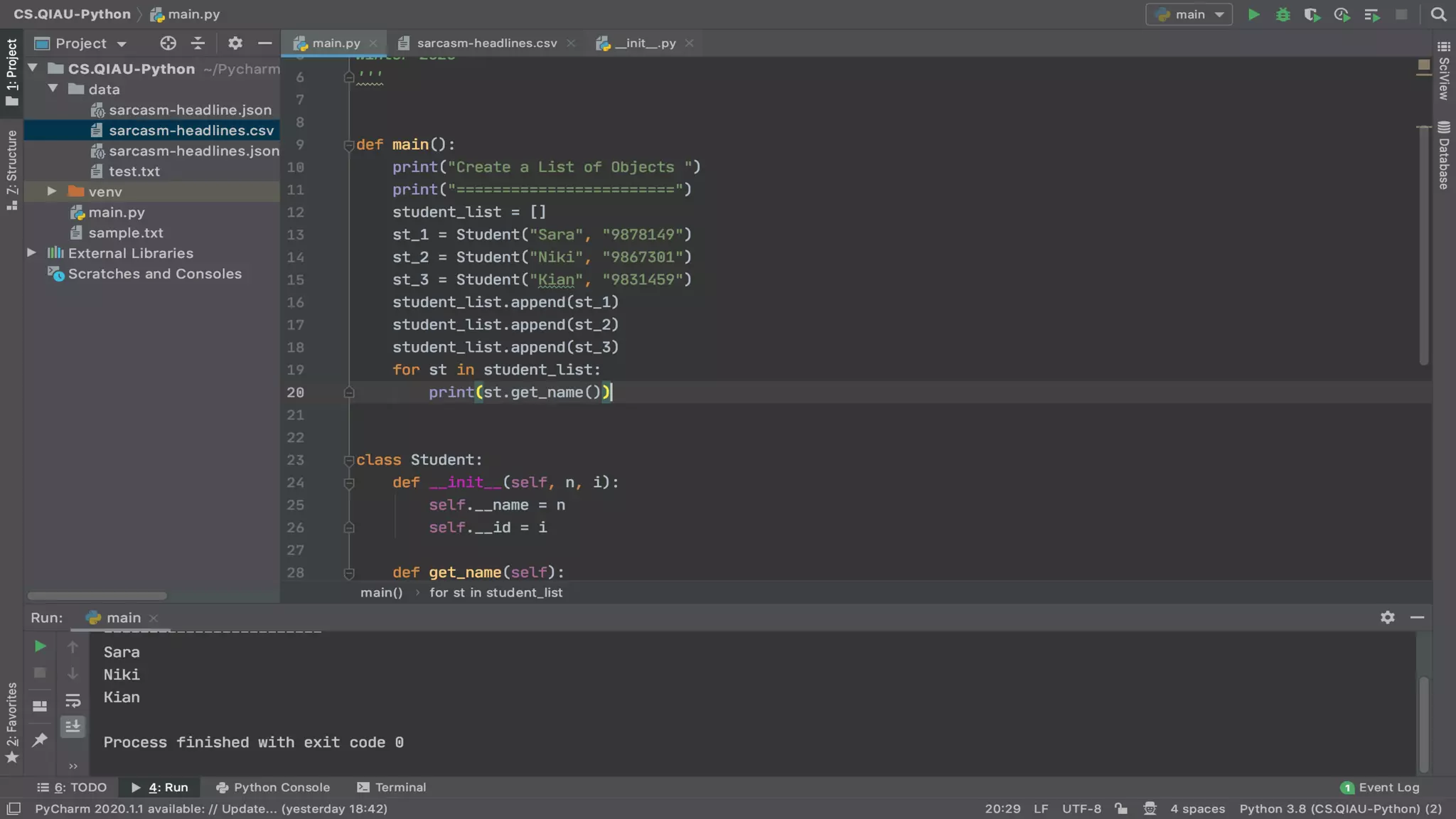
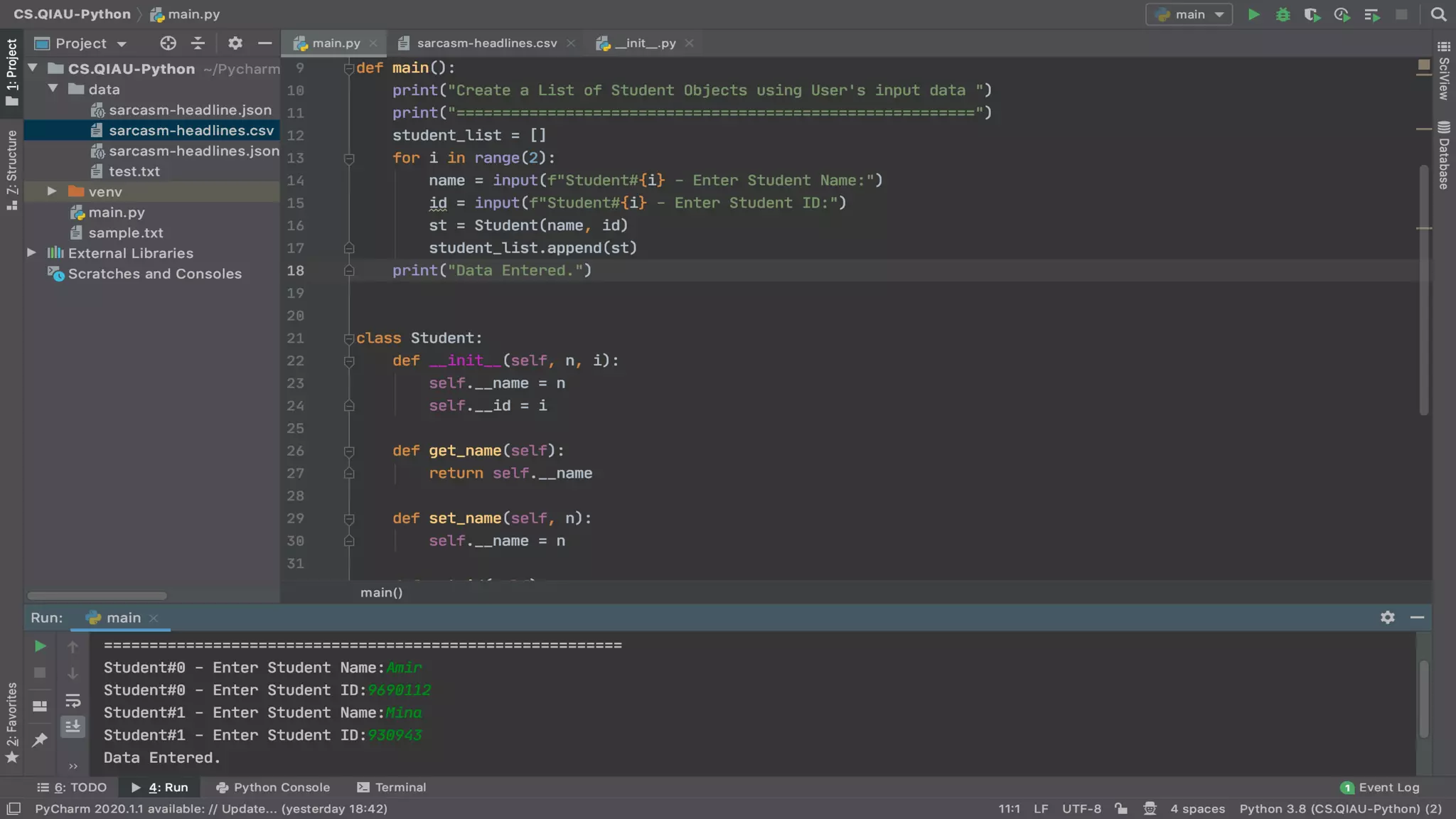
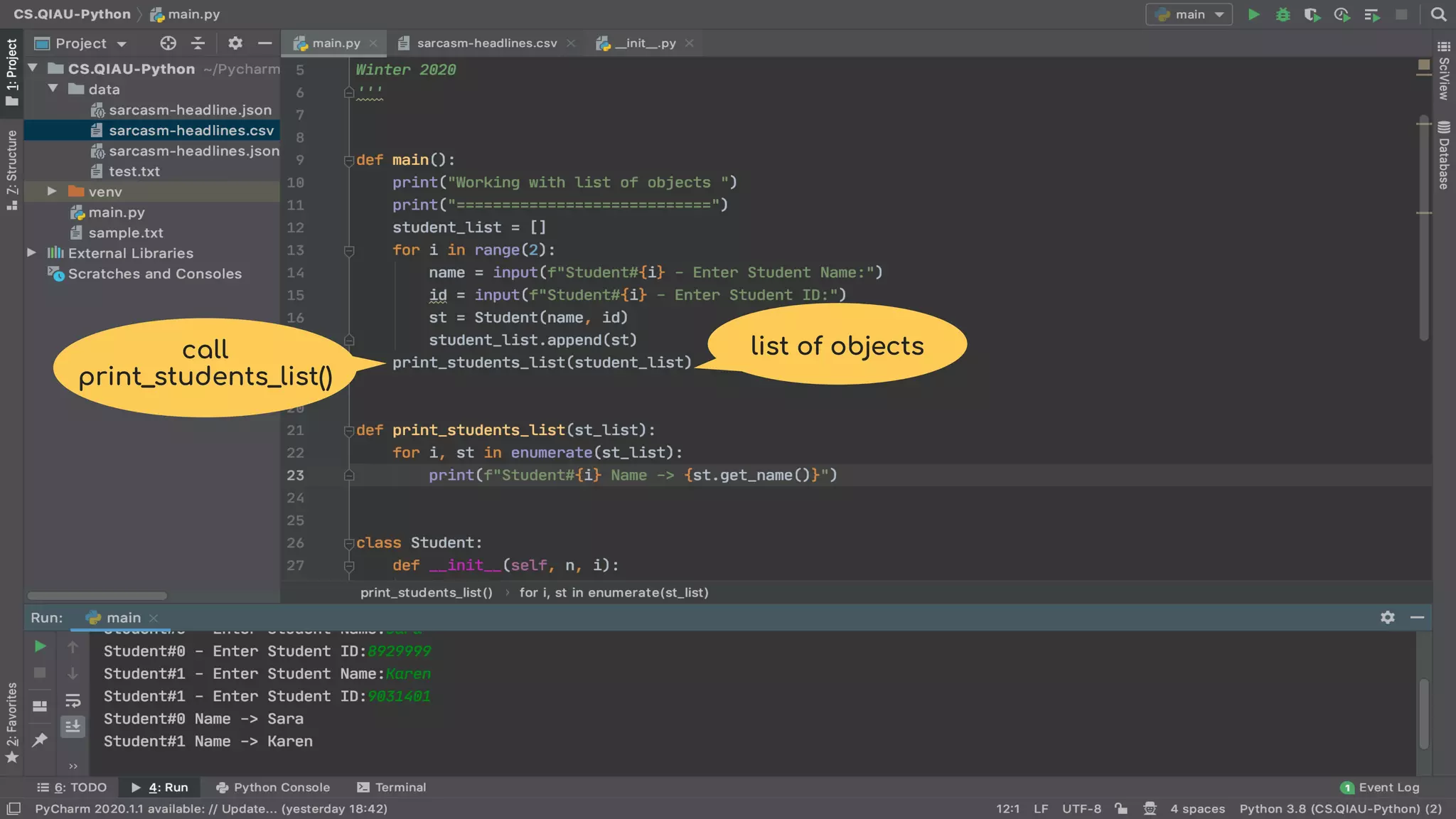
