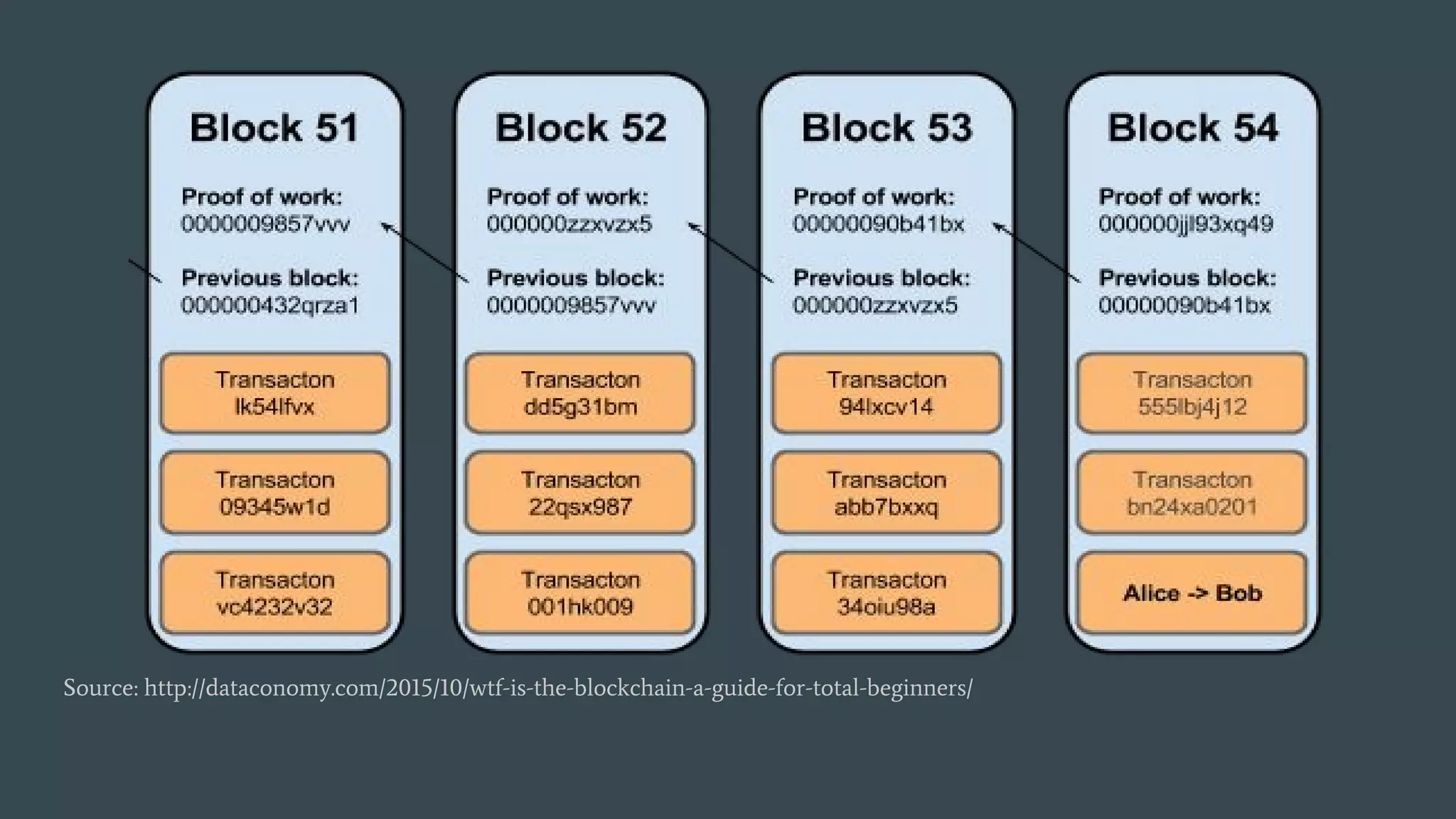
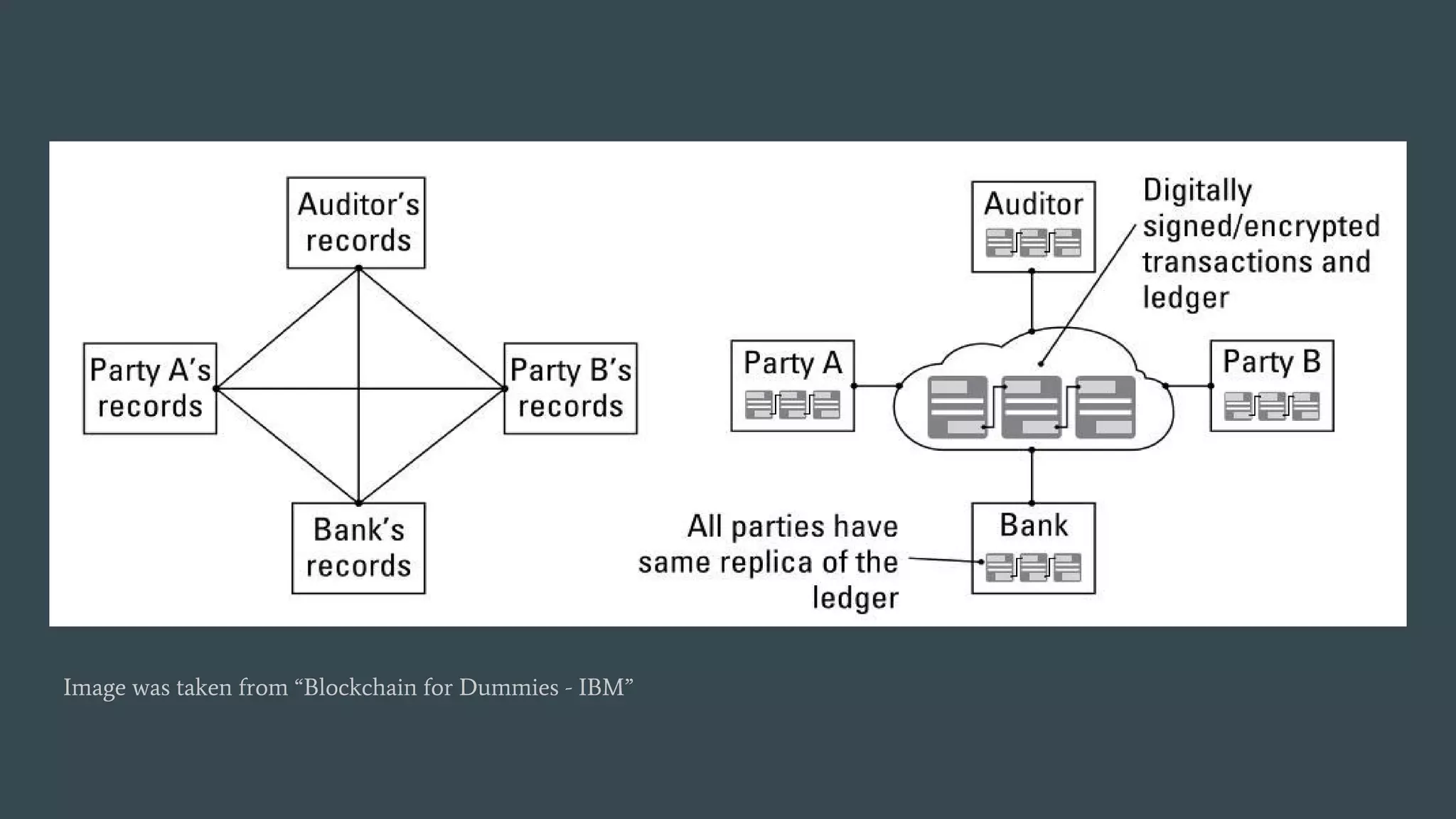
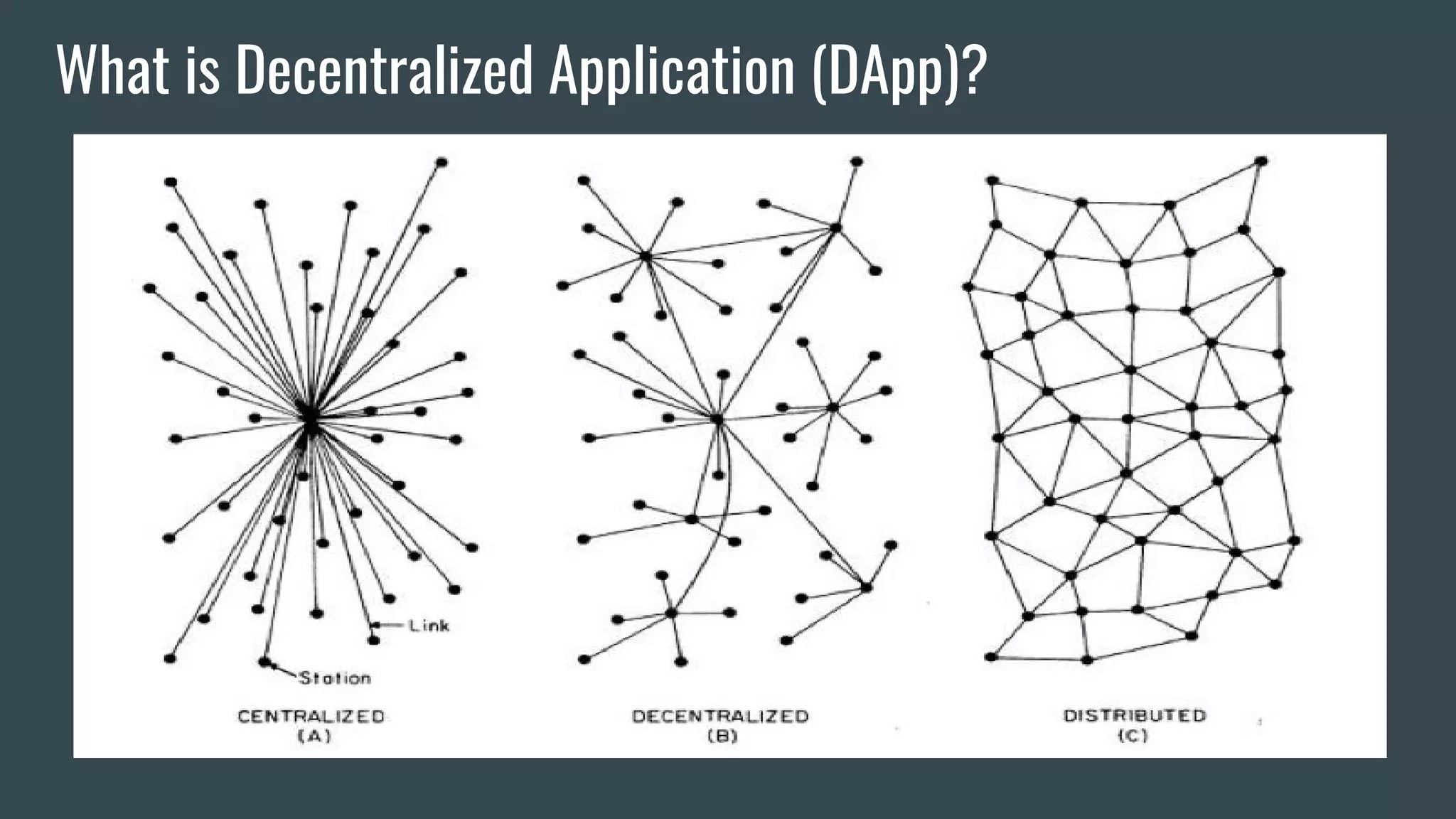
The document discusses programming decentralized applications (dApps) with a focus on blockchain technology, particularly Ethereum. It covers key topics including definitions of blockchain, requirements for developing dApps, various blockchain platforms, and development tools and environments. Additionally, it highlights the importance of smart contracts, transaction fees, and methodologies for deployment using frameworks like Truffle.