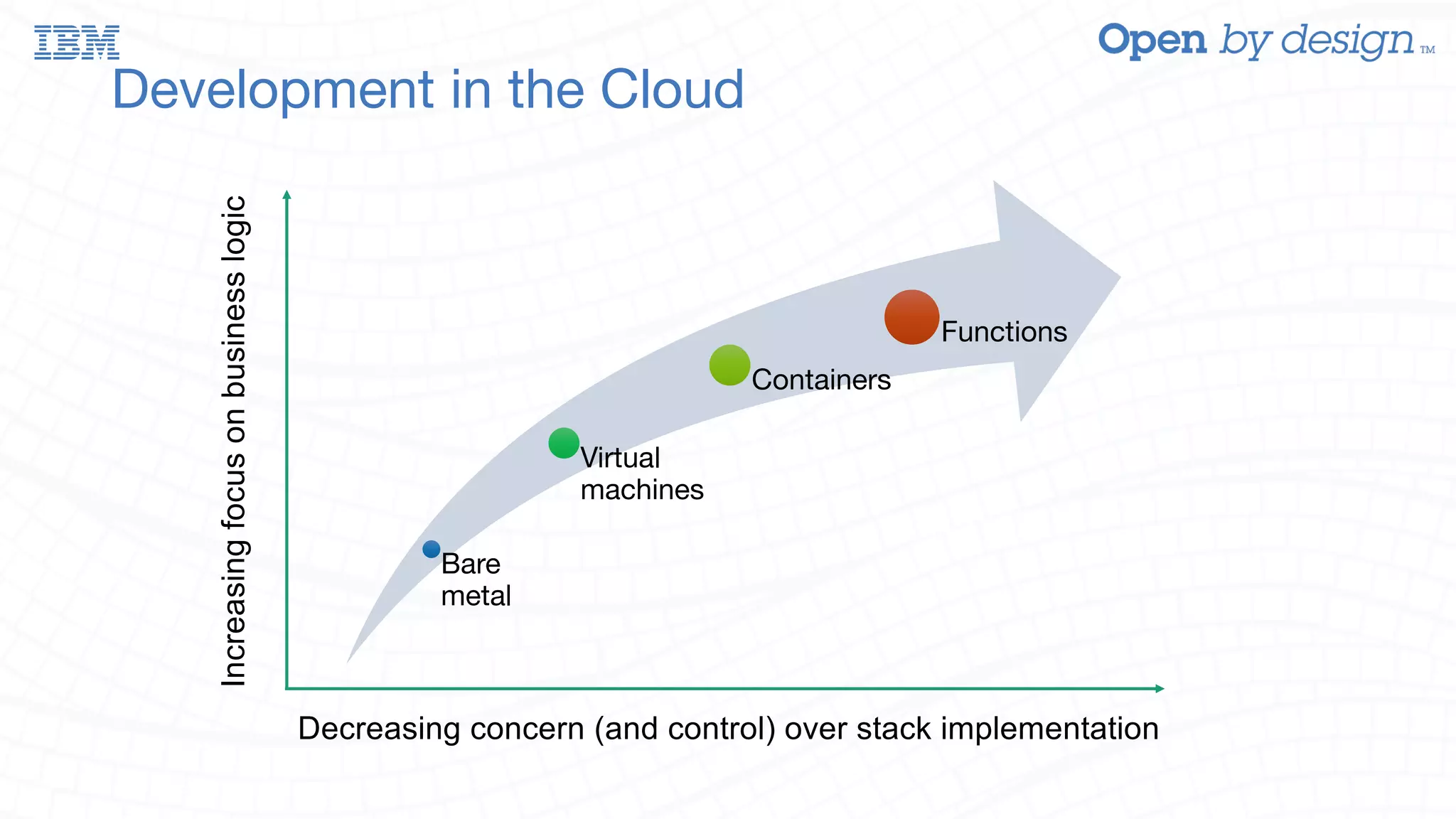
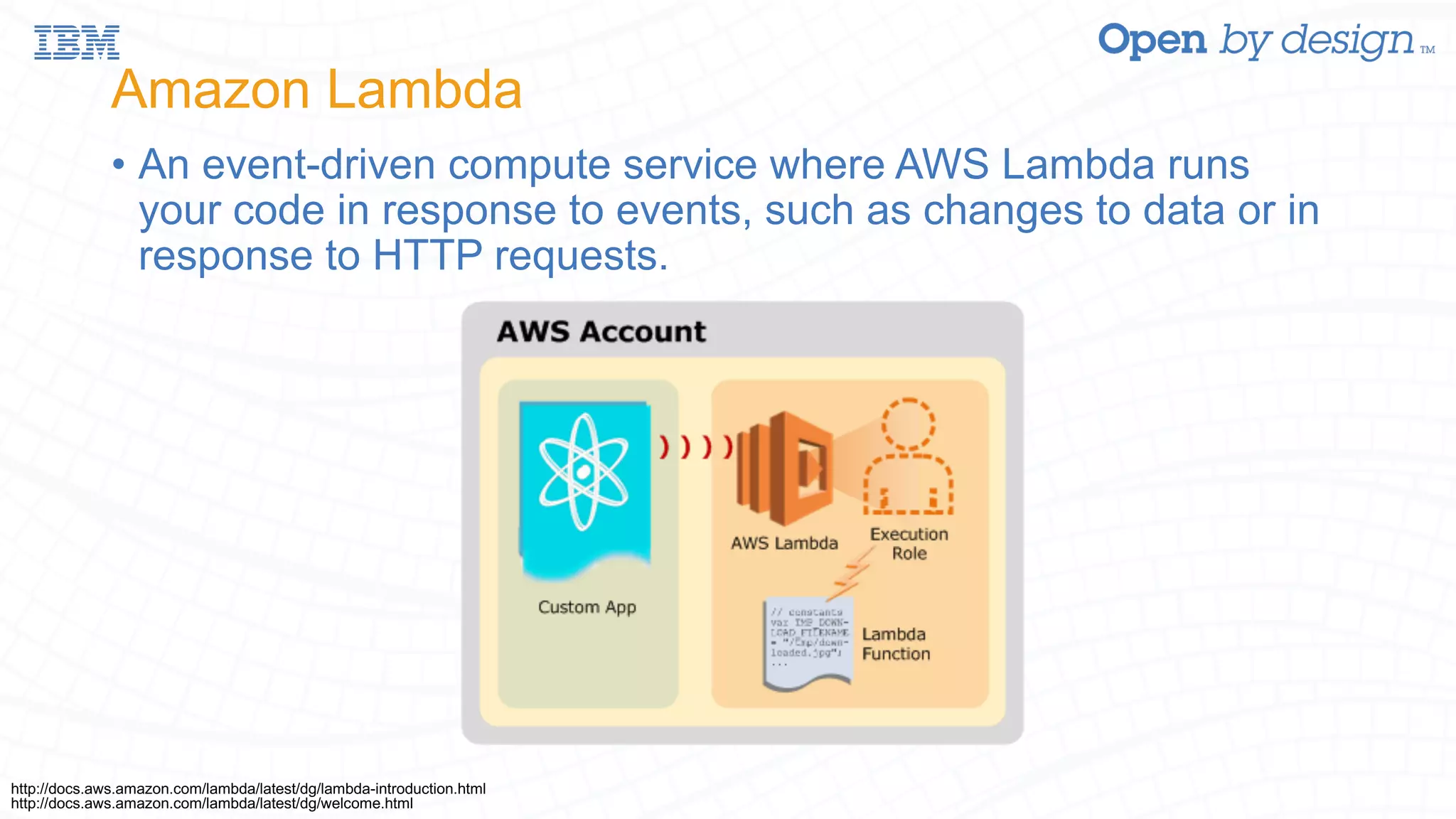
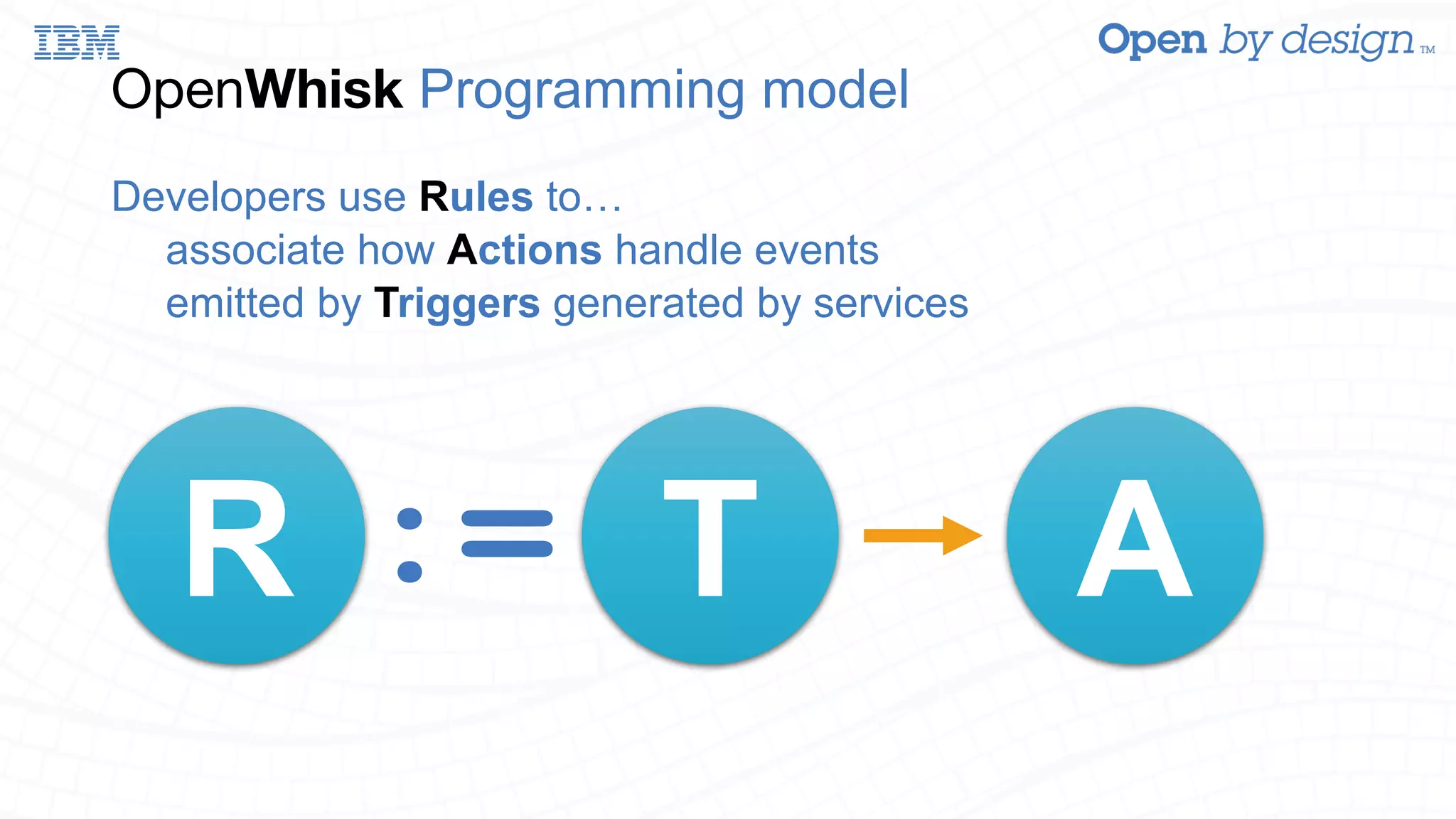
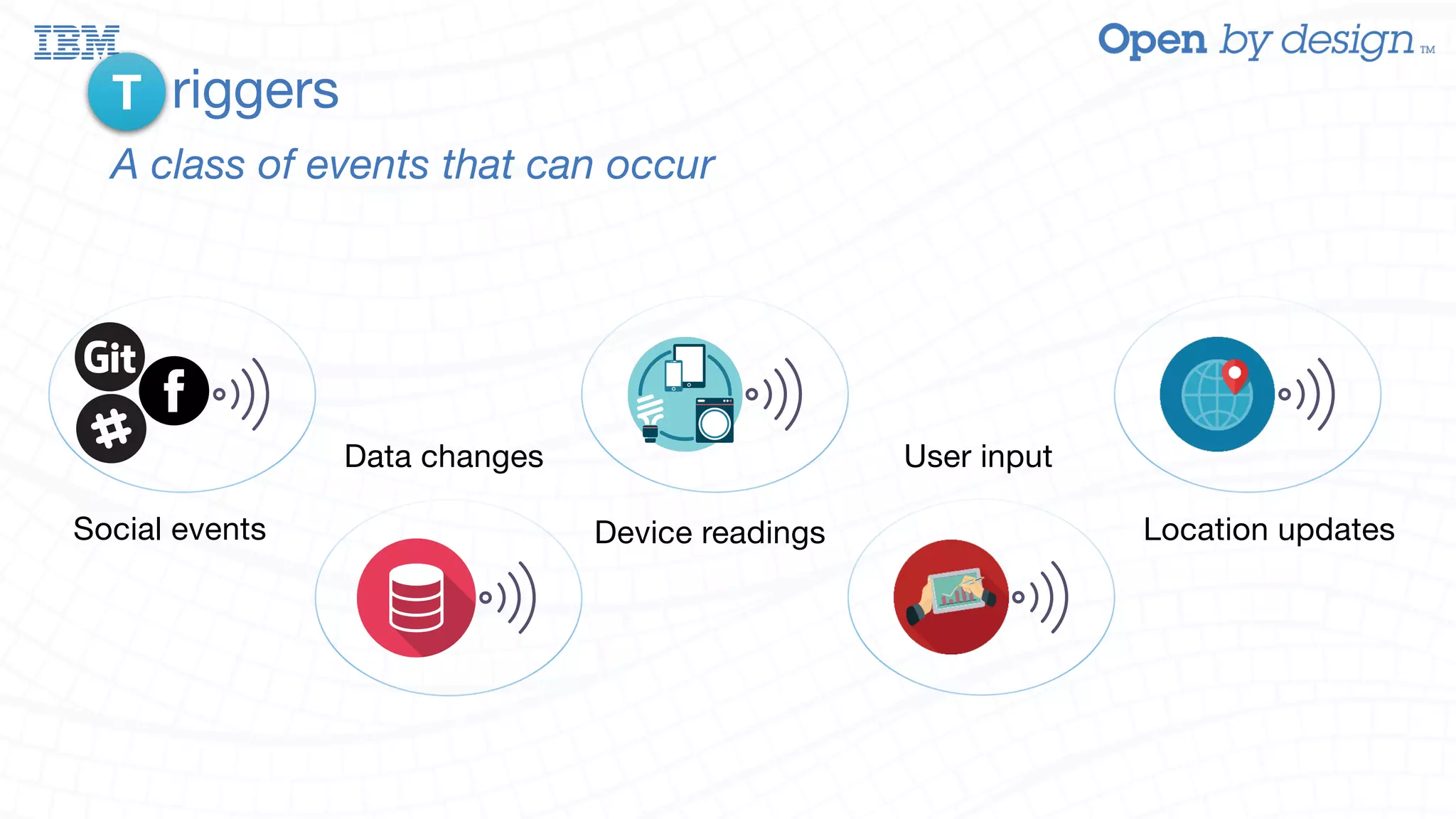
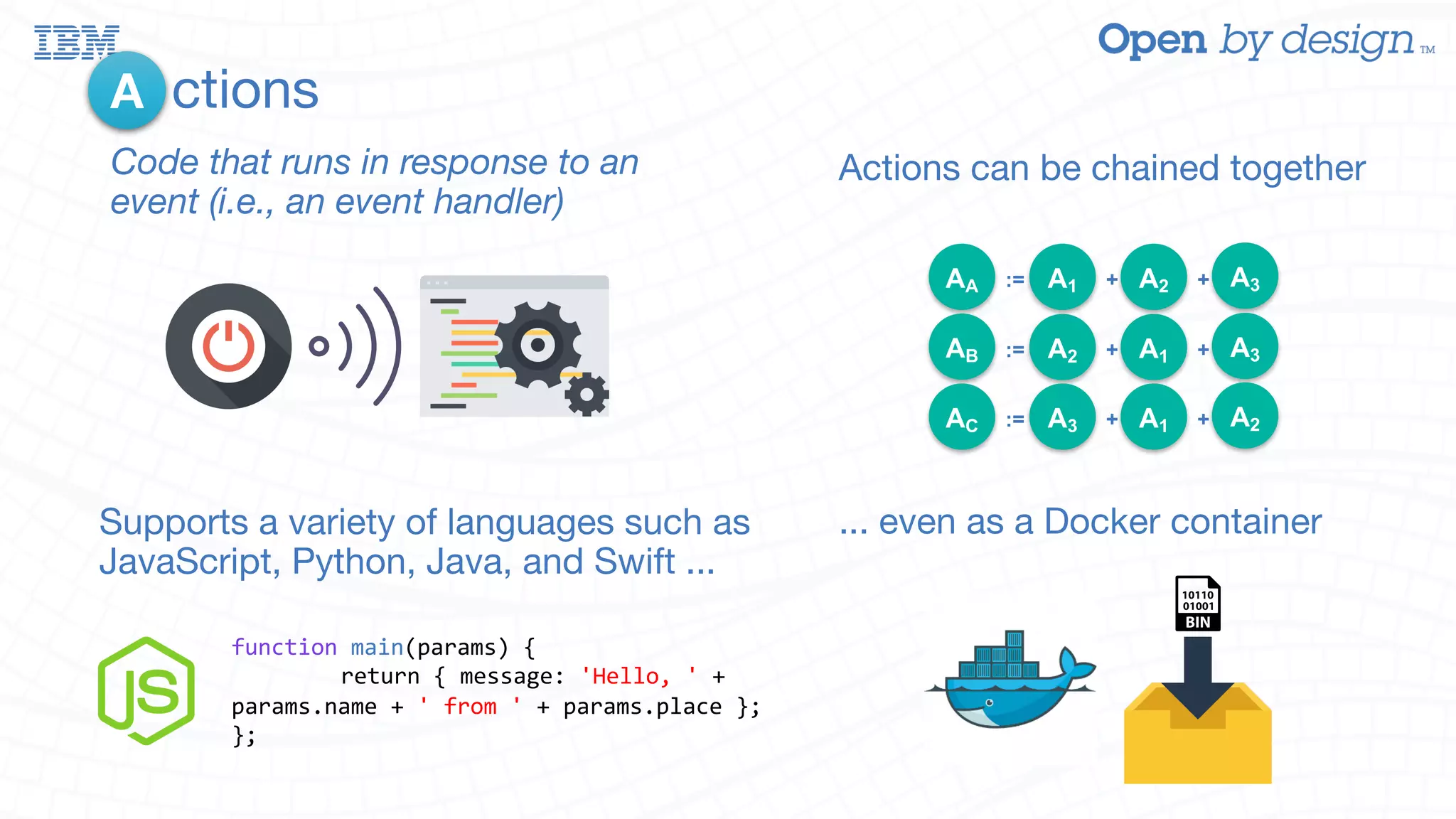
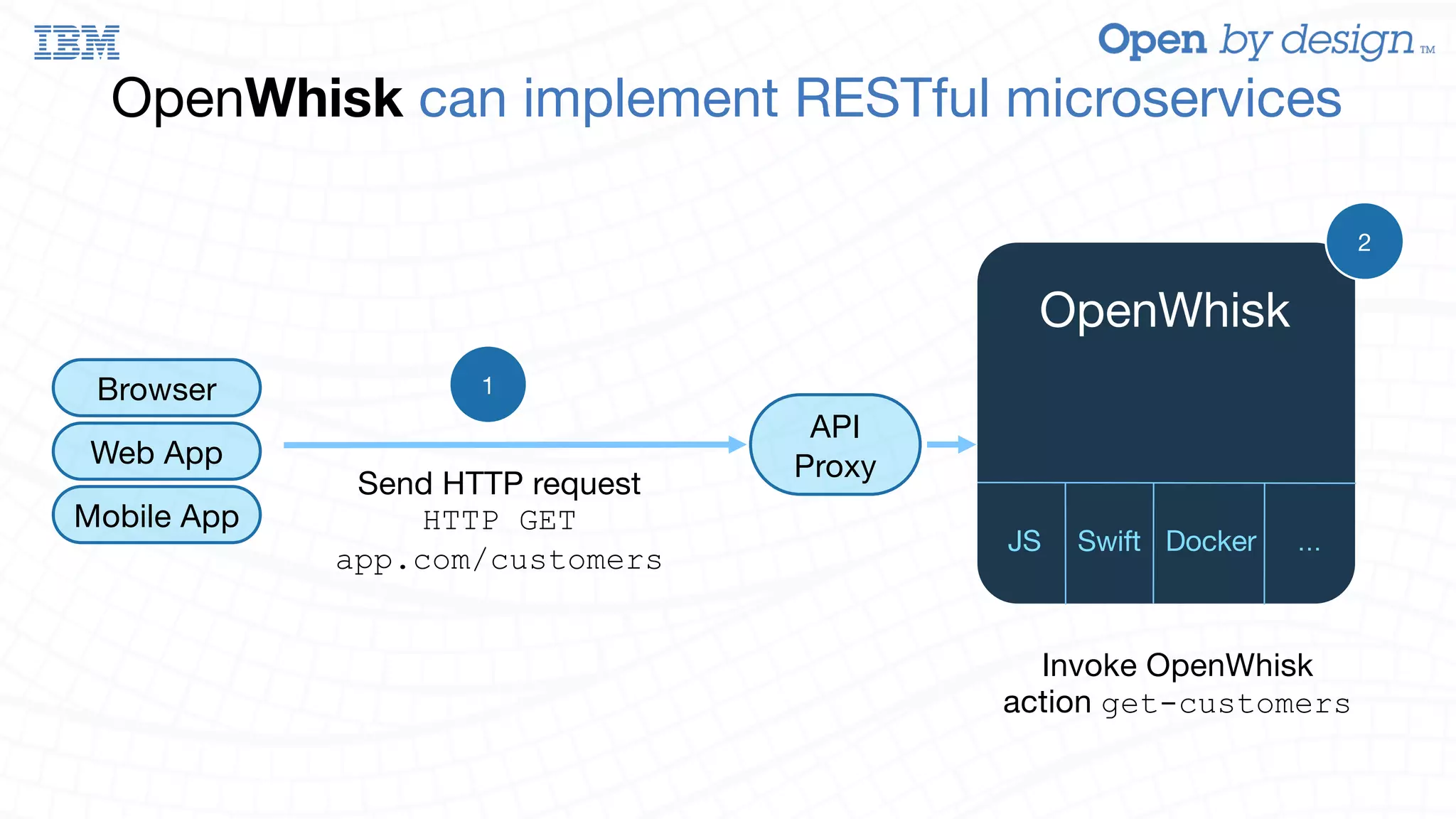
The document discusses enabling AWS Lambda-like functionality using OpenStack Swift and OpenWhisk for