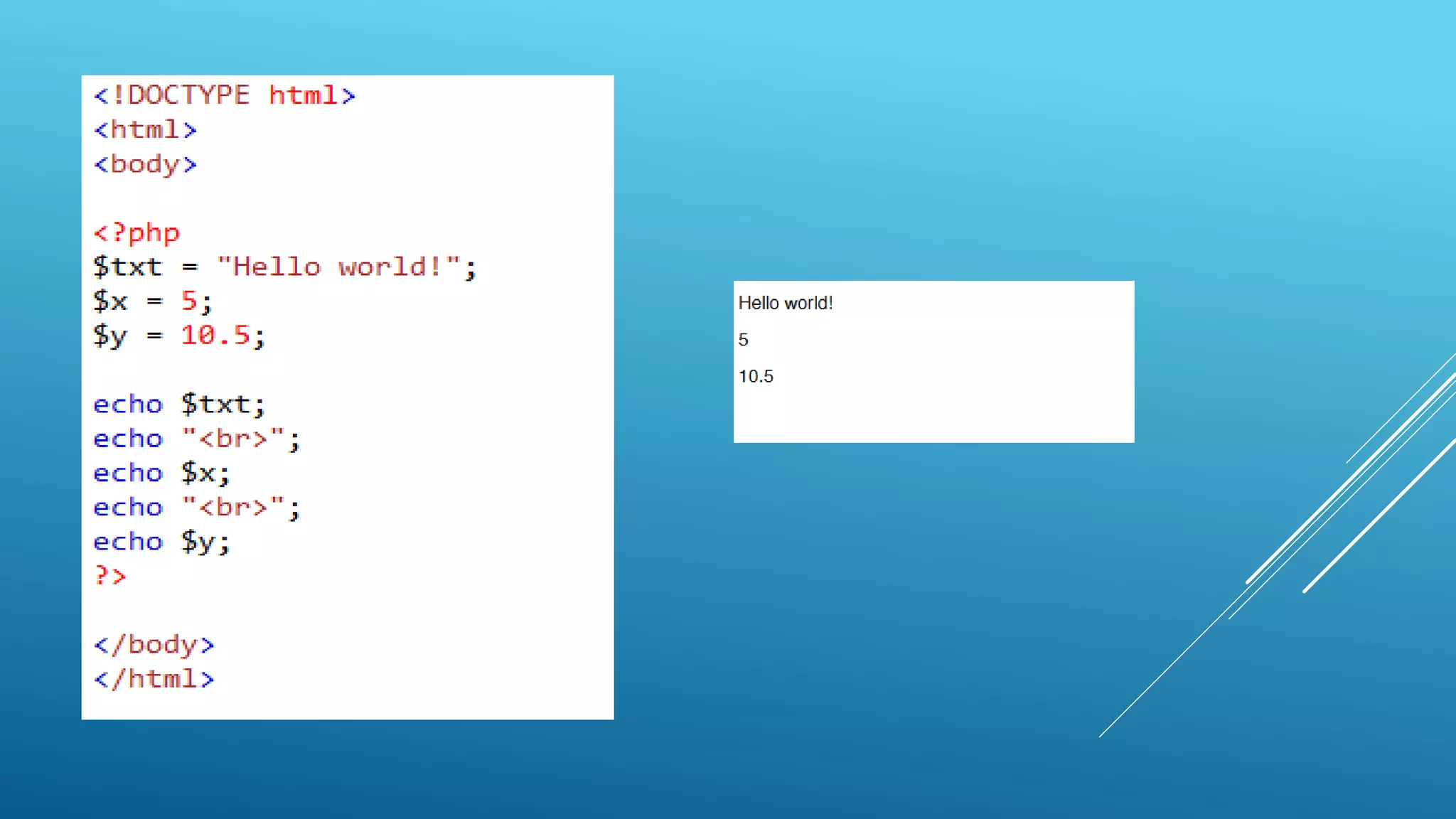
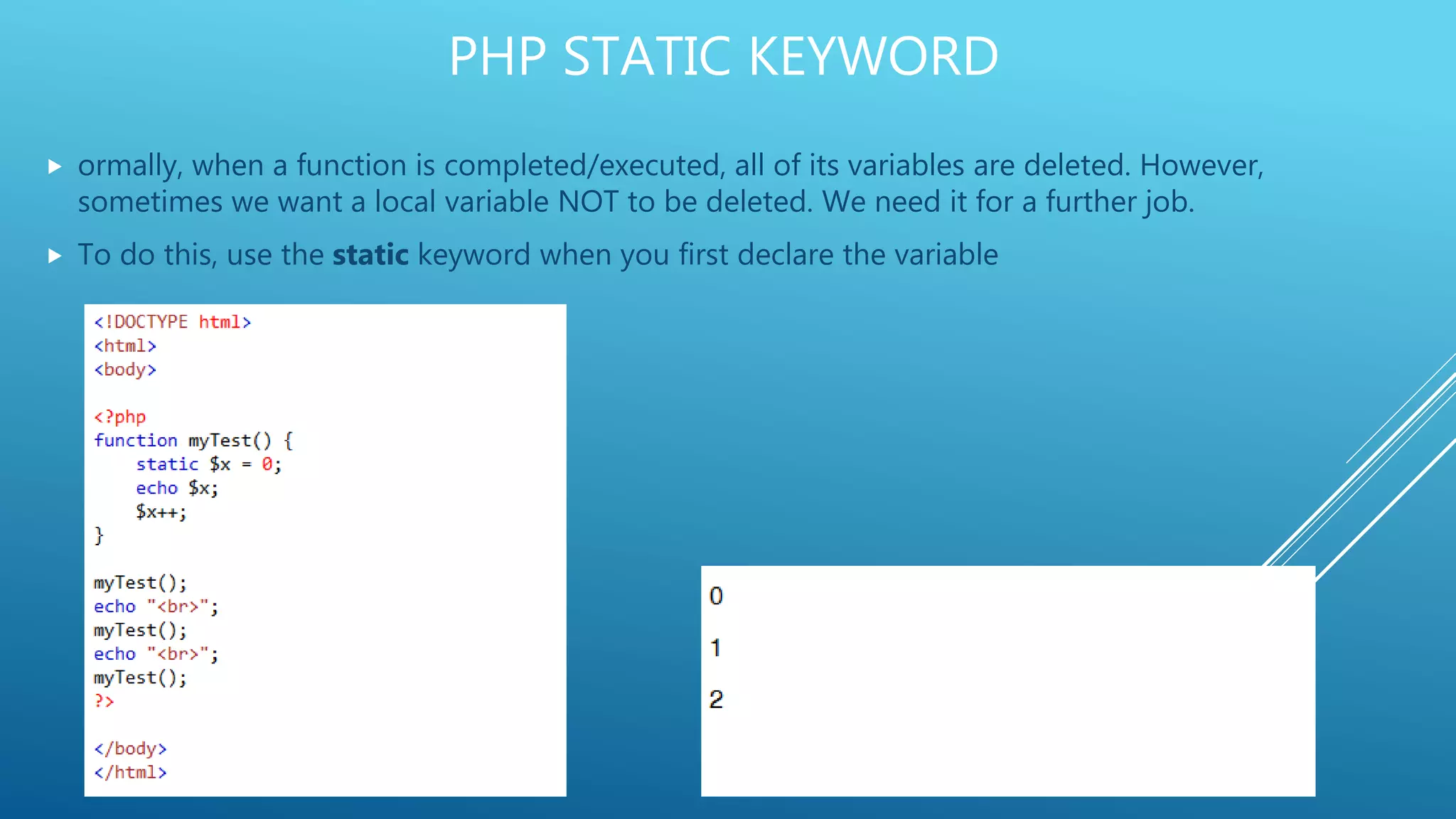
