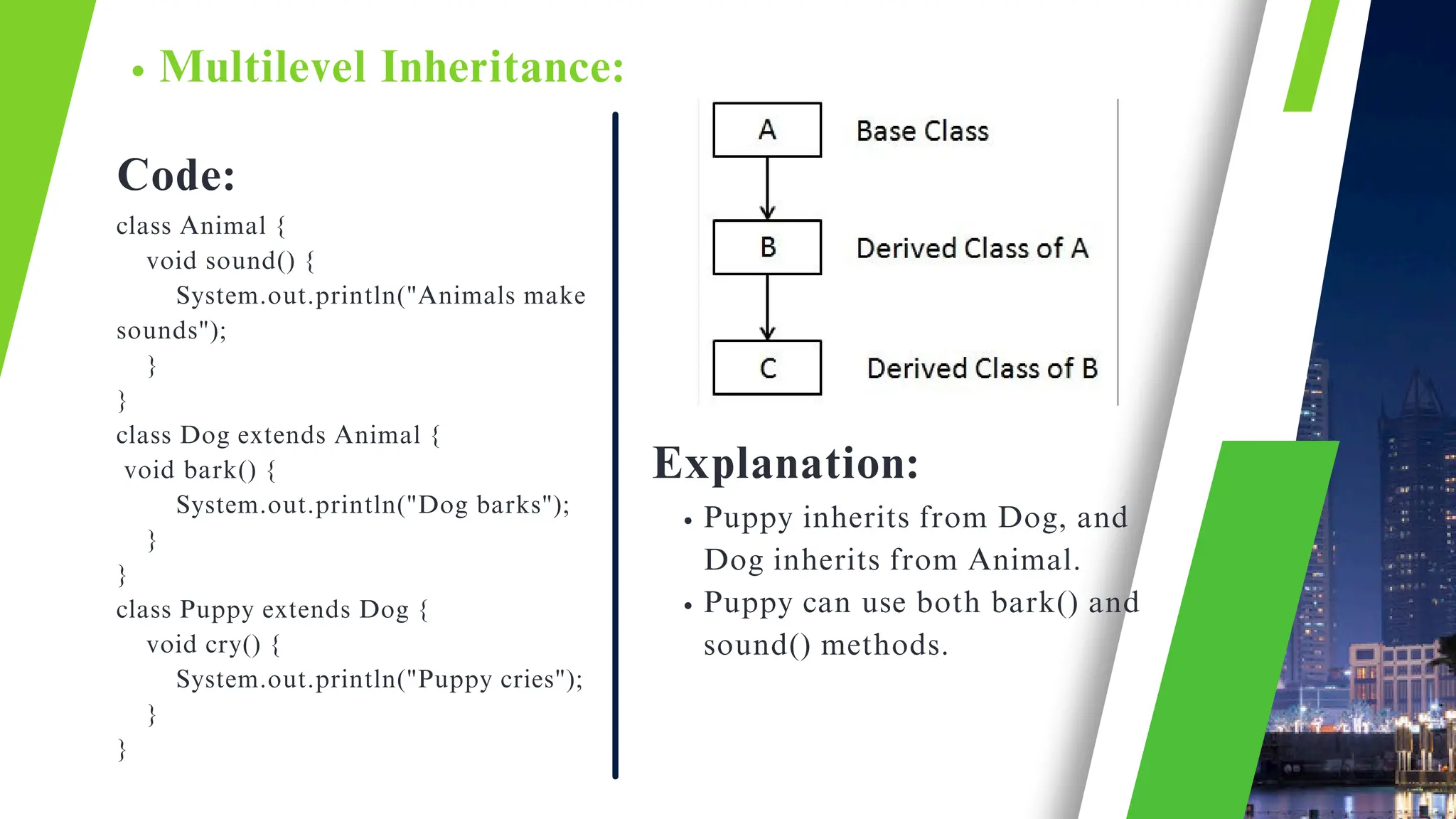
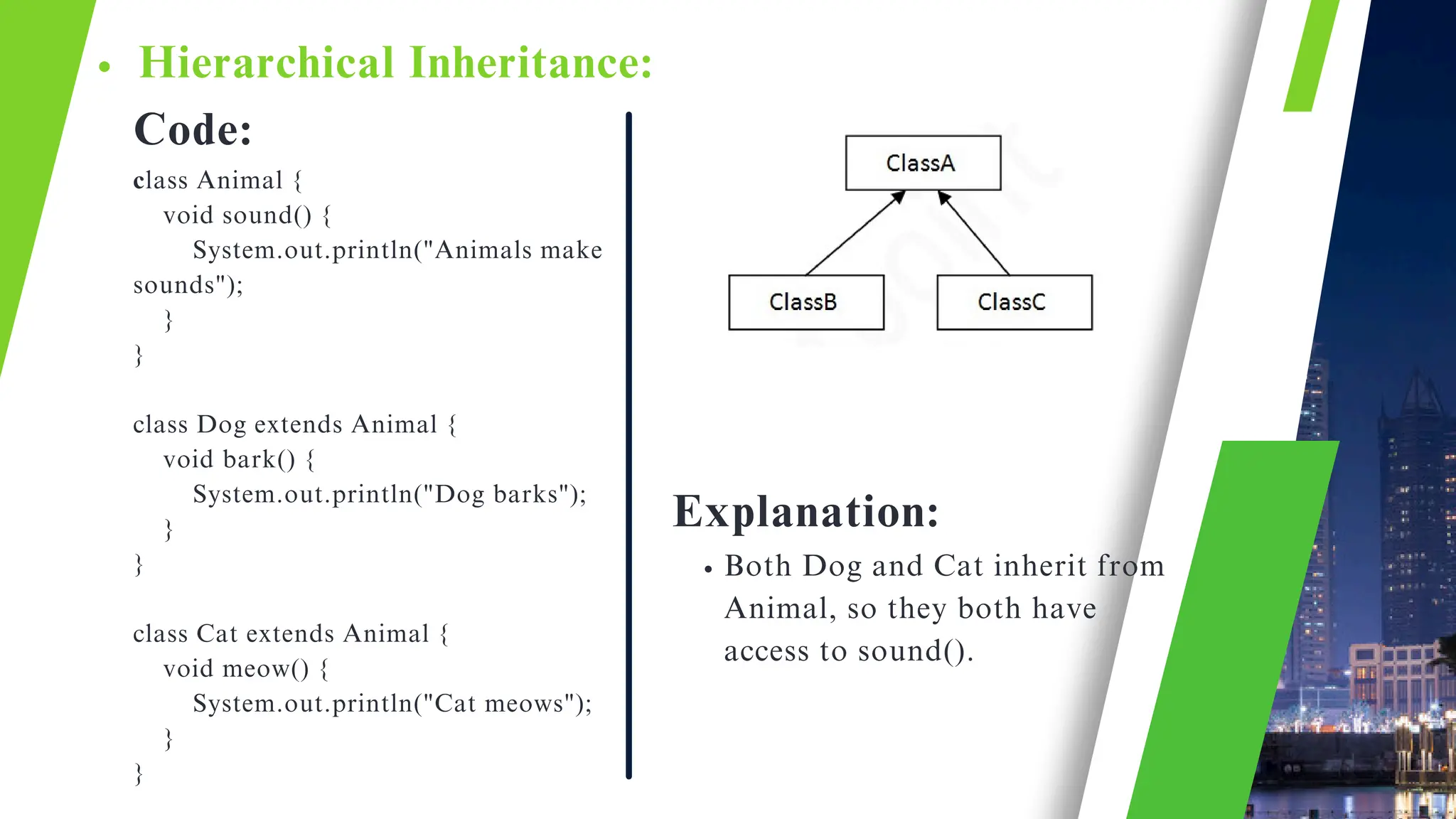
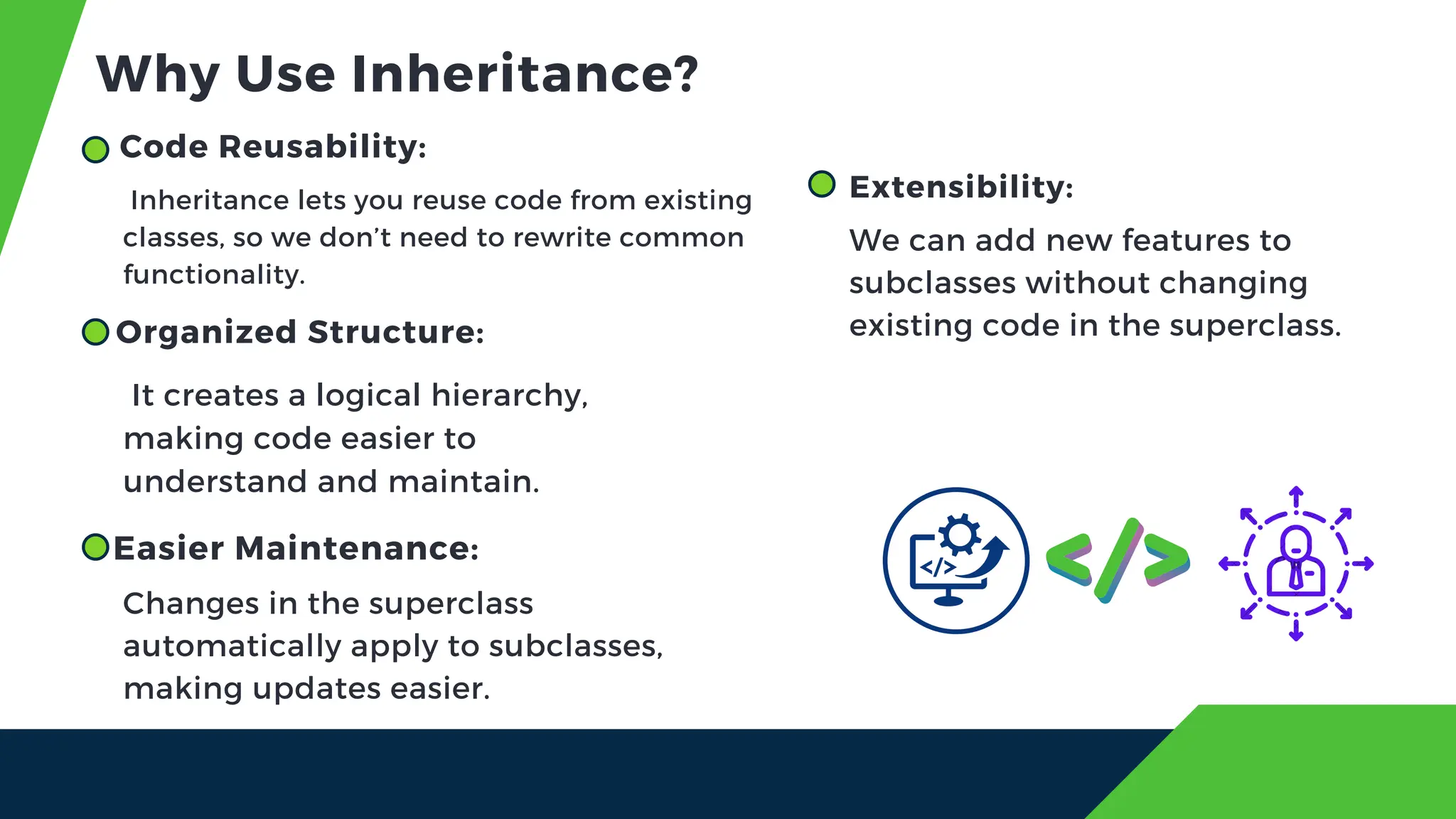
