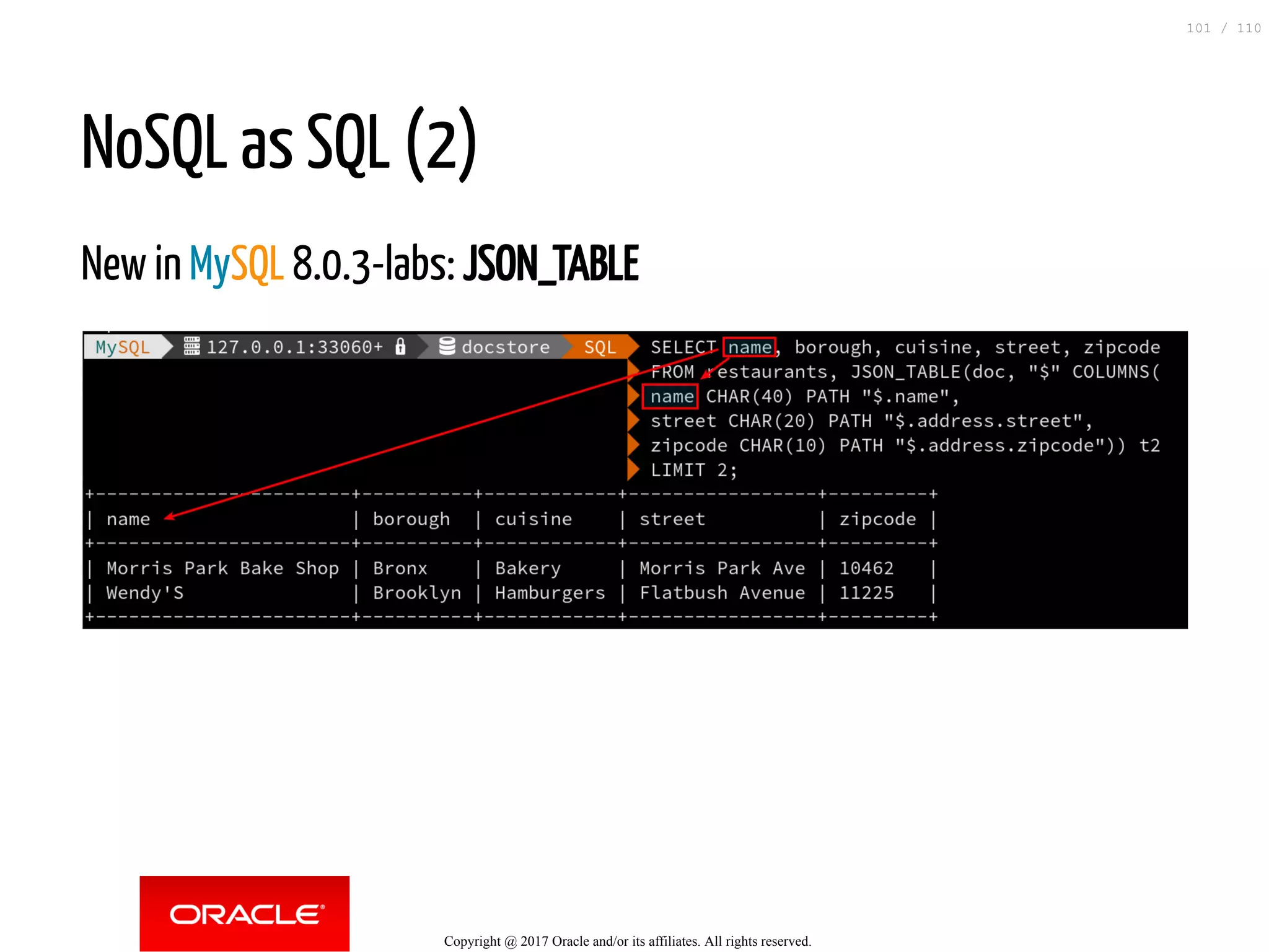
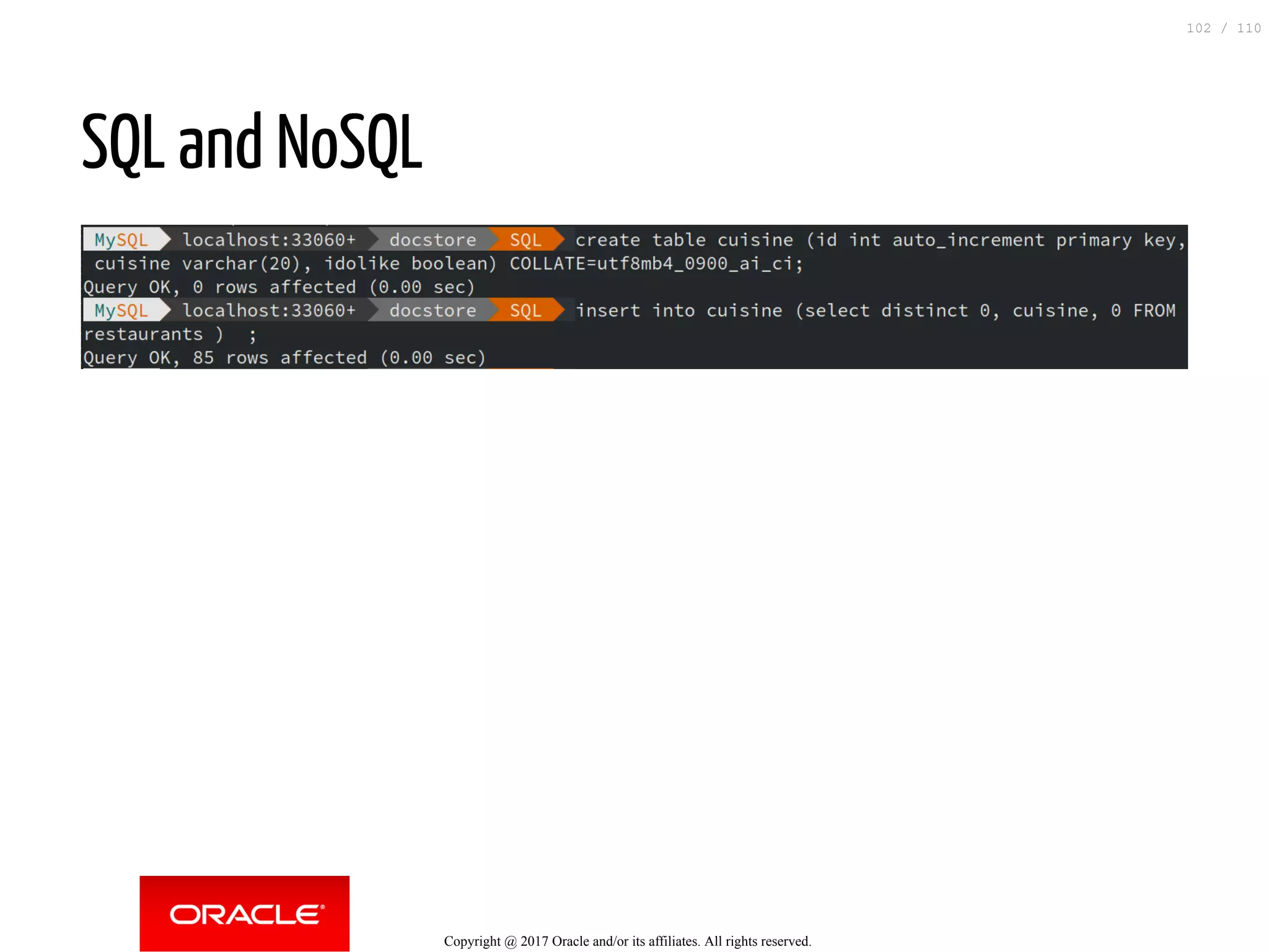
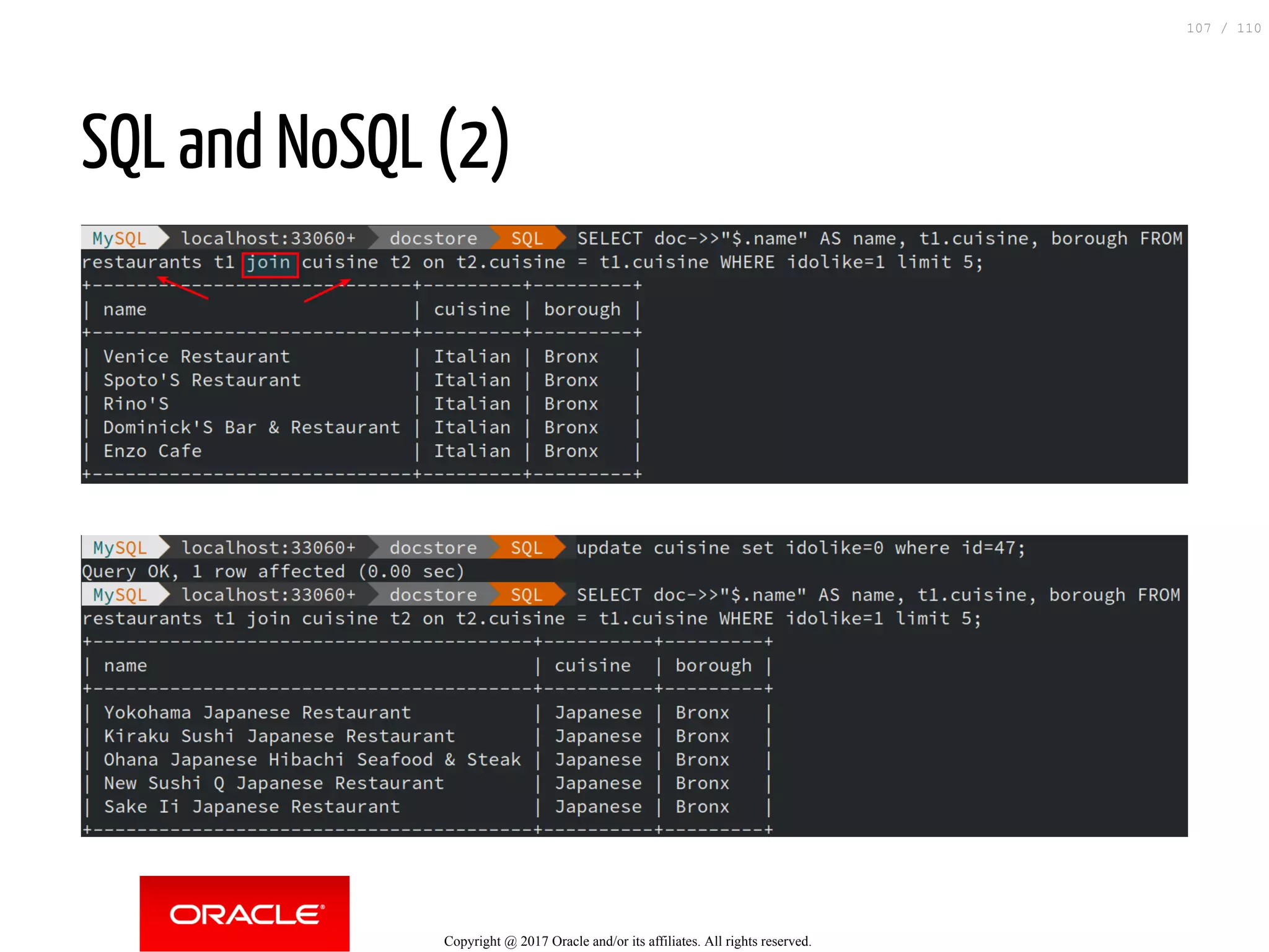
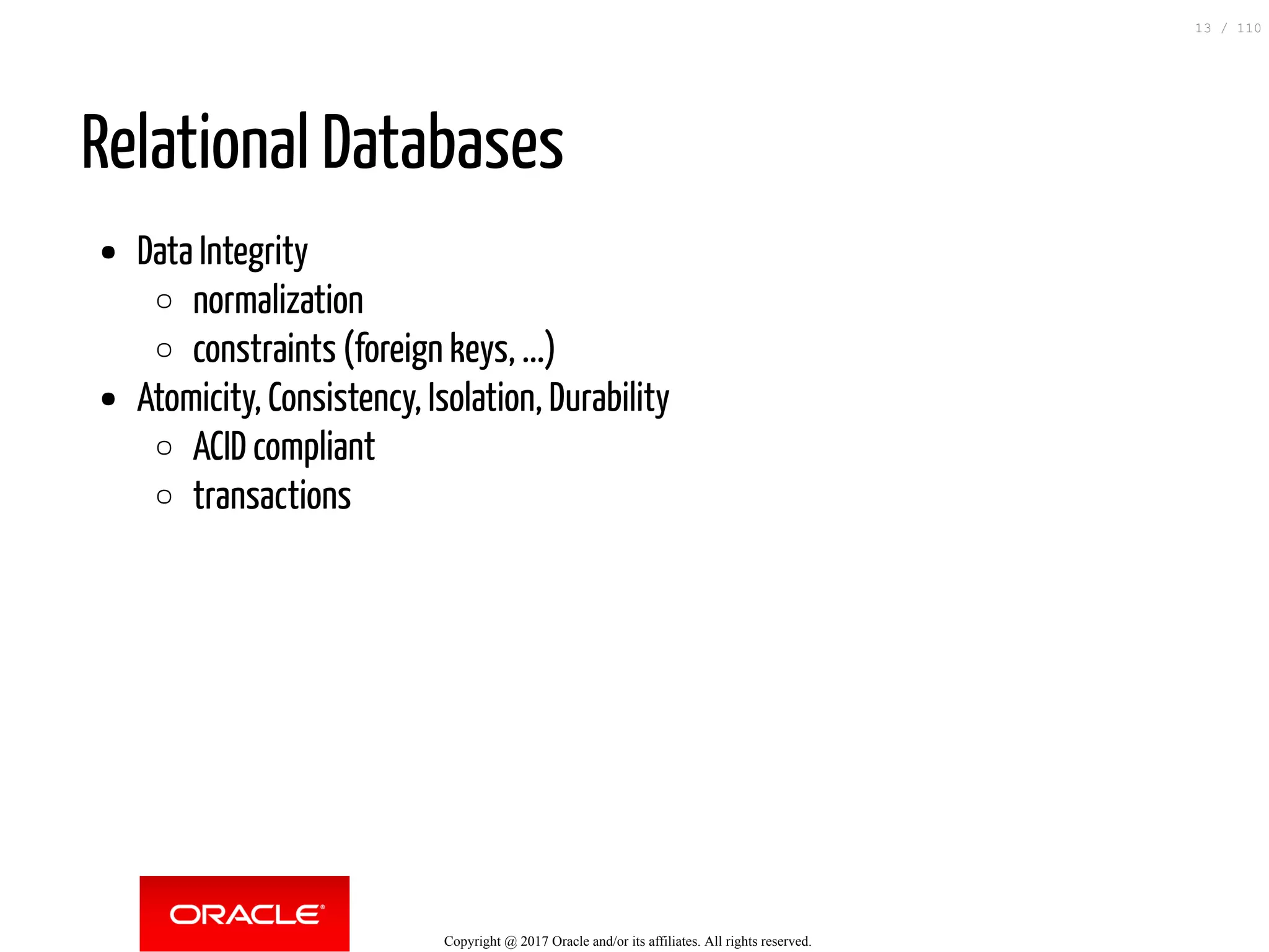
