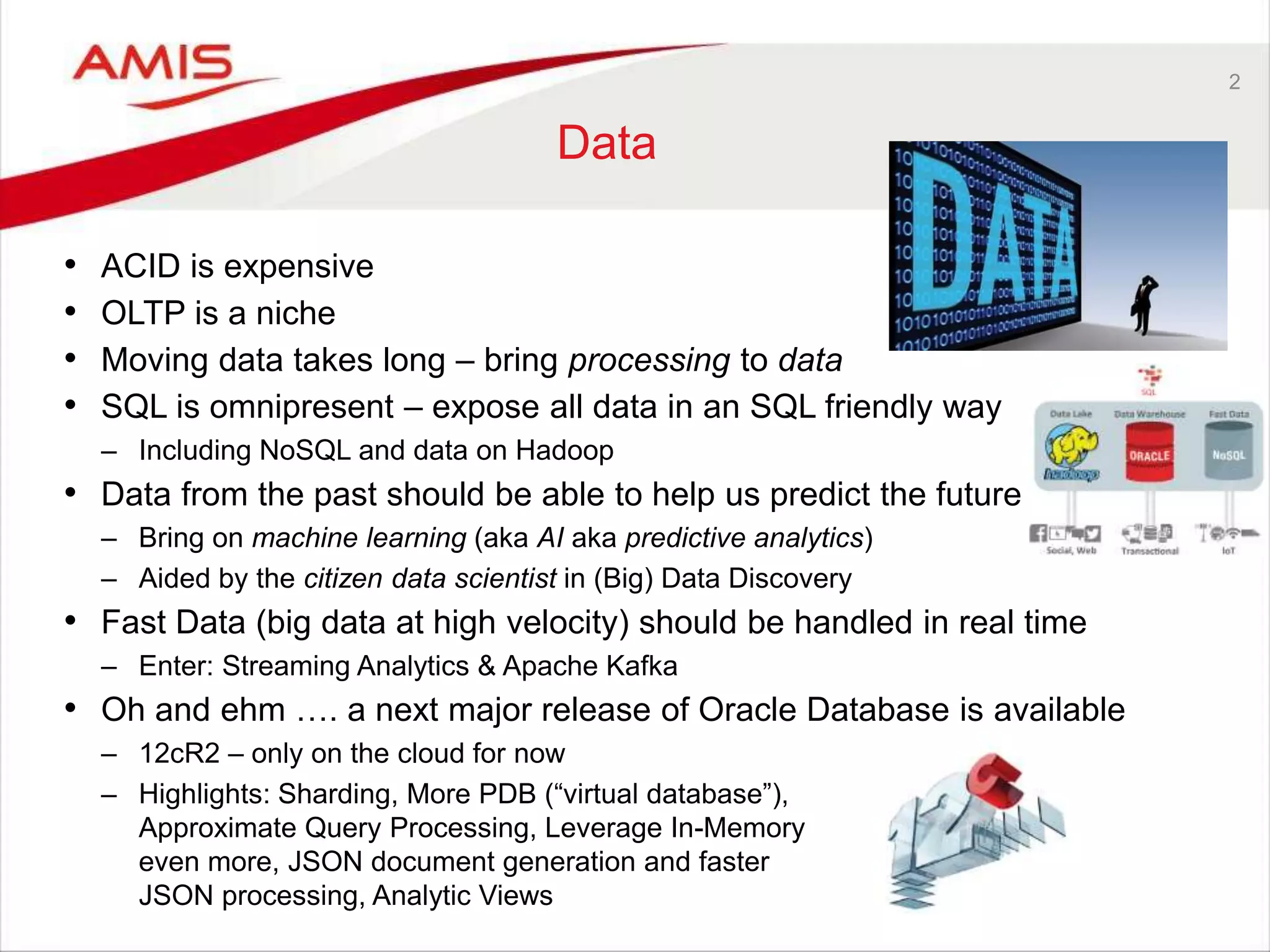
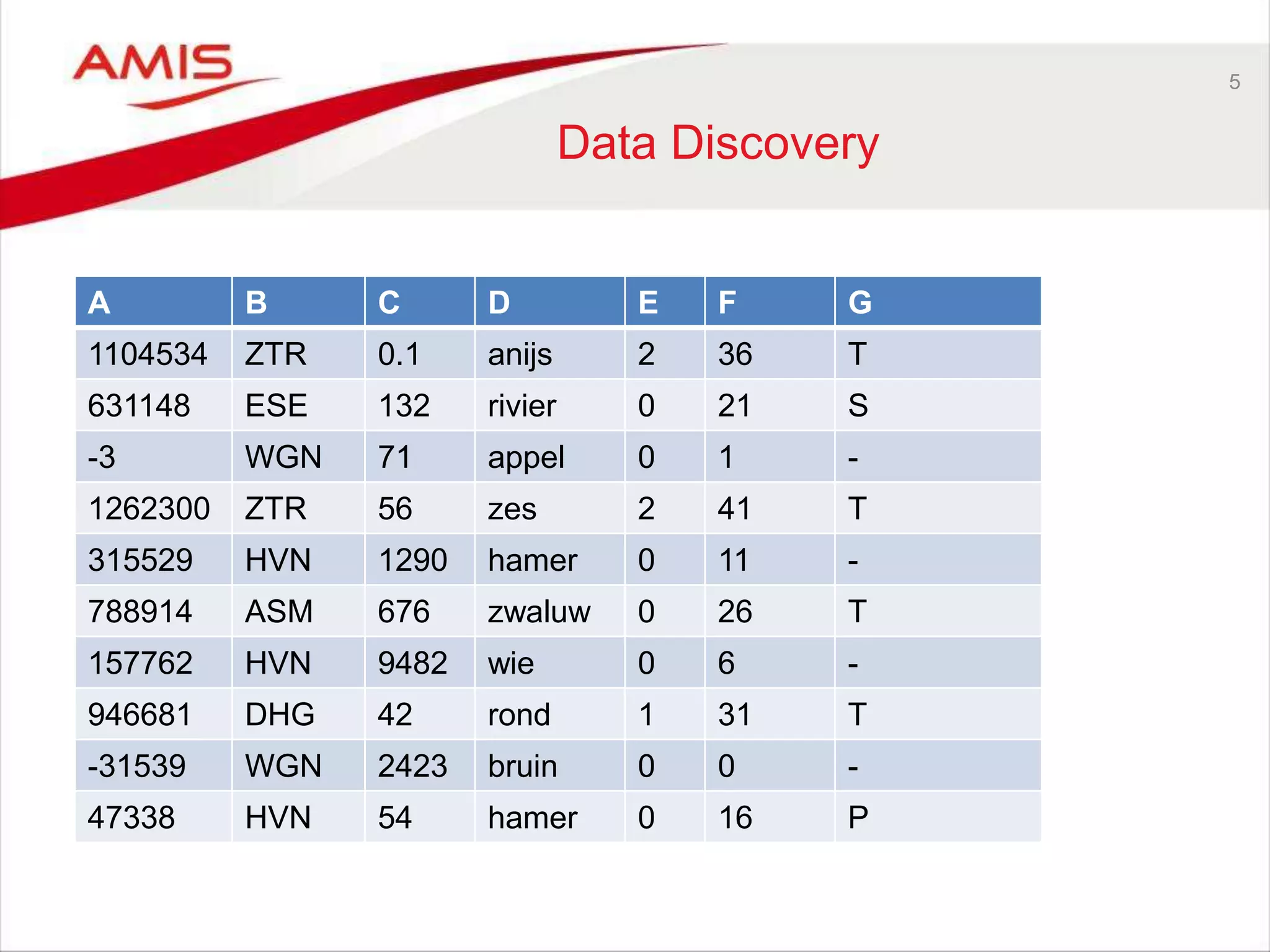
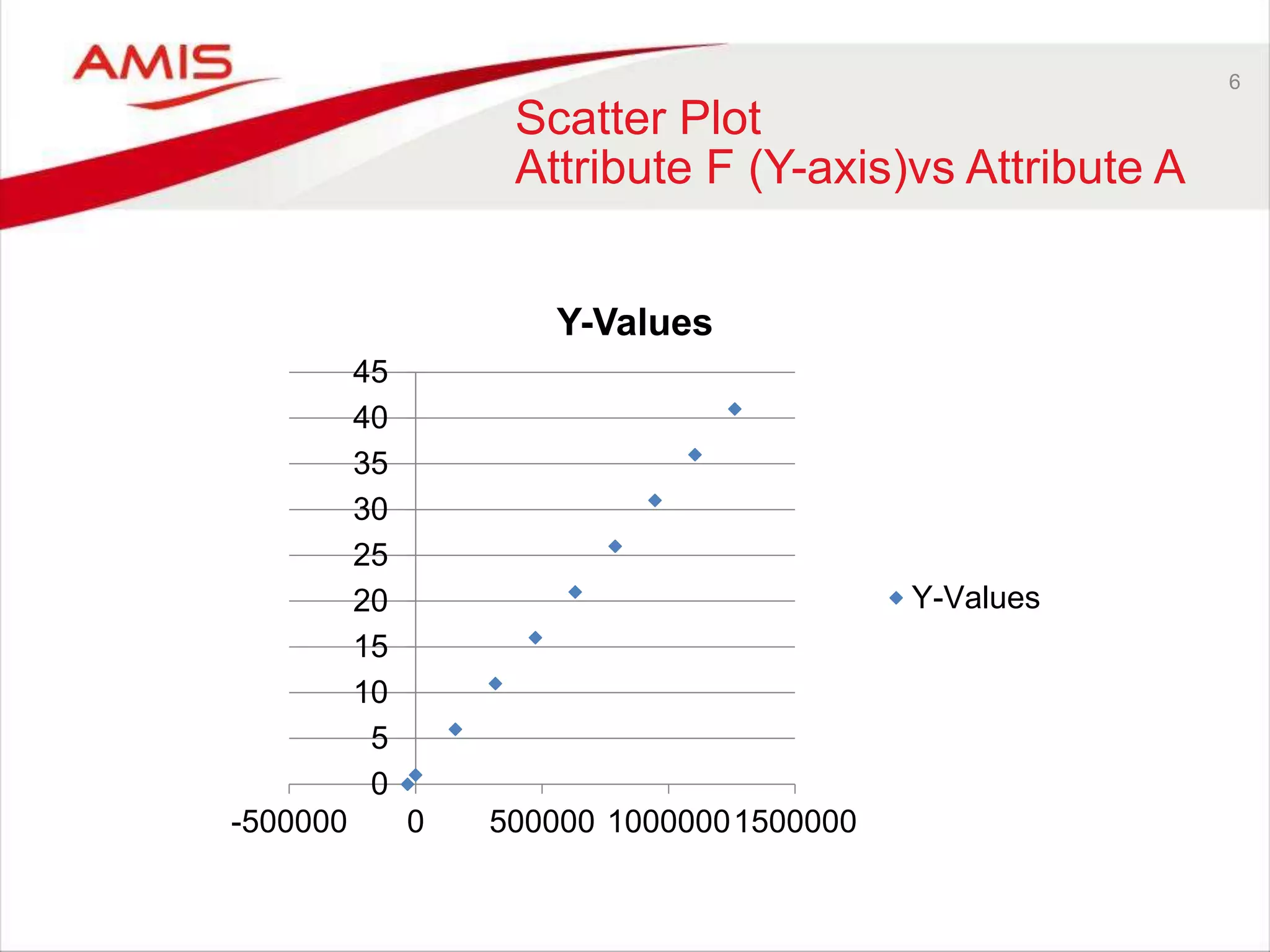
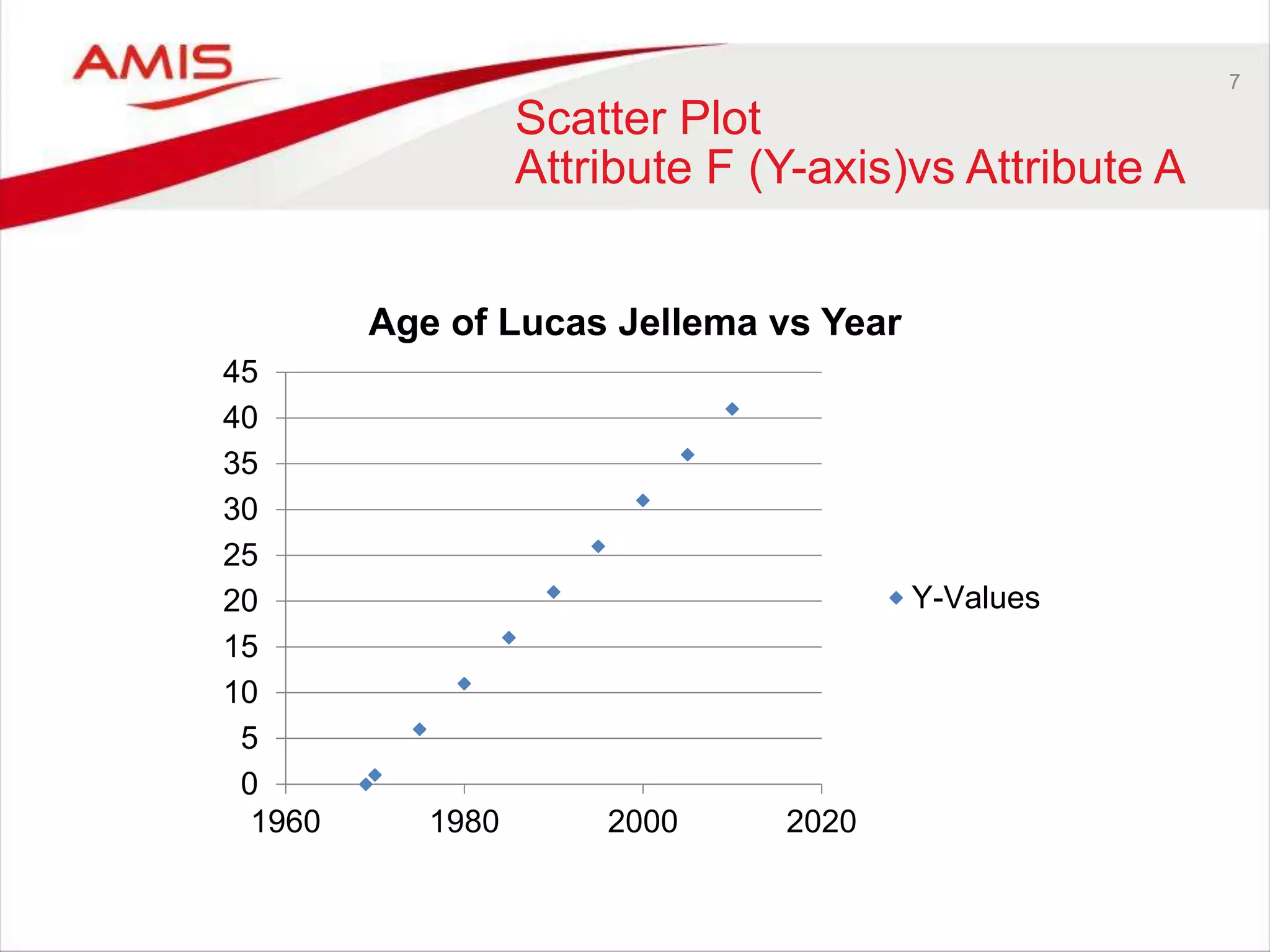
The Oracle OpenWorld 2016 highlighted advancements in database development, including the introduction of Oracle Database 12cR2, machine learning, and real-time analytics. Key discussions focused on the need for better data processing methods, cloud-first strategies, and the evolving role of citizen data scientists. The event emphasized the integration of various technologies and the adoption of open-source projects, reflecting current industry trends.