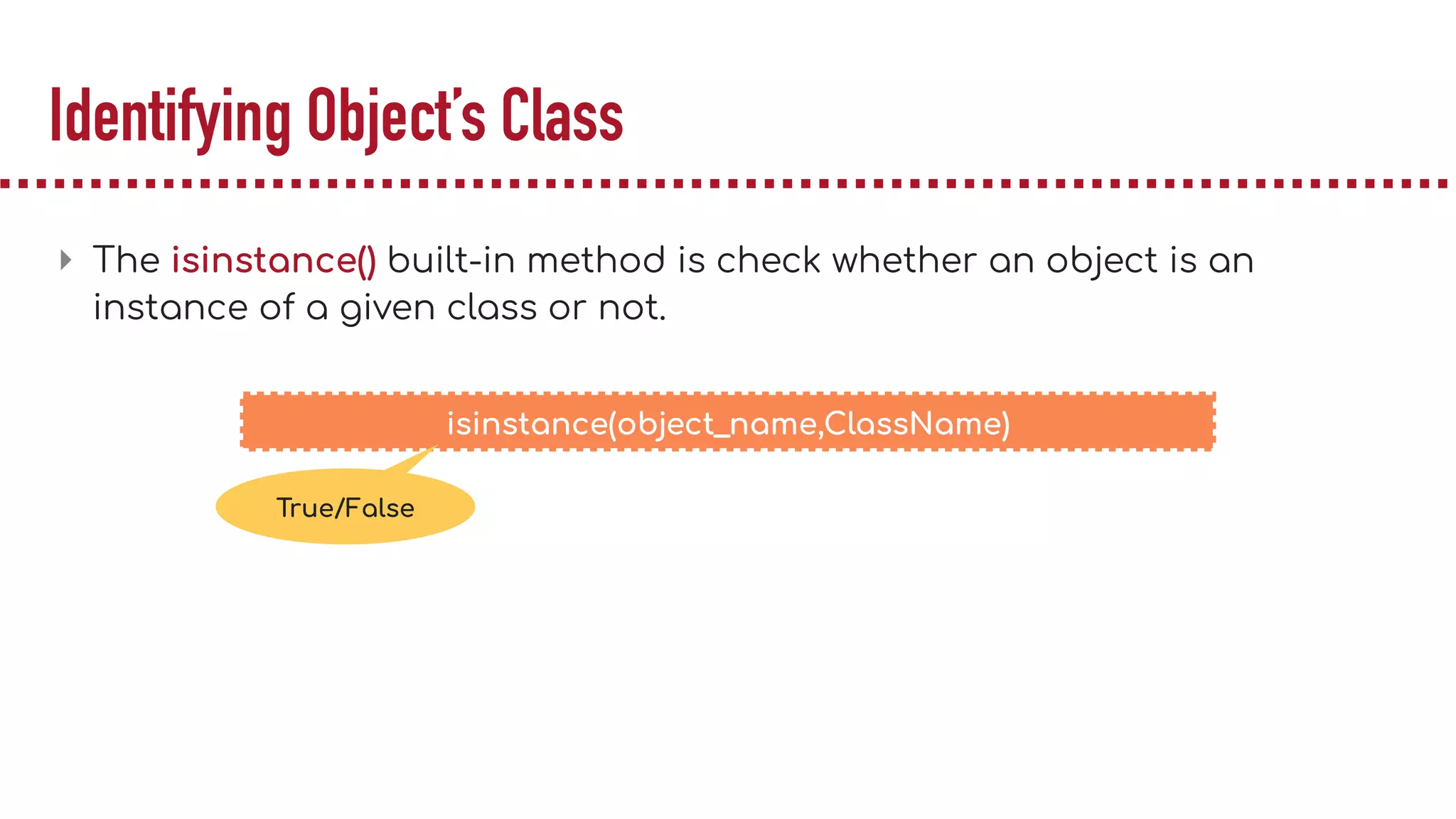
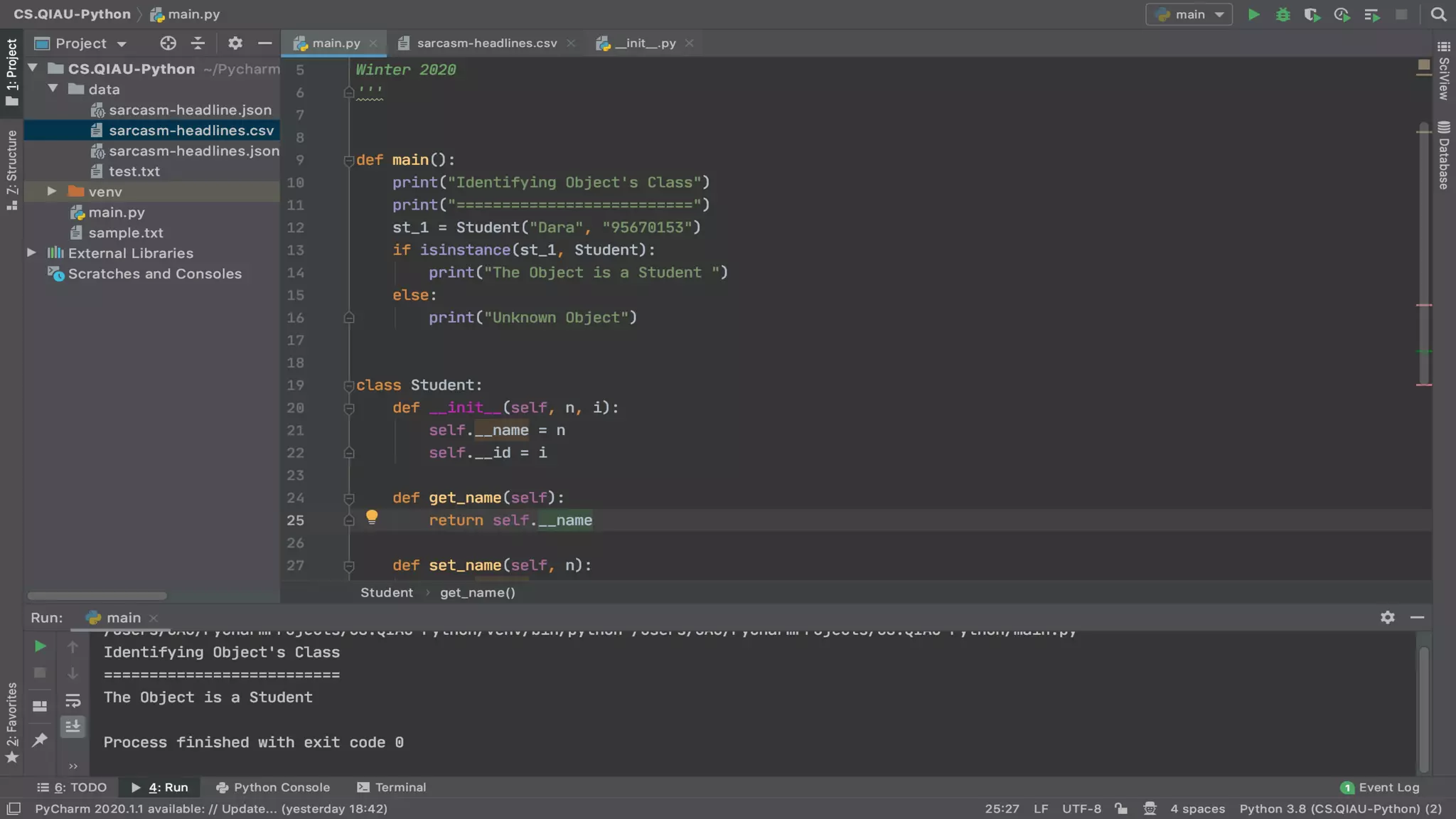
