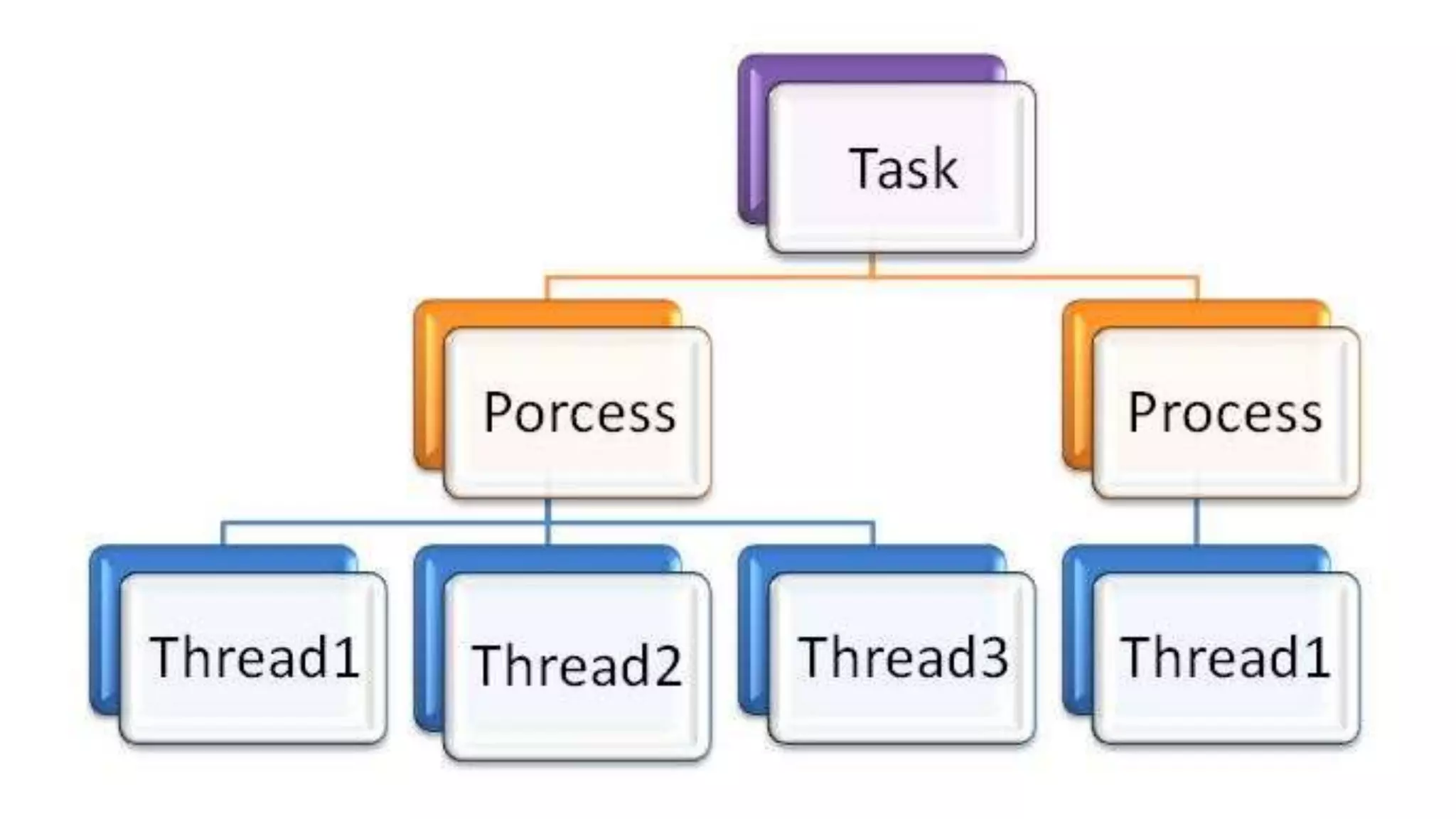
