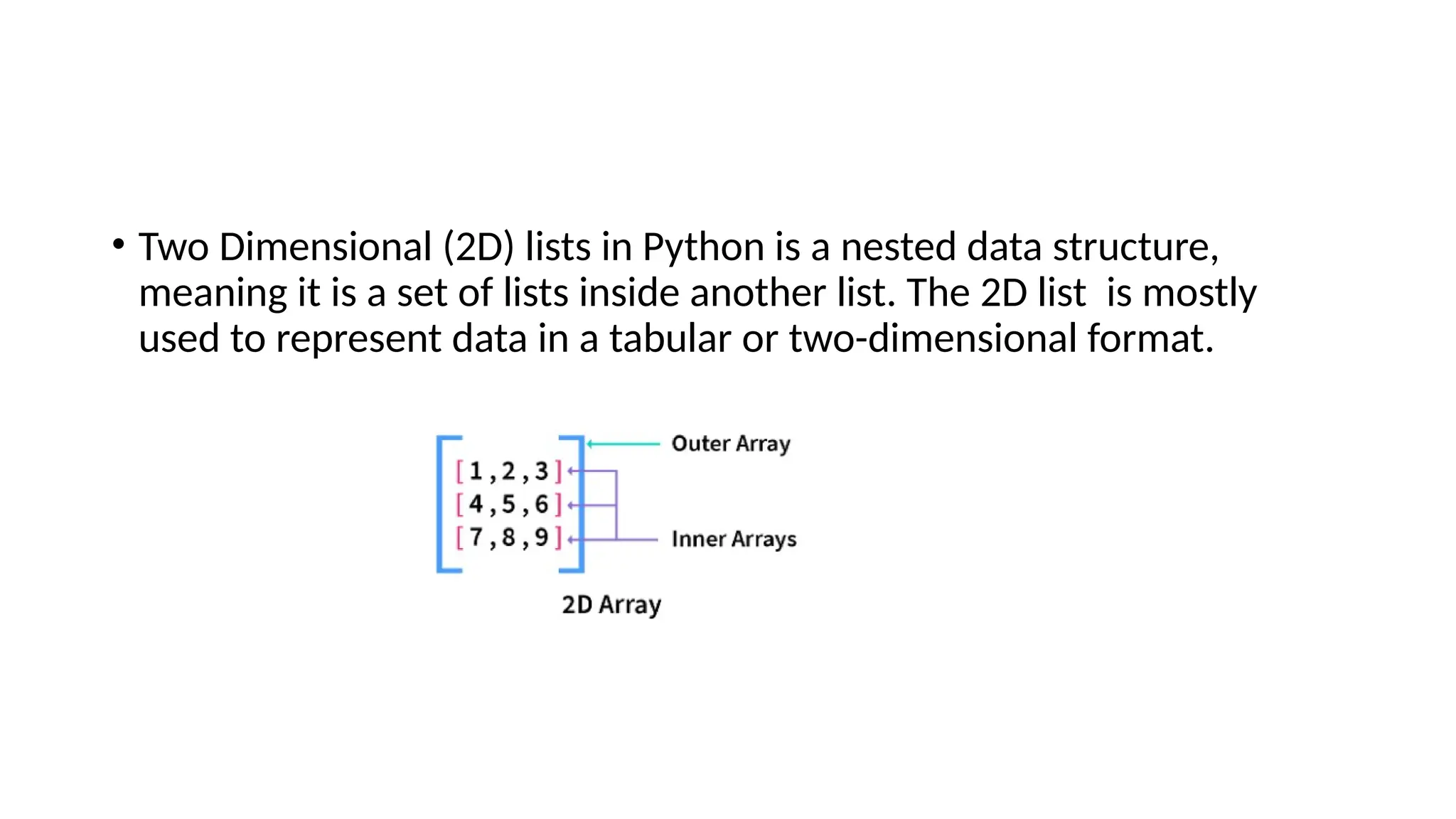
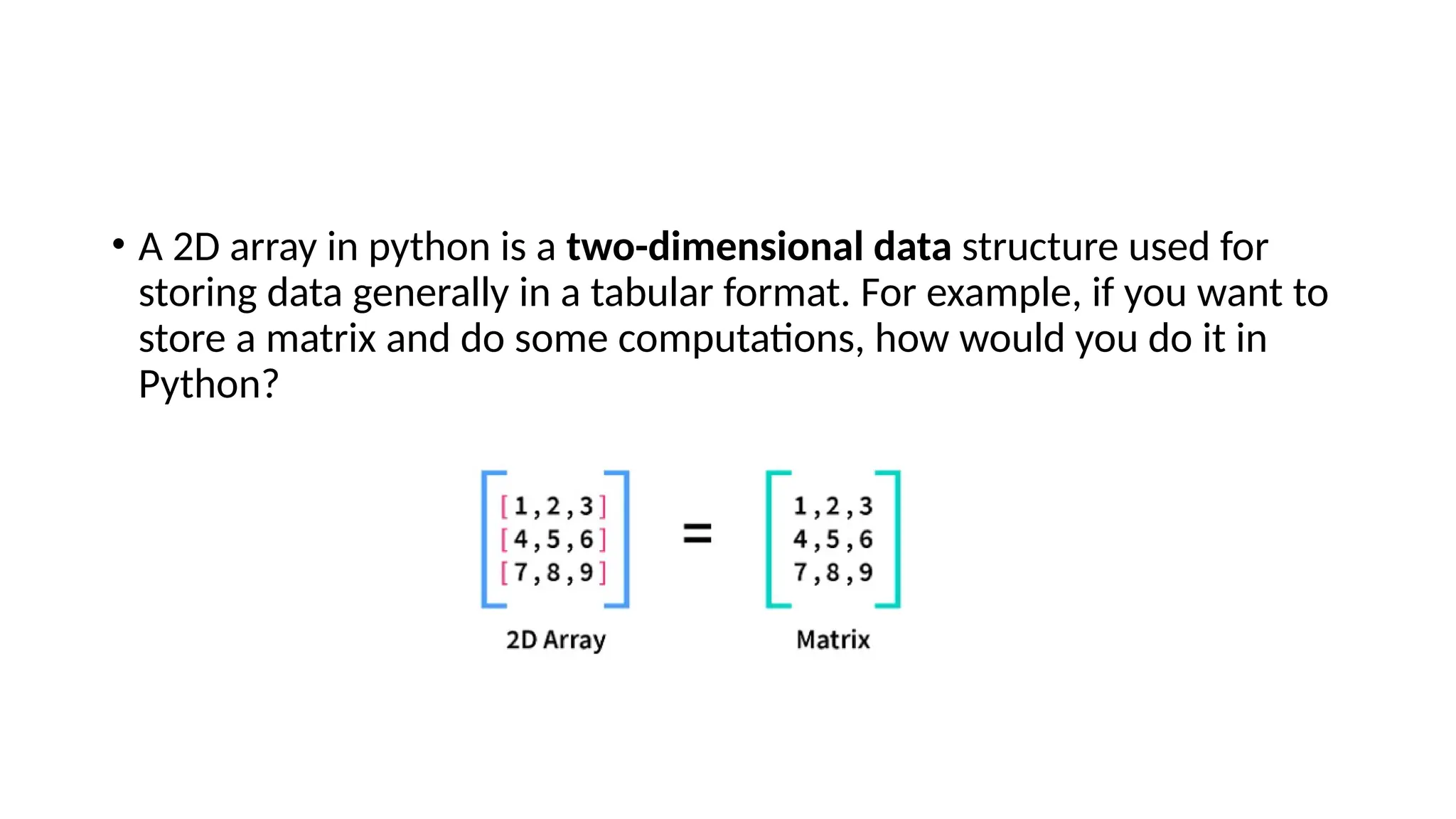
The document explains two-dimensional lists (2D arrays) in Python, which are nested data structures used to represent data in a tabular format. It covers syntax for defining, accessing, traversing, inserting, and updating elements within 2D arrays, emphasizing the use of row and column indices. Examples demonstrate these operations clearly, providing practical insights into working with 2D arrays in Python.