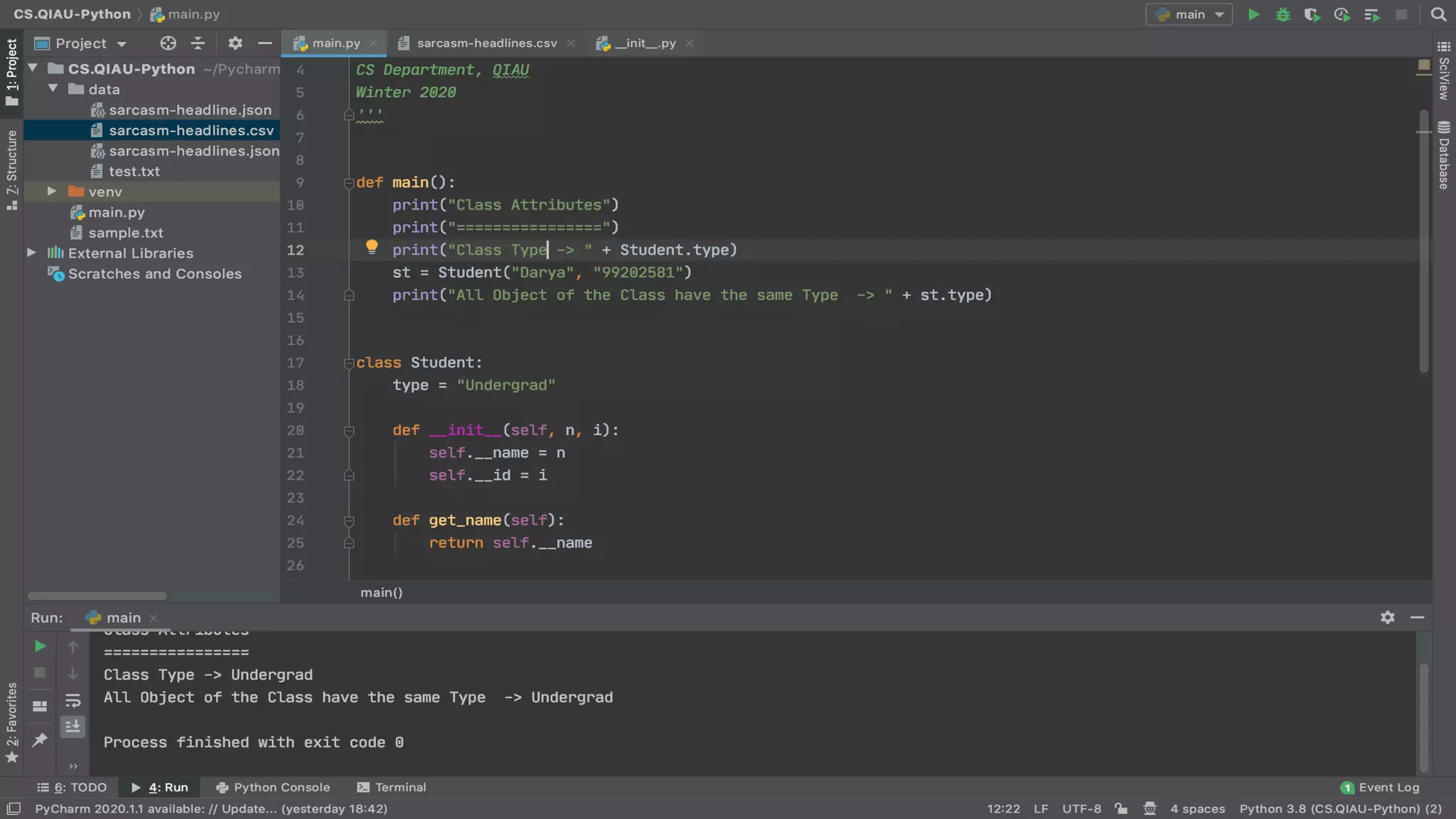
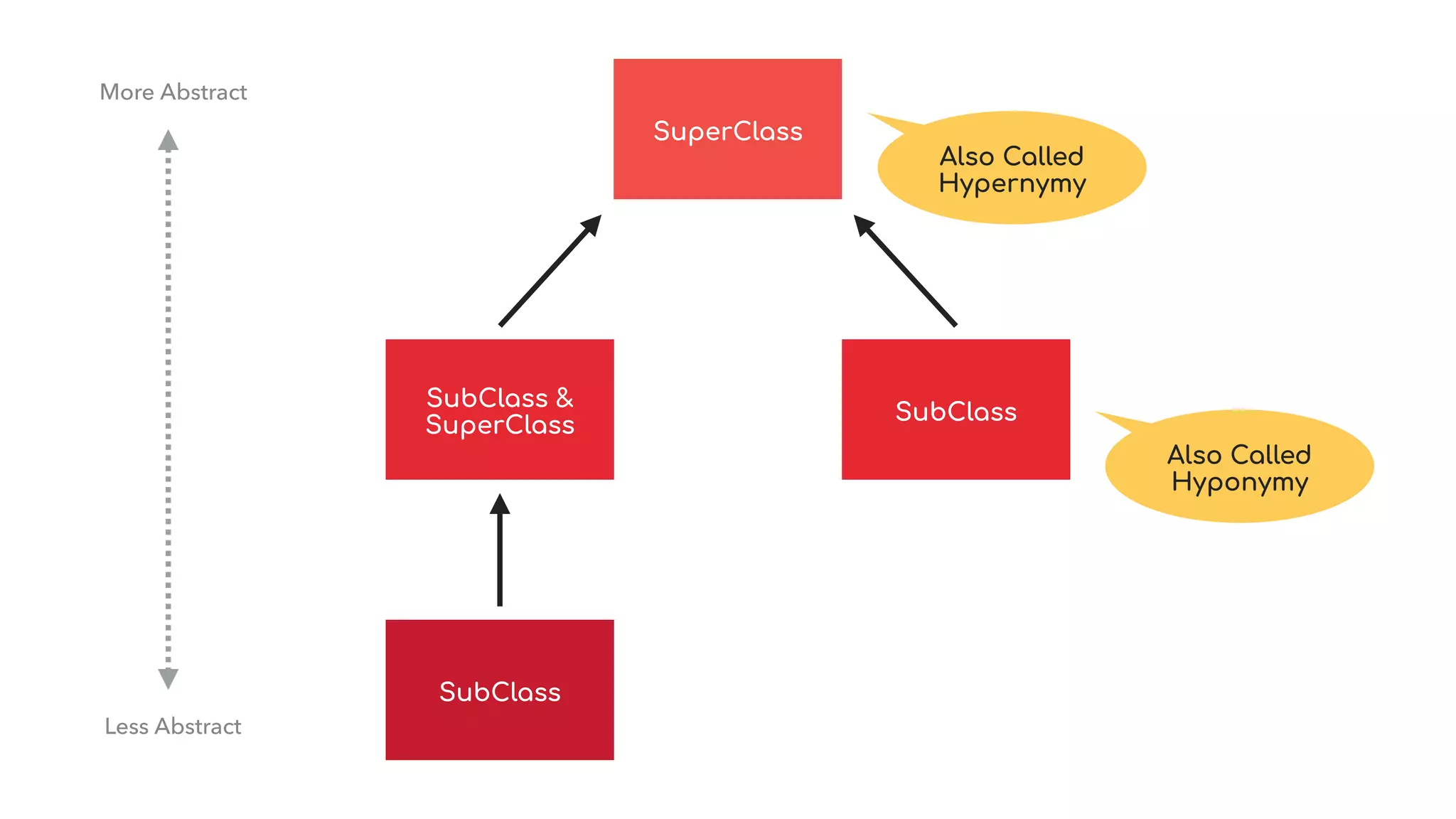
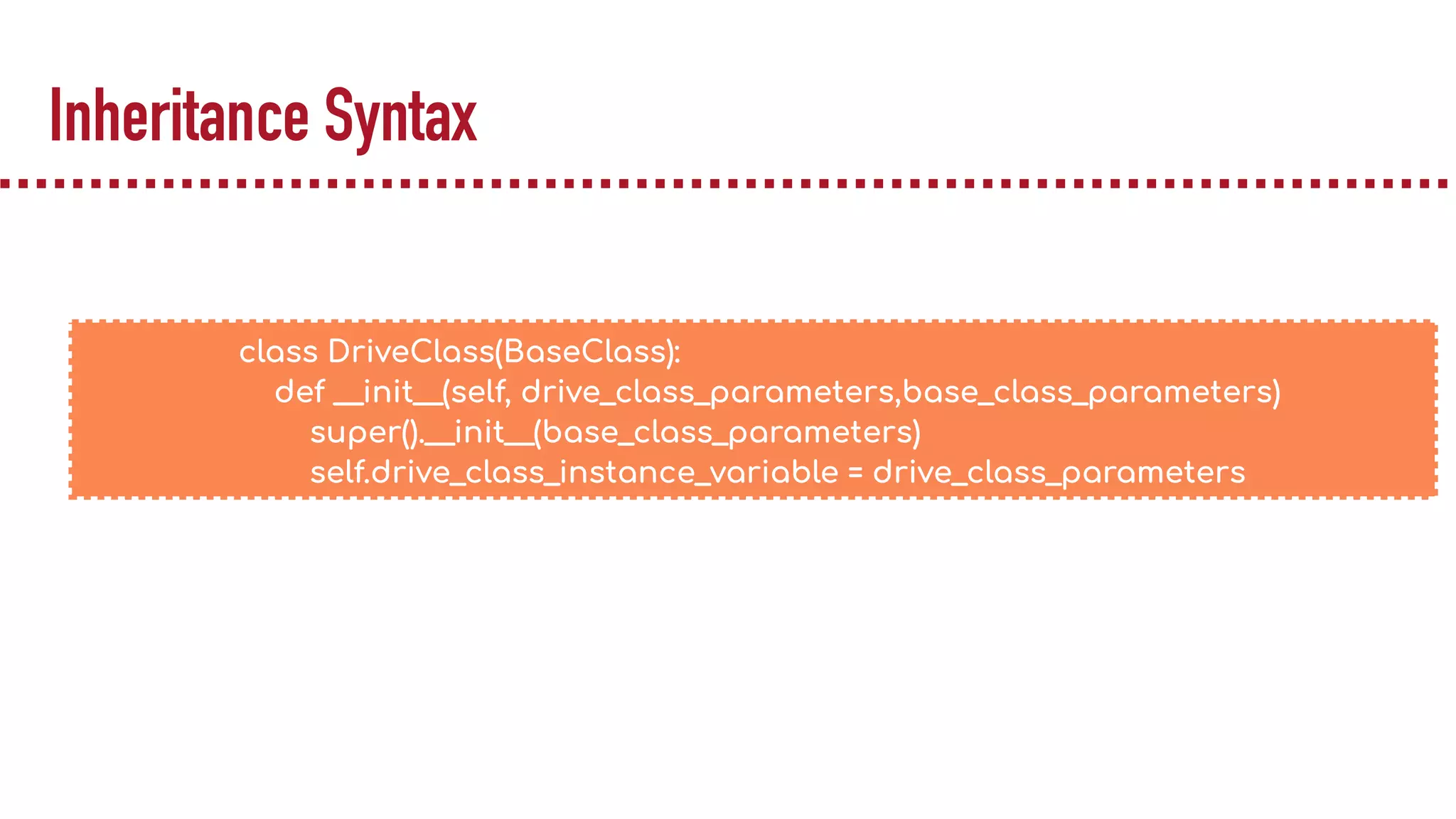