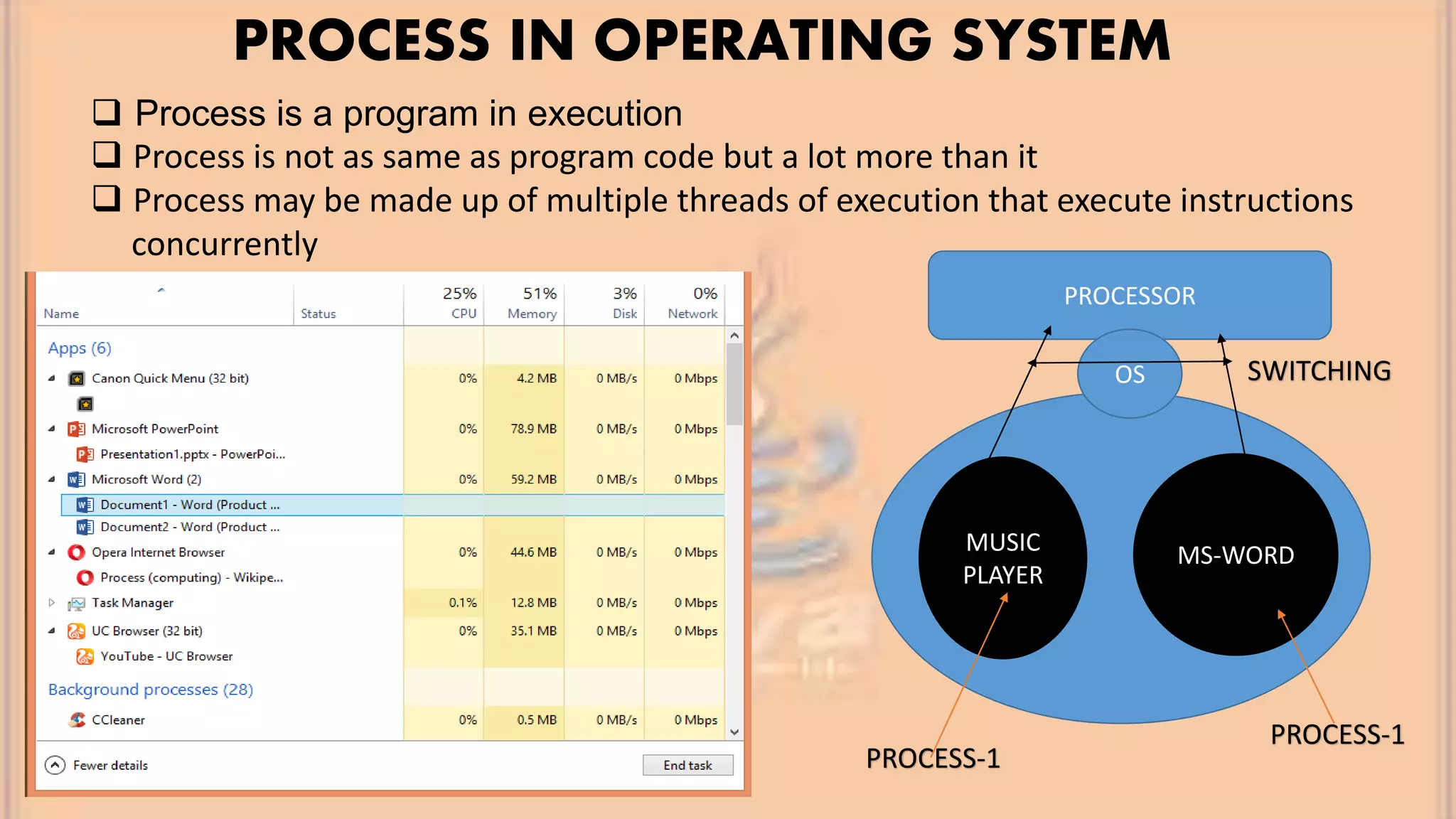