![4 Machine Learning • Analyze Historical Data (input and result – training set) to discover Patterns & Models • Iteratively apply Models to [additional] Input (test set) and compare model outcome with known actual result to improve the model • Use Model to predict outcome for entirely new data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oow2016-review-blocke-dbdev-bigdata-13thoctober-distribution-161019084554/75/Oracle-OpenWorld-2016-Review-Focus-on-Data-BigData-Streaming-Data-Machine-Learning-Database-Development-4-2048.jpg)







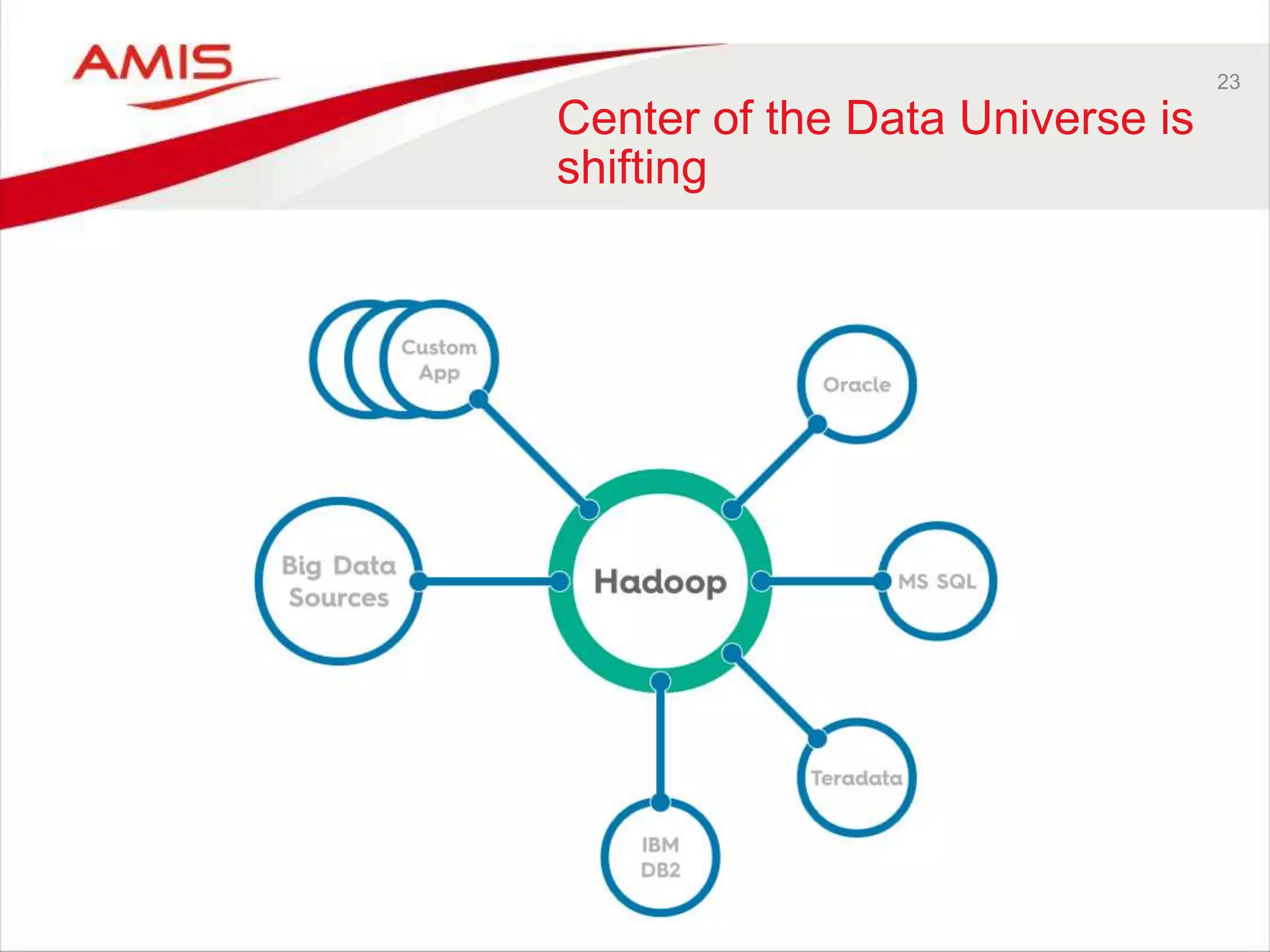
![22 Traditional approach • All enterprise data is in the Oracle [relational] Database – Except very unstructured documents - and sometimes even those](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oow2016-review-blocke-dbdev-bigdata-13thoctober-distribution-161019084554/75/Oracle-OpenWorld-2016-Review-Focus-on-Data-BigData-Streaming-Data-Machine-Learning-Database-Development-22-2048.jpg)
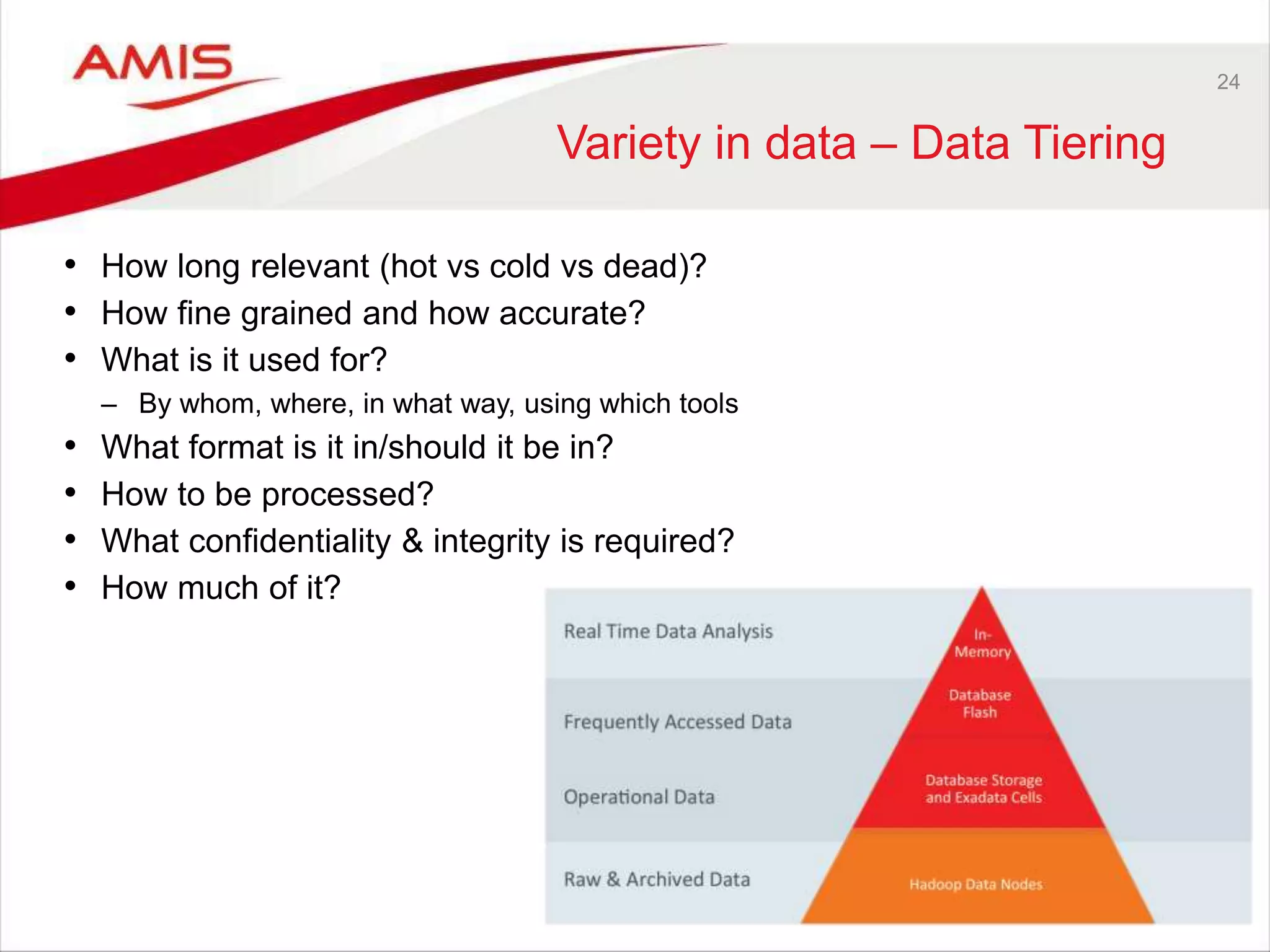
![25 Trends around data storage and data processing • Take processing to data [to reduce data movement] – Exadata SmartScan in Storage Cells (SQL & R processing) – Hadoop MapReduce/Spark – Coherence Processors – Streaming Analytics – Microservices, stand alone data domains • Distributed data partitions – for scalability and parallelization [and fault tolerance when also replicated]: – Shards (Oracle Database 12cR2) and Partitioned External Tables – TimesTen Velocity Scale – distributed In-Memory OLTP – Hadoop HDFS, Apache Kafka • New paradigms regarding transactional data – CQRS (for example Oracle Database In Memory (read) / In Flash/On disk (read/write), Write behind cache) – Event Sourcing, Transaction Log](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oow2016-review-blocke-dbdev-bigdata-13thoctober-distribution-161019084554/75/Oracle-OpenWorld-2016-Review-Focus-on-Data-BigData-Streaming-Data-Machine-Learning-Database-Development-25-2048.jpg)
