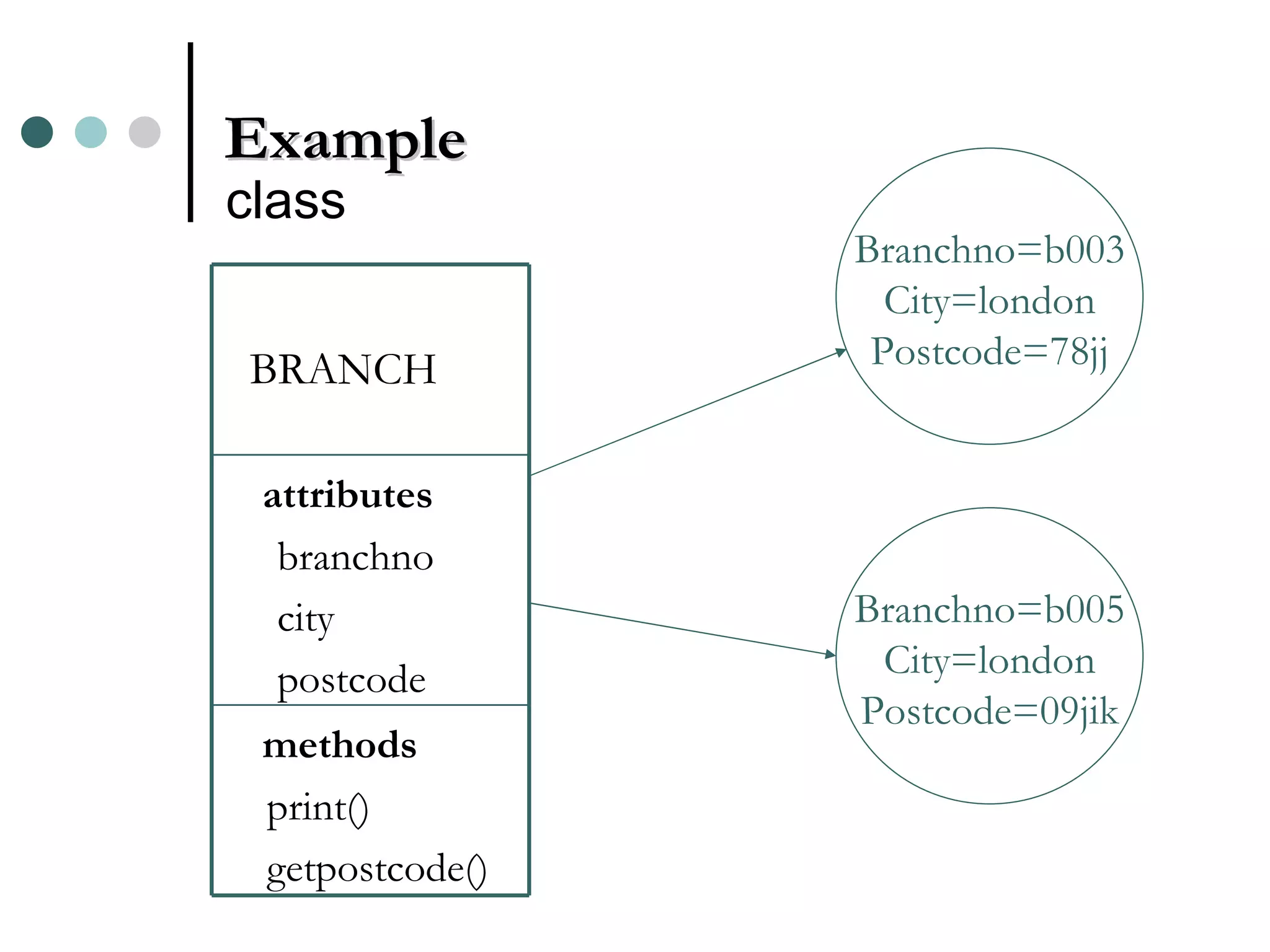
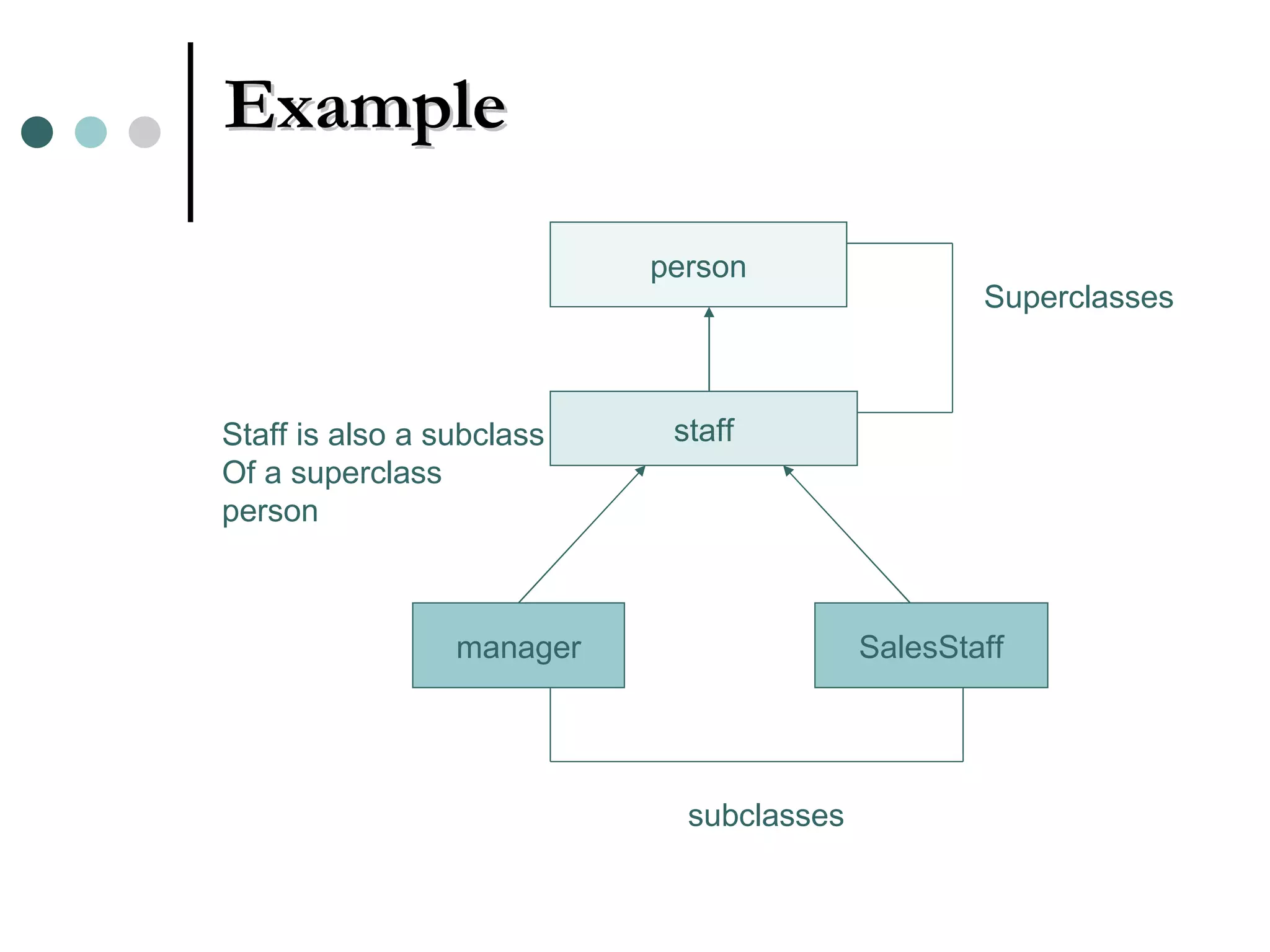
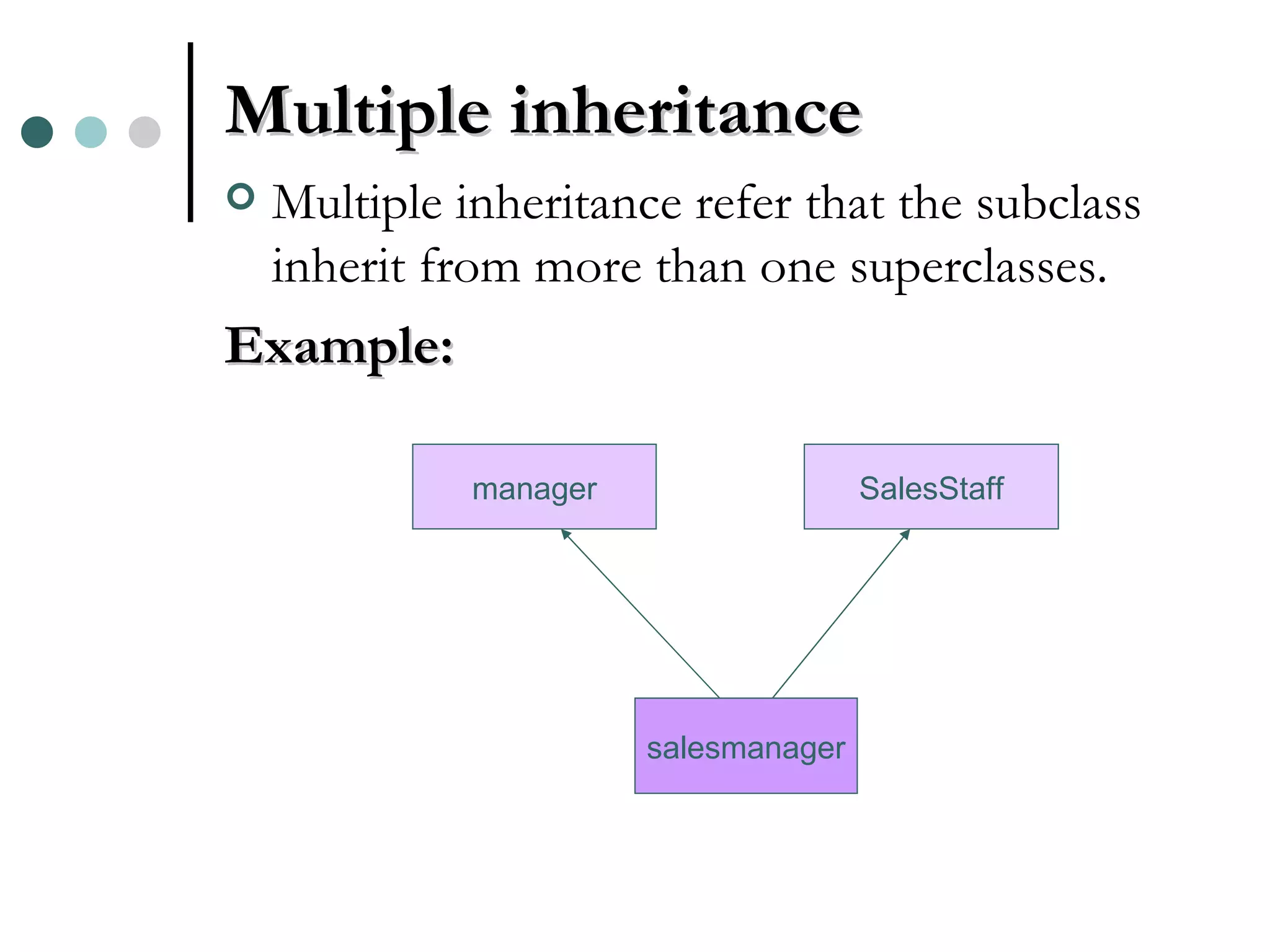