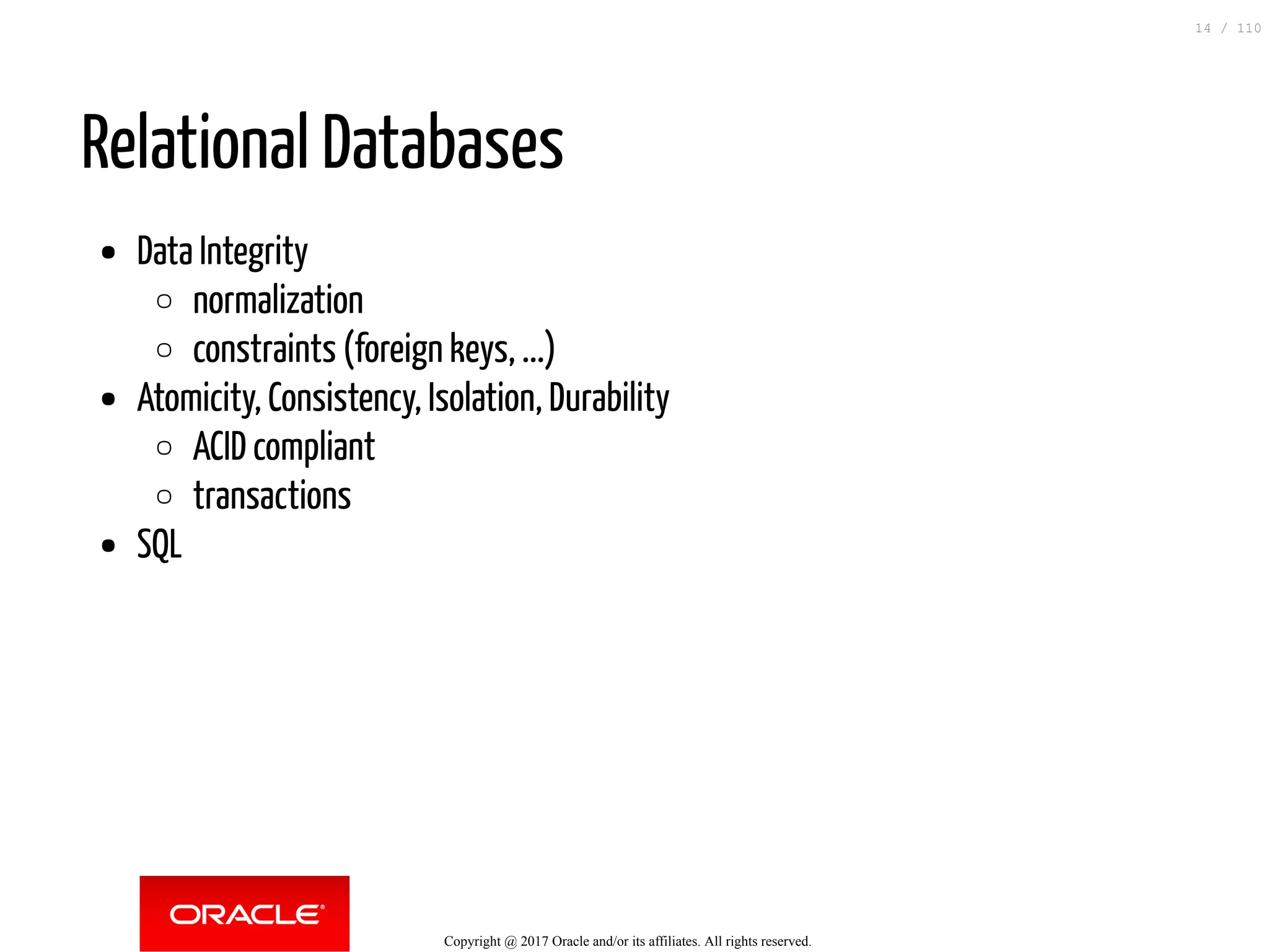
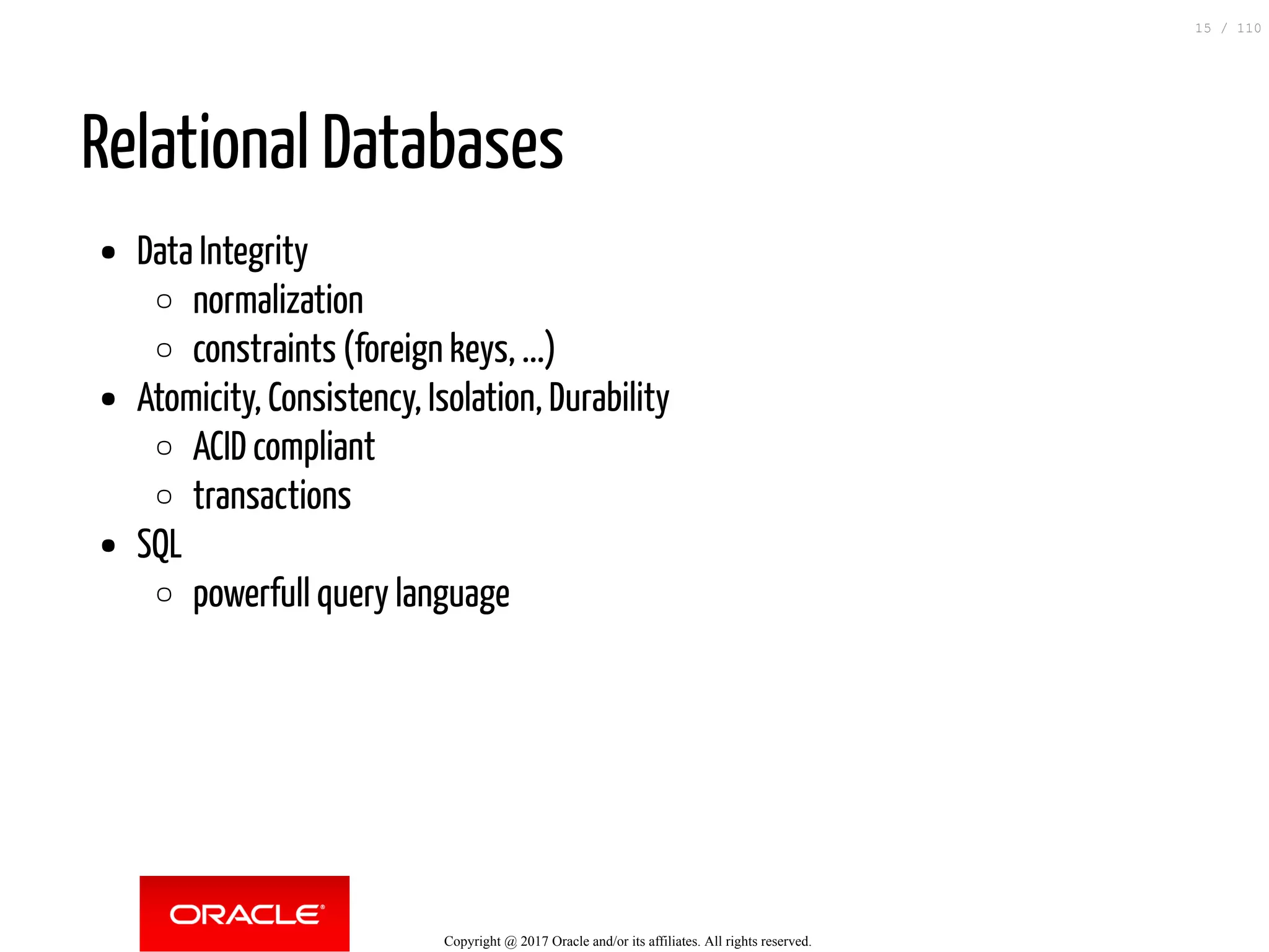
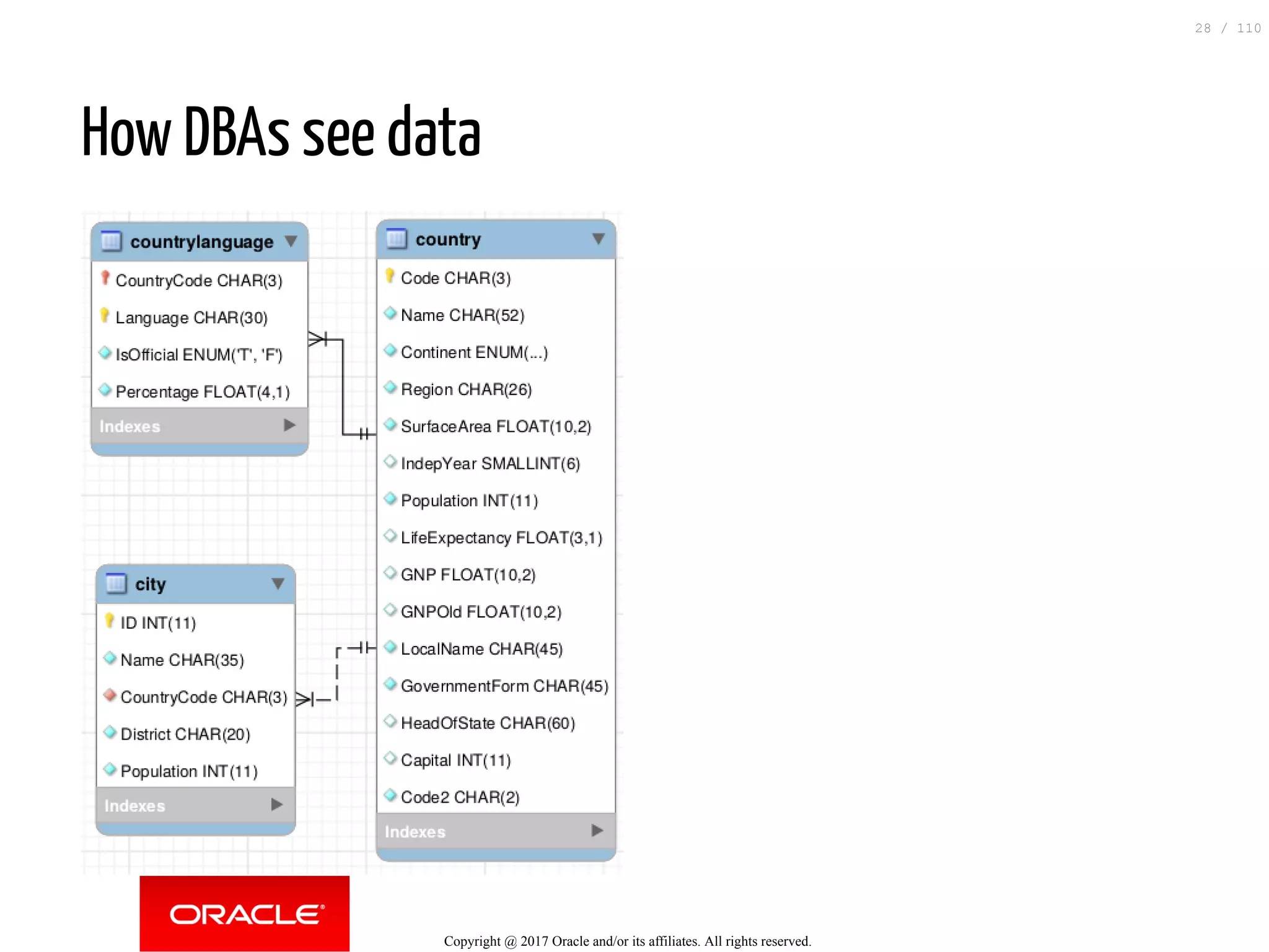
