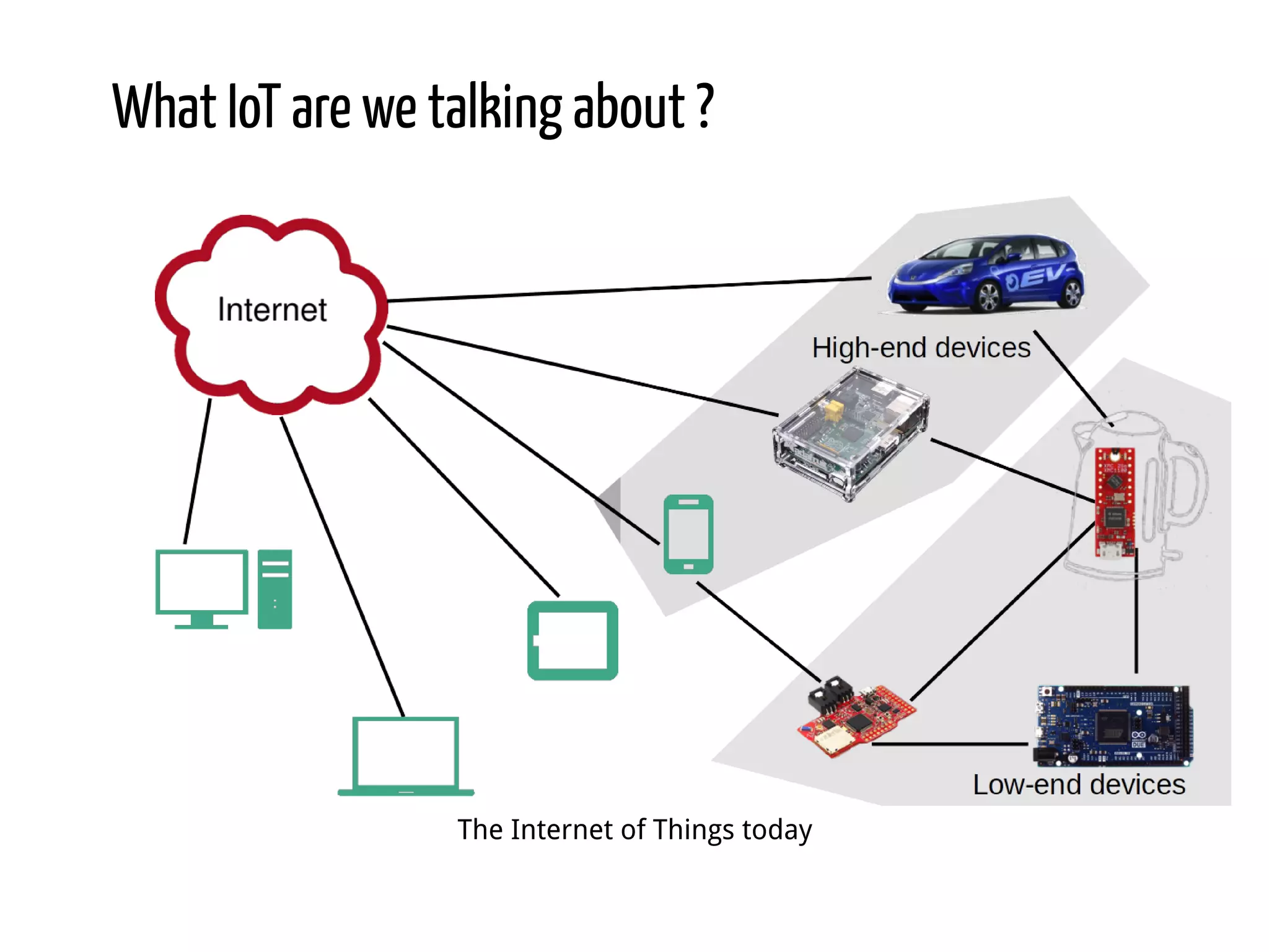
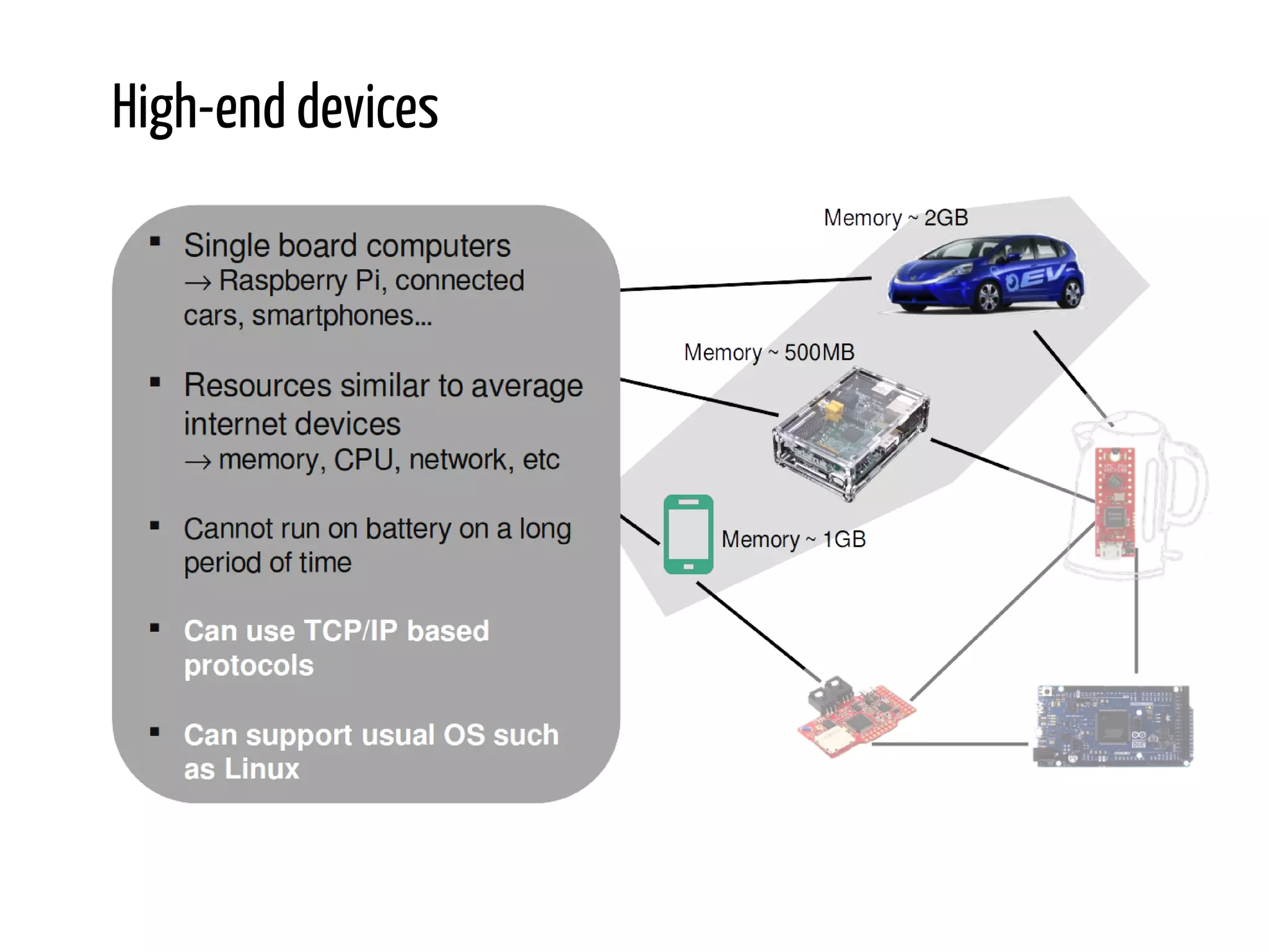
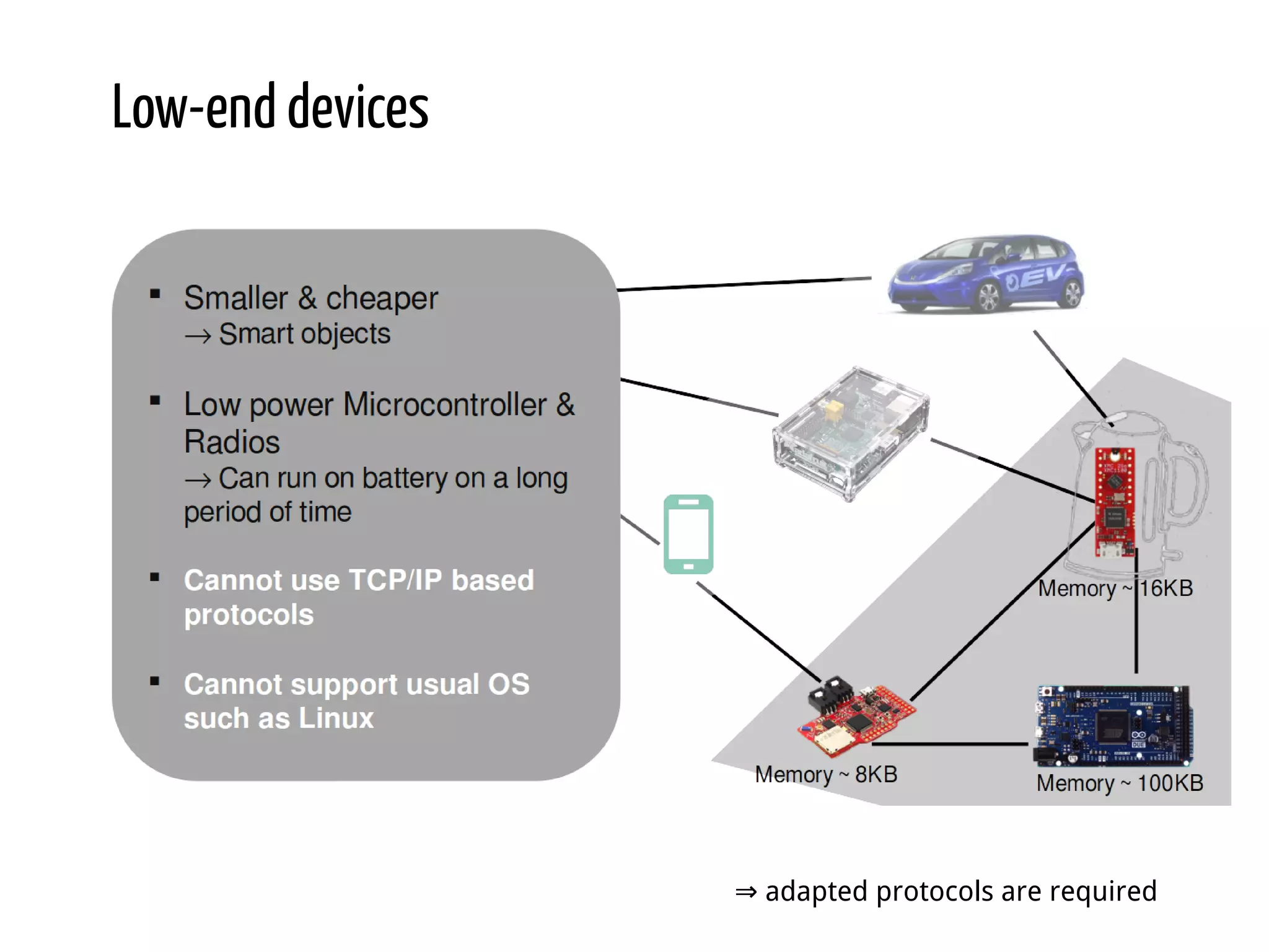