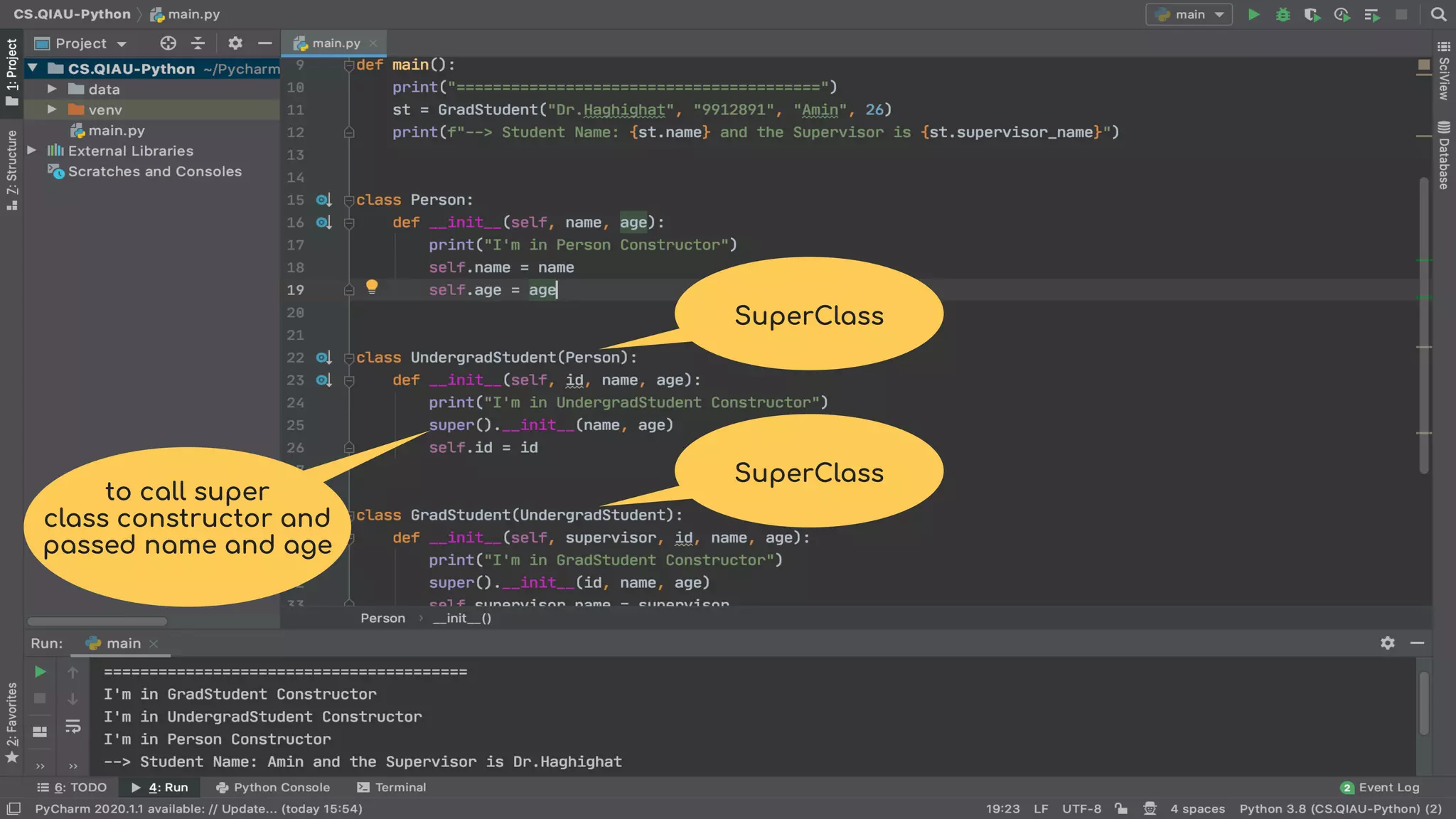
The document discusses object-oriented programming (OOP), highlighting its paradigms, concepts, and benefits such as code reusability and cleaner architecture. It explains key elements like classes, objects, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism, providing examples of their implementation in Python. The document also emphasizes the importance of abstraction and how objects model real-world scenarios while maintaining complexity behind high-level interfaces.