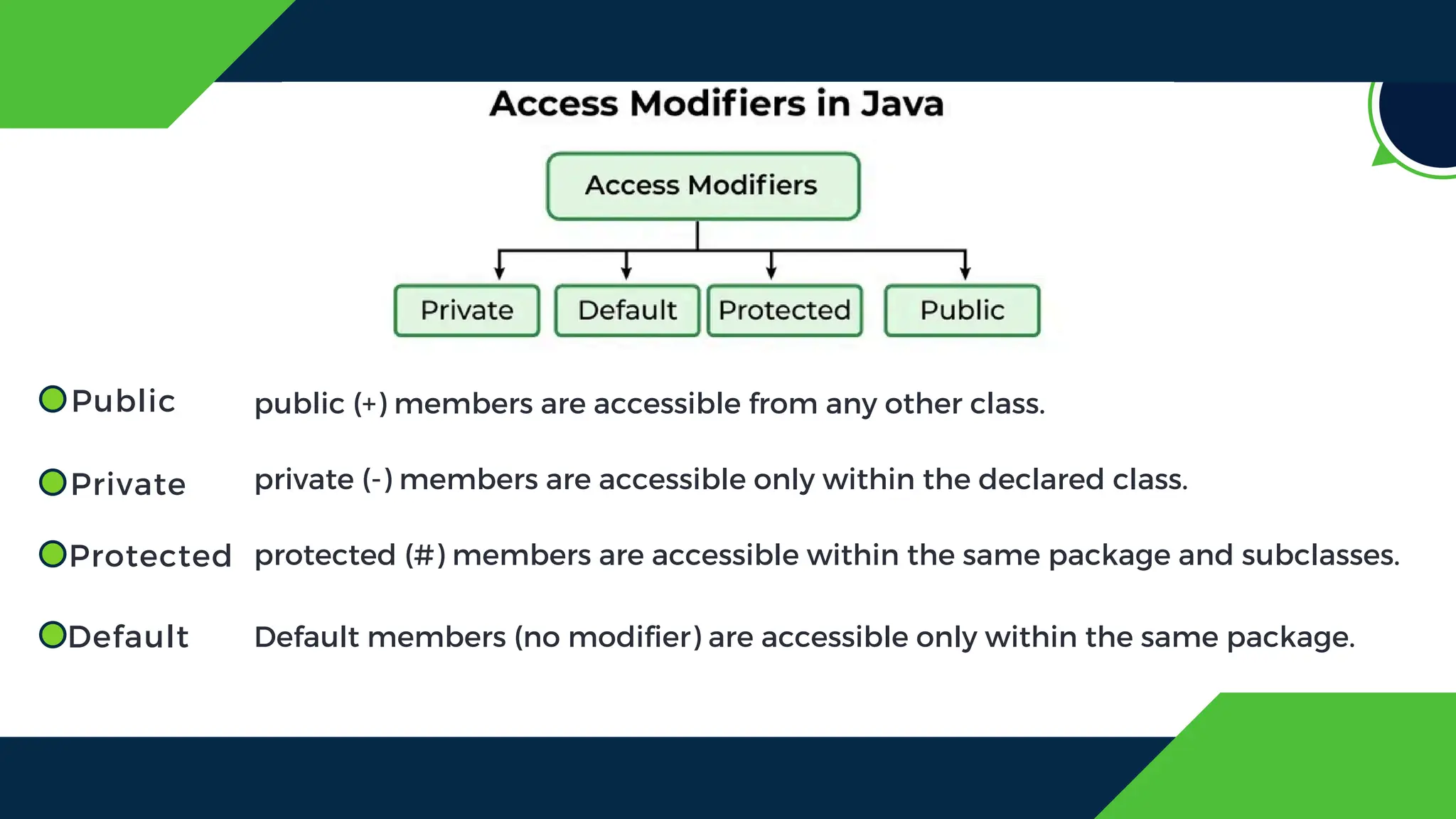
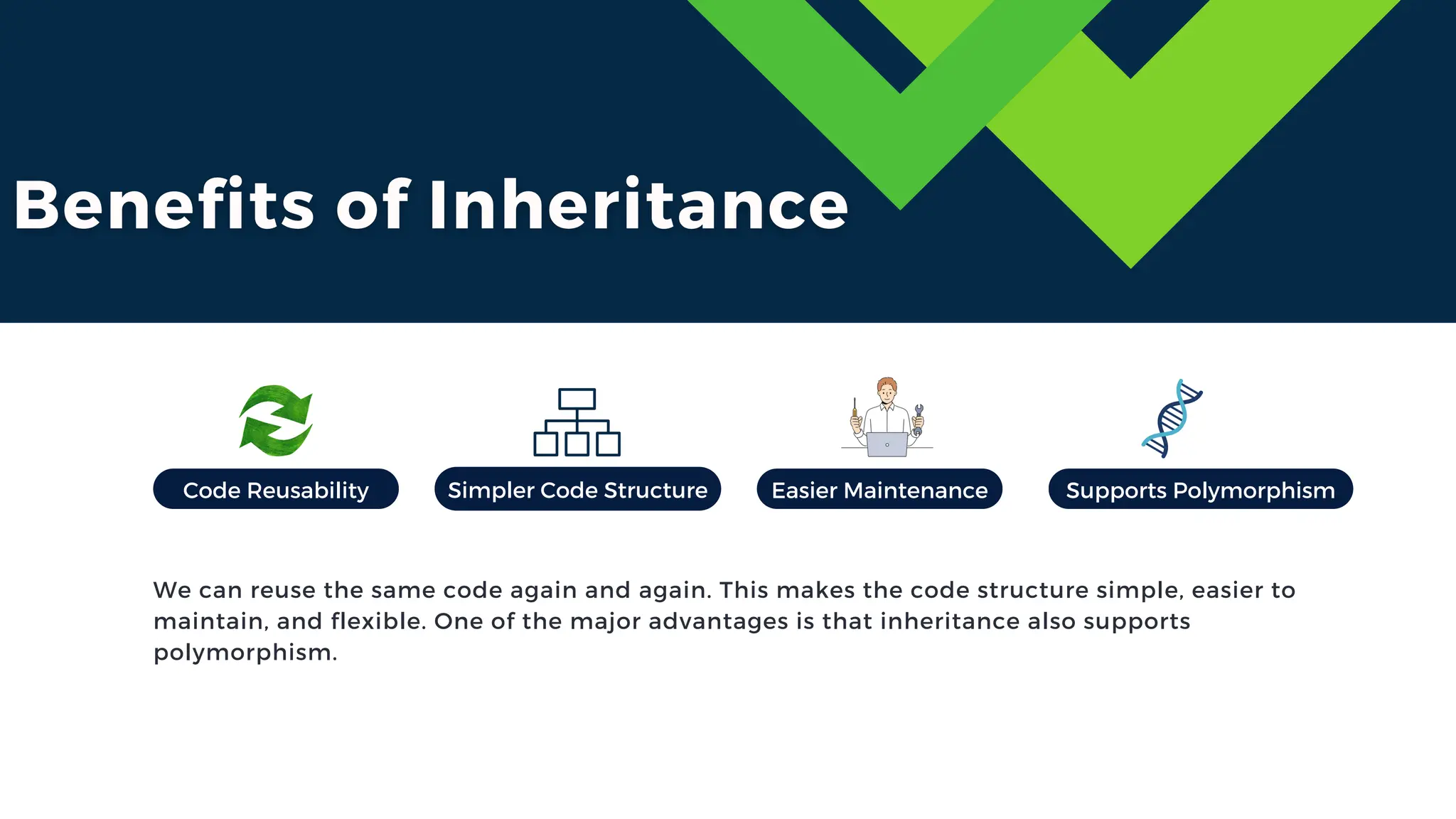
The document discusses the concept of inheritance in object-oriented programming, emphasizing its advantages such as code reusability, easier maintenance, and organized structure. It explains key concepts including parent and child classes, method overriding, and types of inheritance like single, multilevel, and hierarchical inheritance. Additionally, it highlights real-life applications and potential disadvantages of inheritance.