serverless computing. It covers how serverless architectures can streamline application development by automating dependencies, configurations, and resource management, while also detailing the integration of OpenWhisk for event-driven programming and microservices. Additionally, it highlights future work on enhancing Swift with asynchronous notifications, aiming for broader capabilities in resource management and inter-service communication.




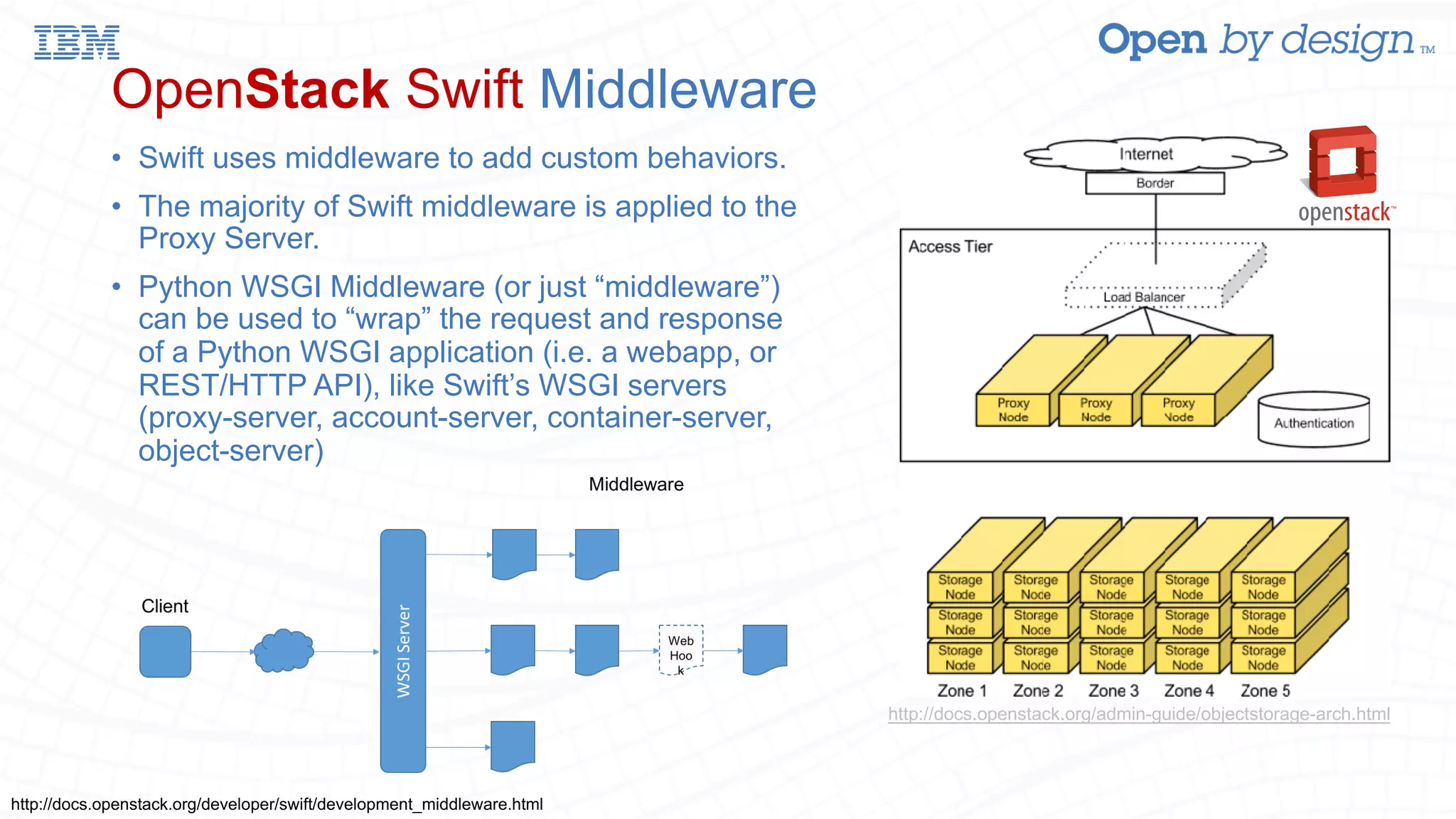


![OpenStack Swift Middleware (webhook.py) class WebhookMiddleware(object): @wsgify def __call__(self, req): req.headers[SYSMETA_WEBHOOK] = req.headers['x-webhook'] req.headers[SYSMETA_WEBHOOK_AUTH] = req.headers['x-webhook-auth'] resp = req.get_response(self.app) if obj and is_success(resp.status_int) and req.method in [’PUT’,’DELETE’]: webhook_req = urllib2.Request(container_info['sysmeta'].get('webhook')) webhook_req.add_header('Authorization', base64.b64encode(container_info['sysmeta'].get('webhook-auth'))) webhook_req.add_data(json.dumps({ ’url’: swiftUrl, ‘token’: req.headers[‘x-auth-token’], ‘container’: container, ‘object’: obj, ‘method’: req.method })) ... try: webhook_resp = urllib2.urlopen(webhook_req).read() …. return resp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openstackocatasummit-enablingawslambda-likefunctionalitywithopenstackswiftandopenwhisk-170310181126/75/Open-stack-ocata-summit-enabling-aws-lambda-like-functionality-with-openstack-swift-and-openwhisk-18-2048.jpg)
![Install Webhook Middleware 1. Place webhook.py in middleware of swift-proxy …/swift/common/middleware/webhook.py 2. Update proxy-server.conf … [pipeline:main] pipeline = catch_errors gatekeeper healthcheck ... webhook proxy-server [filter:webhook] paste.filter_factory = swift.common.middleware.webhook:webhook_factory ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openstackocatasummit-enablingawslambda-likefunctionalitywithopenstackswiftandopenwhisk-170310181126/75/Open-stack-ocata-summit-enabling-aws-lambda-like-functionality-with-openstack-swift-and-openwhisk-19-2048.jpg)




