Download to read offline


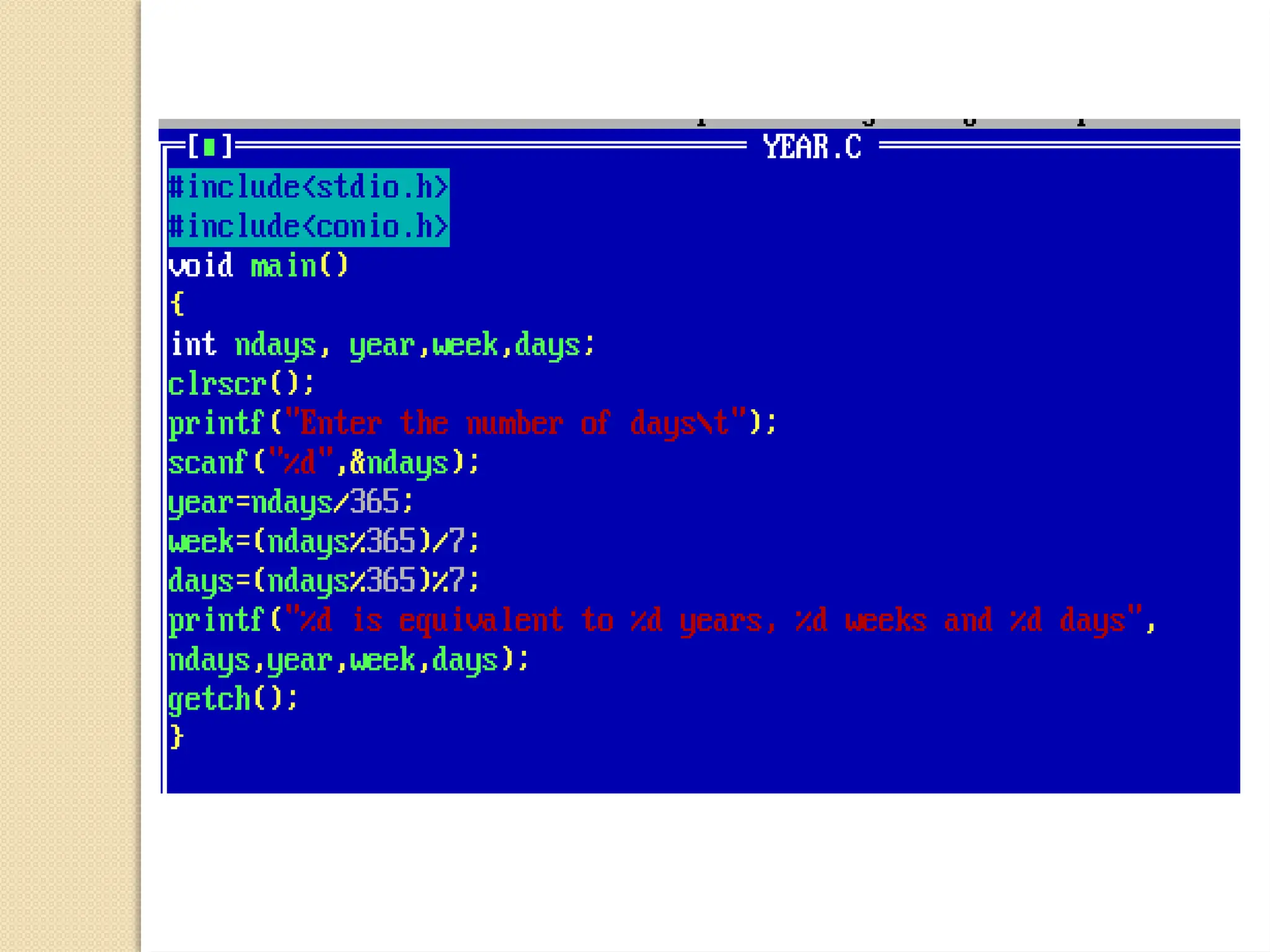
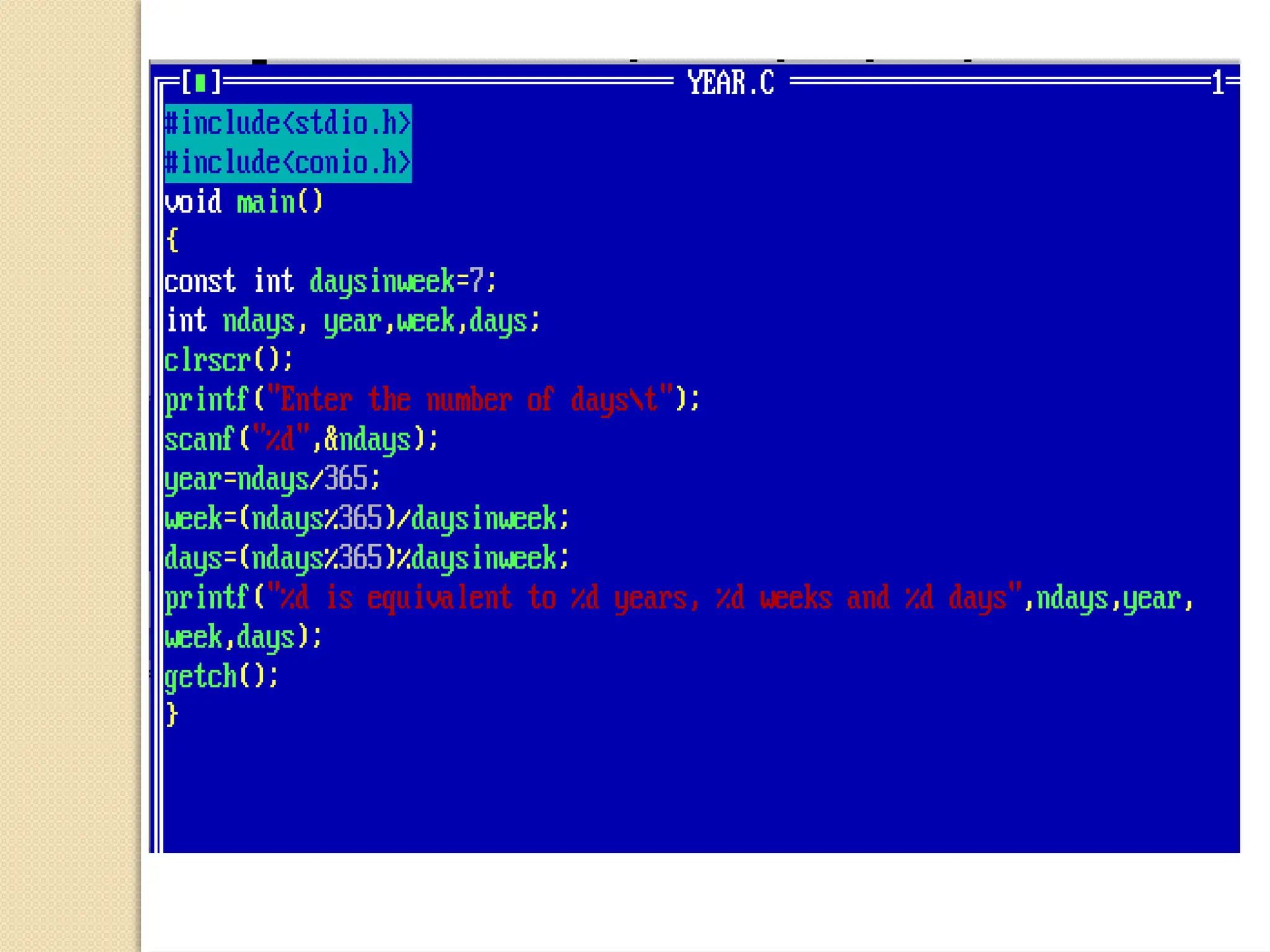