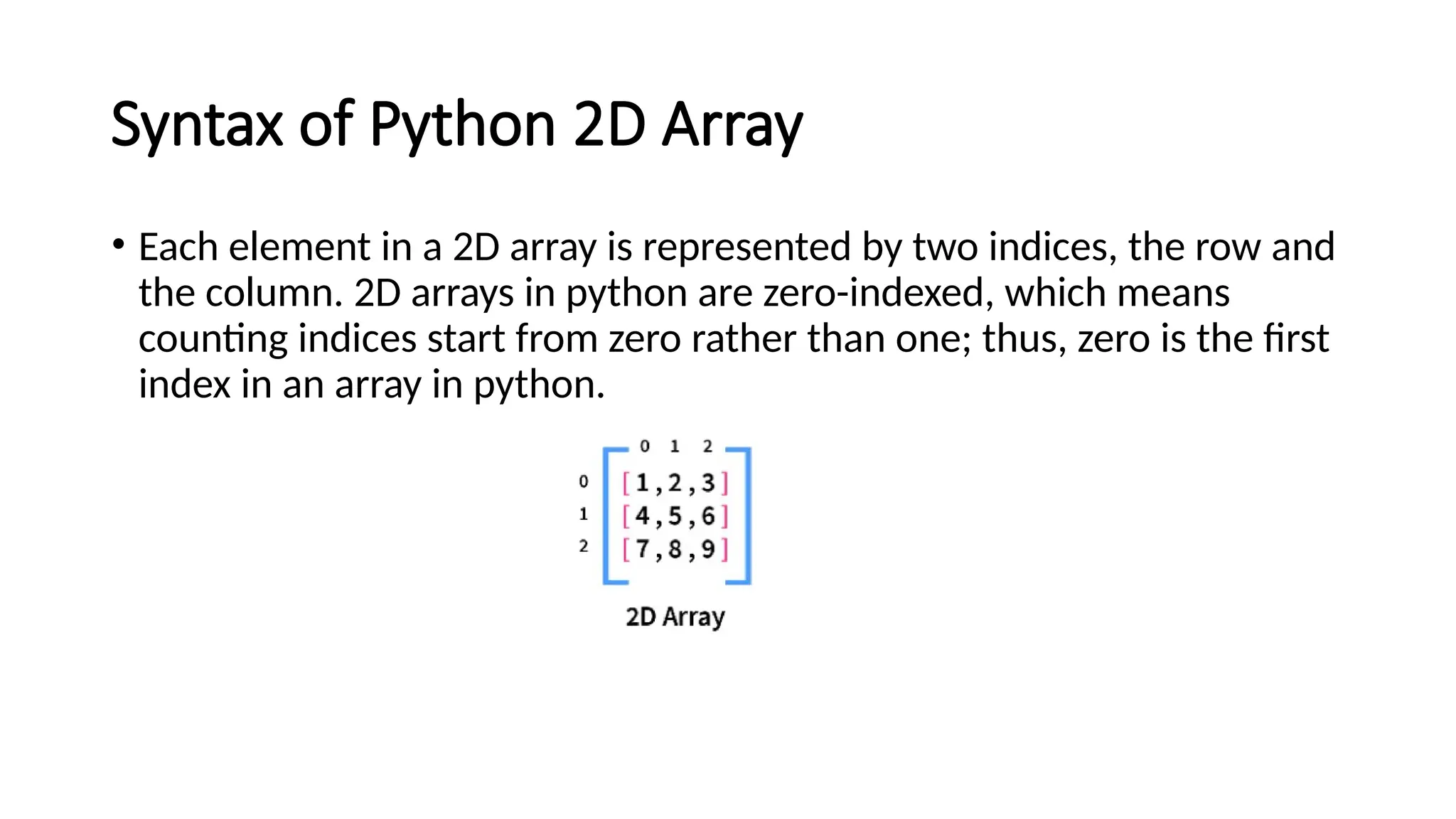
![Syntax of Python 2D Array • array_name=[[r1c1,r1c2,r1c3,..],[r2c1,r2c2,r2c3,...],. . . .] • Where array_name is the array's name, r1c1, r1c1 etc., are elements of the array. Here r1c1 means that it is the element of the first column of the first row. A 2D array is an array of arrays. • Example: • # Define the two-dimensional list • array_name = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionallist-241007082934-653b6311/75/Nested-lists-Two-dimensional-lists-for-Python-6-2048.jpg)
