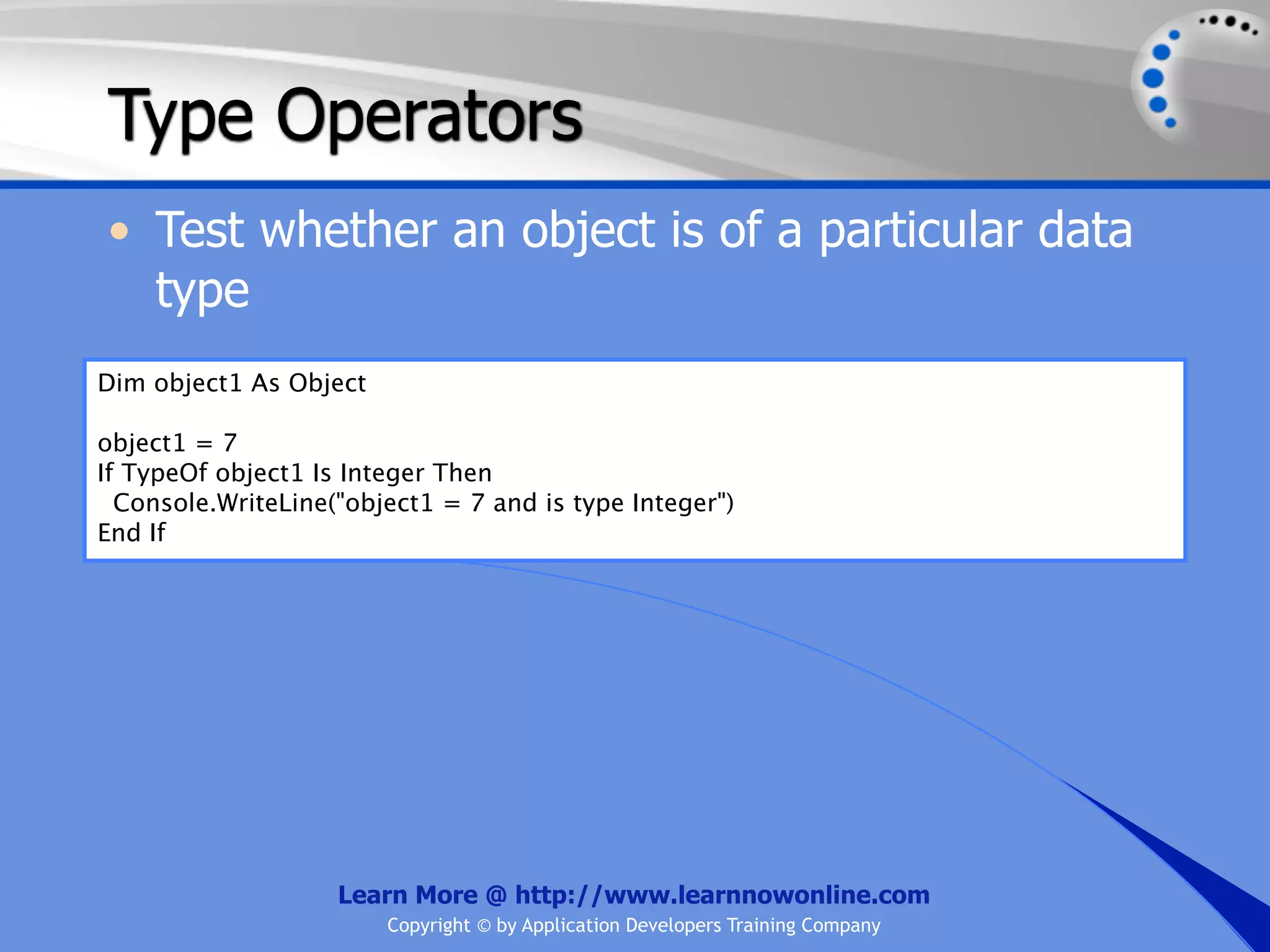
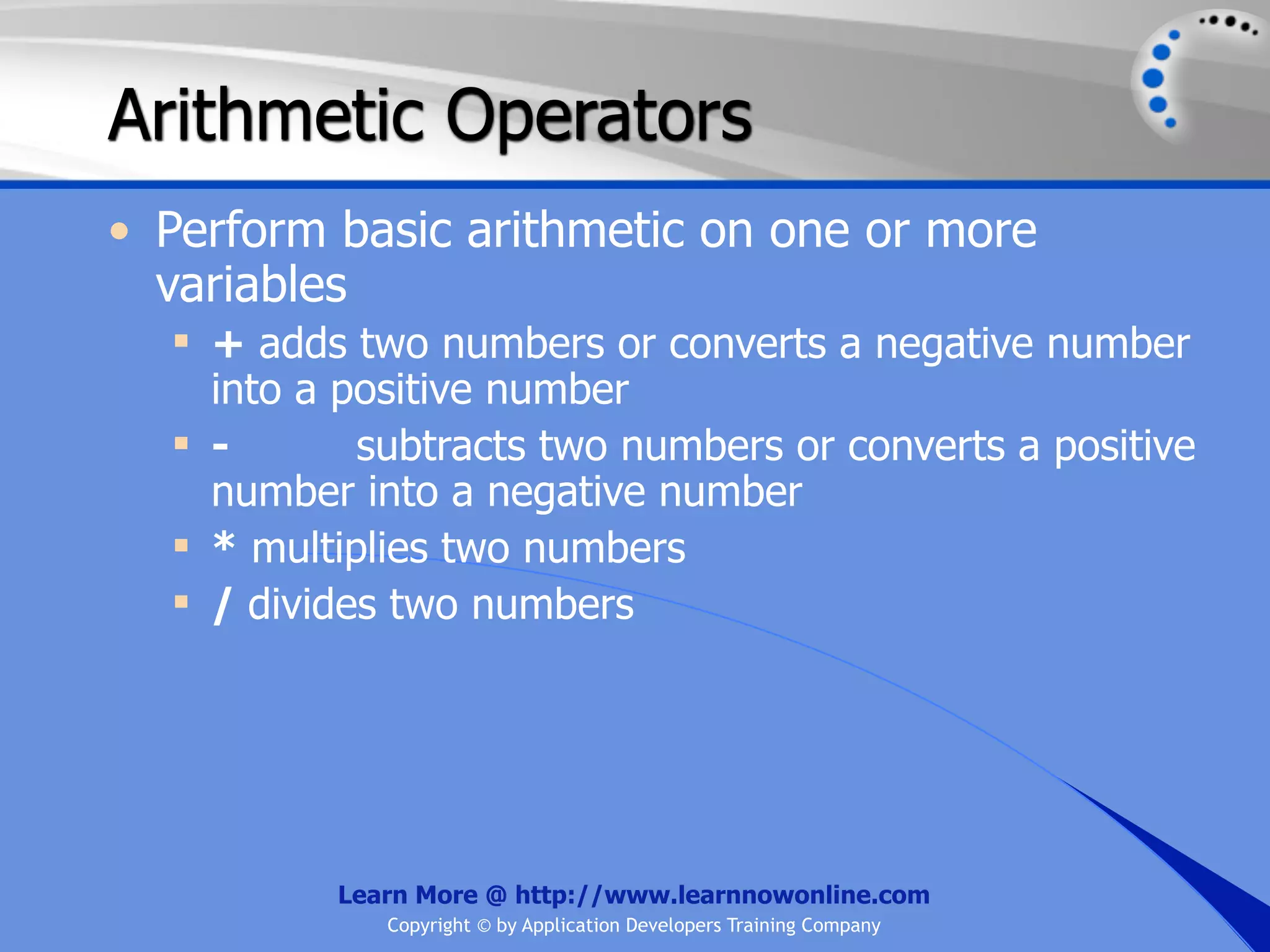
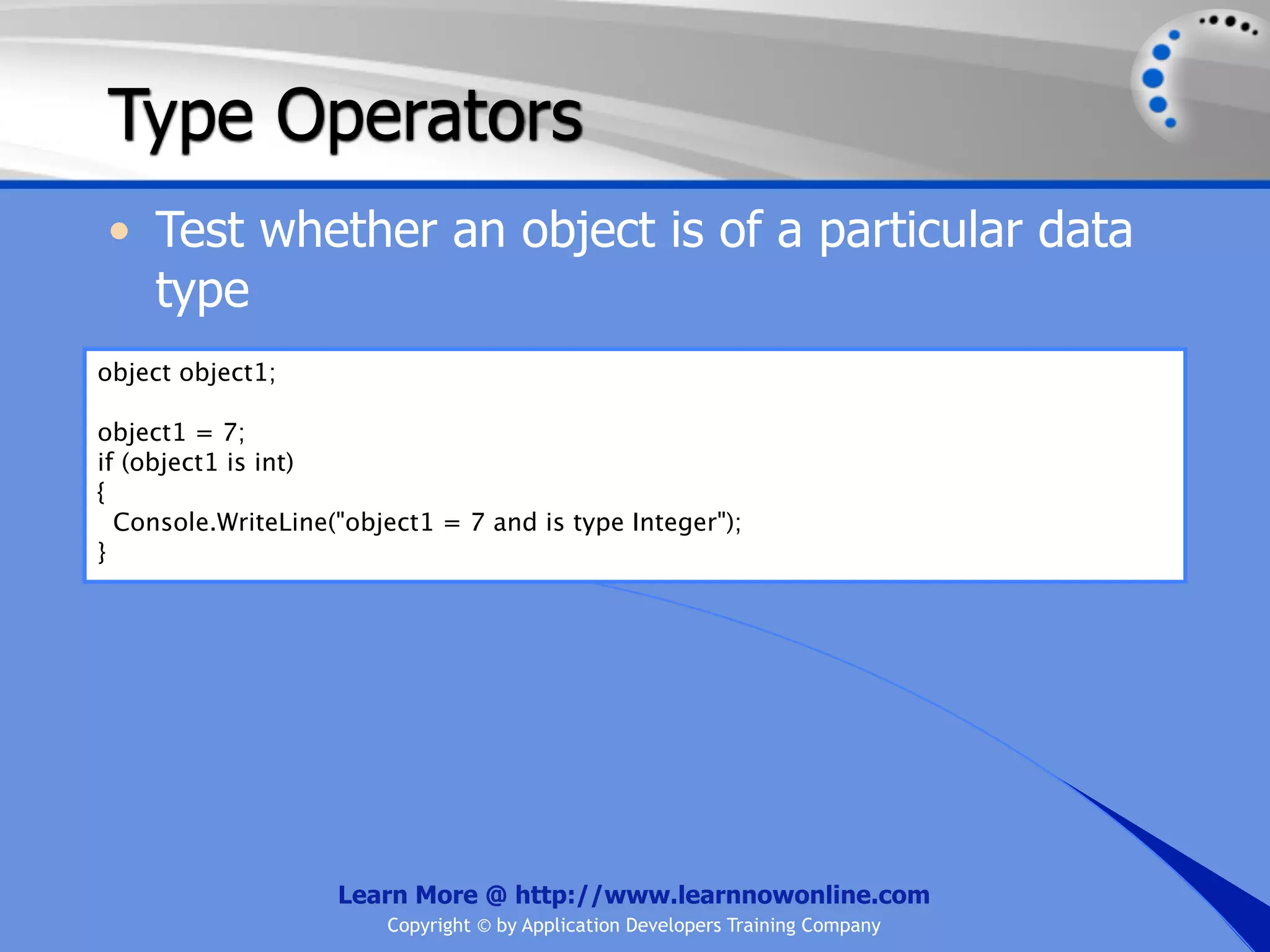
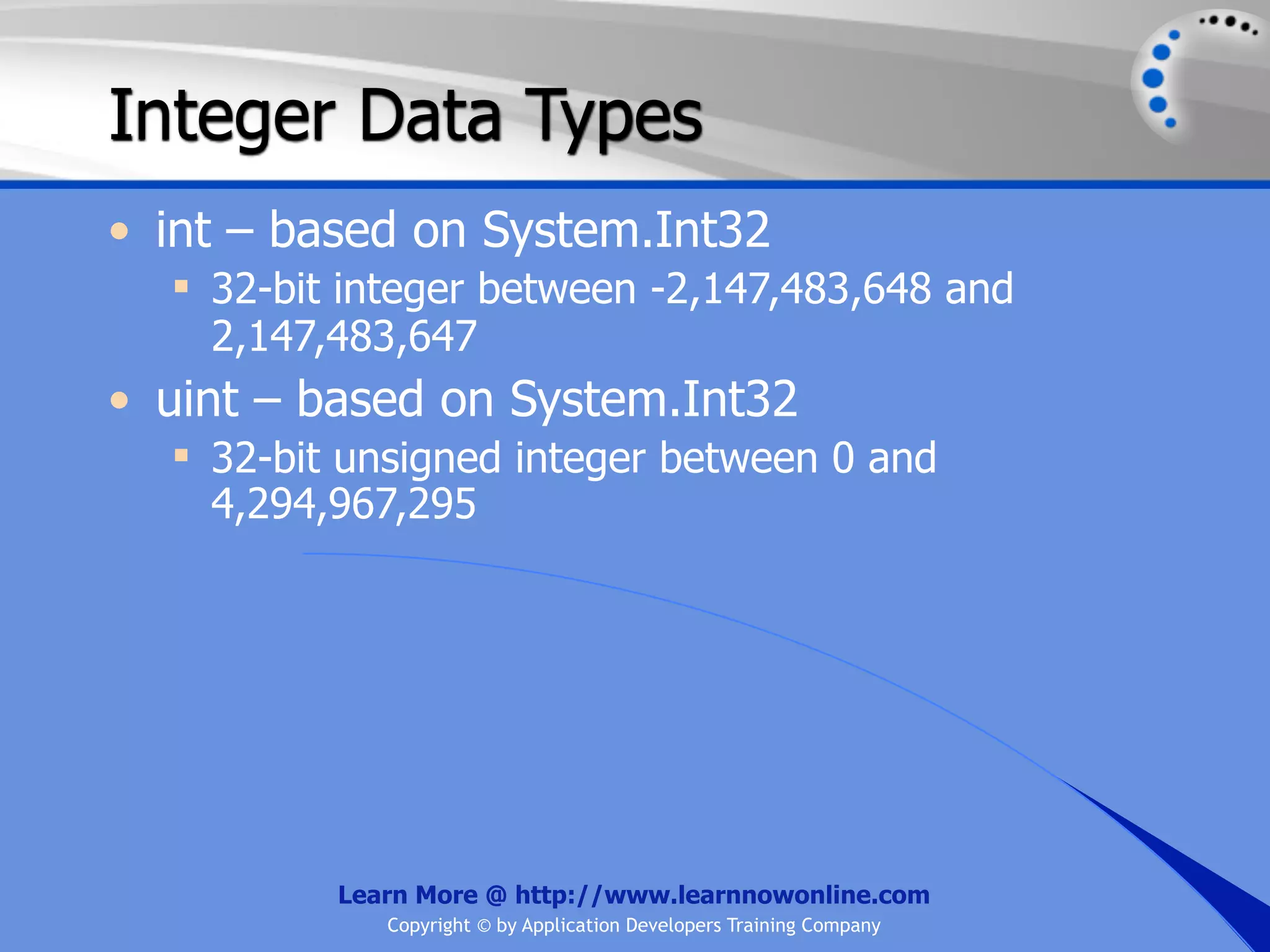
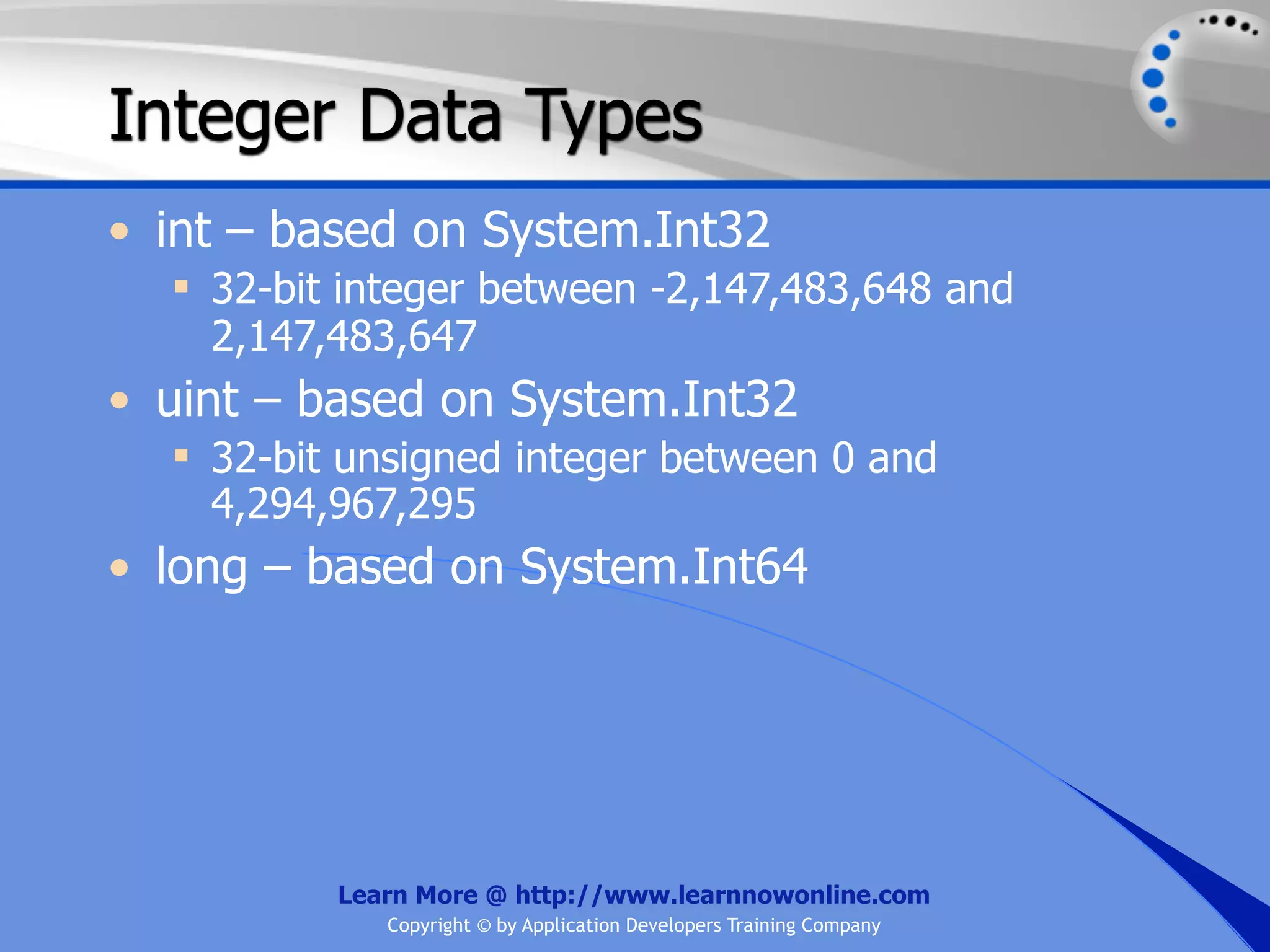
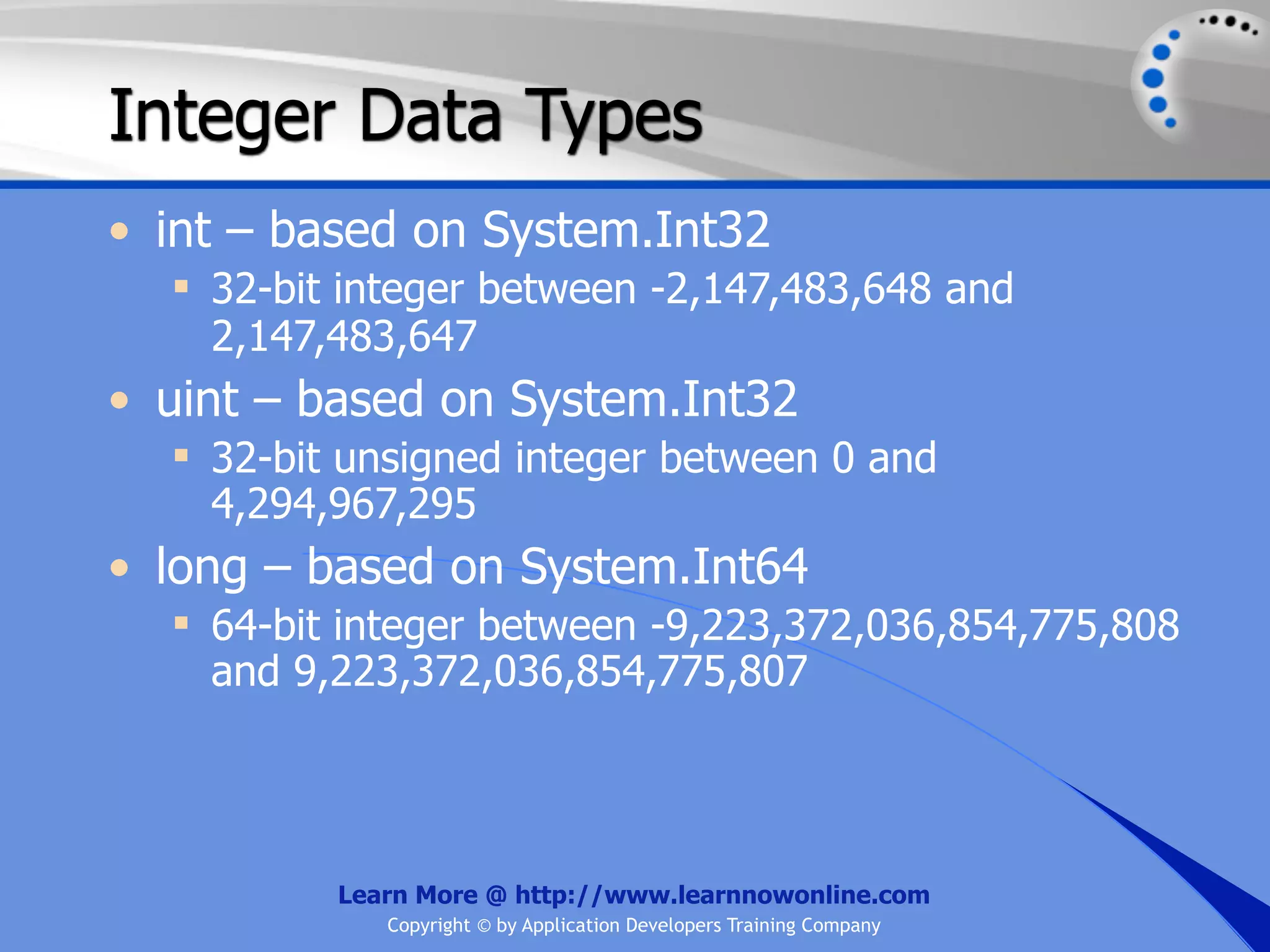
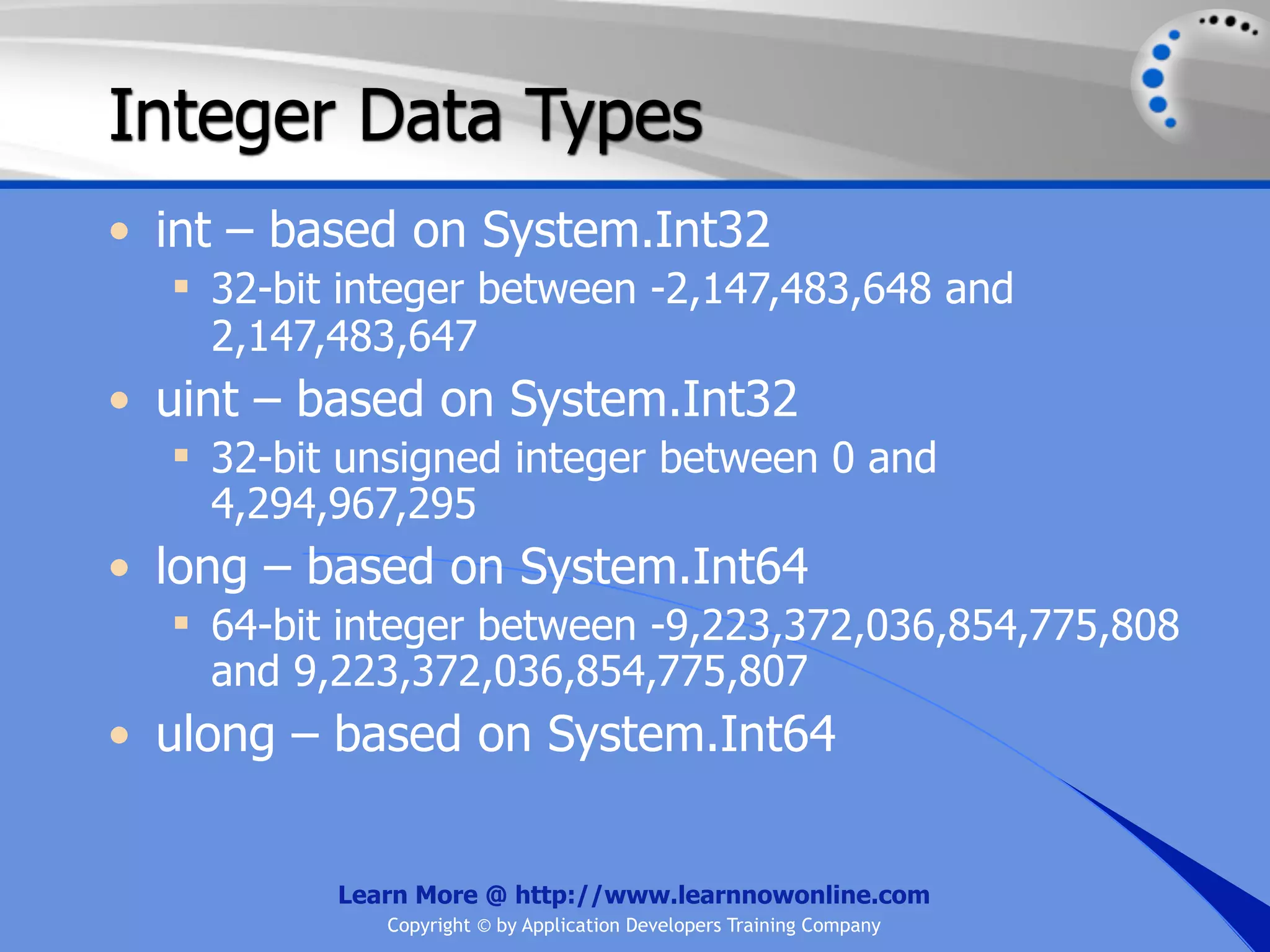
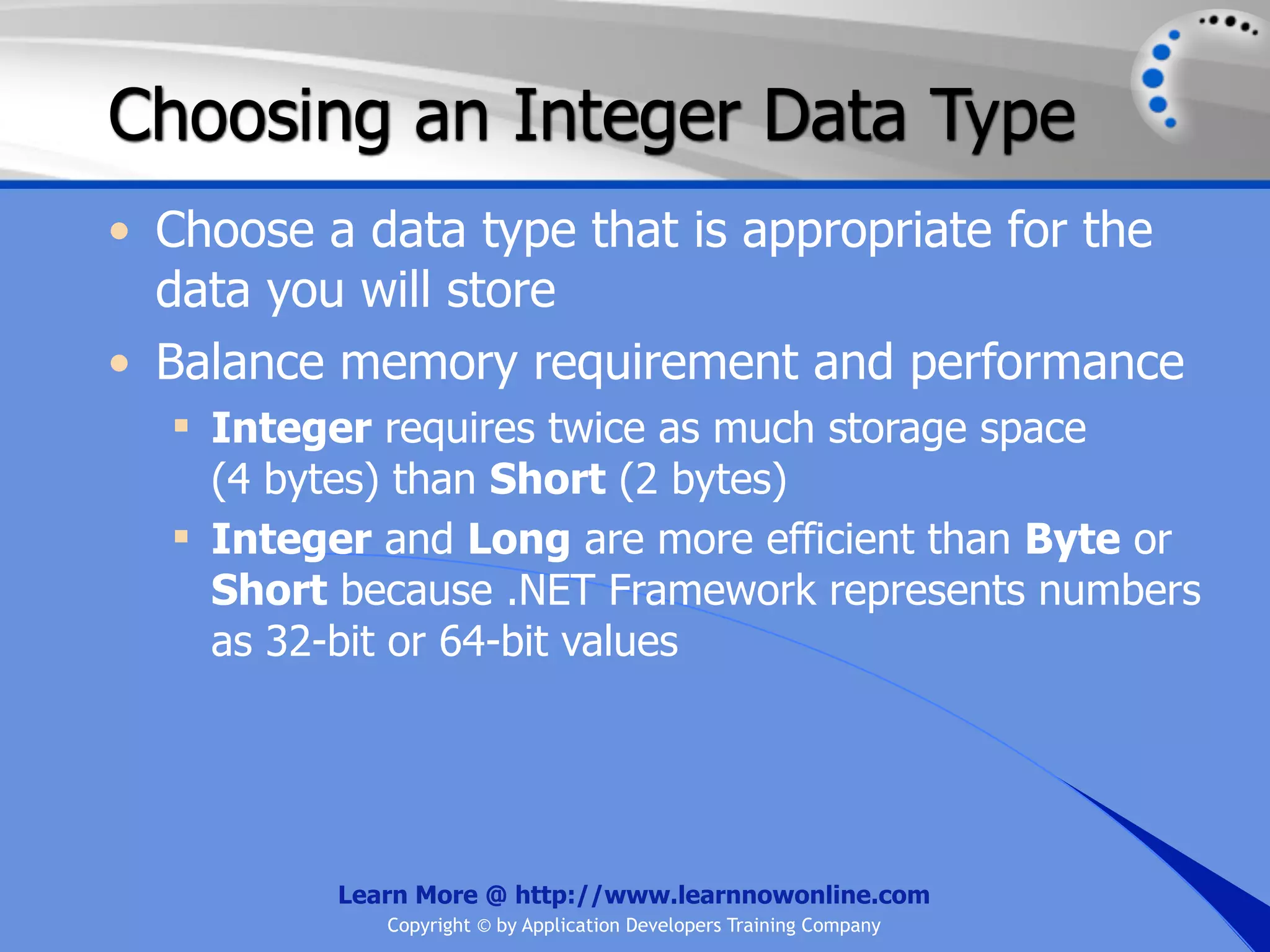
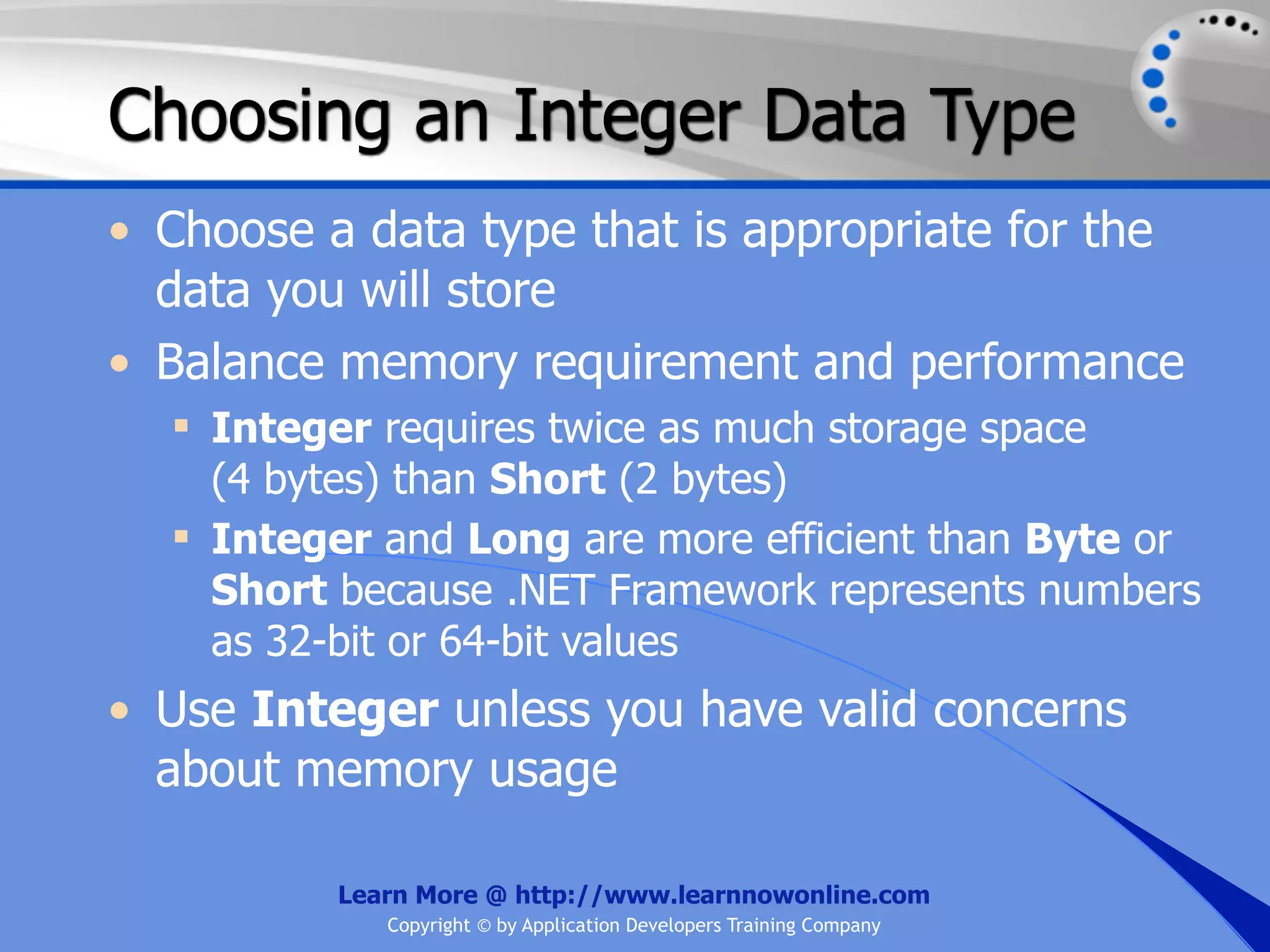
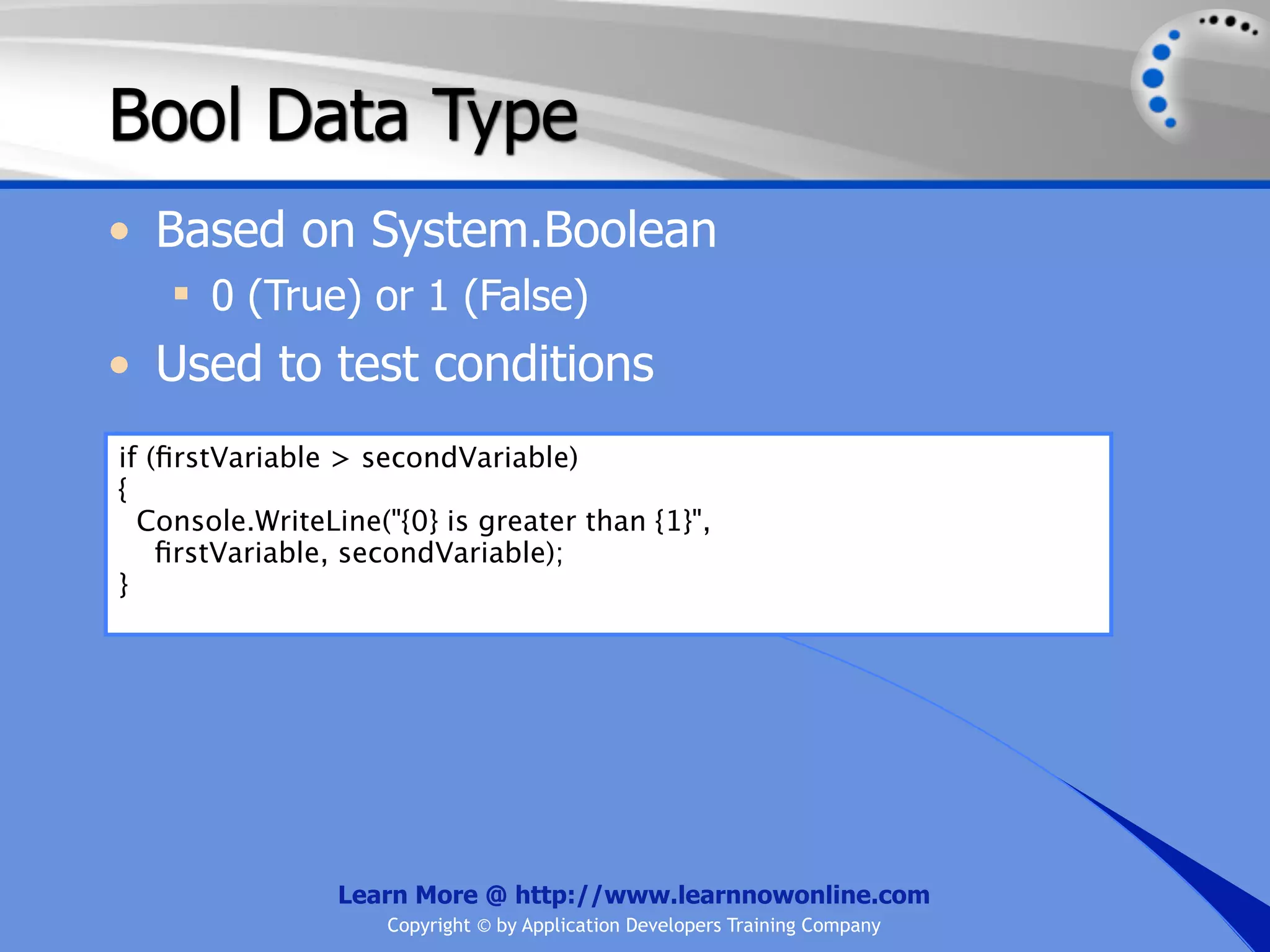
The document covers essential programming concepts related to variables and data types, including how to create and assign values and the rules for naming variables. It outlines the .NET framework's data types, their uses, and the lifetime and scope of variables within programming contexts. Additionally, specific data types are discussed, including integer data types and their various applications in memory allocation.

































