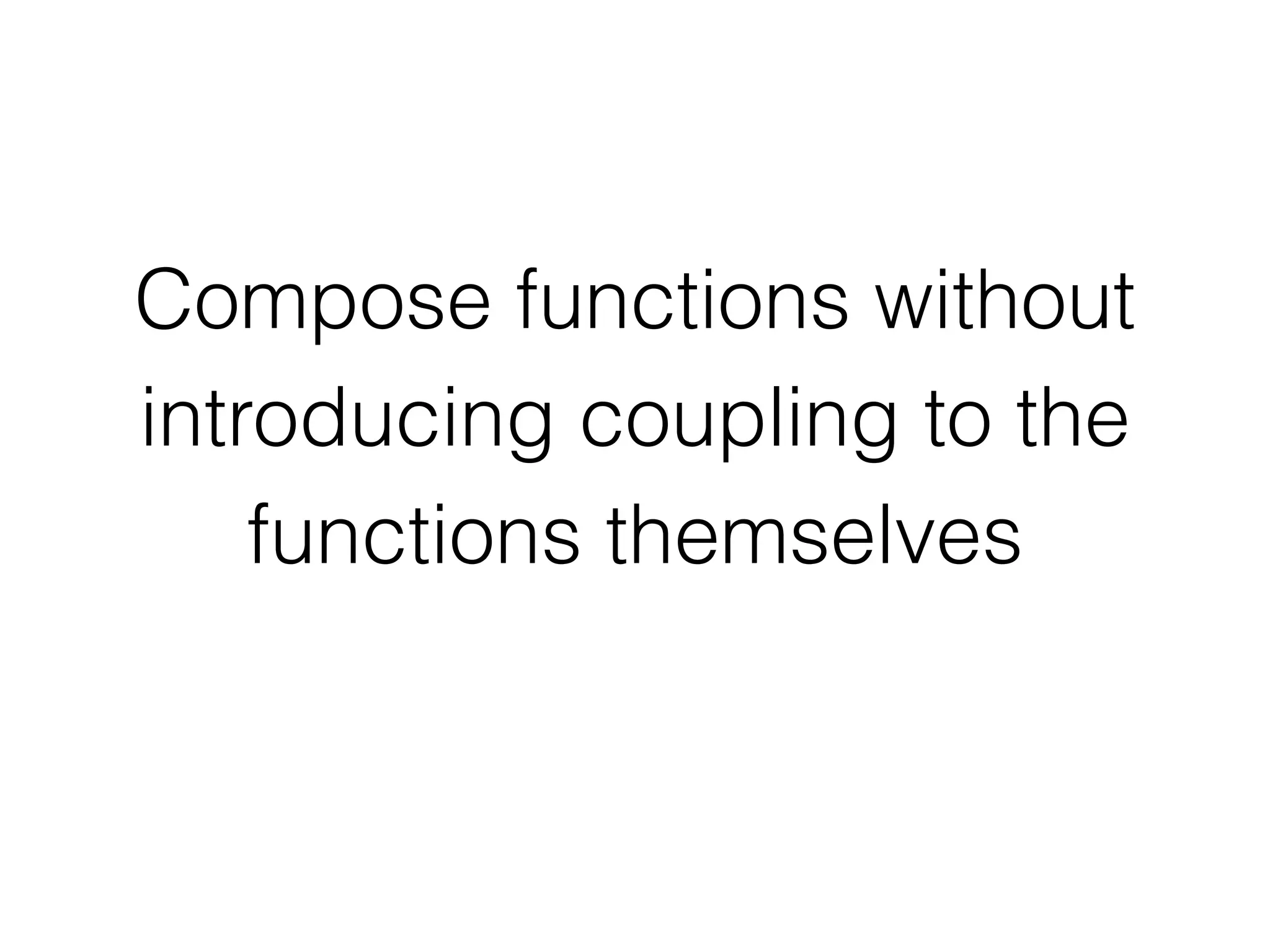
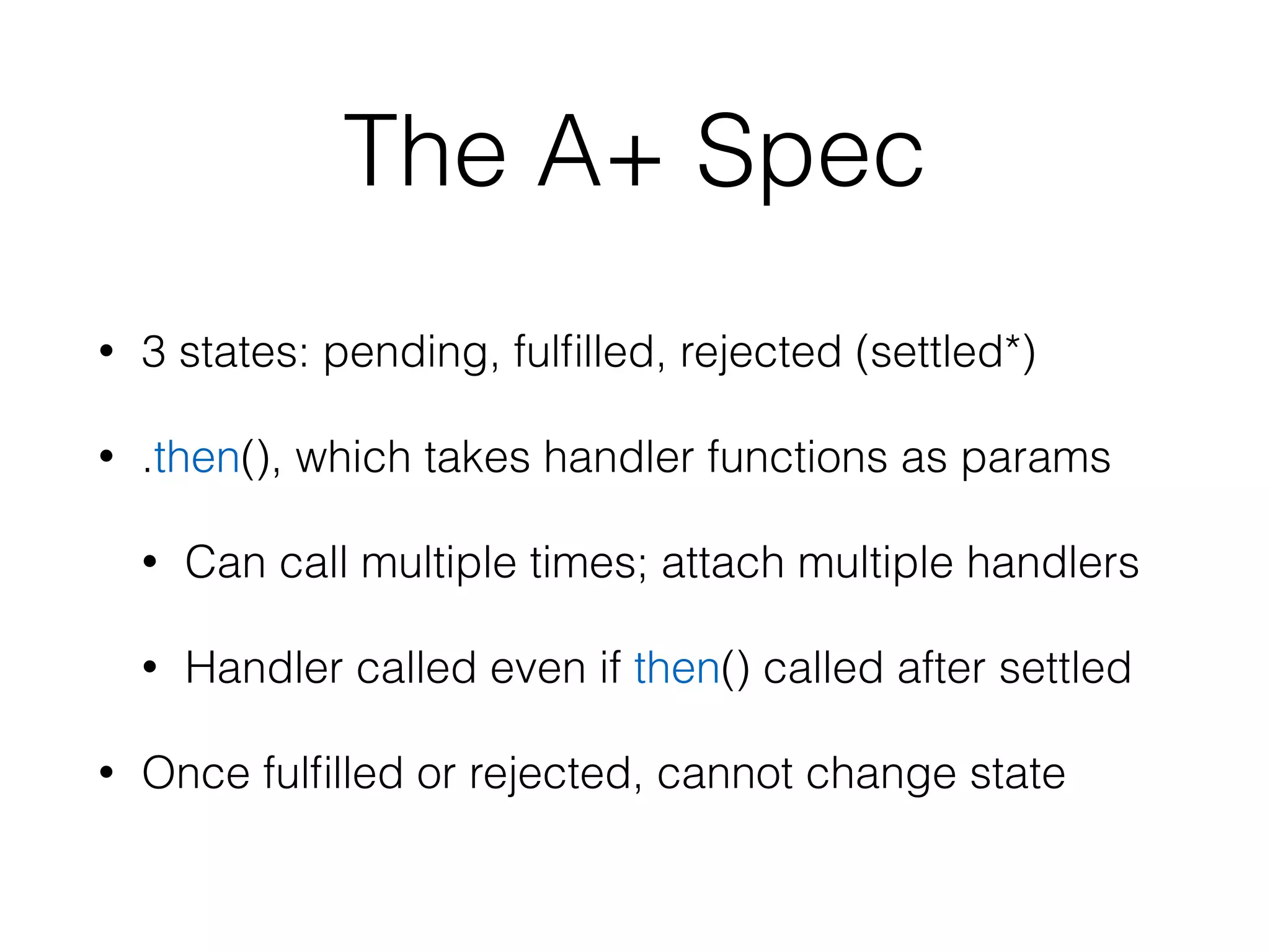
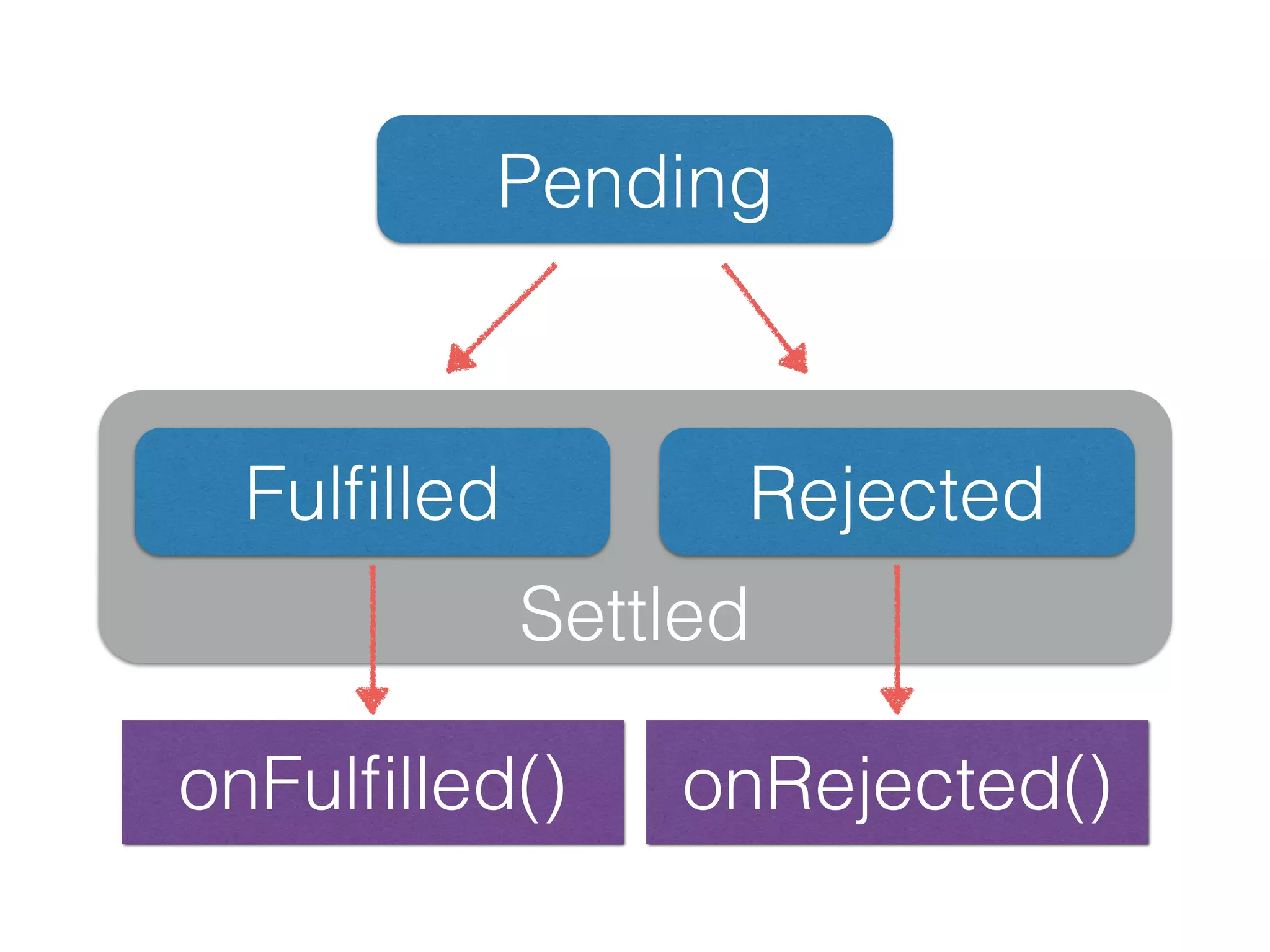
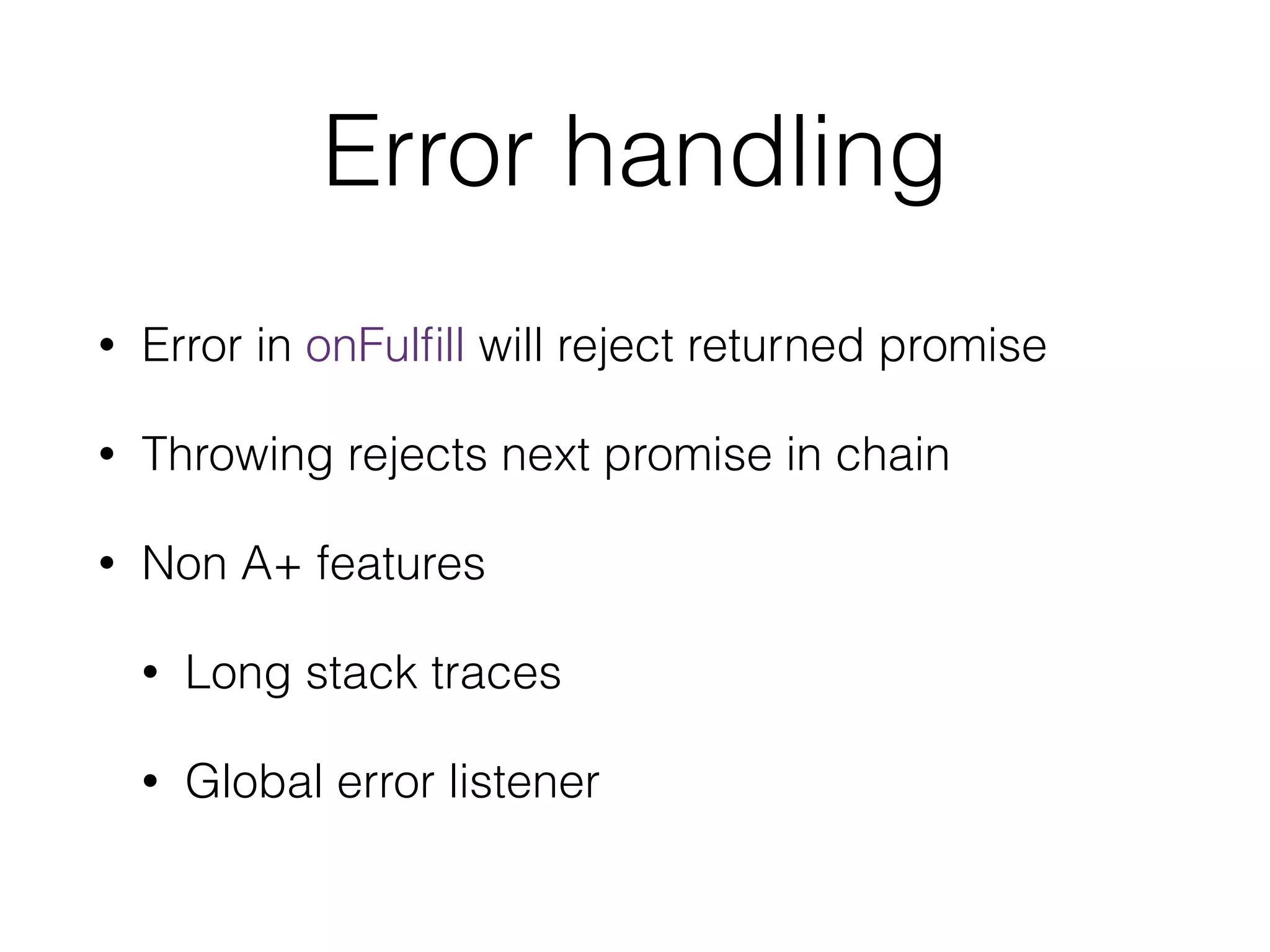
This document discusses JavaScript promises and asynchronous programming. It covers how promises represent asynchronous operations as objects, how to chain promises together using .then(), and how promises can be created using the closure or deferred syntax. It also discusses promise terminology, states, error handling, and common promise patterns and use cases. High-order functions and promise utility functions provided by promise libraries are presented. Guidelines for testing promises are also included.


![var loadContainer = showPage('#photo-view'); var loadController = Controller.load(id, authToken); ! Promises.all([ loadContainer, loadController ]).then(Controller.pageDidLoad) .then(null, handleError); ! loadController.then(null, handleError);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practical-js-promises-140904030346-phpapp01/75/Practical-JavaScript-Promises-3-2048.jpg)
![pageDidLoad: function(results) { var loadContainerResult = results[0]; var loadControllerResult = results[1]; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/practical-js-promises-140904030346-phpapp01/75/Practical-JavaScript-Promises-4-2048.jpg)