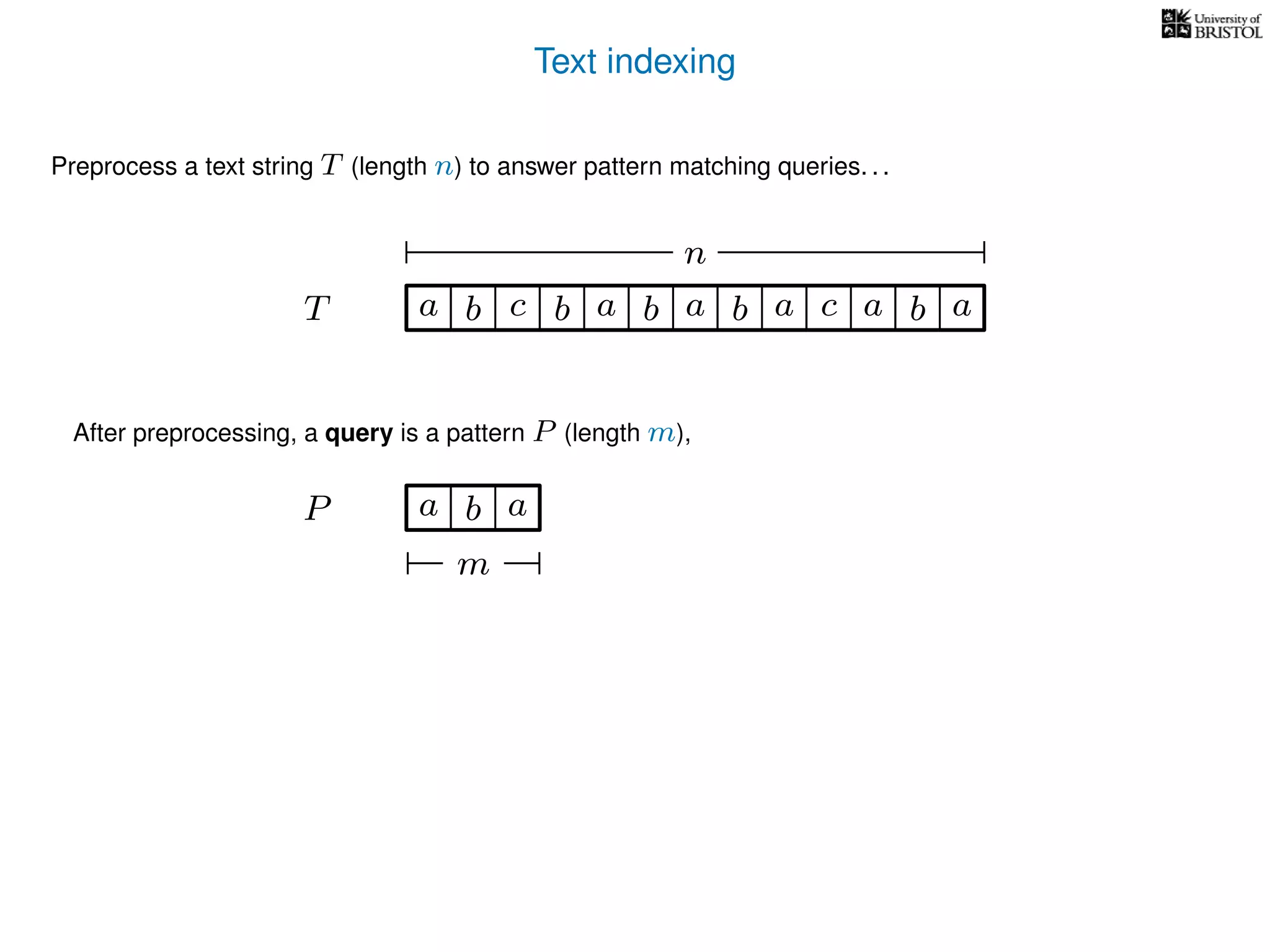
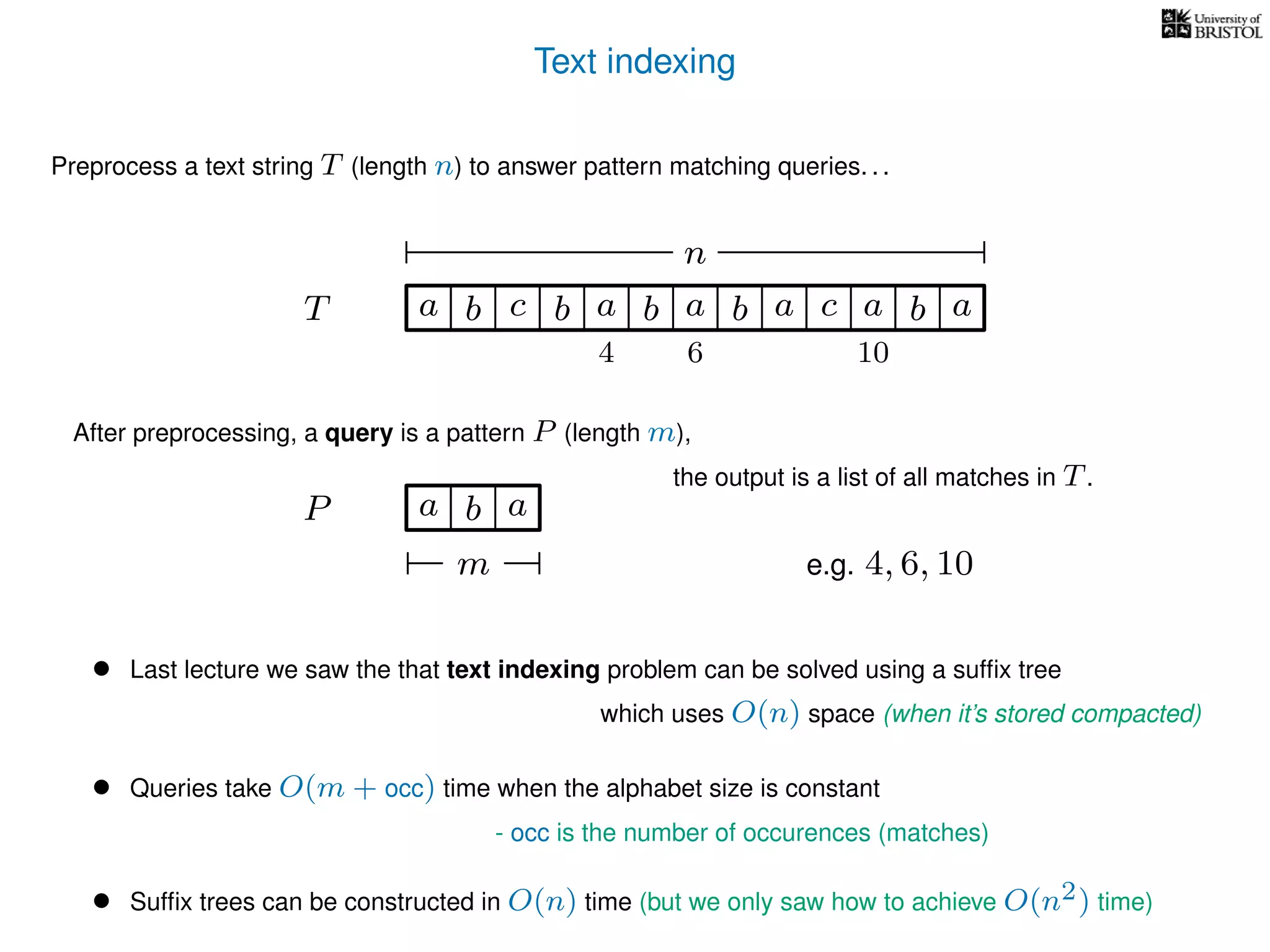
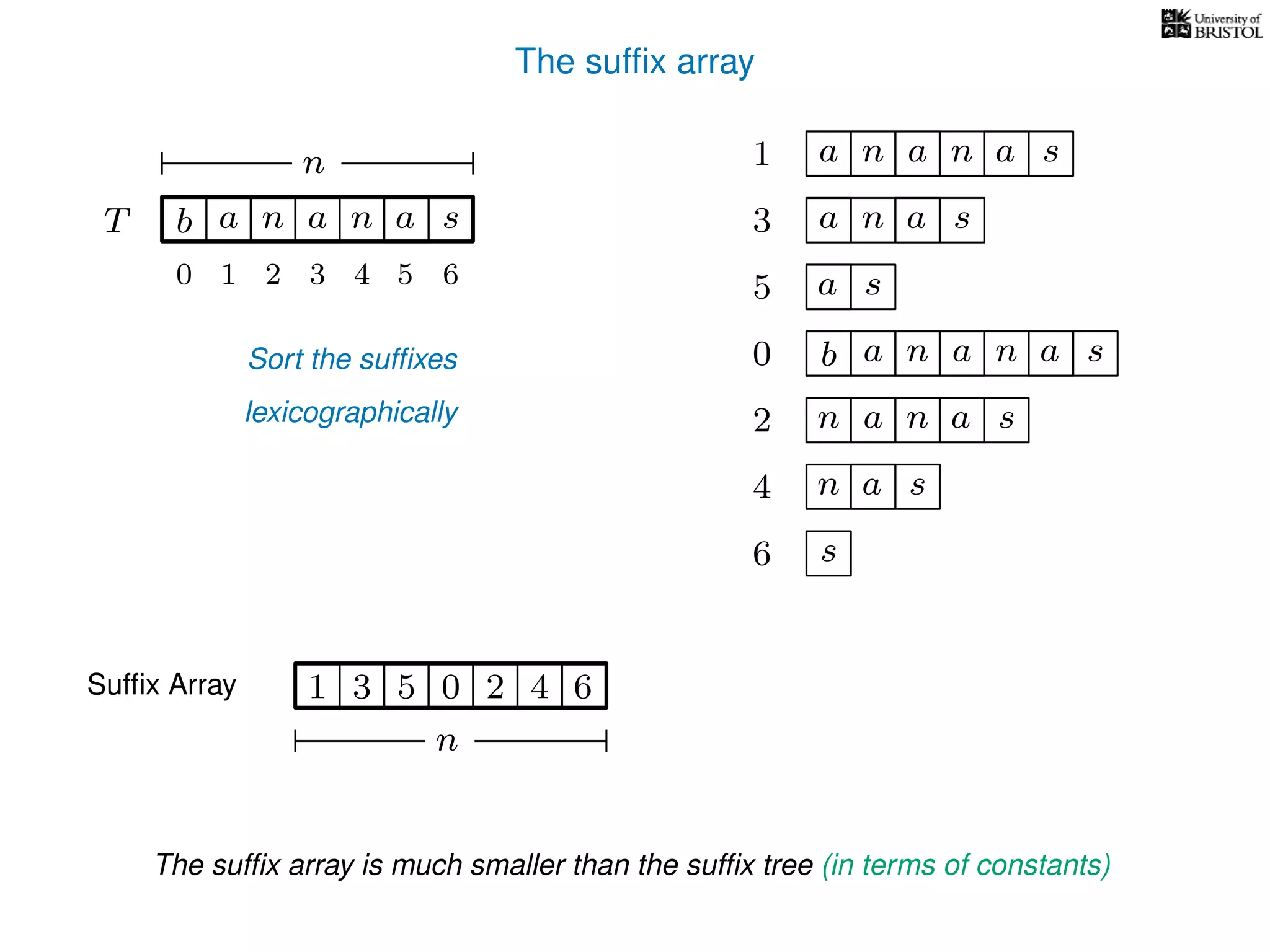
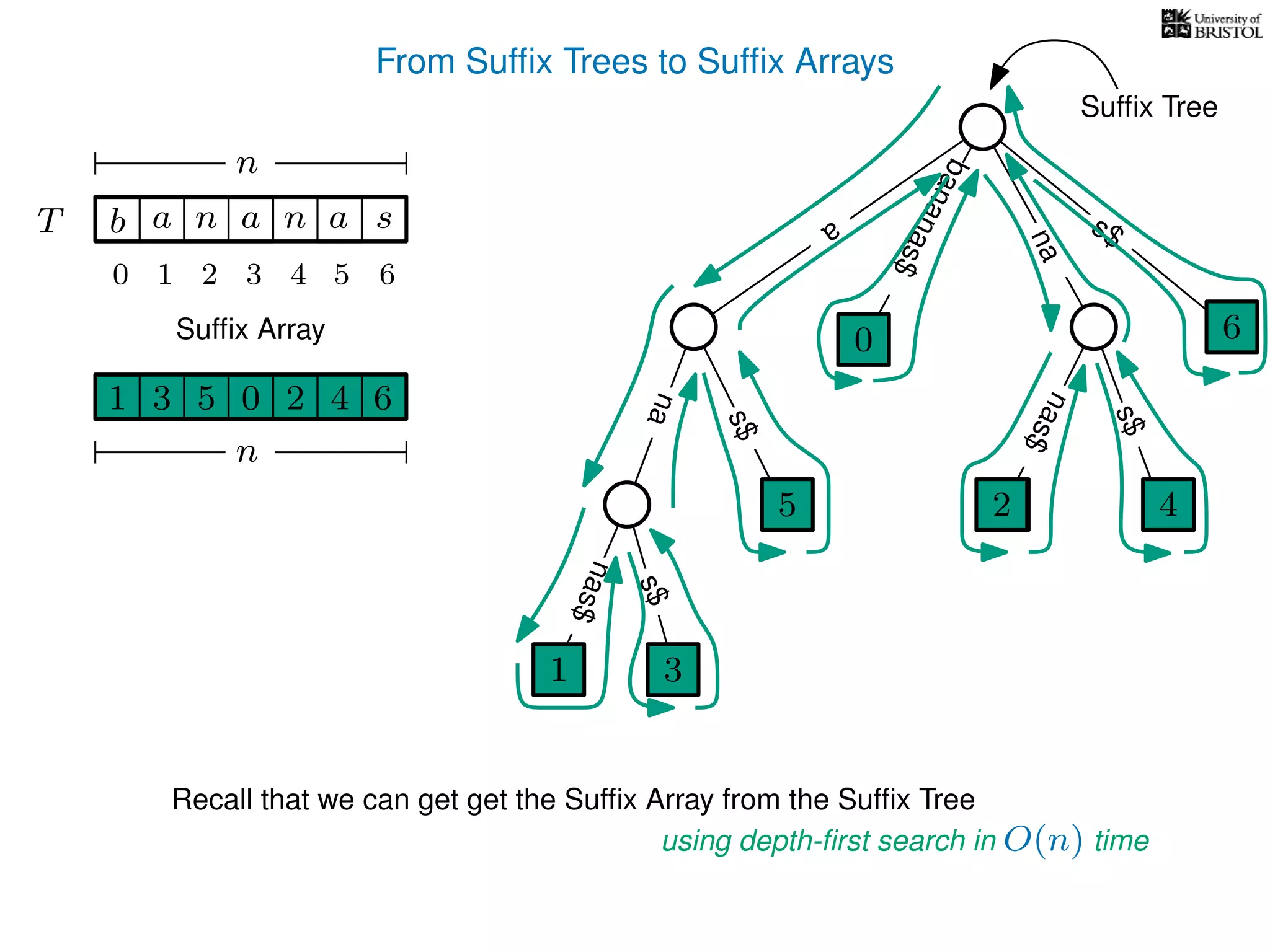
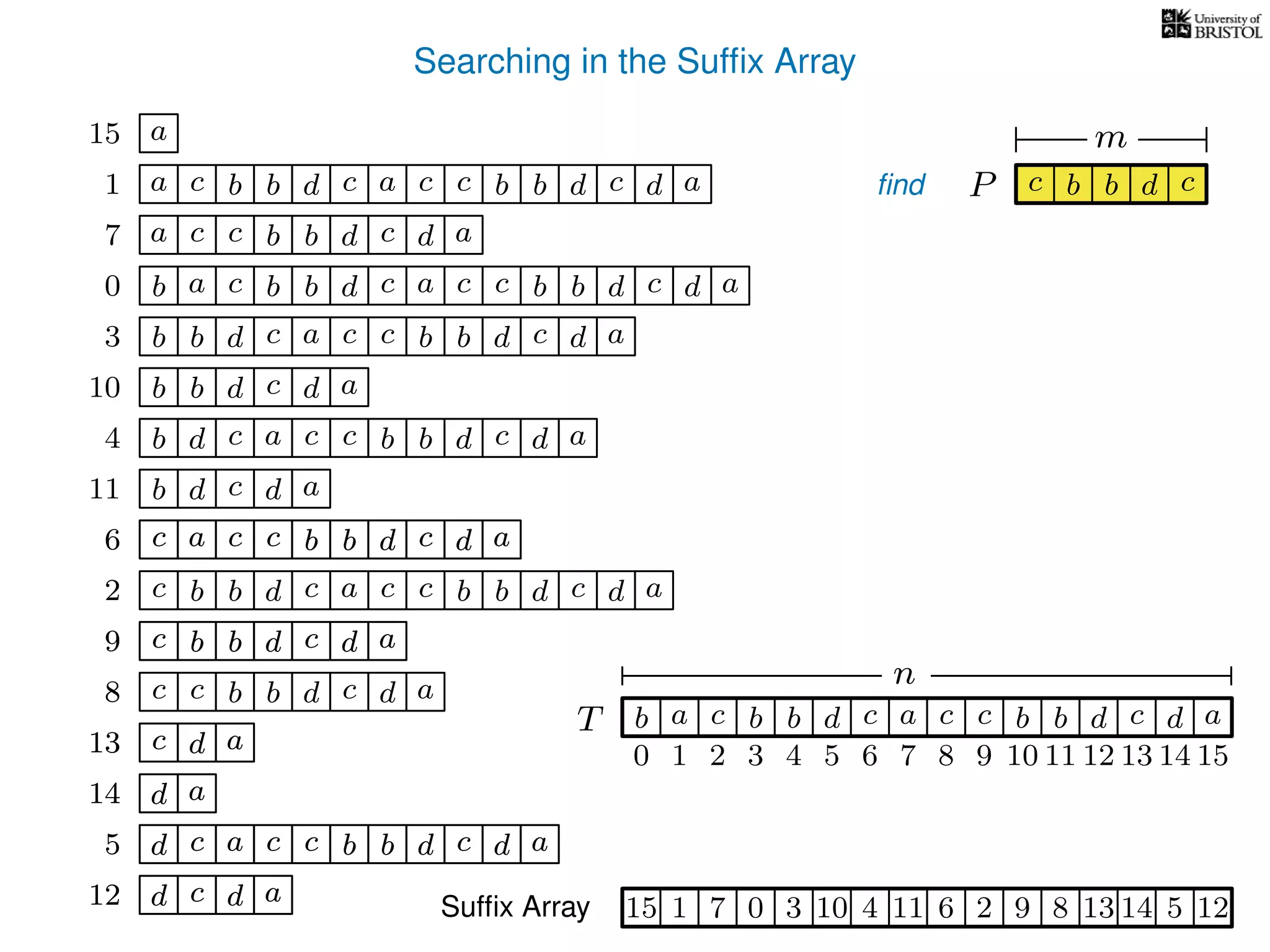
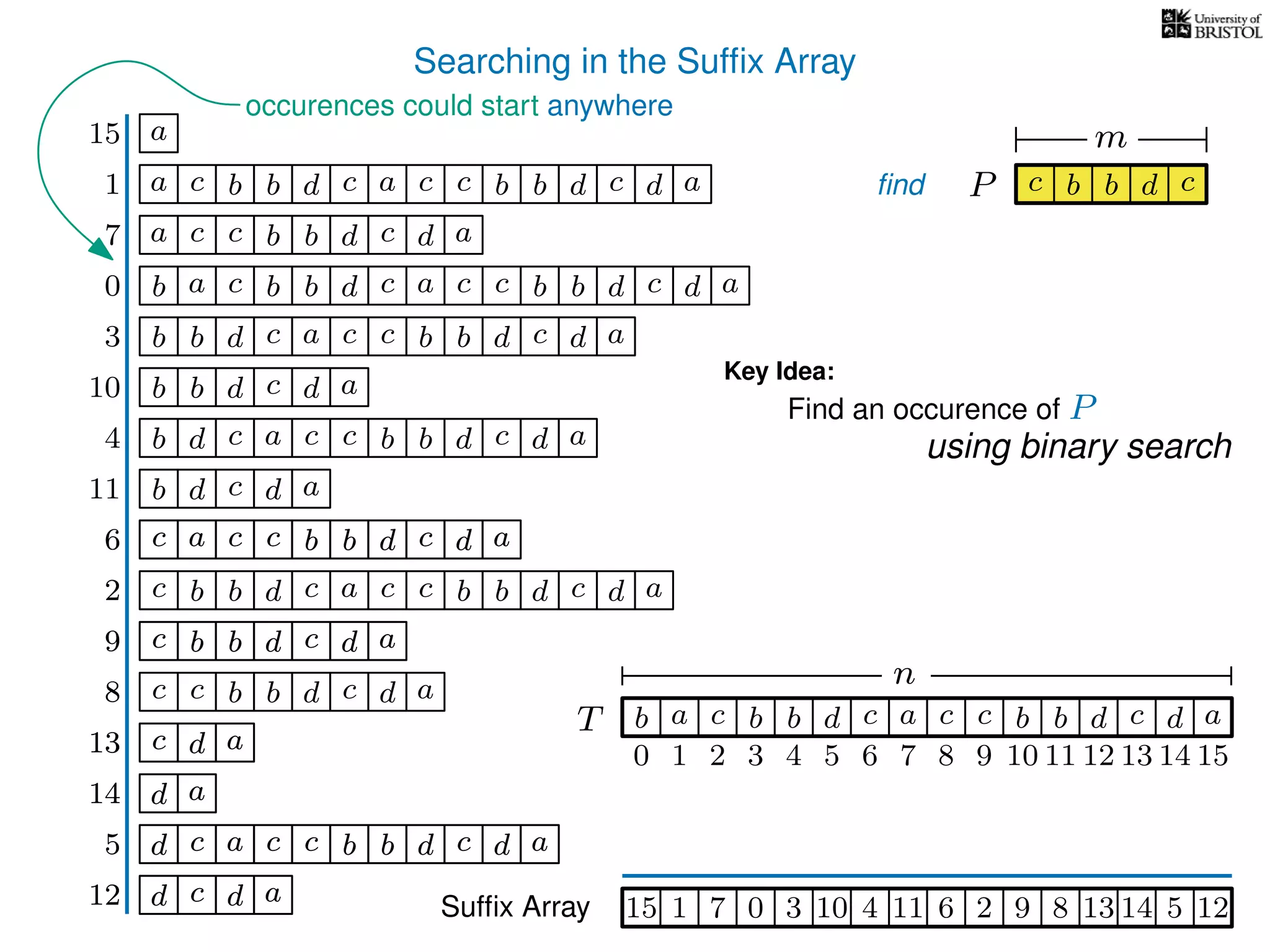
The document discusses advanced algorithms for text indexing and pattern matching using suffix arrays and trees. It explains the processes of preprocessing a text string to answer pattern matching queries, the efficiency of suffix trees in terms of space and query time, and how to construct suffix arrays. It also highlights the lexicographical sorting of suffixes and the transition from suffix trees to suffix arrays for more compact representation.




































































































































