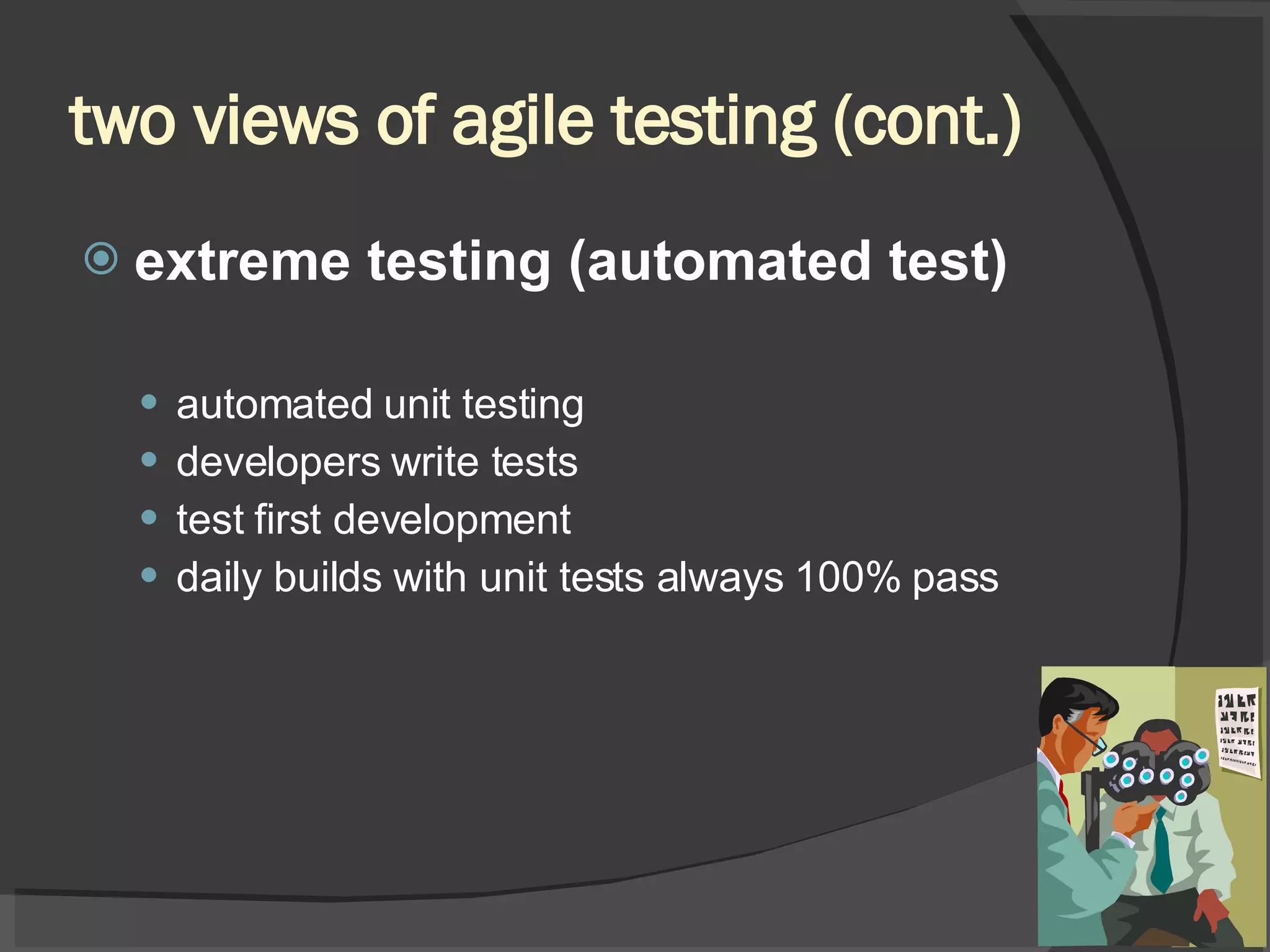
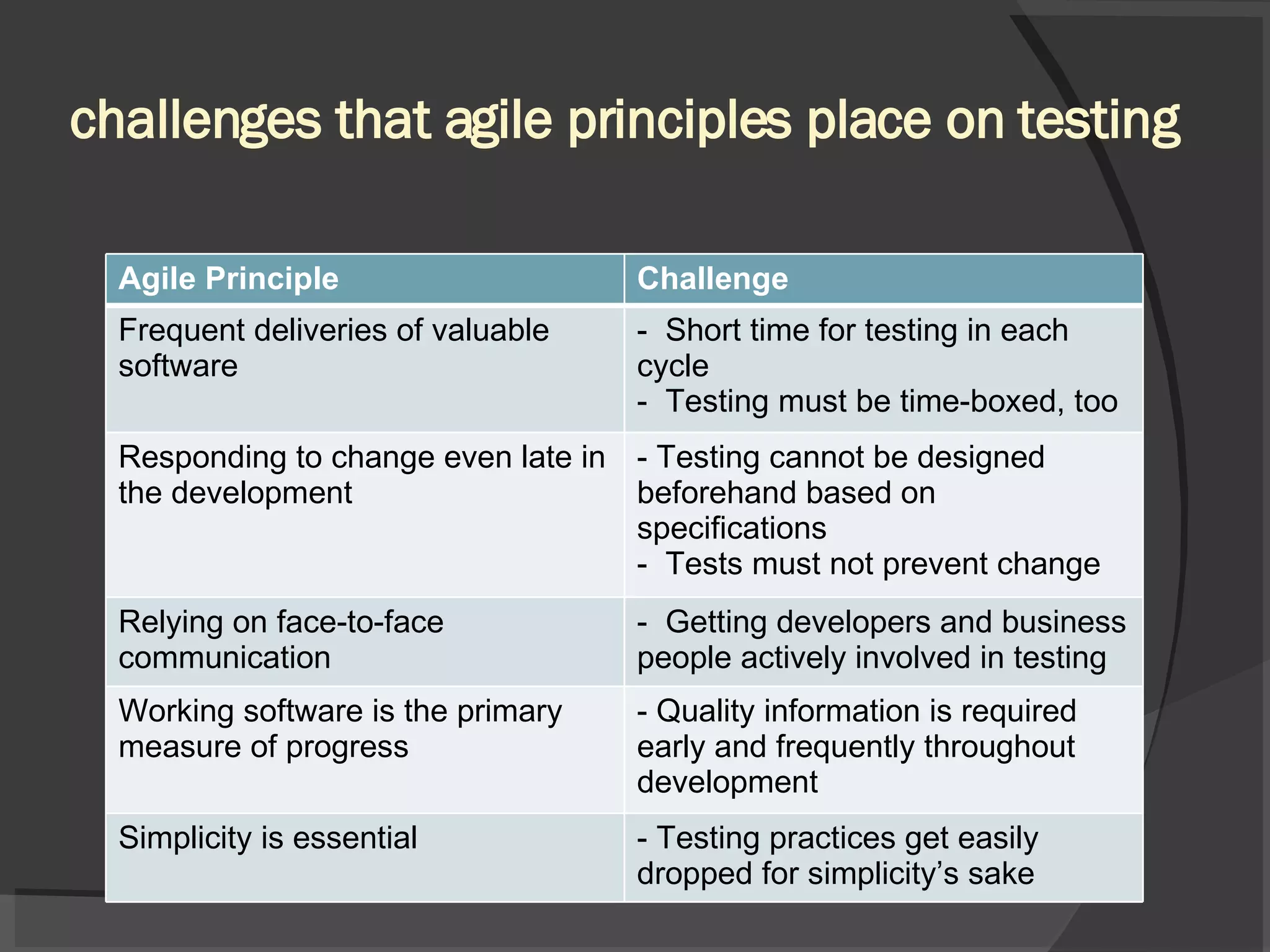
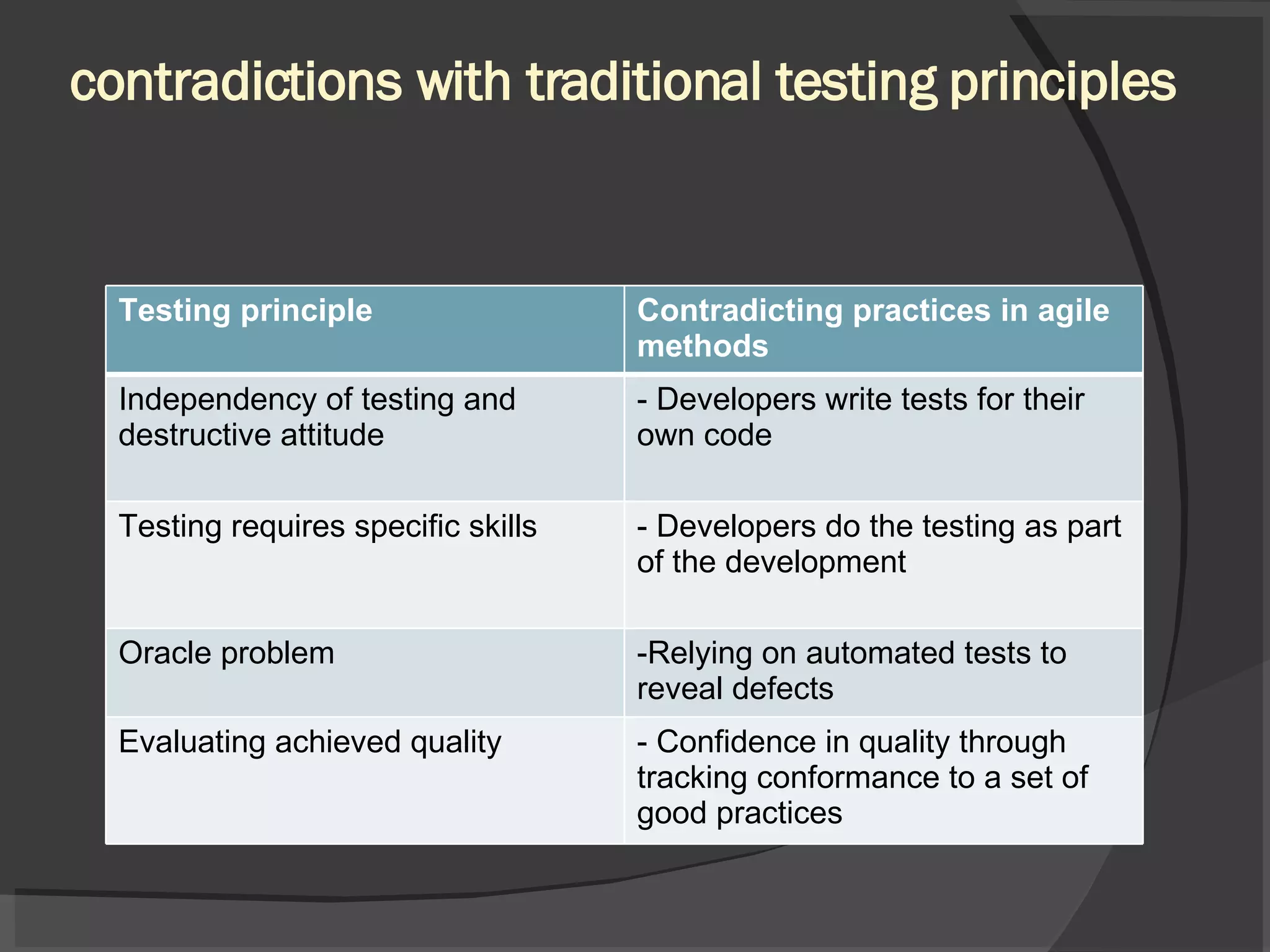