![26 Oracle Database • How much of your data – Arrives through (business) transactions that require true ACID? – Is involved in current business operations? – Will ever be updated [again]? – Plays a direct role in integrity [of other records]? – Is actively accessed [on a regular basis] ? – Really has to be in the OLTP engine? • How much of the data currently in your OLTP engine could be off-loaded – If that data remains accessible through SQL (even from within the OLTP engine, without altering existing queries) with reasonable response times • What if such off-loading – Improves performance of the OLTP engine for transactions – Shortens batch jobs [by engaging distributed, scale out processing options] – Opens up possibilities for advanced analytics – Potentially lowers the cost [licenses & specialized hardware] for the OLTP engine – Introduces some change and complexity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oow2016-review-blocke-dbdev-bigdata-13thoctober-distribution-161019084554/75/Oracle-OpenWorld-2016-Review-Focus-on-Data-BigData-Streaming-Data-Machine-Learning-Database-Development-26-2048.jpg)




![33 New in PL/SQL in 12cR2 • Deprecated procedures and functions • Accessible by at procedure or function level • JSON support: generation of JSON documents using PL/SQL API and Oracle supplied Object Types (somewhat akin to XMLType) – JSON SQL functions available in PL/SQL expressions • Supplied package dbms_plsql_code_coverage to identify code units not touched in specific [test] scenarios • PL/Scope enhancements – more fine grained reporting • Edition Based Redefinition does ‘garbage collection’ – editioned objects no longer in use are cleaned up](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oow2016-review-blocke-dbdev-bigdata-13thoctober-distribution-161019084554/75/Oracle-OpenWorld-2016-Review-Focus-on-Data-BigData-Streaming-Data-Machine-Learning-Database-Development-33-2048.jpg)