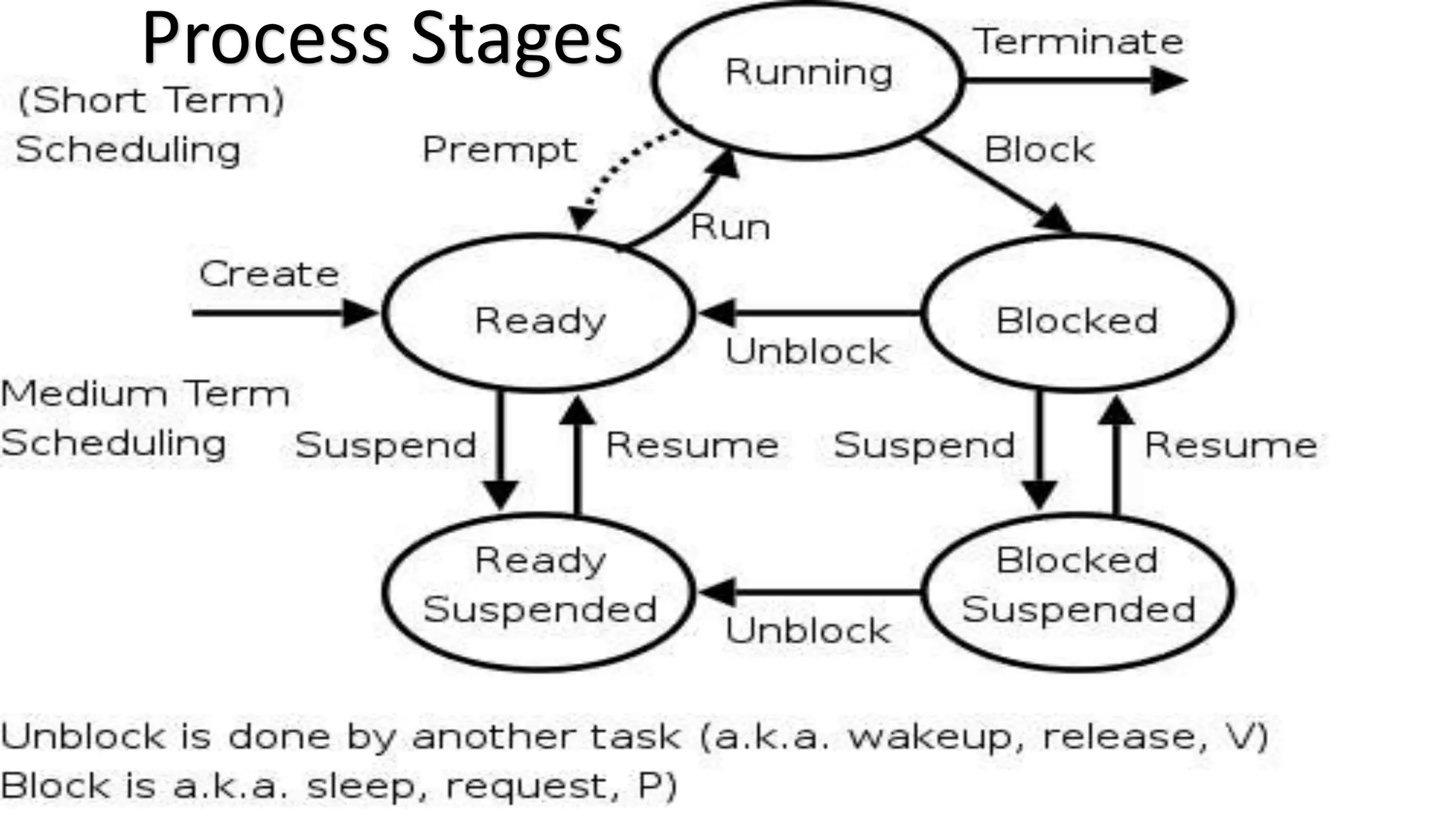