![The DC3 method y a b d ob a a b b a d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 110 T = B1 contains indices with i mod 3 = 1 B2 contains indices with i mod 3 = 2 How do we find the ordering of the suffixes from B0? (where i mod 3 = 0) Suffix array for just B1 ∪ B2 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 y a b d ob a a b b a d d ob a a b b a d oa b b a d oa d 0 3 6 9 = + 1y = + 4b = + 7a = +a 10 Each suffix i ∈ B0 is represented by (T[i], r) where r is the rank of suffix (i + 1) 1 24 111058 7 (the ranks are given by the array below) rank:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa-06-160916143738/75/Pattern-Matching-Part-Two-Suffix-Arrays-139-2048.jpg)
![The DC3 method y a b d ob a a b b a d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 110 T = B1 contains indices with i mod 3 = 1 B2 contains indices with i mod 3 = 2 How do we find the ordering of the suffixes from B0? (where i mod 3 = 0) Suffix array for just B1 ∪ B2 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 y a b d ob a a b b a d d ob a a b b a d oa b b a d oa d 0 3 6 9 = + 1y = + 4b = + 7a = +a 10 (y, 0) (b, 1) (a, 4) (a, 6) Each suffix i ∈ B0 is represented by (T[i], r) where r is the rank of suffix (i + 1) 1 24 111058 7 (the ranks are given by the array below) rank:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa-06-160916143738/75/Pattern-Matching-Part-Two-Suffix-Arrays-140-2048.jpg)
![The DC3 method y a b d ob a a b b a d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 110 T = B1 contains indices with i mod 3 = 1 B2 contains indices with i mod 3 = 2 How do we find the ordering of the suffixes from B0? (where i mod 3 = 0) Suffix array for just B1 ∪ B2 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 y a b d ob a a b b a d d ob a a b b a d oa b b a d oa d 0 3 6 9 = + 1y = + 4b = + 7a = +a 10 (y, 0) (b, 1) (a, 4) (a, 6) Each suffix i ∈ B0 is represented by (T[i], r) where r is the rank of suffix (i + 1) 1 24 111058 7 (the ranks are given by the array below) rank: We then sort in O(n) time using radix sort](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa-06-160916143738/75/Pattern-Matching-Part-Two-Suffix-Arrays-141-2048.jpg)
