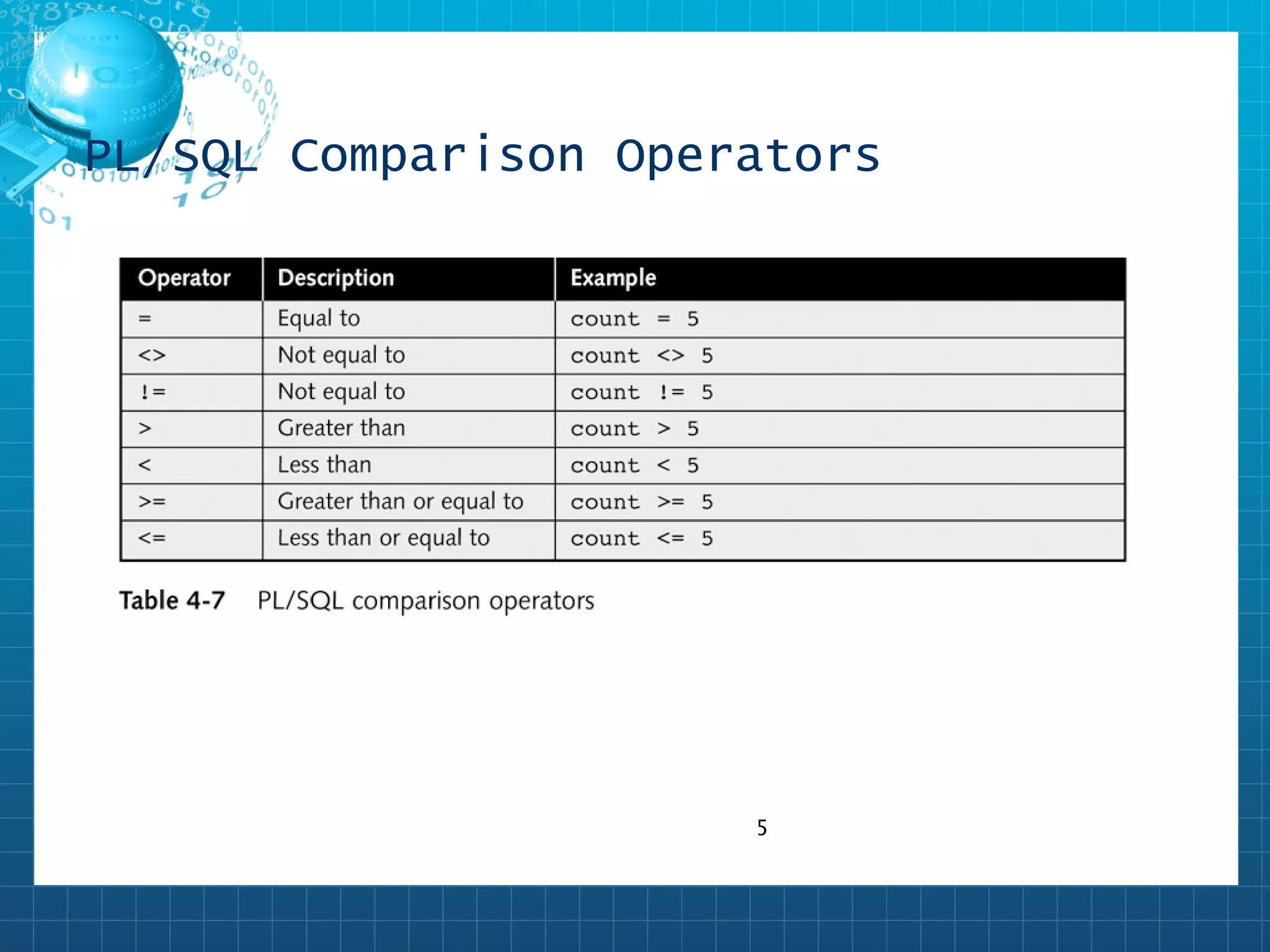
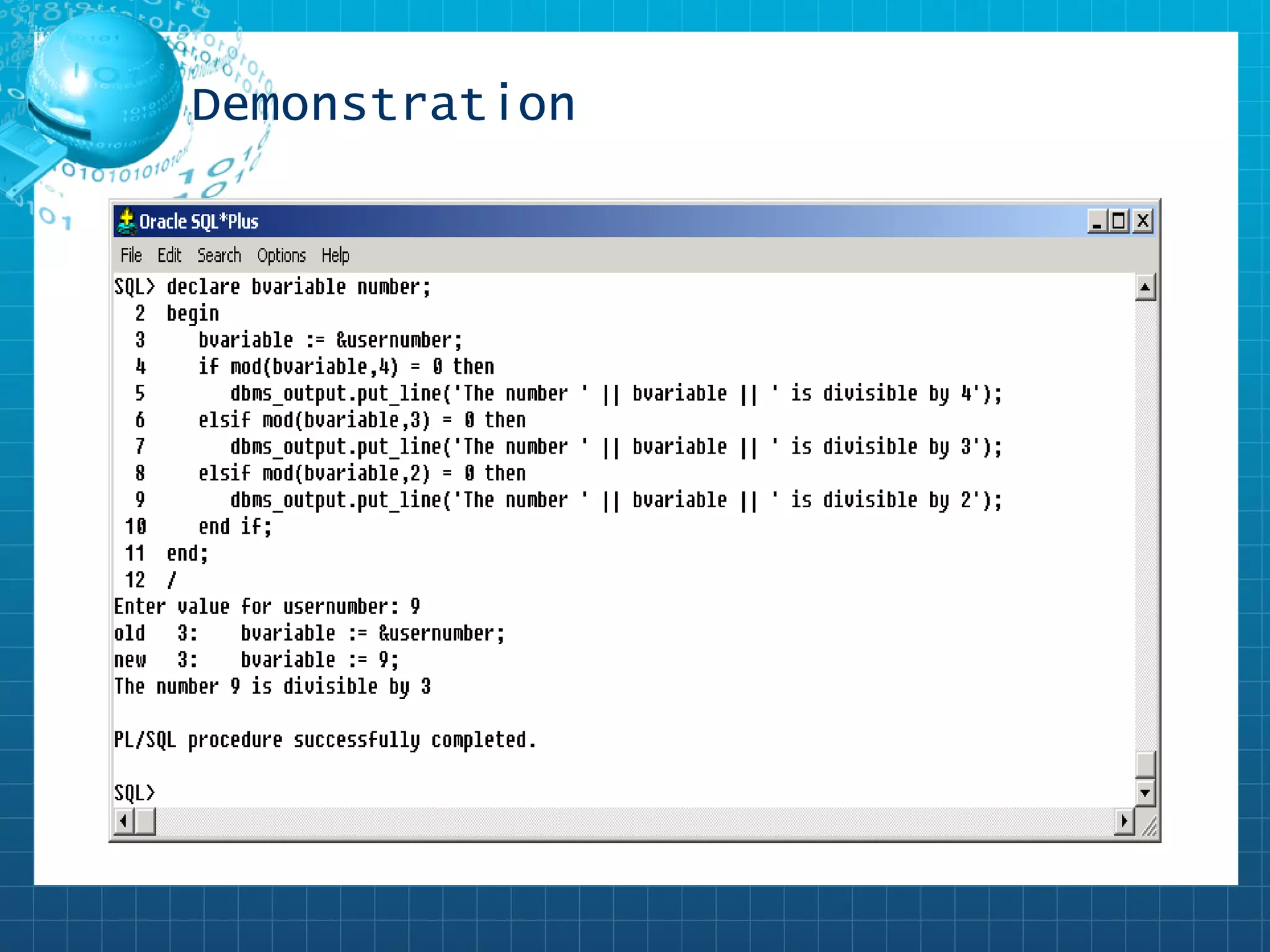
The PL/SQL IF/THEN statement checks a Boolean condition and executes statements in the THEN clause if true. It can check simple or complex expressions. There are single-level IF/THEN and multi-level IF/THEN/ELSE, IF/THEN/ELSIF/END IF, and nested IF statements to handle different outcomes. Operators like =, <>, <, > etc. are used to build conditional expressions.