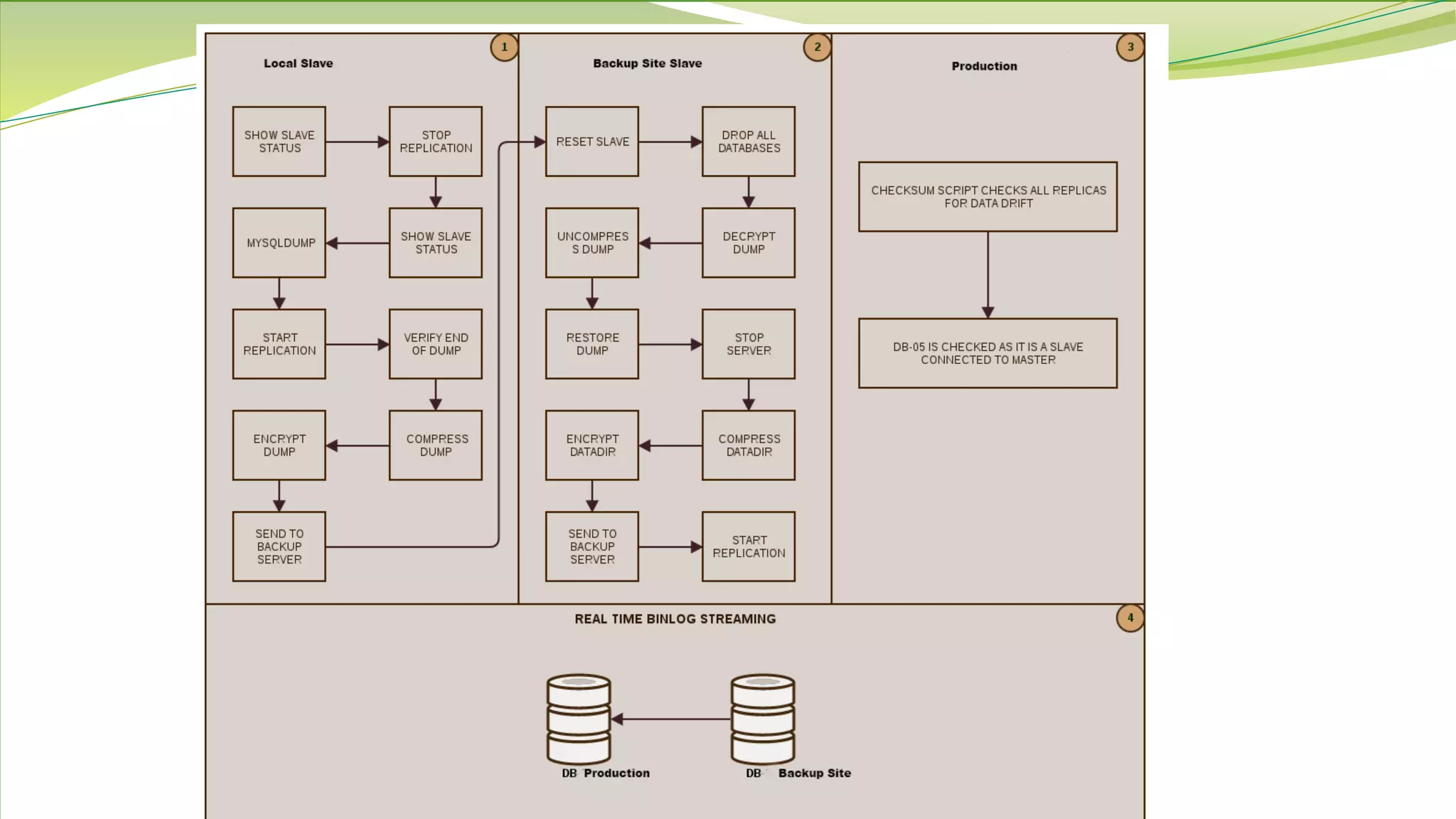
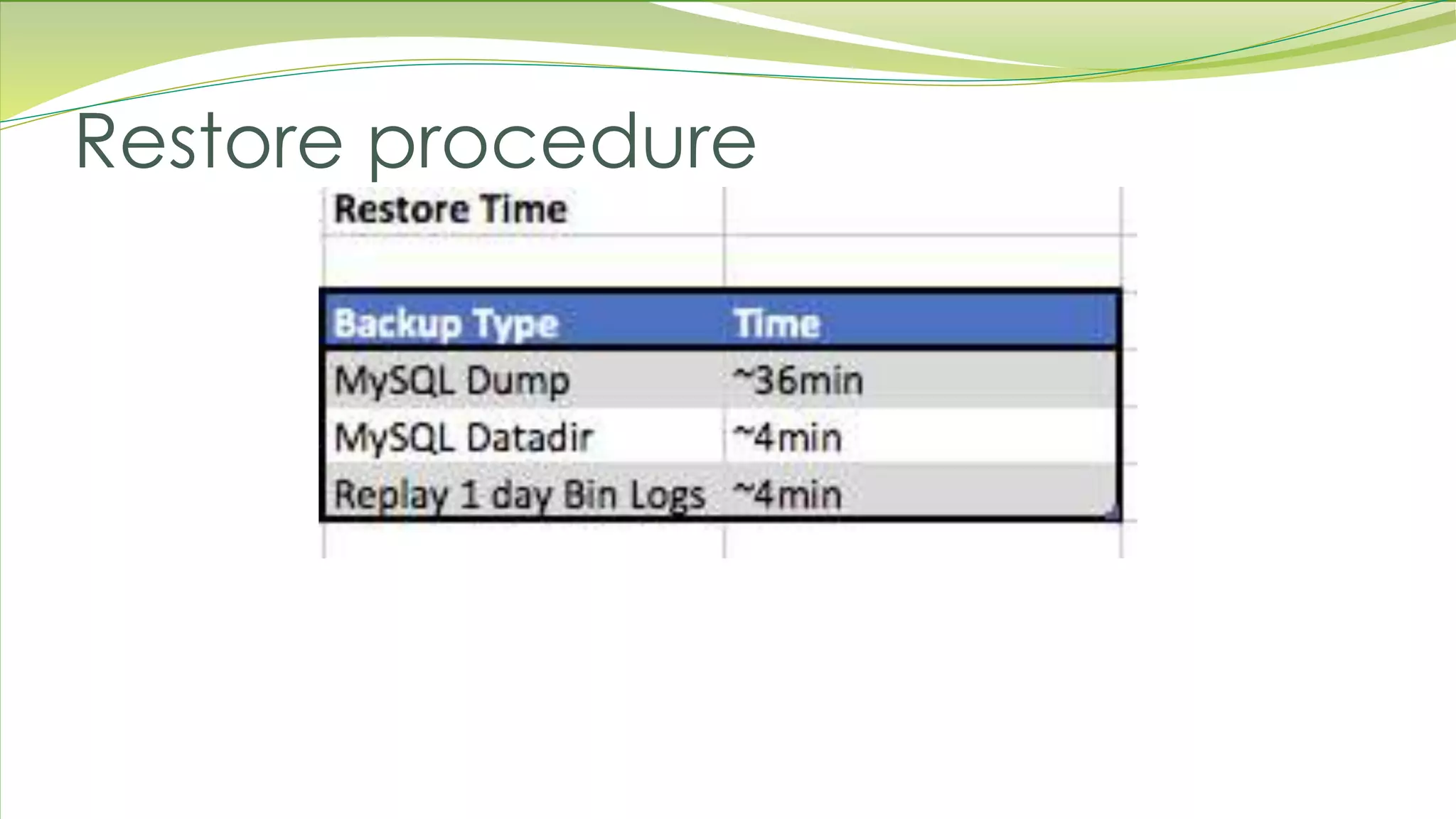
The document outlines best practices for MySQL backups, detailing the types of backups (logical, physical, incremental, and differential), the importance of encryption and compression, and strategies for proper storage. It emphasizes the necessity of testing backup restorations to ensure reliability and addresses the management of binlogs and data retention. Additionally, a case study is presented by the IE Domain Registry team, highlighting their backup setup and restoration processes.