![The DC3 method y a b d ob a a b b a d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 110 T = B1 contains indices with i mod 3 = 1 B2 contains indices with i mod 3 = 2 How do we find the ordering of the suffixes from B0? (where i mod 3 = 0) Suffix array for just B1 ∪ B2 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 Each suffix i ∈ B0 is represented by (T[i], r) where r is the rank of suffix (i + 1) 1 24 111058 7 (the ranks are given by the array below) rank: We then sort in O(n) time using radix sort y a b d ob a a b b a d d ob a a b b a d oa b b a d oa d 0 3 6 9 = + 1y = + 4b = + 7a = +a 10 (y, 0) (b, 1) (a, 4) (a, 6)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa-06-160916143738/75/Pattern-Matching-Part-Two-Suffix-Arrays-142-2048.jpg)
![The DC3 method y a b d ob a a b b a d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 110 T = B1 contains indices with i mod 3 = 1 B2 contains indices with i mod 3 = 2 How do we find the ordering of the suffixes from B0? (where i mod 3 = 0) Suffix array for just B1 ∪ B2 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 Each suffix i ∈ B0 is represented by (T[i], r) where r is the rank of suffix (i + 1) 1 24 111058 7 (the ranks are given by the array below) rank: We then sort in O(n) time using radix sort y a b d ob a a b b a d d ob a a b b a d oa b b a d oa d 0 3 6 9 = + 1y = + 4b = + 7a = +a 10 (y, 0) (b, 1) (a, 4) (a, 6)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa-06-160916143738/75/Pattern-Matching-Part-Two-Suffix-Arrays-143-2048.jpg)
![The DC3 method y a b d ob a a b b a d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 110 T = B1 contains indices with i mod 3 = 1 B2 contains indices with i mod 3 = 2 Suffix array for just B1 ∪ B2 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 