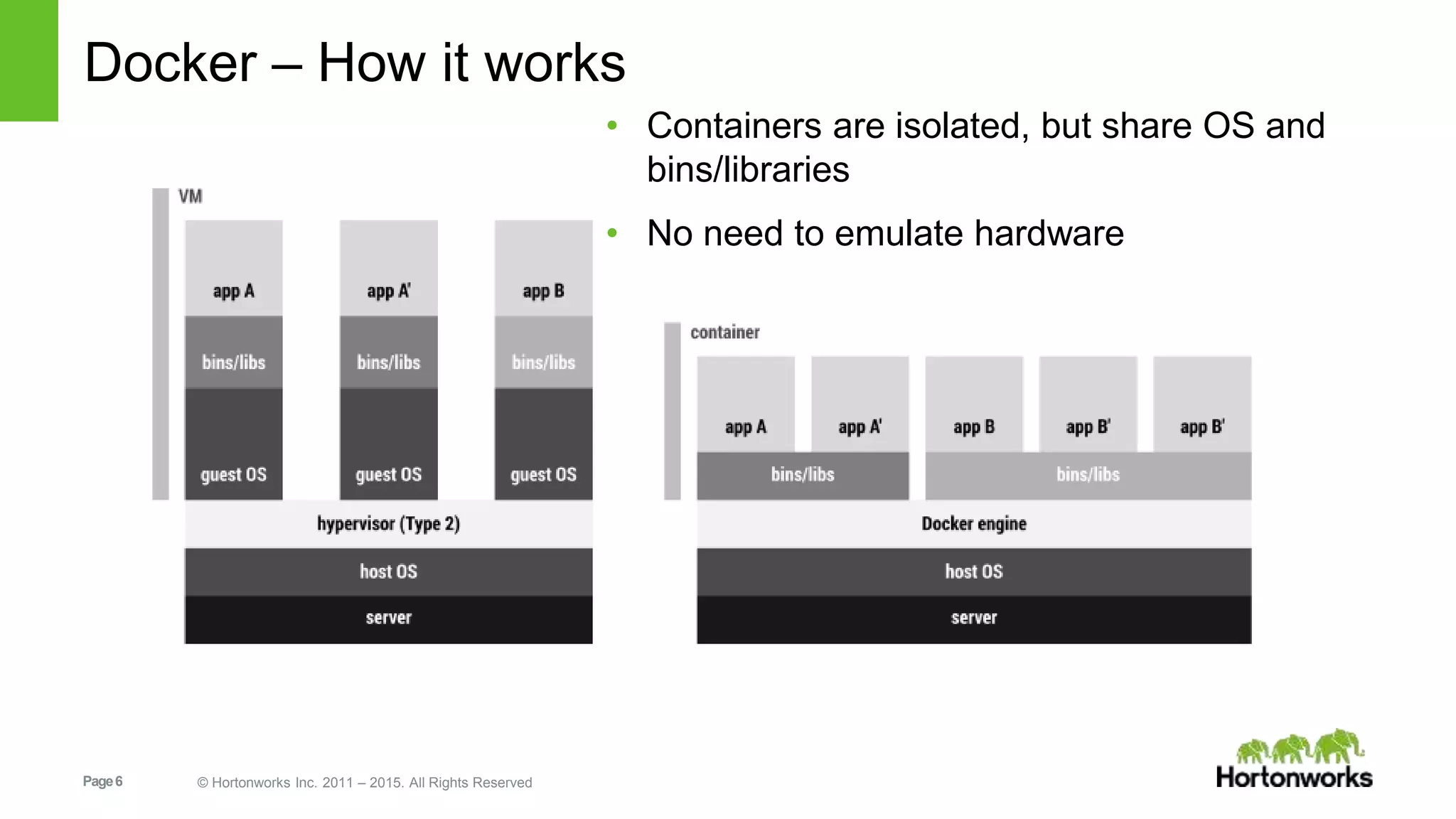
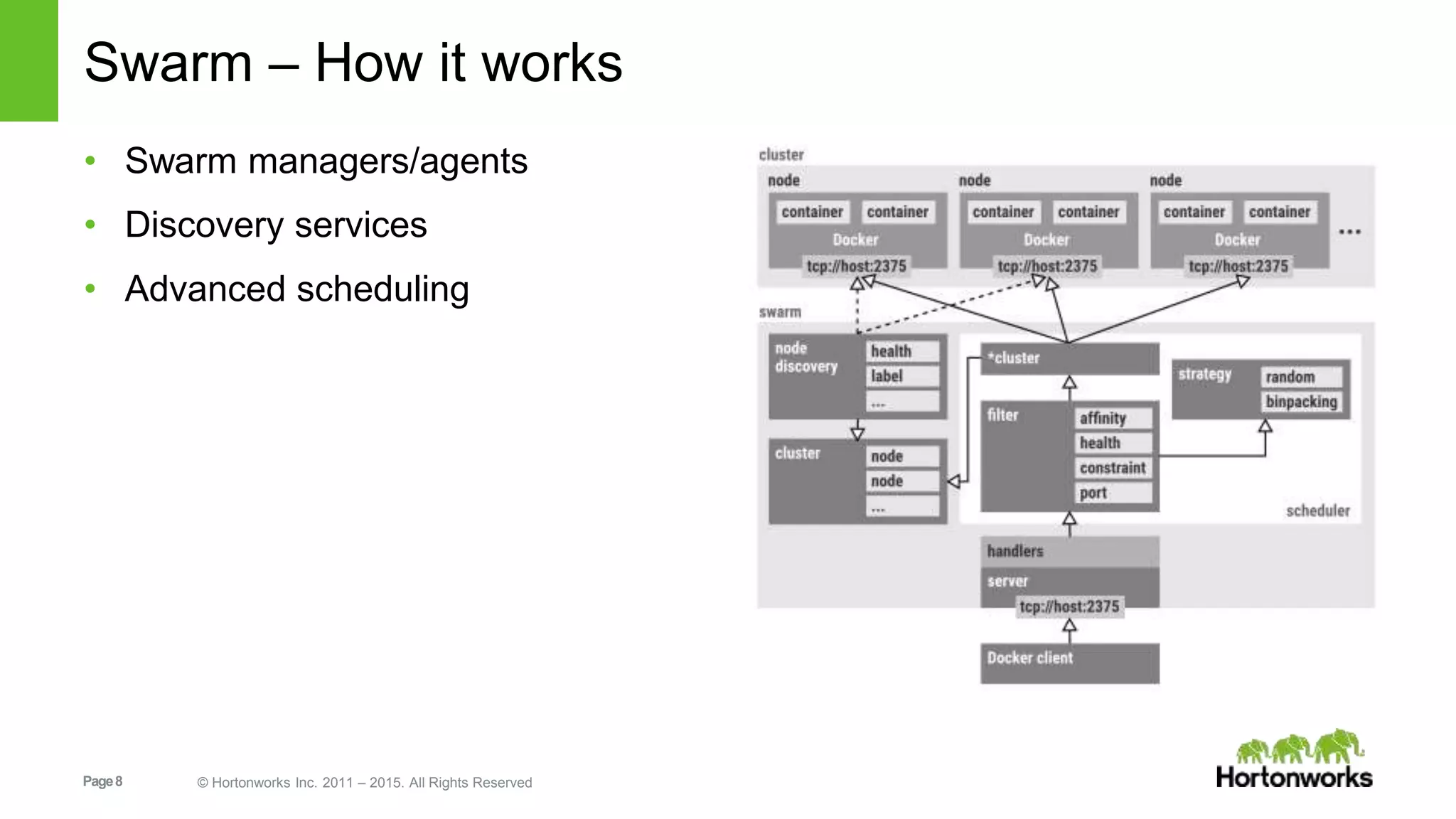
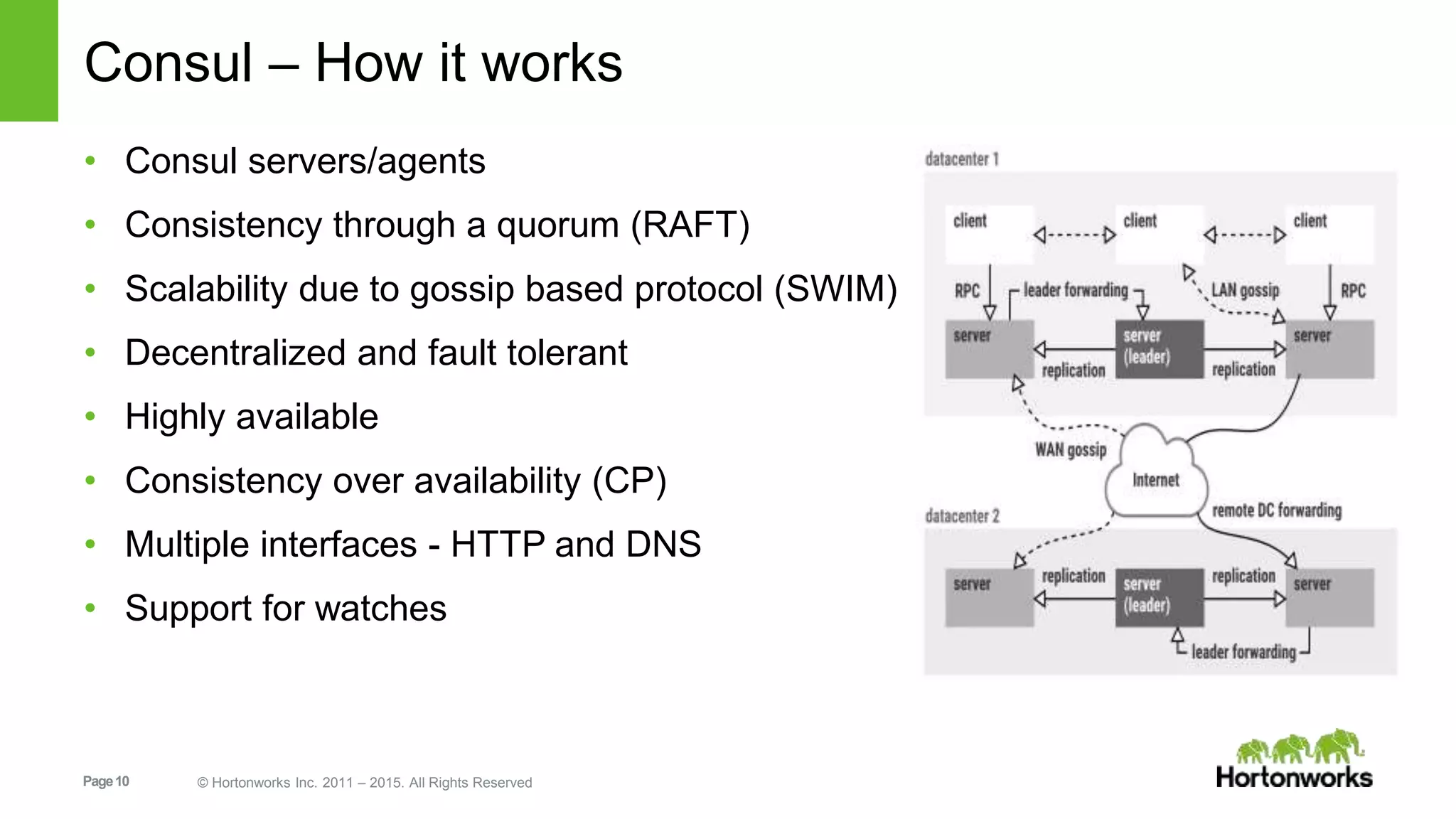
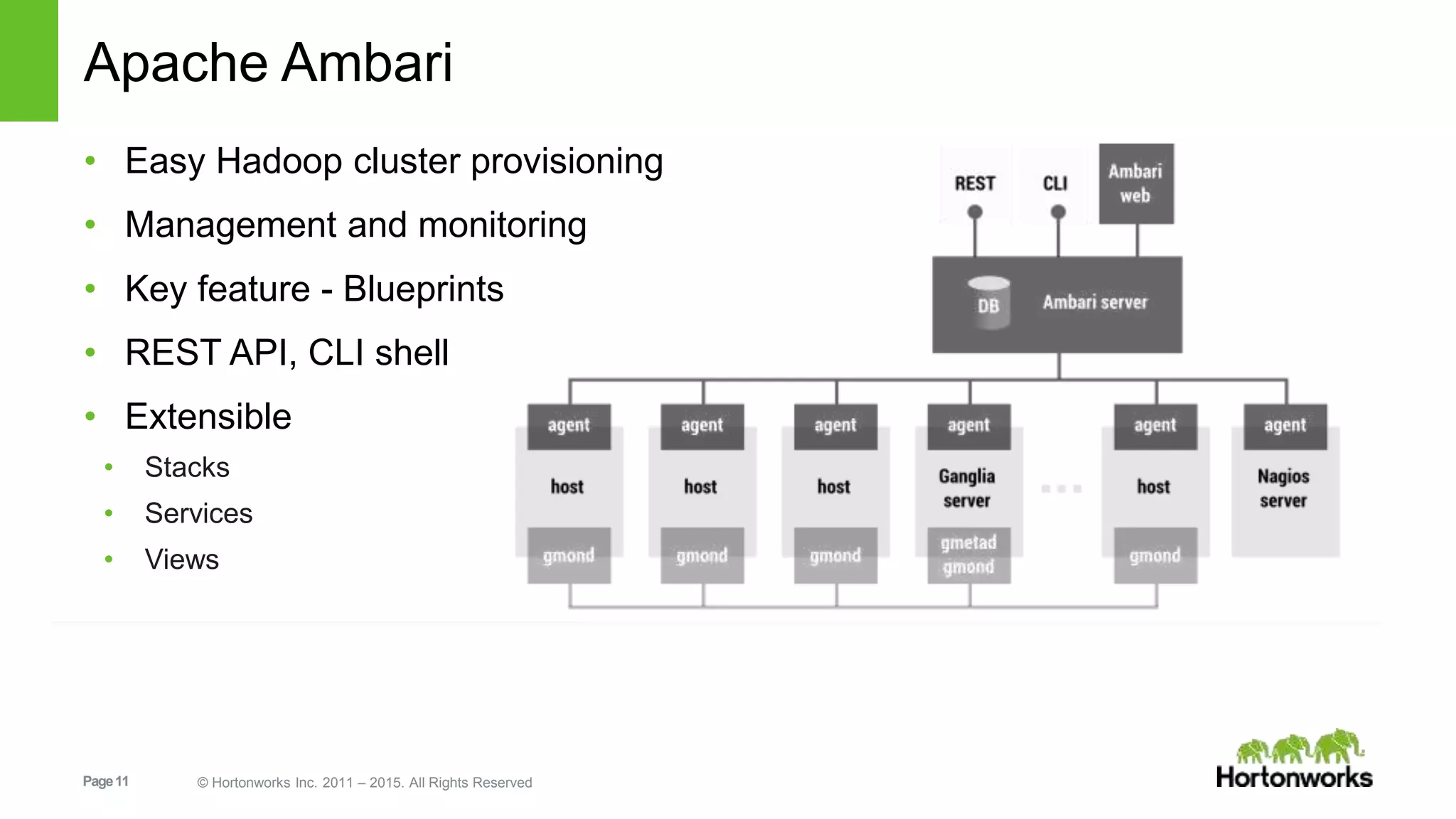
