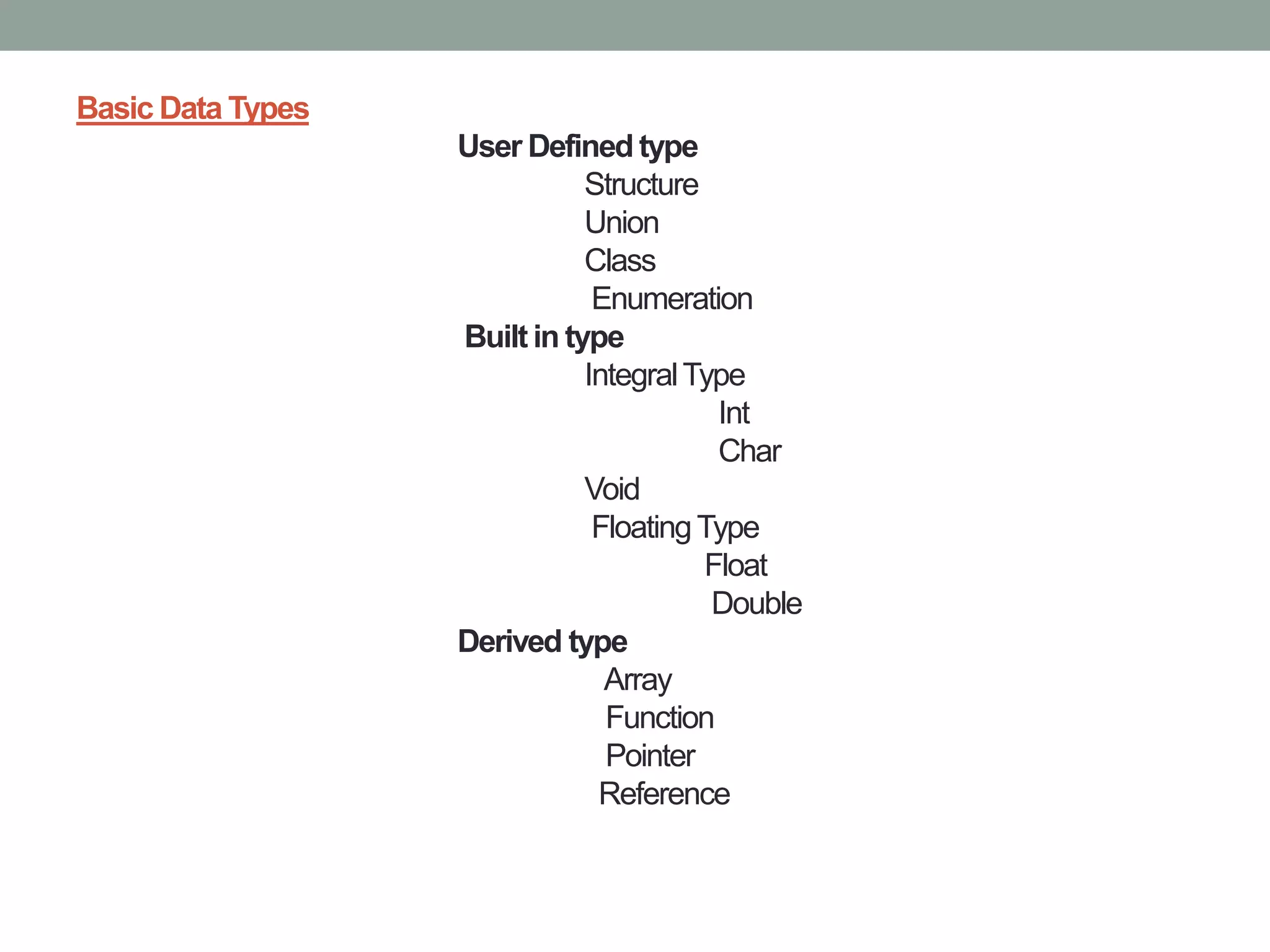
This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming and key C++ concepts. It discusses objects, classes, data abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism and dynamic binding as basic OOP concepts. It also covers basic data types in C++ including user-defined types like structures and classes. The document describes functions in C++, including dividing programs into functions, function prototyping, inline functions, and function overloading which allows using the same function name for different purposes.