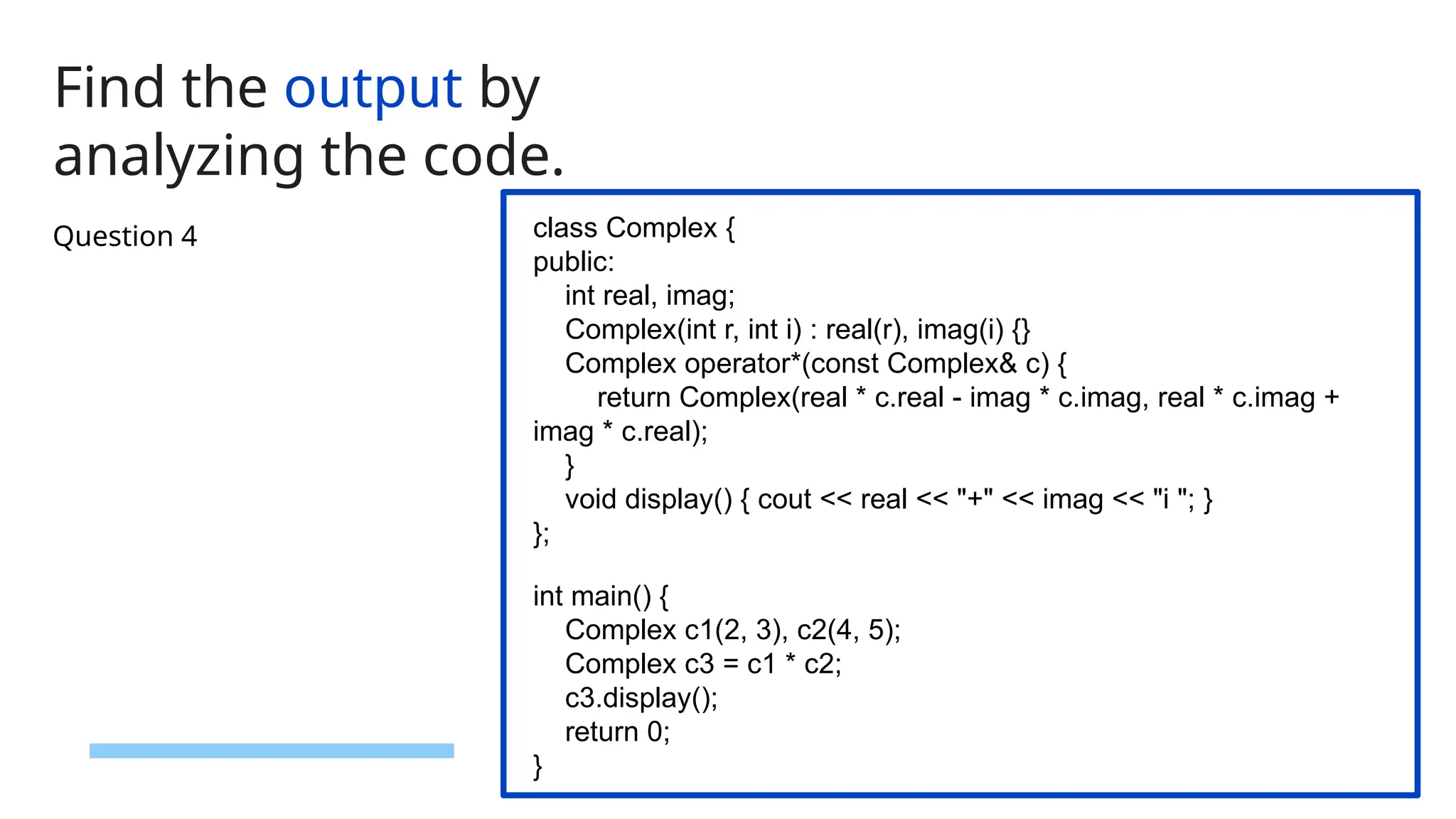
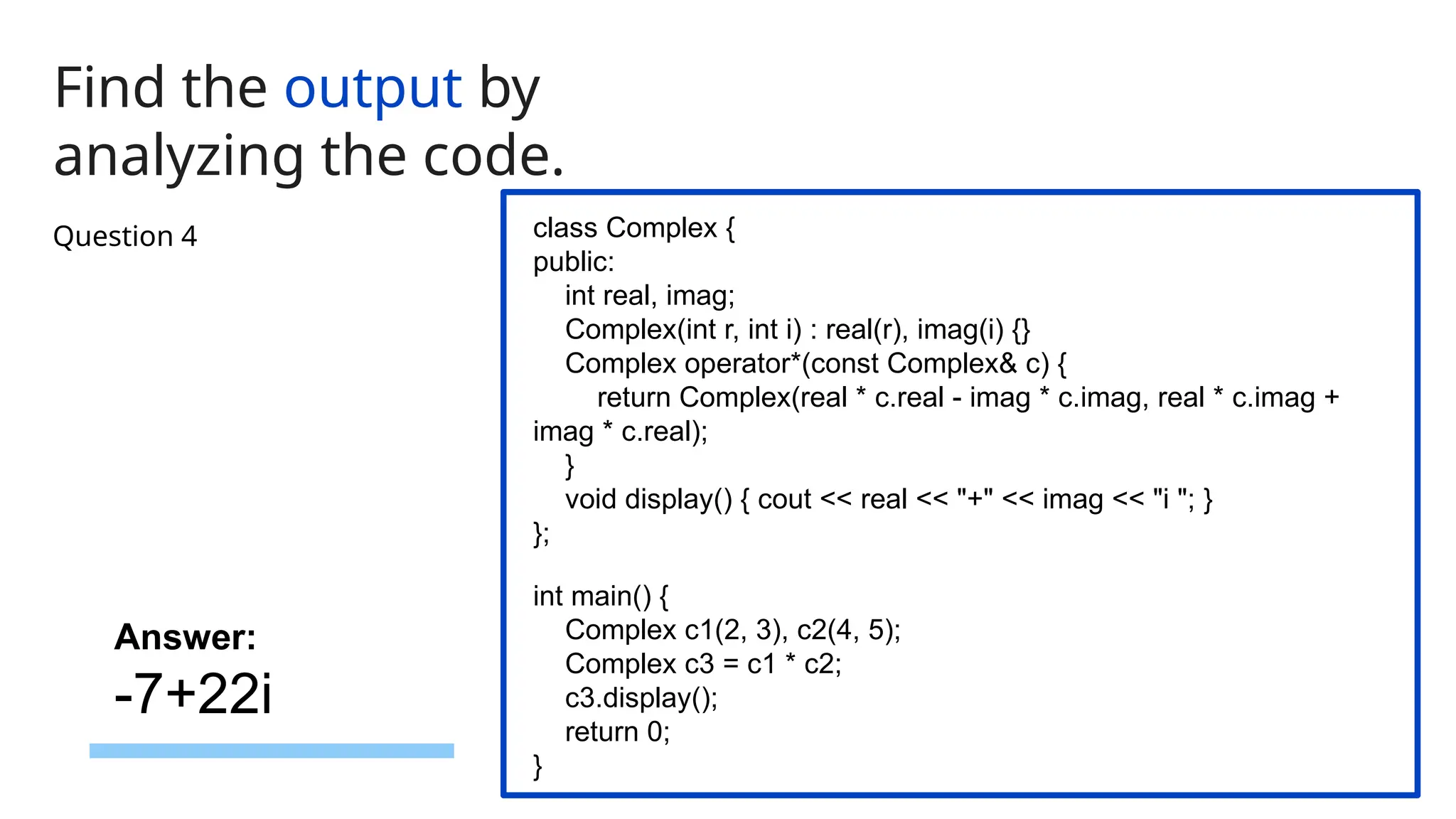
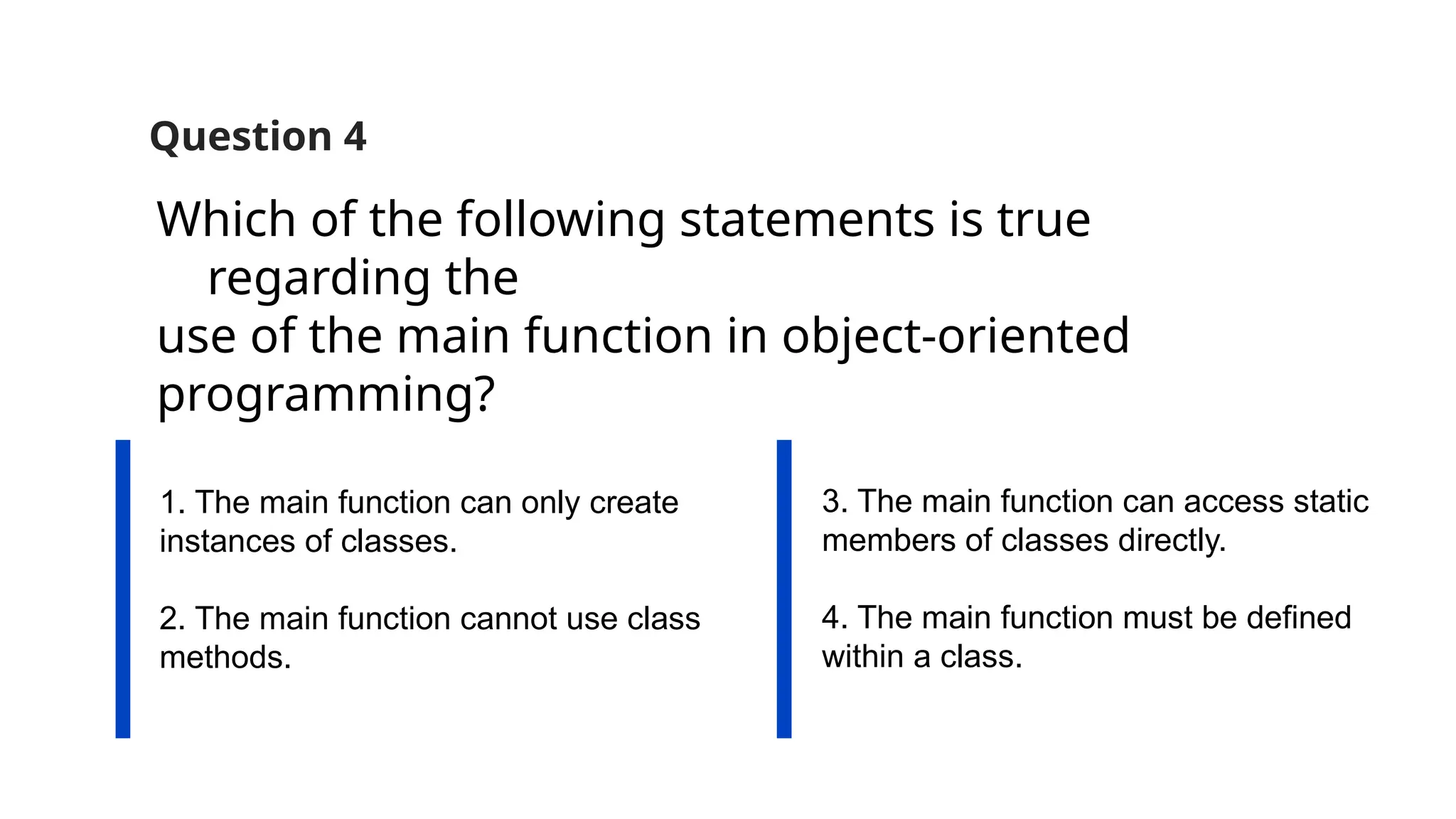