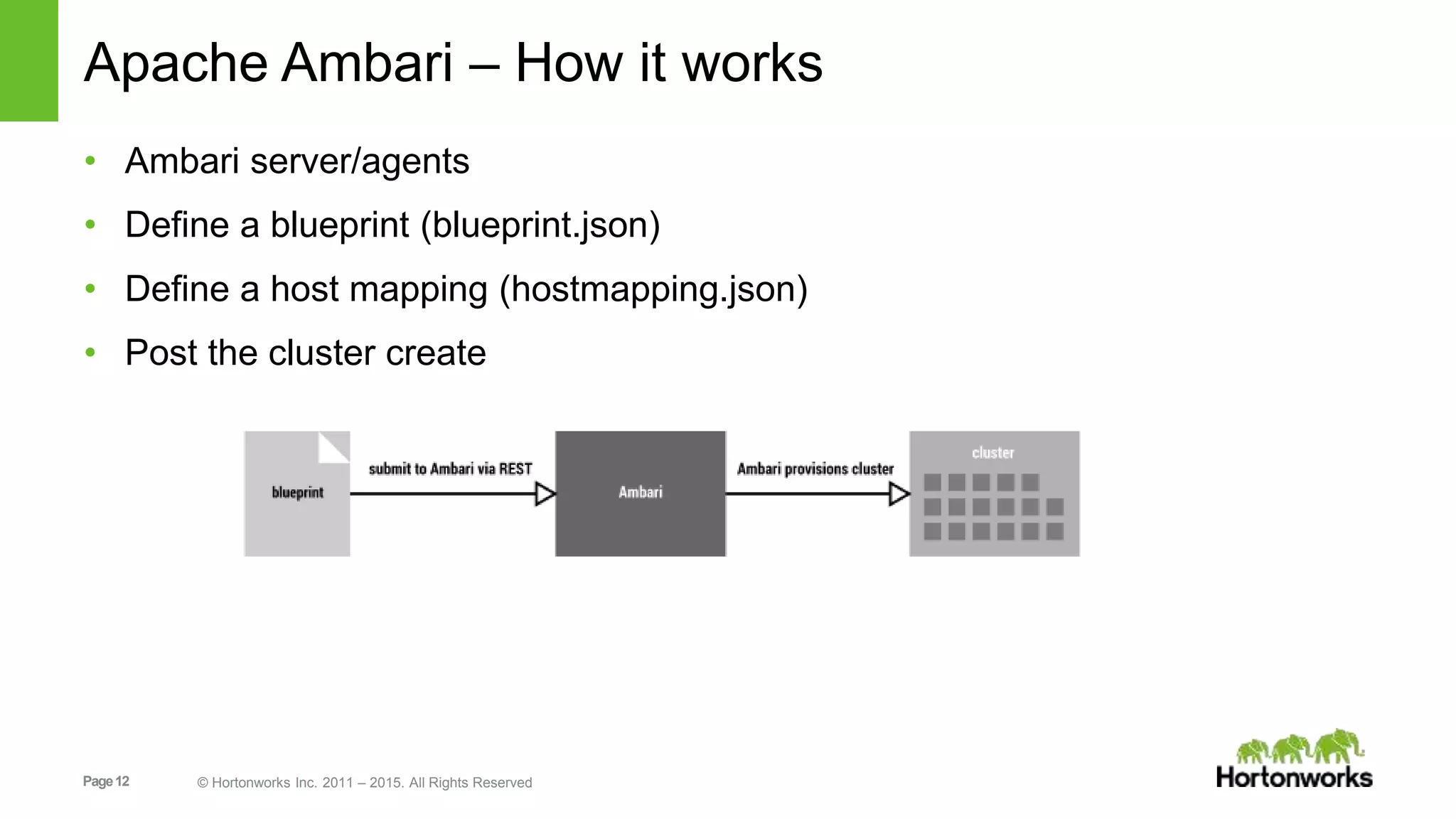
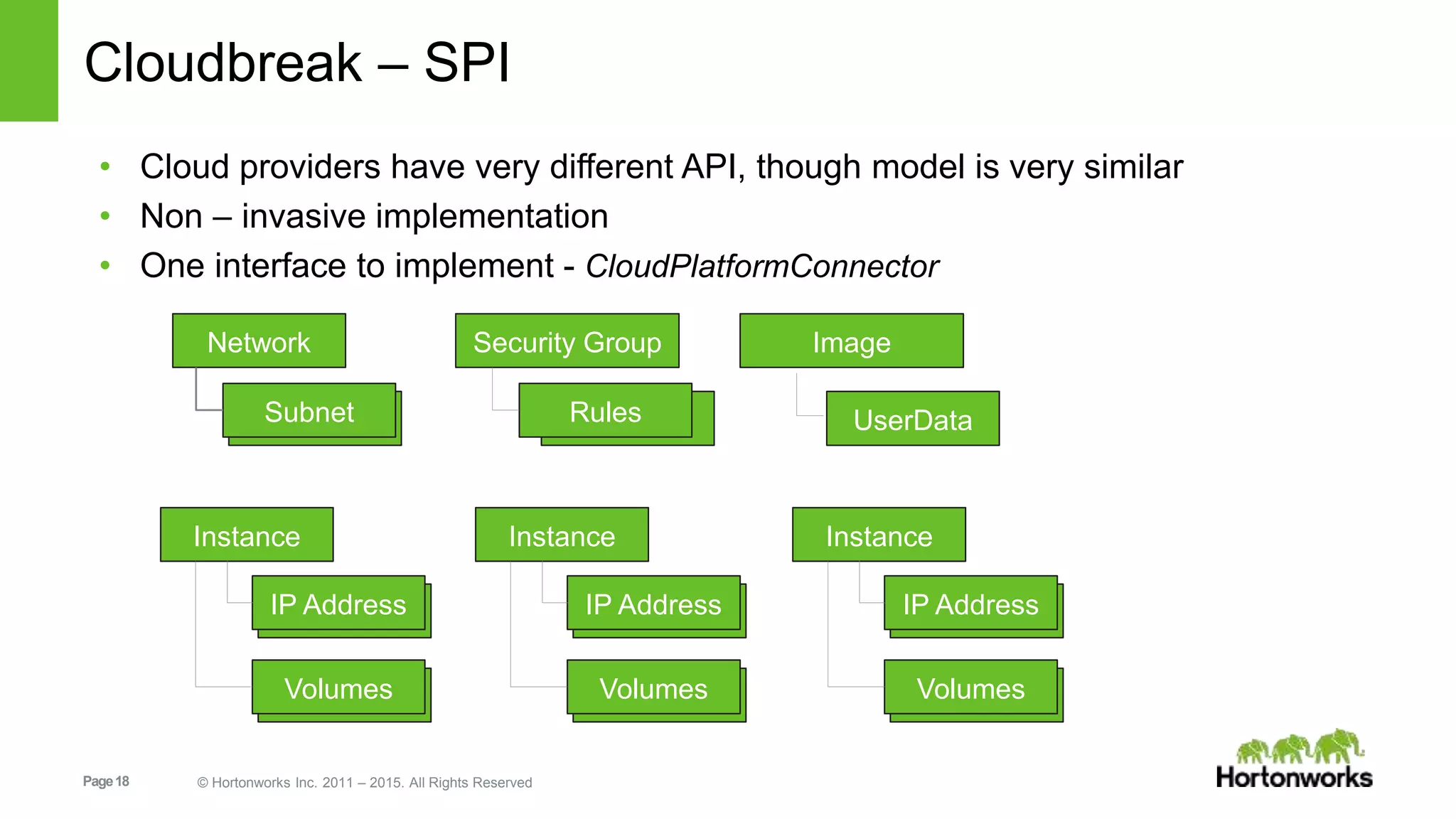
This document provides an overview of Hortonworks' one-click Hadoop clusters solution that uses Docker and Apache Ambari to provision Hadoop clusters on any infrastructure. It discusses the goals of automating and unifying the Hadoop cluster provisioning process. The technology stack uses Docker for containerization, Swarm for clustering and orchestration, Consul for service discovery and registration, and Ambari for provisioning and management. Cloudbreak is introduced as a cloud-agnostic API that abstracts Hadoop cluster provisioning using these tools, while Periscope provides heuristic scheduling and autoscaling of clusters based on service level agreements.