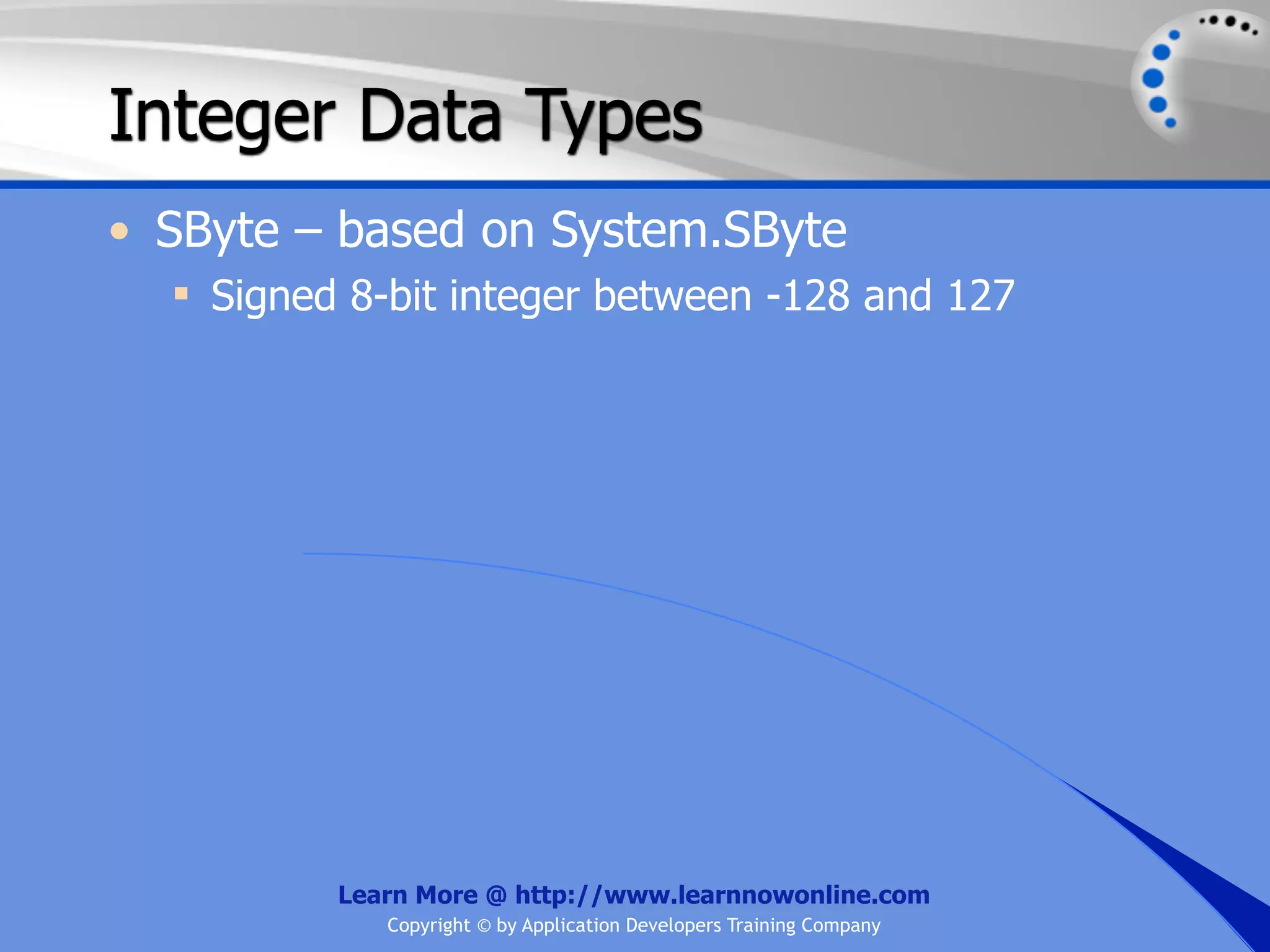
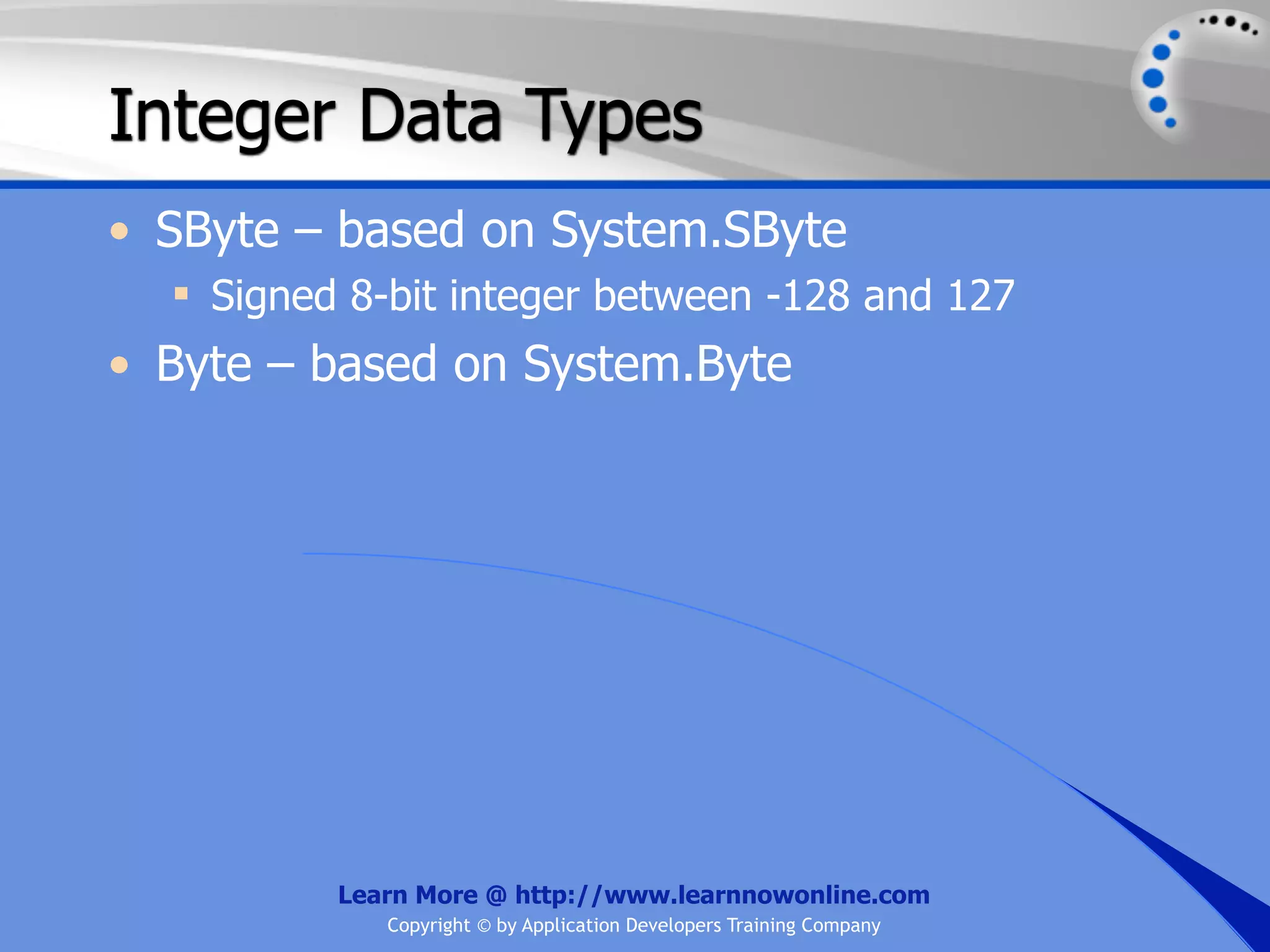
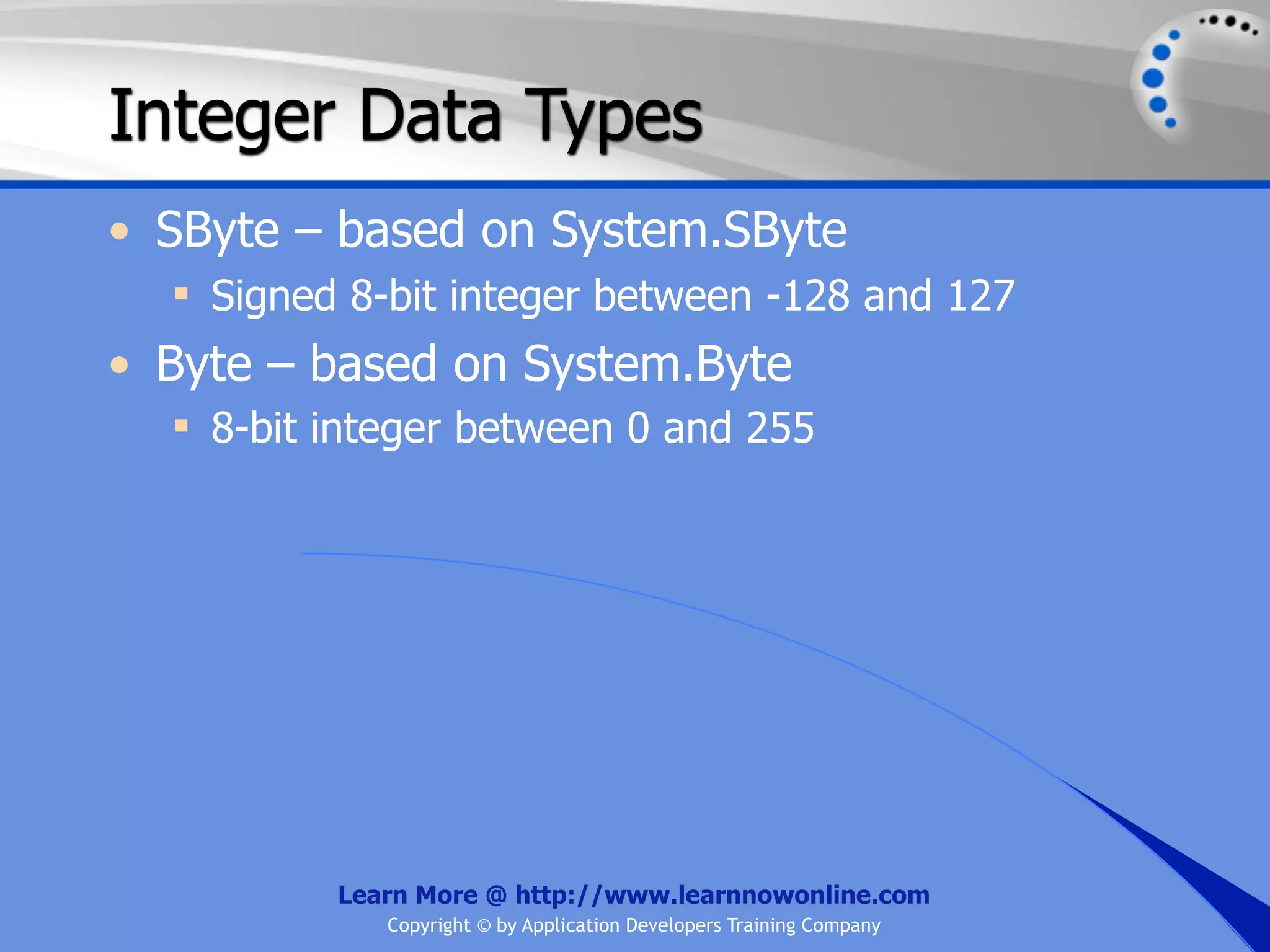
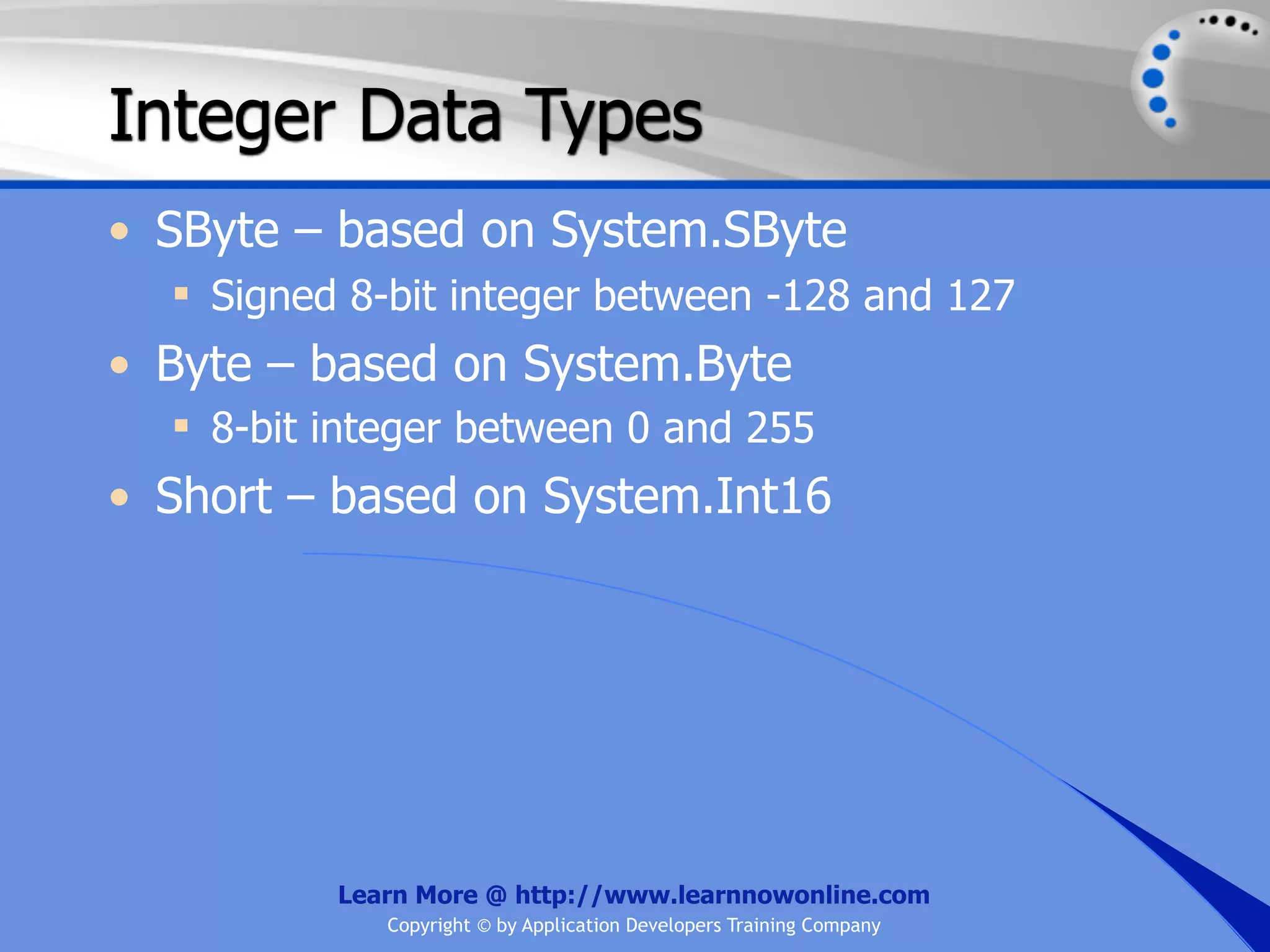
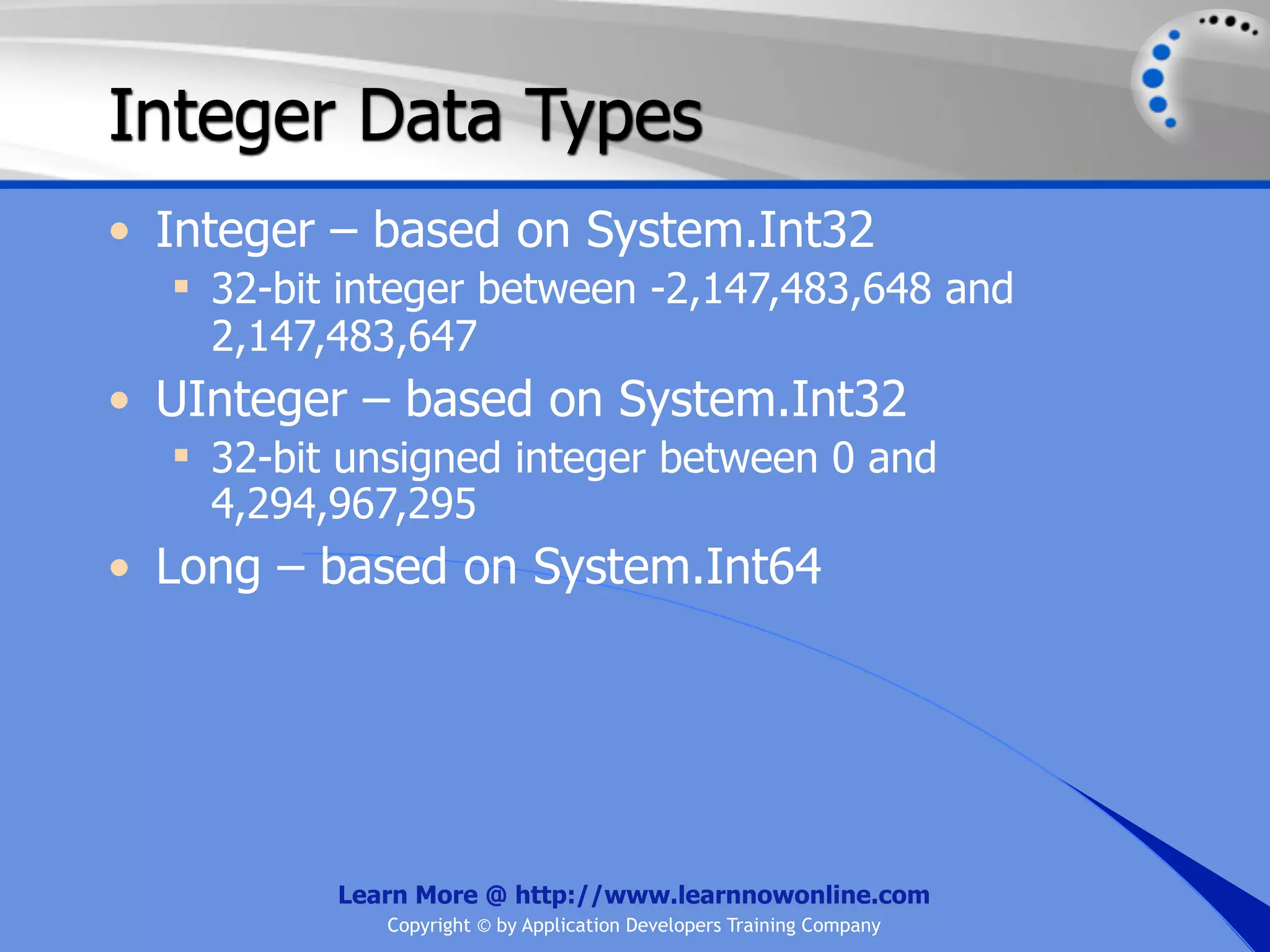
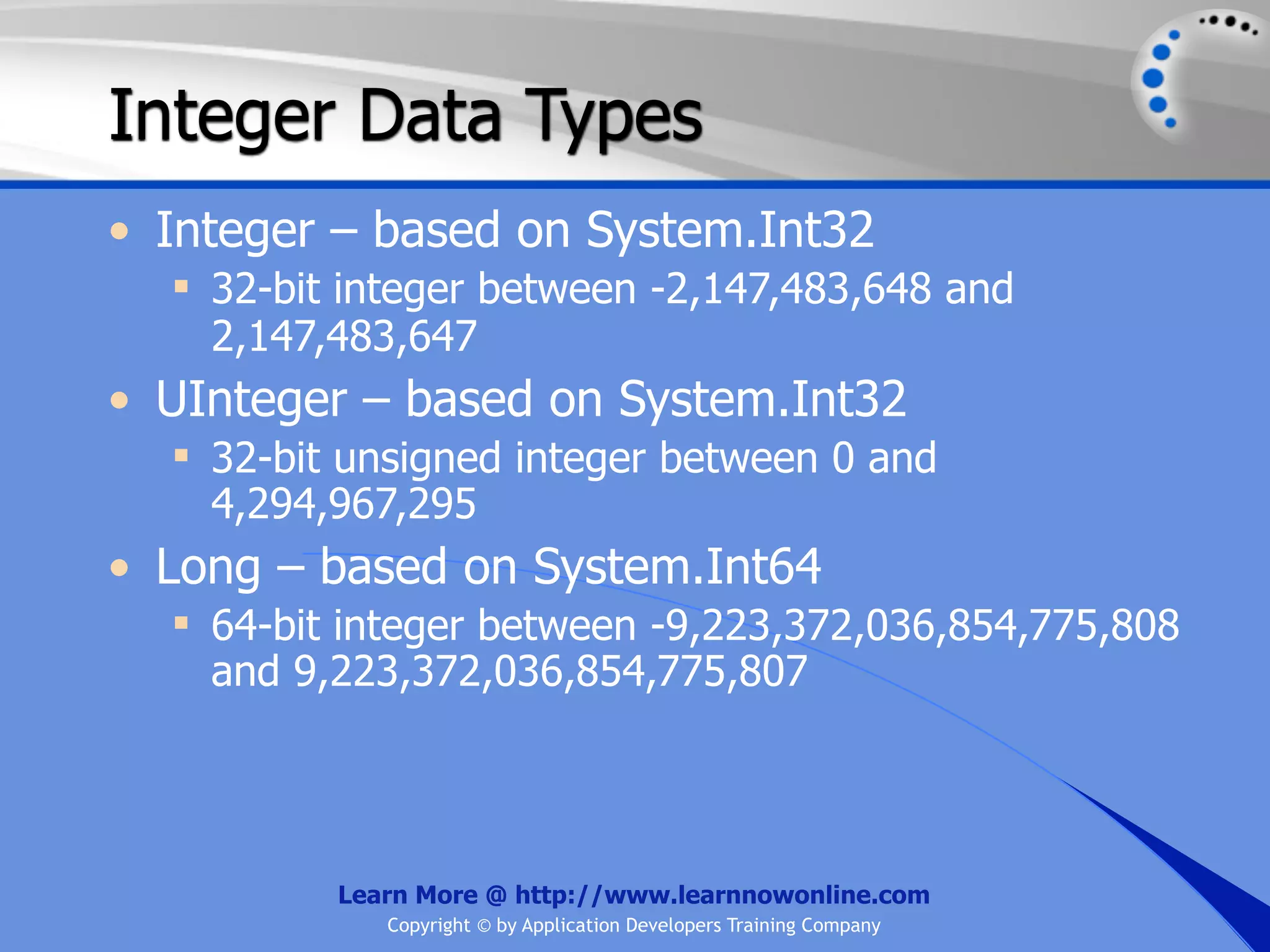
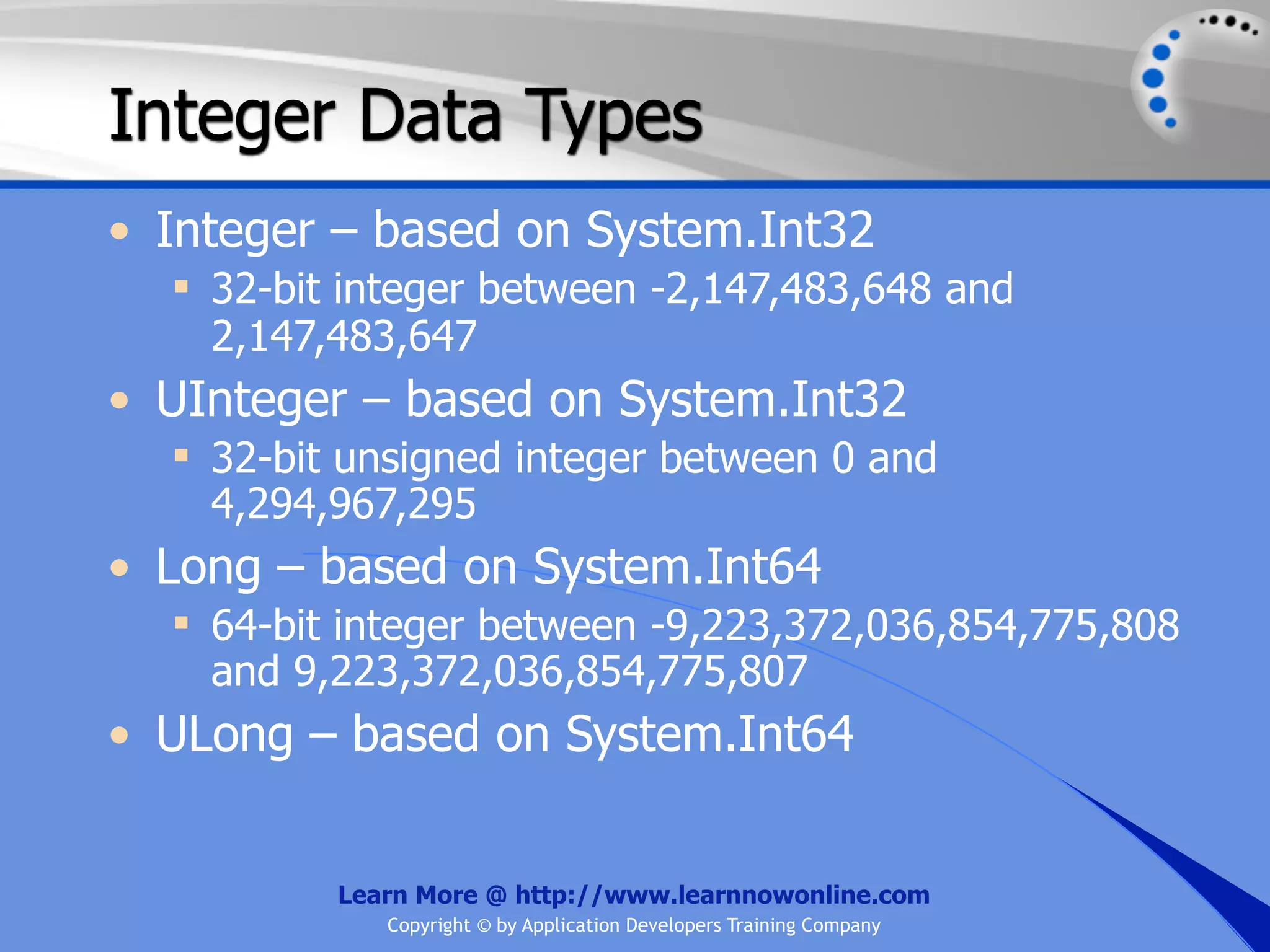
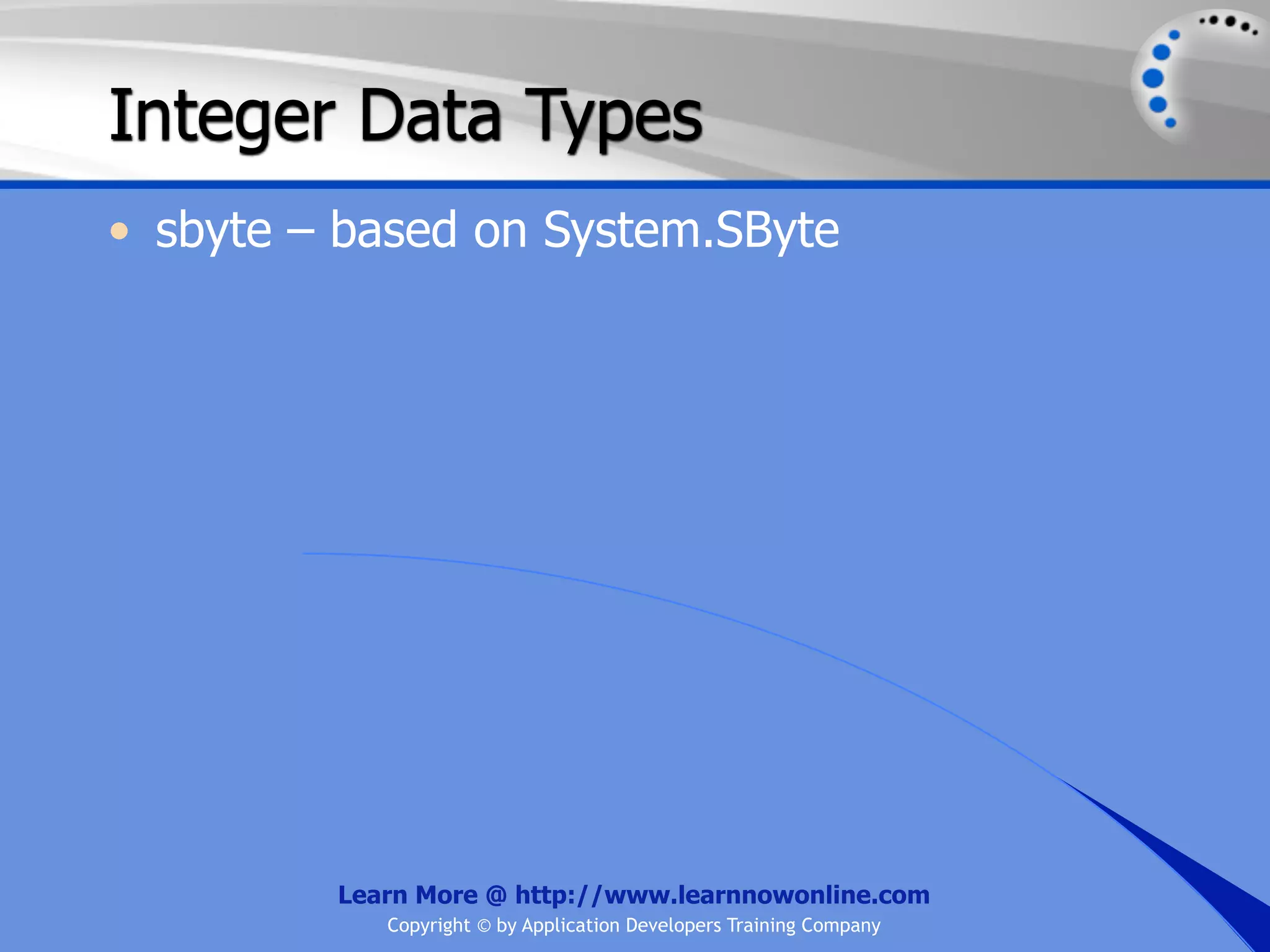
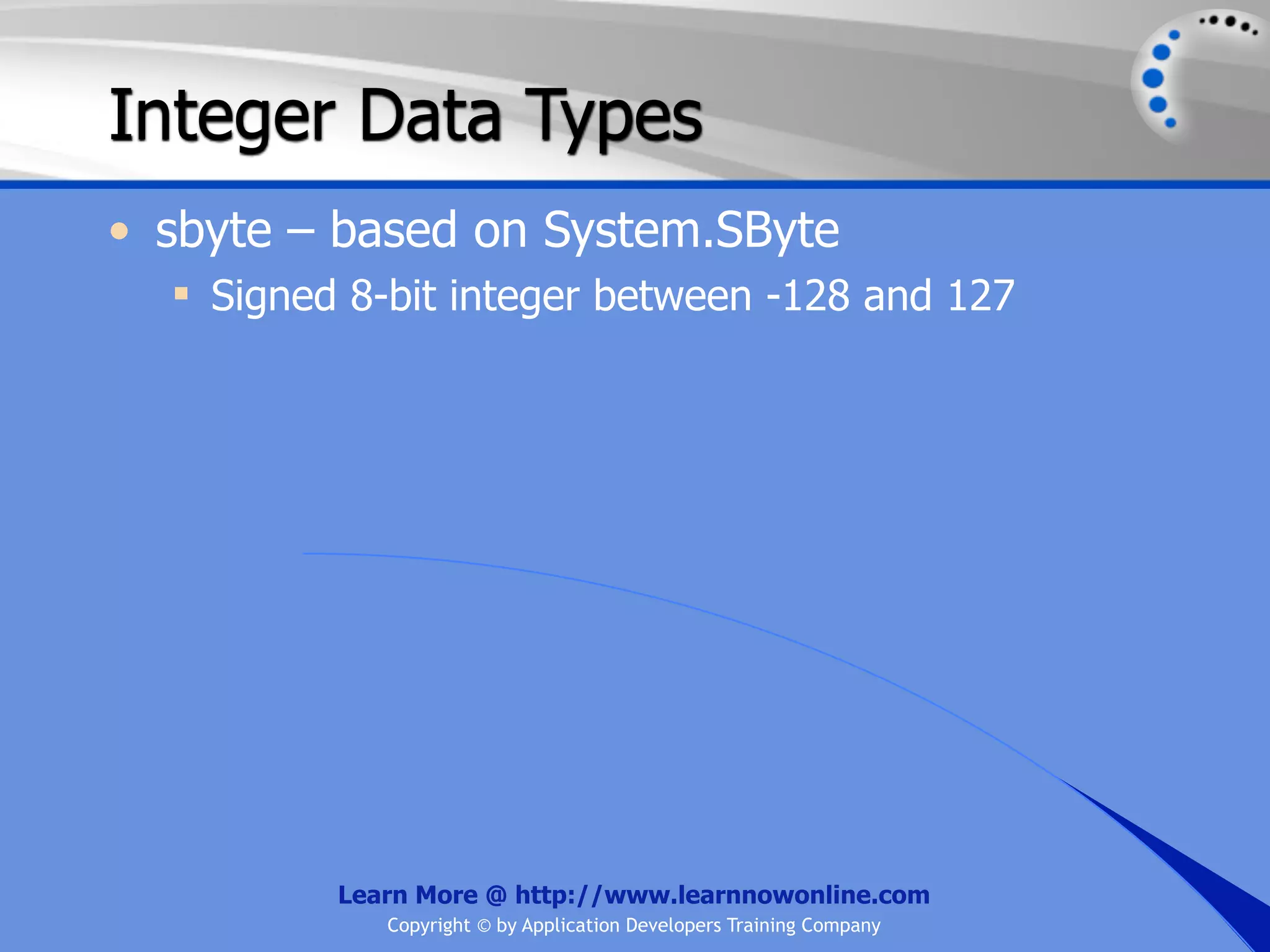
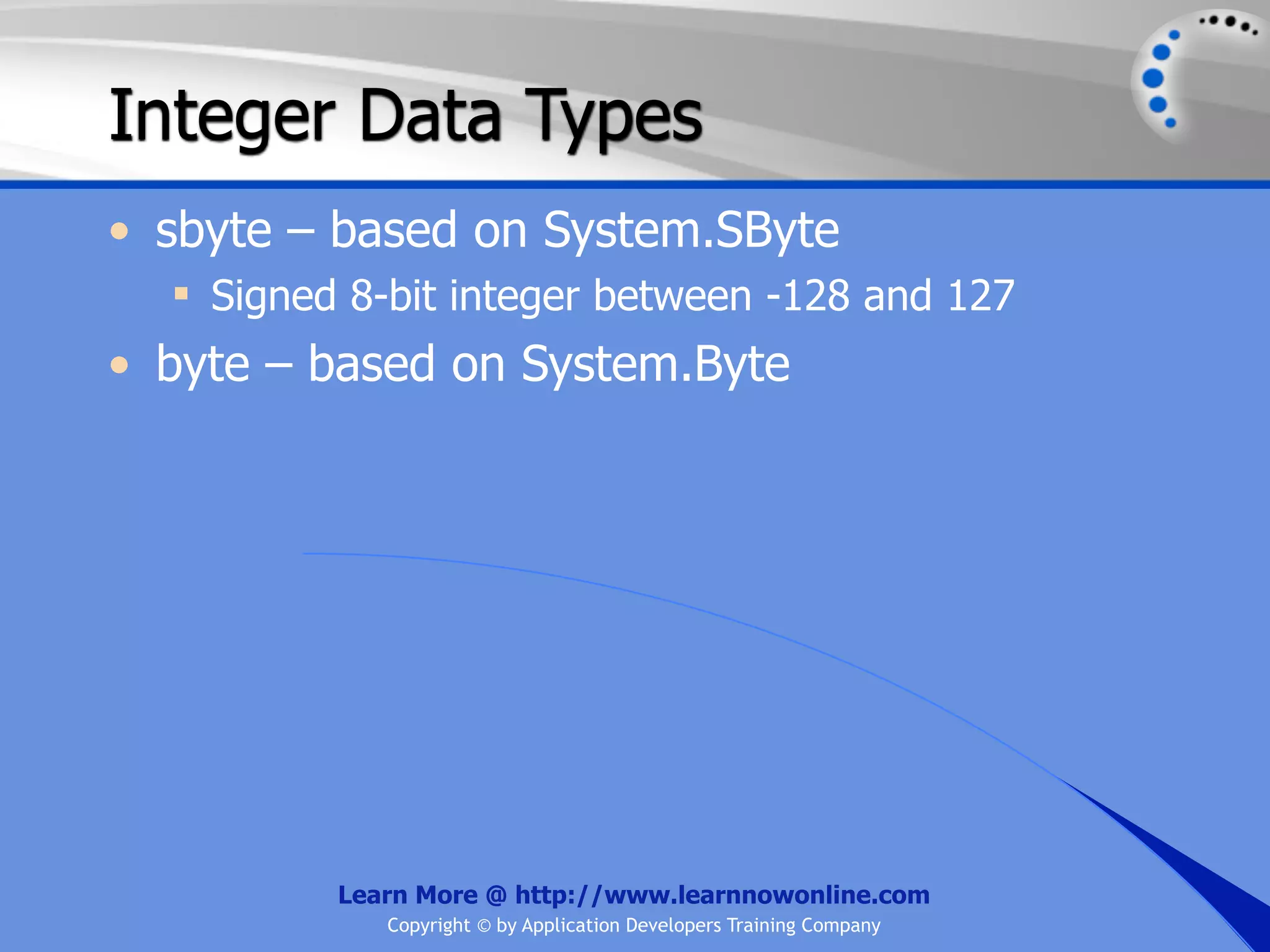