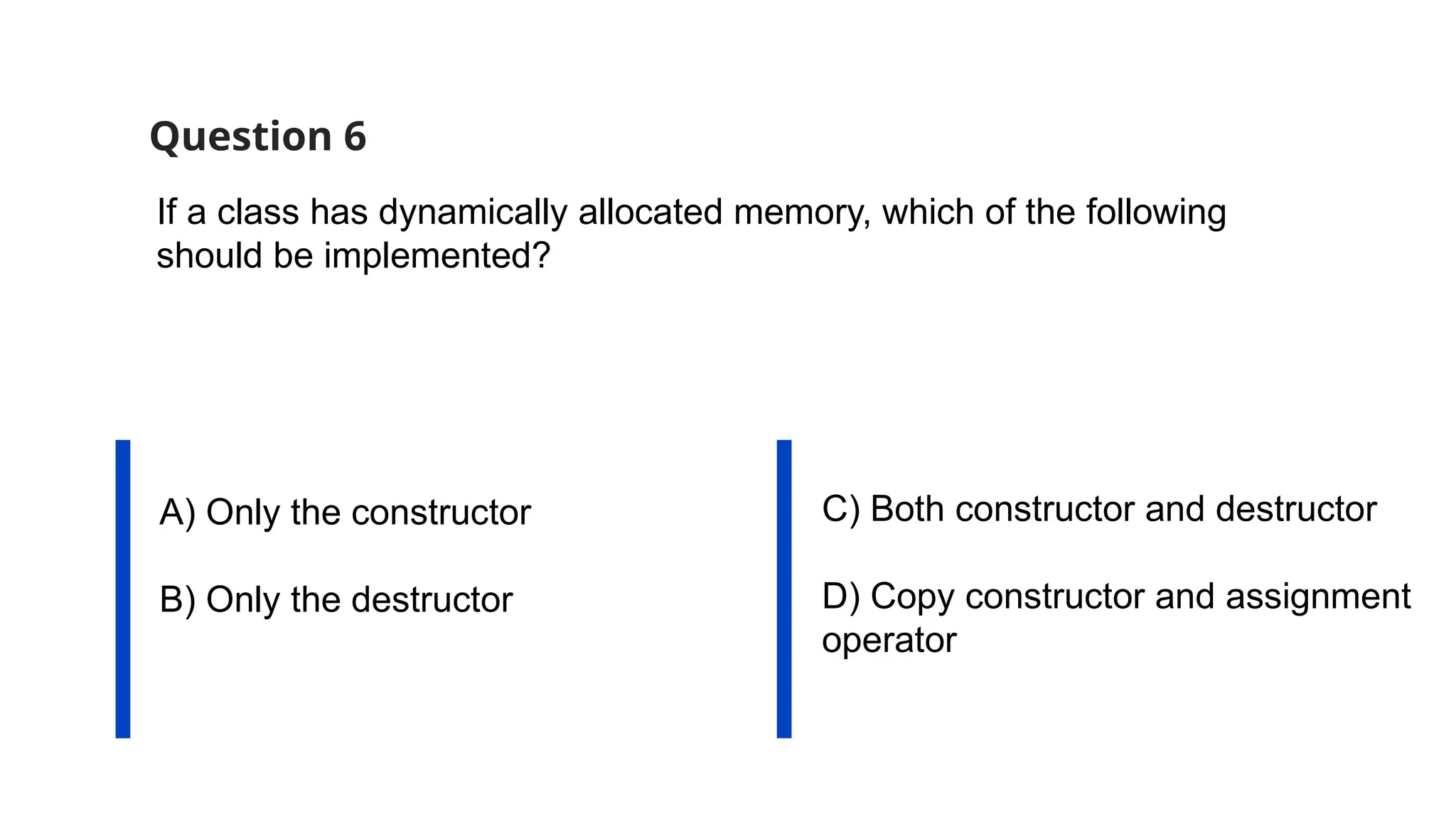
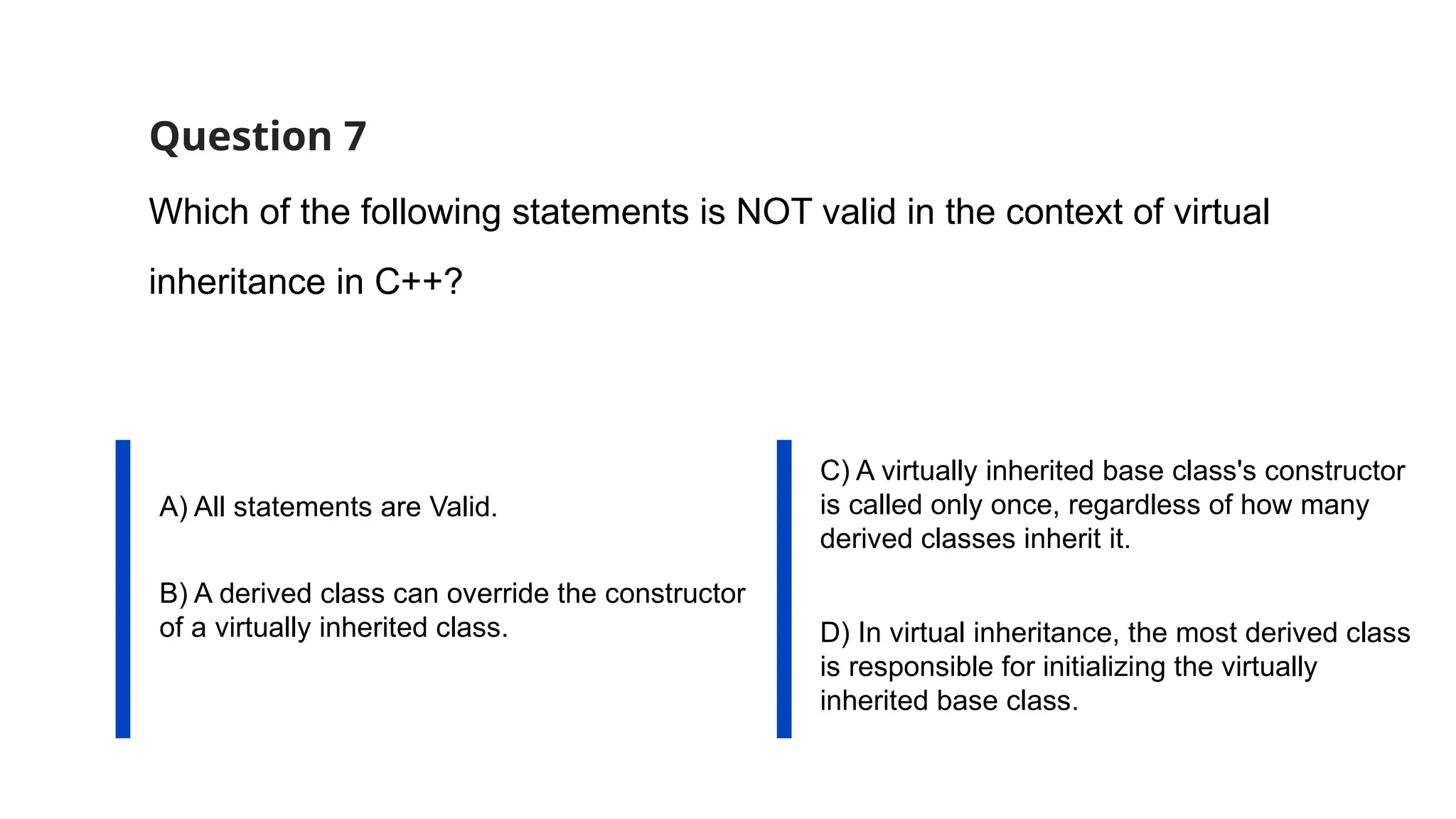
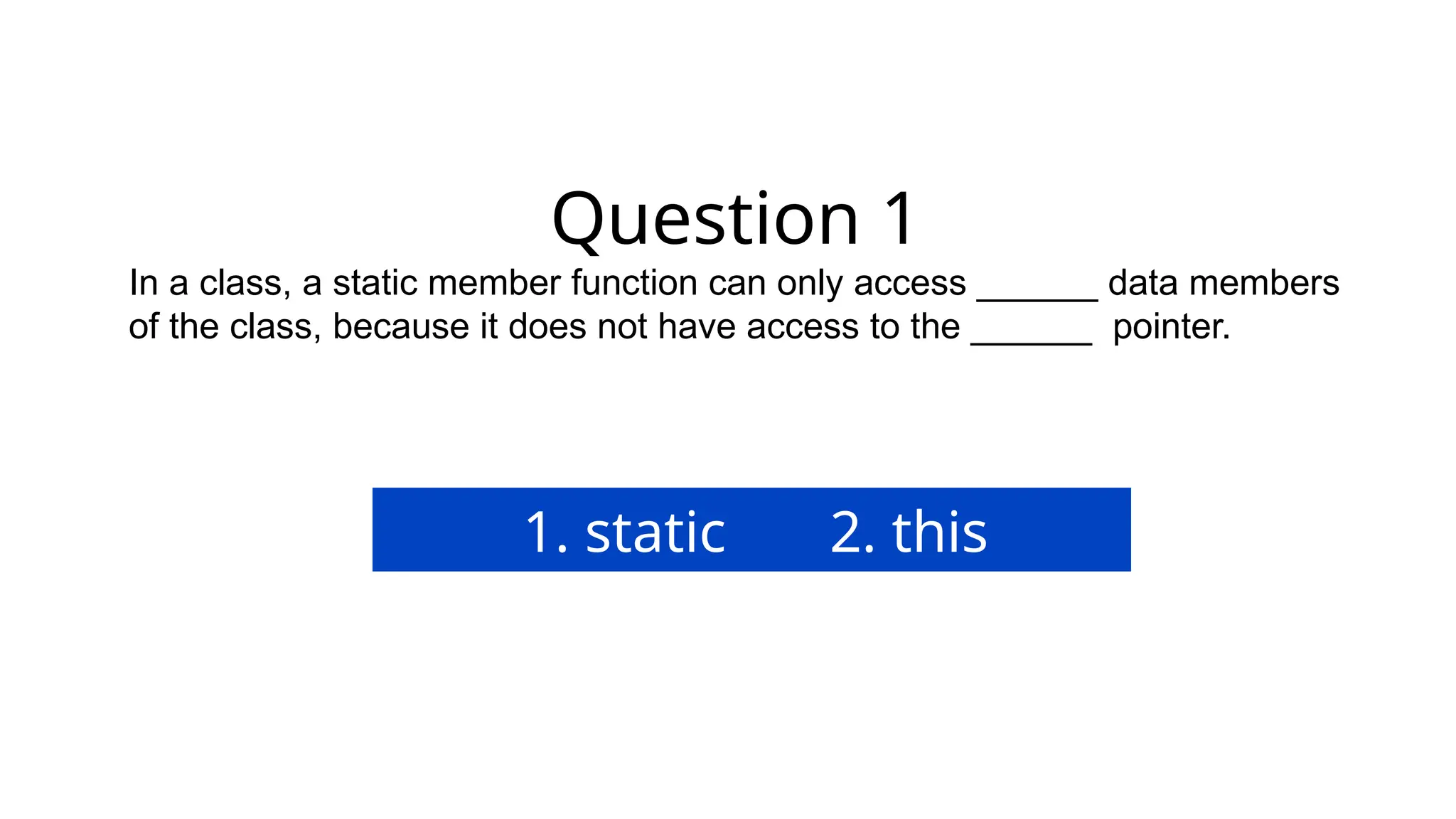
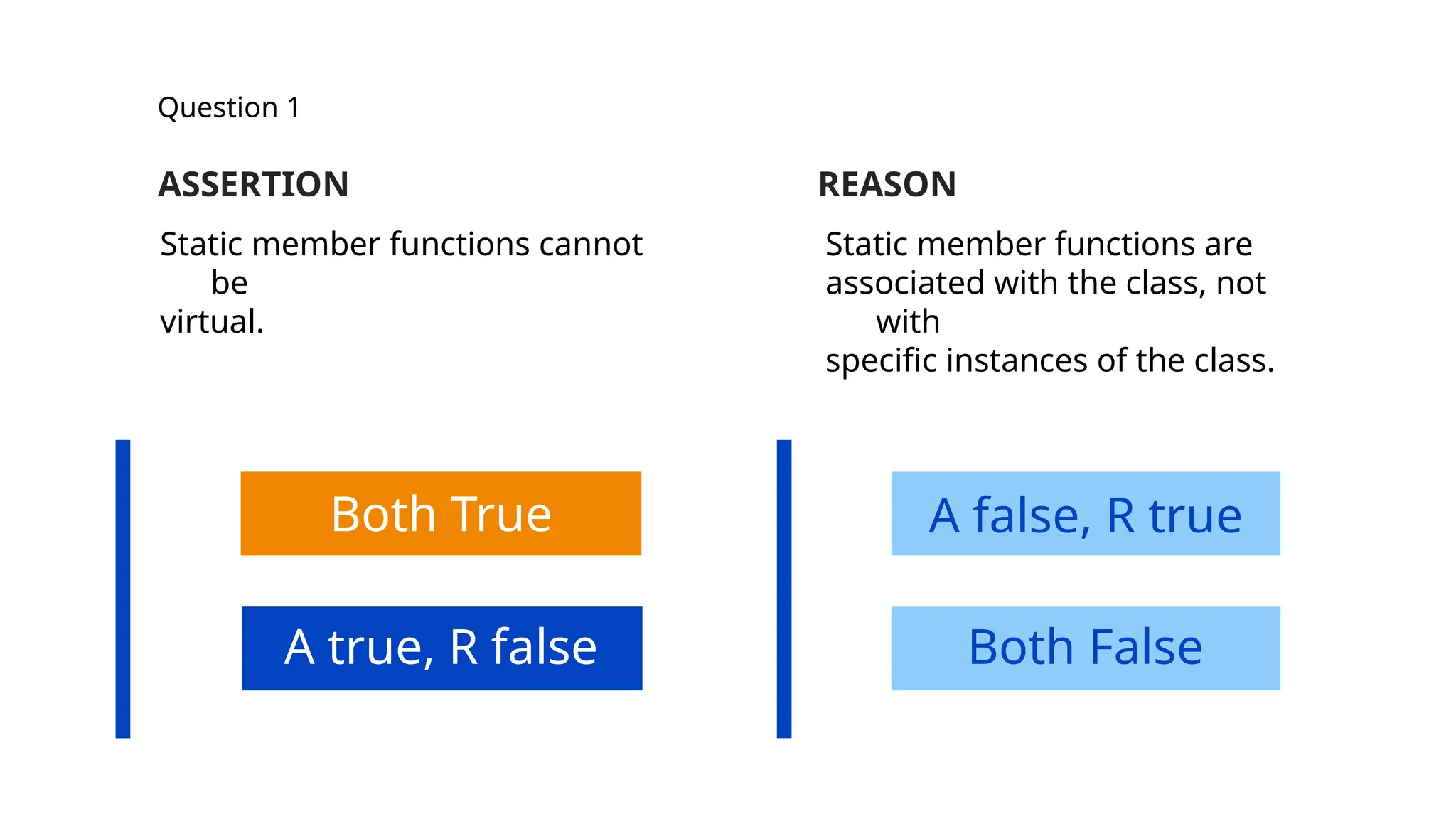