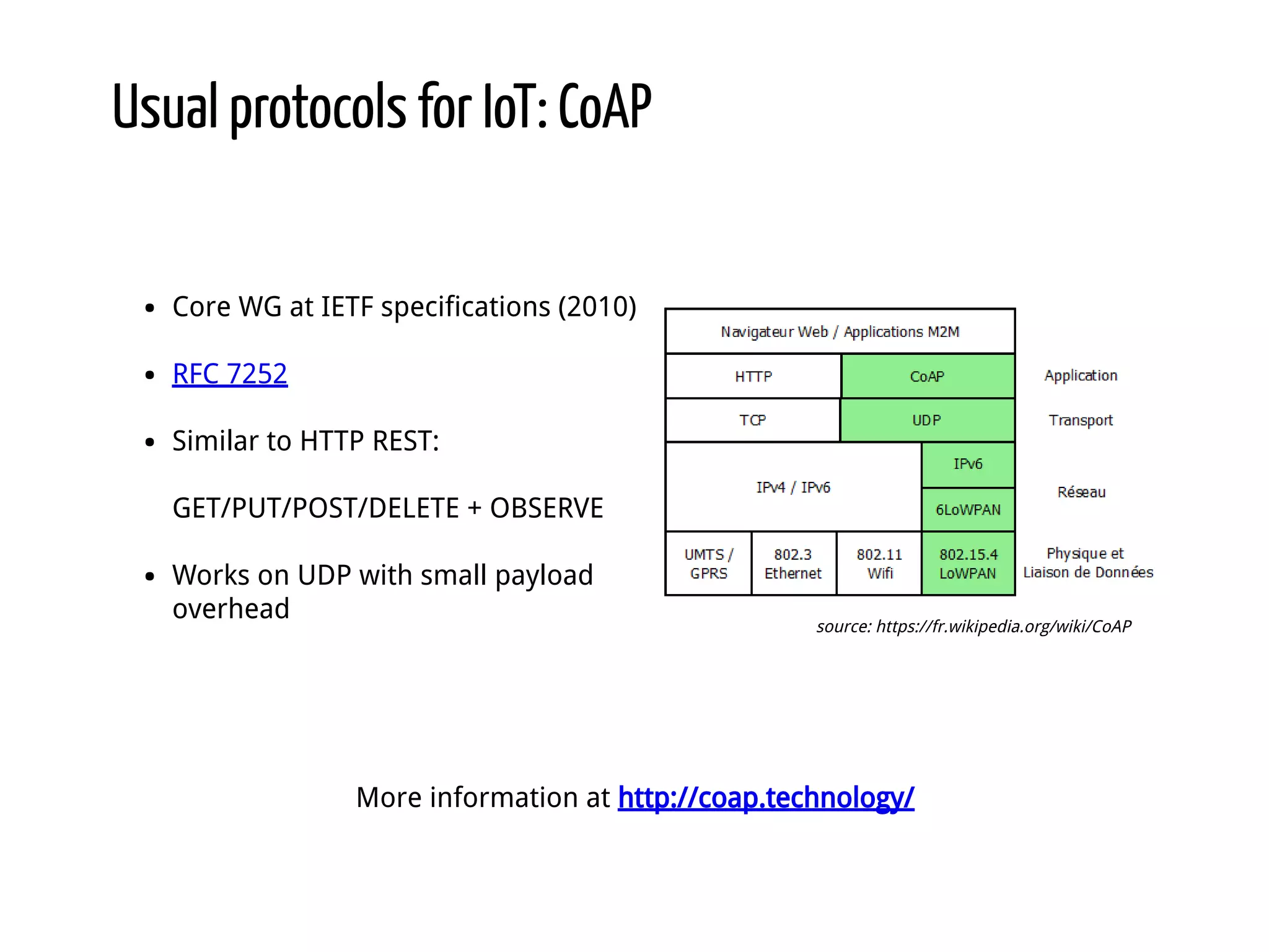
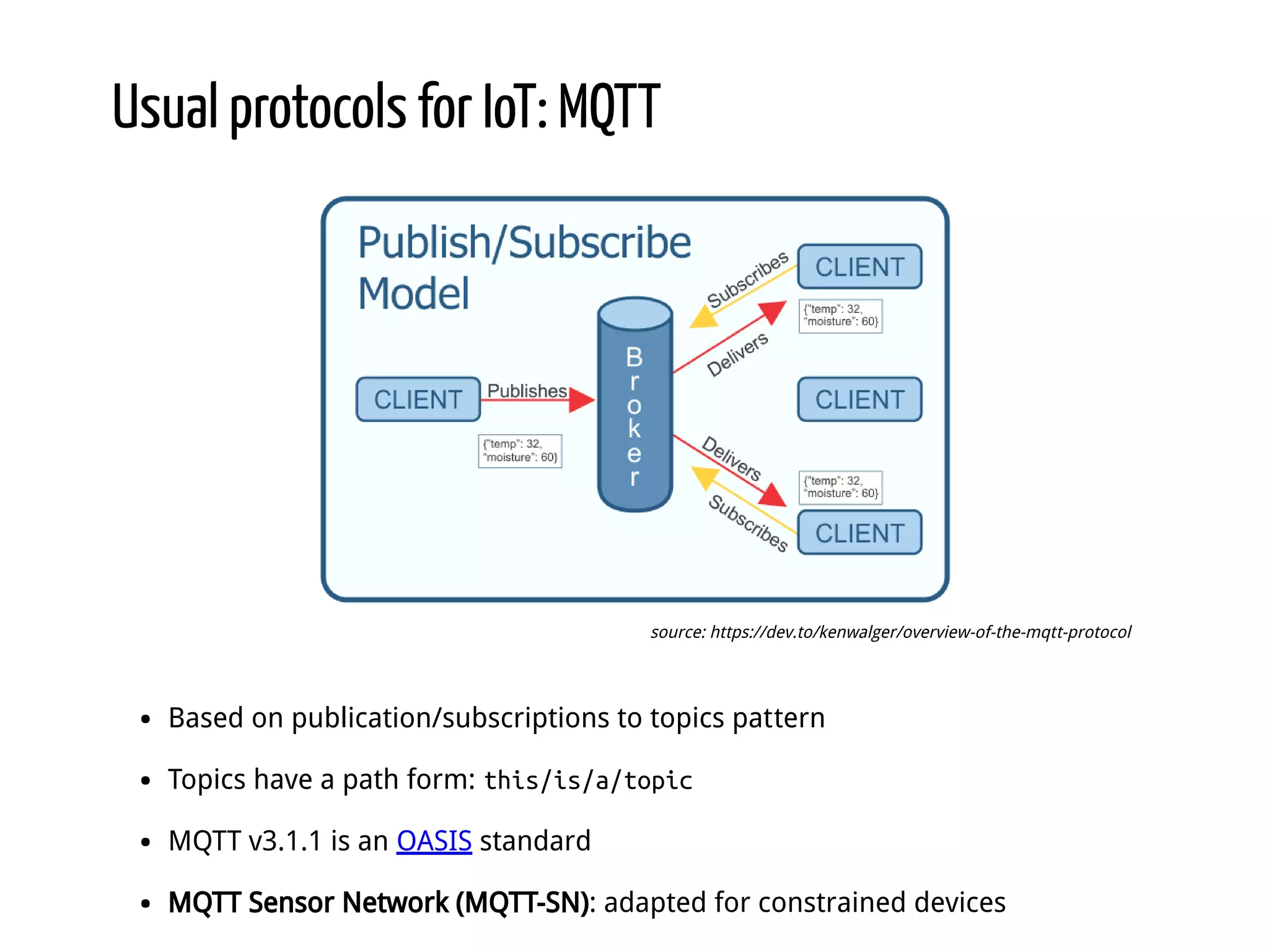
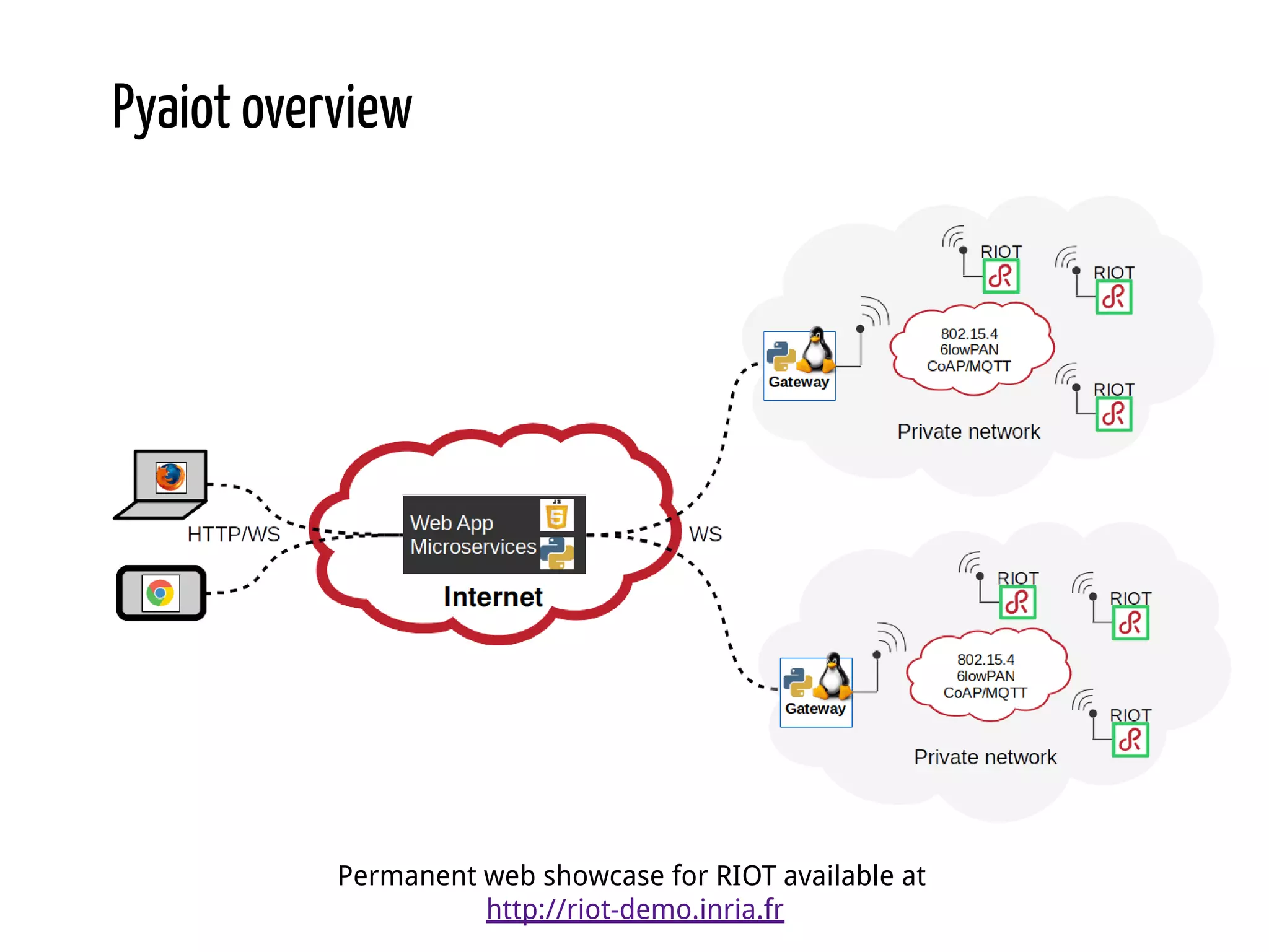
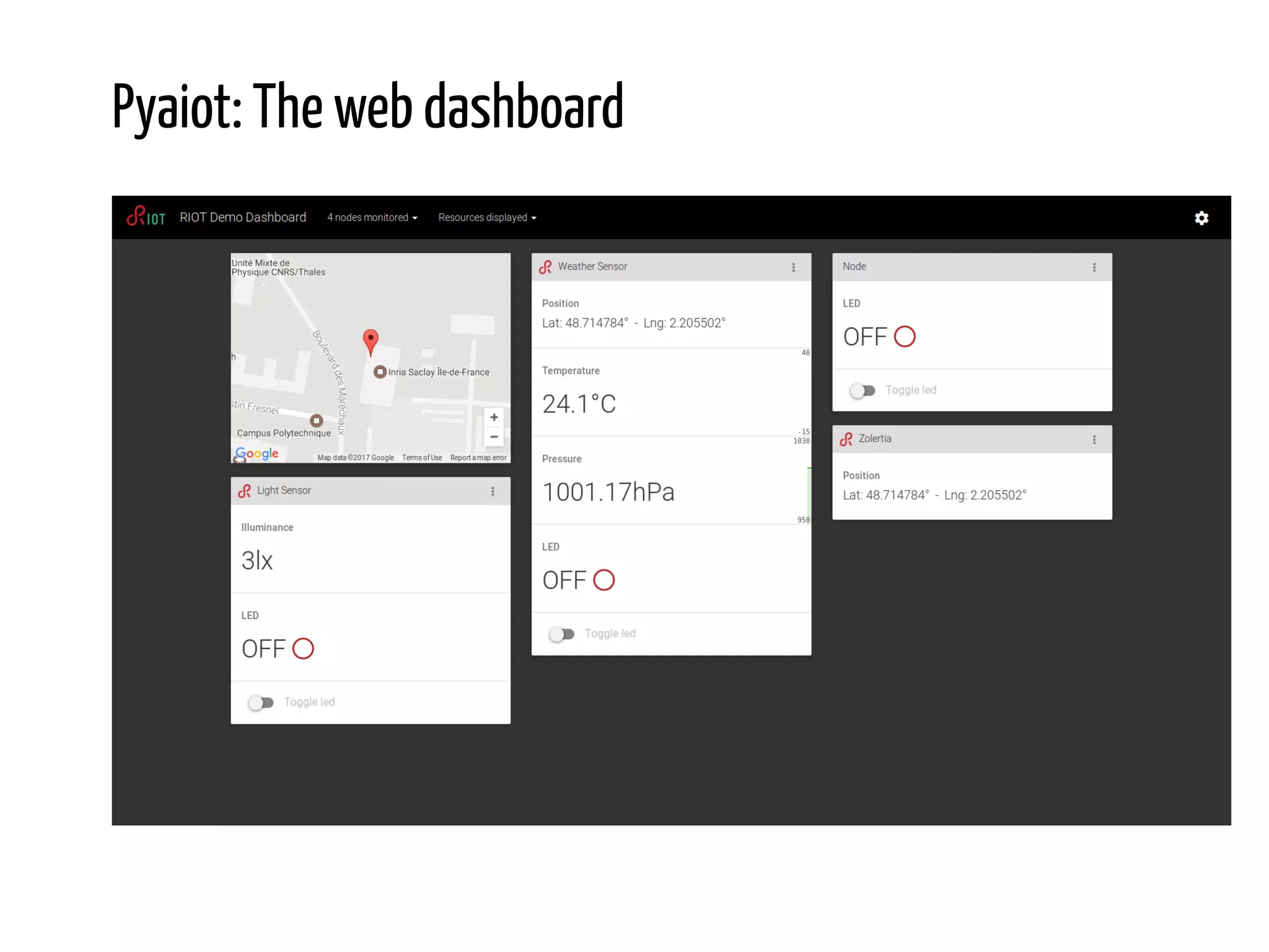