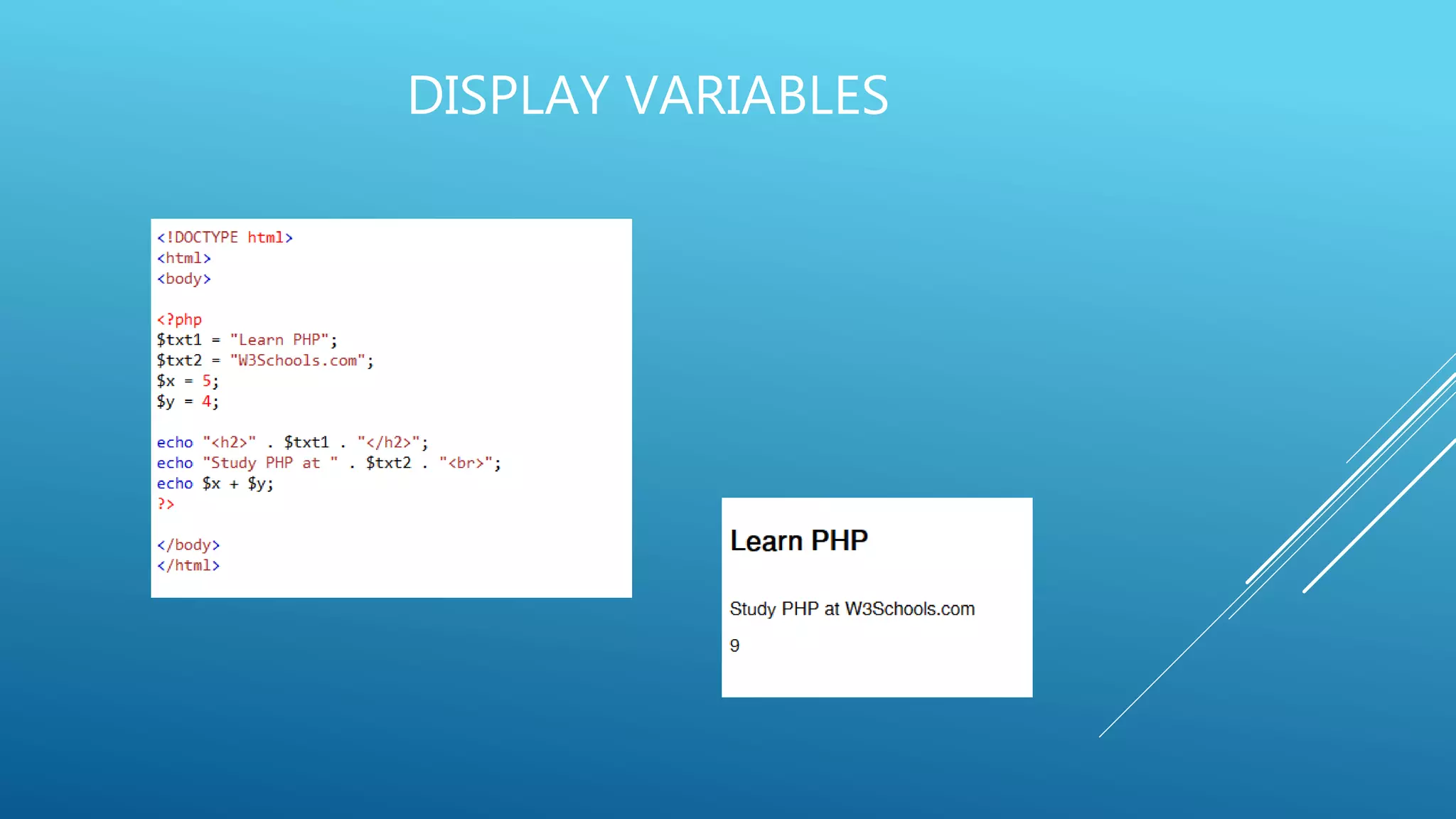
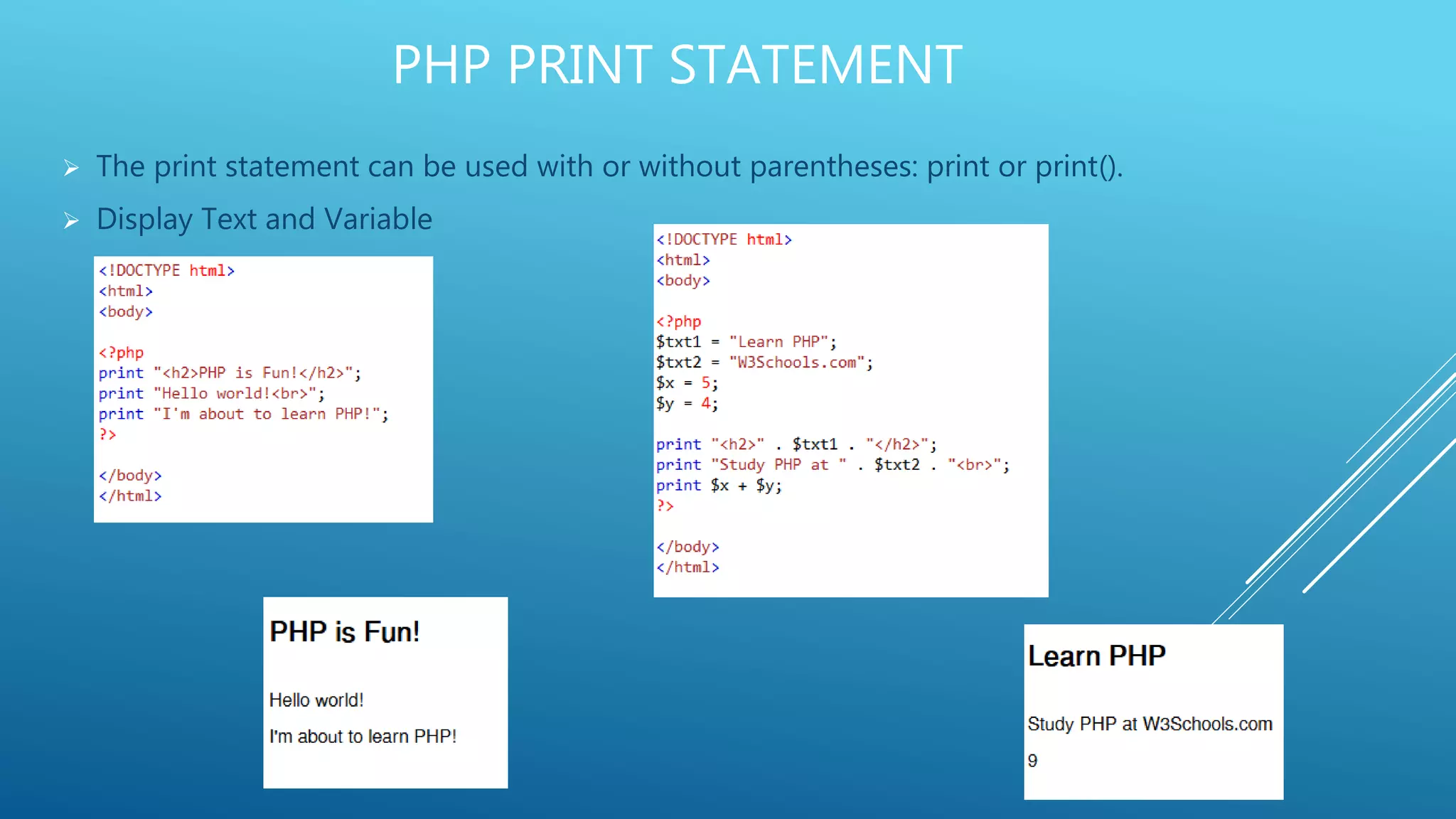
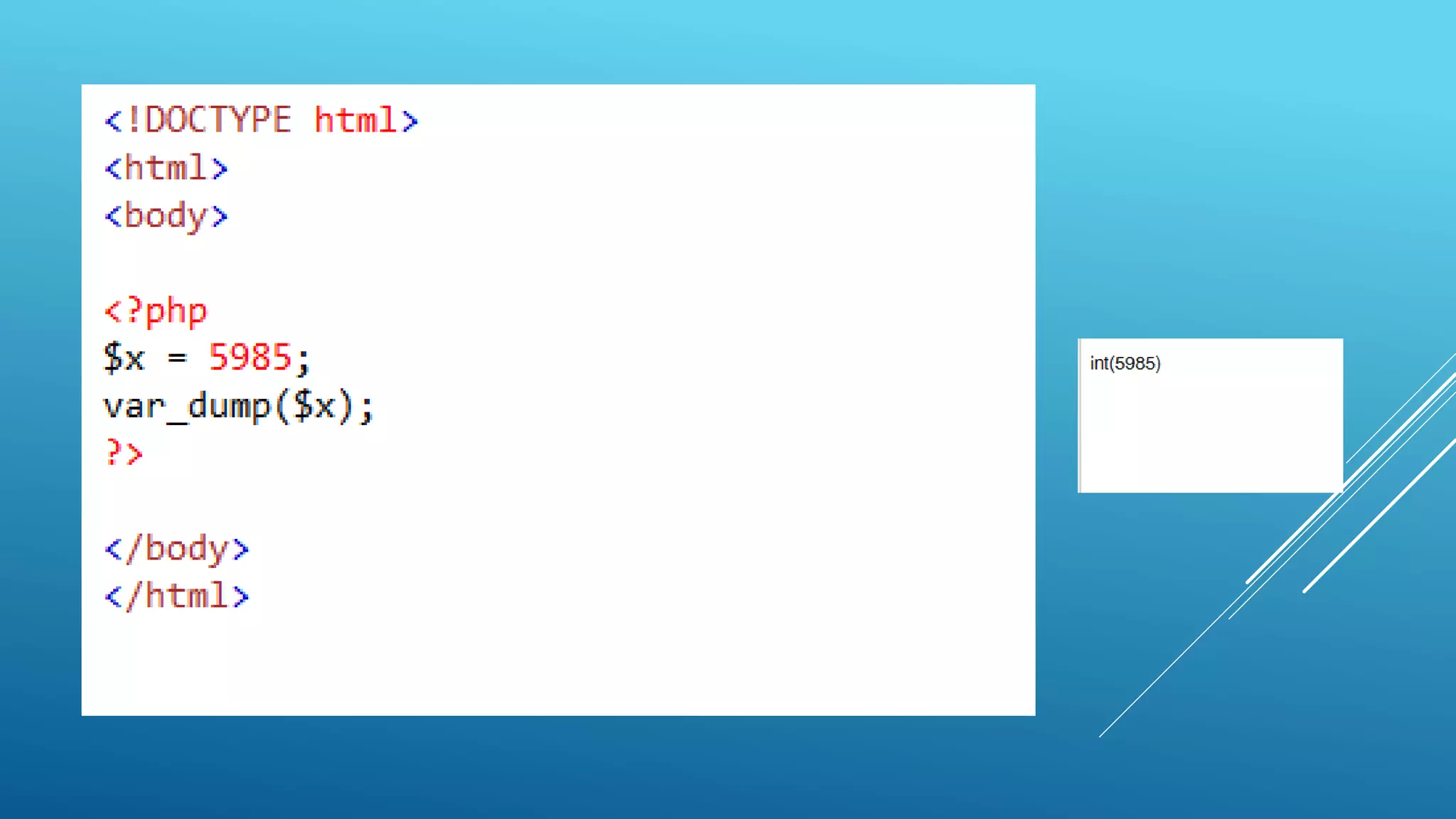