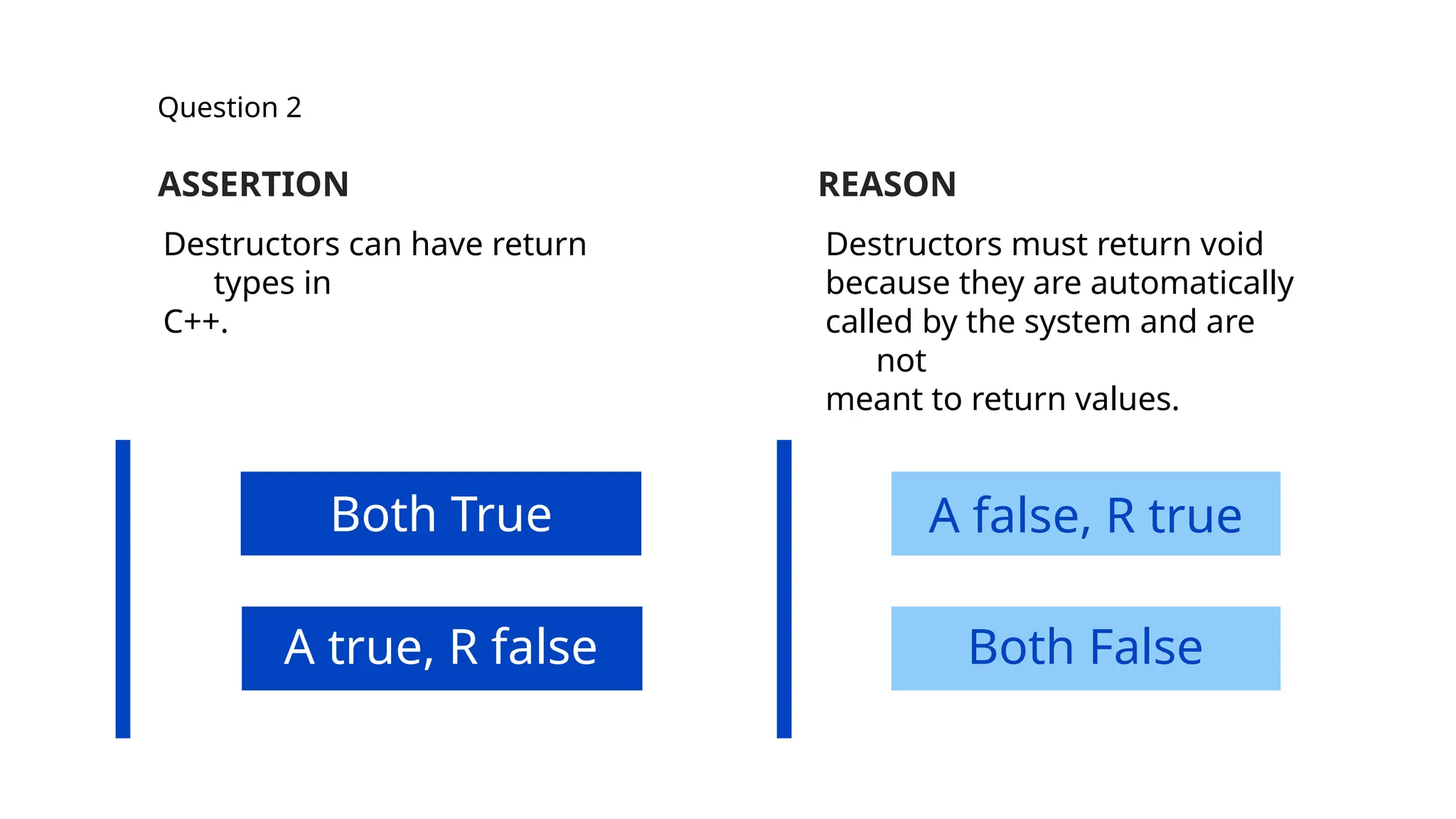
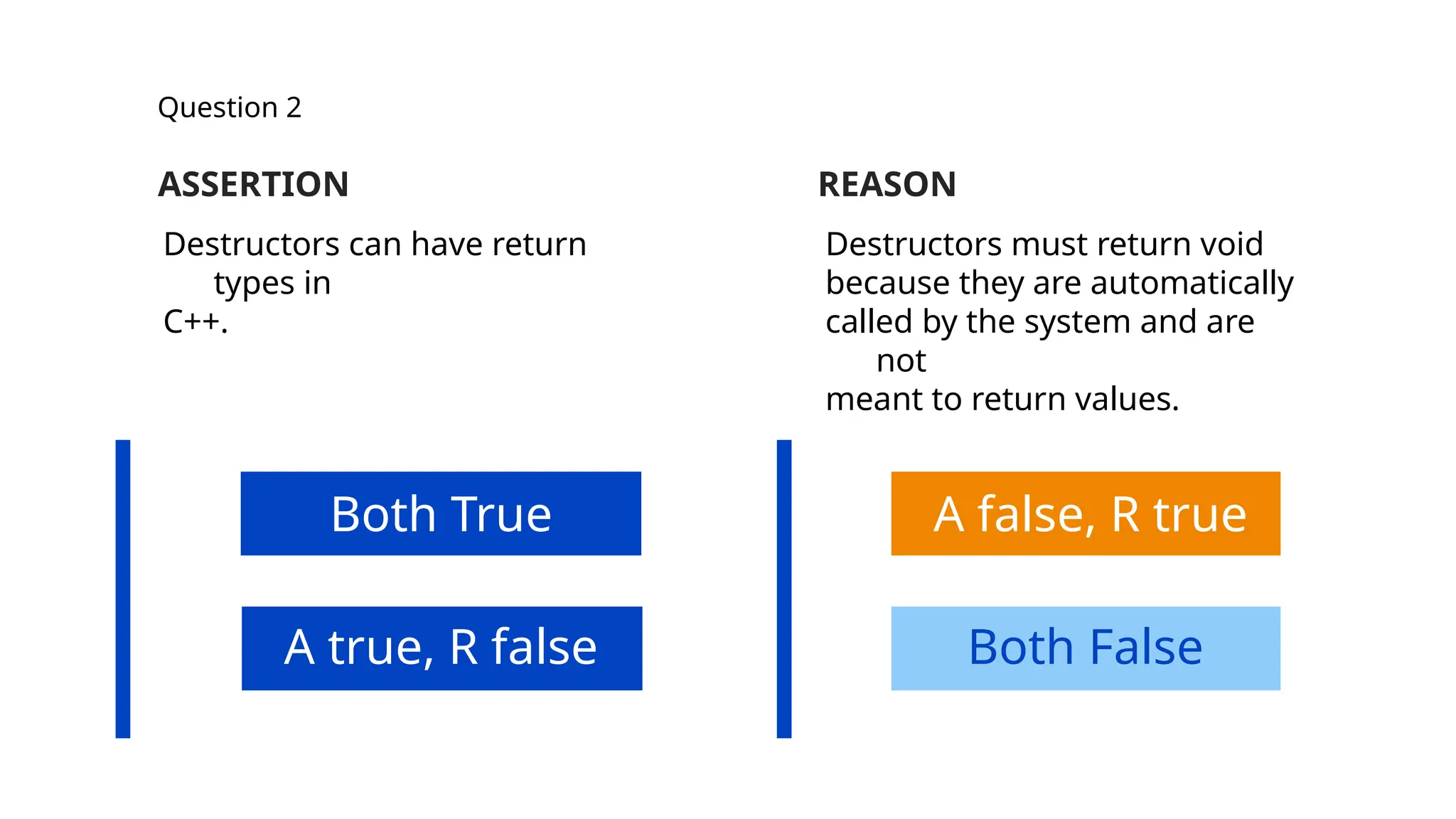
The document consists of multiple-choice questions (MCQs), true/false statements, and fill-in-the-blank questions primarily focusing on C++ programming concepts such as operators, functions, memory management, and object-oriented programming principles. Key topics include the use and meaning of the main function, return statements, static member functions, virtual inheritance, and destructor behavior. The content is structured to evaluate understanding of C++ through a quiz format.




