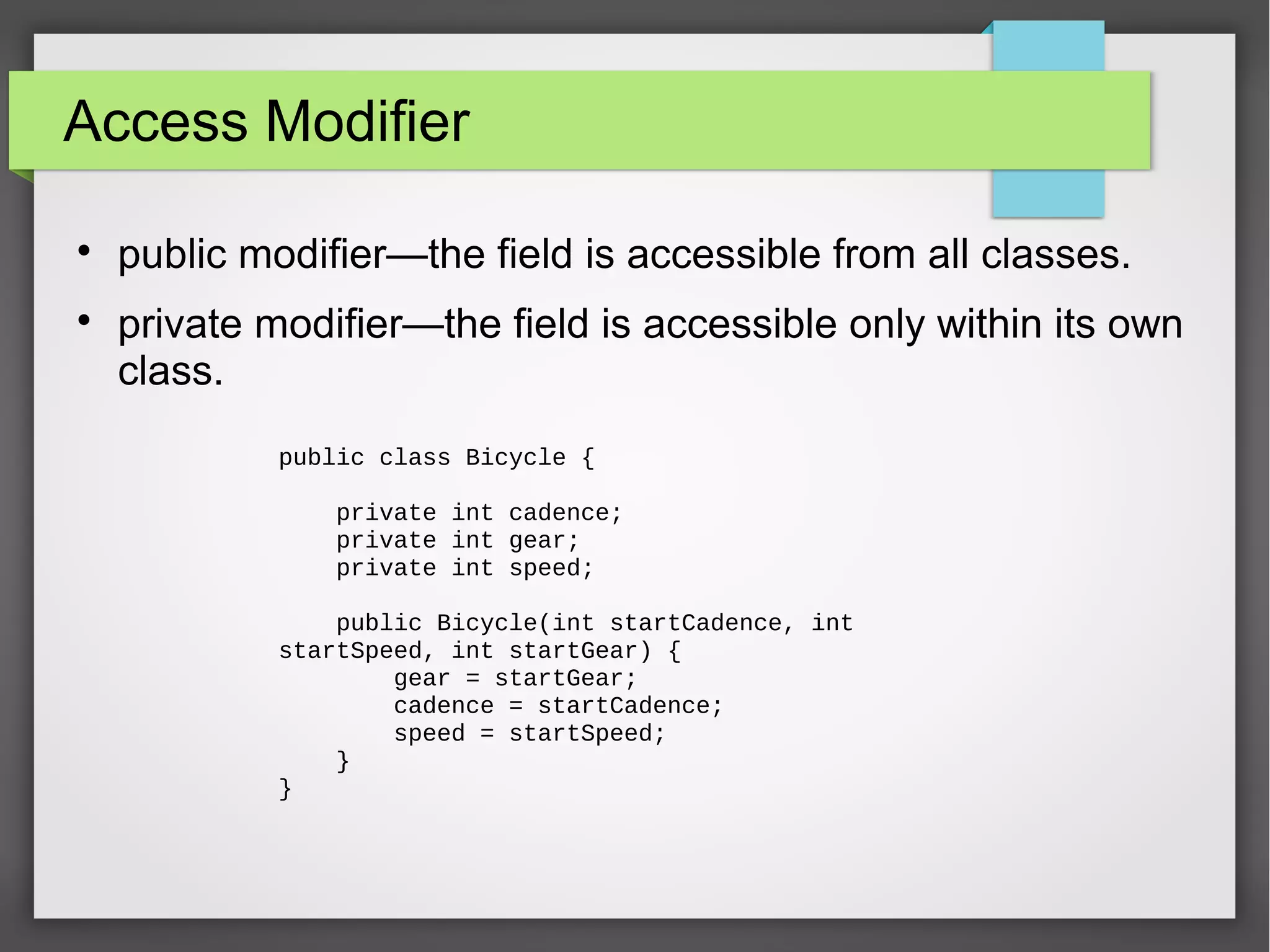
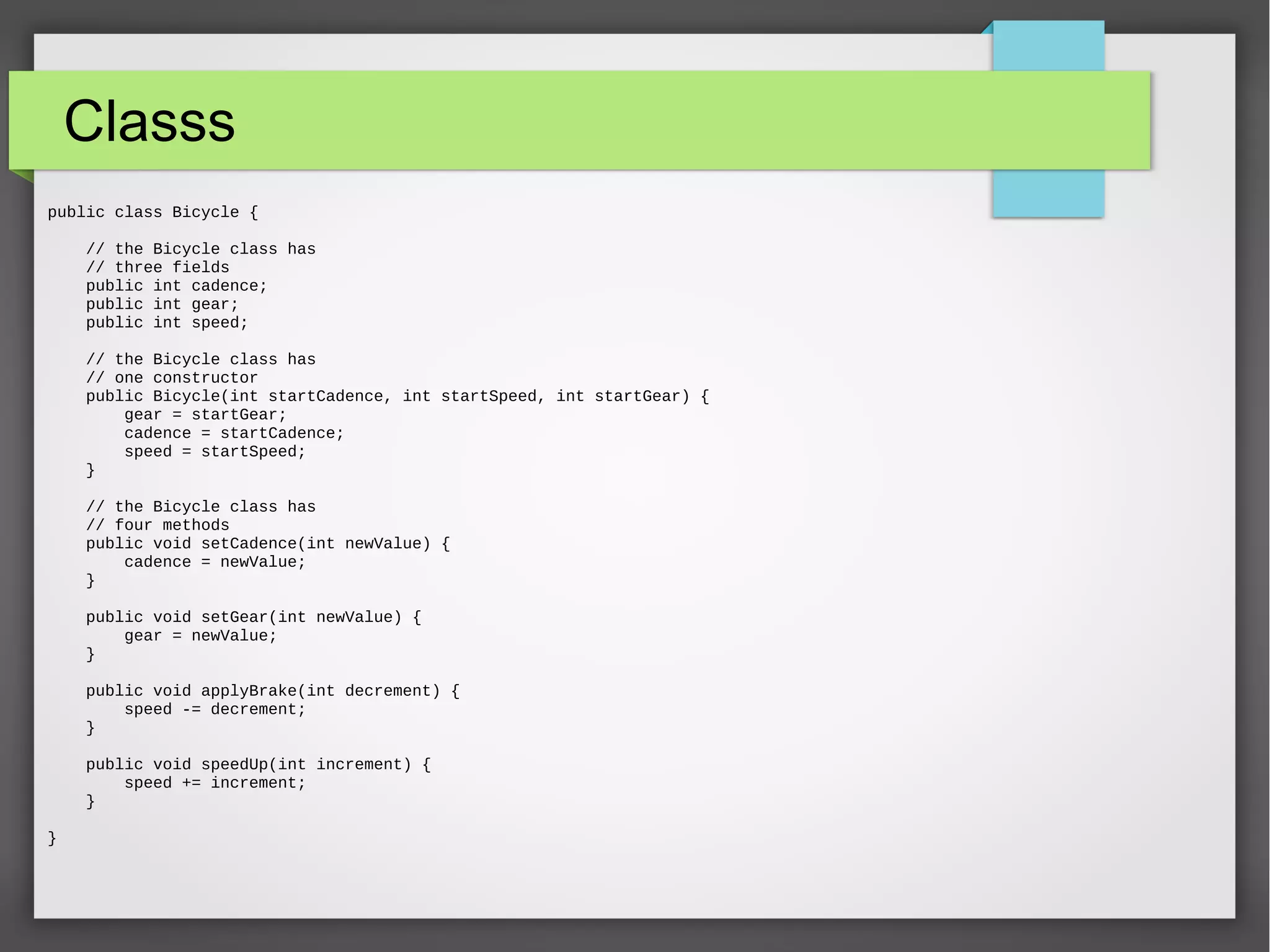
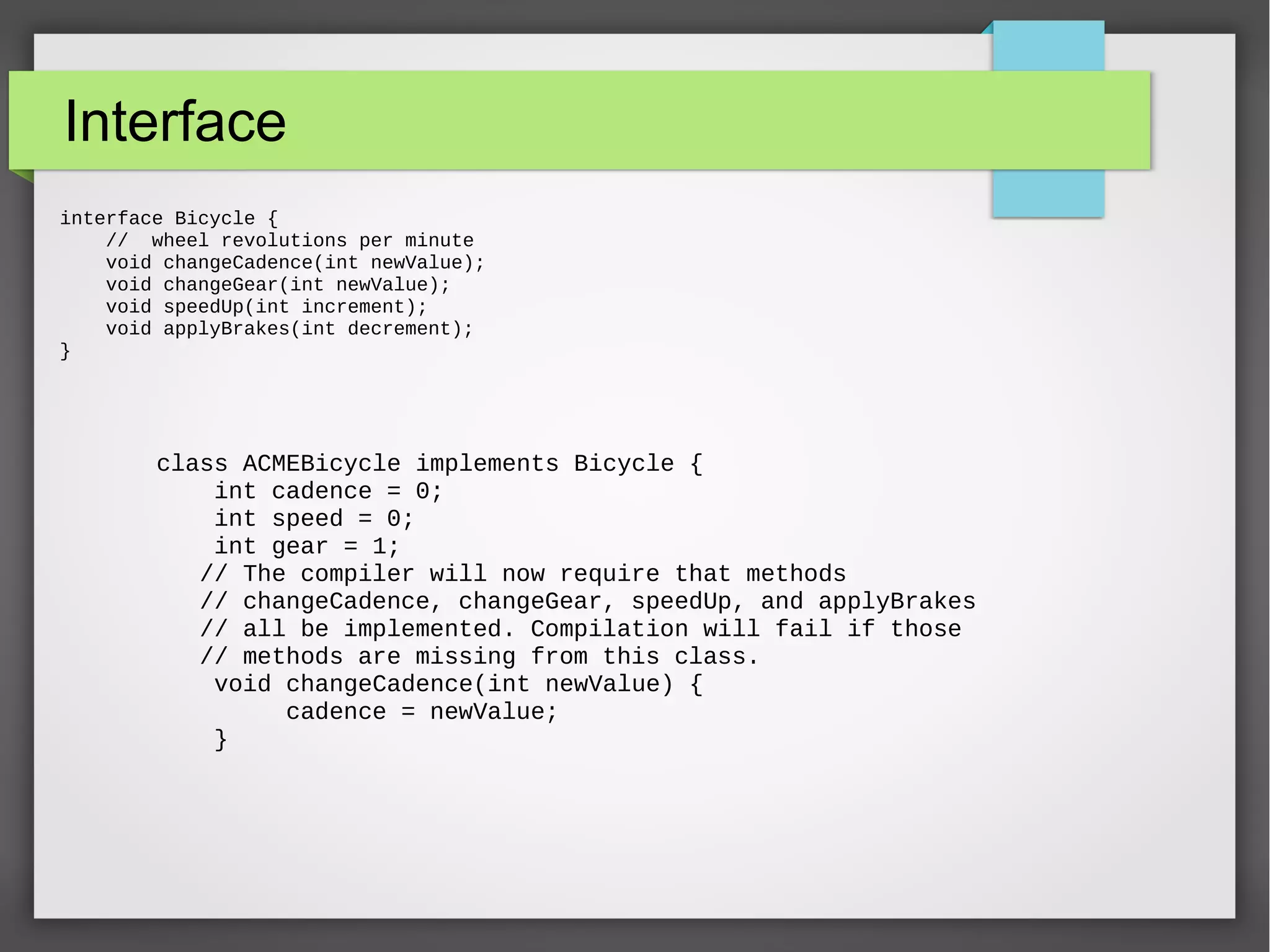
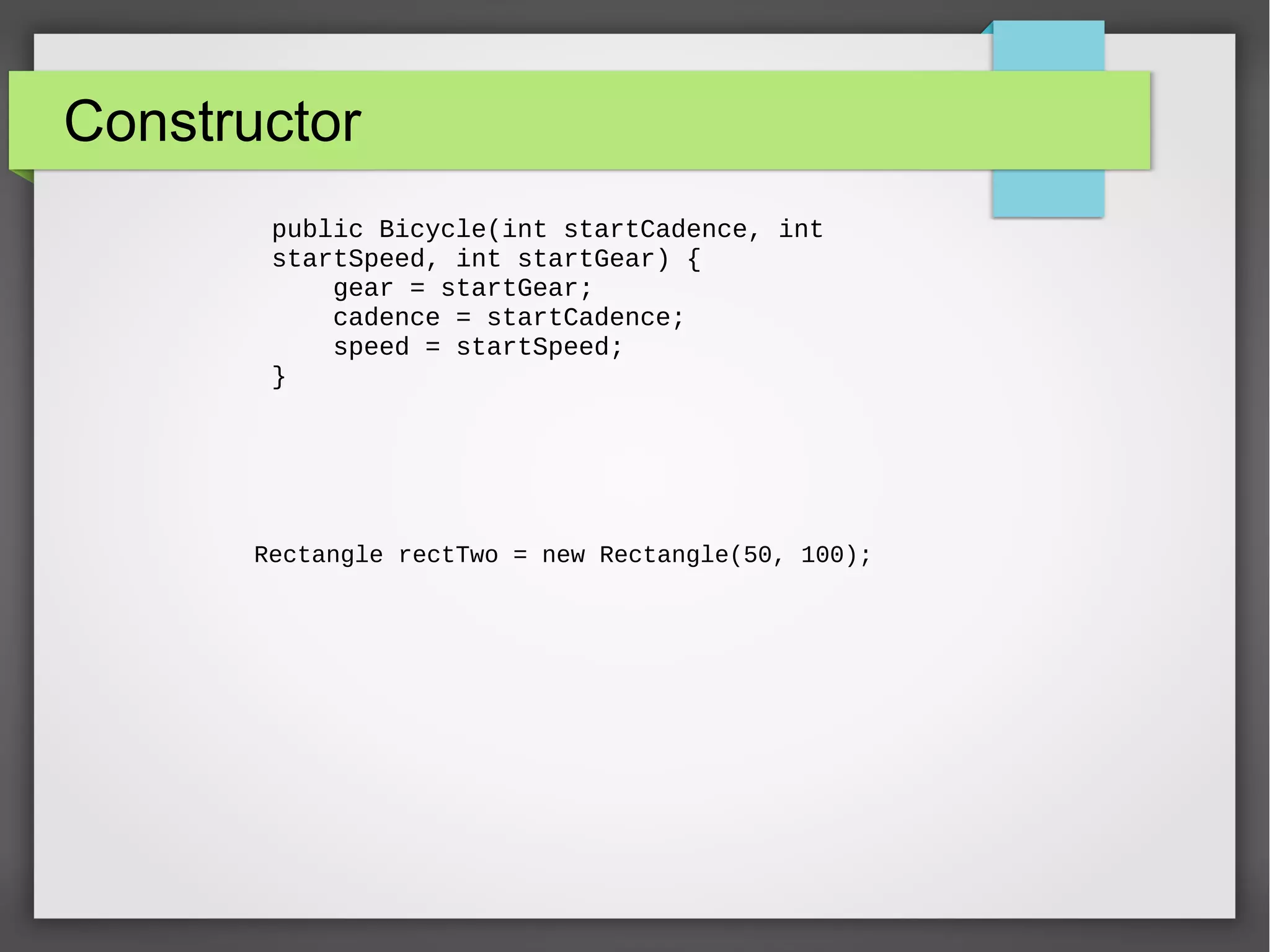
This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts in Java including objects and classes, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and language basics. It discusses key OOP concepts like access modifiers, constructors, interfaces, nested classes, anonymous classes, method overloading. It also covers polymorphism through examples. Finally, it lists some important methods like clone, equals, finalize and language features like final, abstract keywords and exception handling.