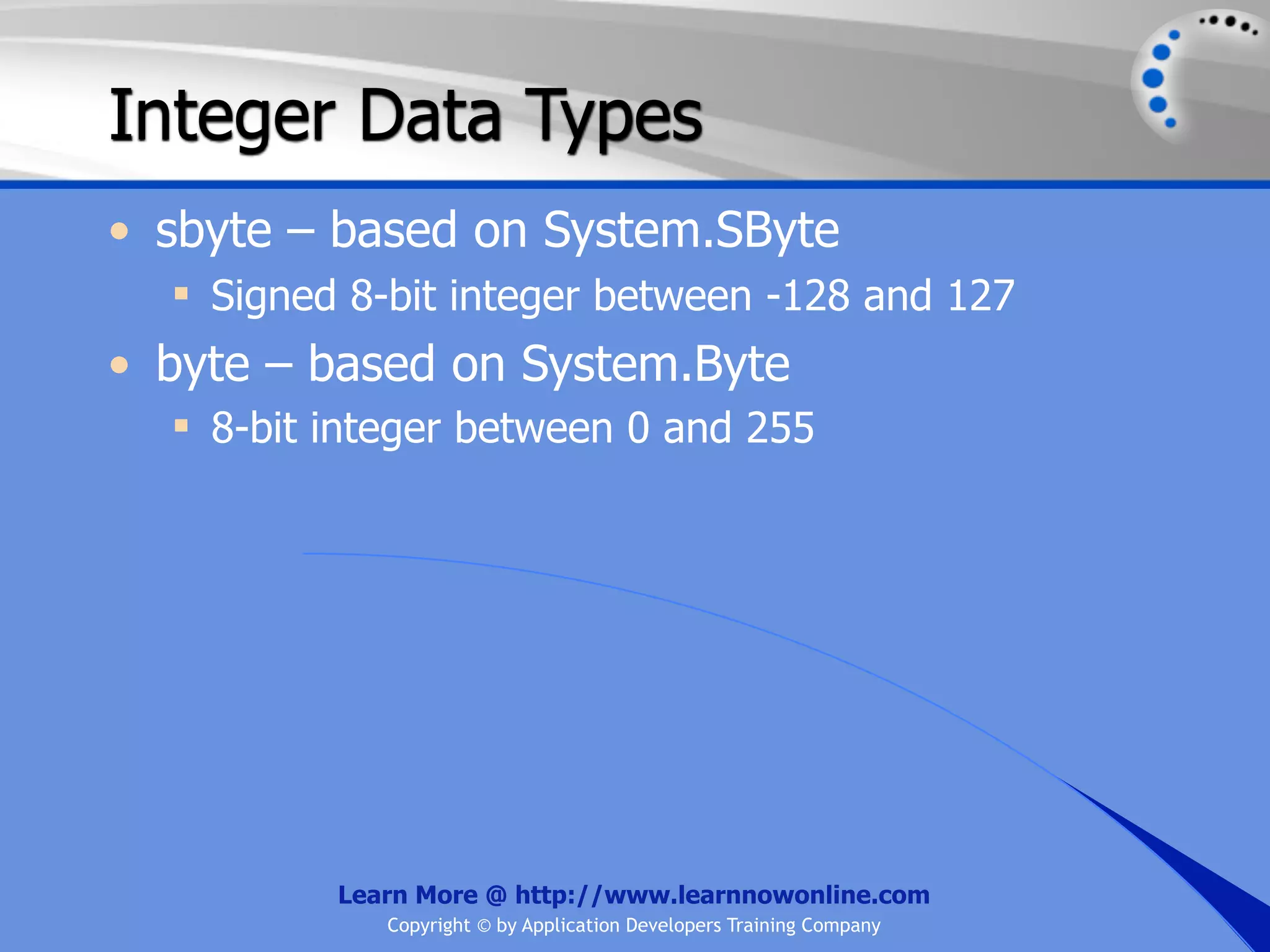
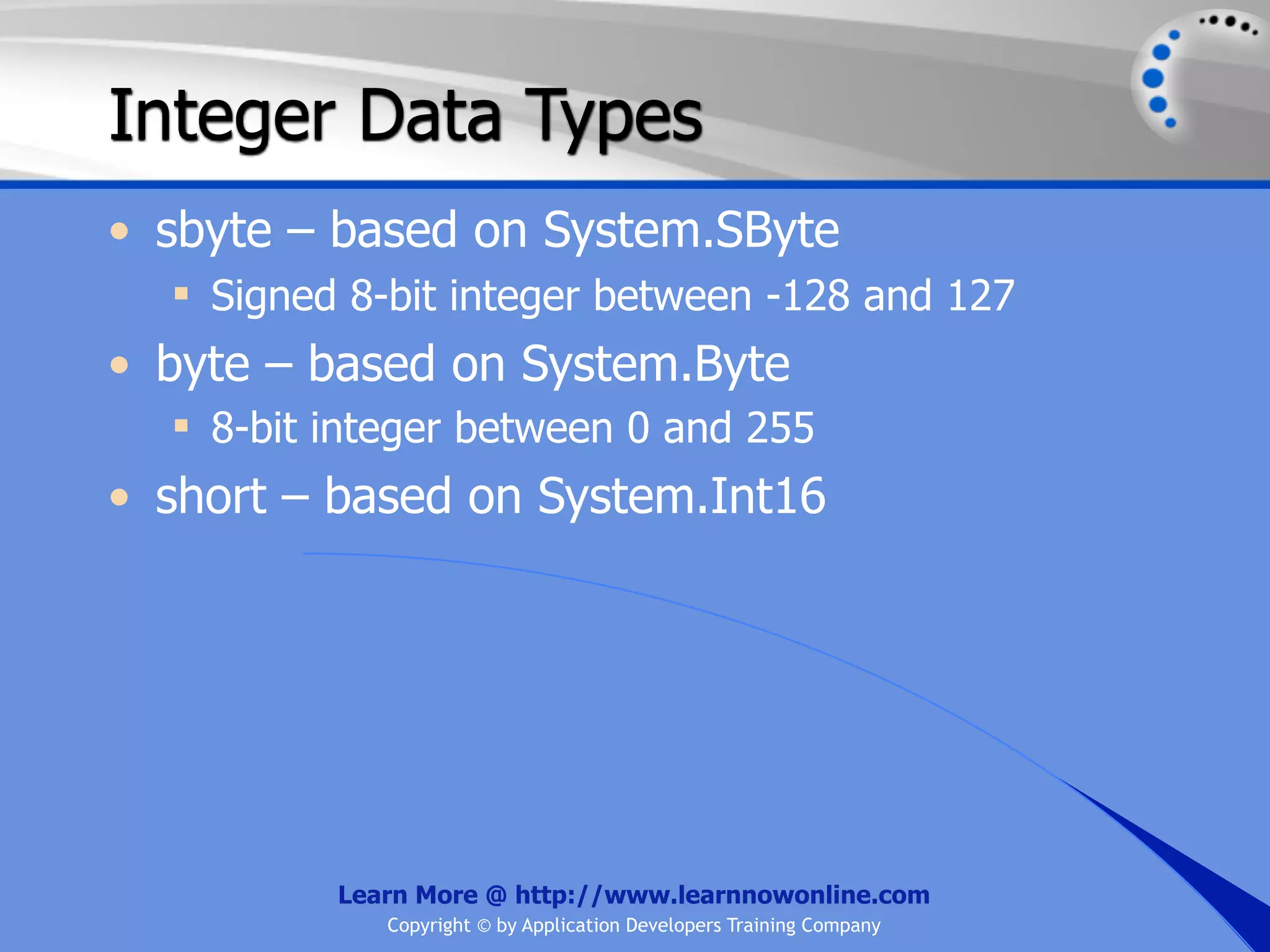
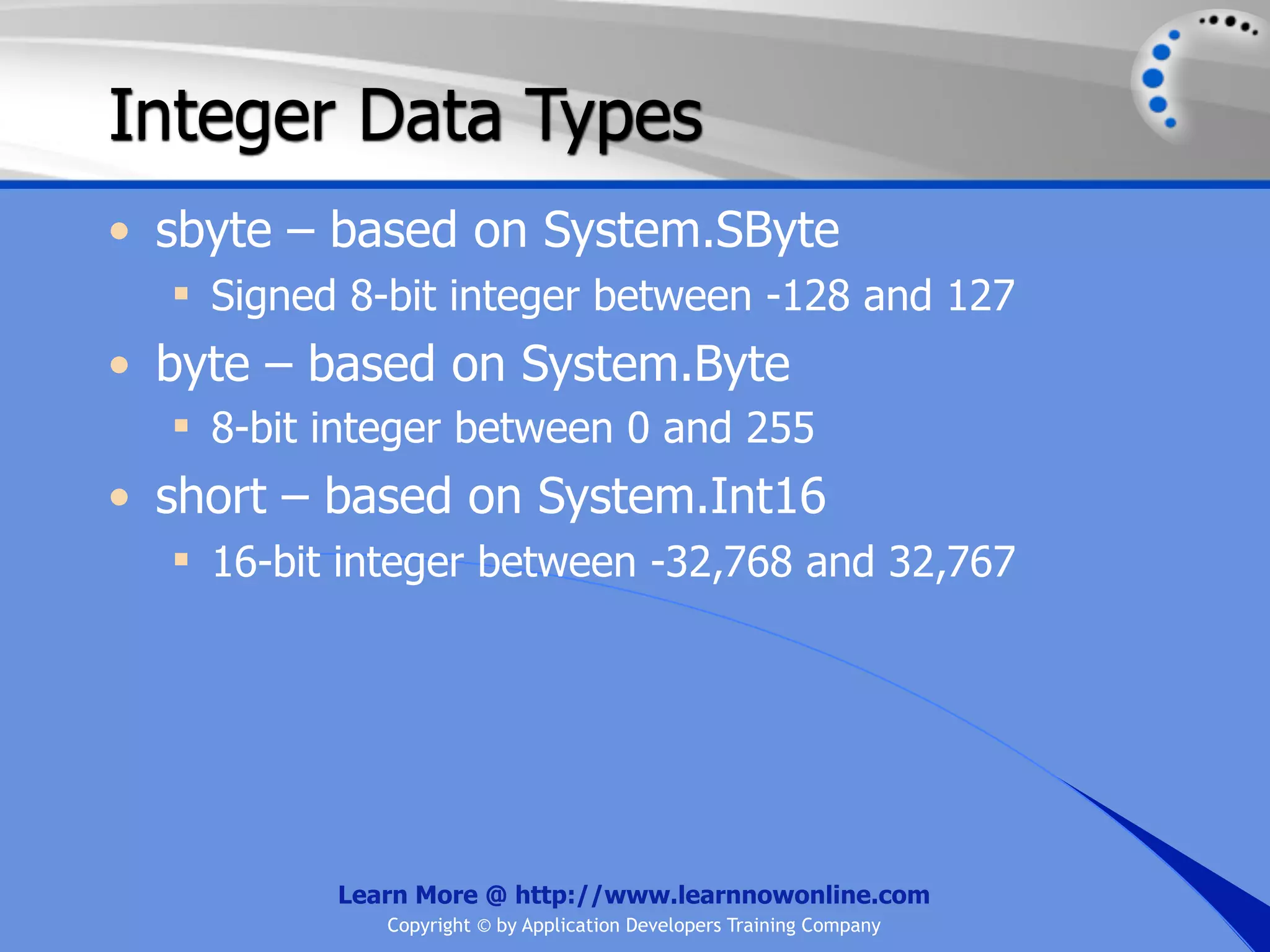
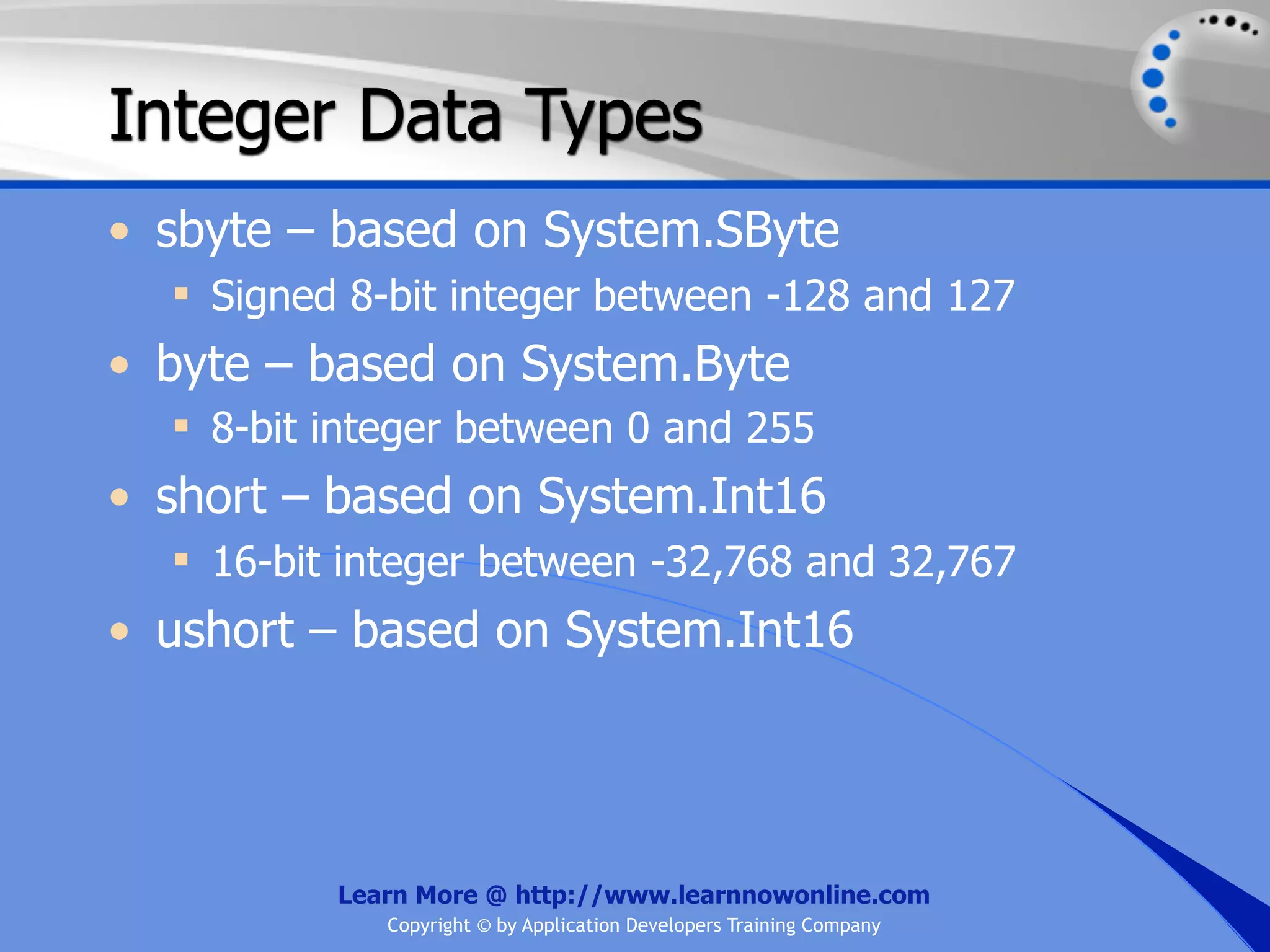
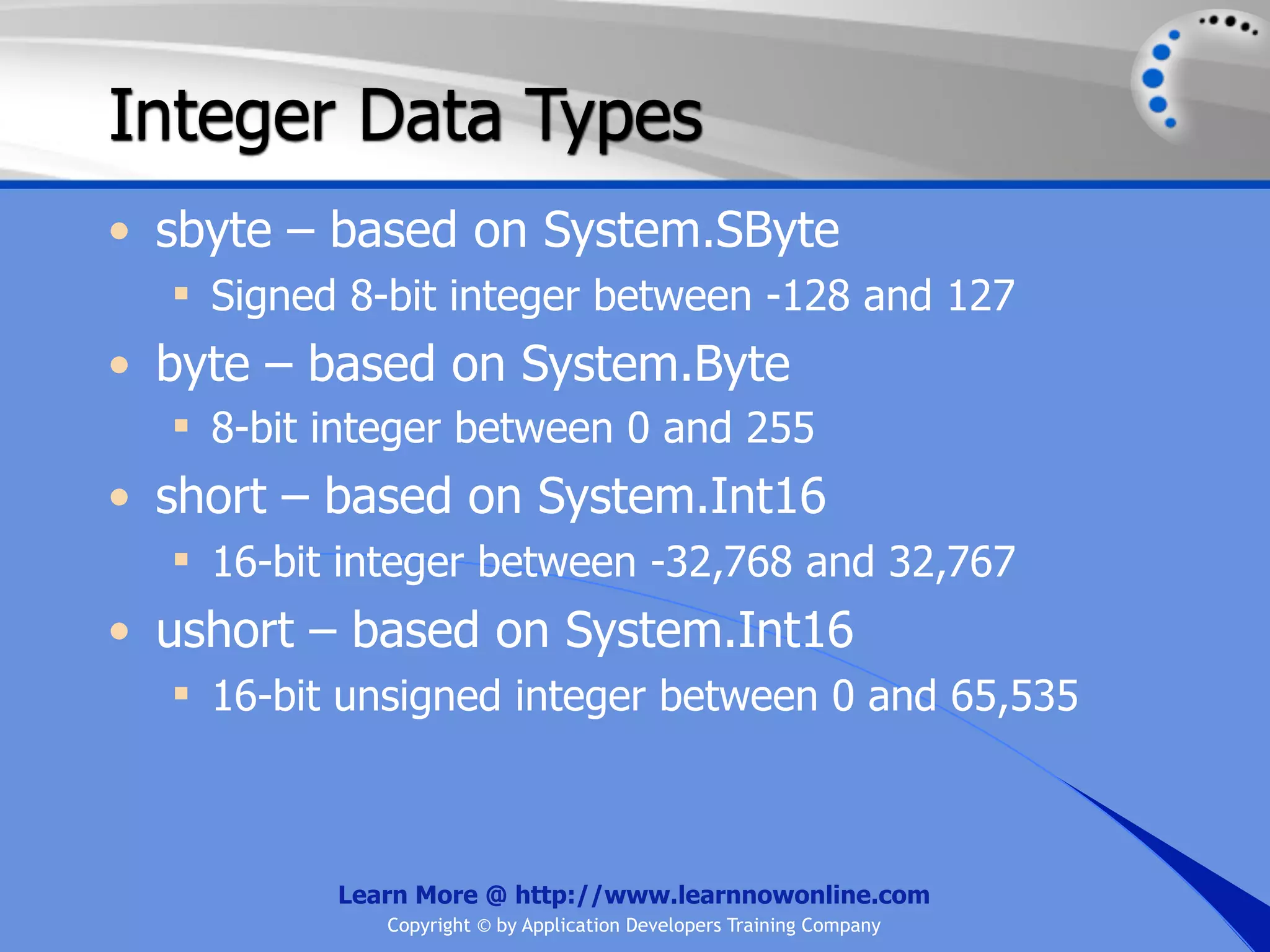
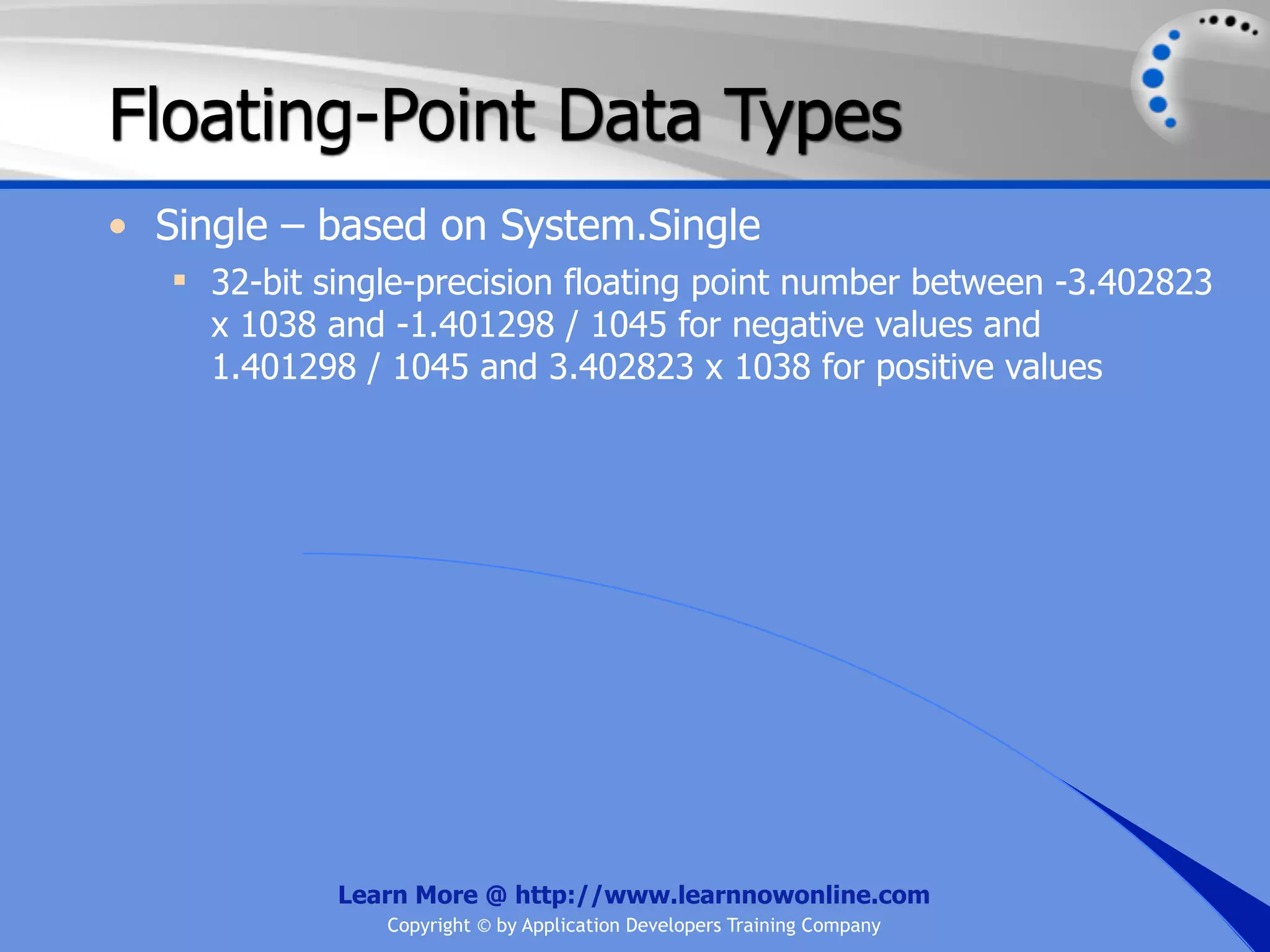
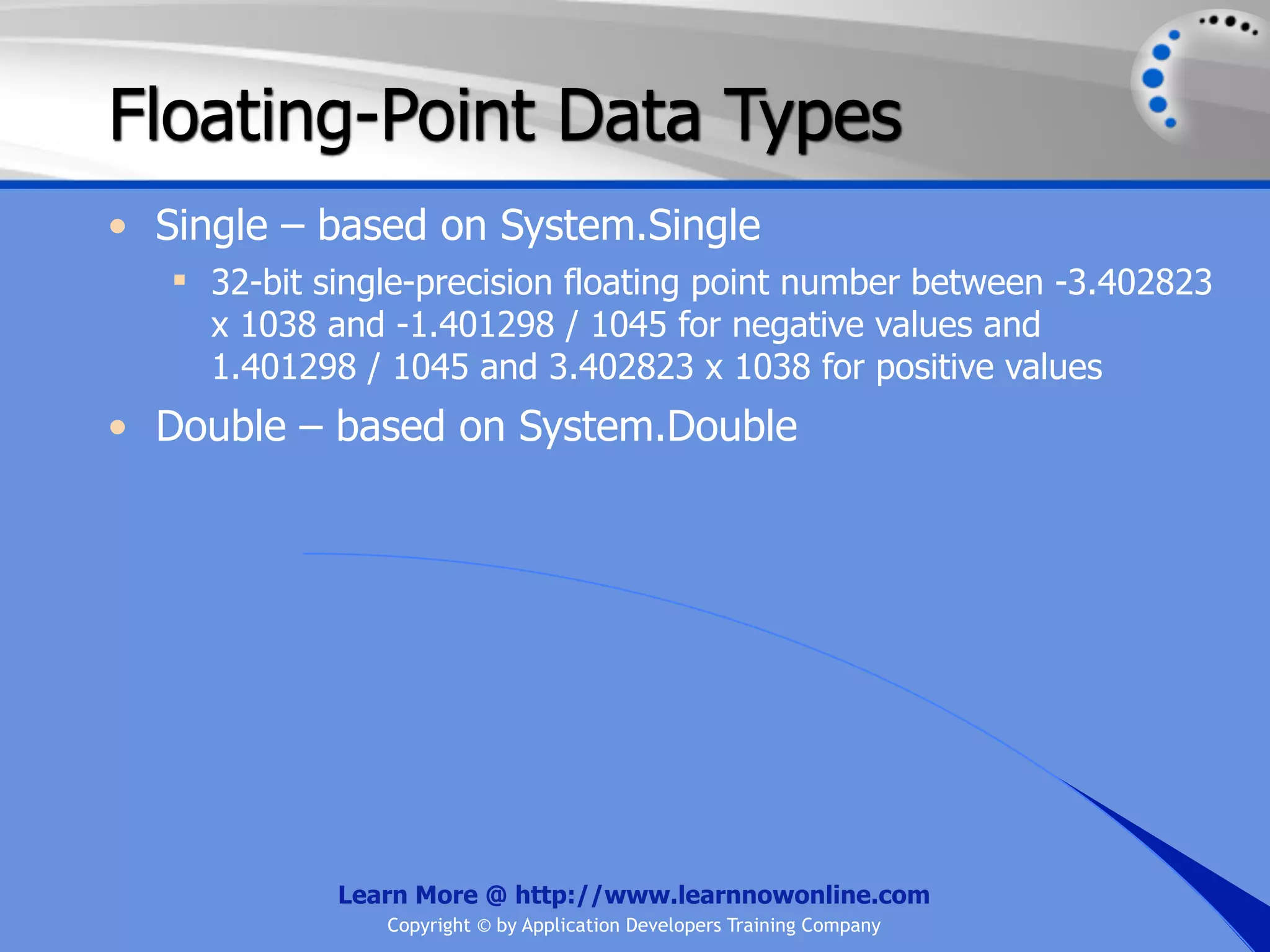
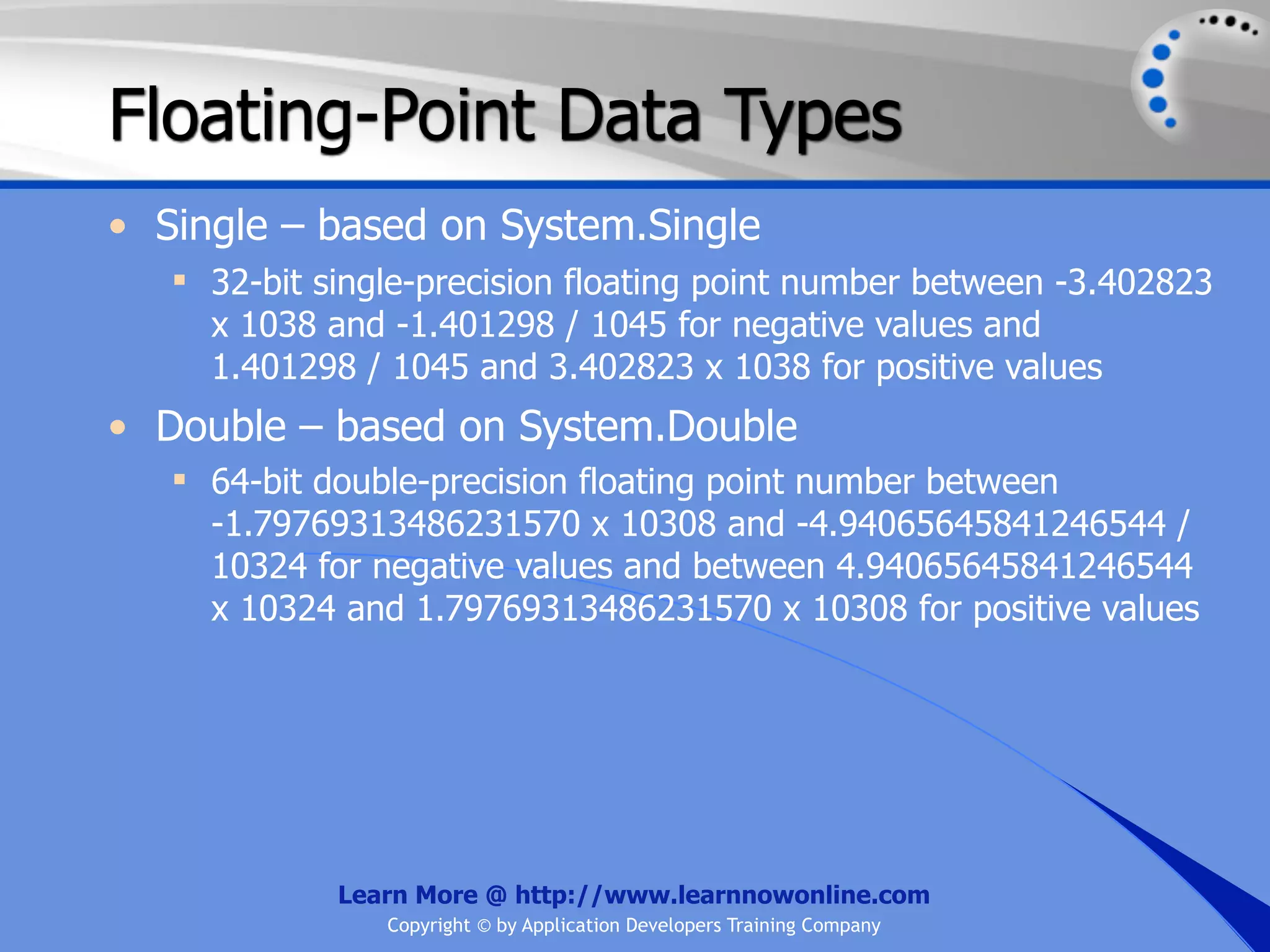
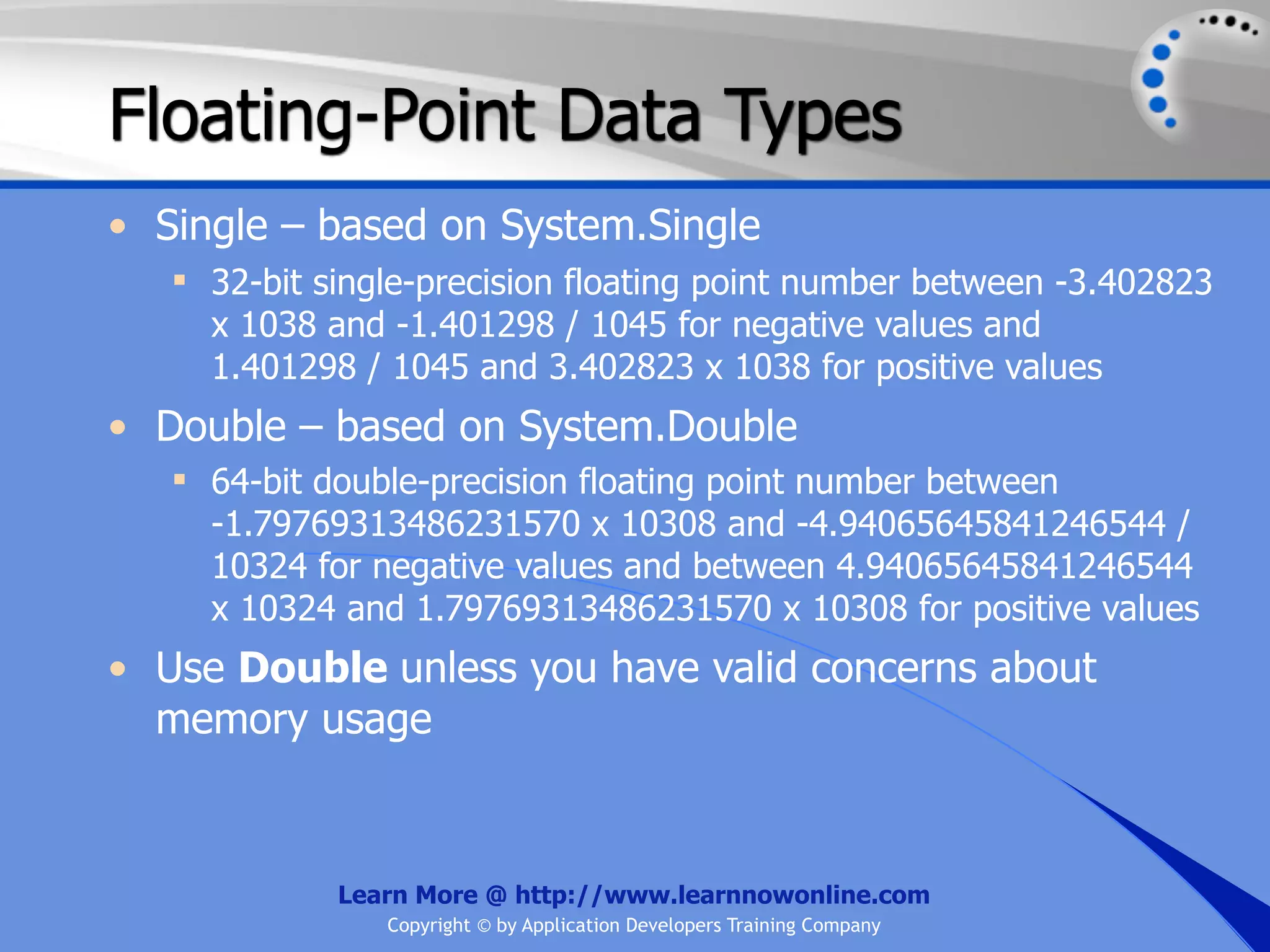
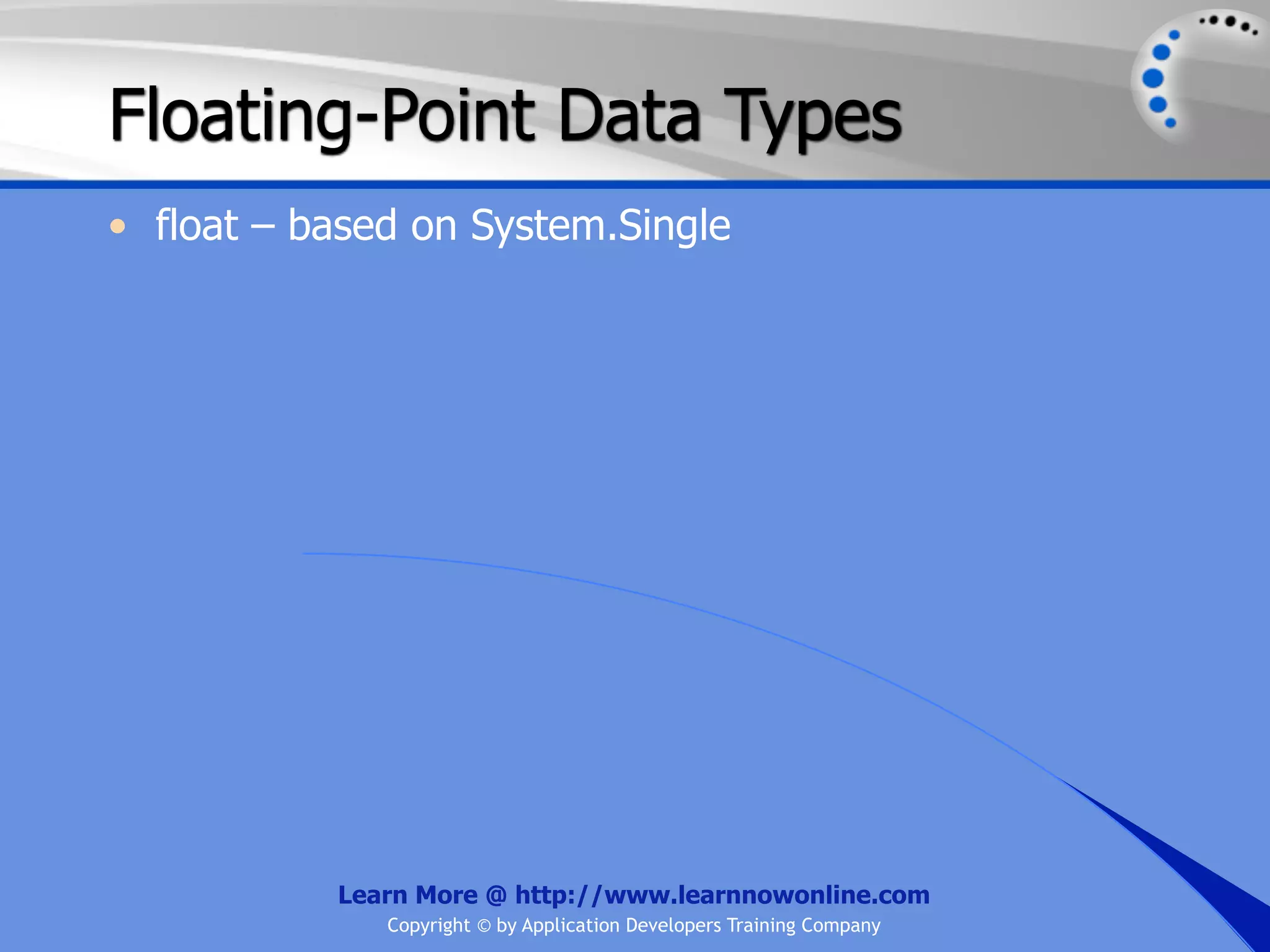
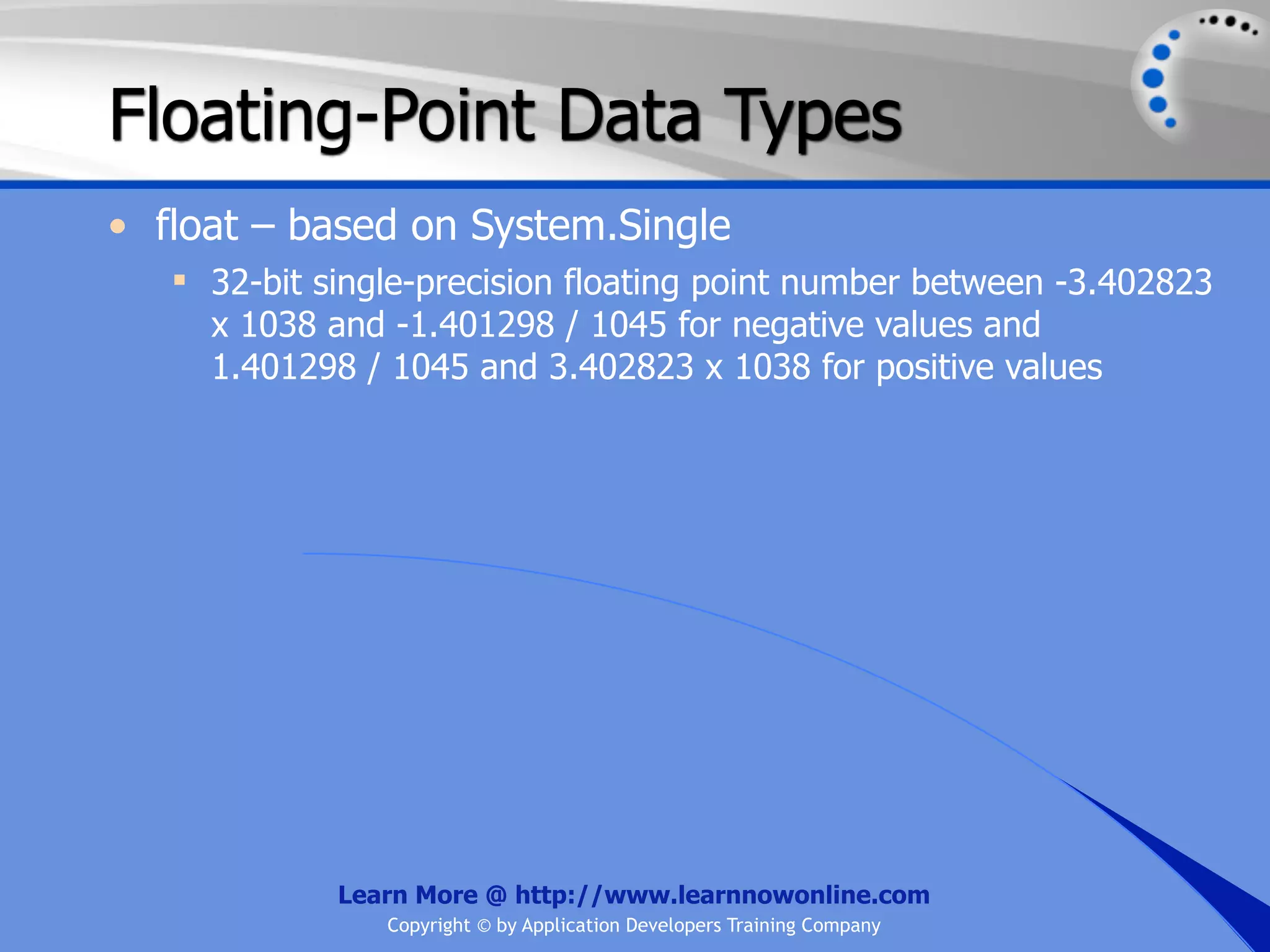