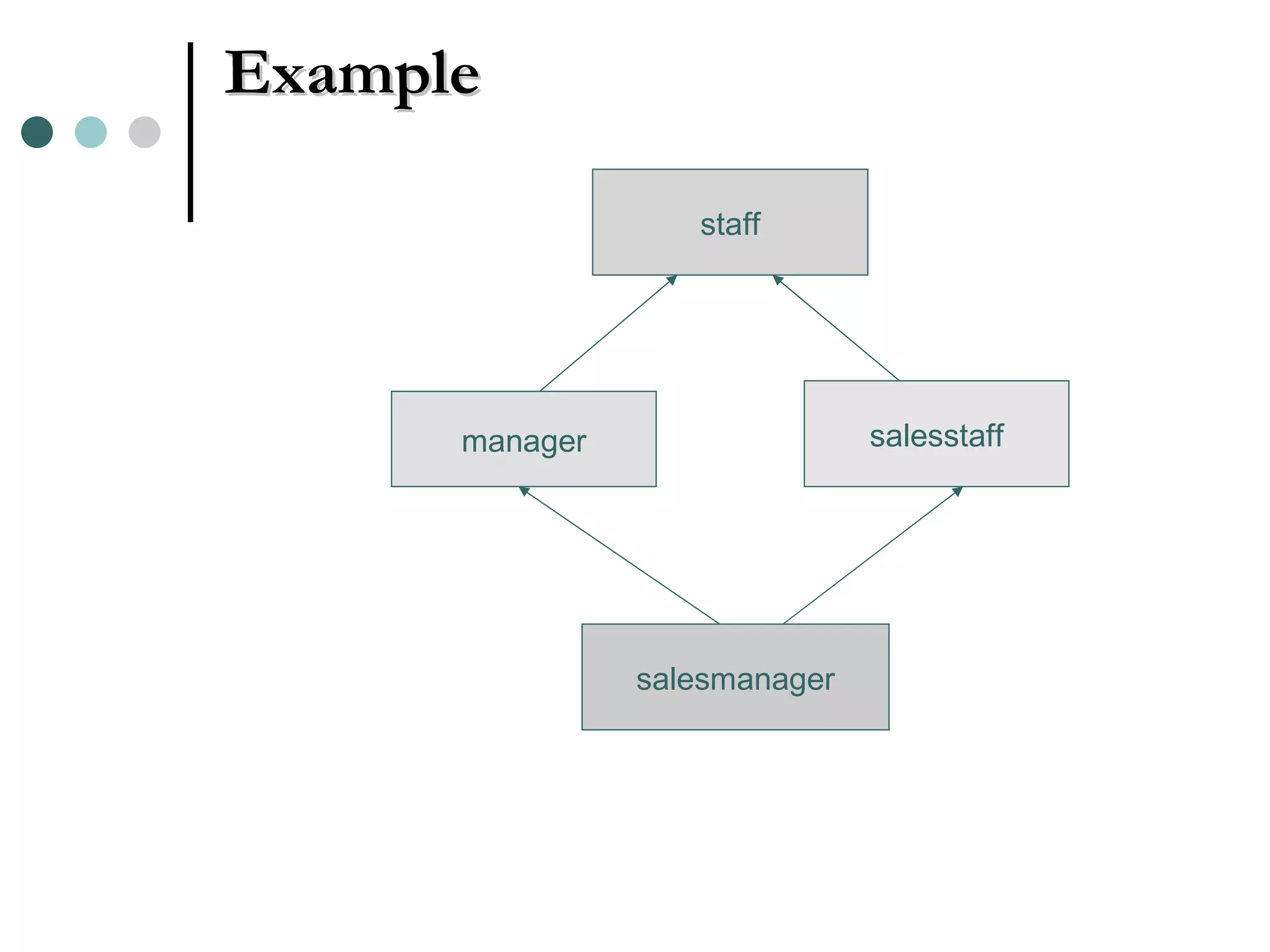
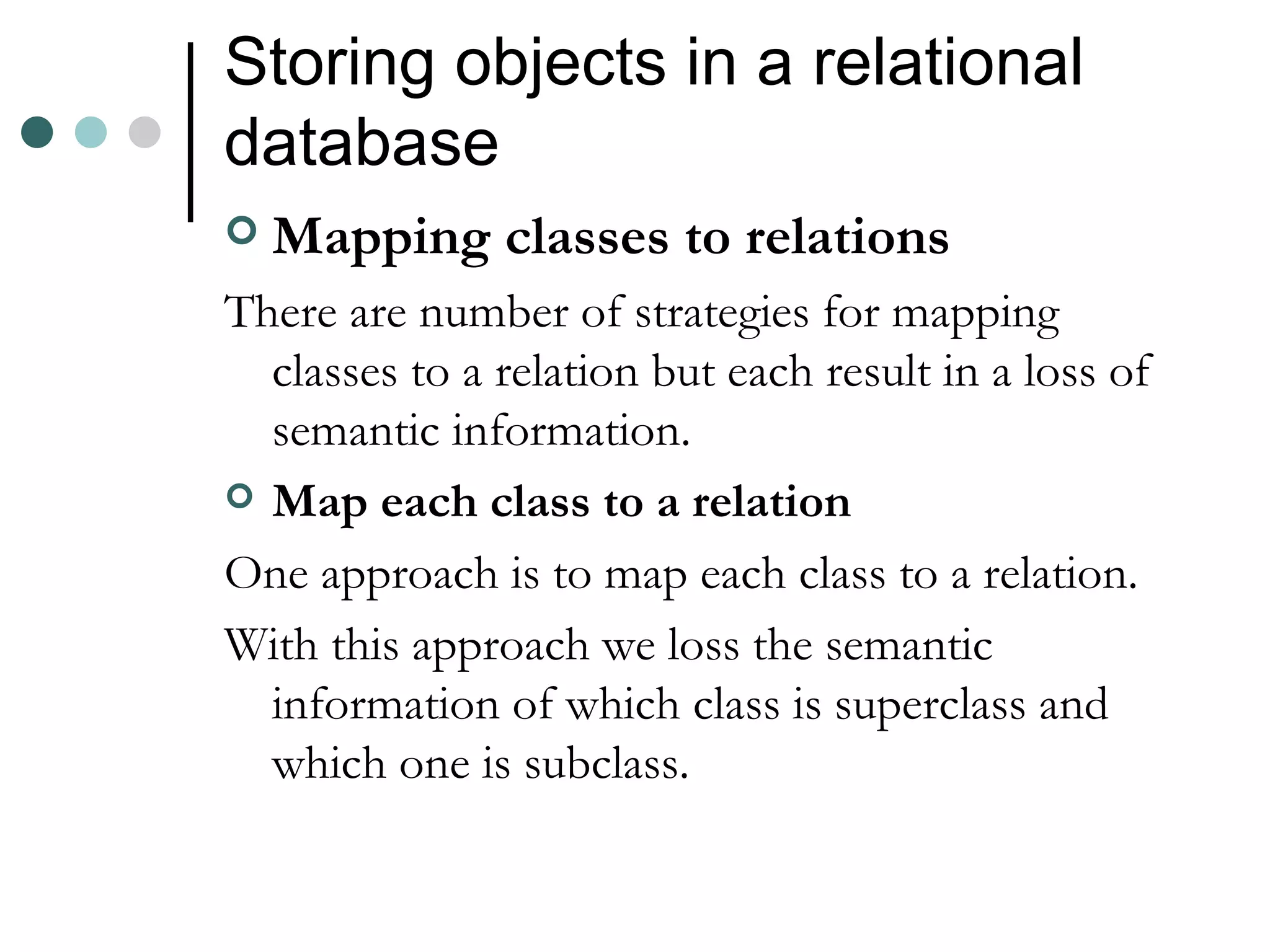