![Which of the following operators is used to access members of a class in C++? Question 1 A)-> B). C) :: D) [ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiztemplatepptrd-241214074244-61a675b2/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-using-C-C-Plus-Plus-QUIZ-7-2048.jpg)

























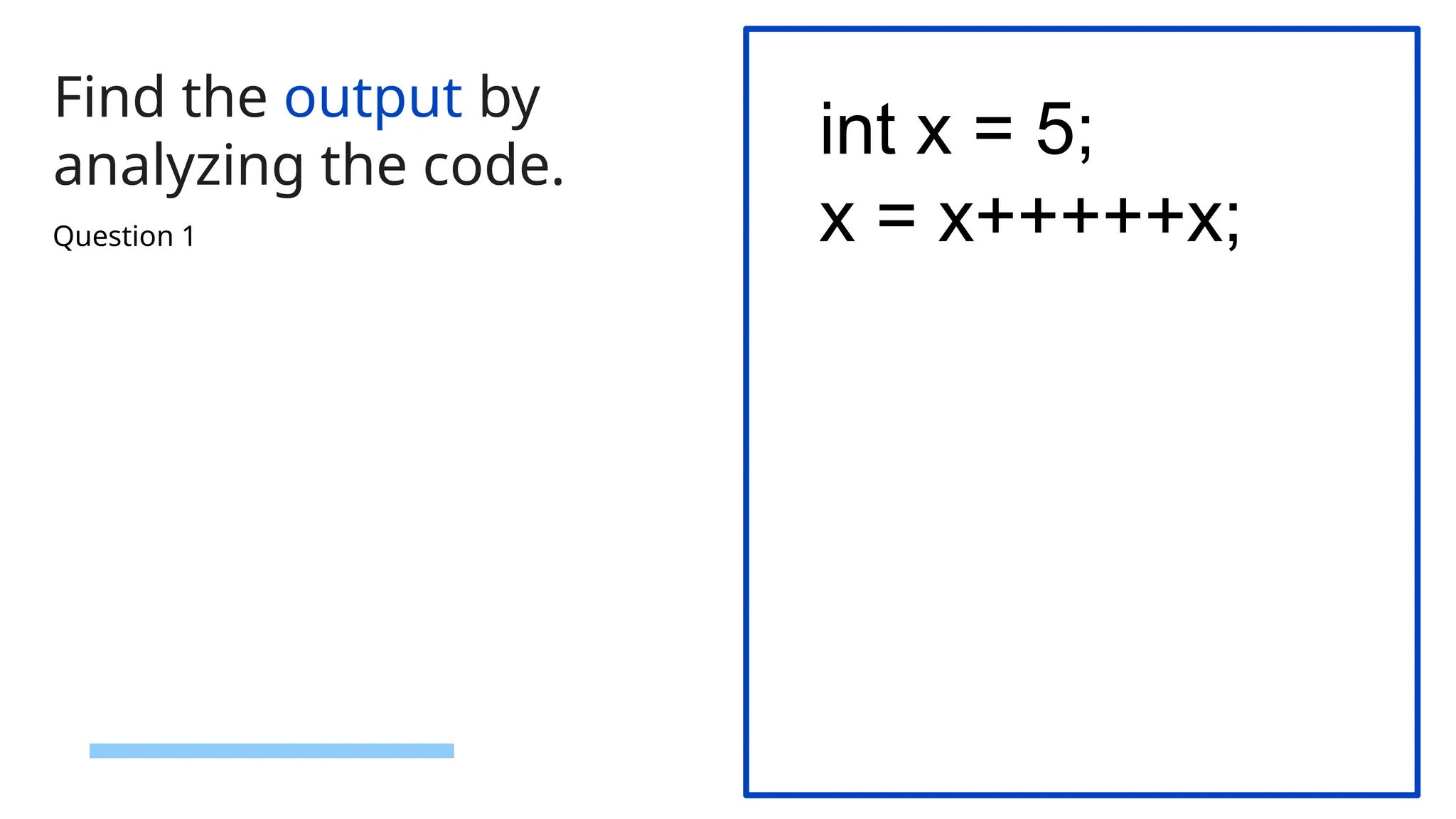
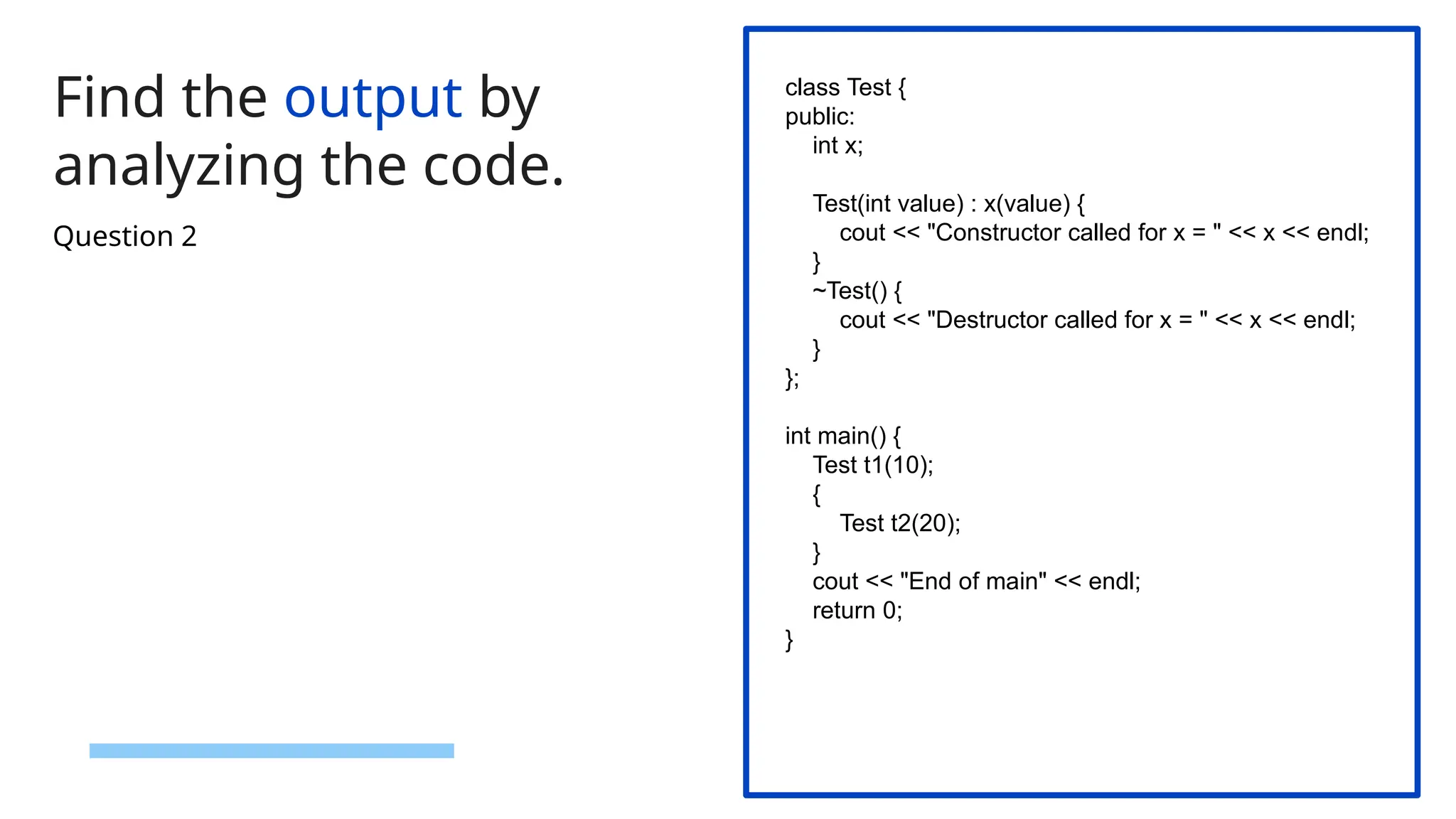

![59 Find the output by analyzing the code. class MyClass { int* ptr; public: MyClass(int size) { ptr = new int[size]; // Dynamically allocate memory cout << "Memory allocated for " << size << " integers." << endl; } ~MyClass() { delete[] ptr; // Deallocate memory cout << "Memory deallocated." << endl; } }; int main() { MyClass obj(5); // Dynamically allocate memory for 5 integers return 0; } Question 