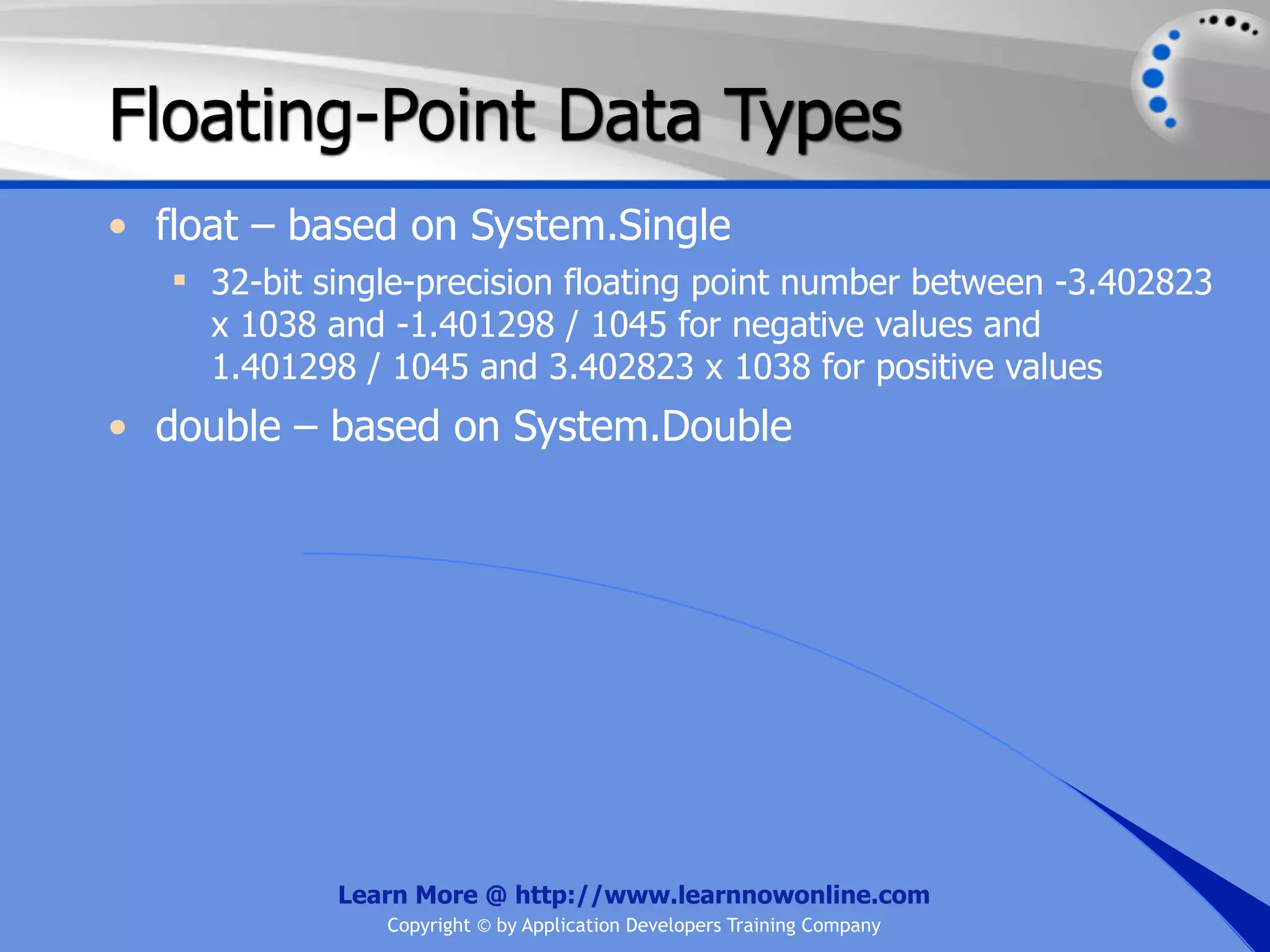
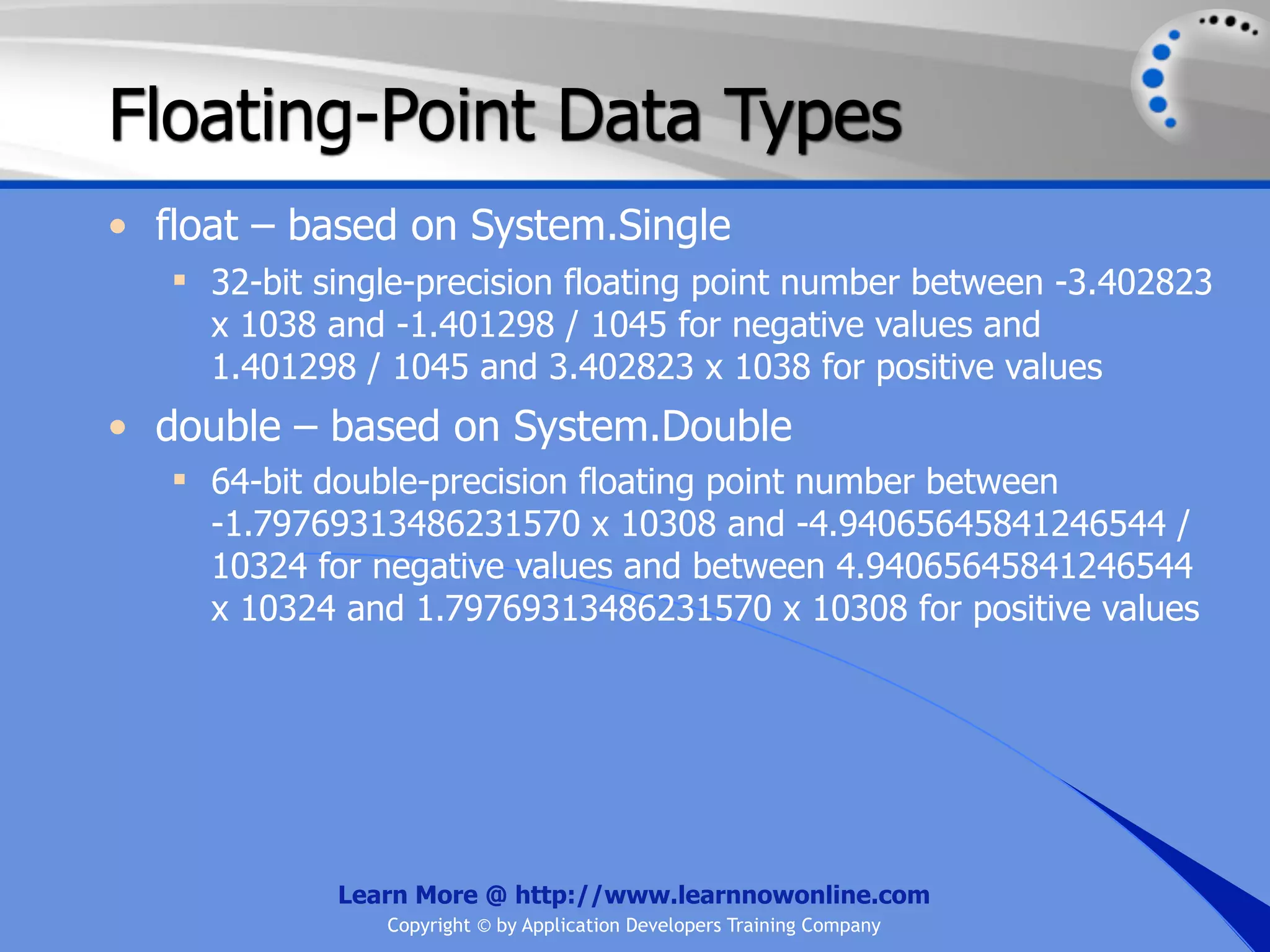
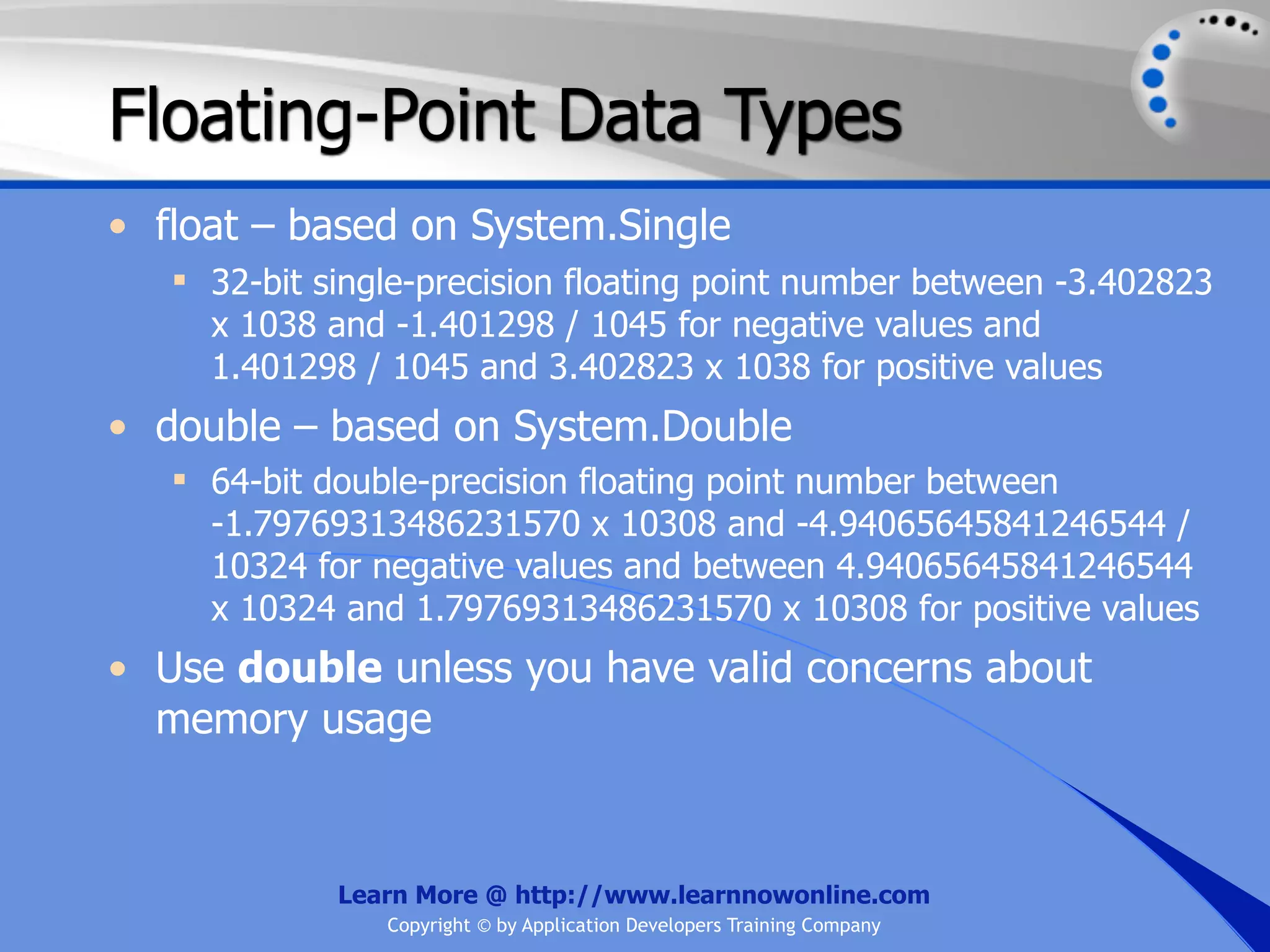
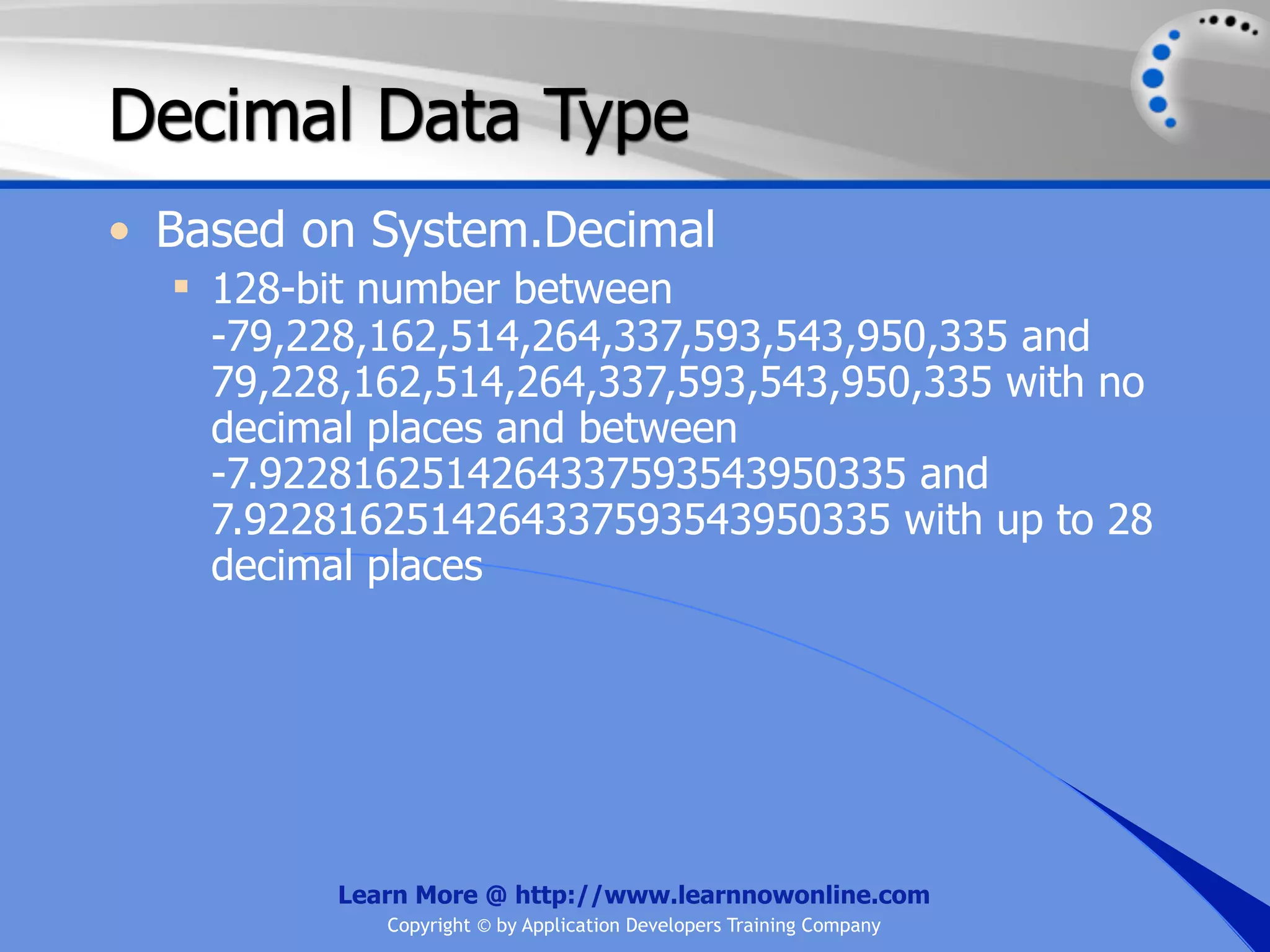
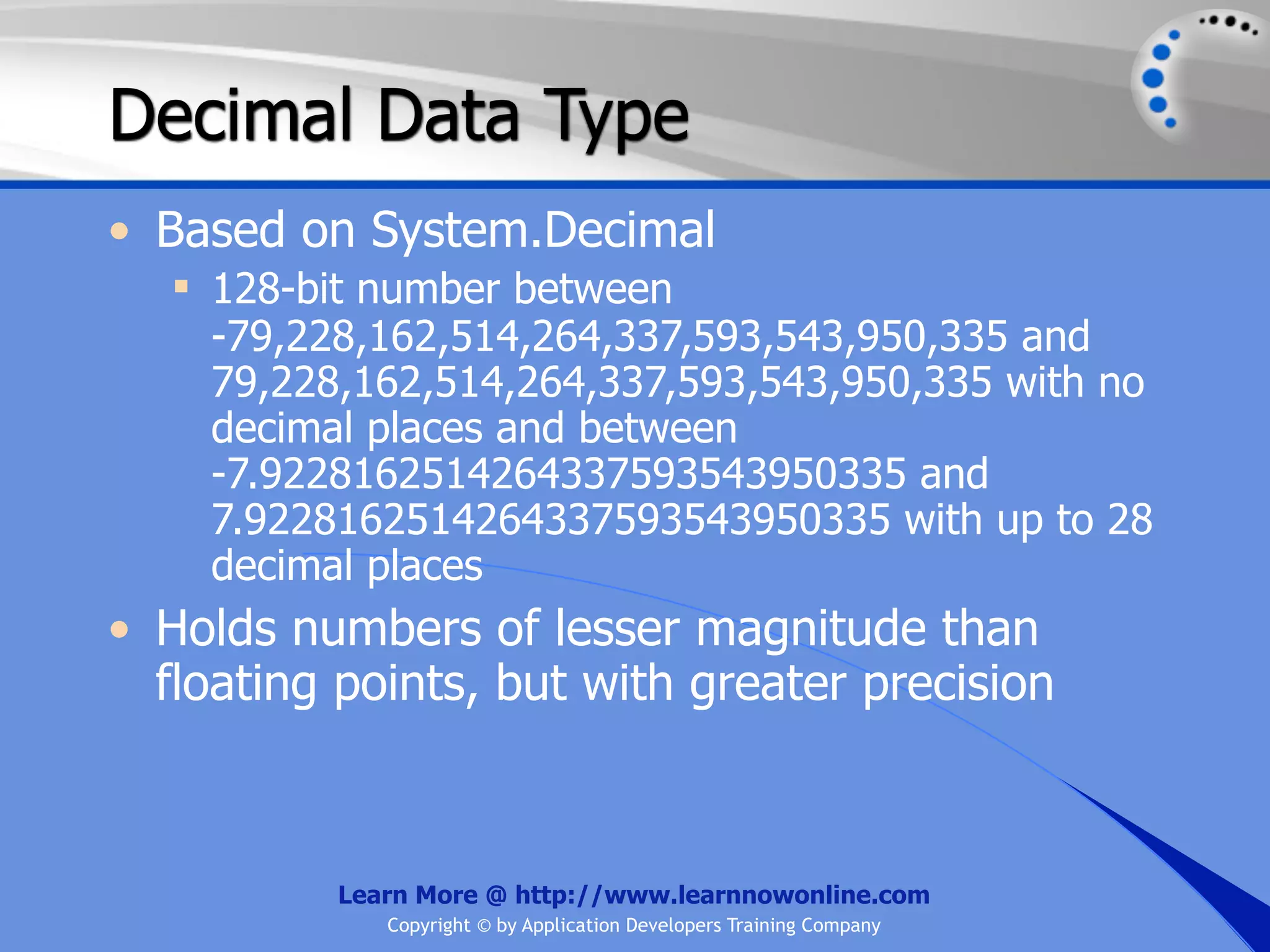
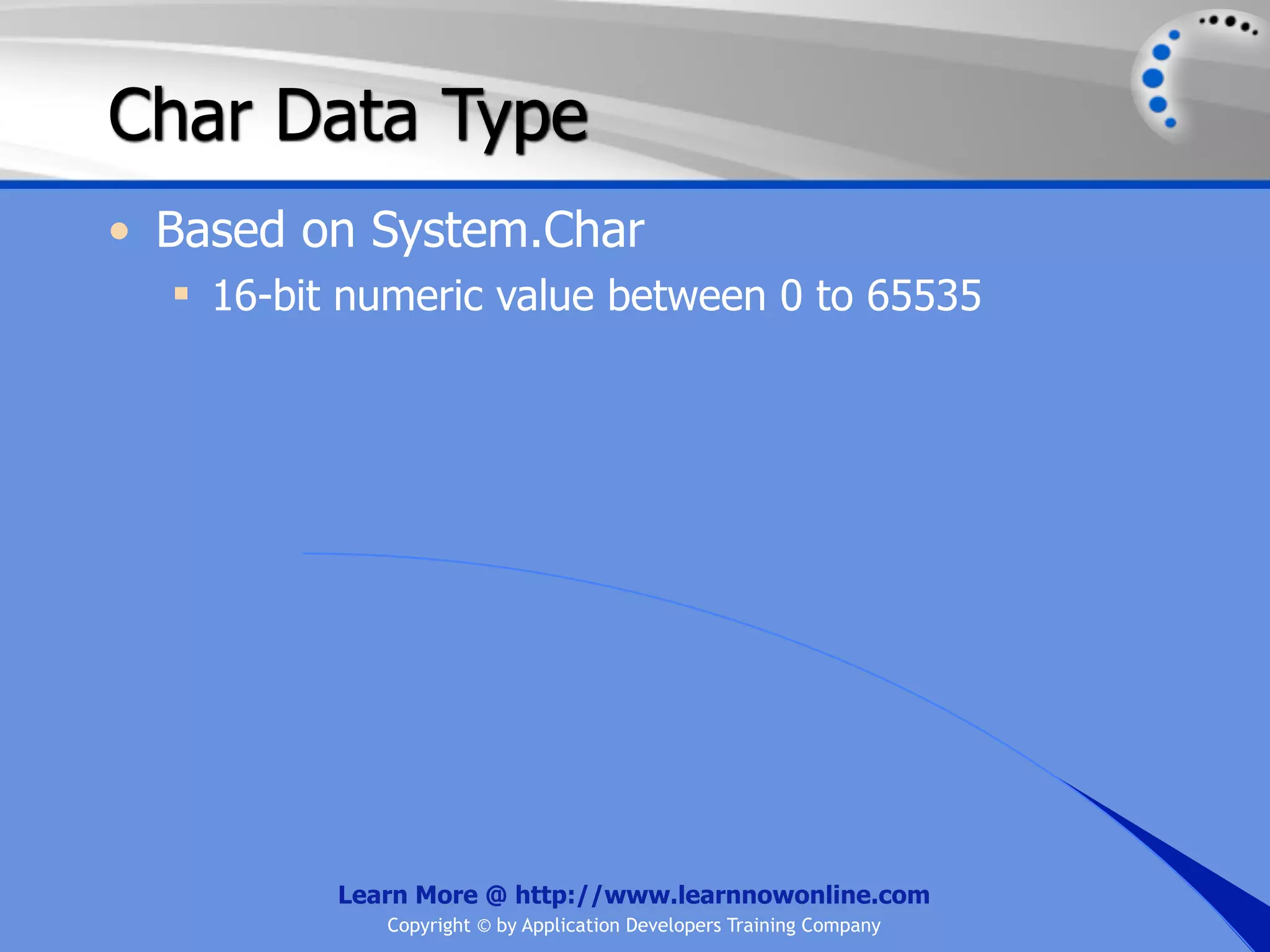
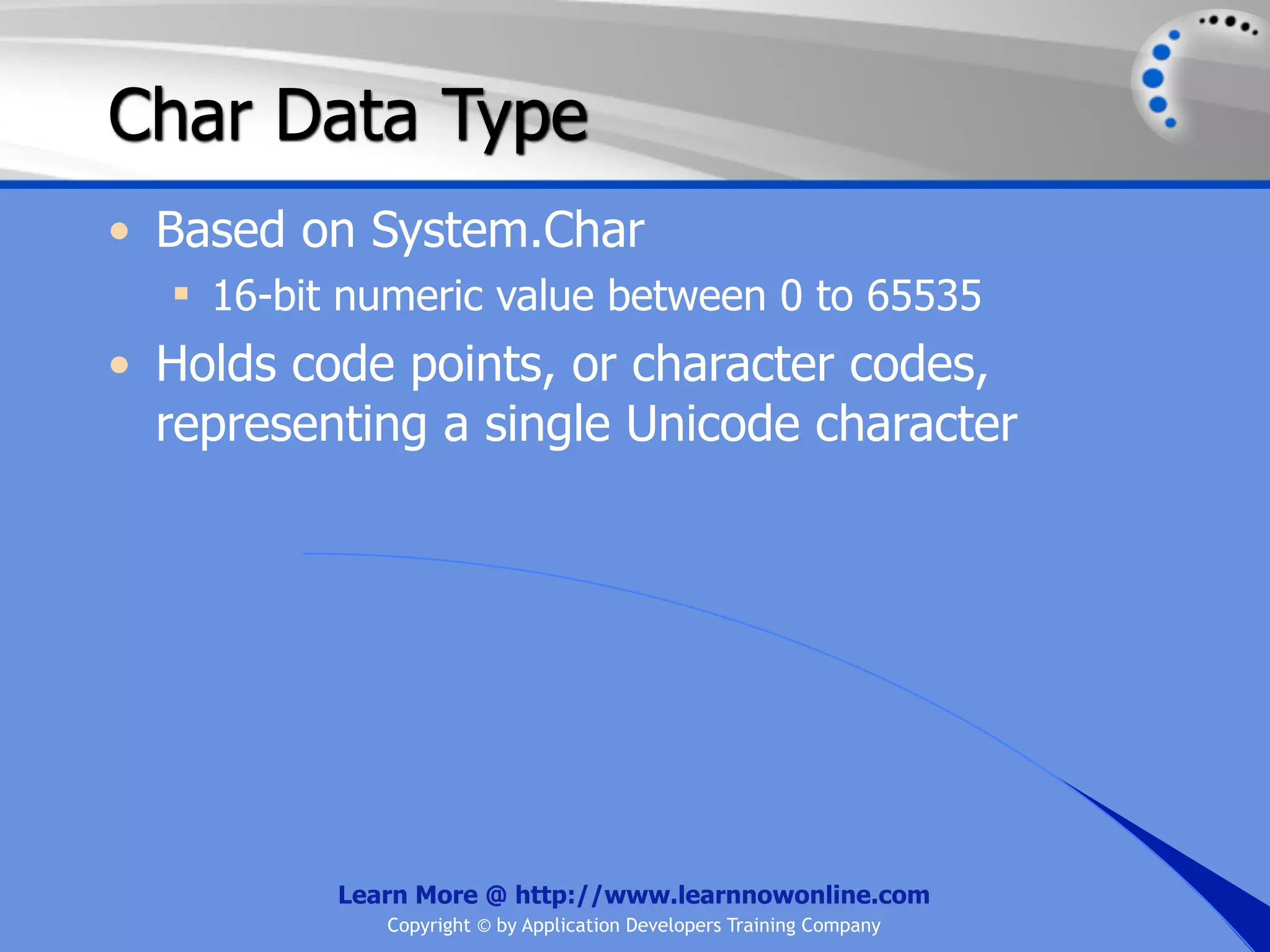
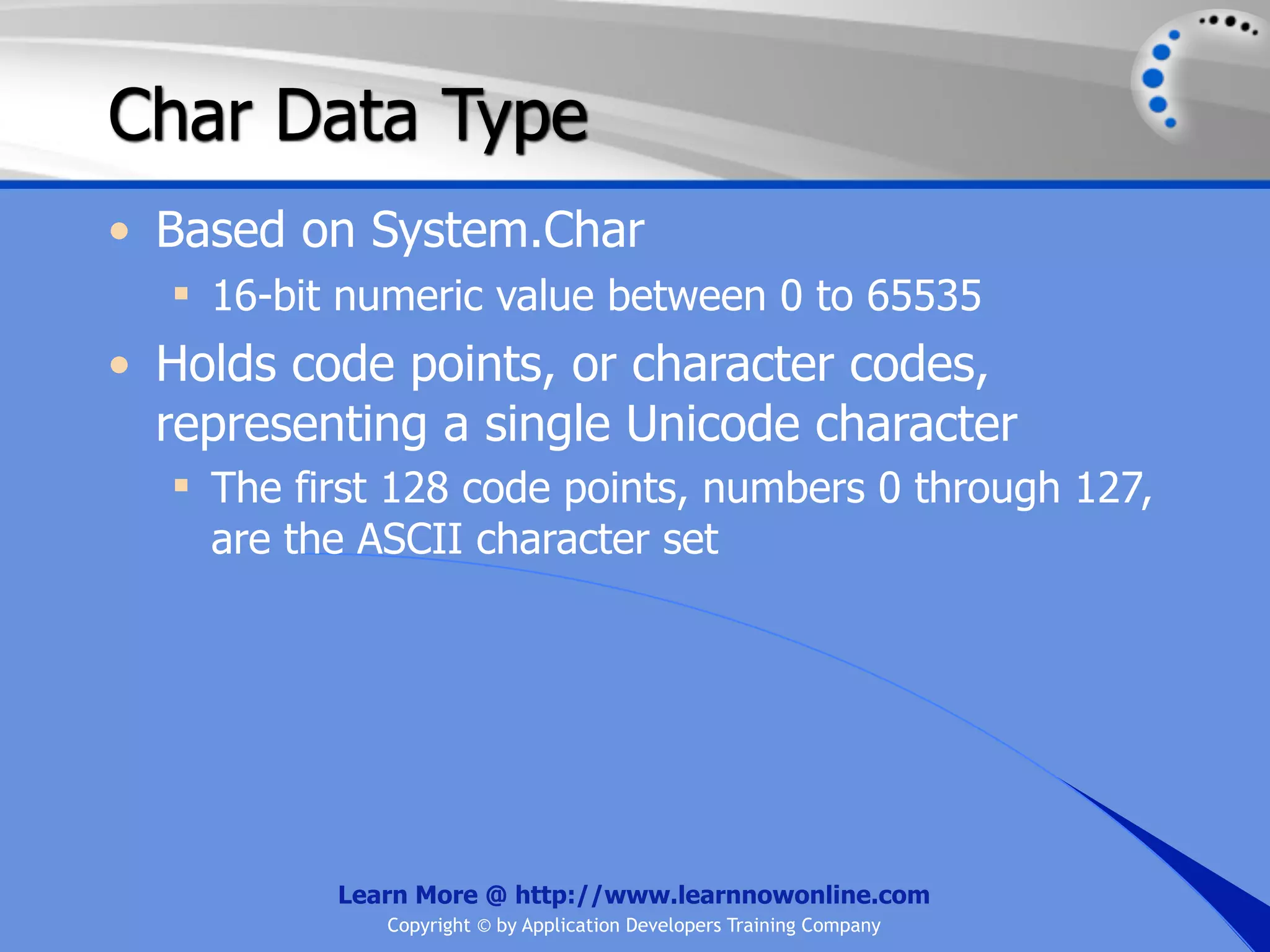
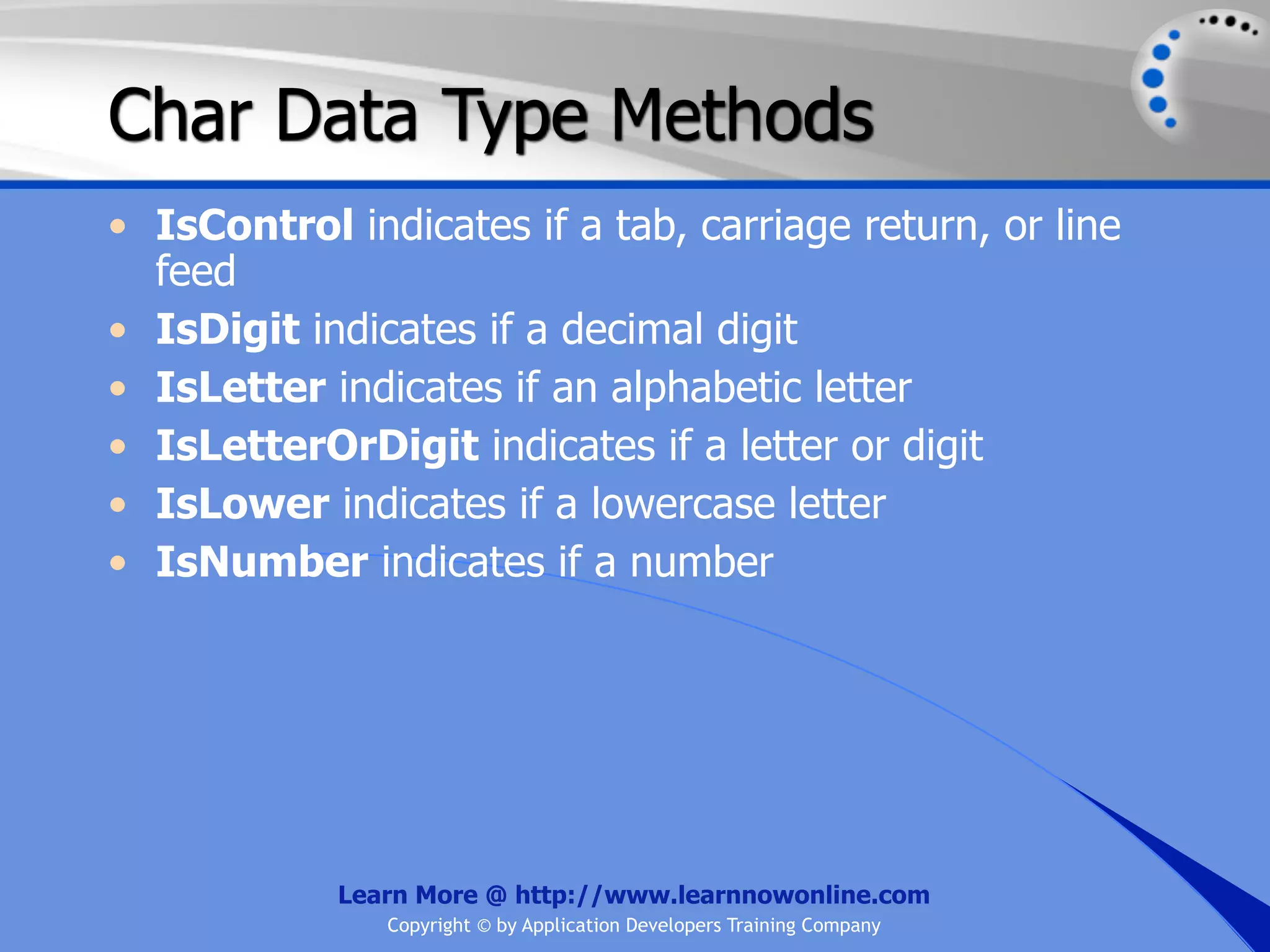
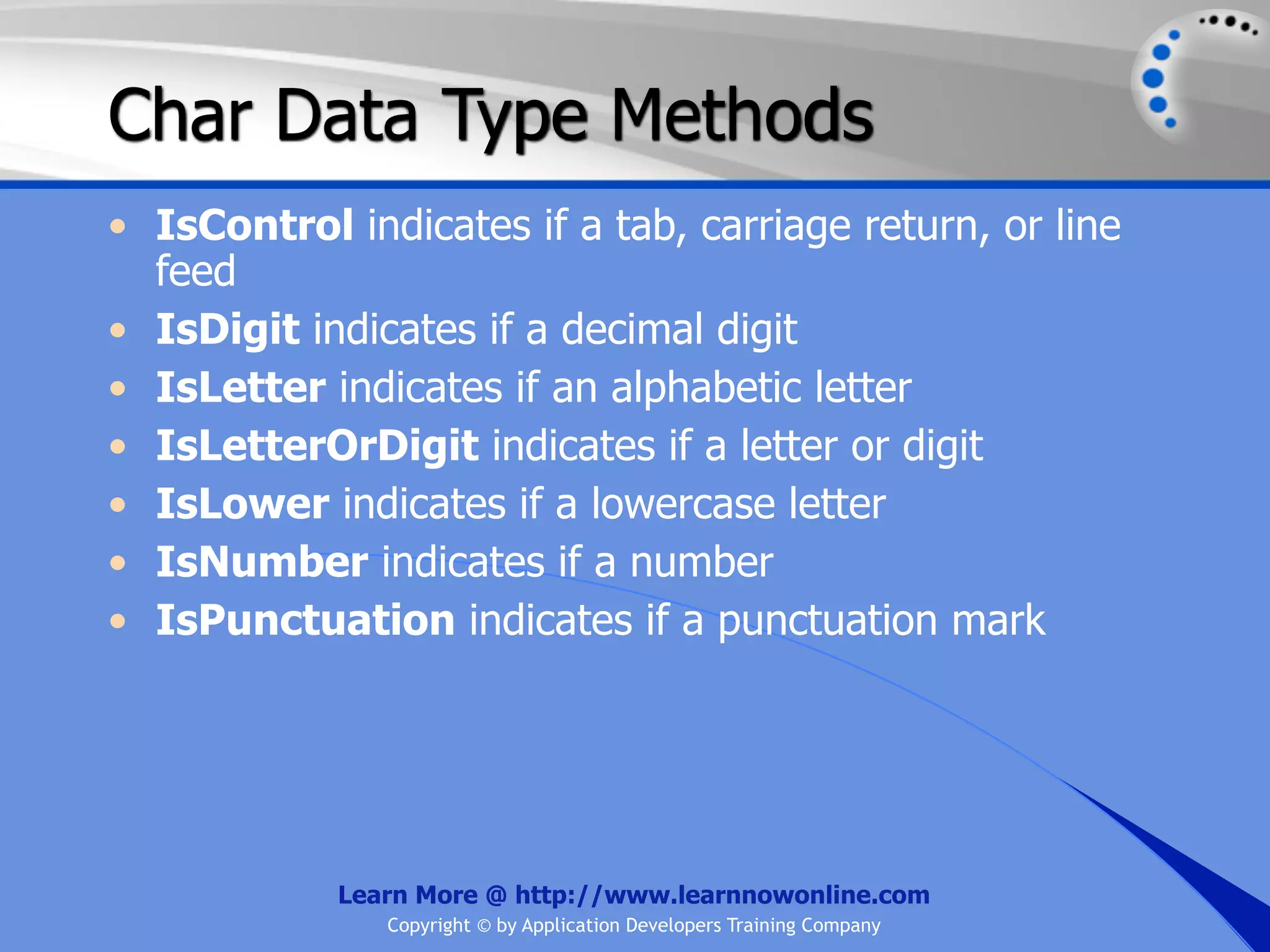
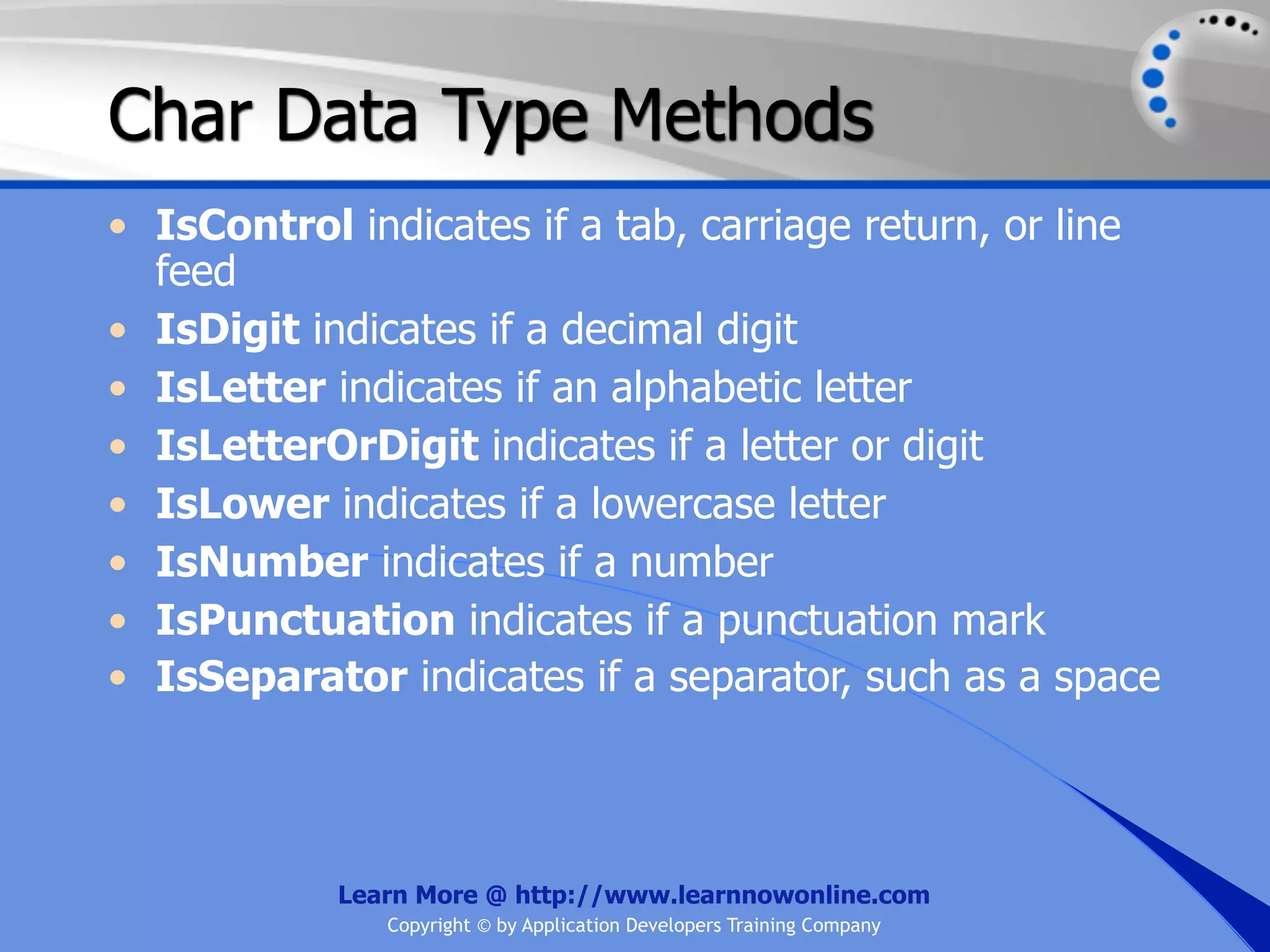