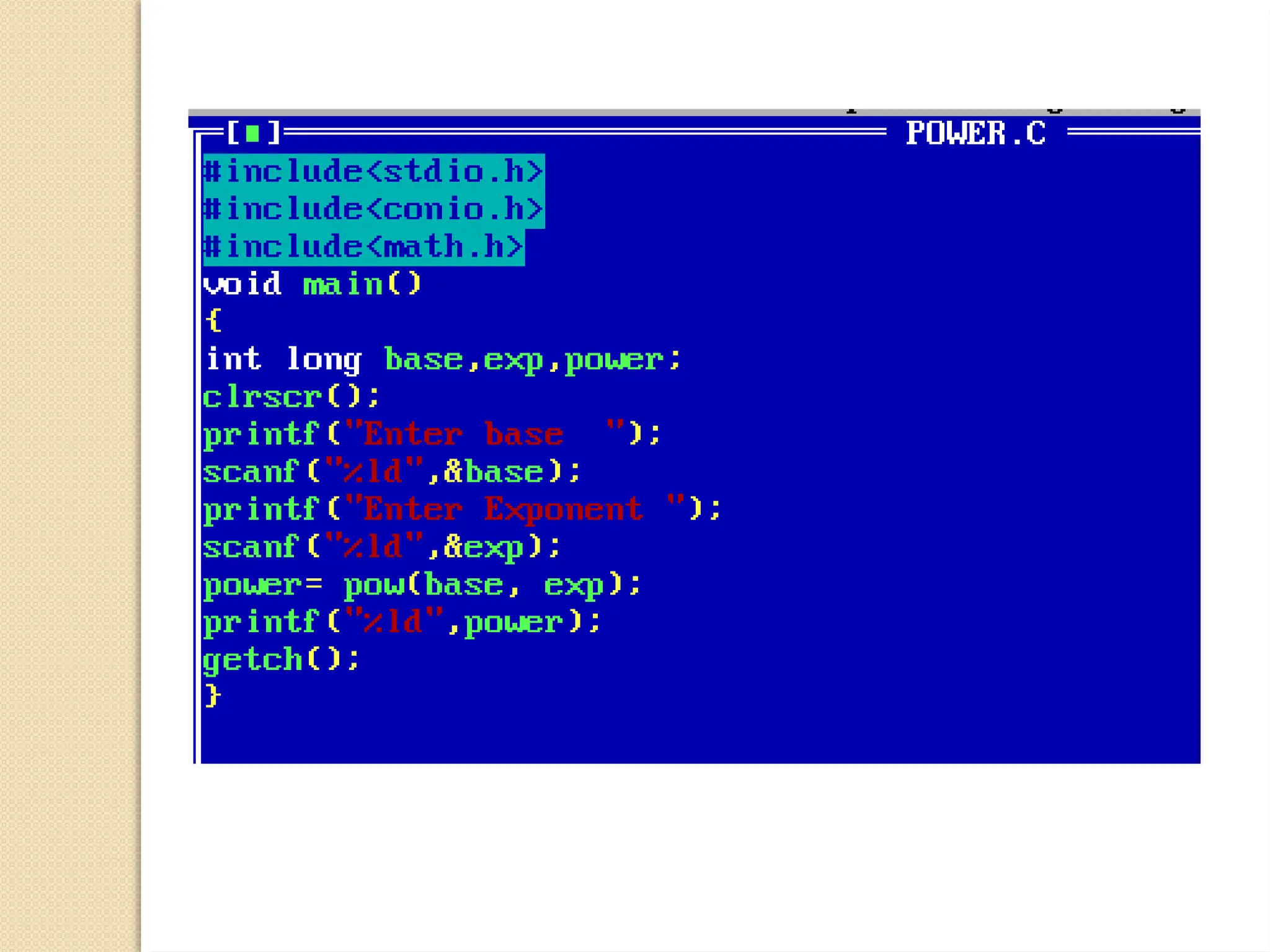

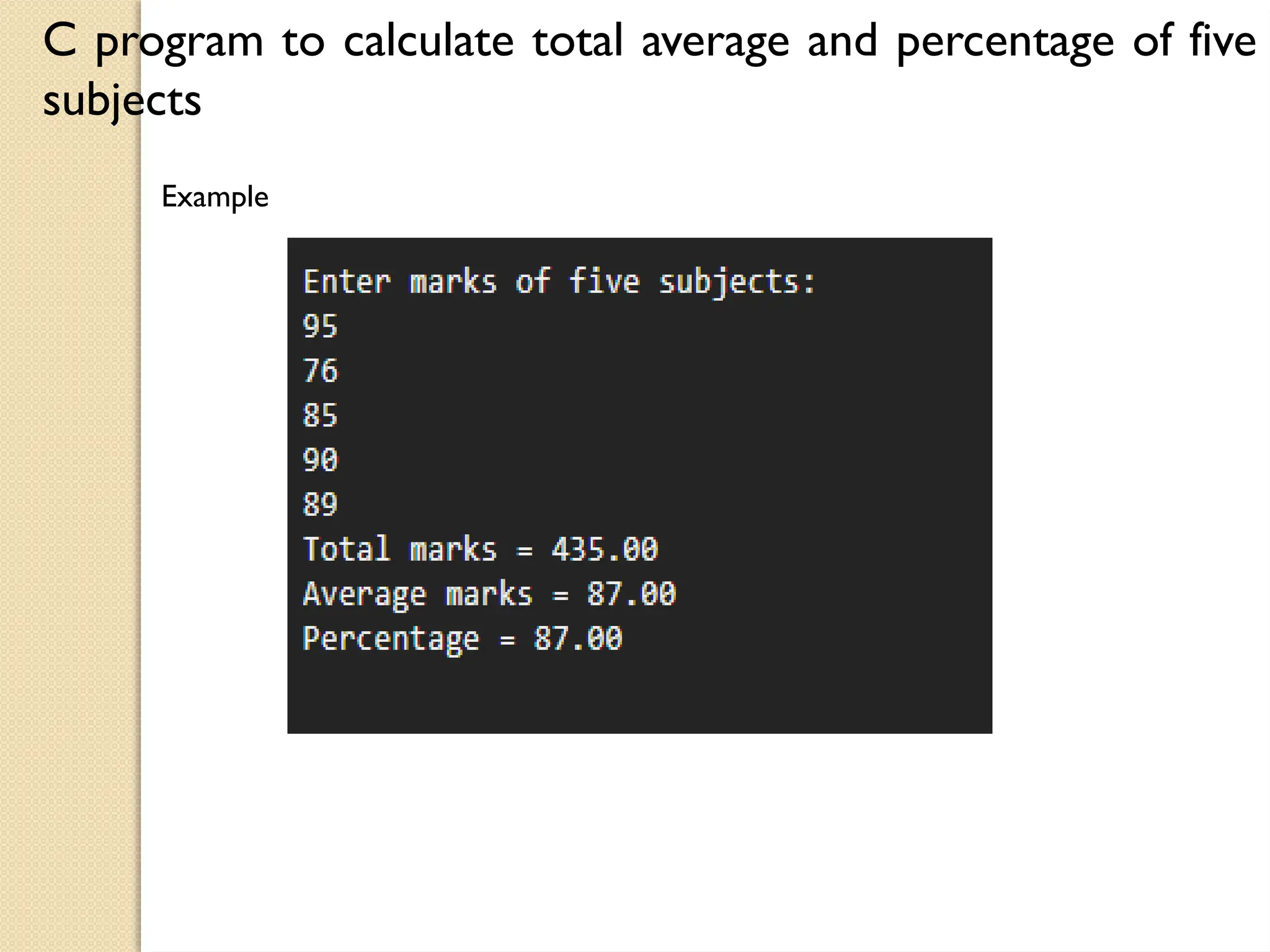


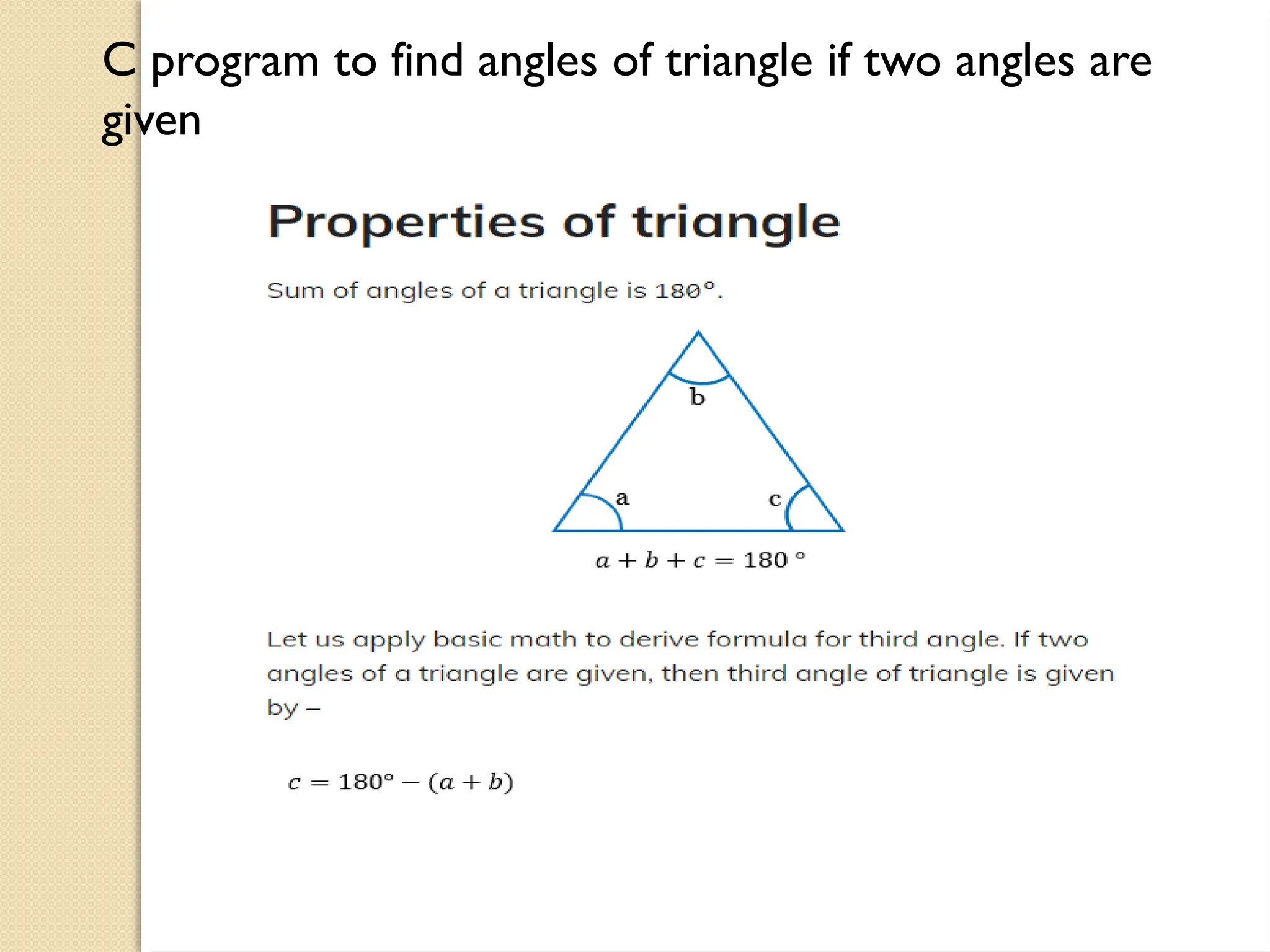