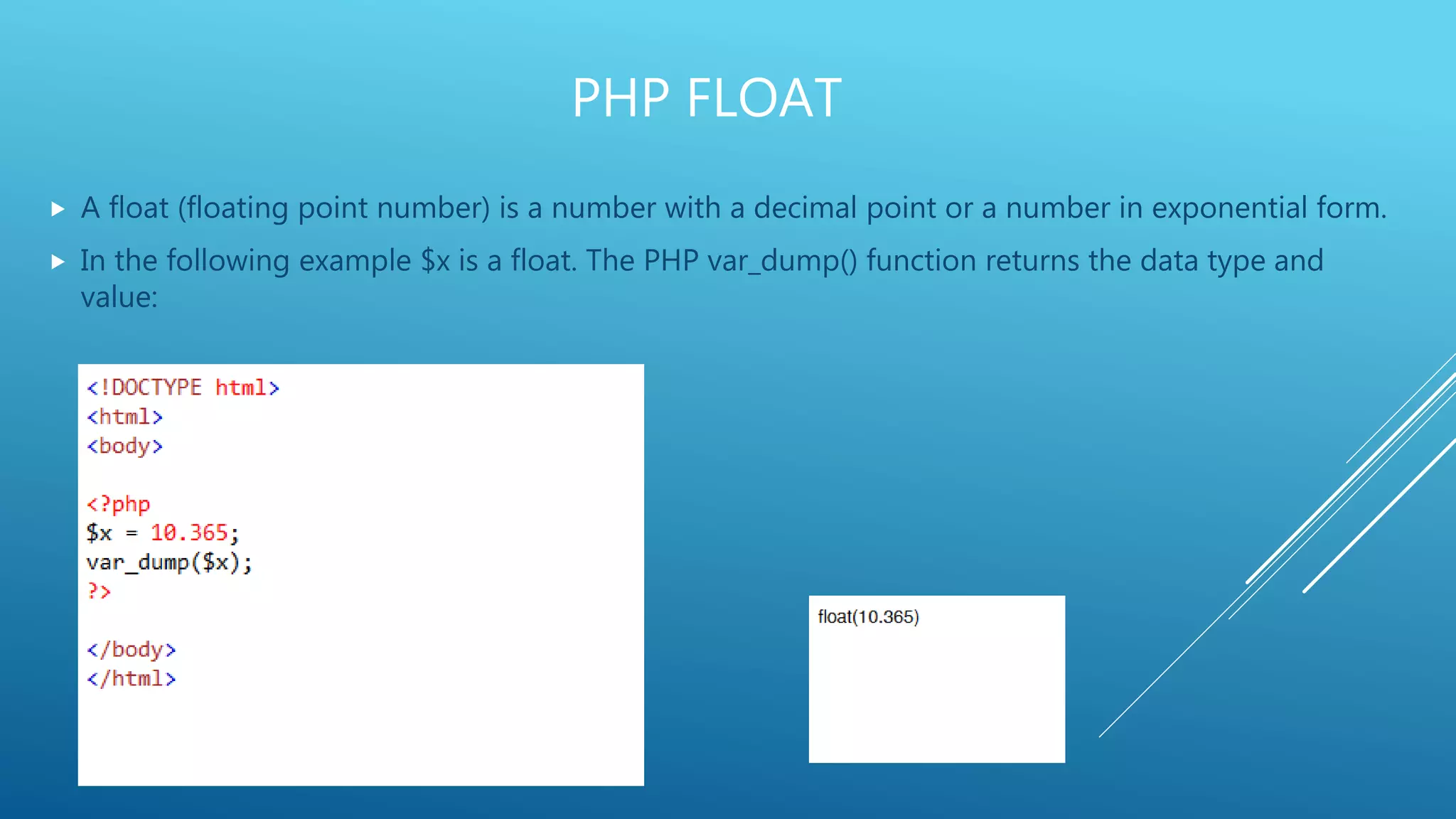
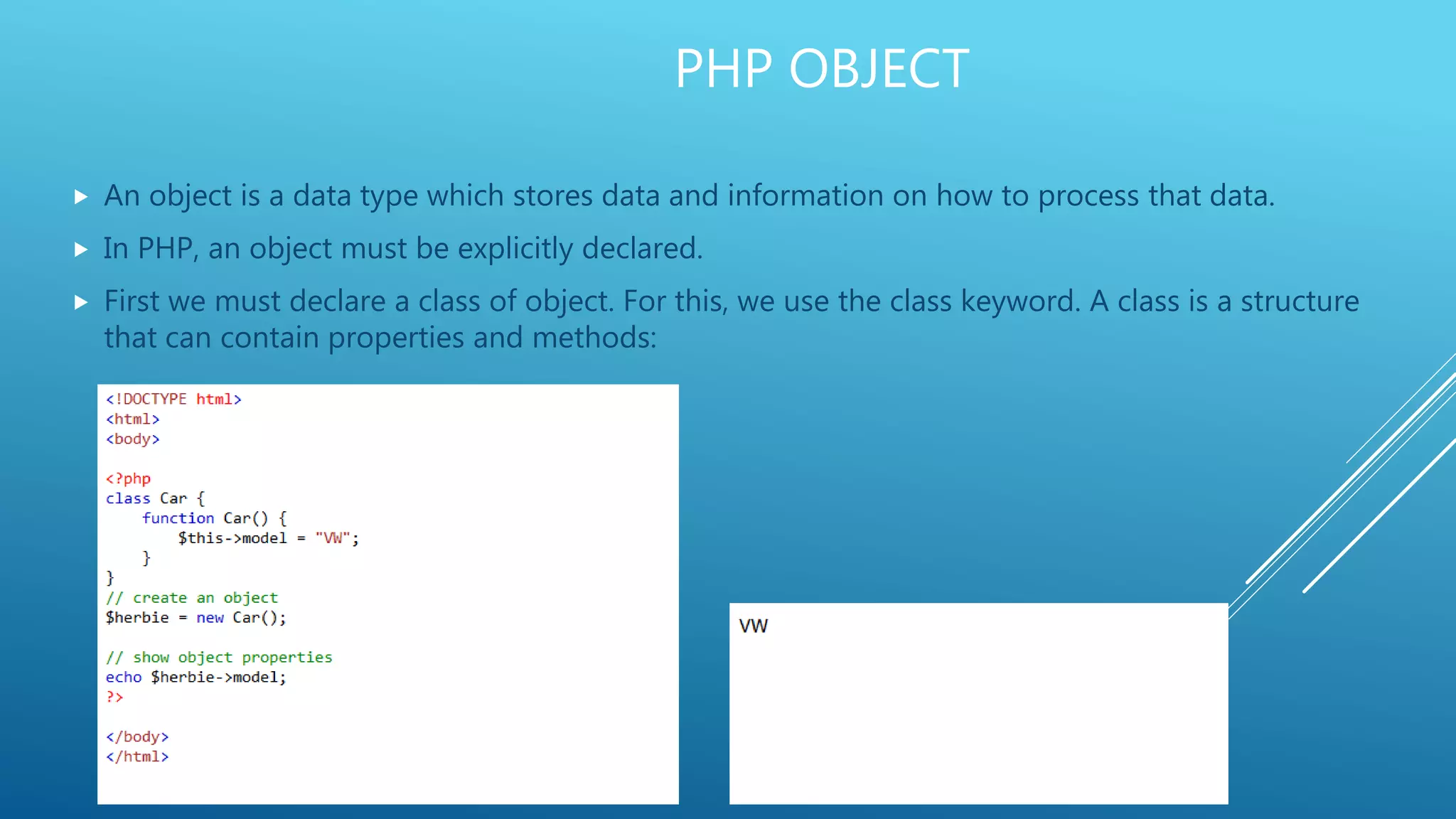