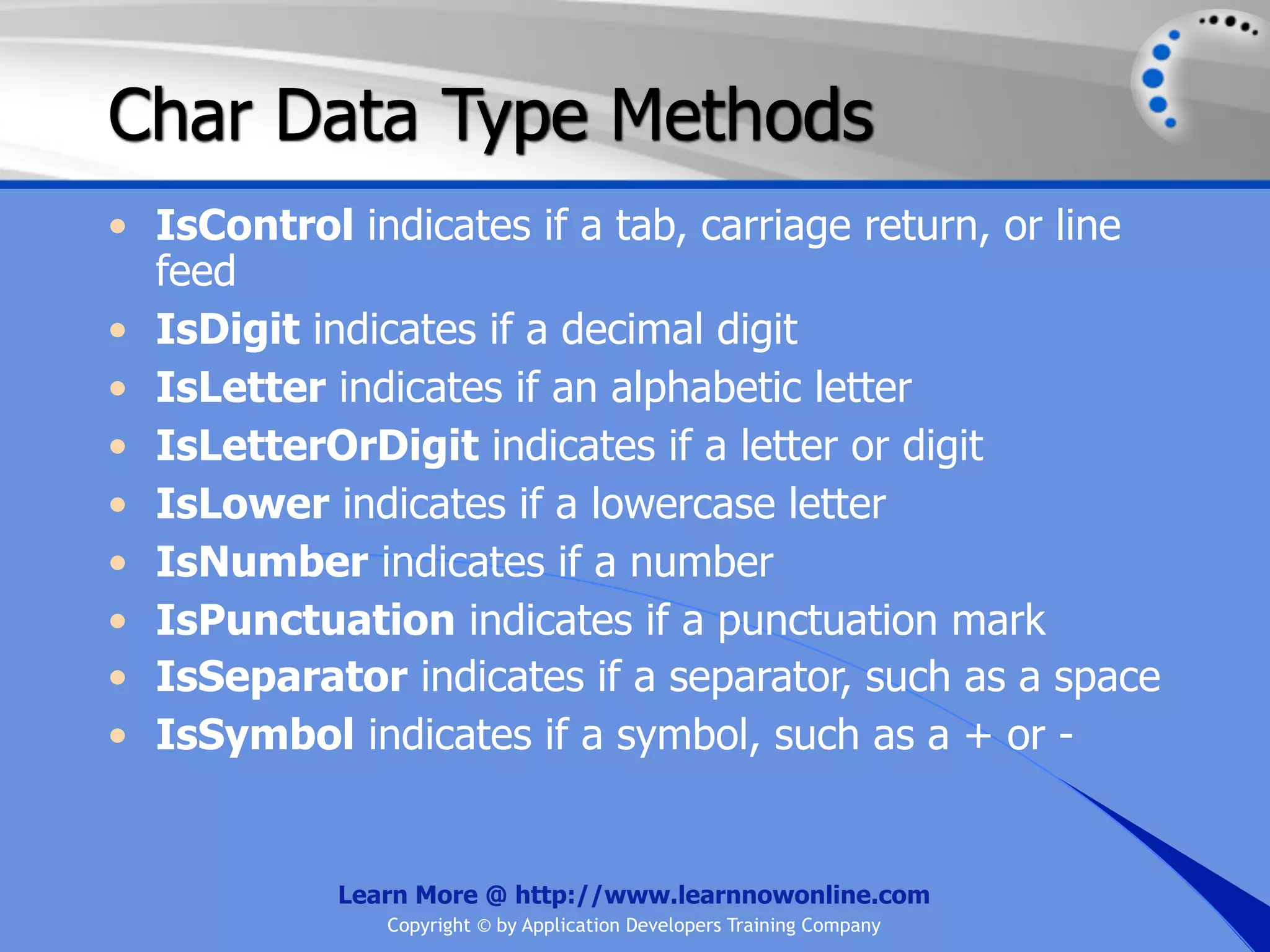
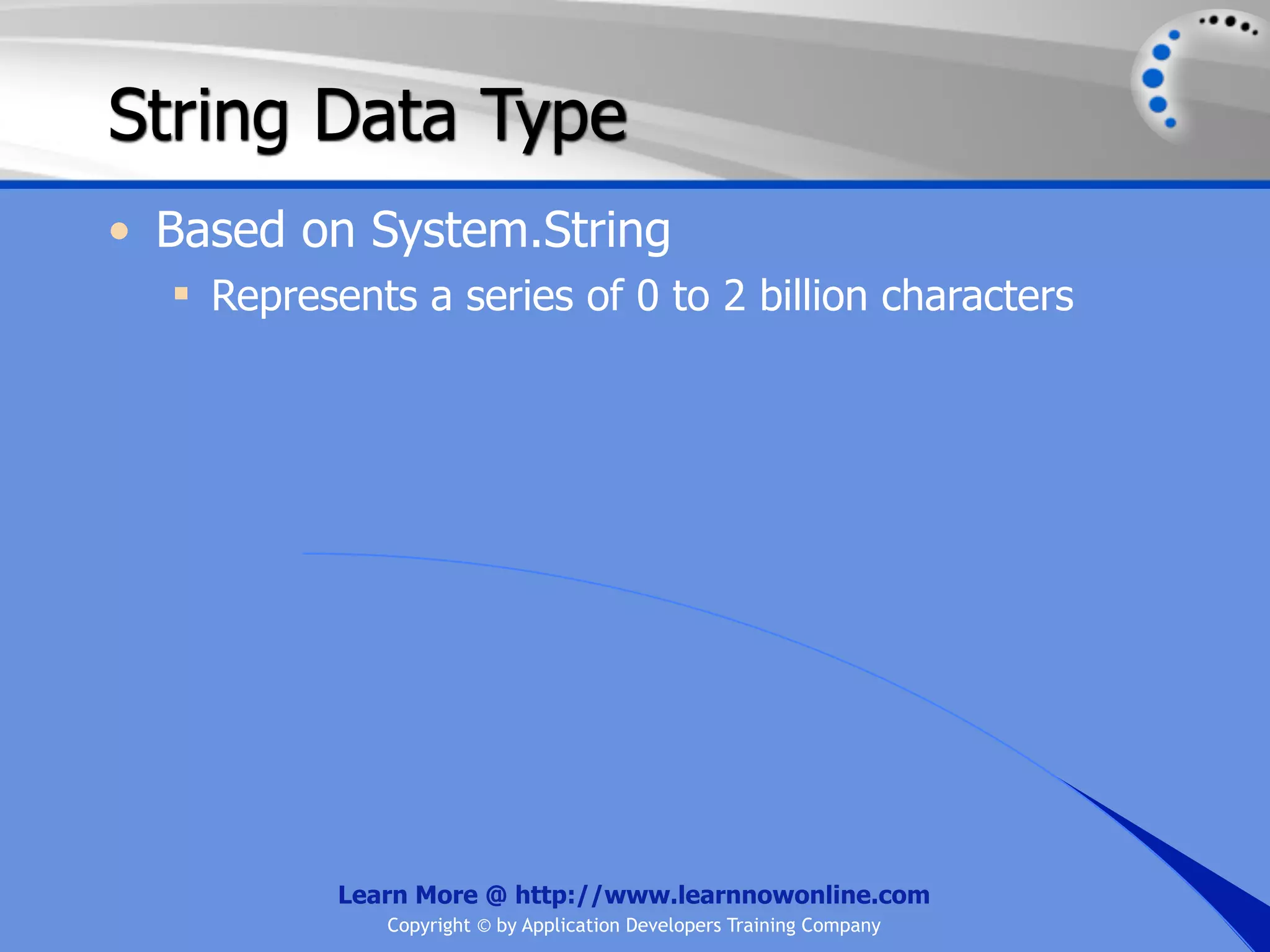
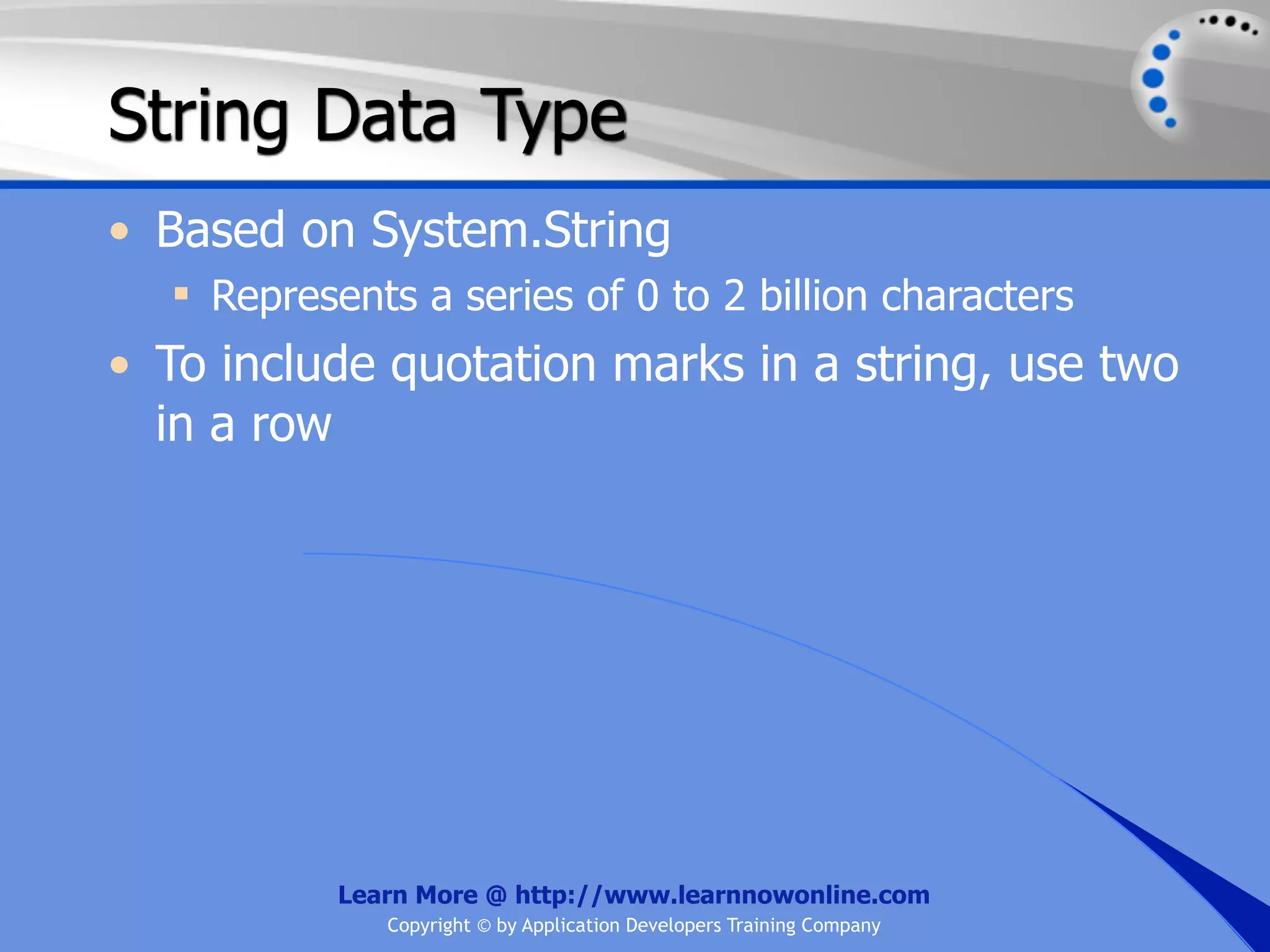
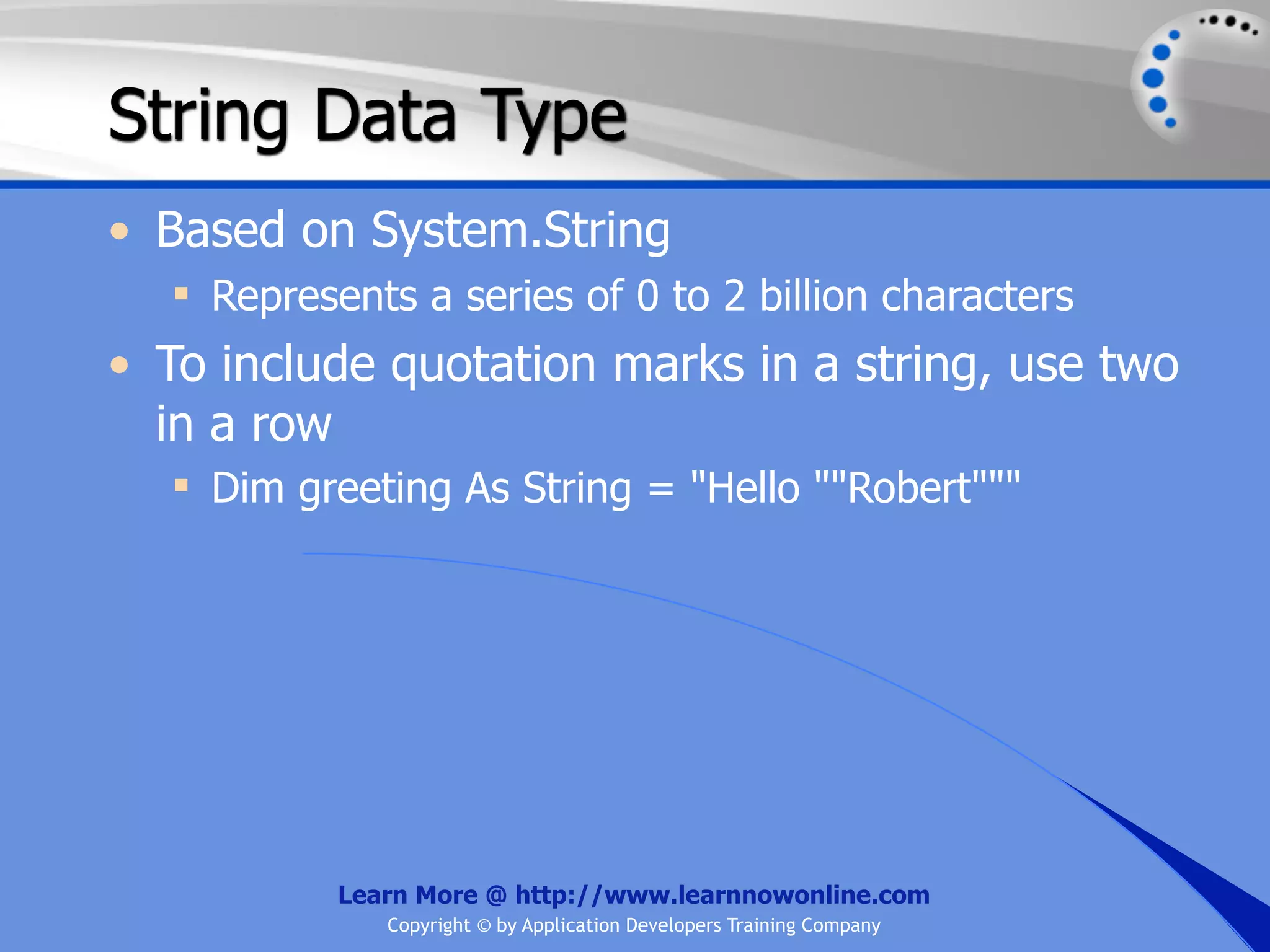
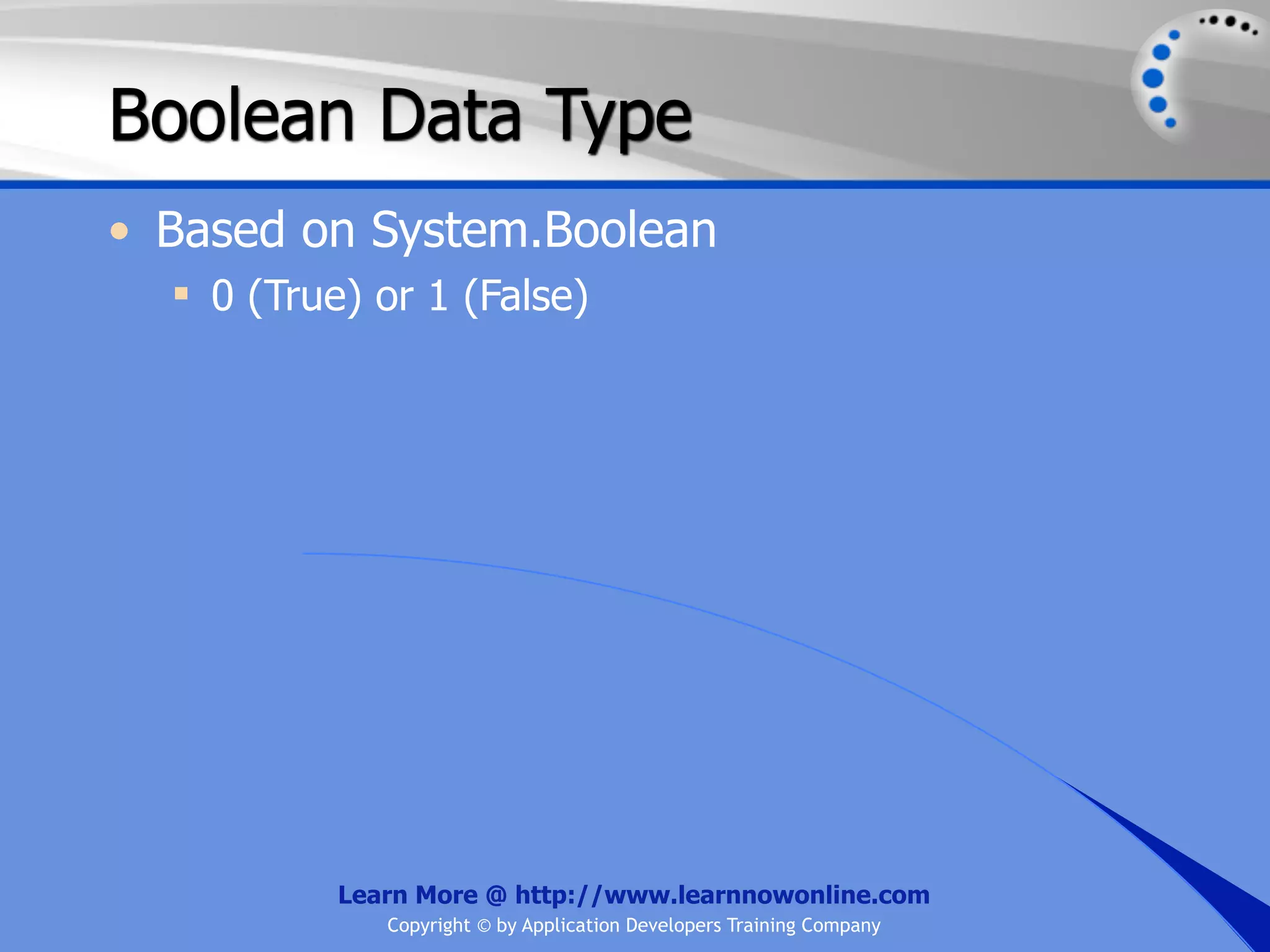
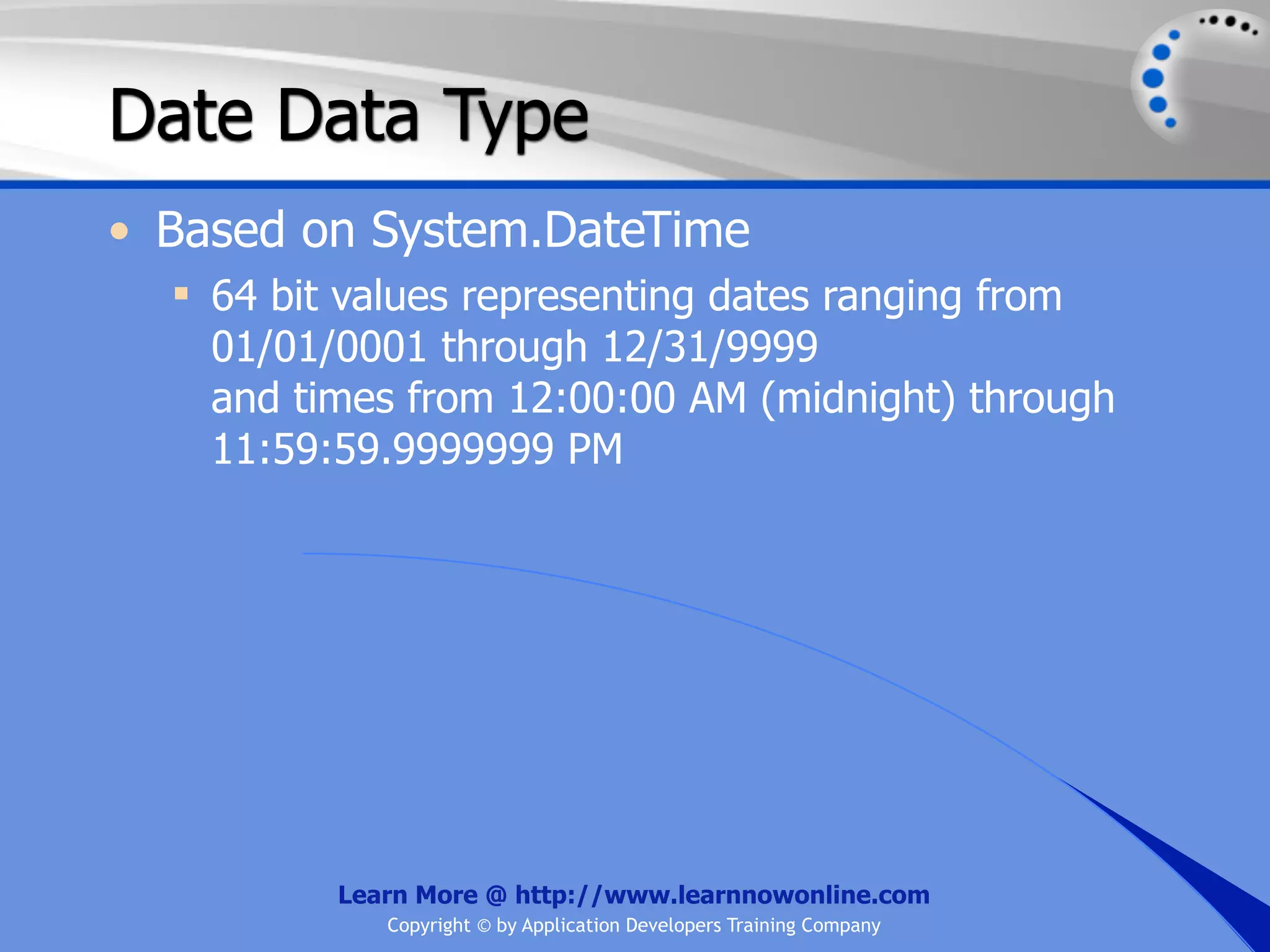
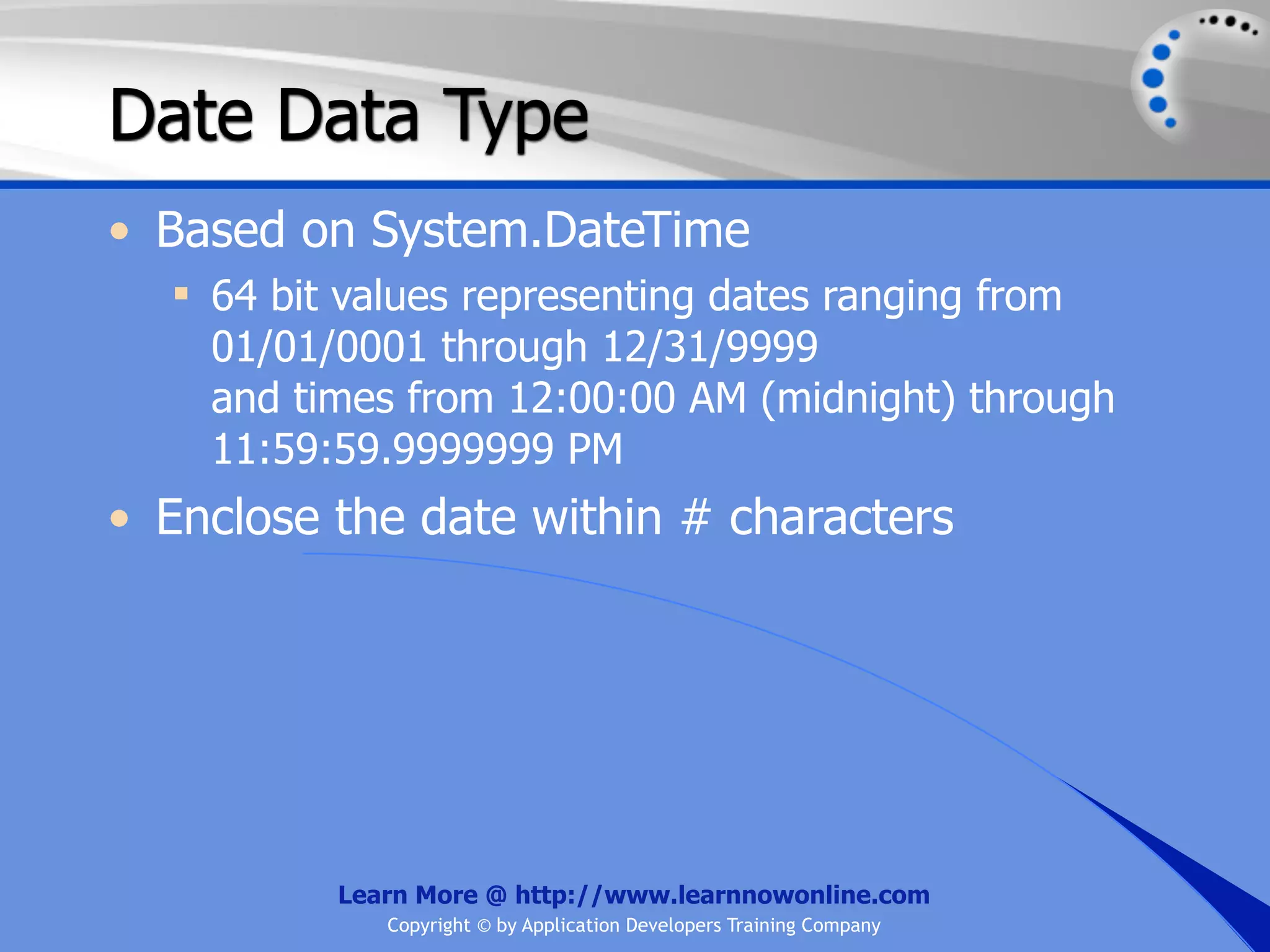

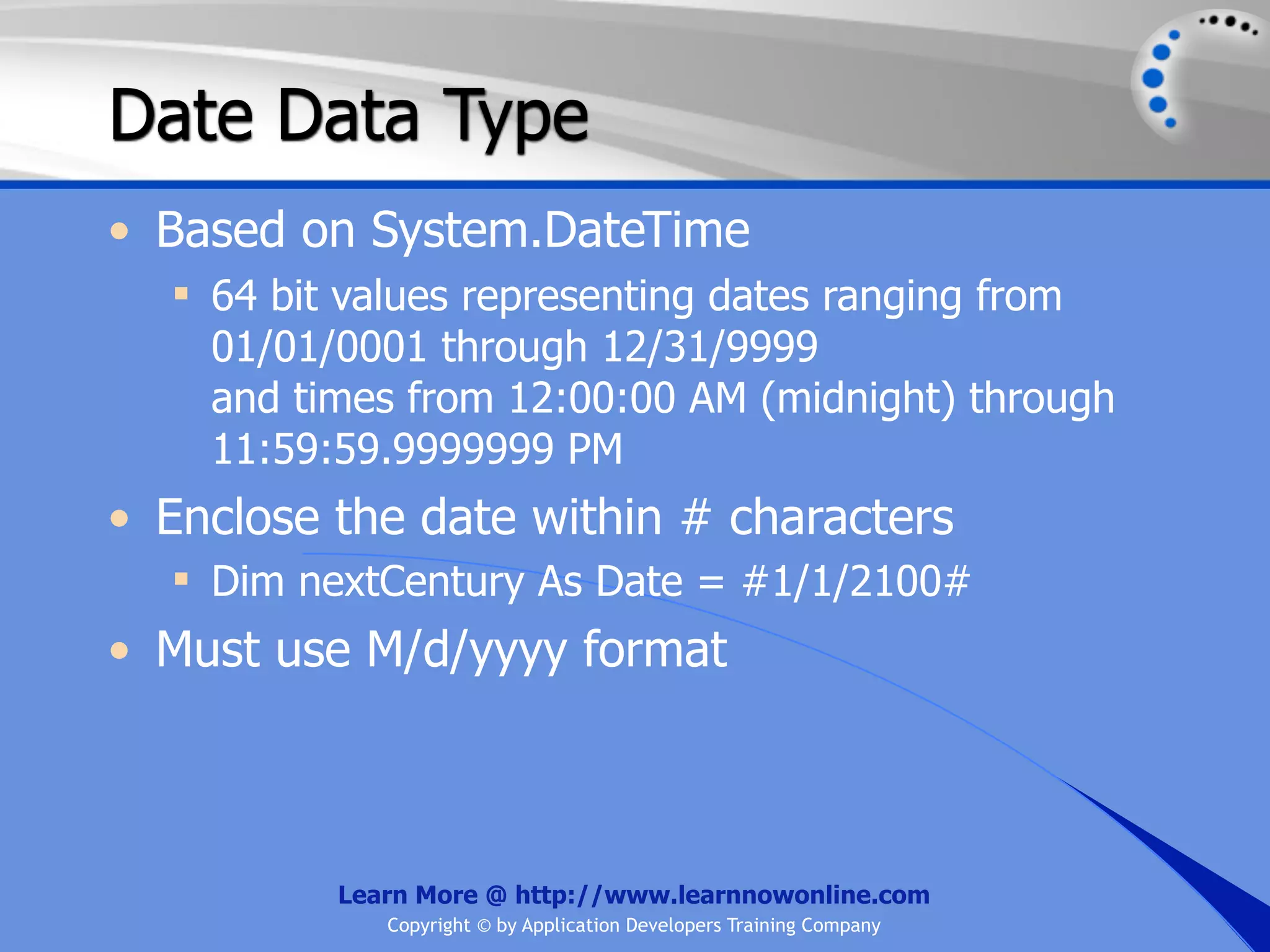
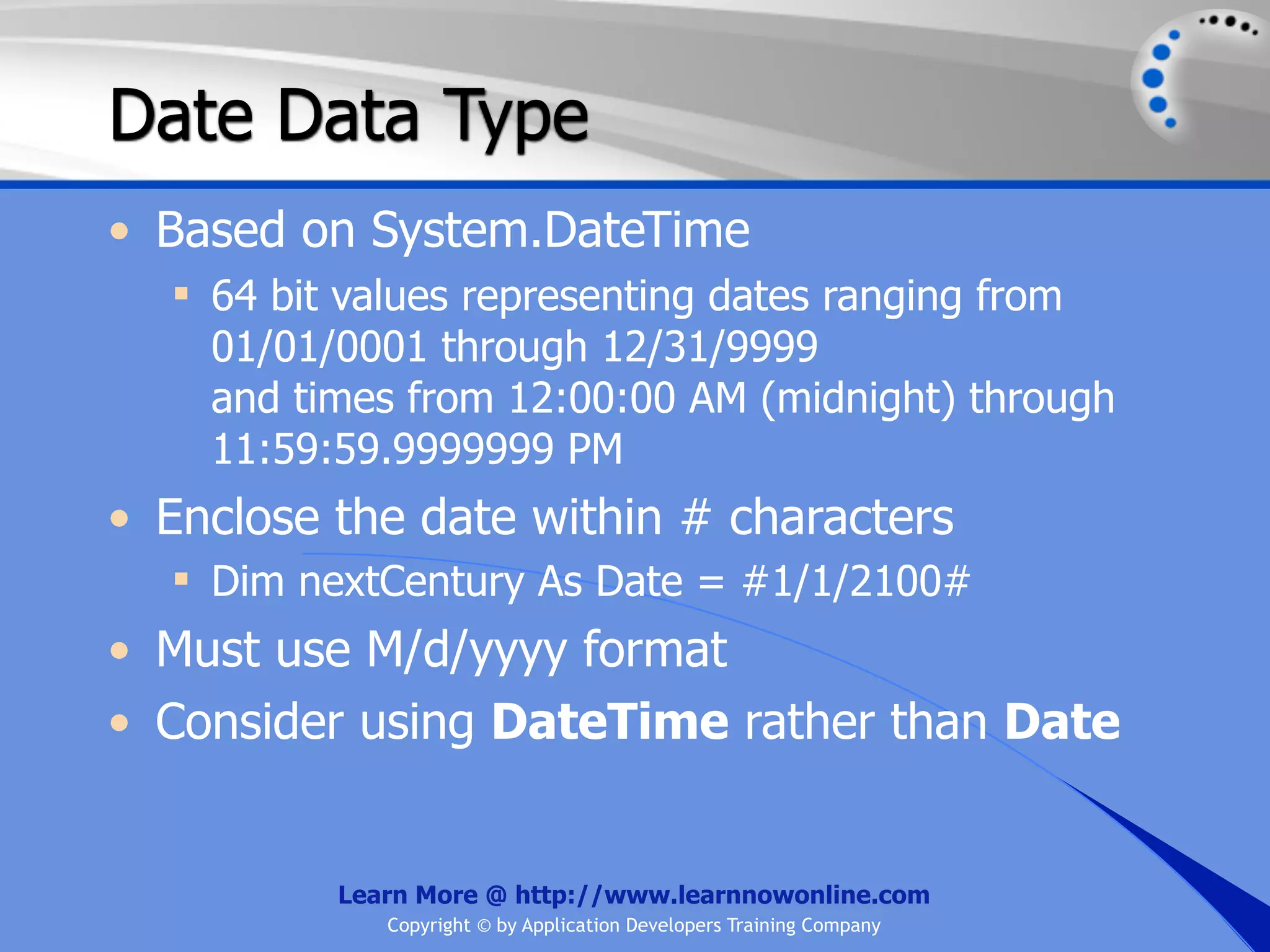
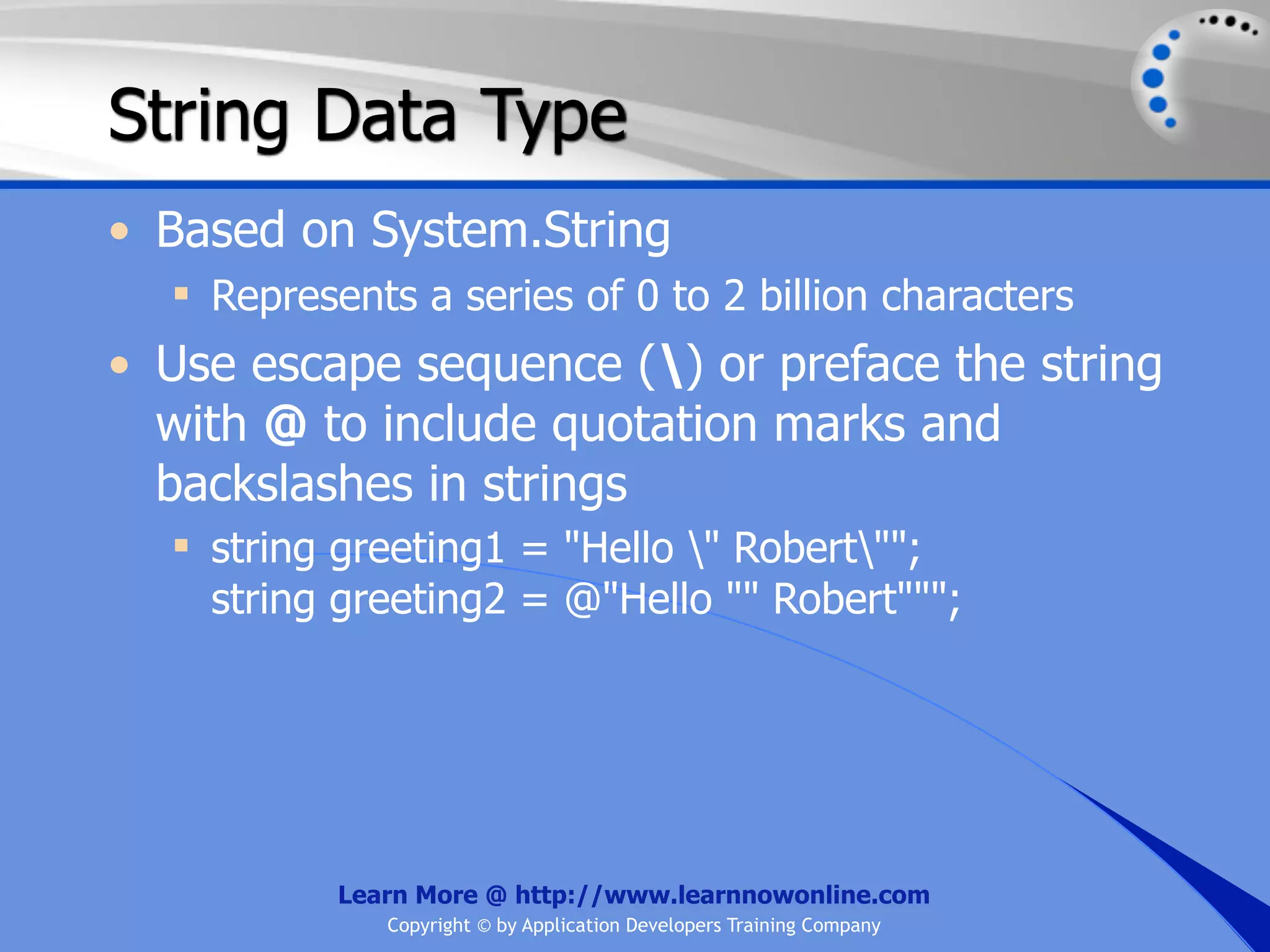