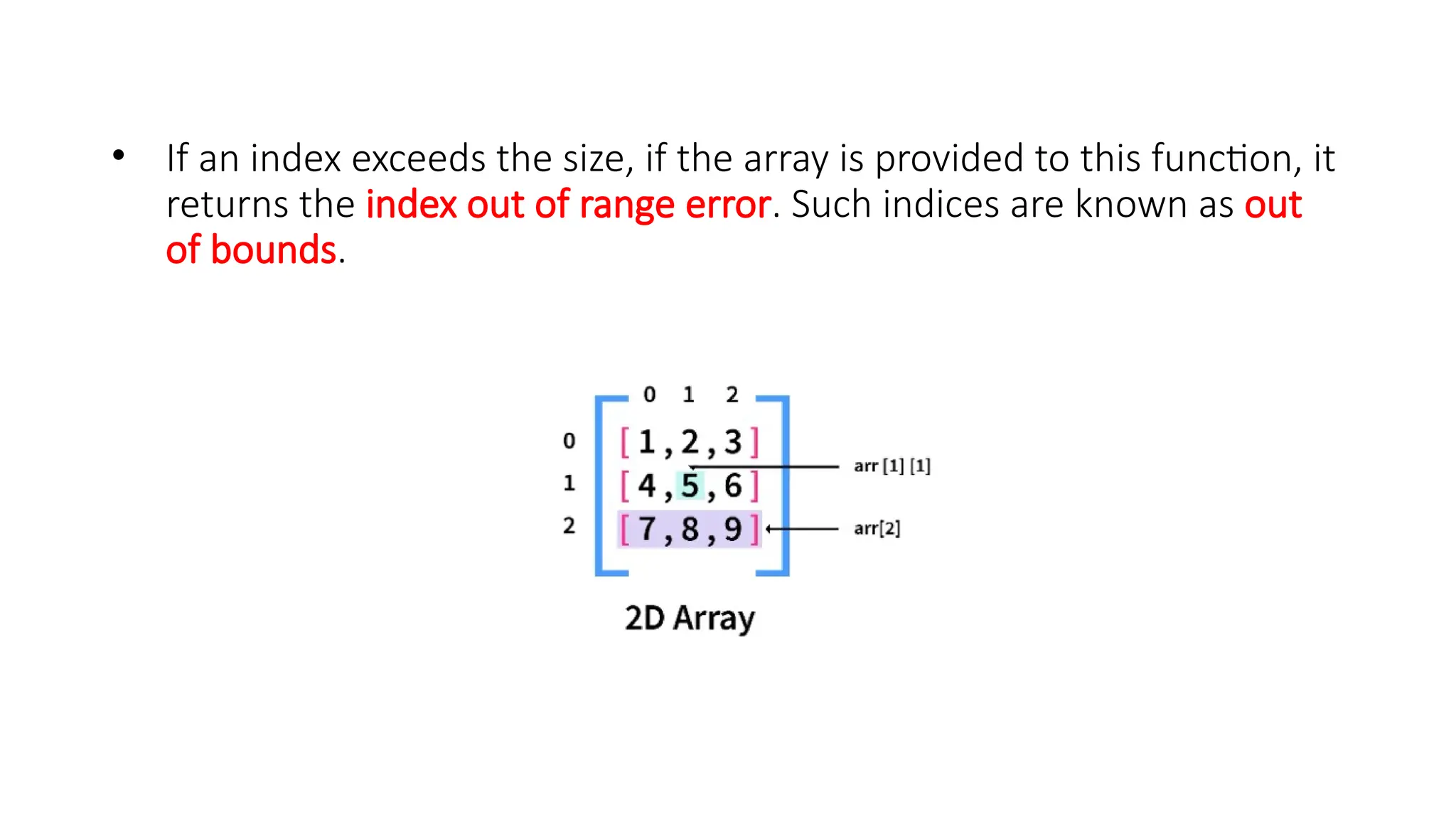
![Accessing Values in Python 2D Array • We can directly access values or elements of a 2D array in Python. It can be done by using the row and column indices of the element to be accessed. It has the following syntax: • array_name[row_ind][col_ind] • EX: # Accessing elements • array_name = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9] ] • print("Element at row 1, column 1:", array_name[0][0]) # Output: 