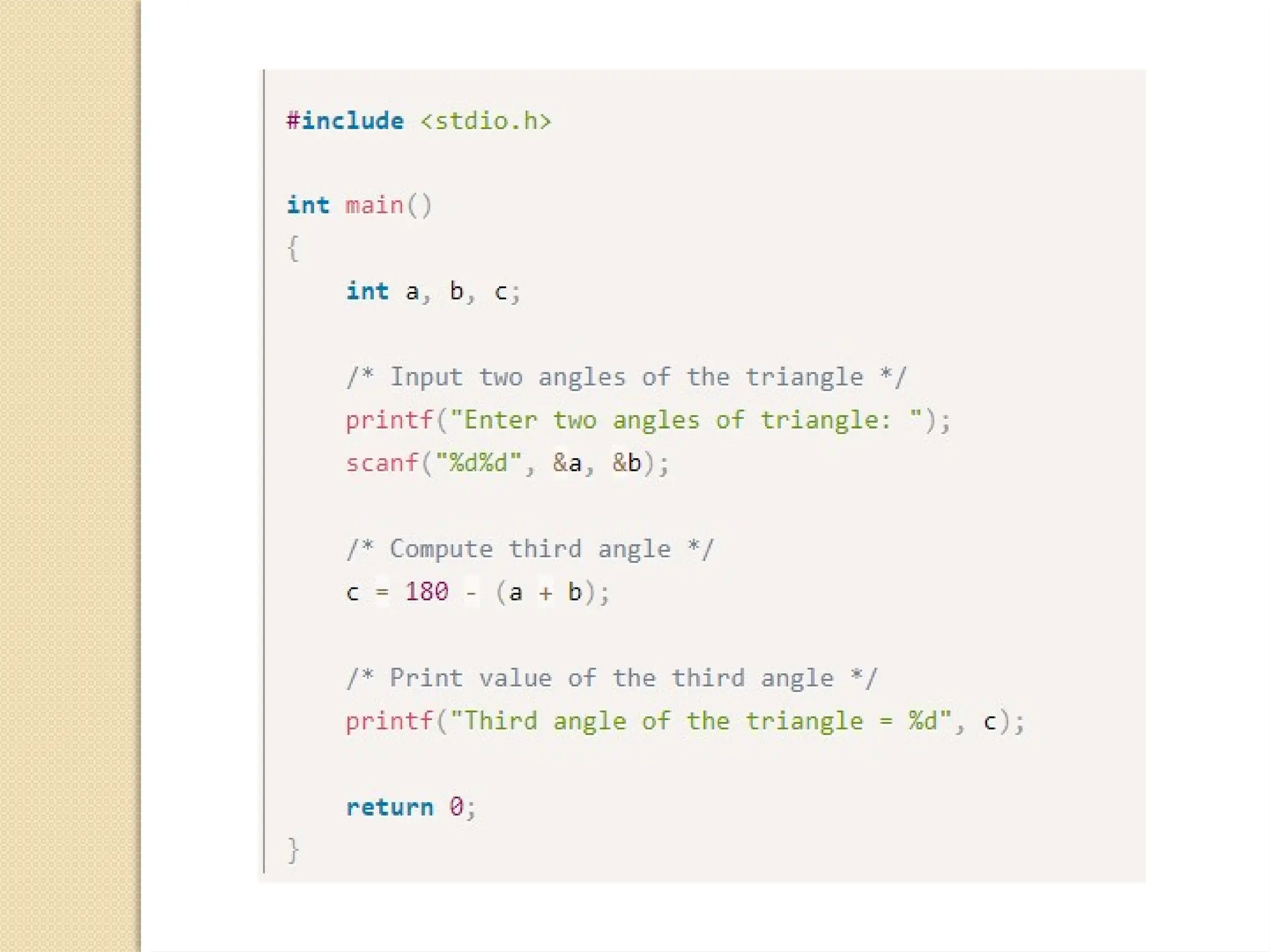
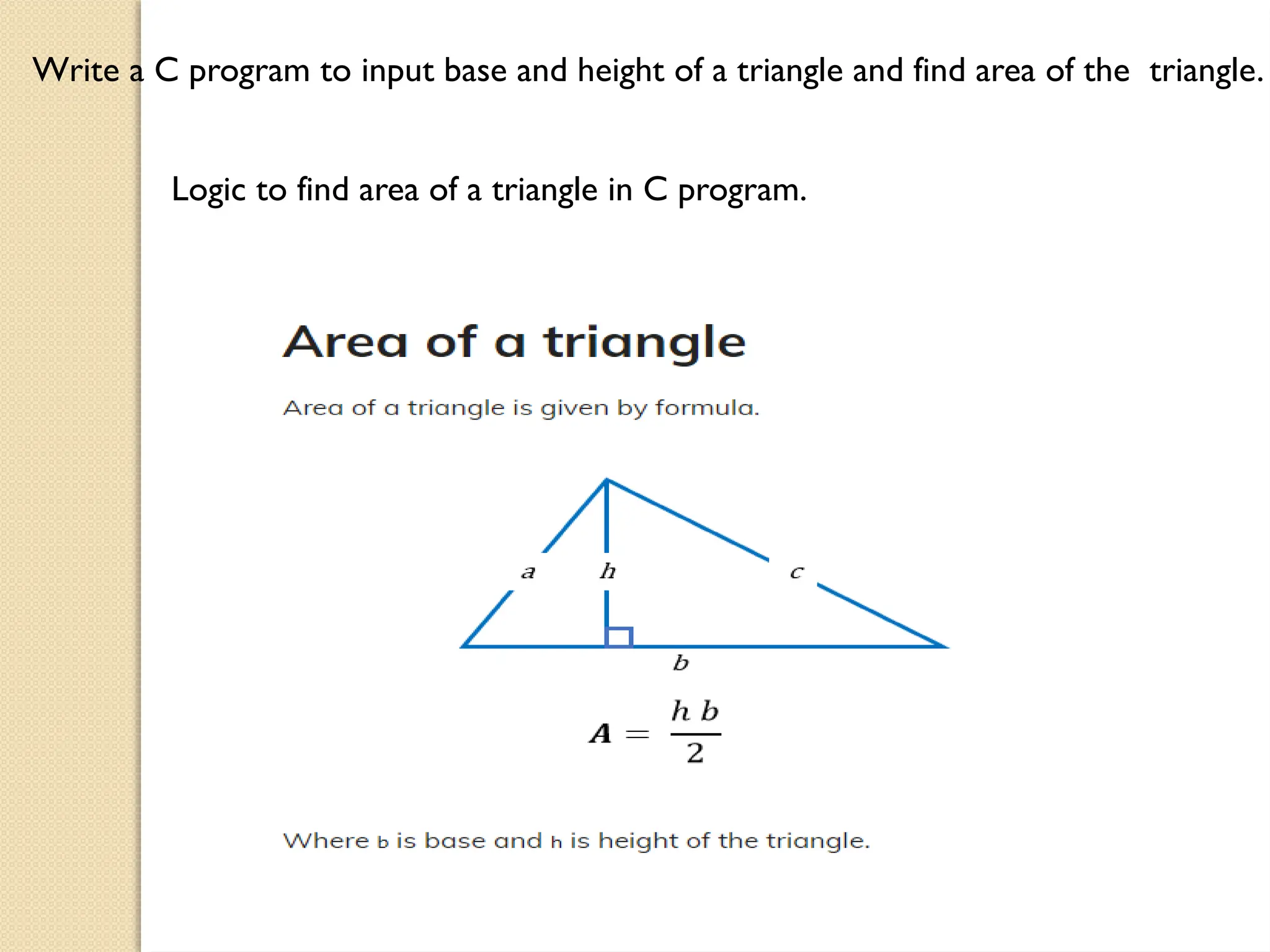