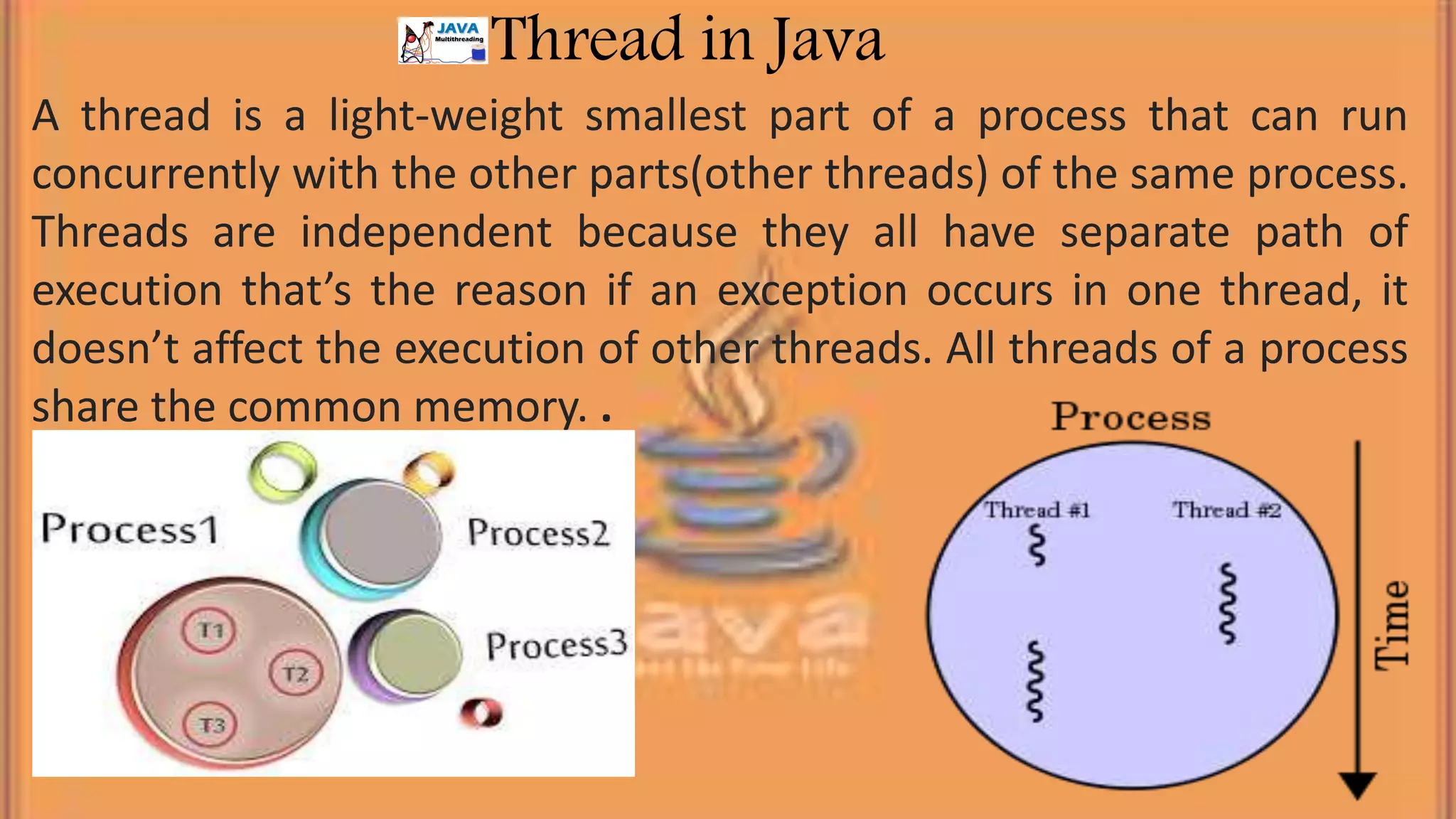
