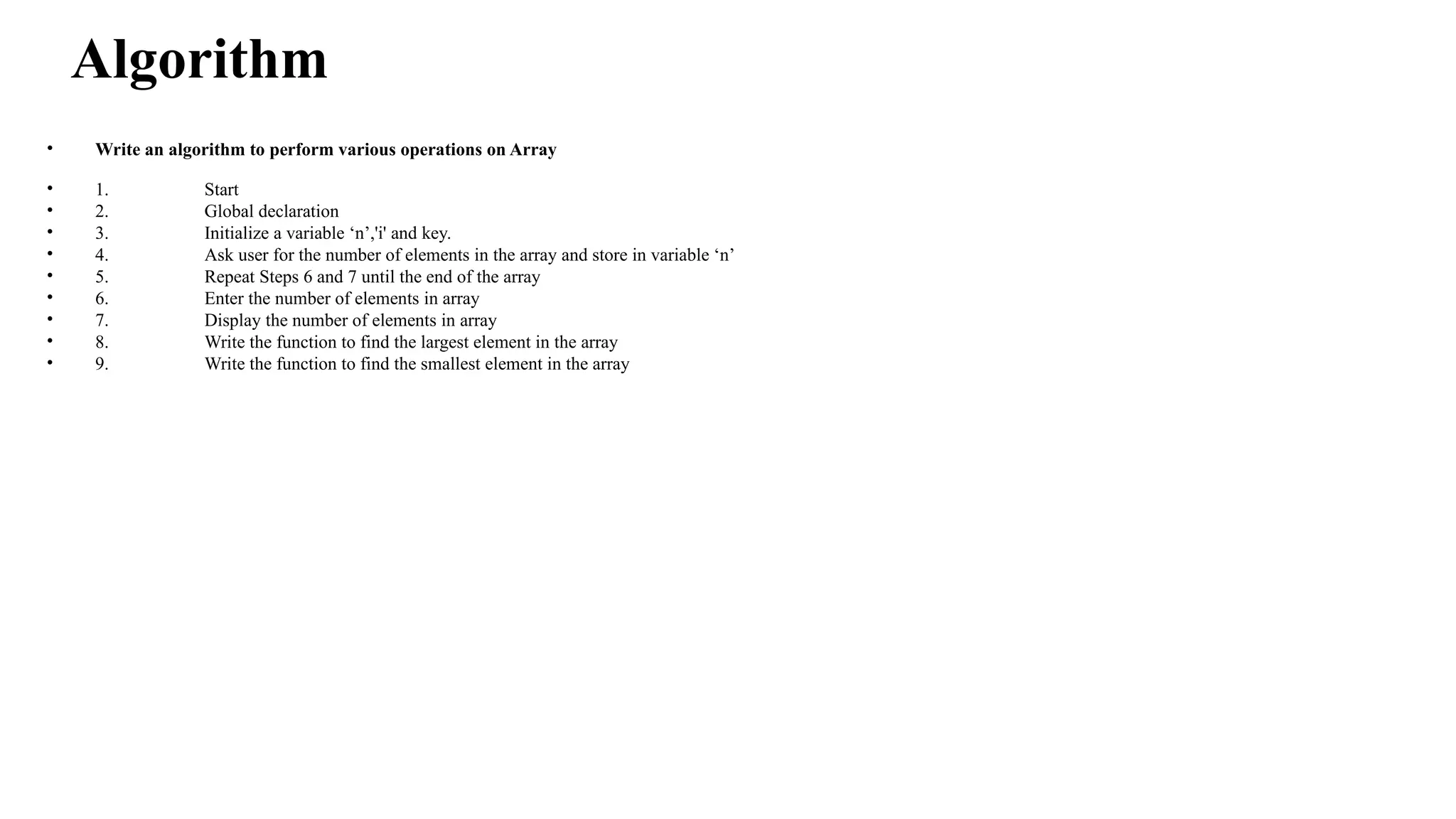
The document outlines a C program for performing various operations on arrays, which are versatile data structures allowing the storage of multiple elements of the same data type. Key operations discussed include traversal, insertion, deletion, searching, sorting, and accessing elements, along with an algorithm and sample code demonstrating these operations. Functions for finding the largest and smallest elements, calculating the sum and average, reversing the array, and searching for an element are also provided.







![• #include <stdio.h> • // Function prototypes • void inputArray(int arr[], int n); • void displayArray(int arr[], int n); • int findLargest(int arr[], int n); • int findSmallest(int arr[], int n); • int sumArray(int arr[], int n); • float averageArray(int arr[], int n); • void reverseArray(int arr[], int n); • int searchElement(int arr[], int n, int key); • int main() • { • int n, i, key; // Ask user for the number of elements in the array • printf("Enter the number of elements: "); • scanf("%d", &n); • int arr[n]; // Input the array elements • inputArray(arr, n); // Display the array • printf("nArray elements: "); • displayArray(arr, n);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab5-241127044305-9a47dbad/75/Program-Practical-to-operations-on-Array-10-2048.jpg)

![inputArray • // Function to input elements into the array • void inputArray(int arr[], int n) • { • for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) • { • printf("Enter element %d: ", i + 1); • scanf("%d", &arr[i]); • } • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab5-241127044305-9a47dbad/75/Program-Practical-to-operations-on-Array-12-2048.jpg)
![displayArray • // Function to display the array elements • void displayArray(int arr[], int n) • { • for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) • { • printf("%d ", arr[i]); • } • printf("n");}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab5-241127044305-9a47dbad/75/Program-Practical-to-operations-on-Array-13-2048.jpg)
![findLargest • // Function to find the largest element in the array • Int findLargest(int arr[], int n) • { • int largest = arr[0]; • for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) • { • if (arr[i] > largest) • { • largest = arr[i]; • } • } • return largest; • } findSmallest • // Function to find the smallest element in the array • int findSmallest(int arr[], int n) • { • int smallest = arr[0]; • for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) • { • if (arr[i] < smallest) • { • smallest = arr[i]; • } • } • return smallest; • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab5-241127044305-9a47dbad/75/Program-Practical-to-operations-on-Array-14-2048.jpg)
![sumArray • // Function to calculate the sum of array elements • int sumArray(int arr[], int n) • { • int sum = 0; • for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) • { • sum += arr[i]; • } • return sum; • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab5-241127044305-9a47dbad/75/Program-Practical-to-operations-on-Array-15-2048.jpg)
![averageArray • // Function to calculate the average of array elements • float averageArray(int arr[], int n) • { • int sum = sumArray(arr, n); • return (float)sum / n; • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab5-241127044305-9a47dbad/75/Program-Practical-to-operations-on-Array-16-2048.jpg)
![reverseArray • // Function to reverse the array • void reverseArray(int arr[], int n) • { • int start = 0, end = n - 1; • while (start < end) • { • int temp = arr[start]; • arr[start] = arr[end]; • arr[end] = temp; • start++; • end--; • } • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab5-241127044305-9a47dbad/75/Program-Practical-to-operations-on-Array-17-2048.jpg)
![searchElement • // Function to search an element in the array • int searchElement(int arr[], int n, int key) • { • for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) • { • if (arr[i] == key) • { • return i; // Element found, return index • } • } • return -1; // Element not found • }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab5-241127044305-9a47dbad/75/Program-Practical-to-operations-on-Array-18-2048.jpg)