![36 Summary of Oracle OpenWorld 2016 • (5 days filled to brim with 1800+ sessions, 12 keynotes, 150+ demo booths, hundreds of vendors and quite a few rumors & hallway tales) • Infrastructure [as a Service] – Generation 2 Data Center – Network & IOPS (storage, NVMe, Flash) – Exadata SL • Abdication of the single, central, enterprise Oracle RDBMS – and the limelight for data – PDBs – Sharding – Hadoop & Spark (& SQL & R) – Machine Learning • Adoption of open source projects, industry trends & community darlings – Node.js, Docker, Microservices, Git(Hub), Python, Slack, …](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oow2016-review-blocke-dbdev-bigdata-13thoctober-distribution-161019084554/75/Oracle-OpenWorld-2016-Review-Focus-on-Data-BigData-Streaming-Data-Machine-Learning-Database-Development-36-2048.jpg)
![37 Summary of Oracle OpenWorld 2016 (2) • Cloud [First] strategy – Migrate & Extend i/o [bidirectional] Lift & Shift – Cloud@Customer – Status and future of On Premises software (and yet Engineered Systems) – Ops in Oracle Data Centers – Subscription Models, Suites (i/o a la carte) – How fast can Oracle move [without spreading itself too thin]? • SaaS and [Unlimited] Applications – SaaS portfolio quite extensive – UX is important asset of the SaaS applications – Real cloud elements are improving (APIs, extensibility) – Traditional Apps are still evolving [as promised] – and seem to benefit from SaaS and technological advances across the board • Oracle Public Cloud consistency, architecture and the Dogfood Doctrine – Fabric and foundational components – Designated capabilities and mutual integration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oow2016-review-blocke-dbdev-bigdata-13thoctober-distribution-161019084554/75/Oracle-OpenWorld-2016-Review-Focus-on-Data-BigData-Streaming-Data-Machine-Learning-Database-Development-37-2048.jpg)