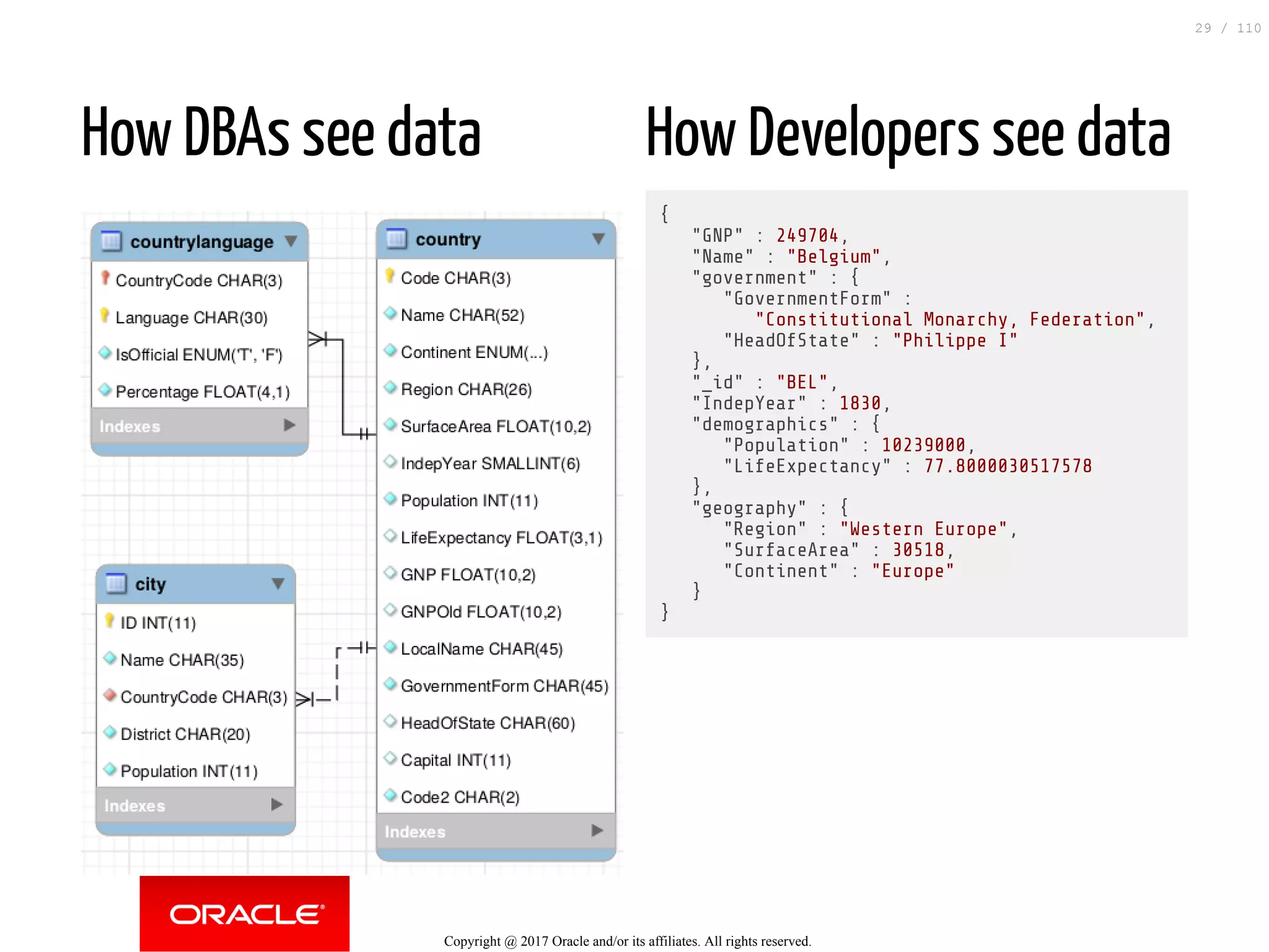
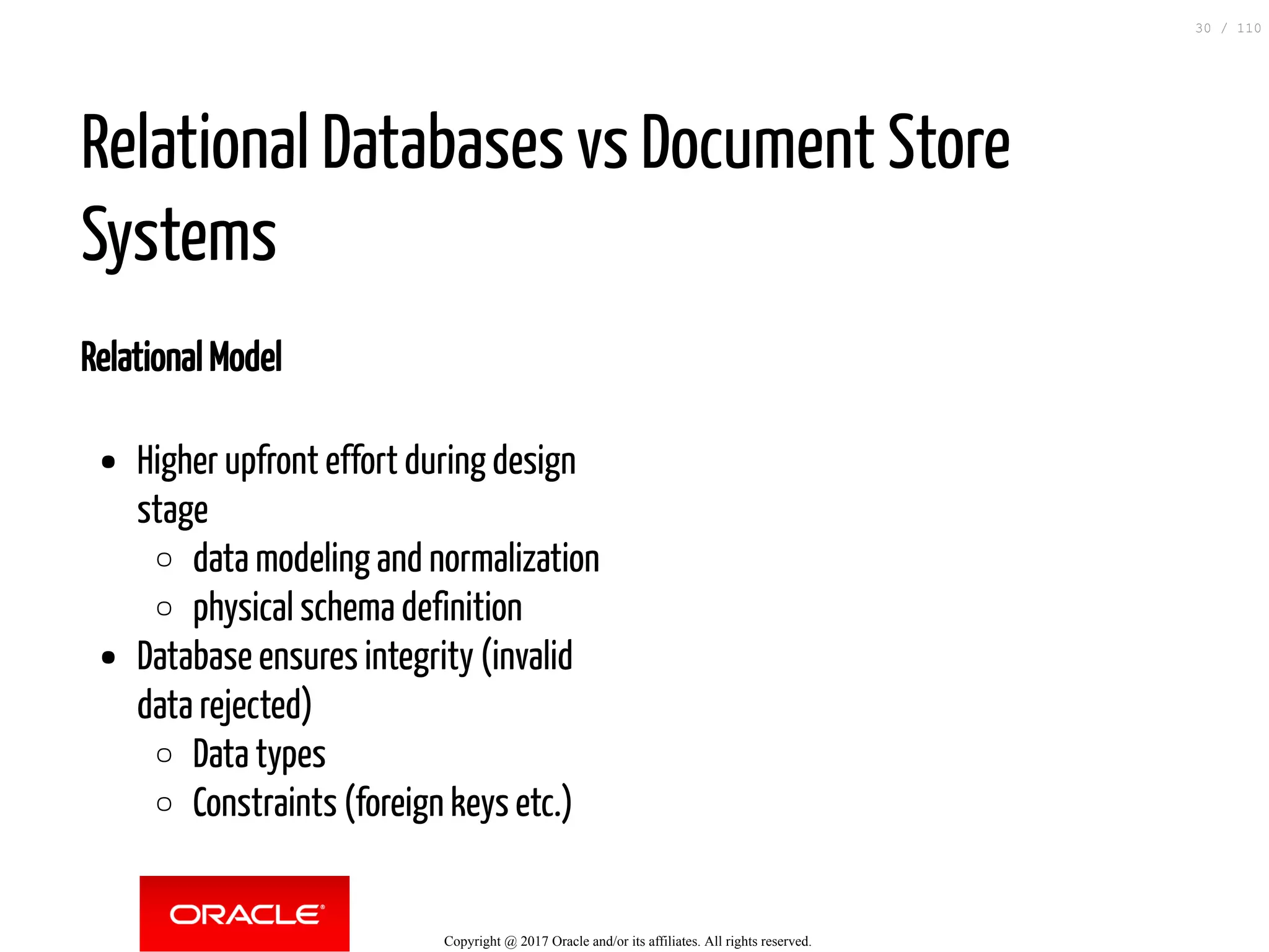
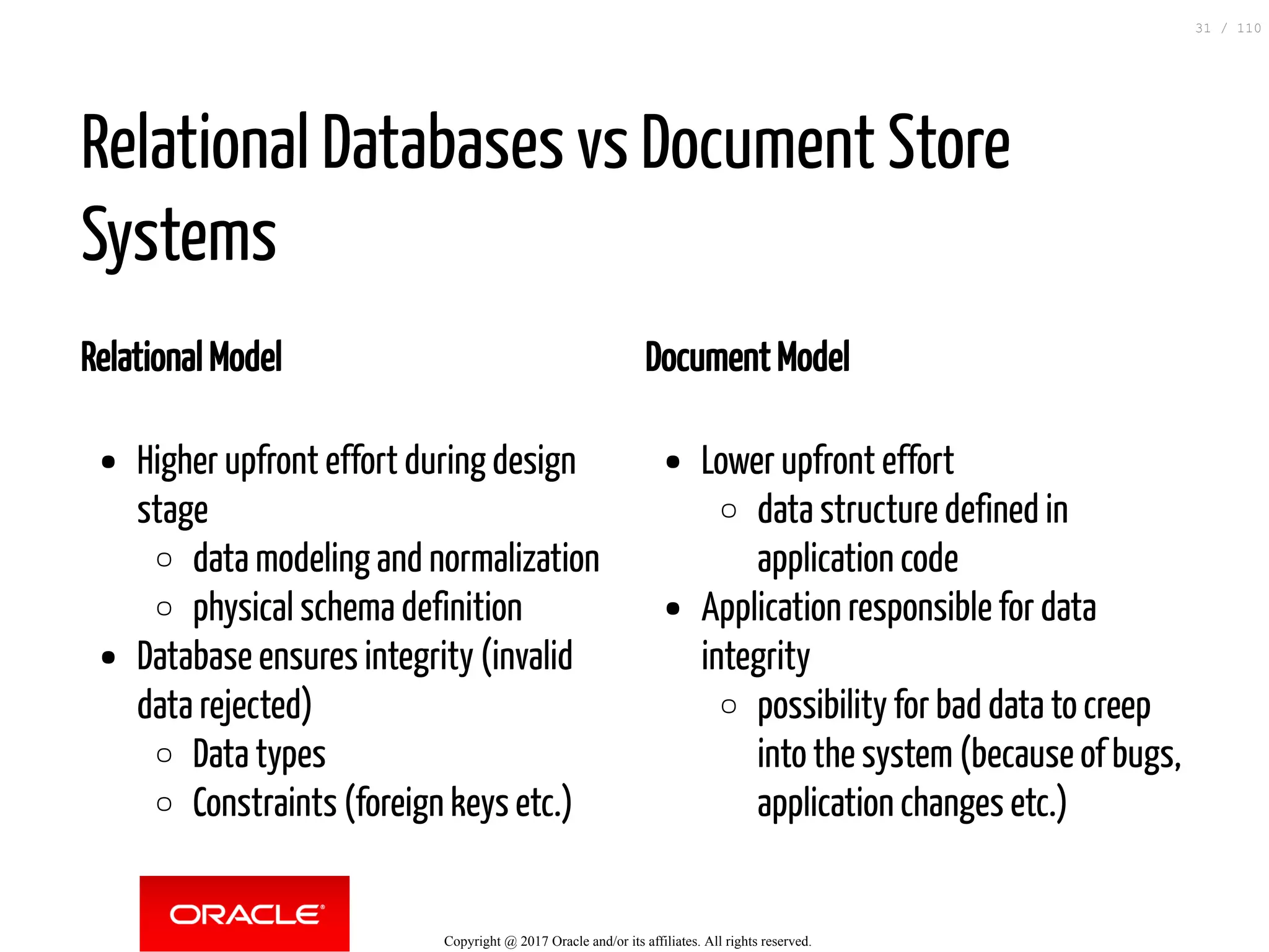
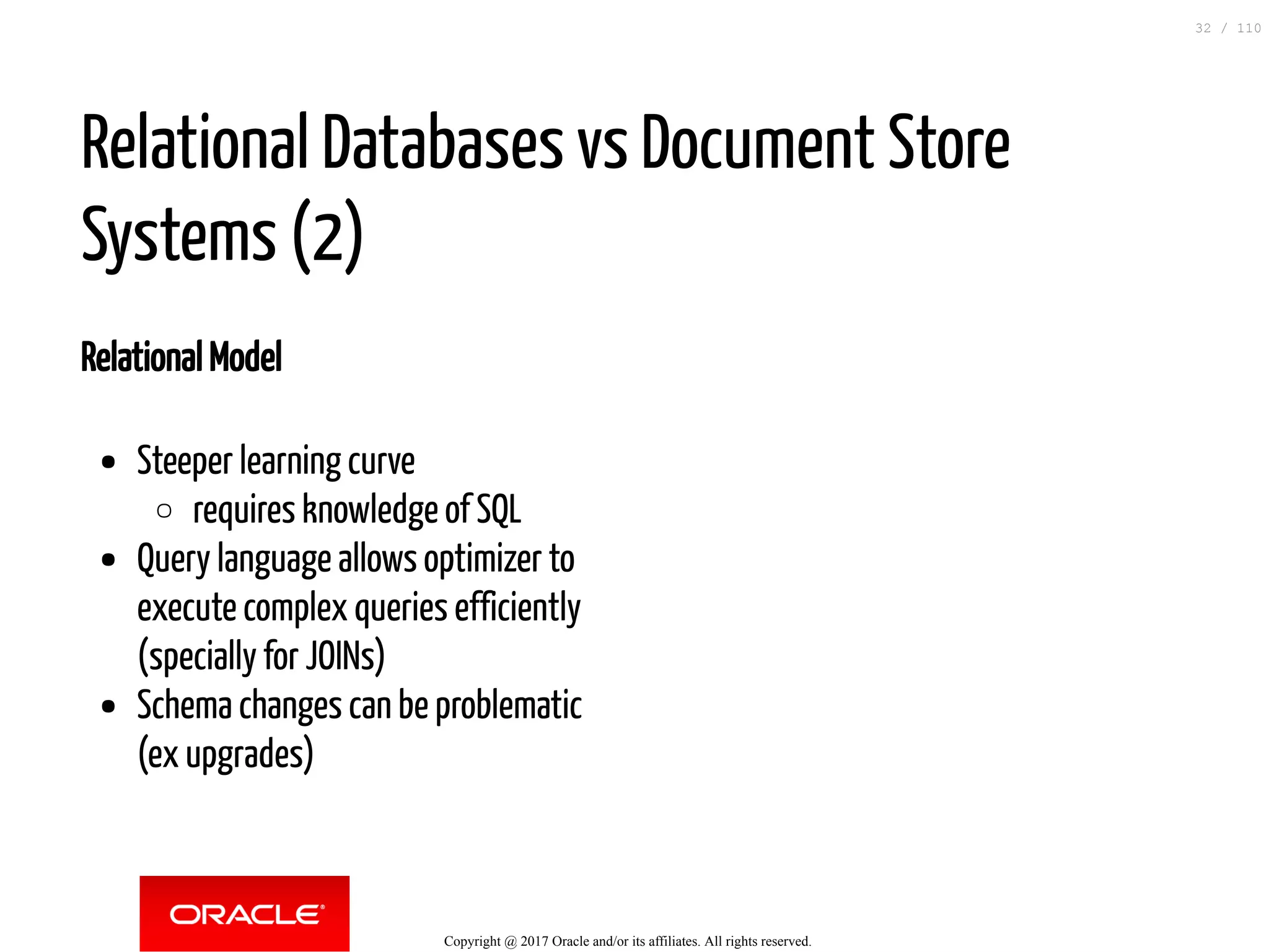