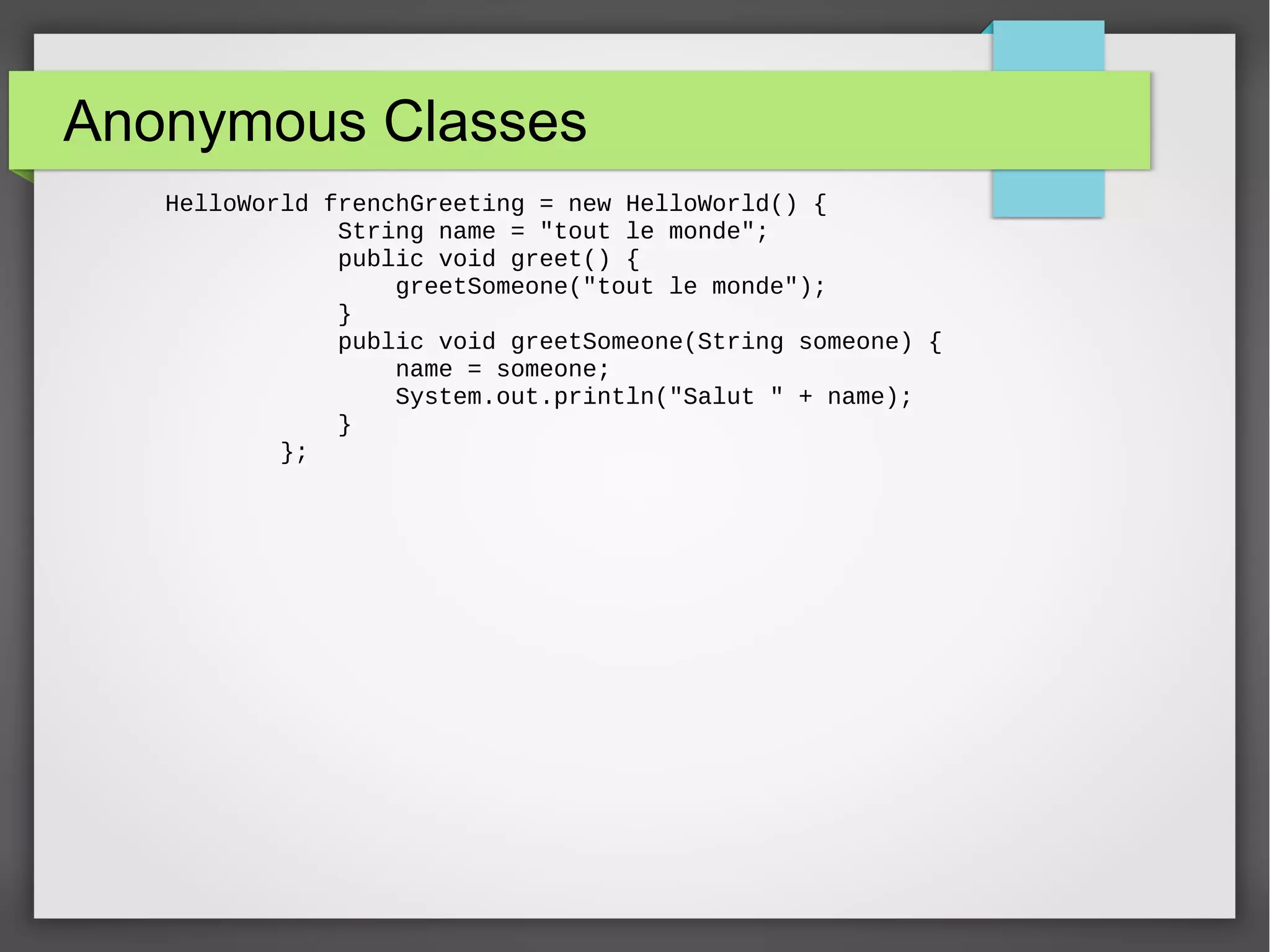
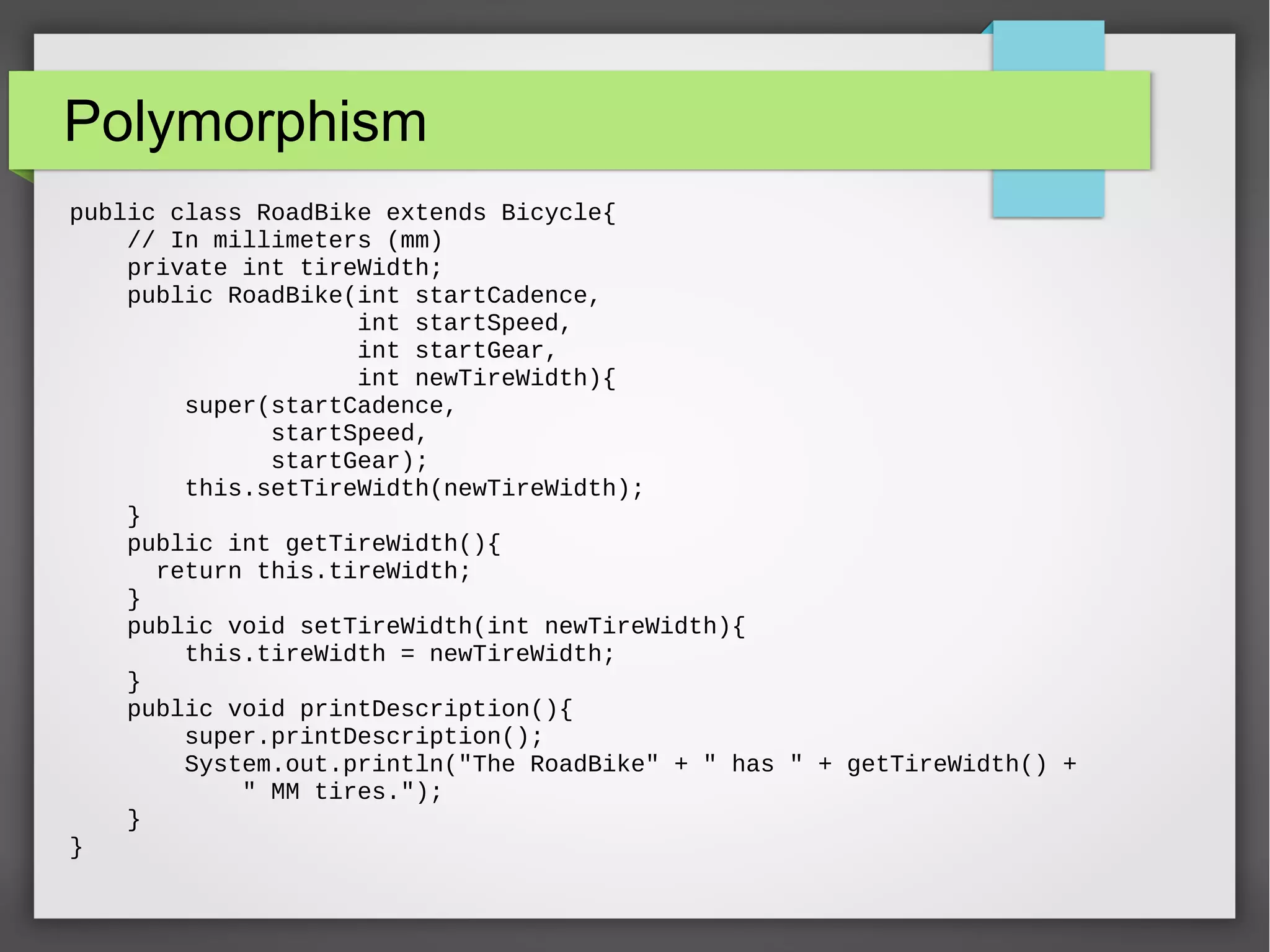
![Polymorphism public class TestBikes { public static void main(String[] args){ Bicycle bike01, bike02, bike03; bike01 = new Bicycle(20, 10, 1); bike02 = new MountainBike(20, 10, 5, "Dual"); bike03 = new RoadBike(40, 20, 8, 23); bike01.printDescription(); bike02.printDescription(); bike03.printDescription(); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsandjavabyaintroductionsandeshsharma-150825054139-lva1-app6891/75/OOP-and-java-by-a-introduction-sandesh-sharma-12-2048.jpg)

![thAnks Email at ersandeshsharma[at]gmail.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsandjavabyaintroductionsandeshsharma-150825054139-lva1-app6891/75/OOP-and-java-by-a-introduction-sandesh-sharma-14-2048.jpg)