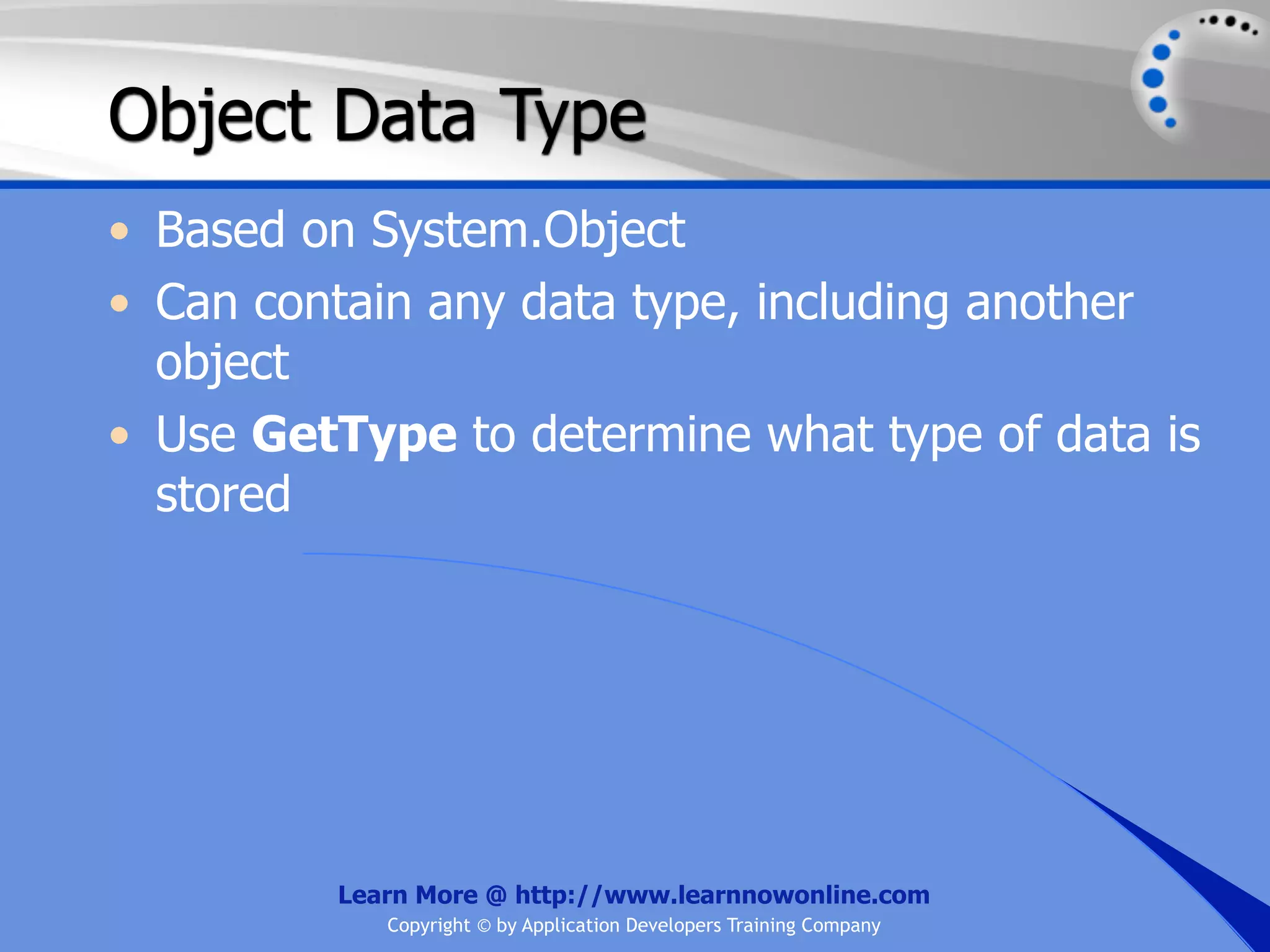
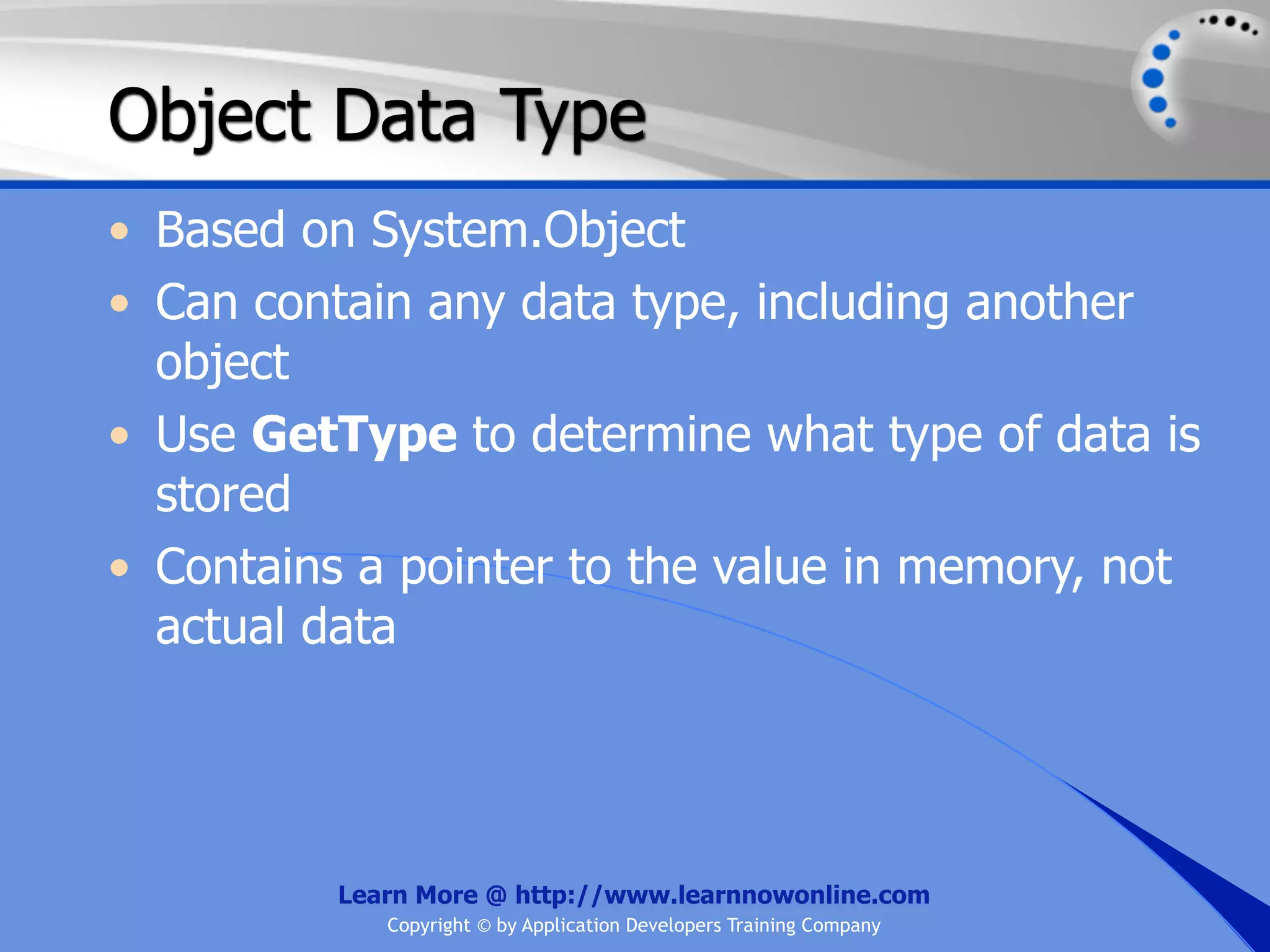







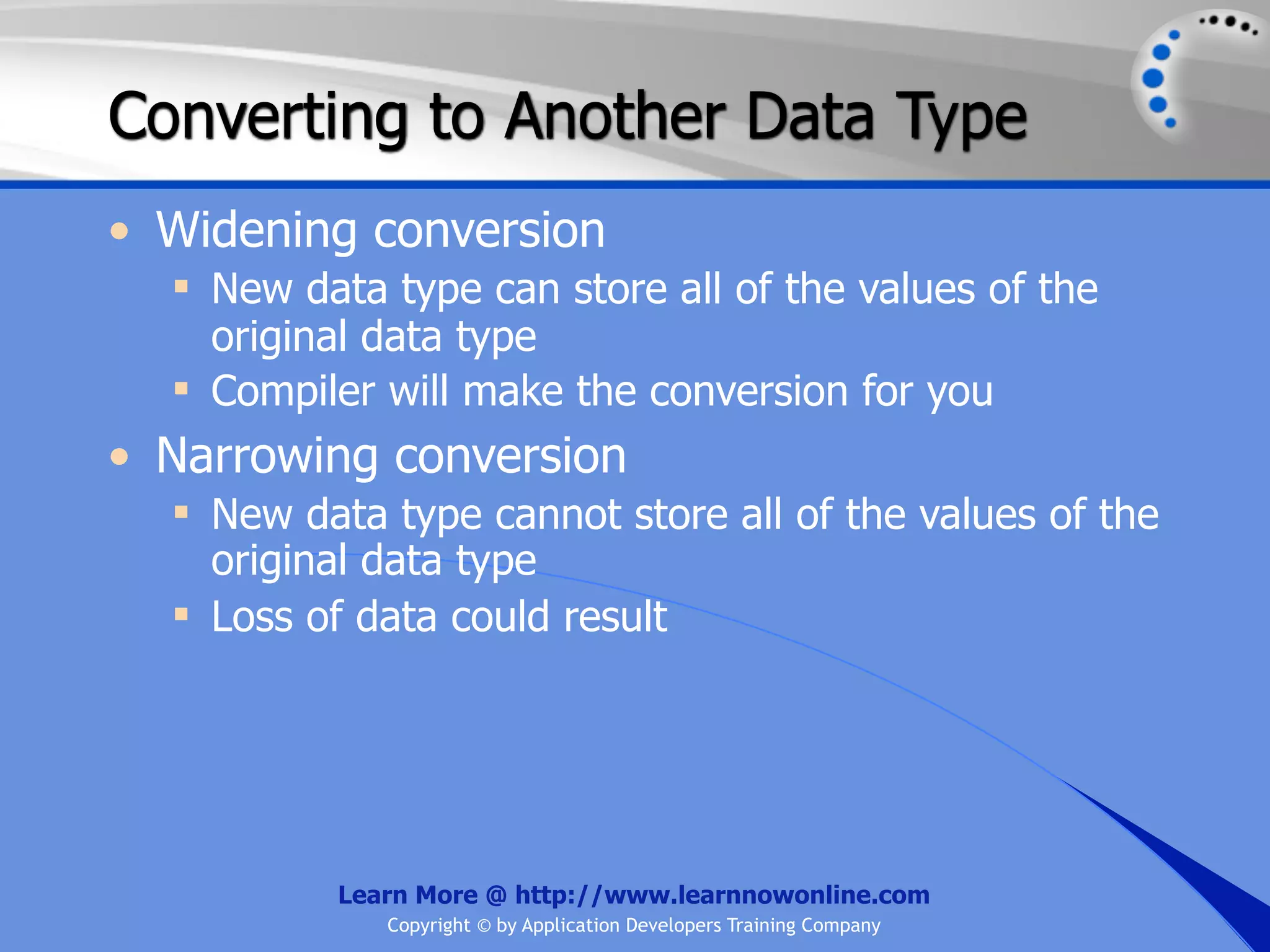
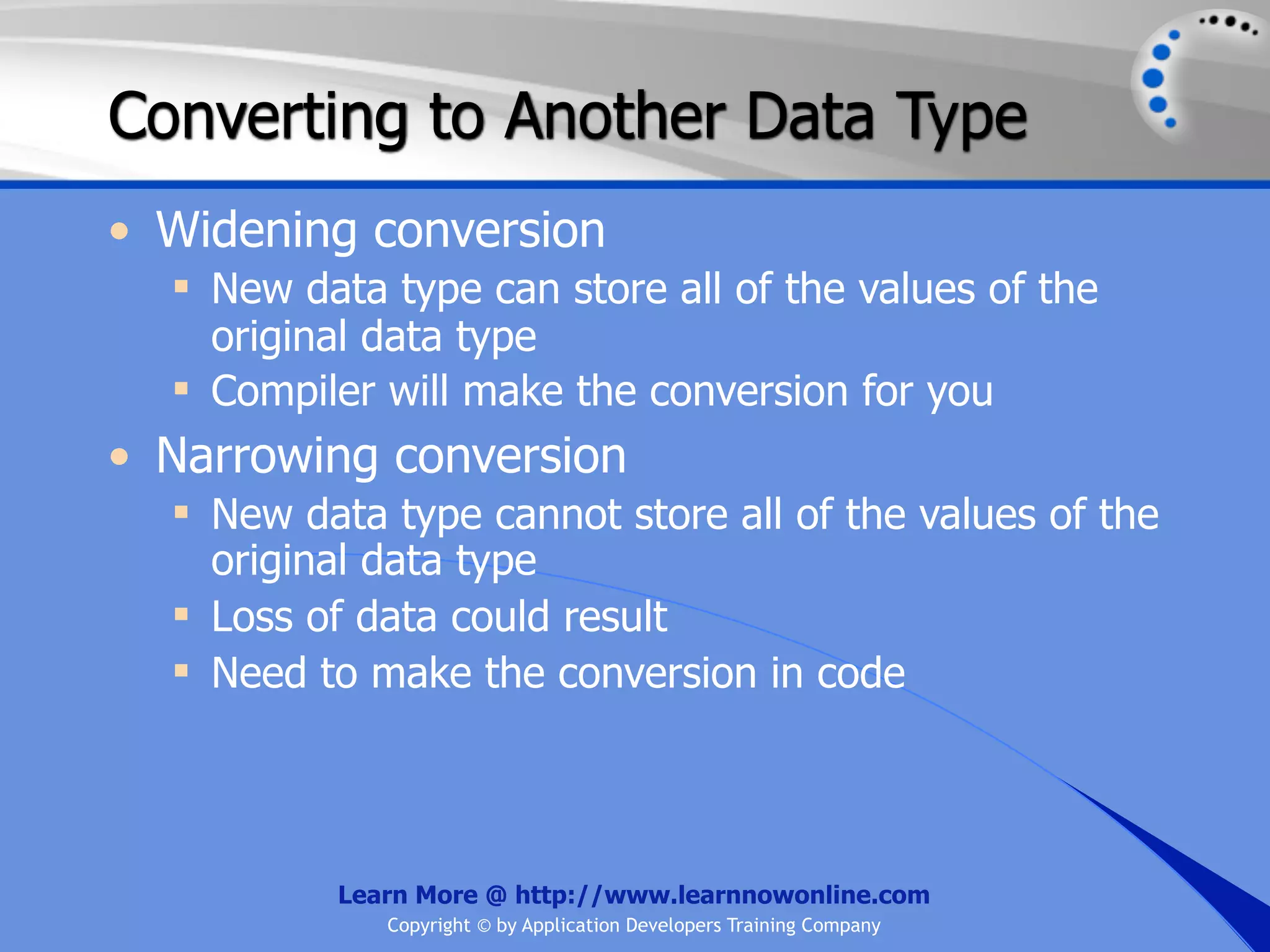
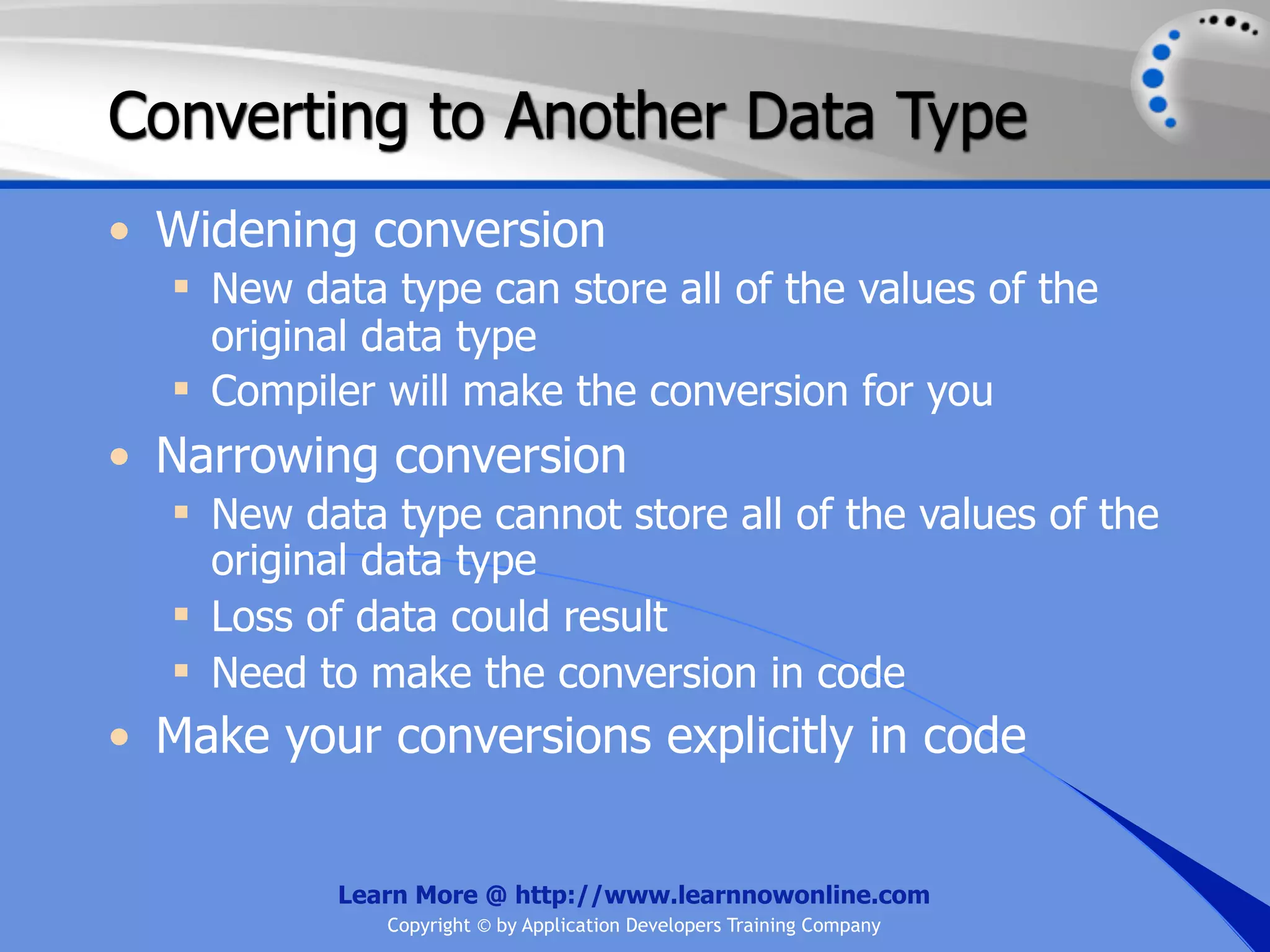
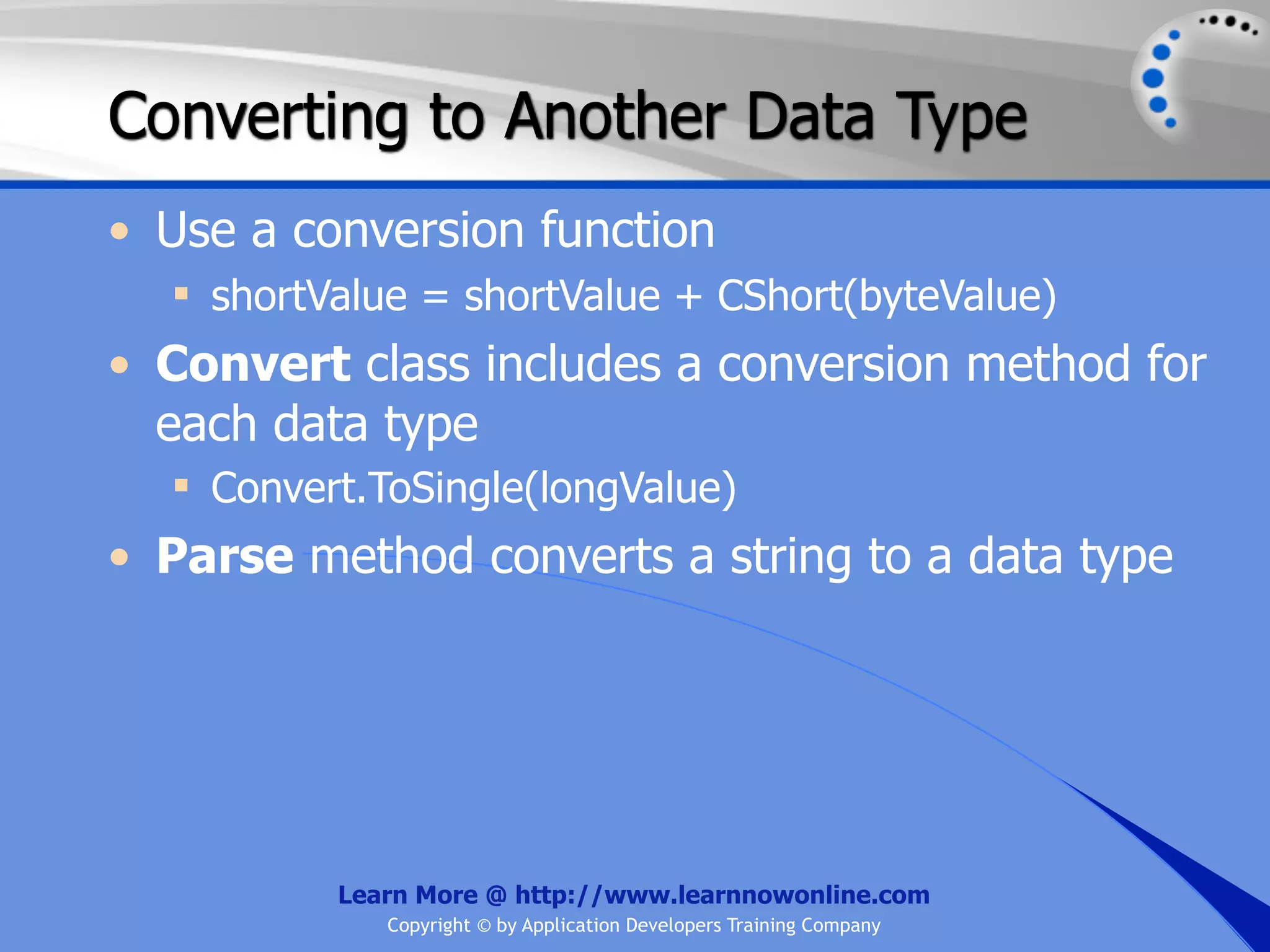
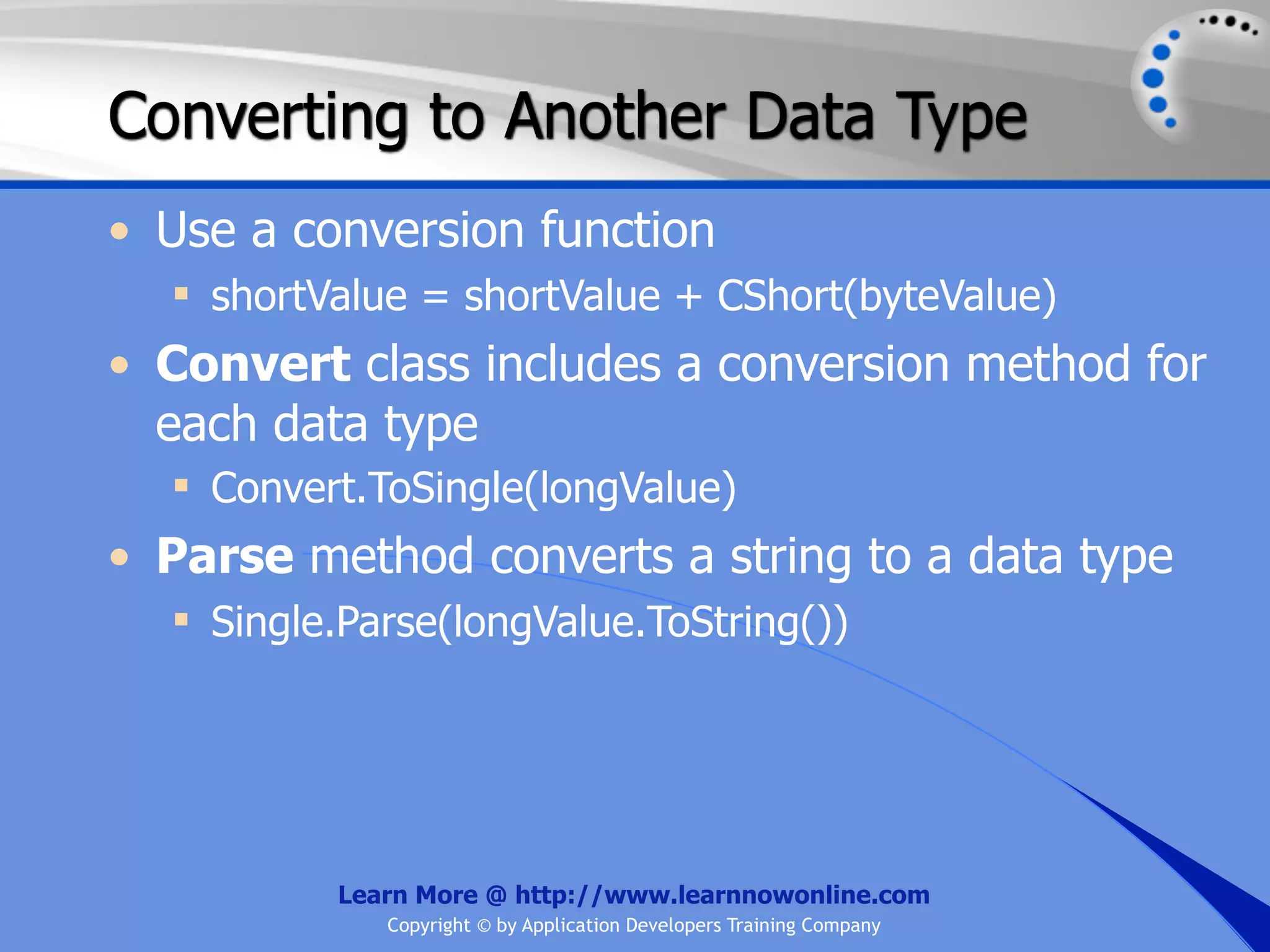
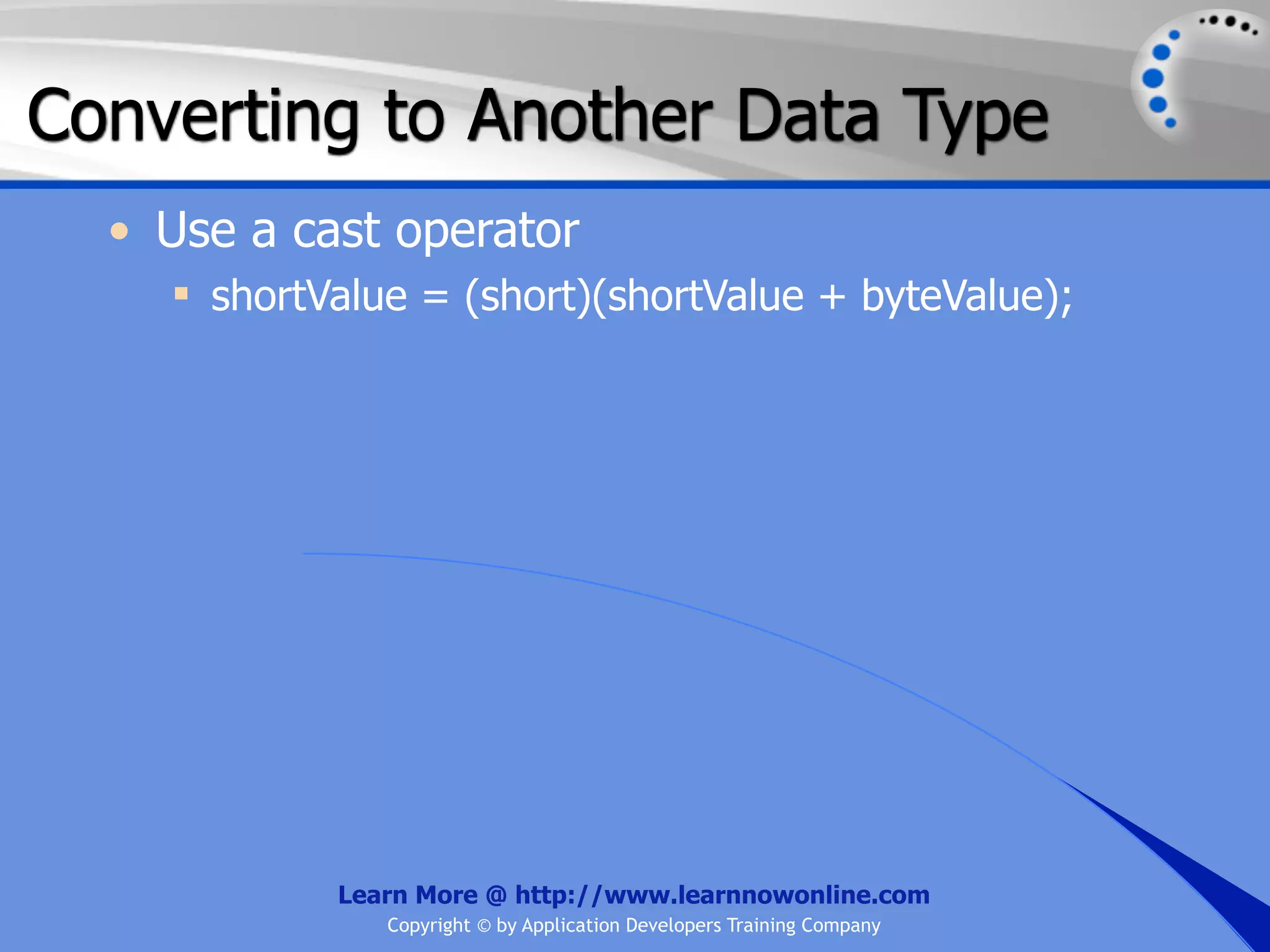
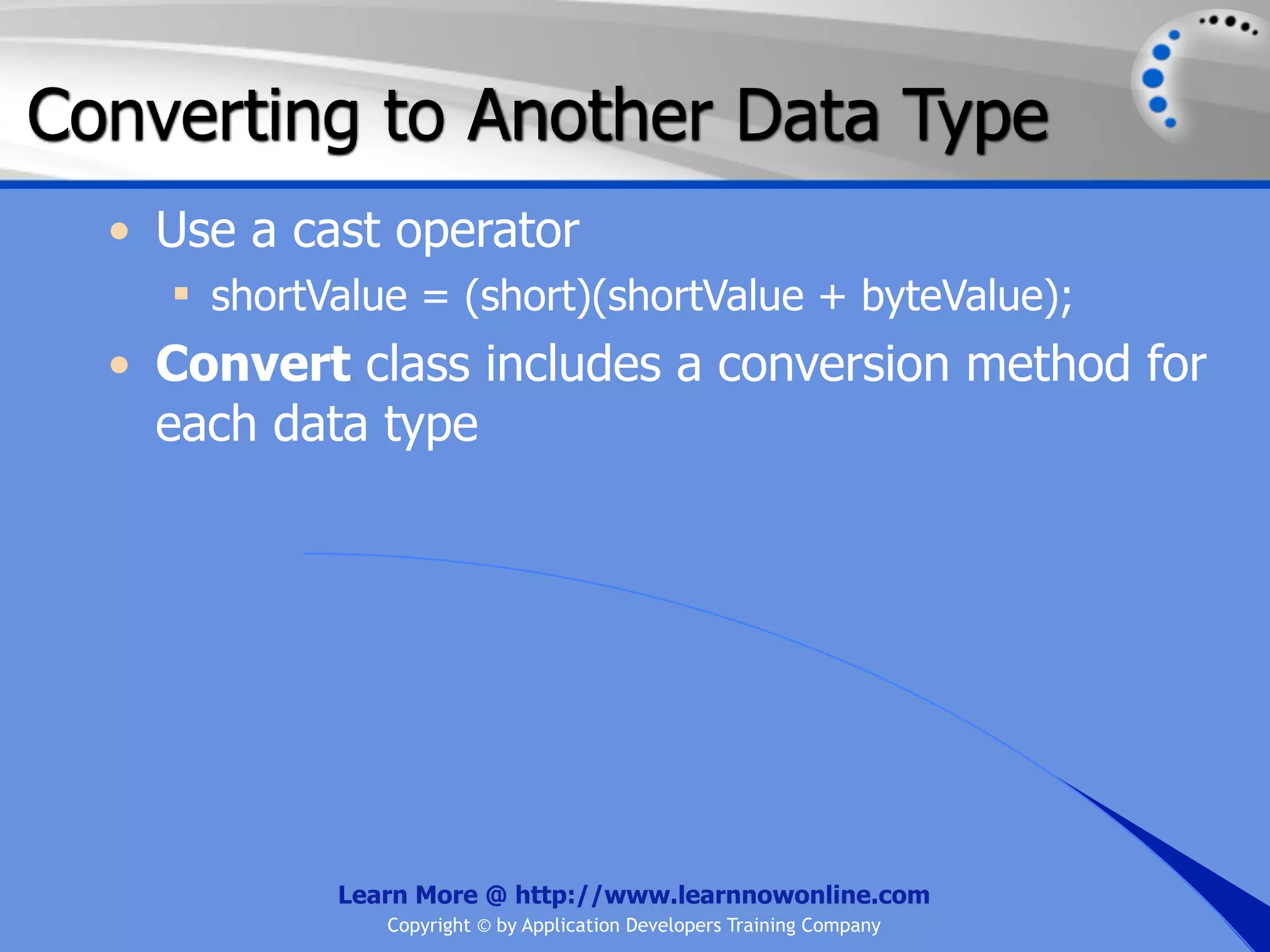
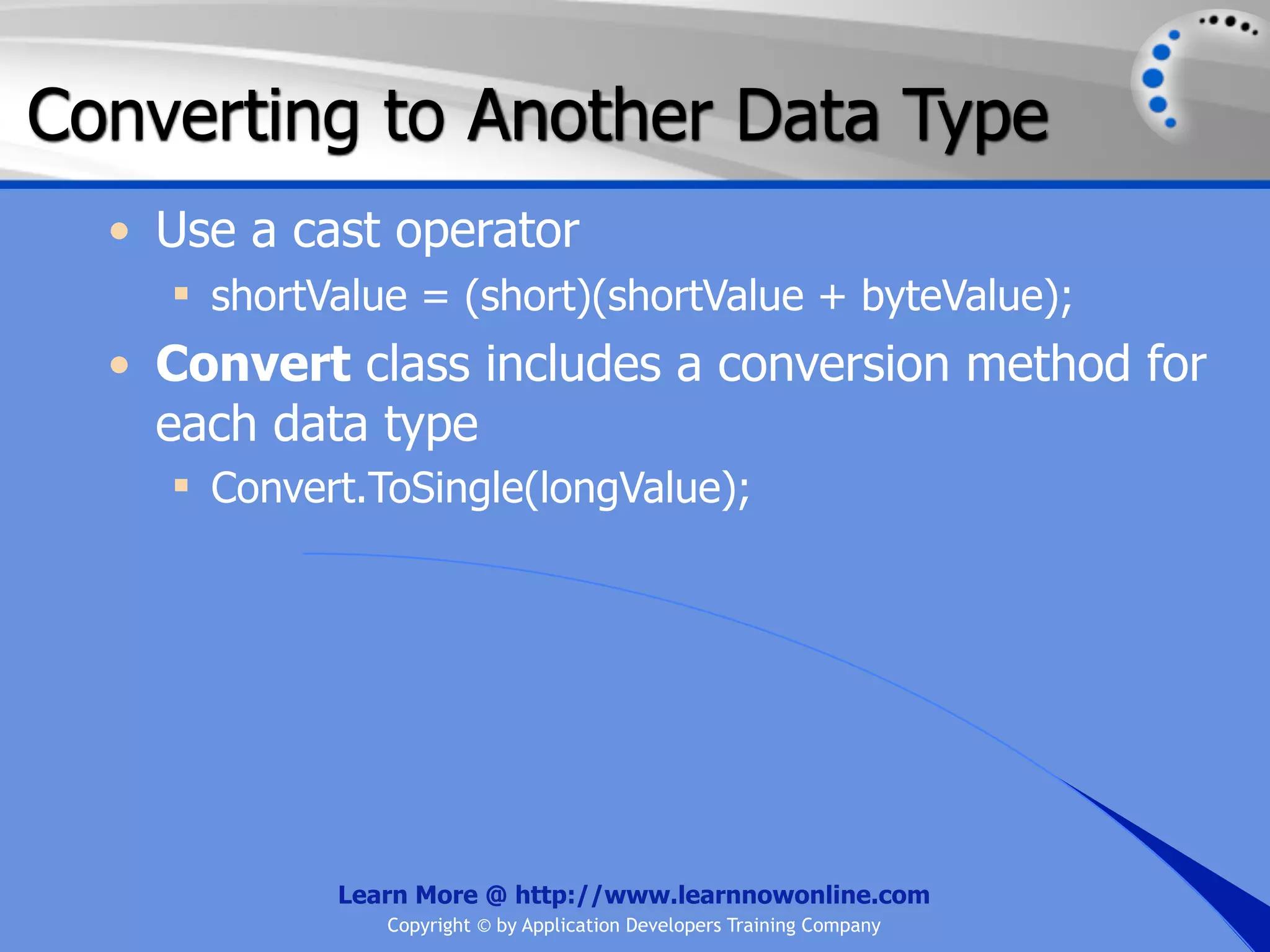
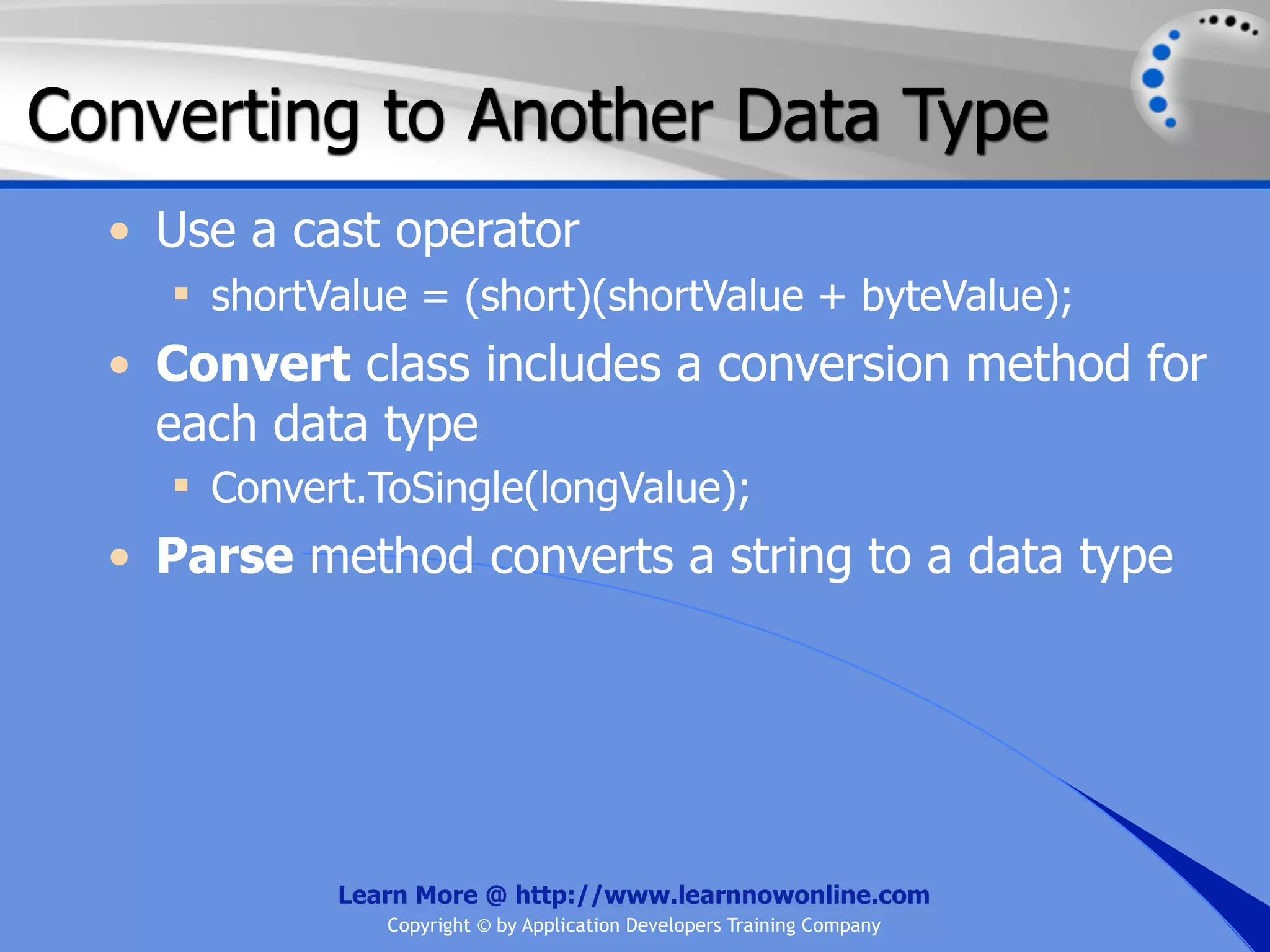