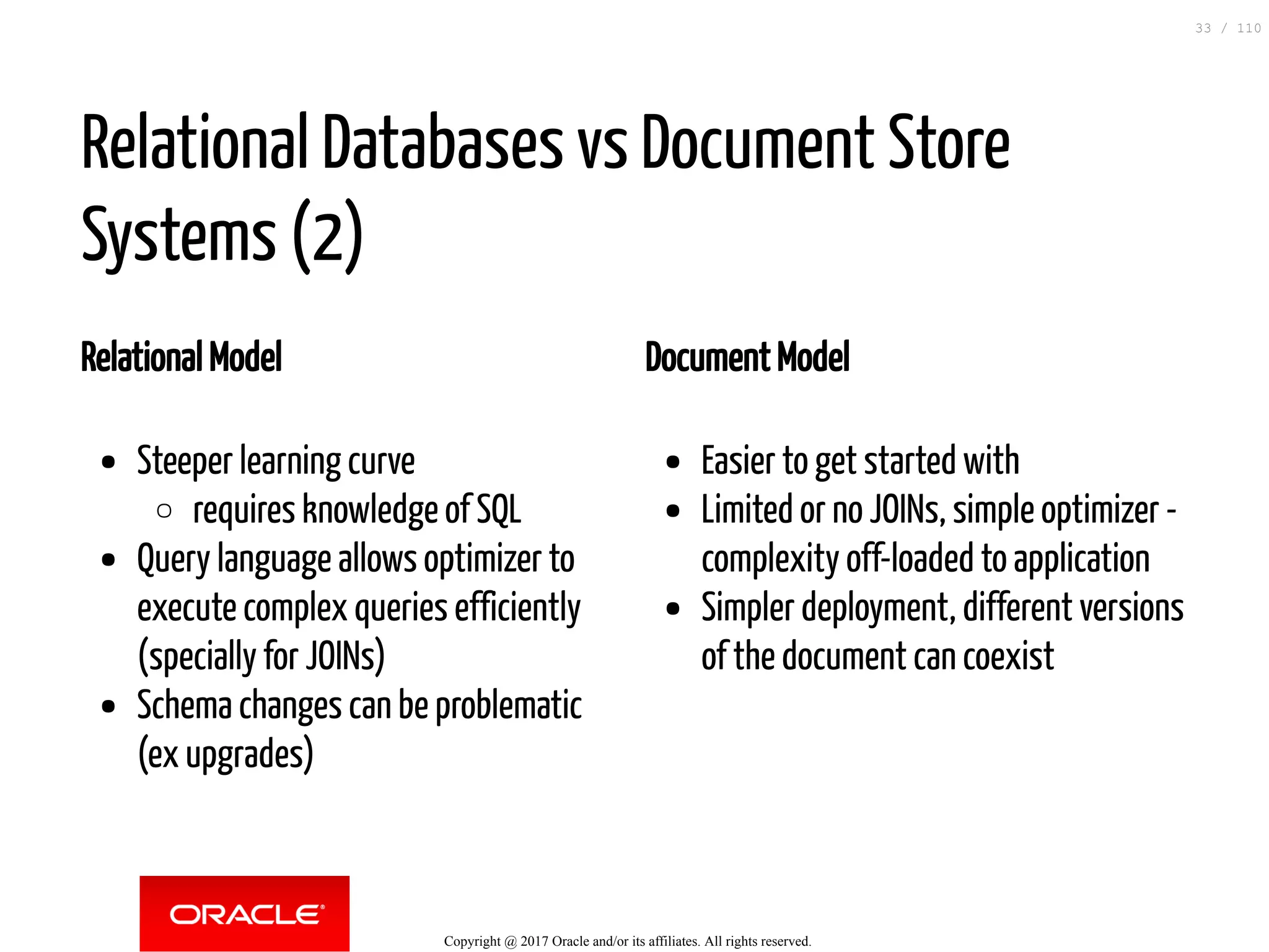
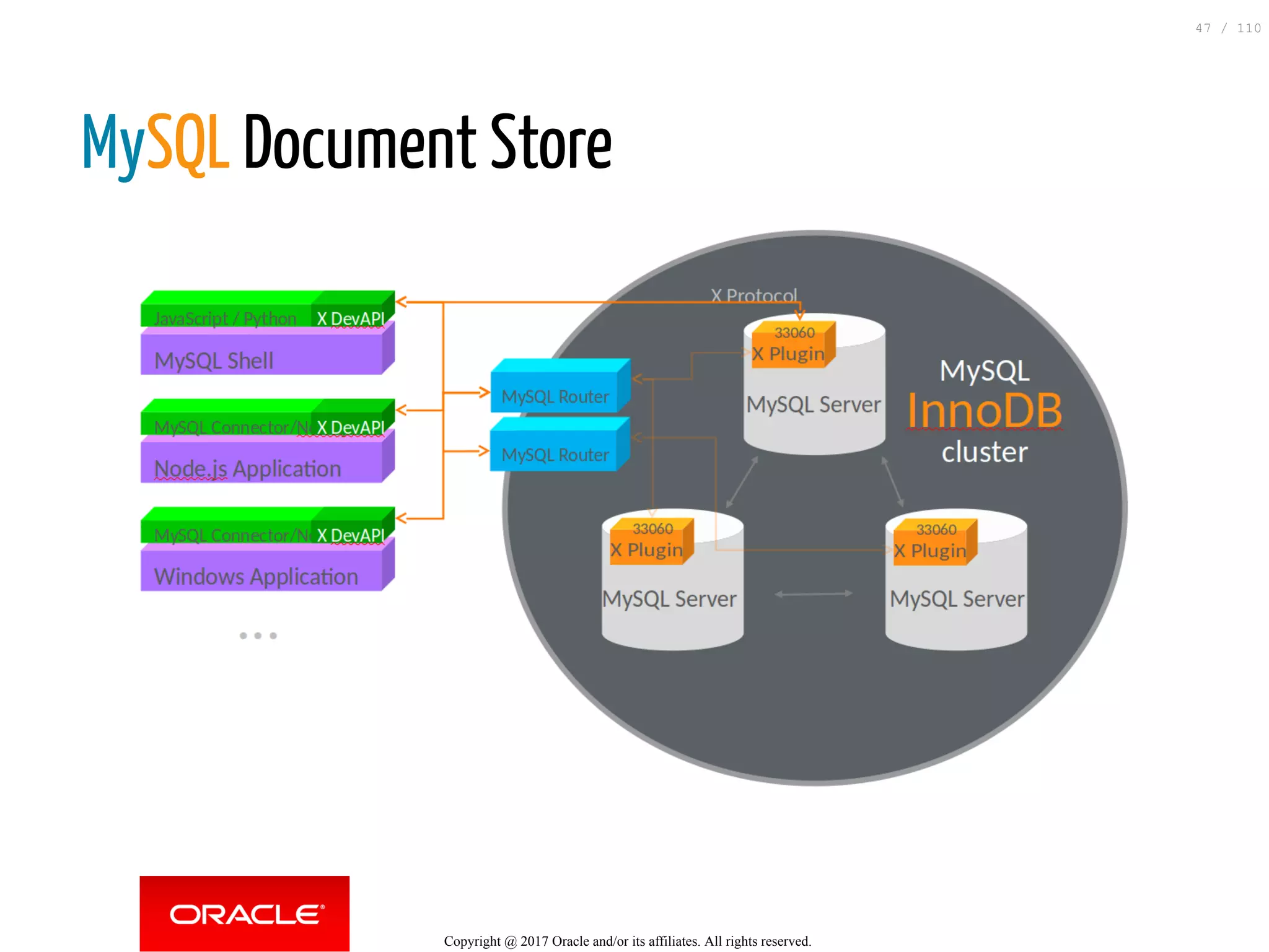
The document discusses how to transition from NoSQL databases to MySQL while highlighting the benefits of using MySQL as a document store, such as support for JSON data types and CRUD operations. It compares relational databases with document stores, focusing on the ease of initial development, data integrity, and adaptability to changes. Additionally, it provides insights into requirements for MySQL as a document store, migration methods from MongoDB, and new features introduced in version 8.0.3.




















