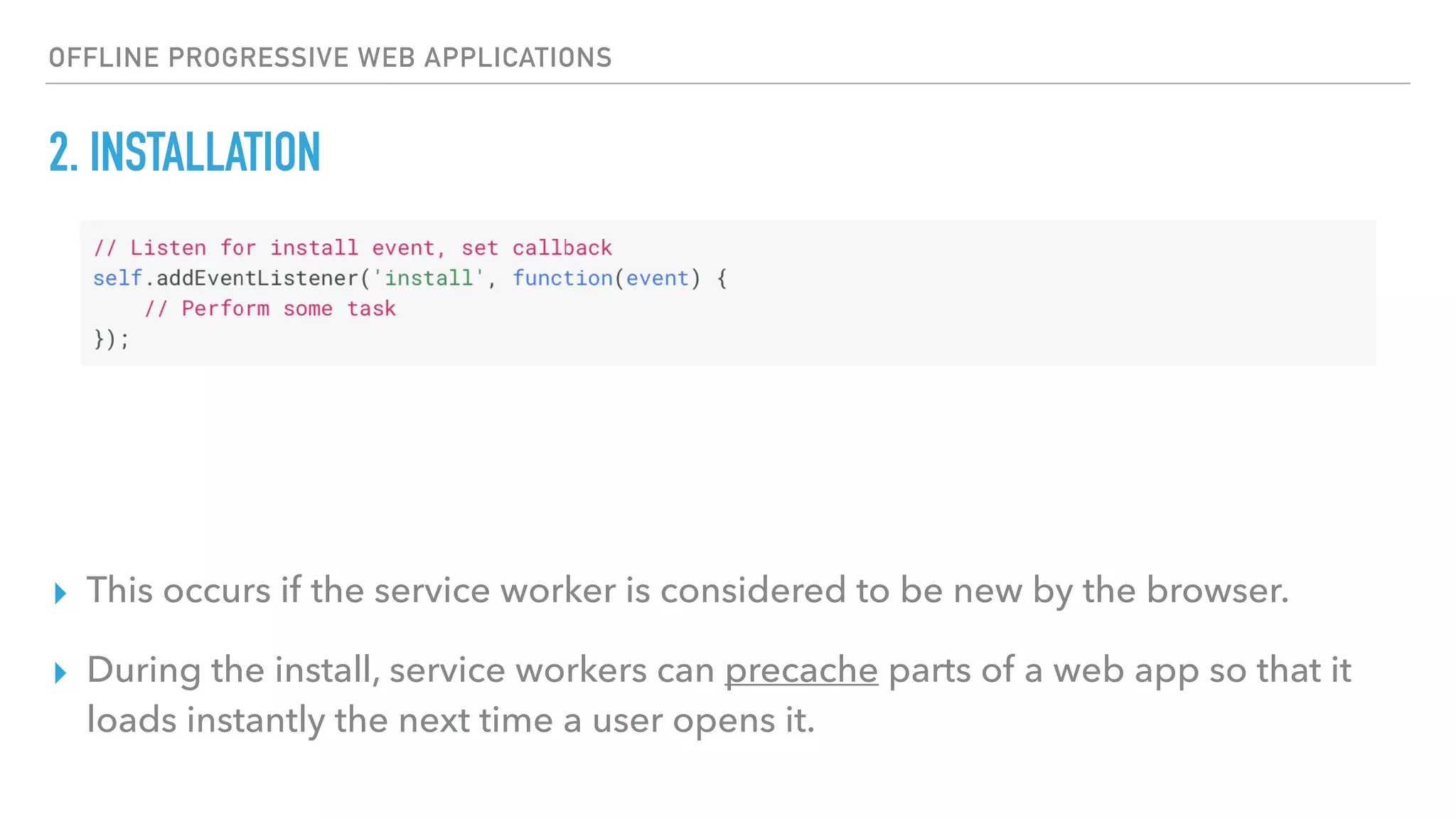
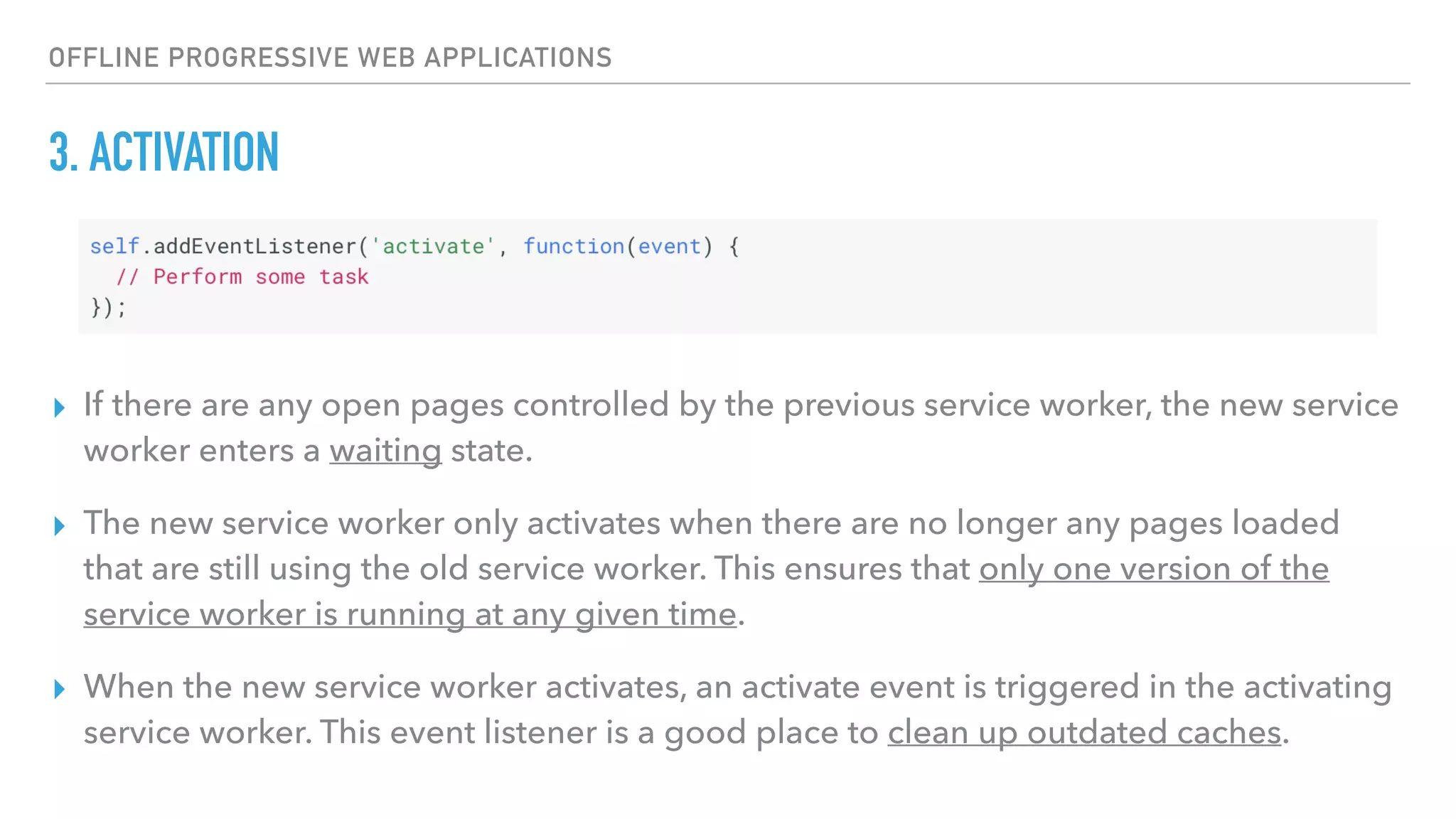
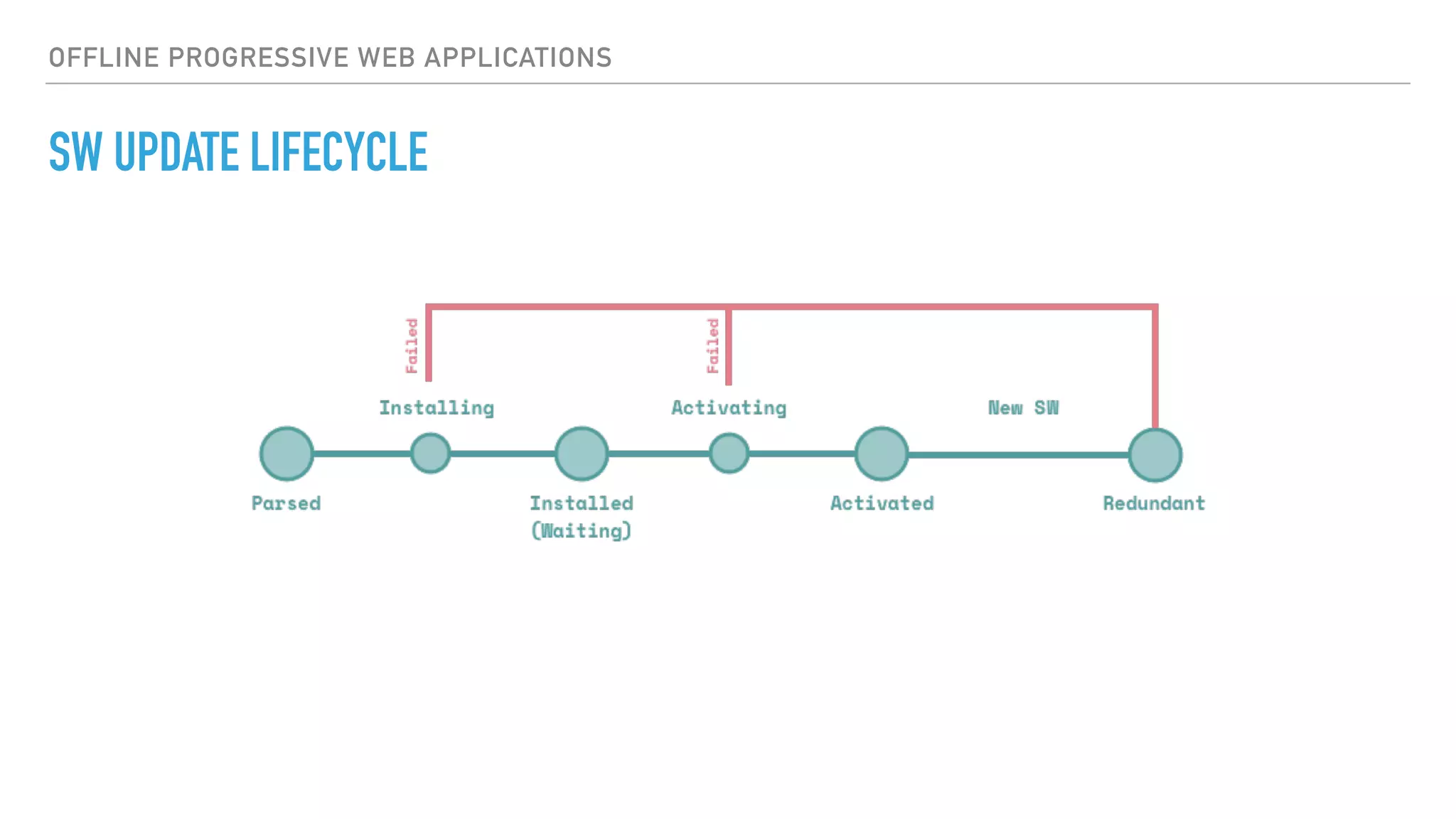
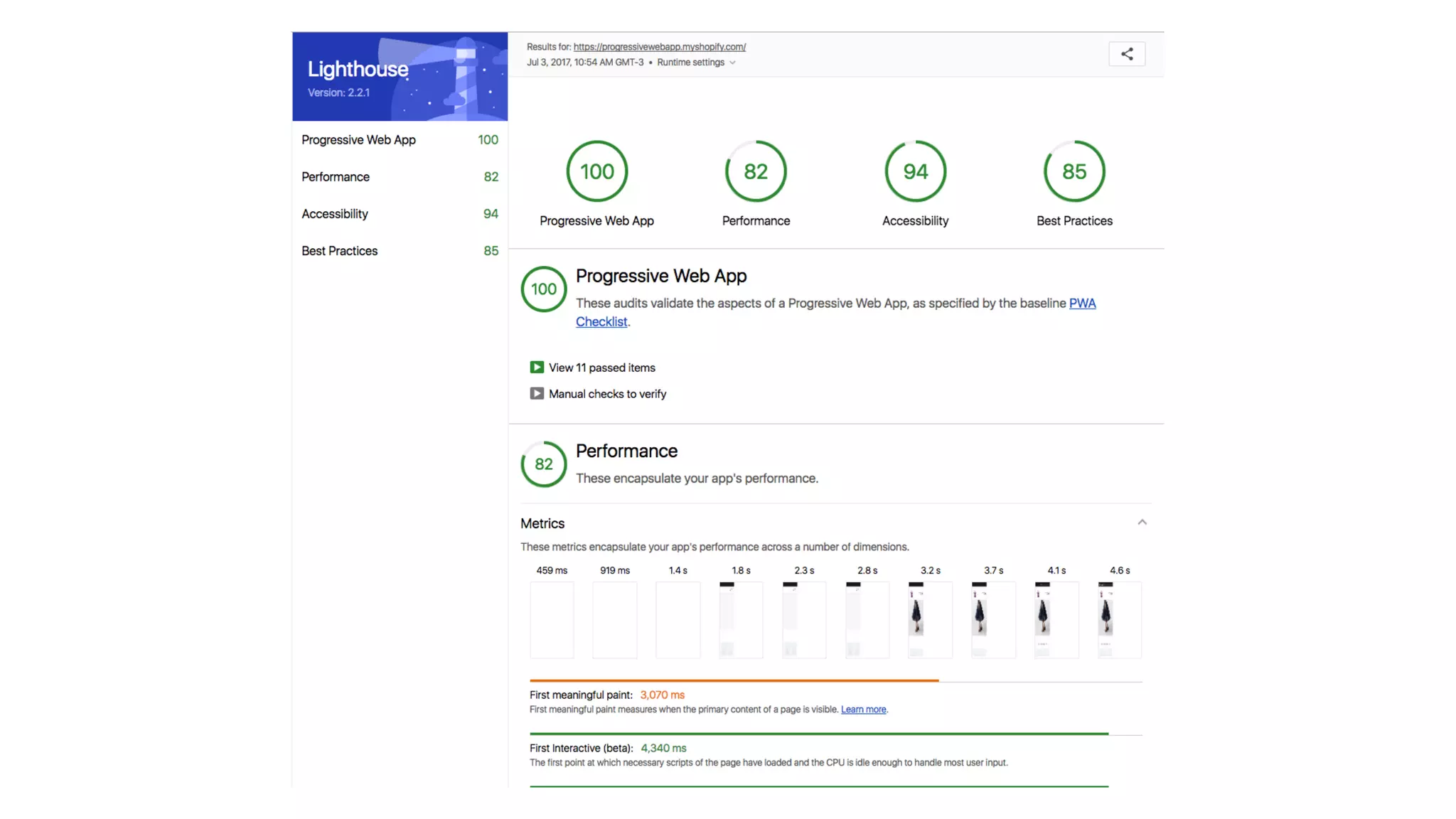
This document provides an overview of progressive web applications (PWAs) and how to build them using service workers, the Cache API, and IndexedDB for offline functionality. It discusses key concepts like the service worker lifecycle, notifications, manifest files, and the Web Push API. The document also explains how to cache assets, handle network requests when offline, and store data locally using IndexedDB.

![{ "name": "Ilia Idakiev", "experience": [ "Lecturer in 'Advanced JS' @ FMI", "Developer / Manager / Owner @ HNS", "Project Contractor / Consultant", "2 Angular Courses @ HB (2016 - 2017)", "Private Courses" ], "involvedIn": [ "SofiaJS", "BeerJS", "Angular Sofia” ] } ABOUT ME](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/reactofflineprogressivewebappswithnode-180221065746/75/Offline-progressive-web-apps-with-NodeJS-and-React-2-2048.jpg)