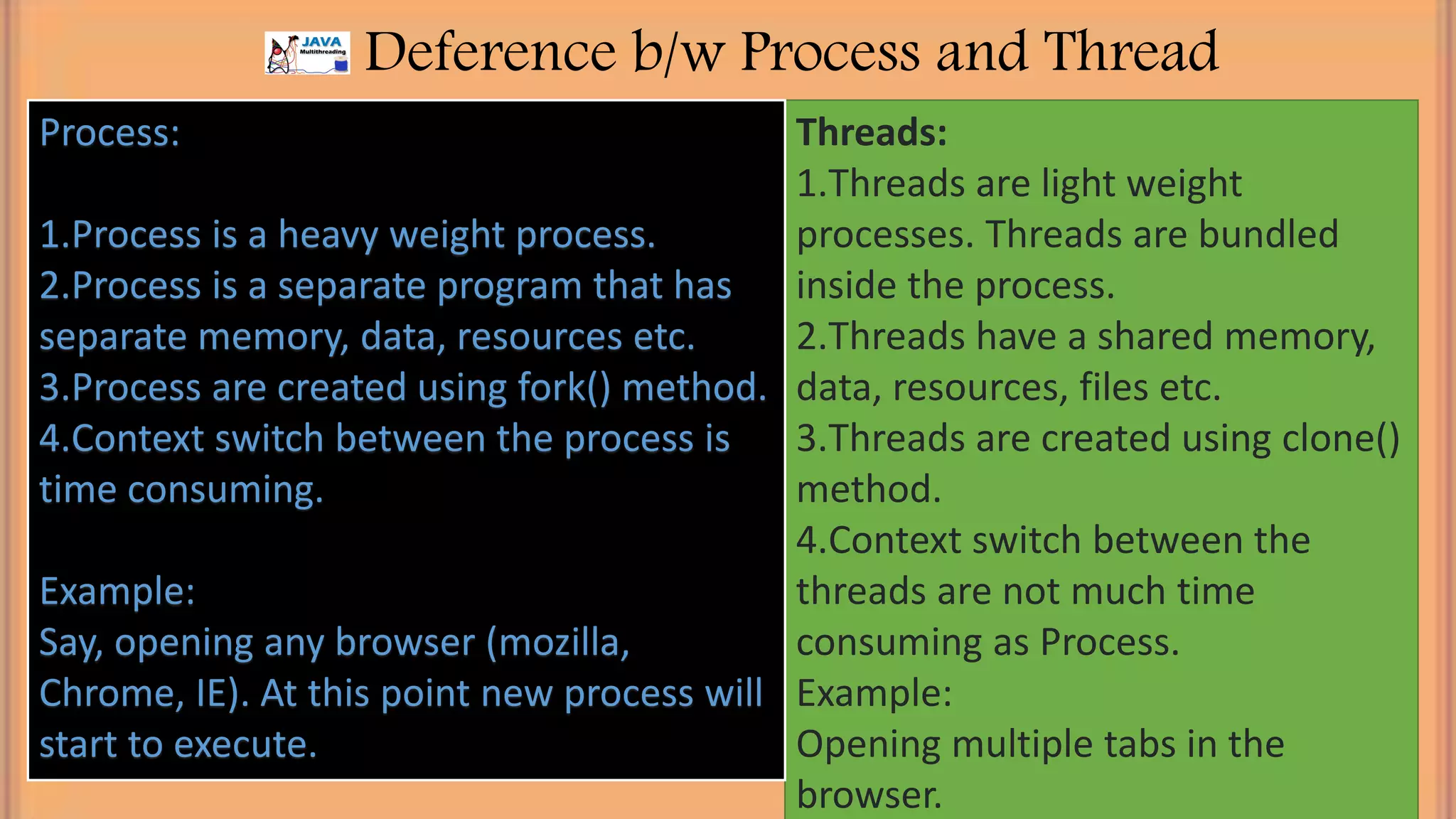