![Developers: [x] schemaless [x] rapid prototying/simpler APIs [x] document model [x] transactions Operations: [x] performance management/visibility [x] robust replication, backup, restore [x] comprehensive tooling ecosystem [x] simpler application schema upgrades Business Owner: [x] don't lose my data == ACID trx [x] capture all my data = extensible/schemaless [x] product on schedule/time to market = rapid developement A solution for all Copyright @ 2017 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 36 / 110](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rooug-bucharestdecember2017-mysqldocumentstore-180102185902/75/MySQL-Document-Store-How-to-replace-a-NoSQL-database-by-MySQL-without-effort-but-with-a-lot-gains-36-2048.jpg)











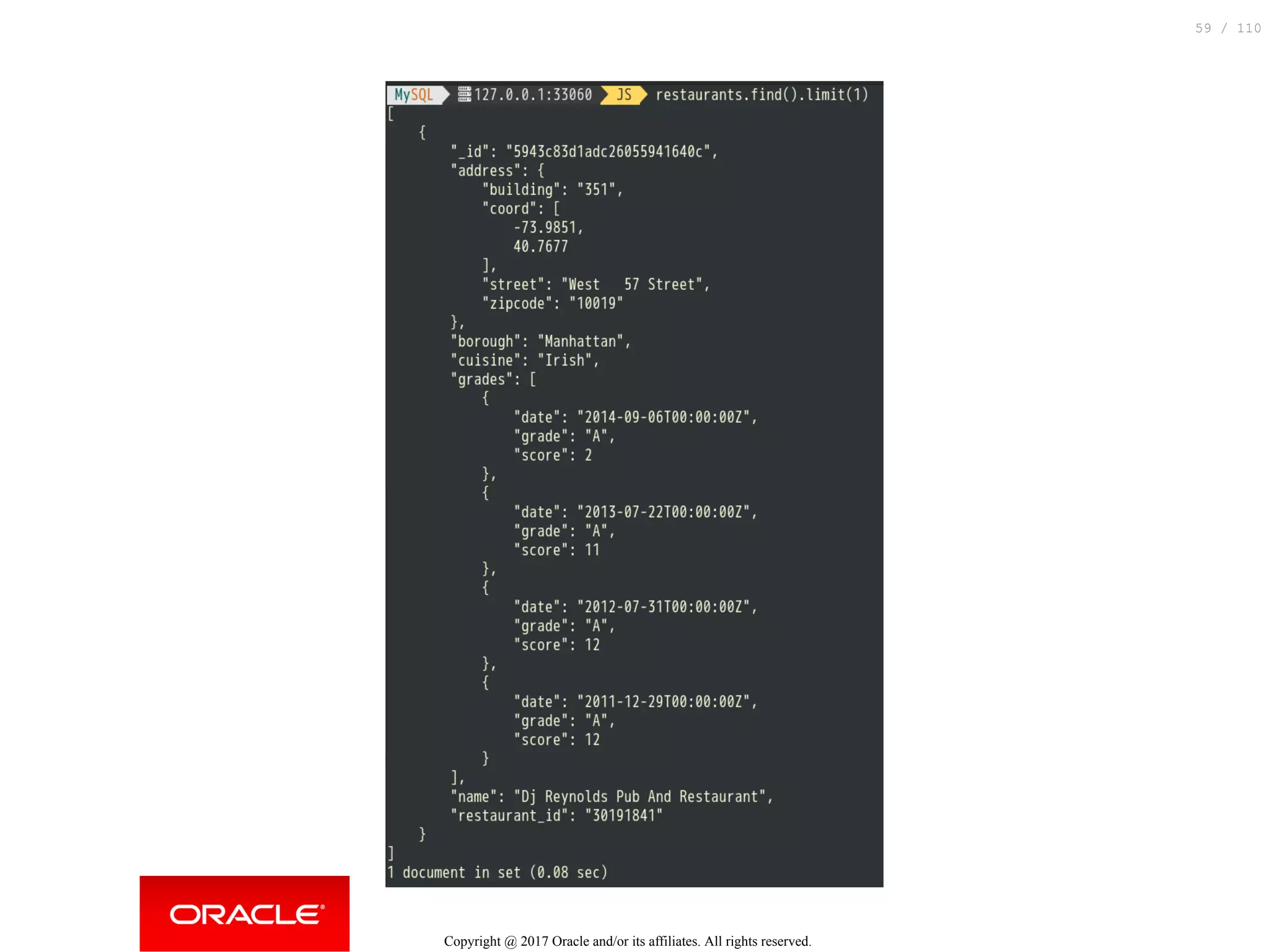
![Dump and load using MySQL Shell & Python this example is inspired by @datacharmer's work: https://www.slideshare.net/datacharmer/mysql-documentstore $ mongo --quiet --eval 'DBQuery.shellBatchSize=30000; db.restaurants. nd().shellPrint()' | perl -pe 's/(?:ObjectId|ISODate)(("[^"]+"))/ $1/g' > all_recs.json Copyright @ 2017 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 54 / 110](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rooug-bucharestdecember2017-mysqldocumentstore-180102185902/75/MySQL-Document-Store-How-to-replace-a-NoSQL-database-by-MySQL-without-effort-but-with-a-lot-gains-54-2048.jpg)
![Dump and load using MySQL Shell & Python this example is inspired by @datacharmer's work: https://www.slideshare.net/datacharmer/mysql-documentstore $ mongo --quiet --eval 'DBQuery.shellBatchSize=30000; db.restaurants. nd().shellPrint()' | perl -pe 's/(?:ObjectId|ISODate)(("[^"]+"))/ $1/g' > all_recs.json Copyright @ 2017 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 55 / 110](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rooug-bucharestdecember2017-mysqldocumentstore-180102185902/75/MySQL-Document-Store-How-to-replace-a-NoSQL-database-by-MySQL-without-effort-but-with-a-lot-gains-55-2048.jpg)