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiztemplatepptrd-241214074244-61a675b2/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-using-C-C-Plus-Plus-QUIZ-59-2048.jpg)
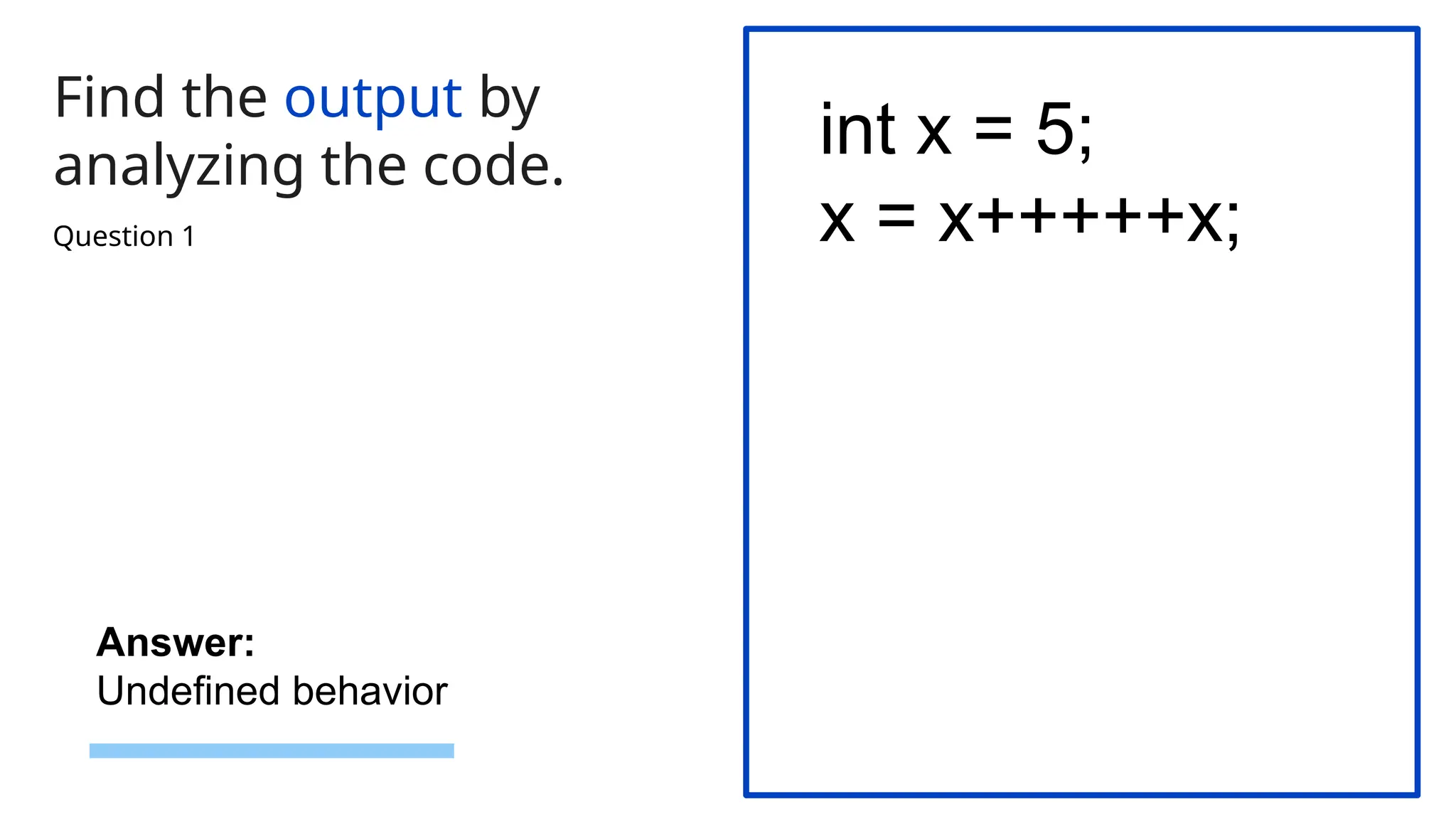
![60 Find the output by analyzing the code. class MyClass { int* ptr; public: MyClass(int size) { ptr = new int[size]; // Dynamically allocate memory cout << "Memory allocated for " << size << " integers." << endl; } ~MyClass() { delete[] ptr; // Deallocate memory cout << "Memory deallocated." << endl; } }; int main() { MyClass obj(5); // Dynamically allocate memory for 5 integers return 0; } Answer: The output will be: Memory allocated for 5 integers. Memory deallocated. Question 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quiztemplatepptrd-241214074244-61a675b2/75/Object-Oriented-Programming-using-C-C-Plus-Plus-QUIZ-60-2048.jpg)