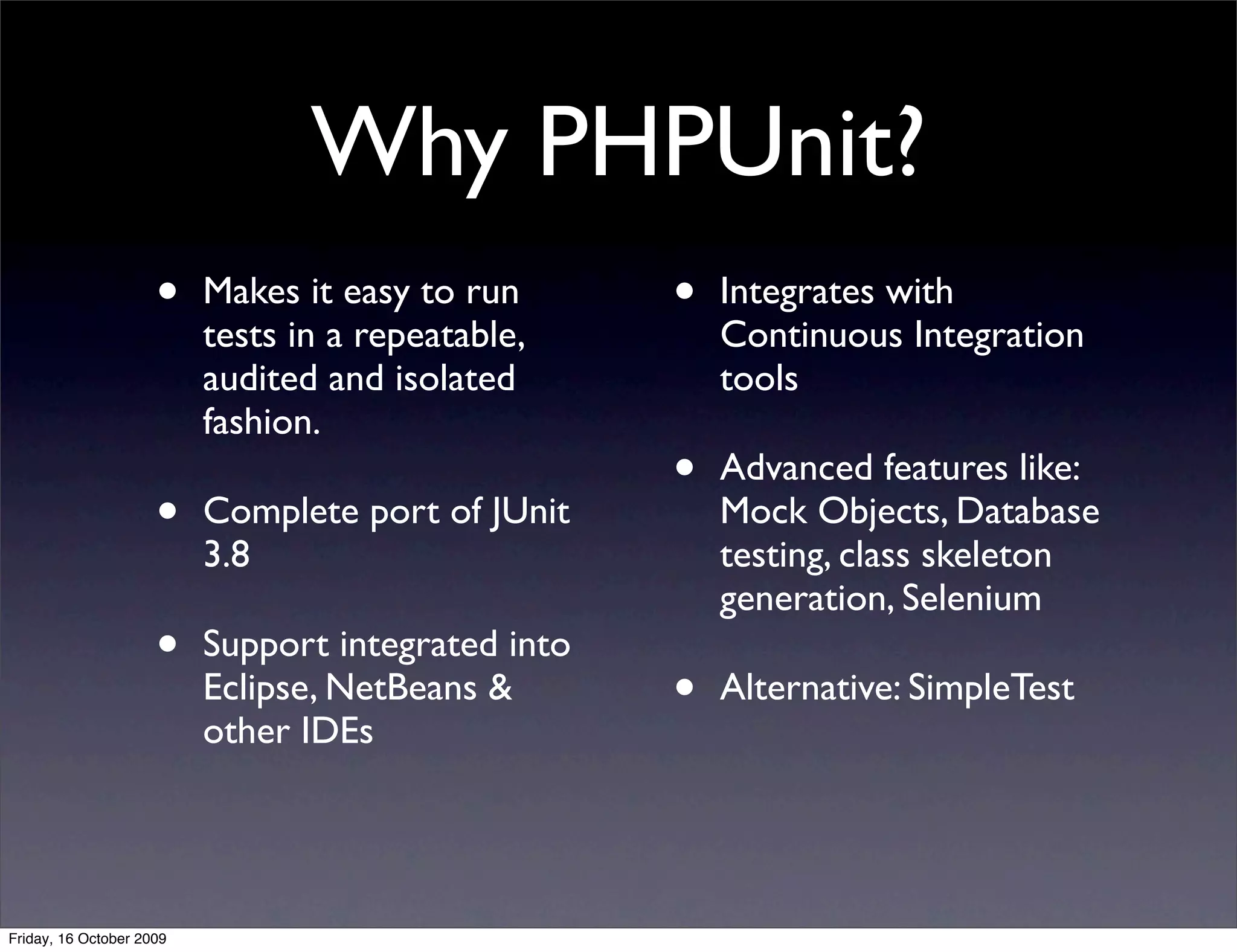
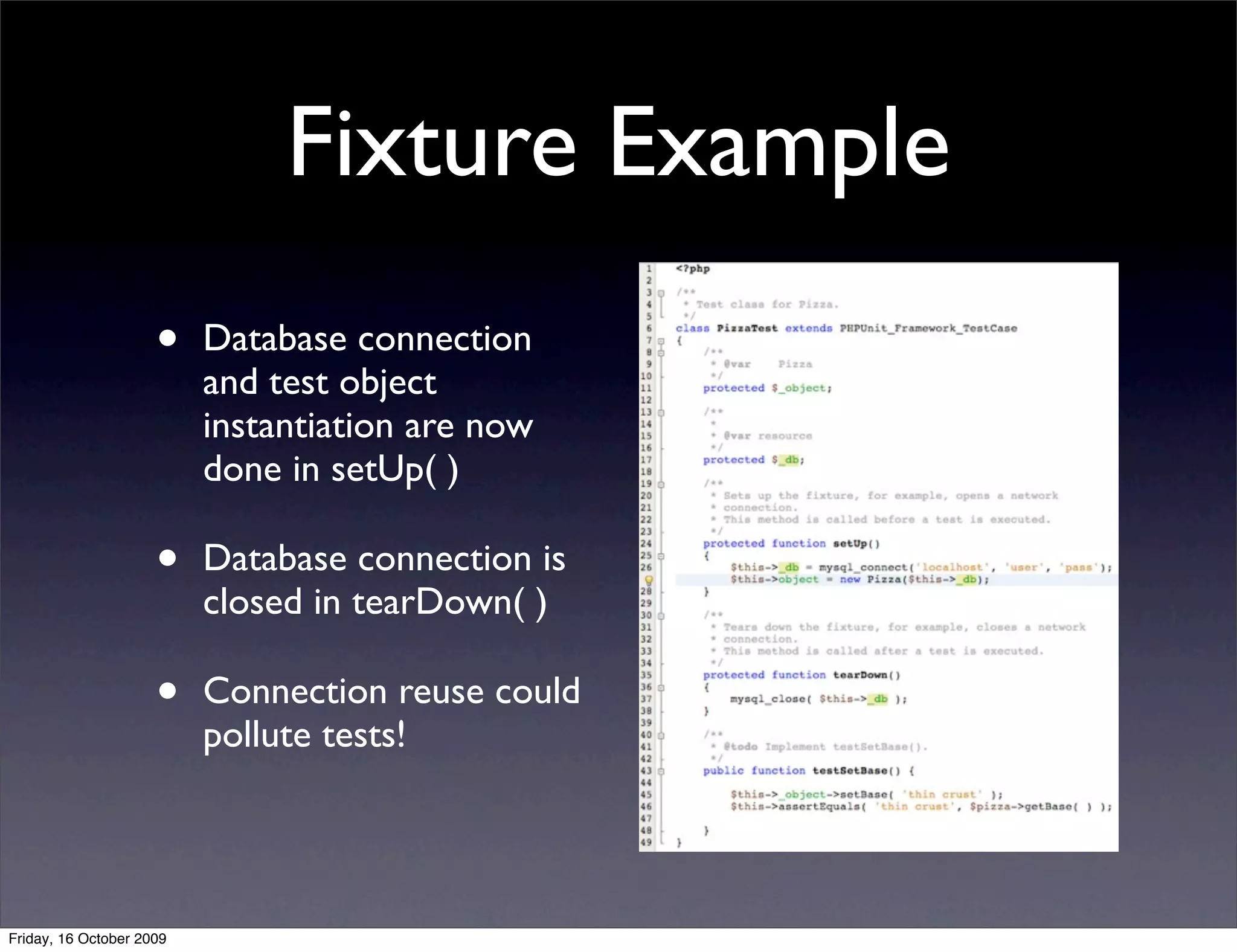
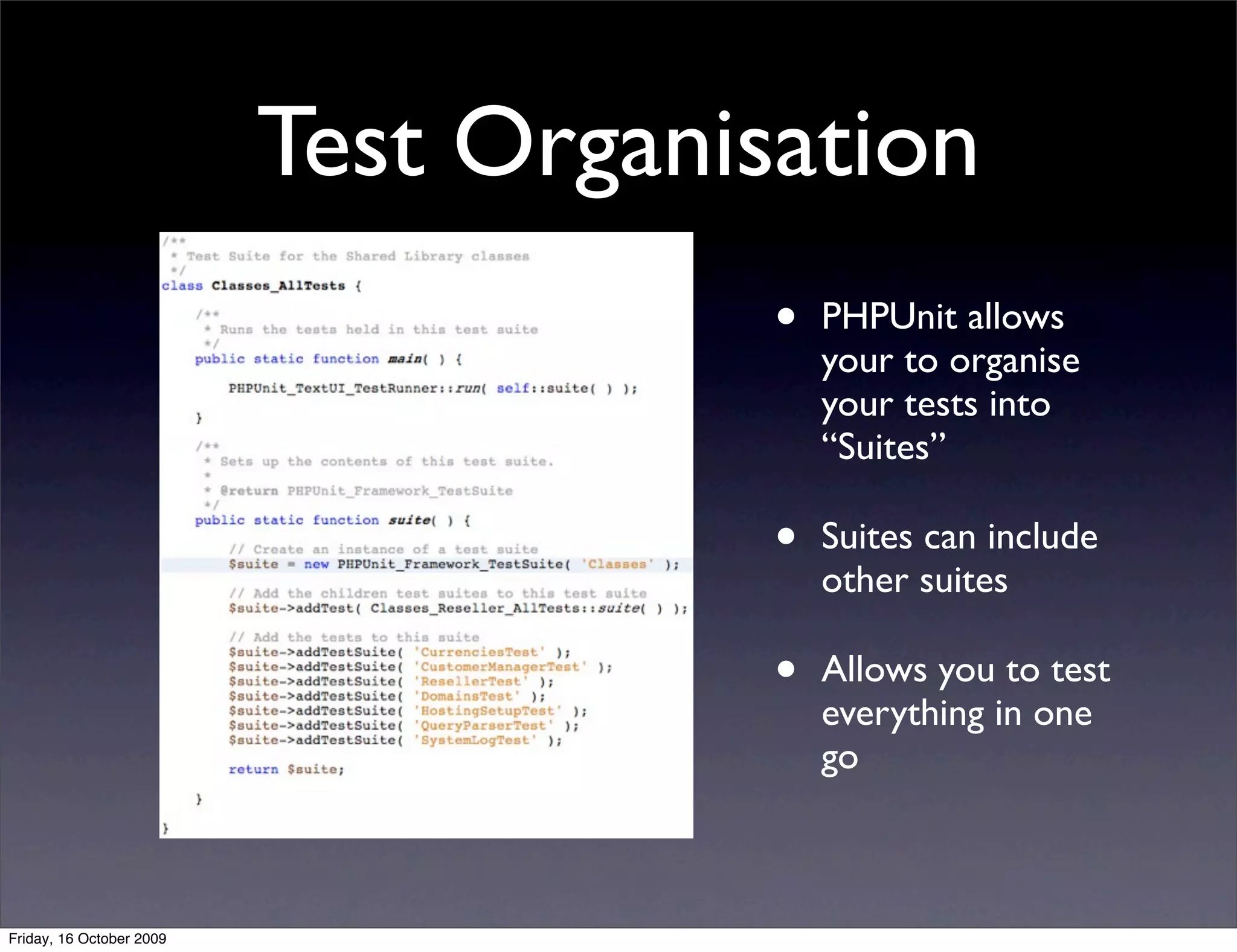
This document introduces PHPUnit for unit testing and continuous integration (CI). It discusses what unit testing is, why it's important, and how to set up and write tests with PHPUnit. It also covers best practices for testing and how CI can automate running tests and integrating code changes. CI helps developers work together and catch bugs early by constantly running tests on new code submissions.