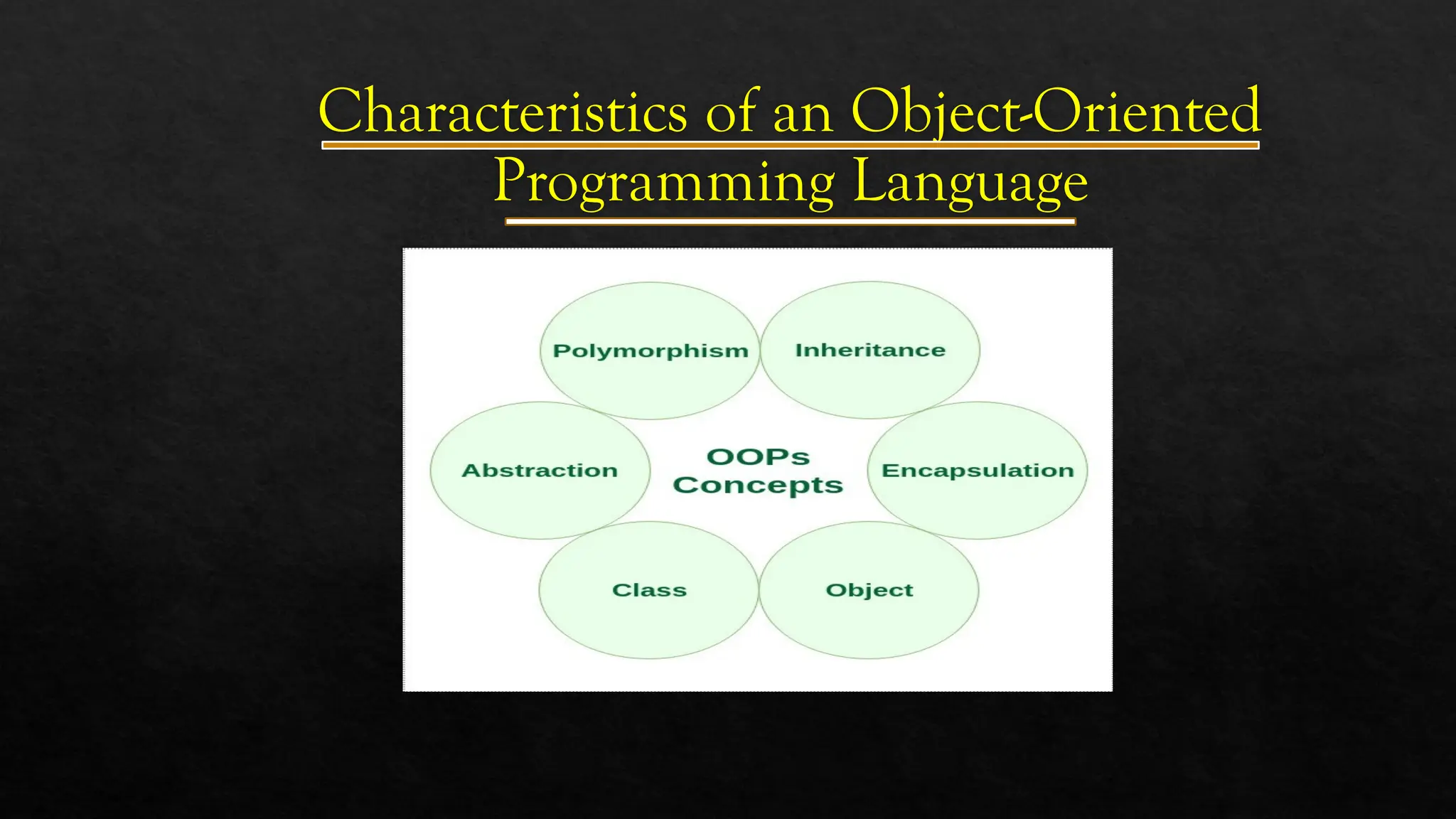
The document discusses Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), focusing on its definition, concepts, and advantages over procedure-oriented programming. Key components include classes, objects, data encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction, emphasizing code modularity and reusability. The document also illustrates these concepts with examples, particularly using C++.