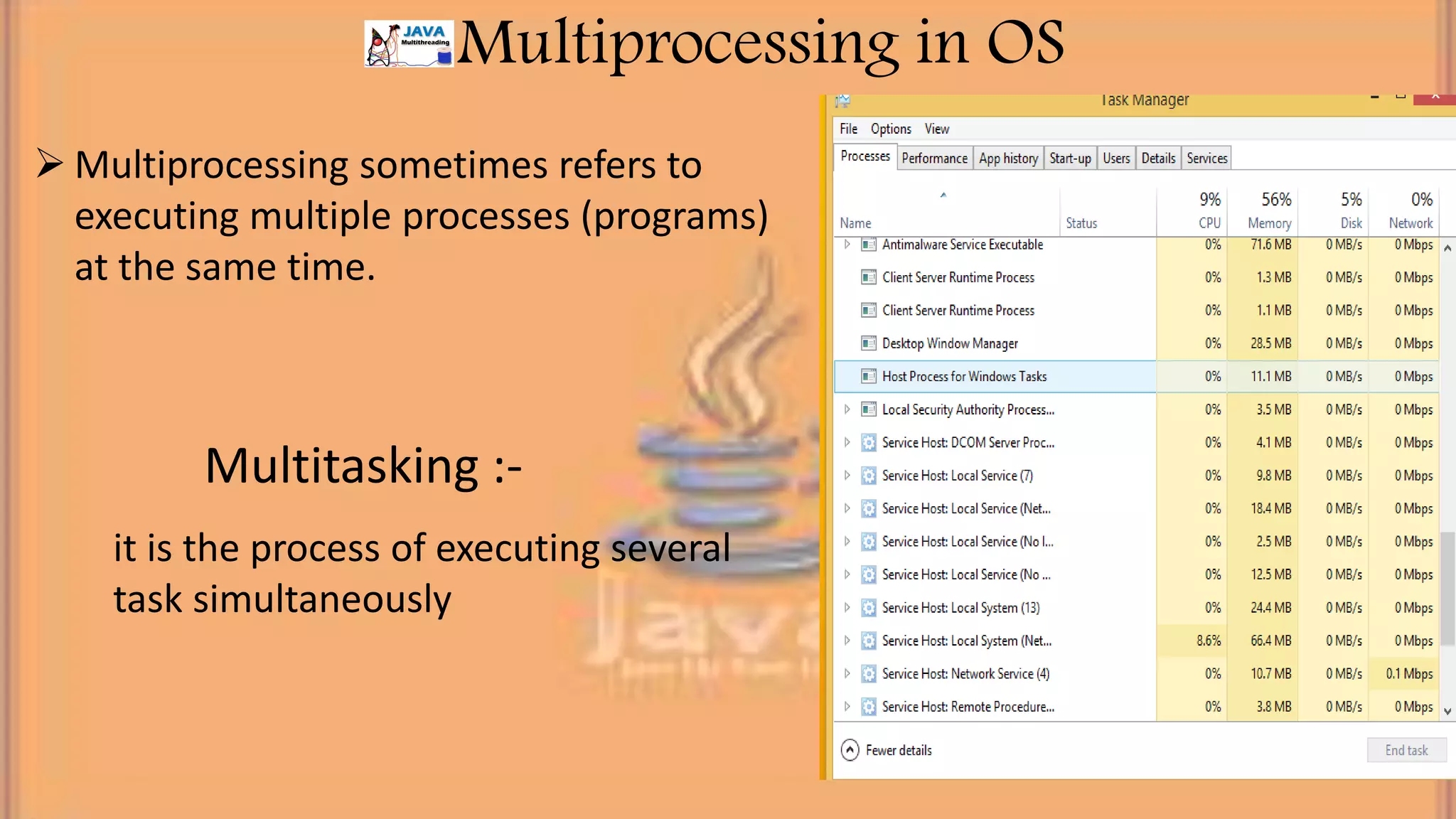