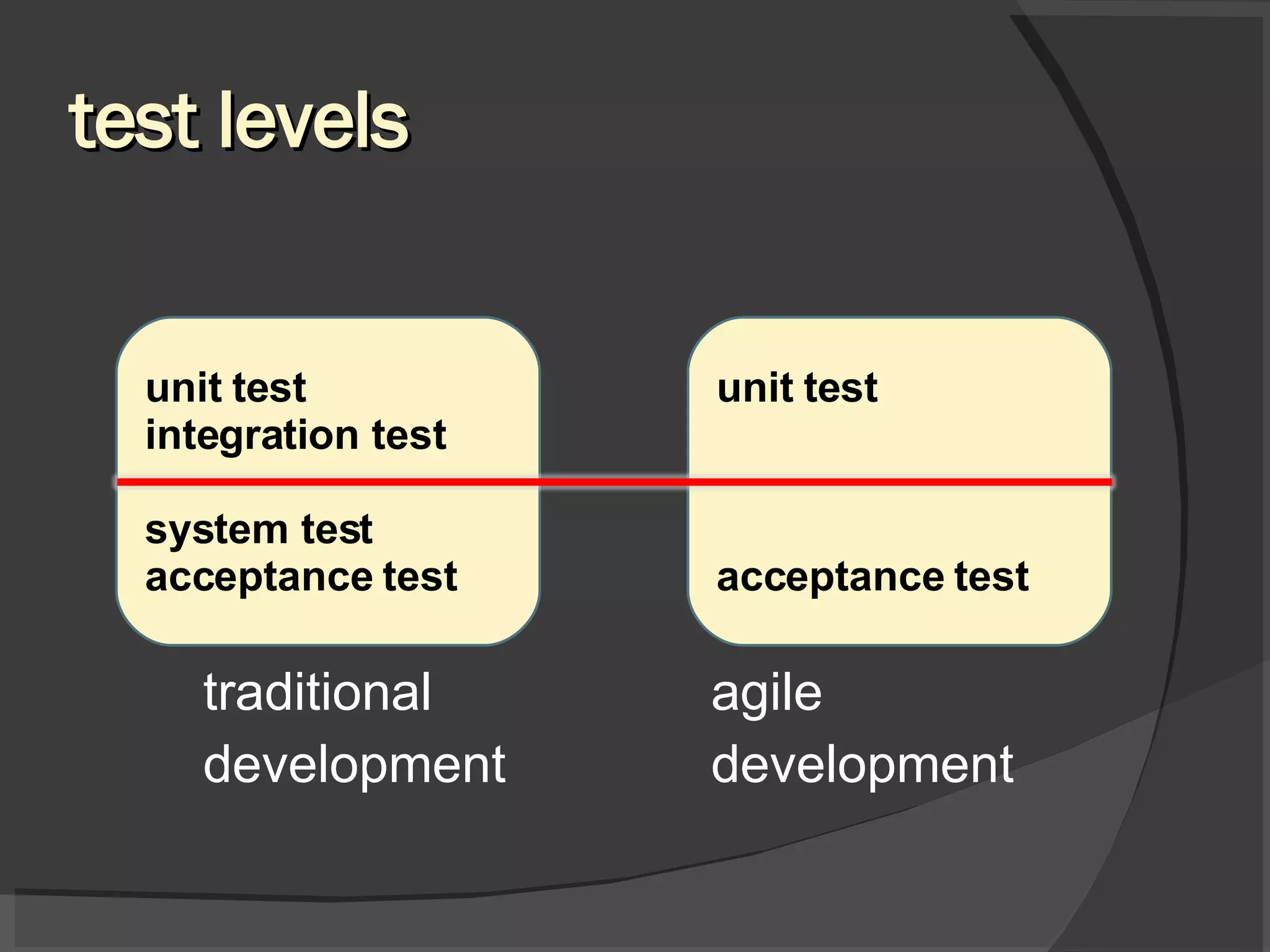
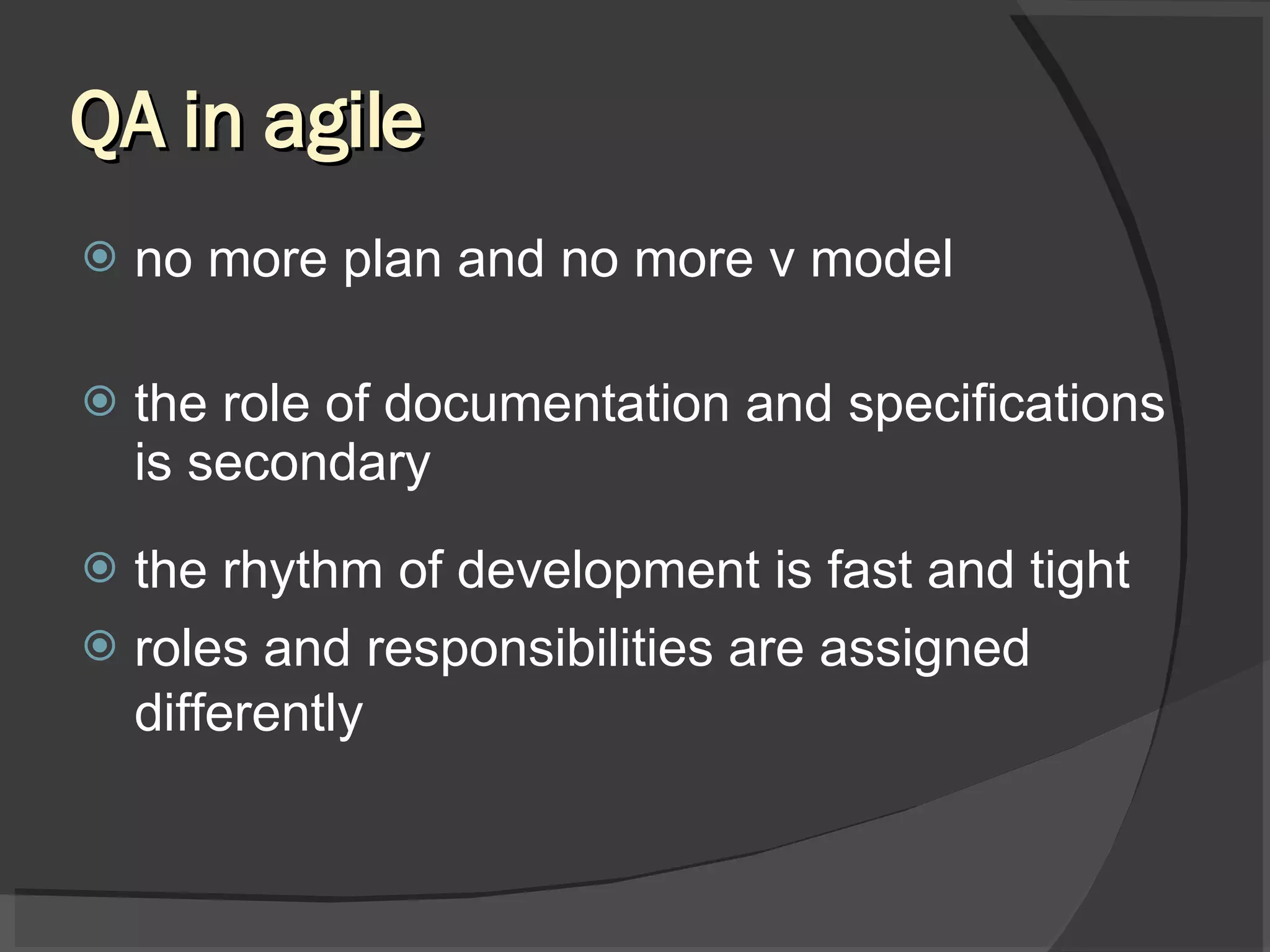
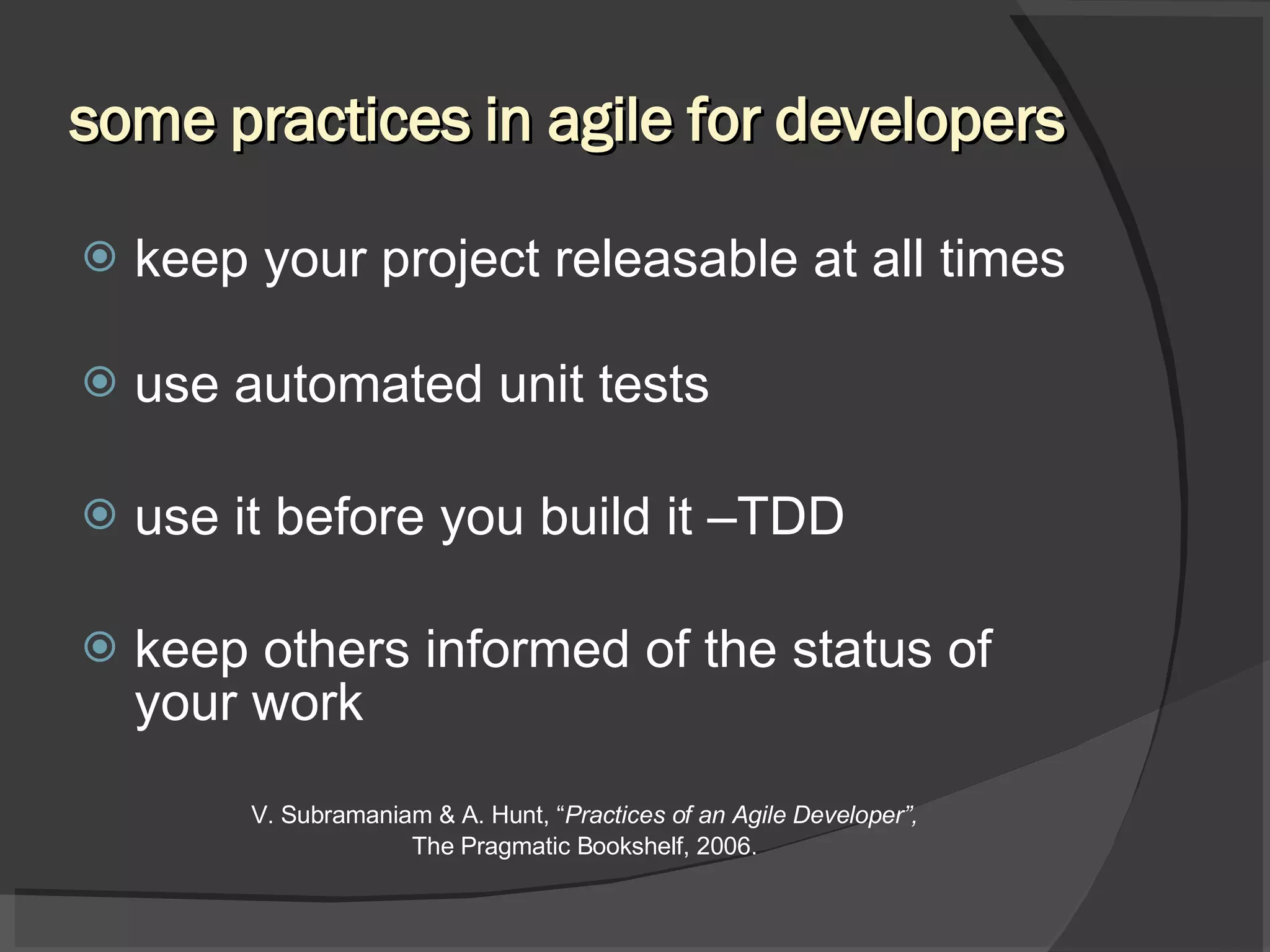