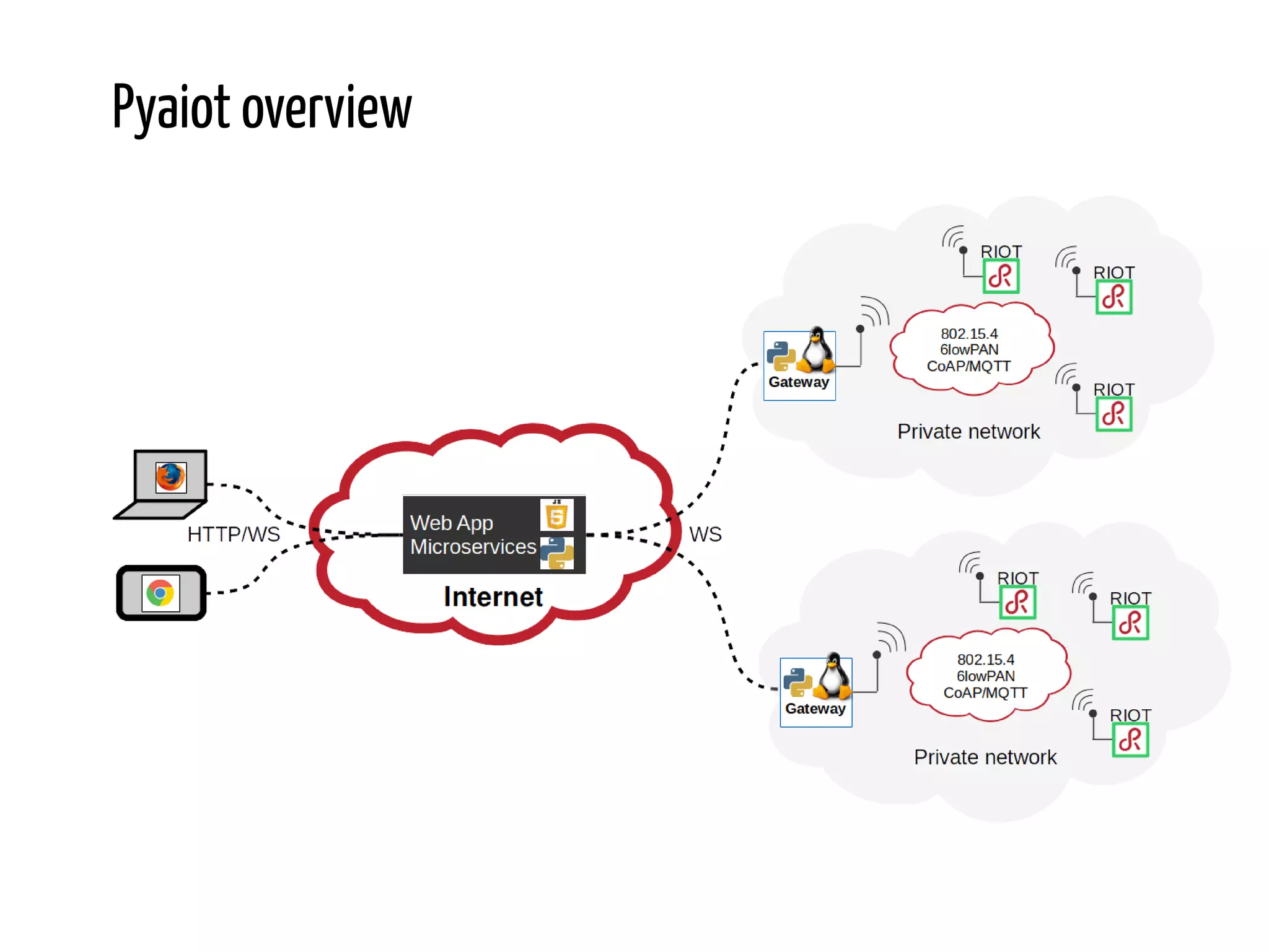
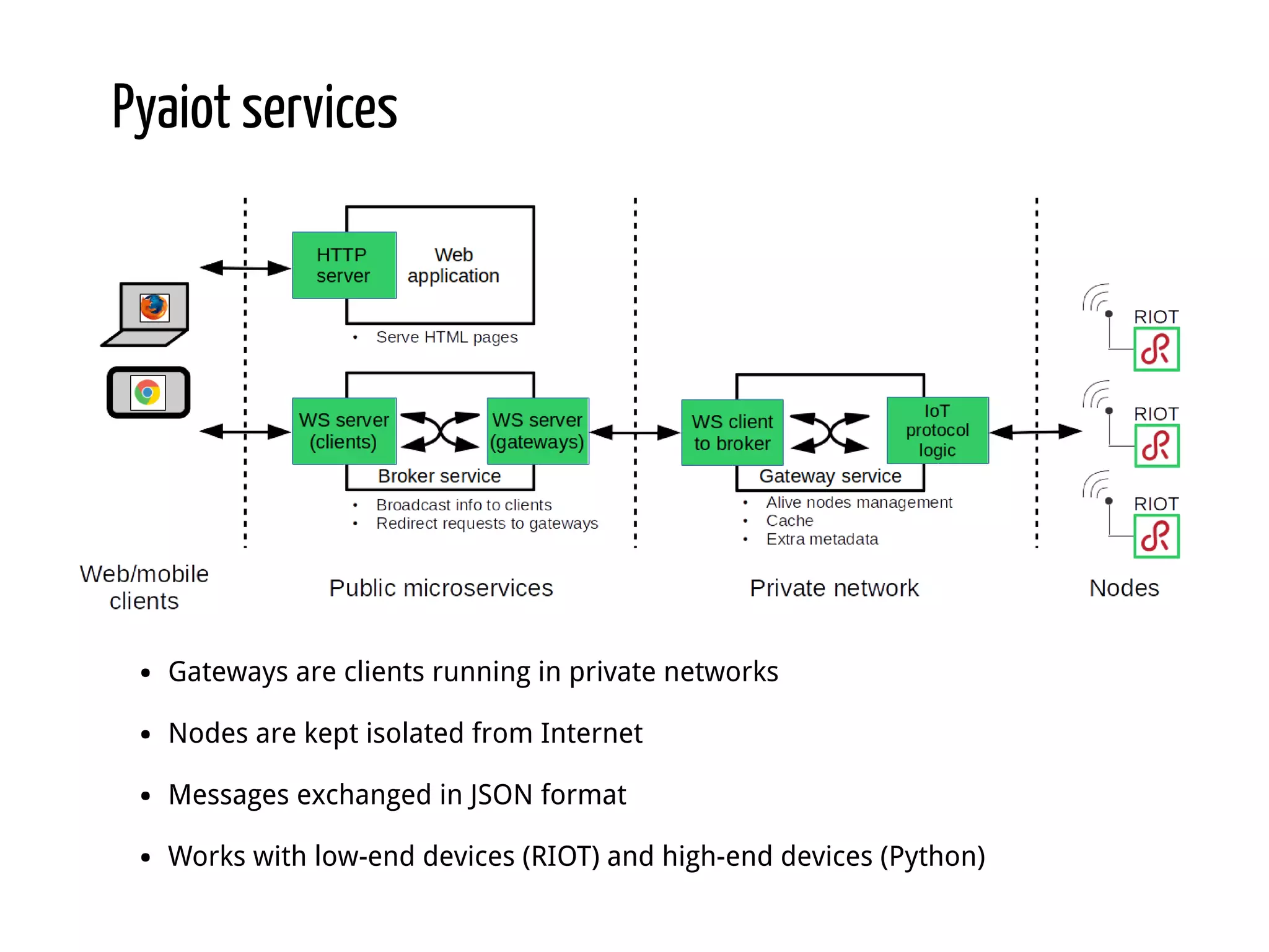
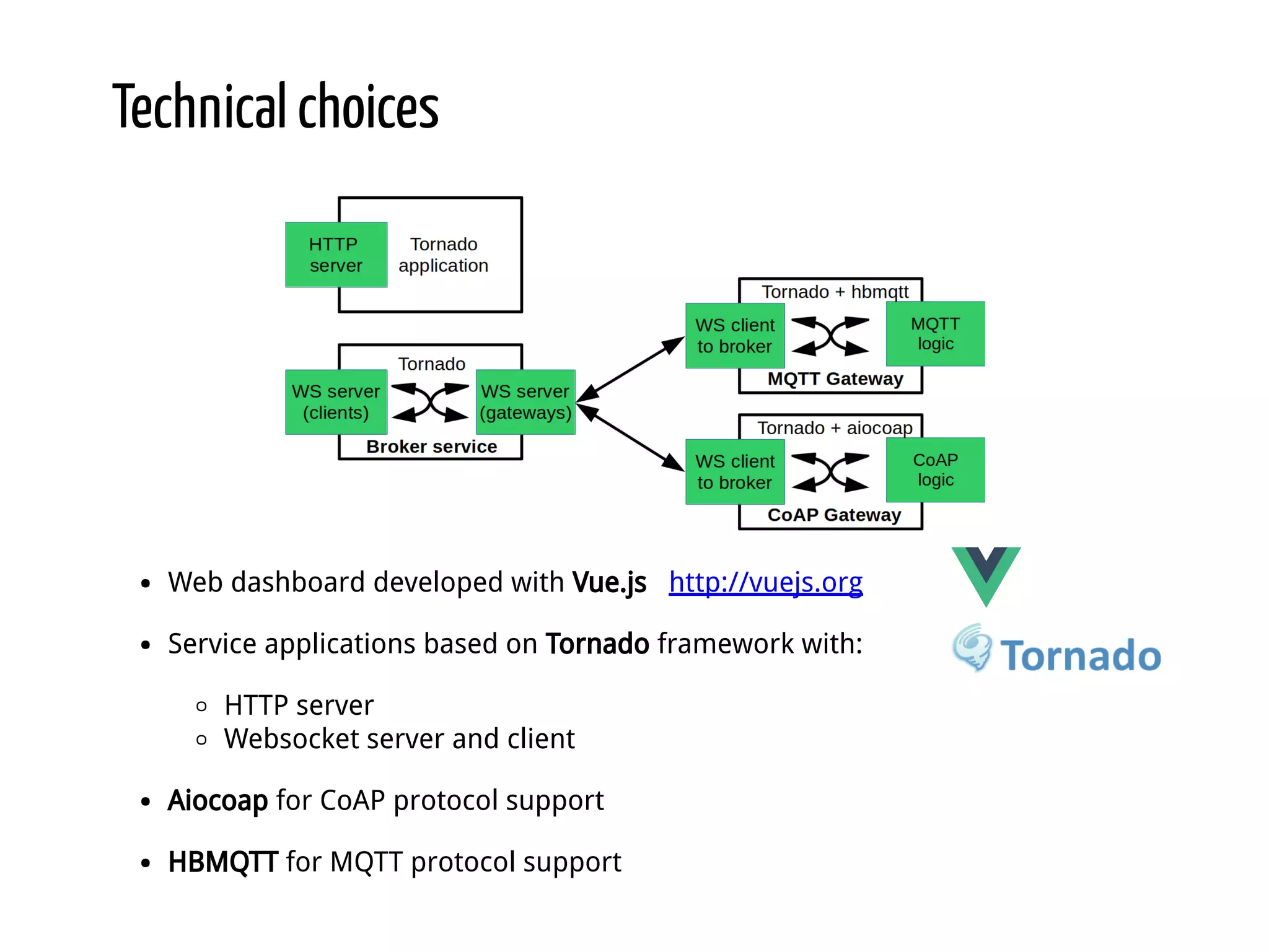