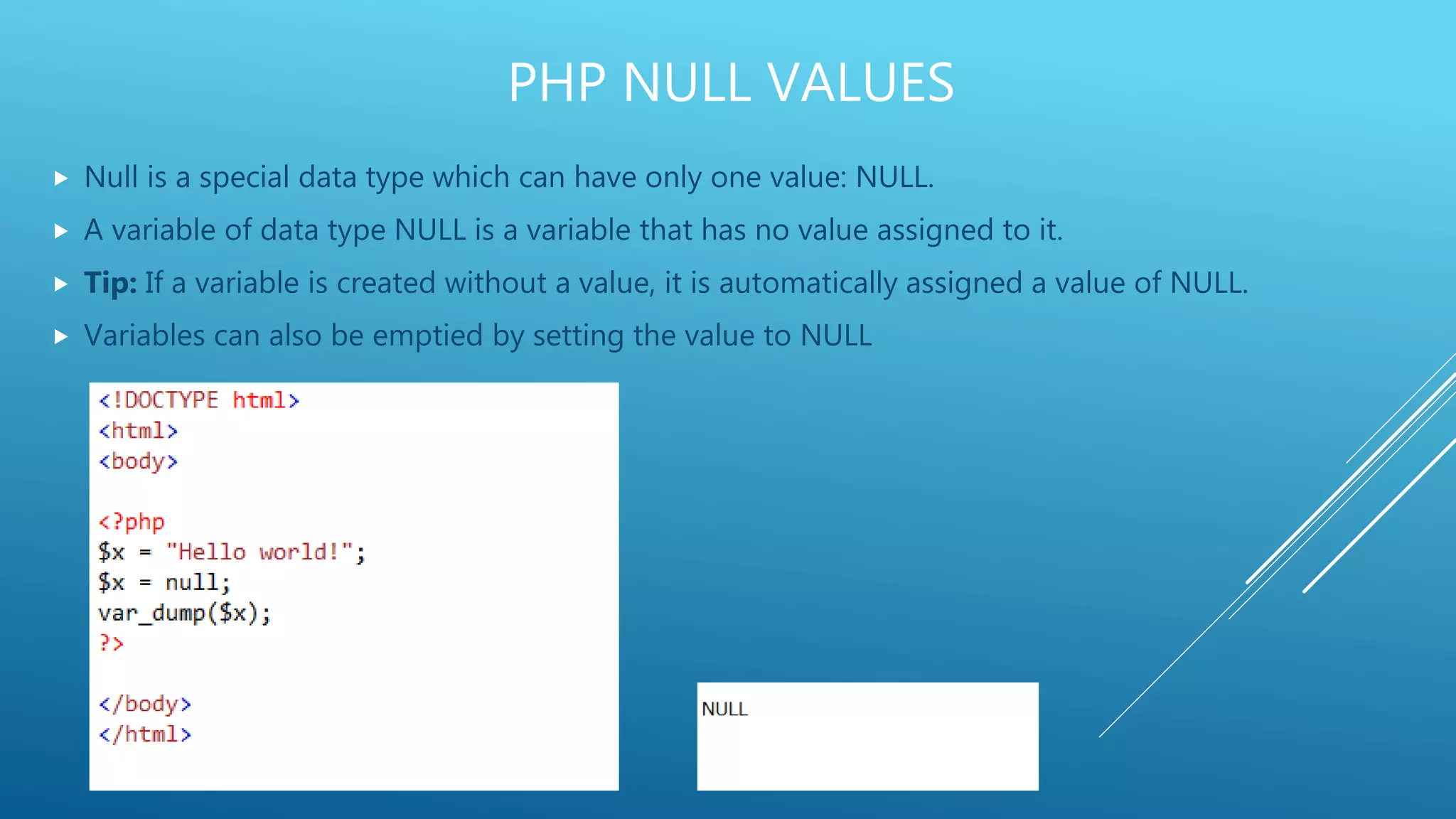
This document provides an introduction to PHP, explaining it as a widely-used, open-source scripting language that is executed on the server and can generate dynamic web content. It covers PHP features including variable declaration, data types, and scripting syntax, outlining how PHP supports various platforms and is compatible with numerous databases. Additionally, it details the use of PHP in handling files, cookies, user access, and data encryption.