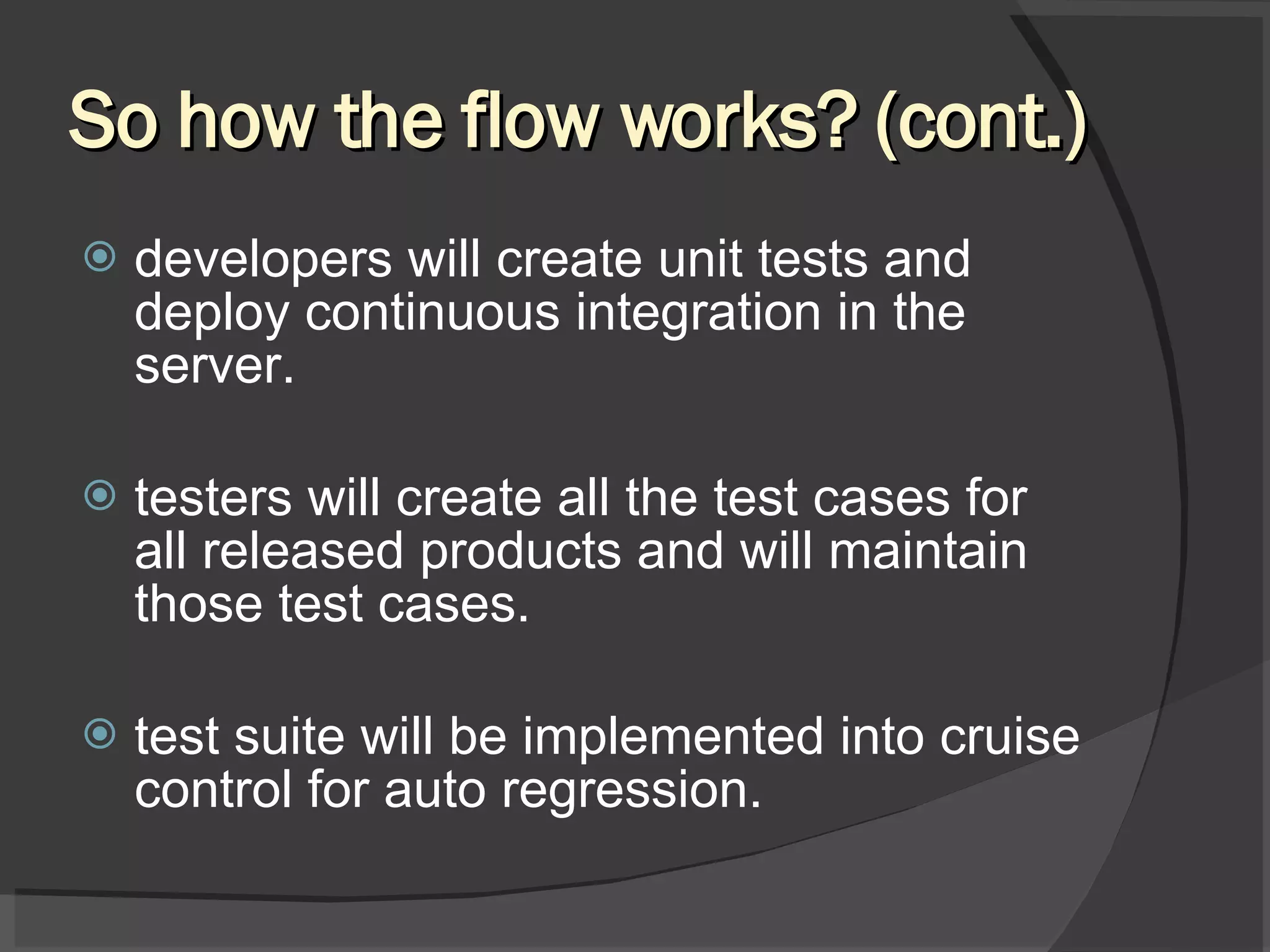
The document discusses different views of testing in agile environments, challenges that agile principles pose for testing, and how QA works with agile development teams. It describes extreme and exploratory testing approaches, contradictions between traditional and agile testing principles, and practices like test-driven development and maintaining a releasable product increment. The workflow involves developers writing unit tests, continuous integration, and QA maintaining test cases and running regressions after releases to assure quality.