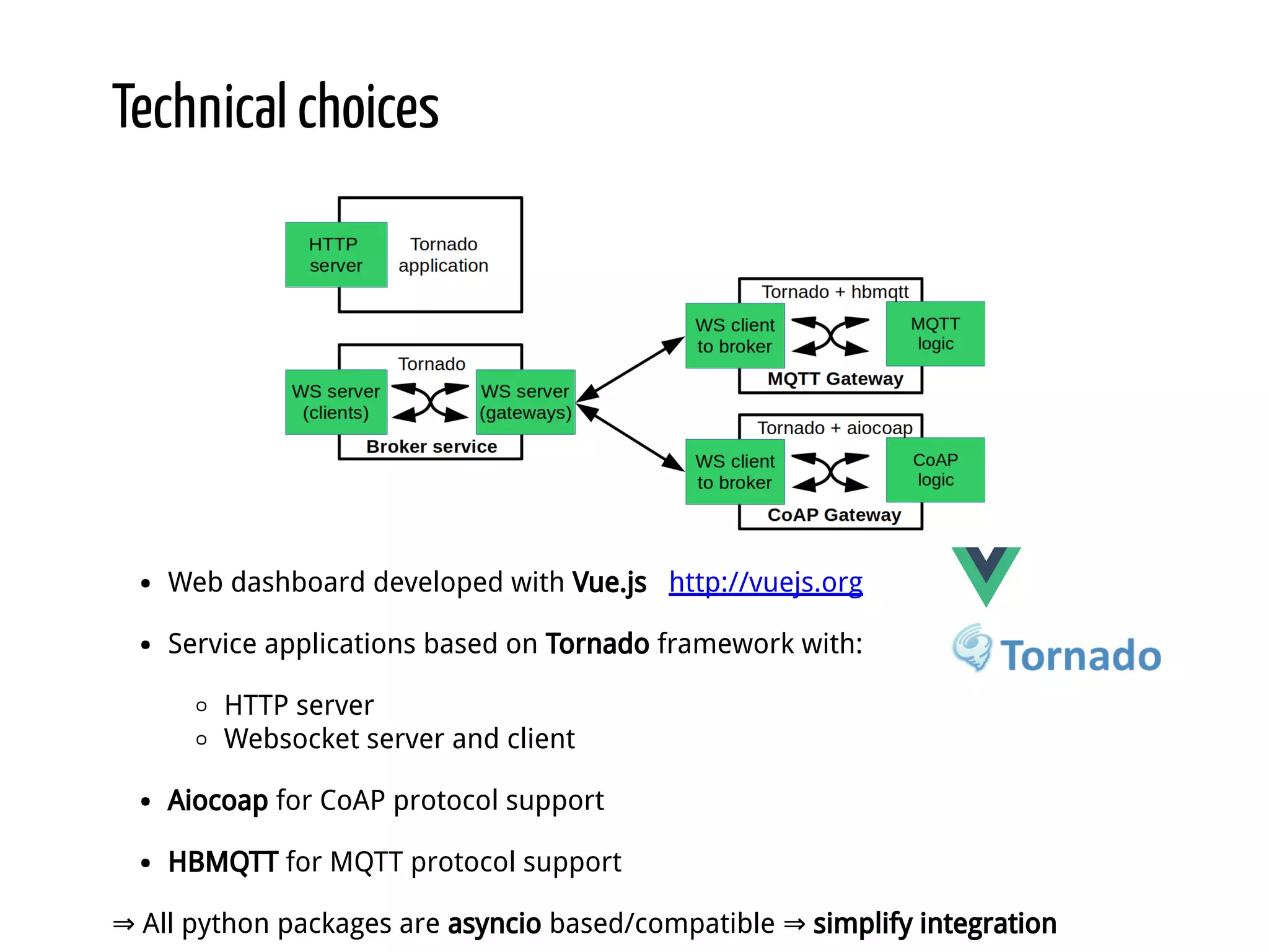
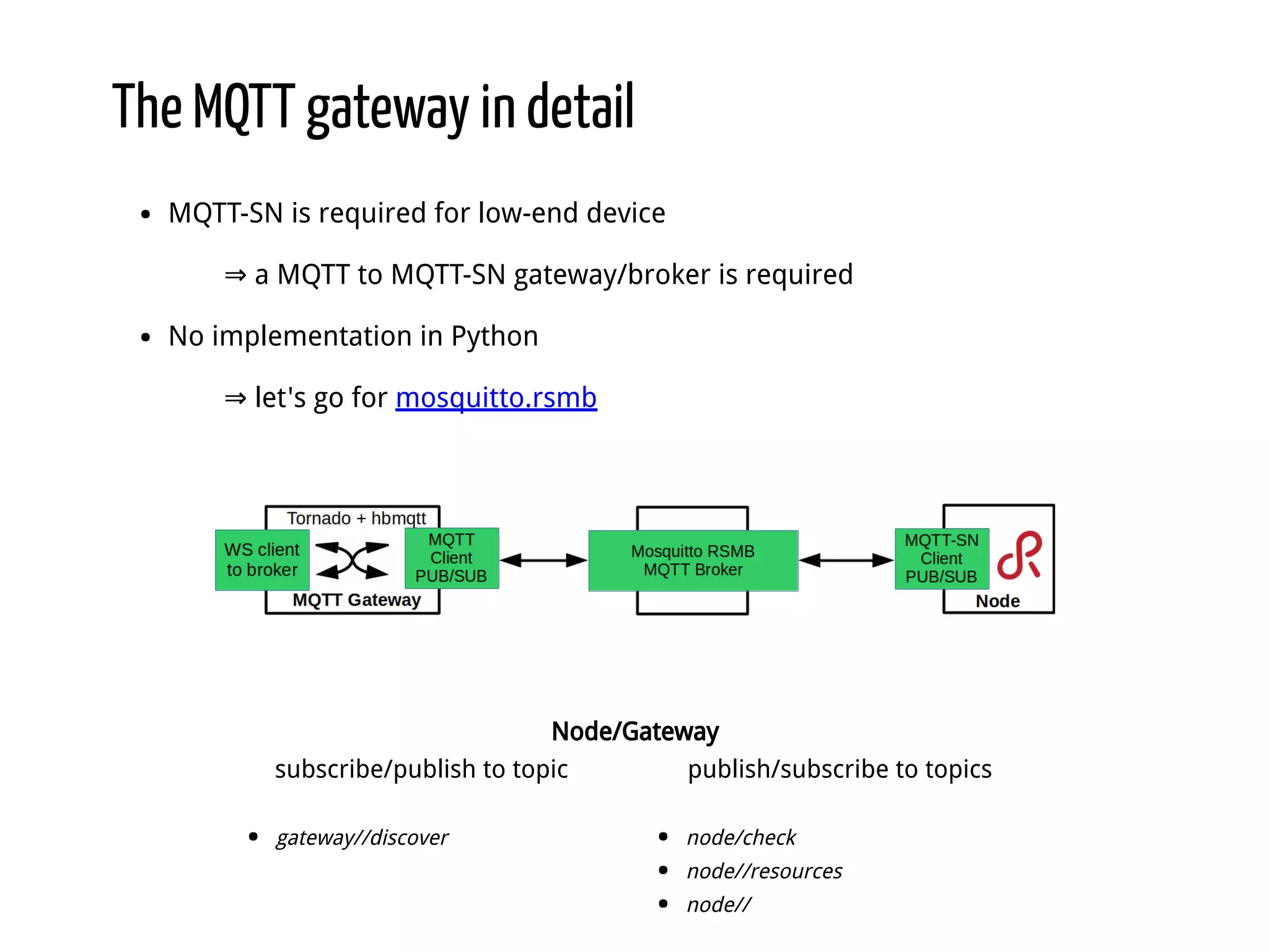
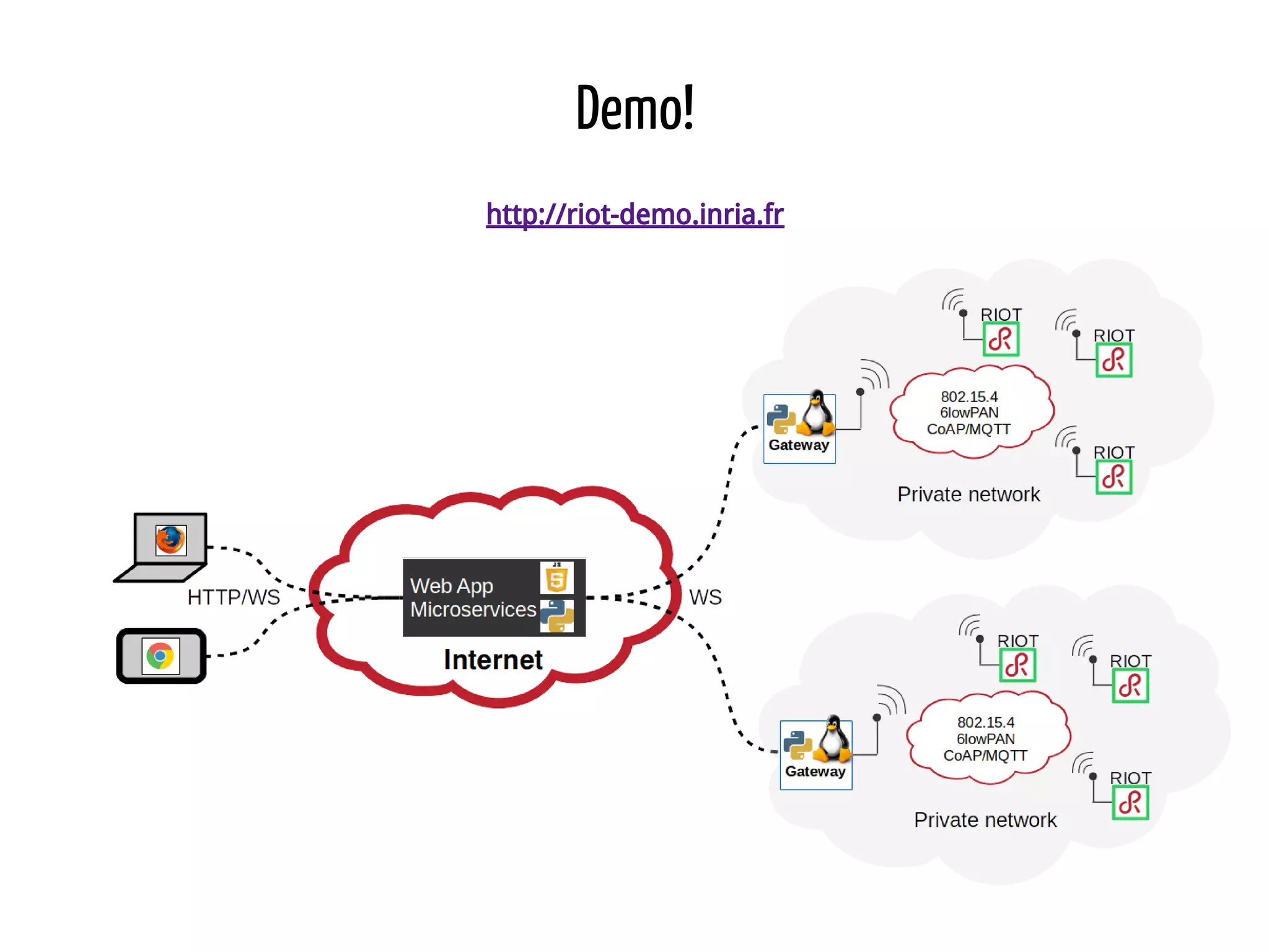
Python for IoT discusses building Pyaiot, a system to connect constrained IoT devices to the web. Pyaiot uses common IoT protocols like CoAP and MQTT to allow bidirectional communication between low-power devices and a web dashboard. The author details how Pyaiot was implemented using Python and asyncio to be multi-protocol, modular, and reactive in a real-time manner. Lessons learned include some initial challenges with asyncio, but that Python facilitated fast development of the complex system to meet the initial requirements.