Each suffix i ∈ B0 is represented by (T[i], r) where r is the rank of suffix (i + 1) 1 24 111058 7 (the ranks are given by the array below) rank: We then sort in O(n) time using radix sort y a b d ob a a b b a d d ob a a b b a d oa b b a d oa d 0 3 6 9 = + 1y = + 4b = + 7a = +a 10 (y, 0) (b, 1) (a, 4) (a, 6)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa-06-160916143738/75/Pattern-Matching-Part-Two-Suffix-Arrays-144-2048.jpg)
![The DC3 method y a b d ob a a b b a d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 110 T = B1 contains indices with i mod 3 = 1 B2 contains indices with i mod 3 = 2 Suffix array for just B1 ∪ B2 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 Each suffix i ∈ B0 is represented by (T[i], r) where r is the rank of suffix (i + 1) 1 24 111058 7 (the ranks are given by the array below) rank: We then sort in O(n) time using radix sort y a b d ob a a b b a d d ob a a b b a d oa b b a d oa d 0 3 6 9 = + 1y = + 4b = + 7a = +a 10 (y, 0) (b, 1) (a, 4) (a, 6) Suffix array for just B0 6 09 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa-06-160916143738/75/Pattern-Matching-Part-Two-Suffix-Arrays-145-2048.jpg)
![The DC3 method y a b d ob a a b b a d 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 110 T = B1 contains indices with i mod 3 = 1 B2 contains indices with i mod 3 = 2 Suffix array for just B1 ∪ B2 1 2 3 4 5 6 70 Each suffix i ∈ B0 is represented by (T[i], r) where r is the rank of suffix (i + 1) 1 24 111058 7 (the ranks are given by the array below) rank: We then sort in O(n) time using radix sort y a b d ob a a b b a d d ob a a b b a d oa b b a d oa d 0 3 6 9 = + 1y = + 4b = + 7a = +a 10 (y, 0) (b, 1) (a, 4) (a, 6) Suffix array for just B0 6 09 3 How do we merge these?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aa-06-160916143738/75/Pattern-Matching-Part-Two-Suffix-Arrays-146-2048.jpg)
























