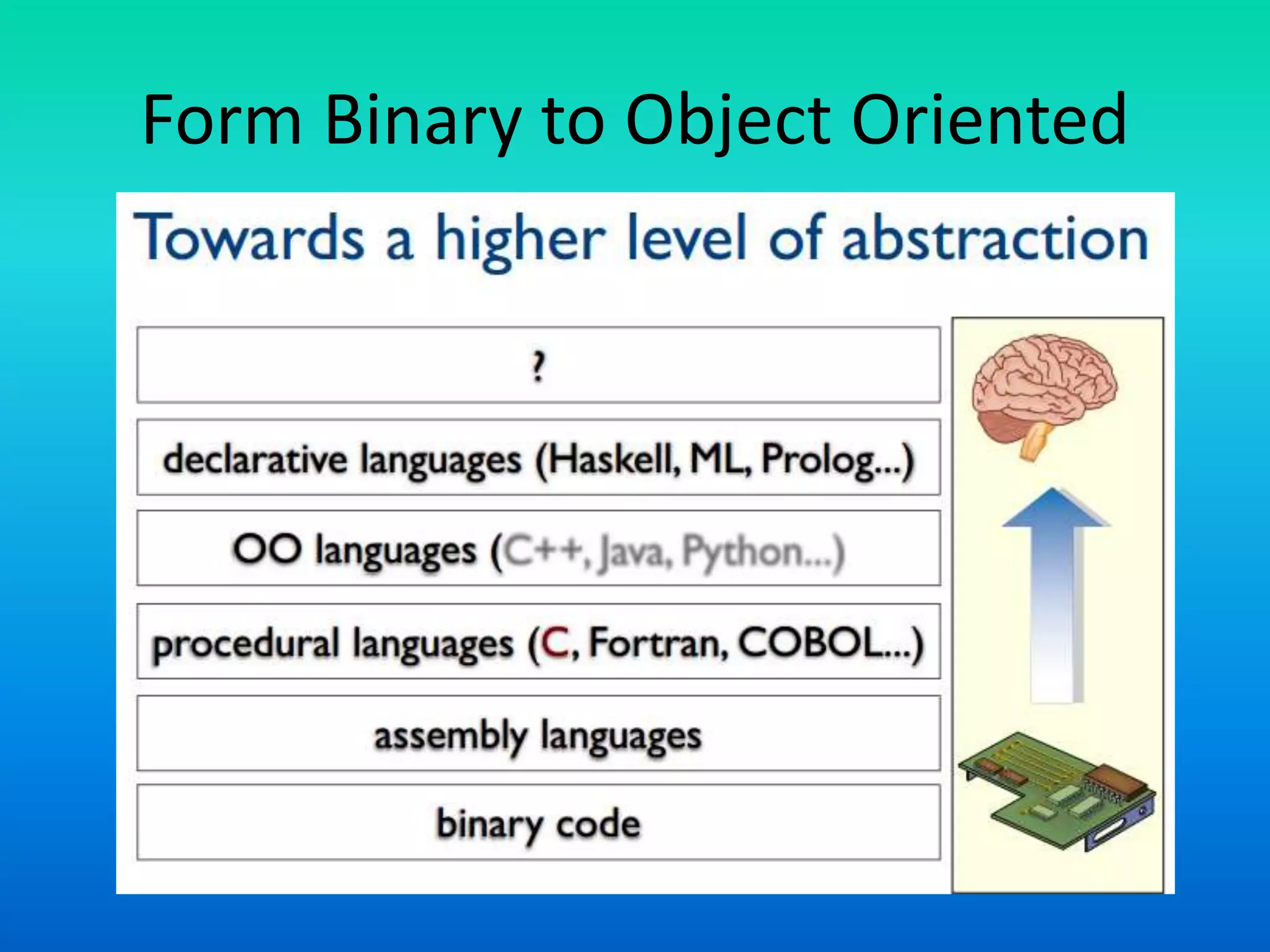
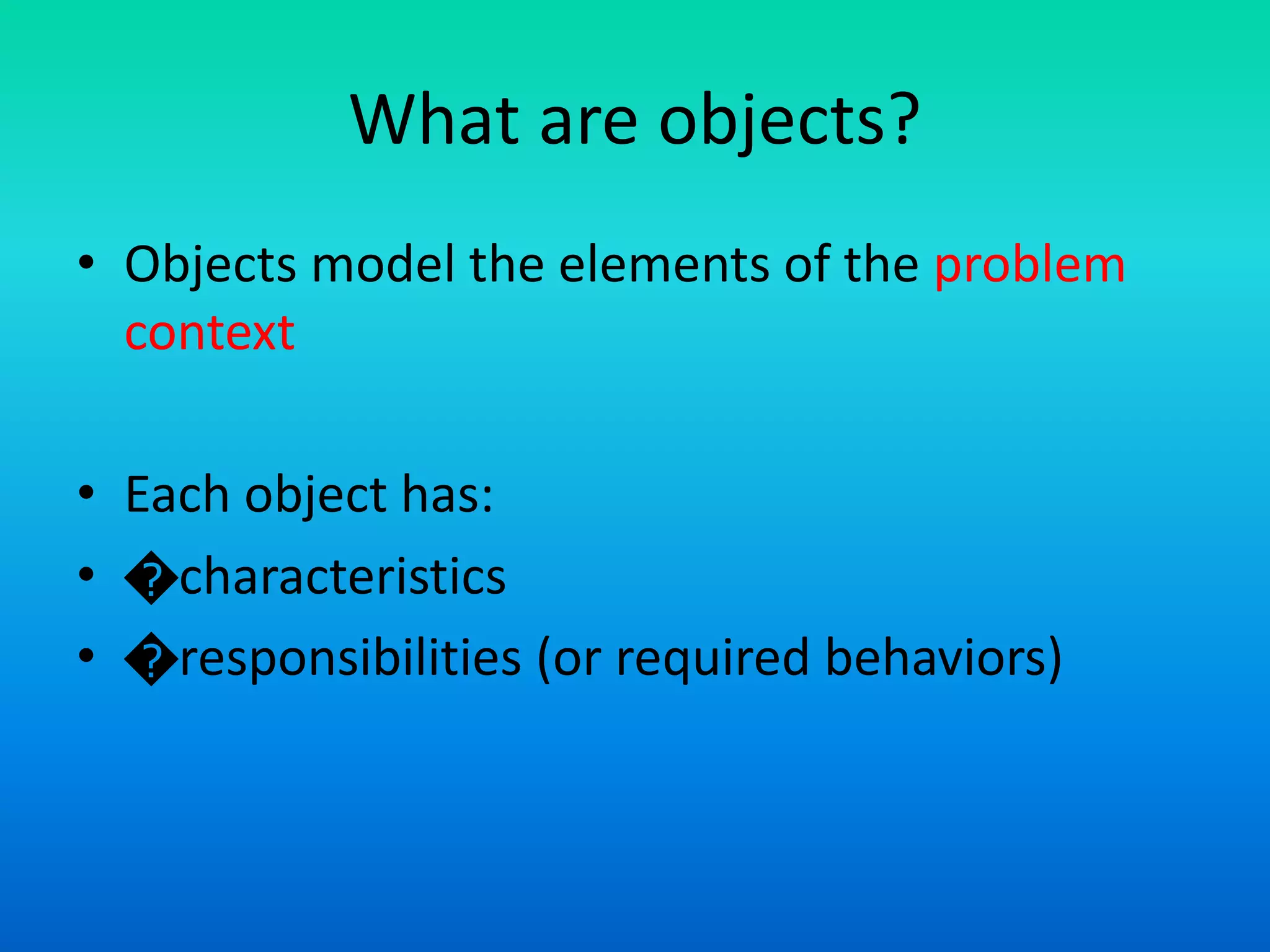
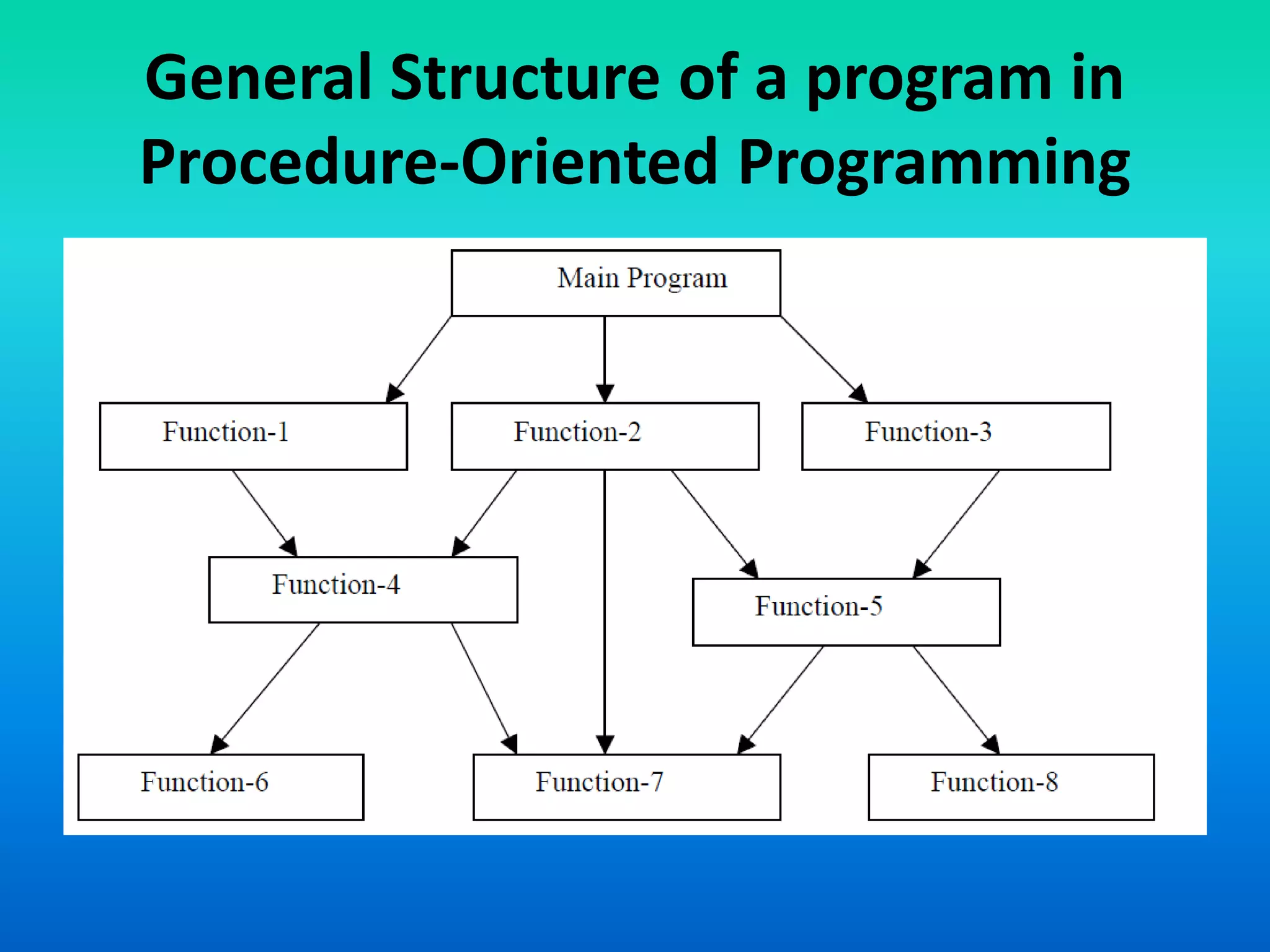
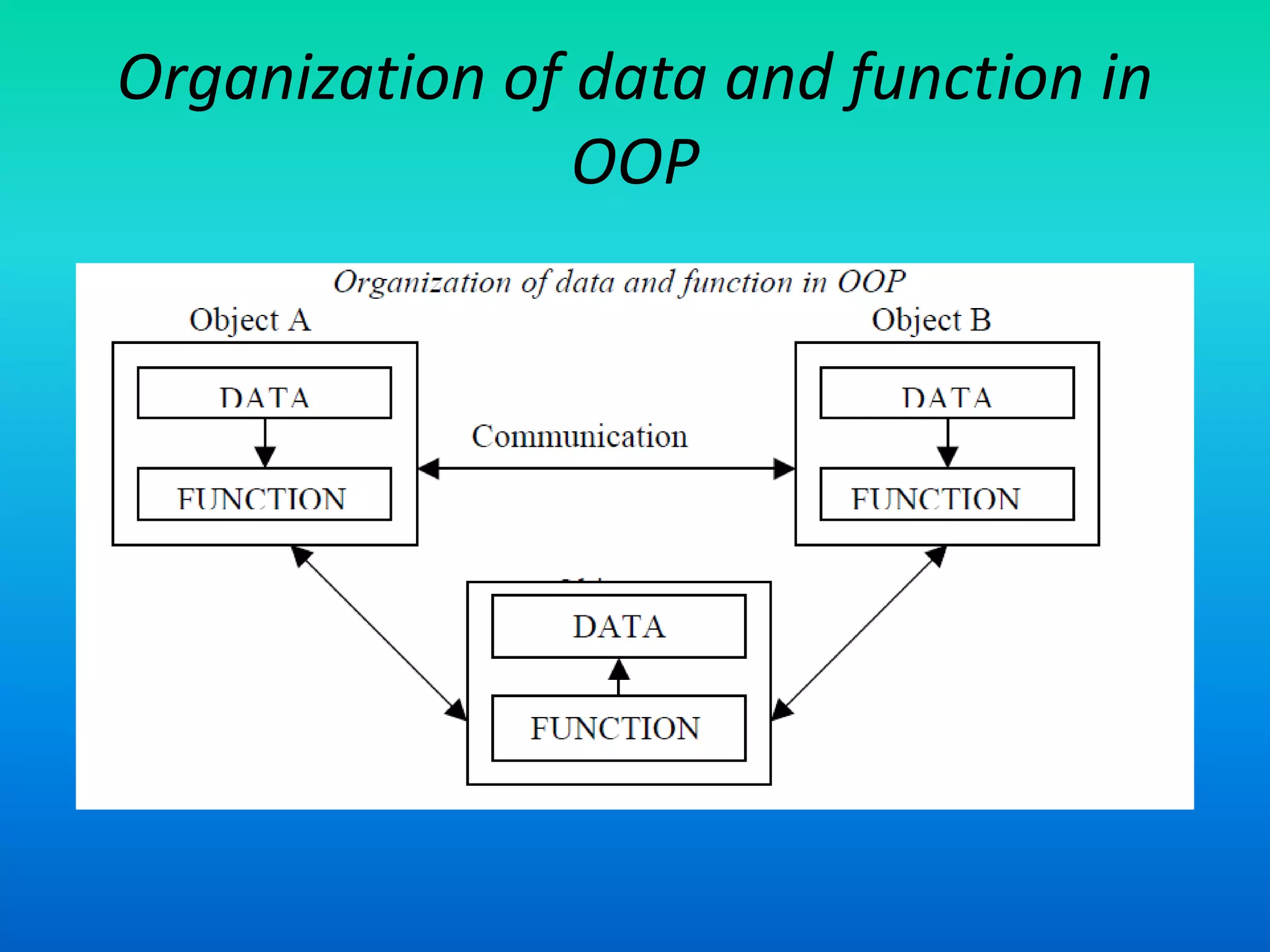
The document discusses the transition from procedure-oriented programming to object-oriented programming (OOP), highlighting the challenges of conventional techniques and the advantages of OOP. It emphasizes the importance of treating data as a key aspect of software development and introduces concepts such as encapsulation and modularity through objects. The document also outlines the characteristics and features of both programming paradigms and encourages understanding of their structural differences.