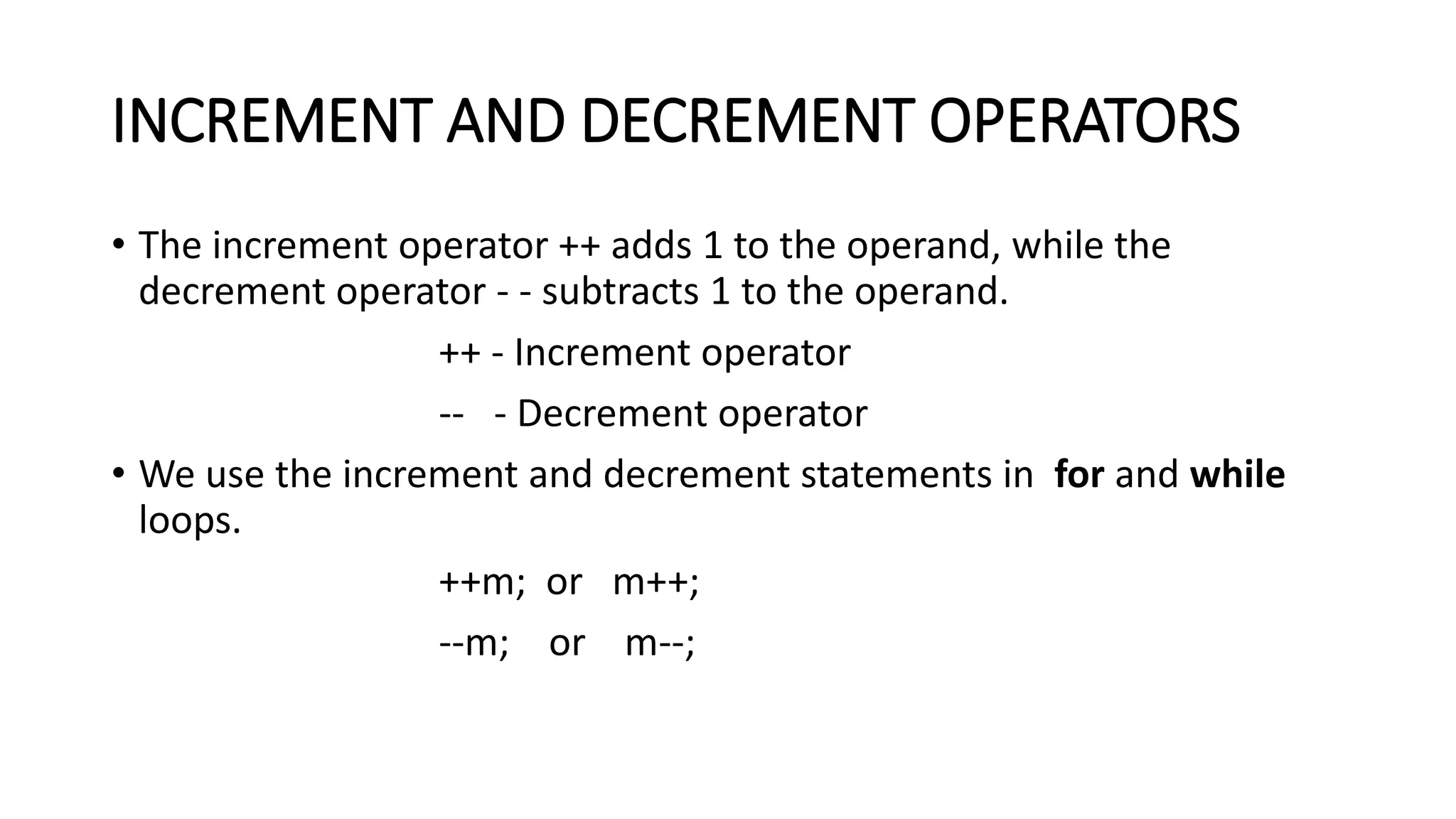
Operators in C allow programmers to manipulate data and variables. There are several categories of operators including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, increment/decrement, conditional, and bitwise operators. Arithmetic operators perform basic math operations like addition and multiplication. Relational operators compare values. Logical operators combine relational expressions. Assignment operators assign values to variables. Increment and decrement operators add or subtract 1 from a variable.