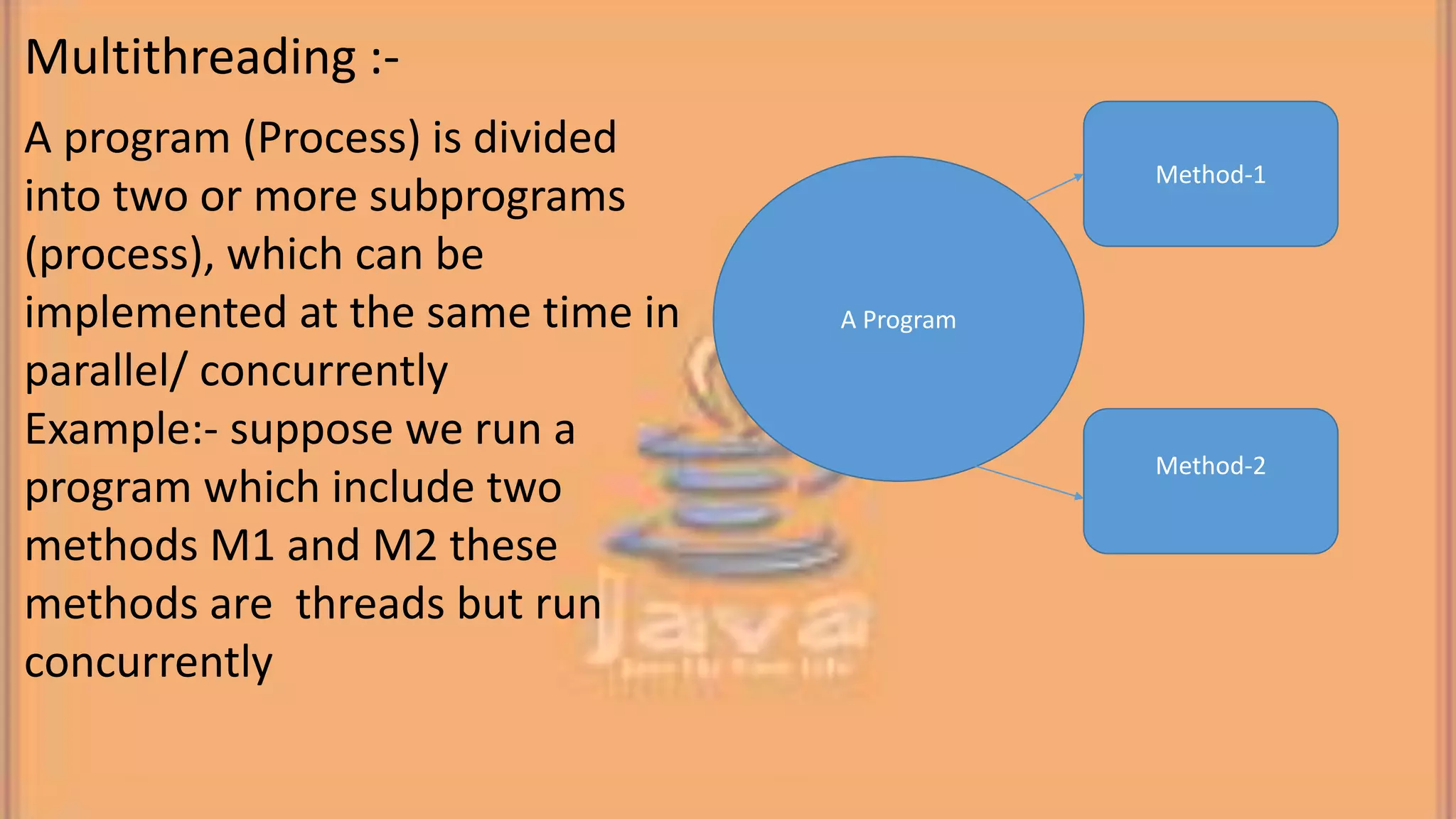