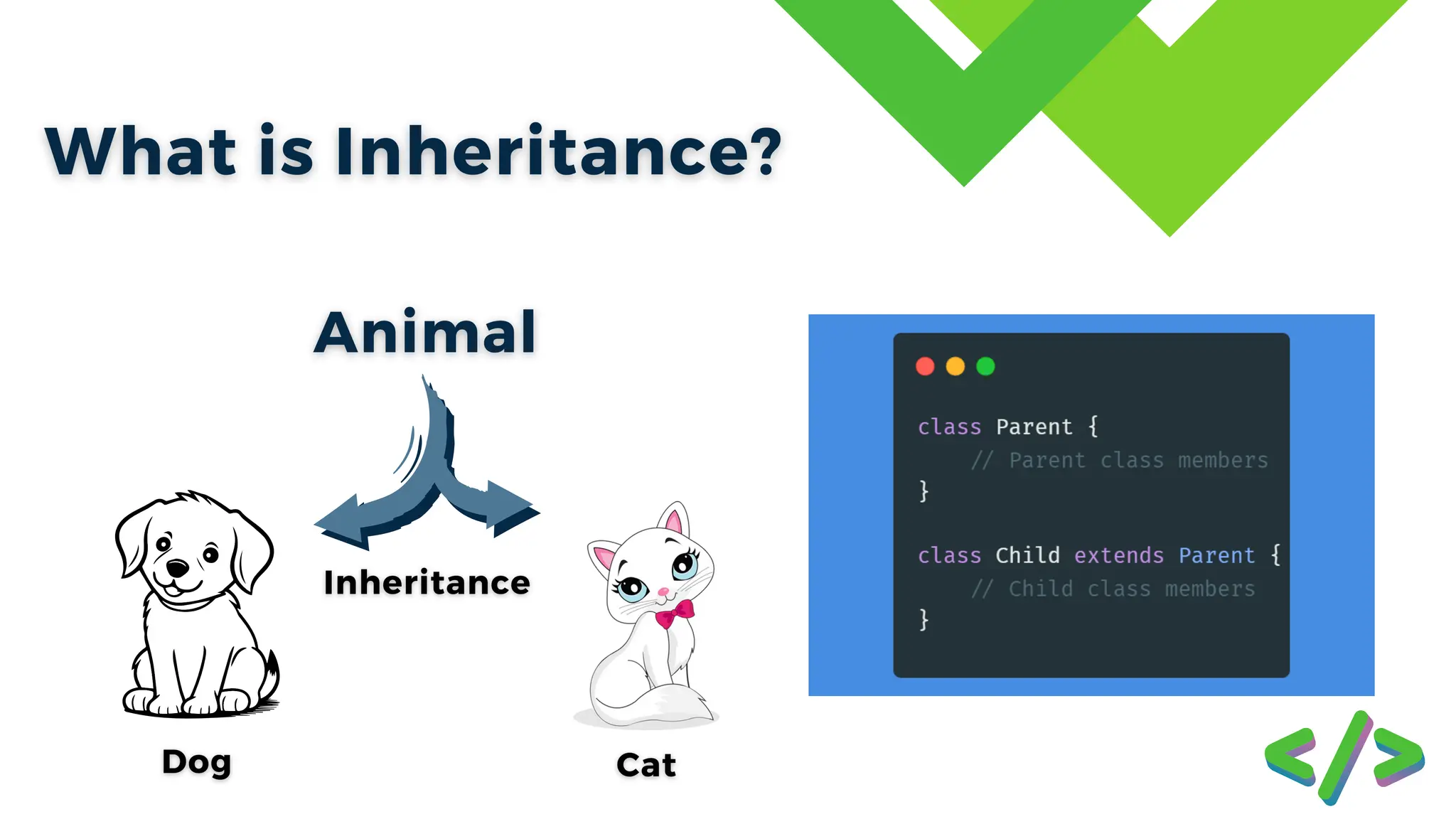

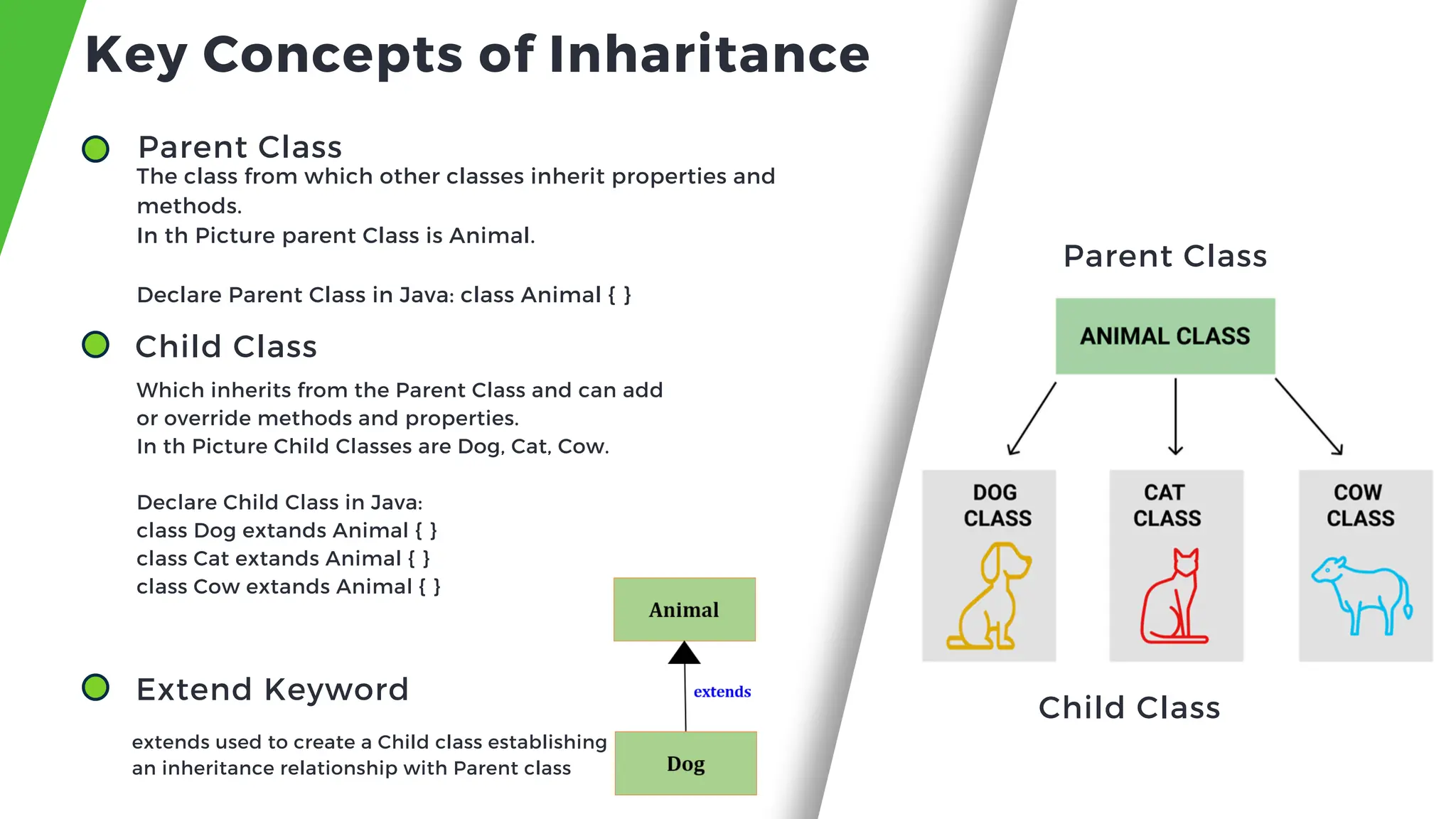

![Parent Class (Animal): This has common features of all animals. Child Class (Dog): This class inherits from Animal and can add extra features specific to dogs. // Parent classclass Animal { void eat() { System.out.println("Animal is eating"); } } // Child classclass Dog extends Animal { void bark() { System.out.println("Dog is barking"); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Dog myDog = new Dog(); // Uses method from parent class(Animal) myDog.eat(); // Uses method from child class (Dog) myDog.bark(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorienteconcepts-241111172711-5ee8a8ed/75/Presentation-Slide-about-Inharitance-in-Java-Object-Oriented-Programming-11-2048.jpg)


![public class test{ public static void main(String[] args) { Teacher t1 = new Teacher(); t1.name = "Mehedi"; t1.age = 25; t1.displayInfo(); Student s1 = new Student(); s1.name= "Nakib"; s1.displayInfo(); } } Example:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorienteconcepts-241111172711-5ee8a8ed/75/Presentation-Slide-about-Inharitance-in-Java-Object-Oriented-Programming-14-2048.jpg)


![Single inheritance: Code: class Animal { void sound() { System.out.println("Animals make sounds"); } } class Dog extends Animal { void bark() { System.out.println("Dog barks"); } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Dog dog = new Dog(); dog.sound(); dog.bark(); } } Explanation: Here, Dog inherits from Animal, so it gets the sound() method for free. This is Single Inheritance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorienteconcepts-241111172711-5ee8a8ed/75/Presentation-Slide-about-Inharitance-in-Java-Object-Oriented-Programming-17-2048.jpg)