1 print("Element at row 2, column 3:", array_name[1][2]) # Output: 6 print("Element at row 3, column 2:", array_name[2][1]) # Output: 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionallist-241007082934-653b6311/75/Nested-lists-Two-dimensional-lists-for-Python-7-2048.jpg)


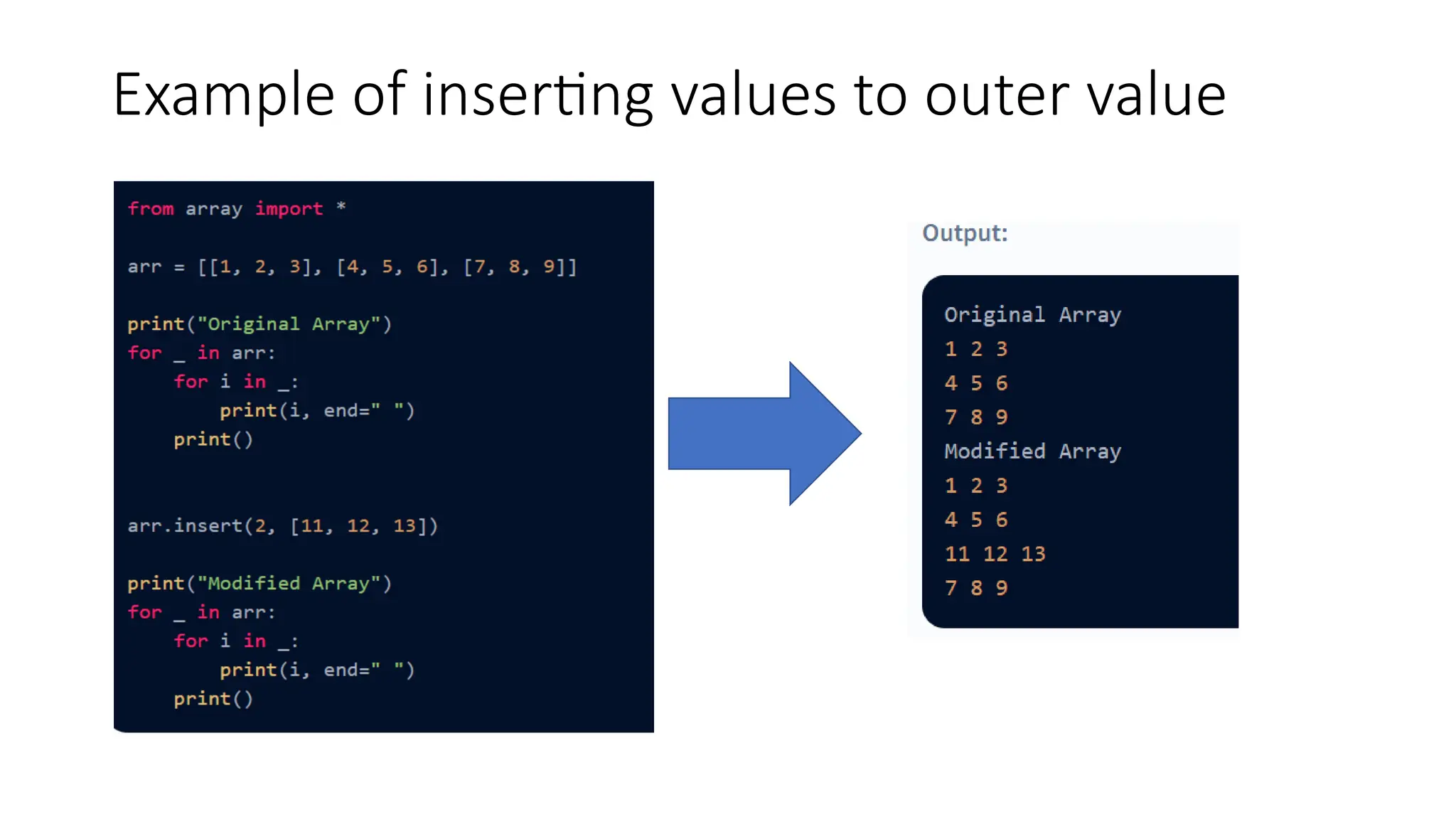
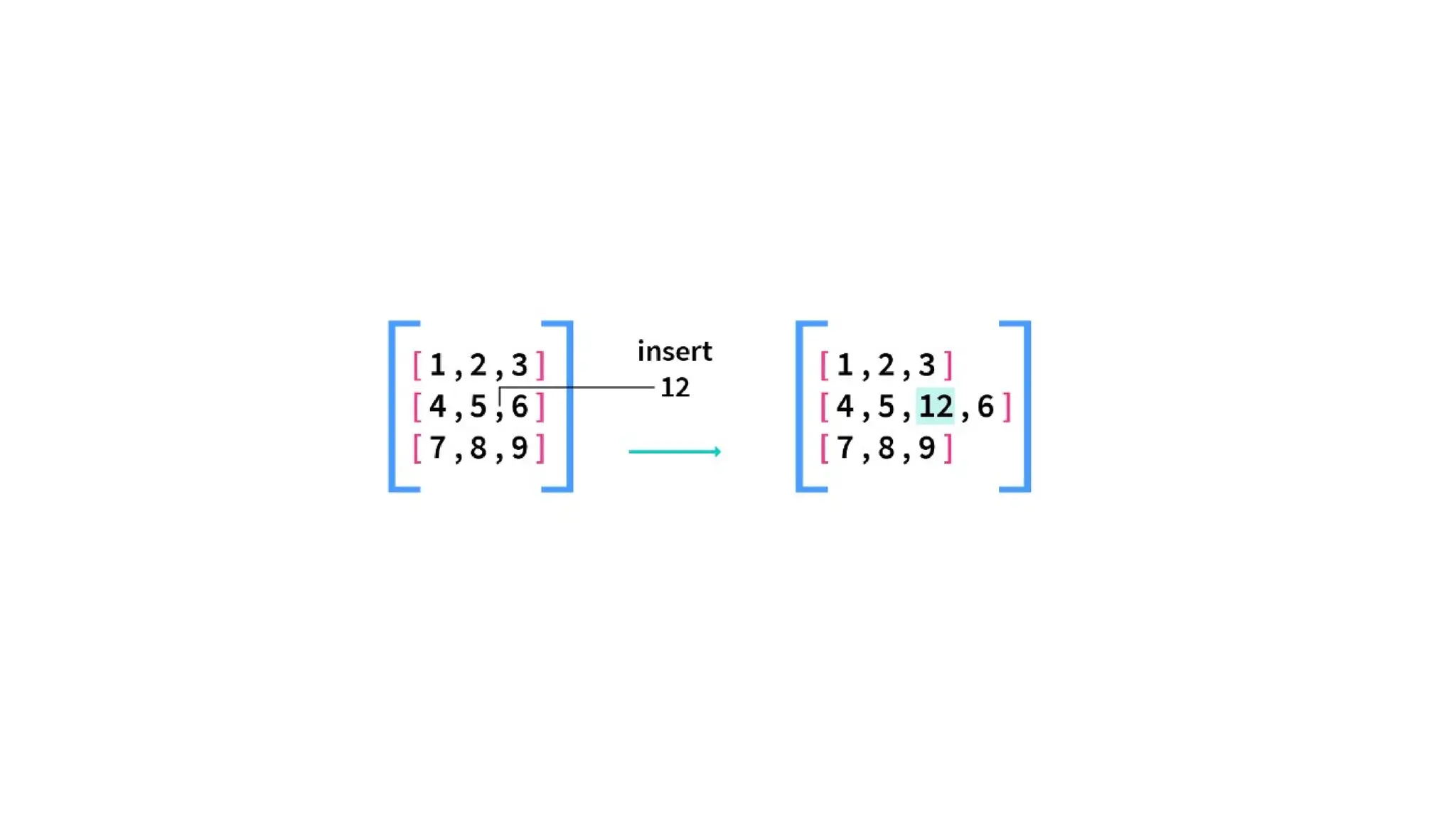
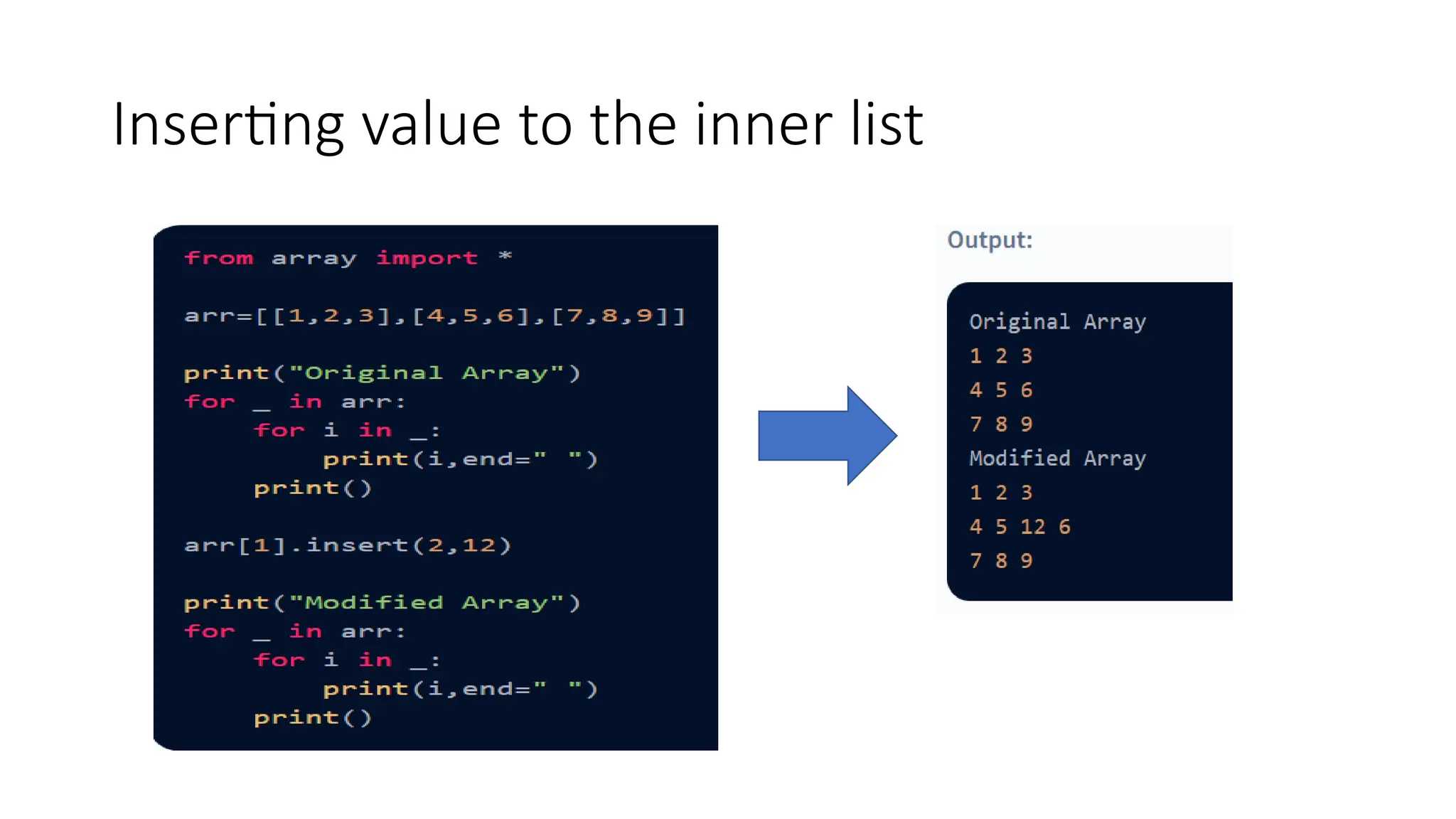
![Inserting Values in Python 2D Array • Inserting a value in an array means adding a new element at a given index in the array and then shifting the remaining elements accordingly. 1. Adding a New Element in the Outer Array. arr1.insert(ind,arr_insert) 2. Adding a New Element in the Inner Array. arr1[r].insert(ind,arr_insert)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionallist-241007082934-653b6311/75/Nested-lists-Two-dimensional-lists-for-Python-11-2048.jpg)
![Updating Values in Python 2D Array • arr_name[r][c]=new_element • It Single element and inner list update types • Example: arr[1][2]=16 will update single element of list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionallist-241007082934-653b6311/75/Nested-lists-Two-dimensional-lists-for-Python-15-2048.jpg)
![Updating inner list • If you want to update inner list • new_arr=[10,11,12] • arr[1]=new_arr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twodimensionallist-241007082934-653b6311/75/Nested-lists-Two-dimensional-lists-for-Python-16-2048.jpg)