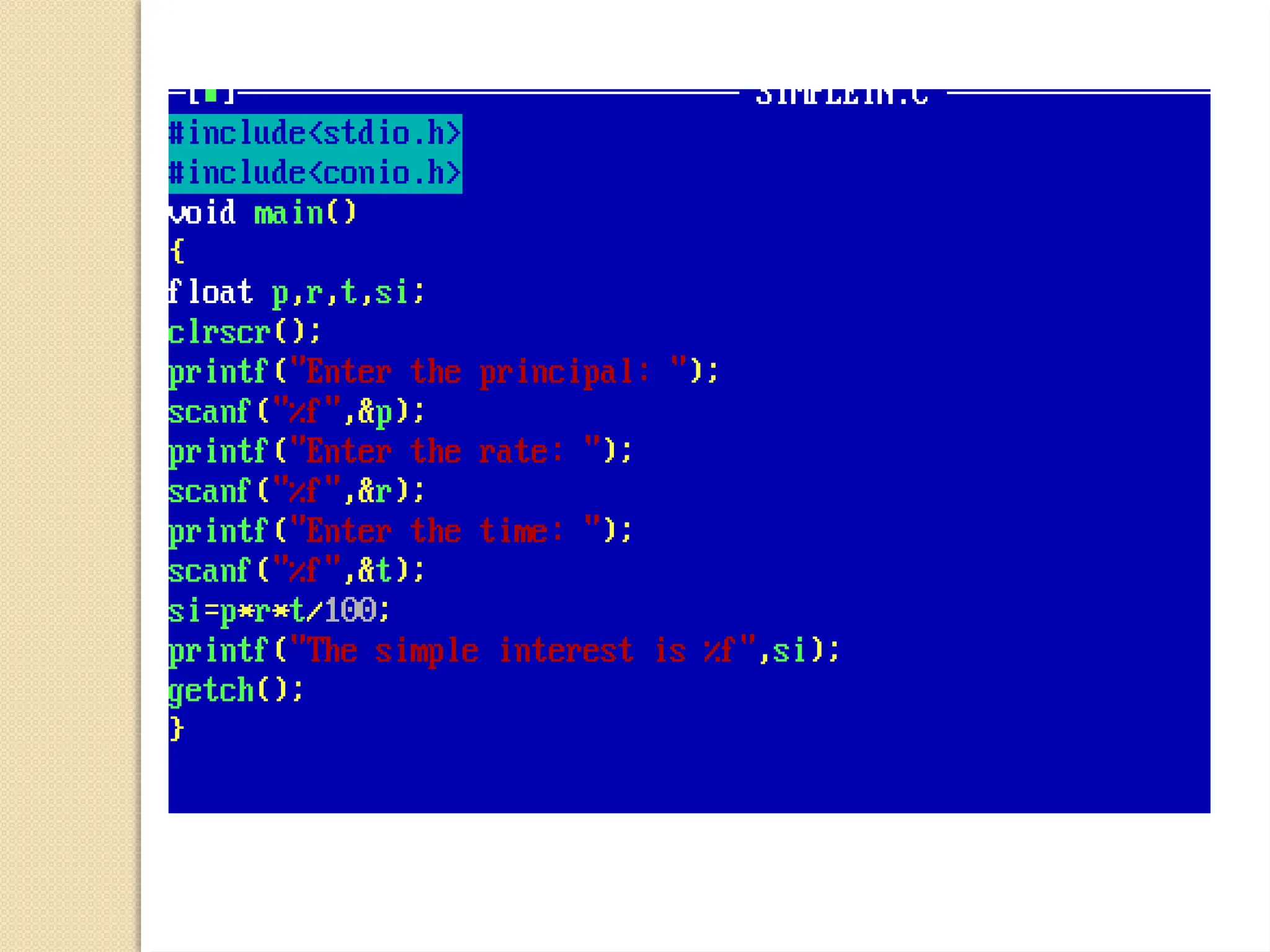



The document contains several C programming examples including converting days to years, weeks, and days, calculating powers of numbers, determining averages and percentages of subjects, finding angles of triangles, and computing the area of a triangle. It also explains simple and compound interest, highlighting the differences between them and the implications of compounding in finance. The code snippets demonstrate practical applications of mathematical concepts in programming.





