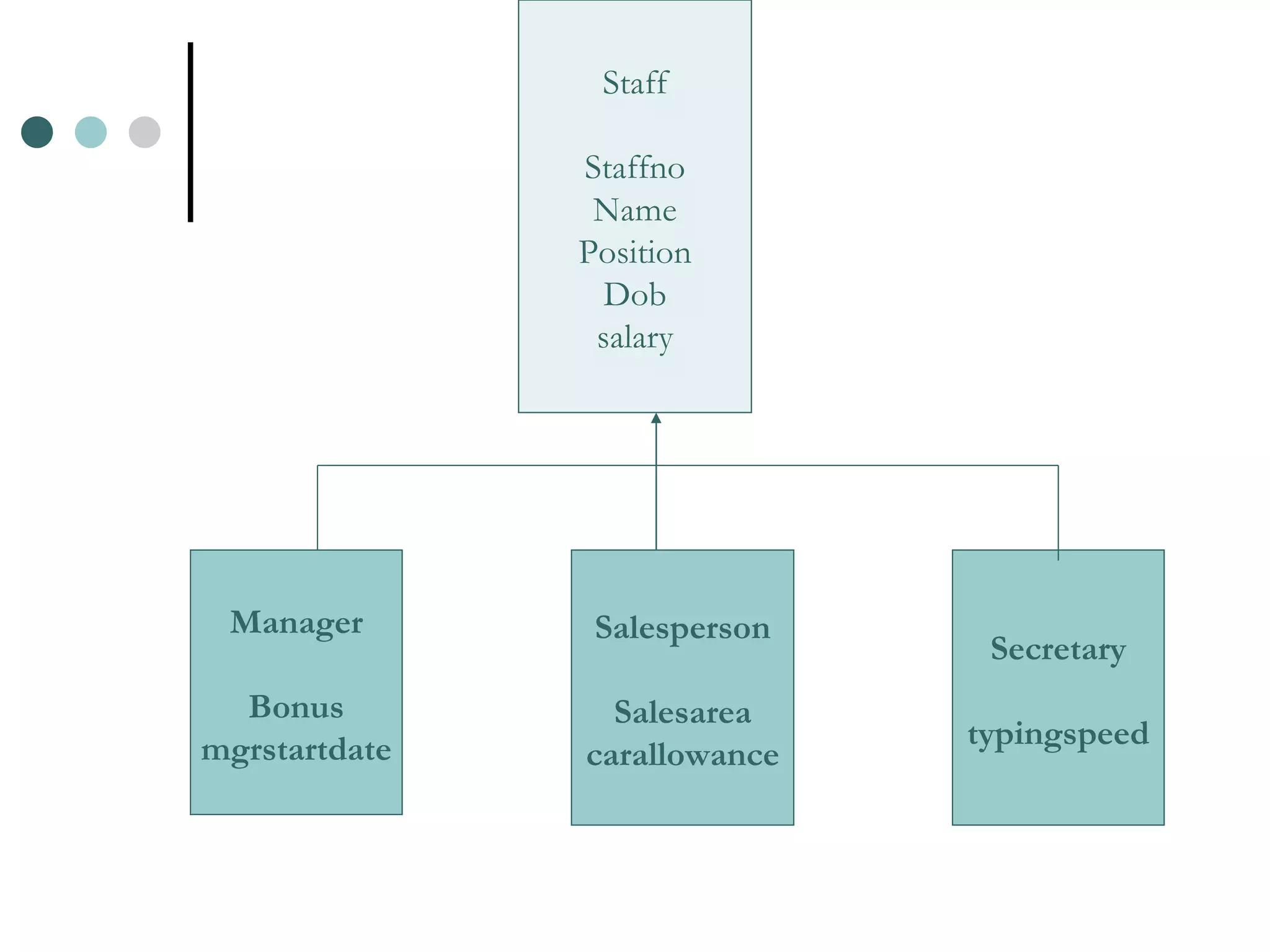
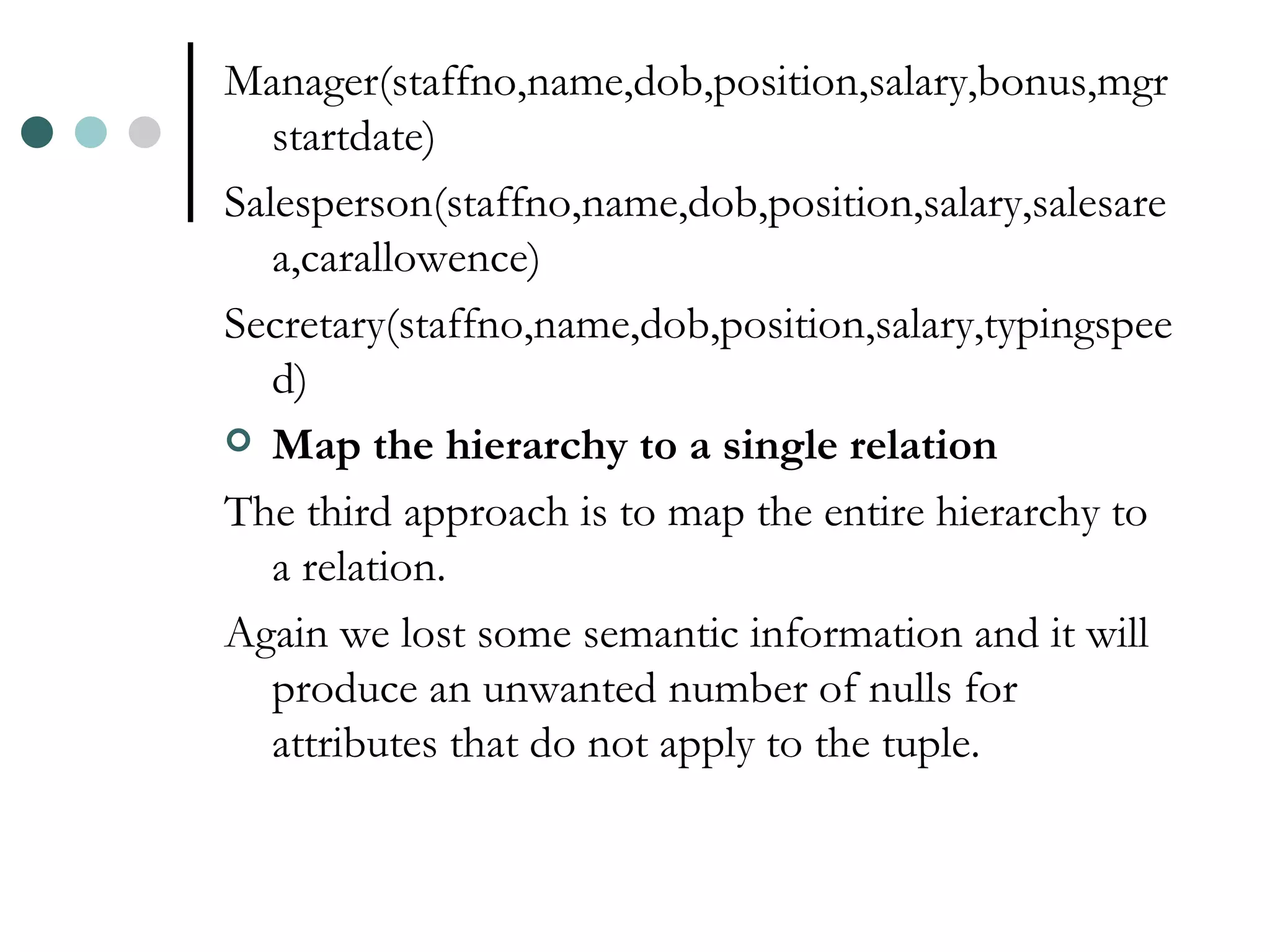
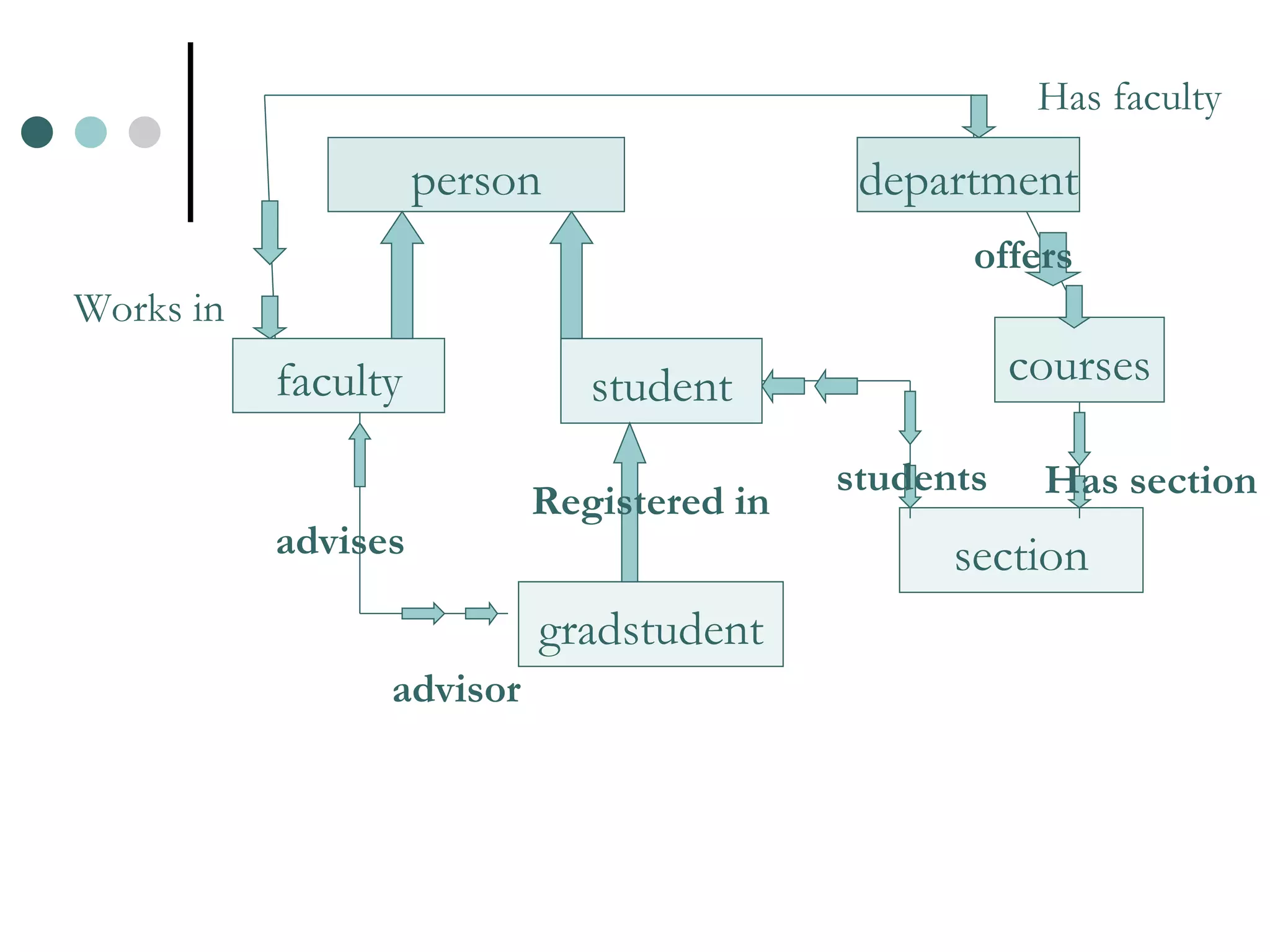
An Object Oriented DBMS stores data as objects that use object-oriented concepts like classes, inheritance, and encapsulation. Objects have attributes that can be simple like integers or complex like collections. Classes group similar objects and subclasses inherit attributes and behaviors from superclasses. Objects communicate through messages that invoke methods. The DBMS maps classes and objects to tables and tuples in a relational database, which loses some semantic information about class hierarchies.