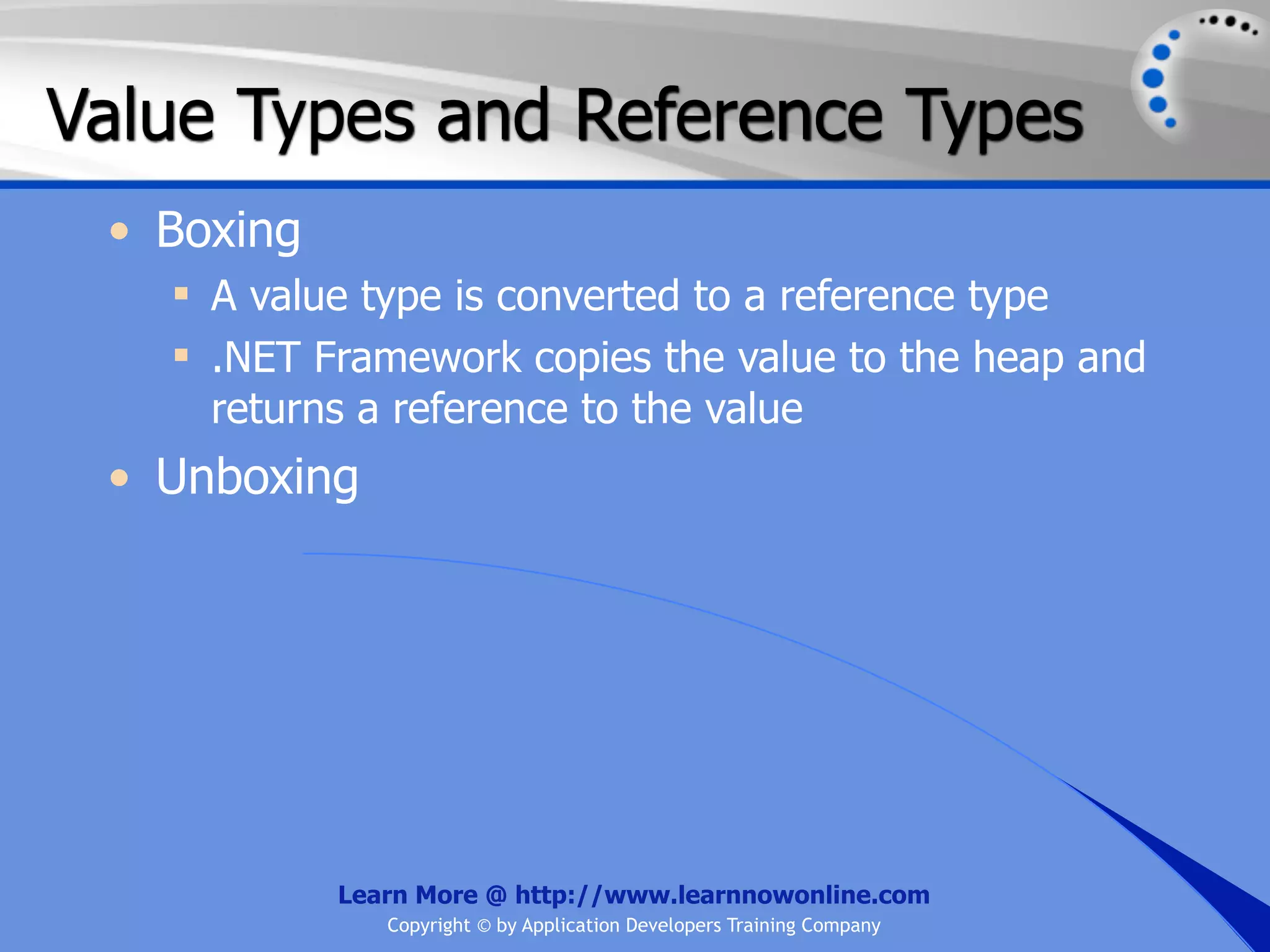
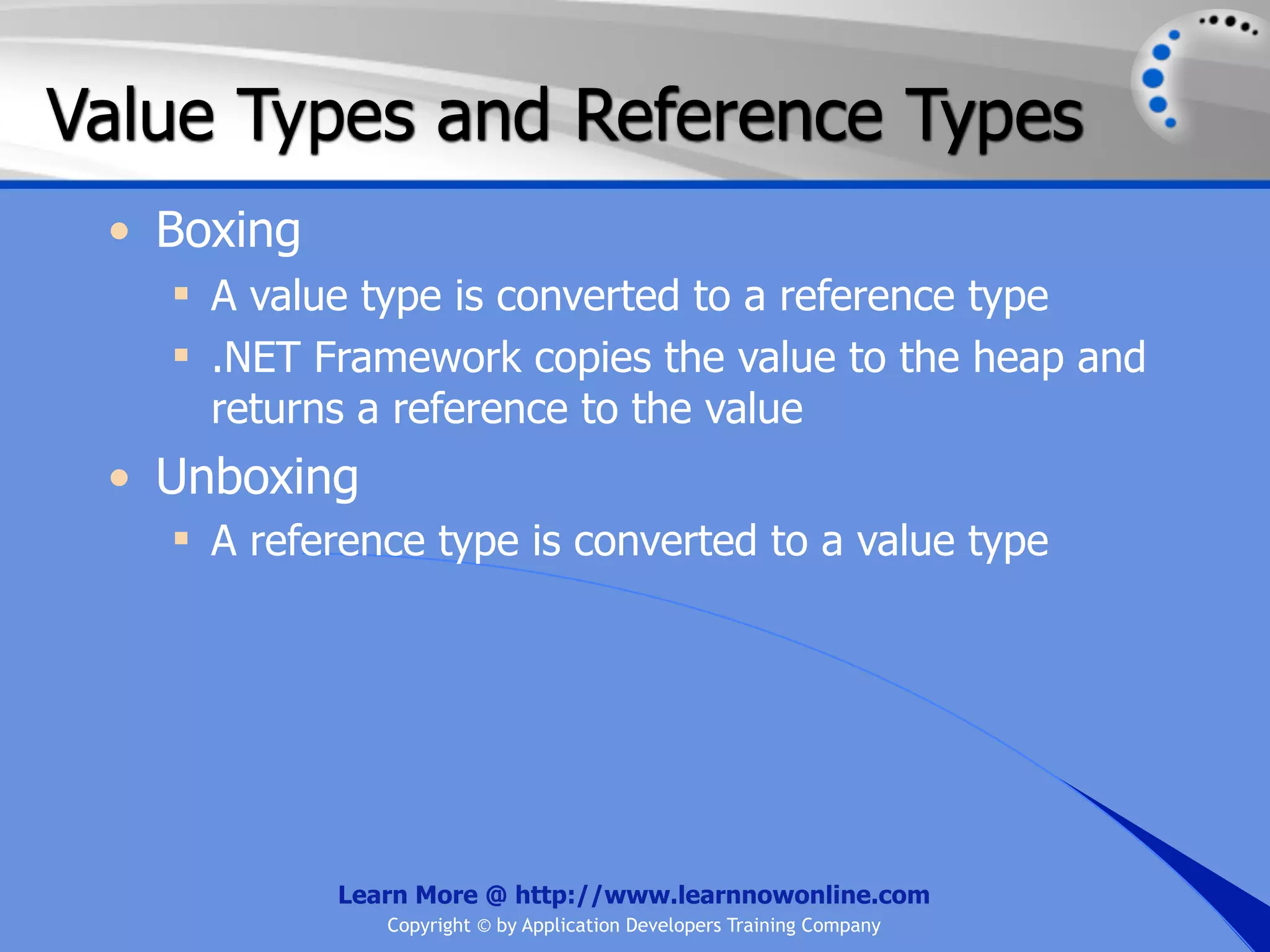
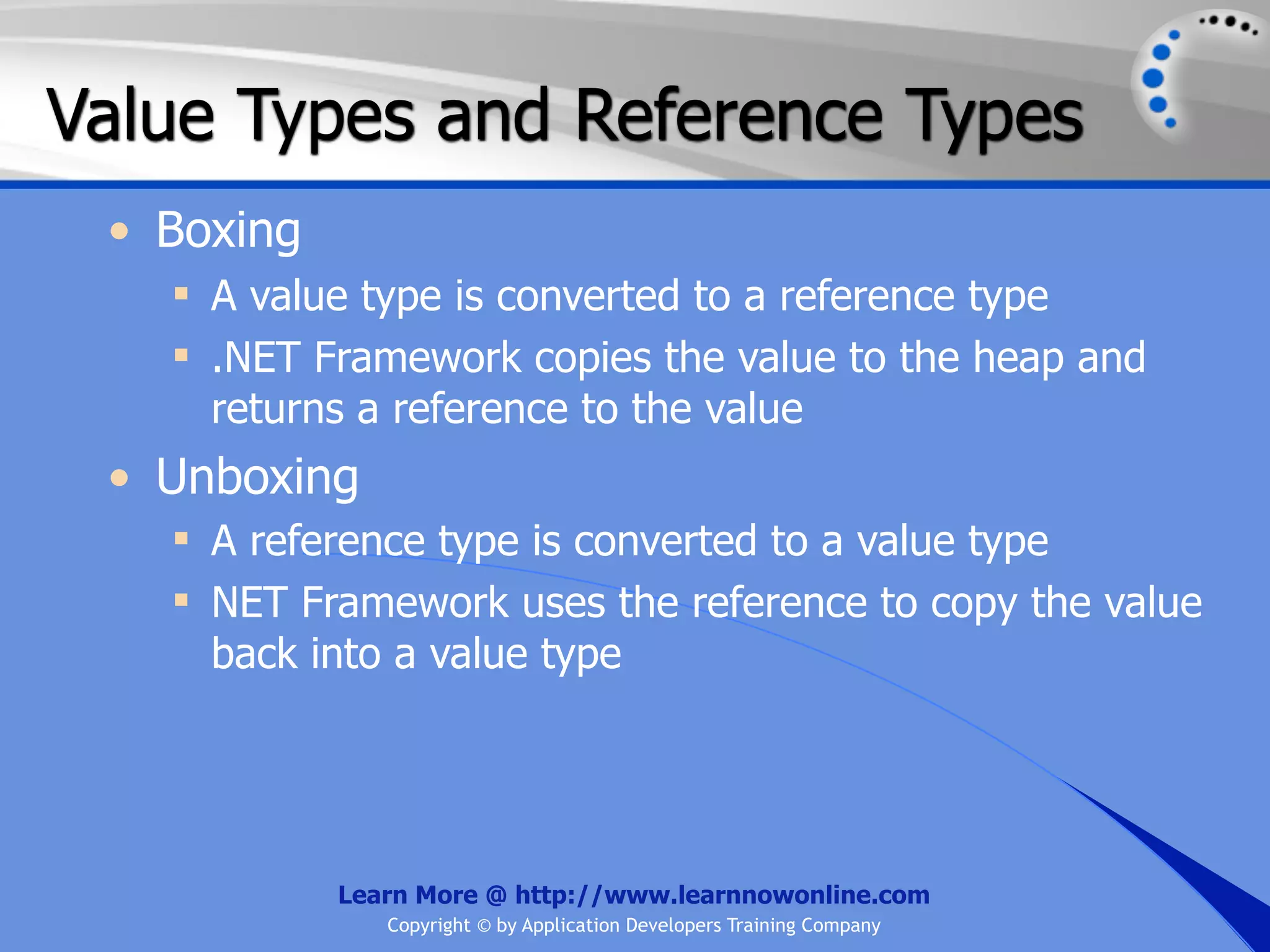

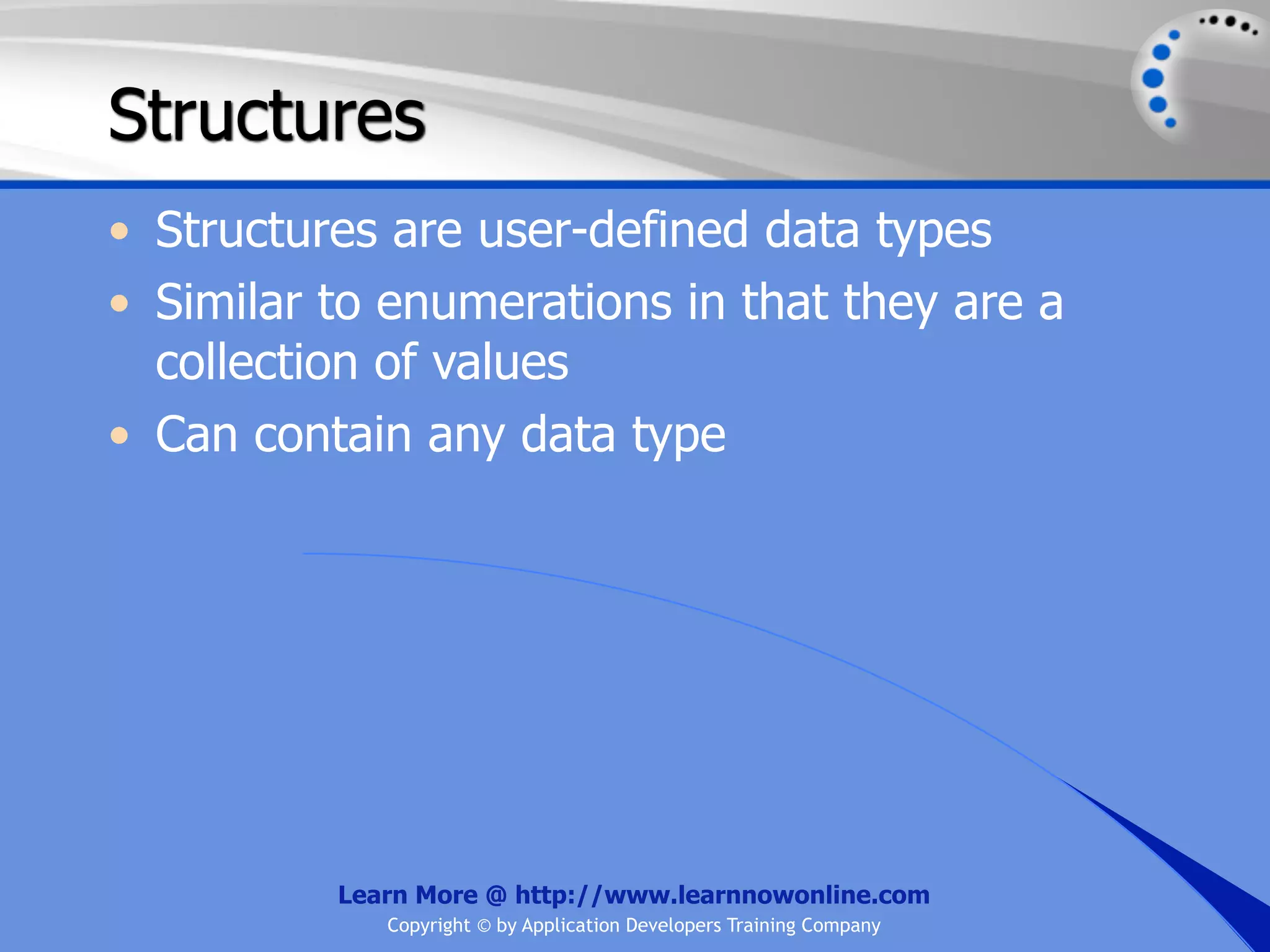
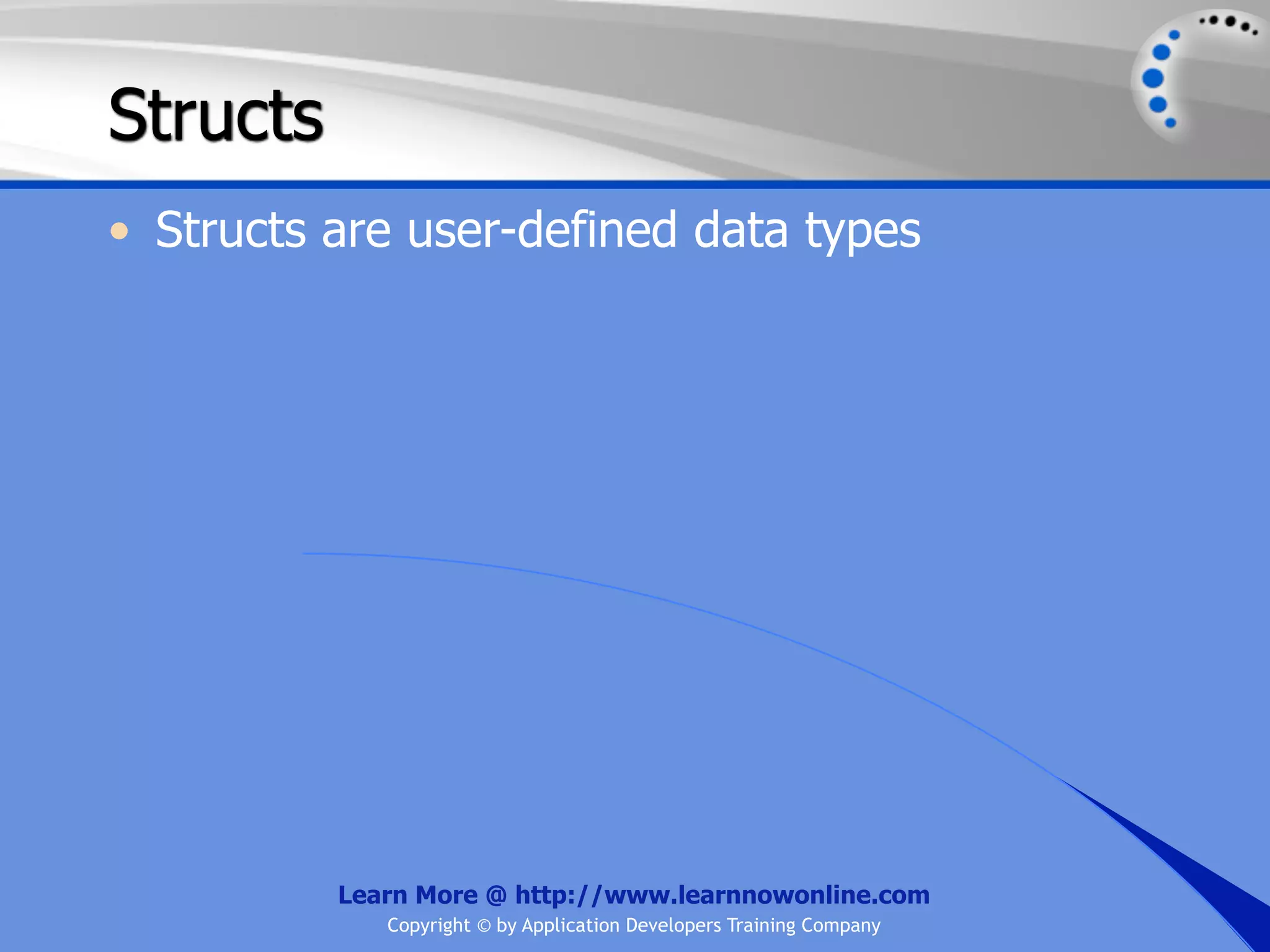
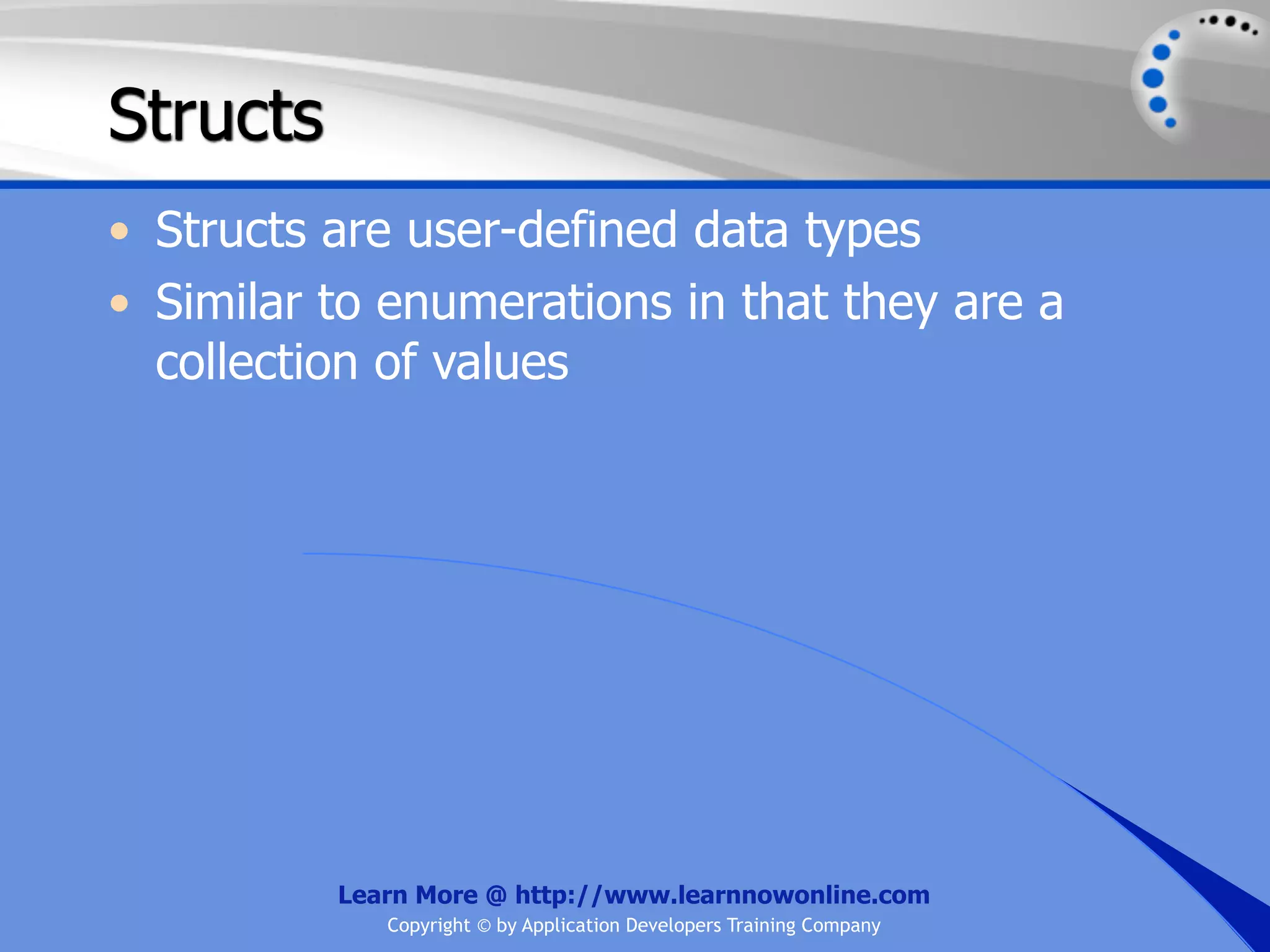



























![String Operators • & and + operators concatenate, or add, two strings together to produce a new string • Use Like to determine if a string matches a pattern Use a * in the pattern to match to zero or more characters Use a ? in the pattern to match to any single character Use a # in the pattern to match to any single digit Use a [] in the pattern to match to a list of Learn More @ http://www.learnnowonline.com Copyright © by Application Developers Training Company](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch02-variablesanddatatypes-120913140740-phpapp01/75/NET-Variables-and-Data-Types-263-2048.jpg)