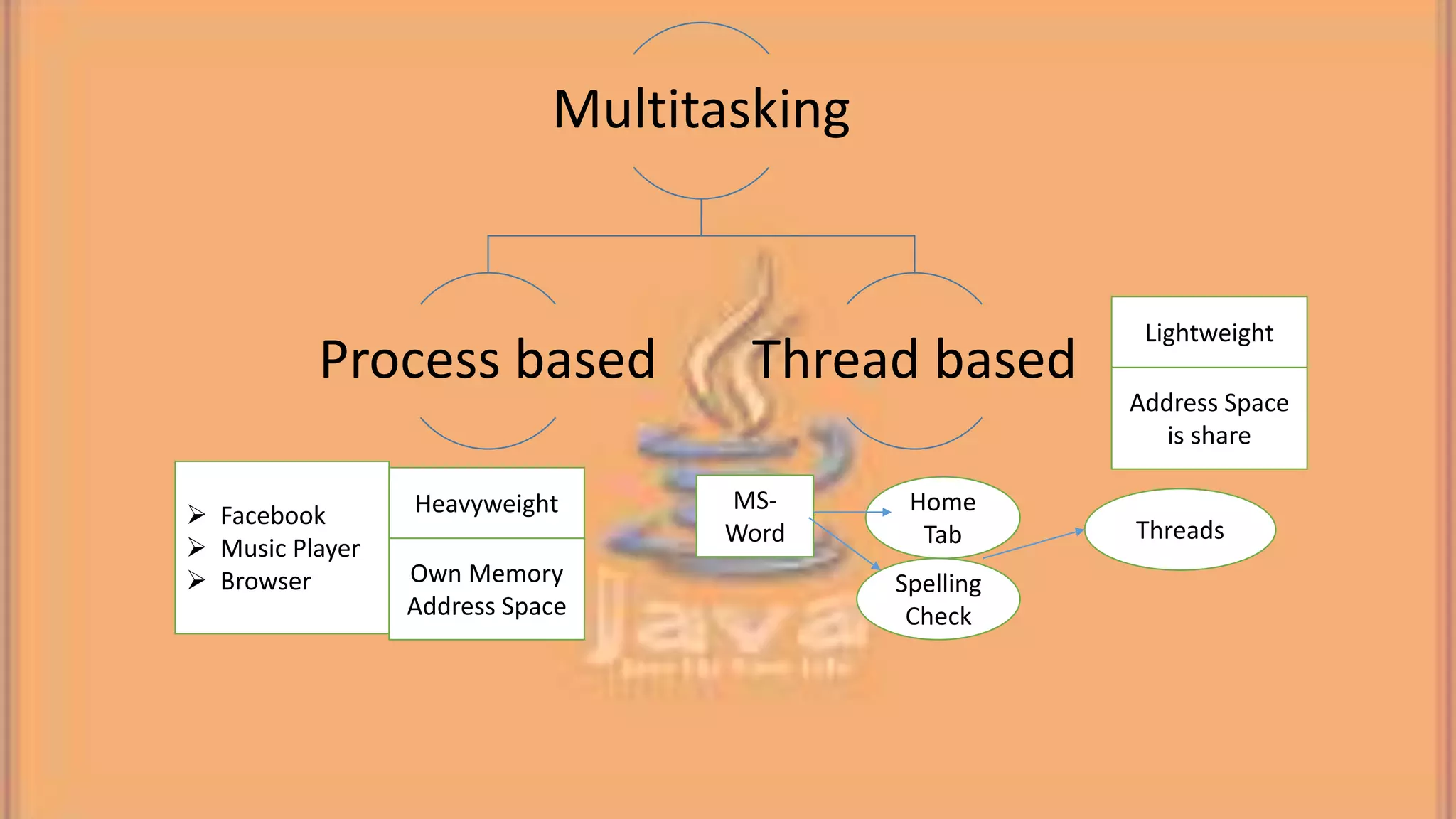
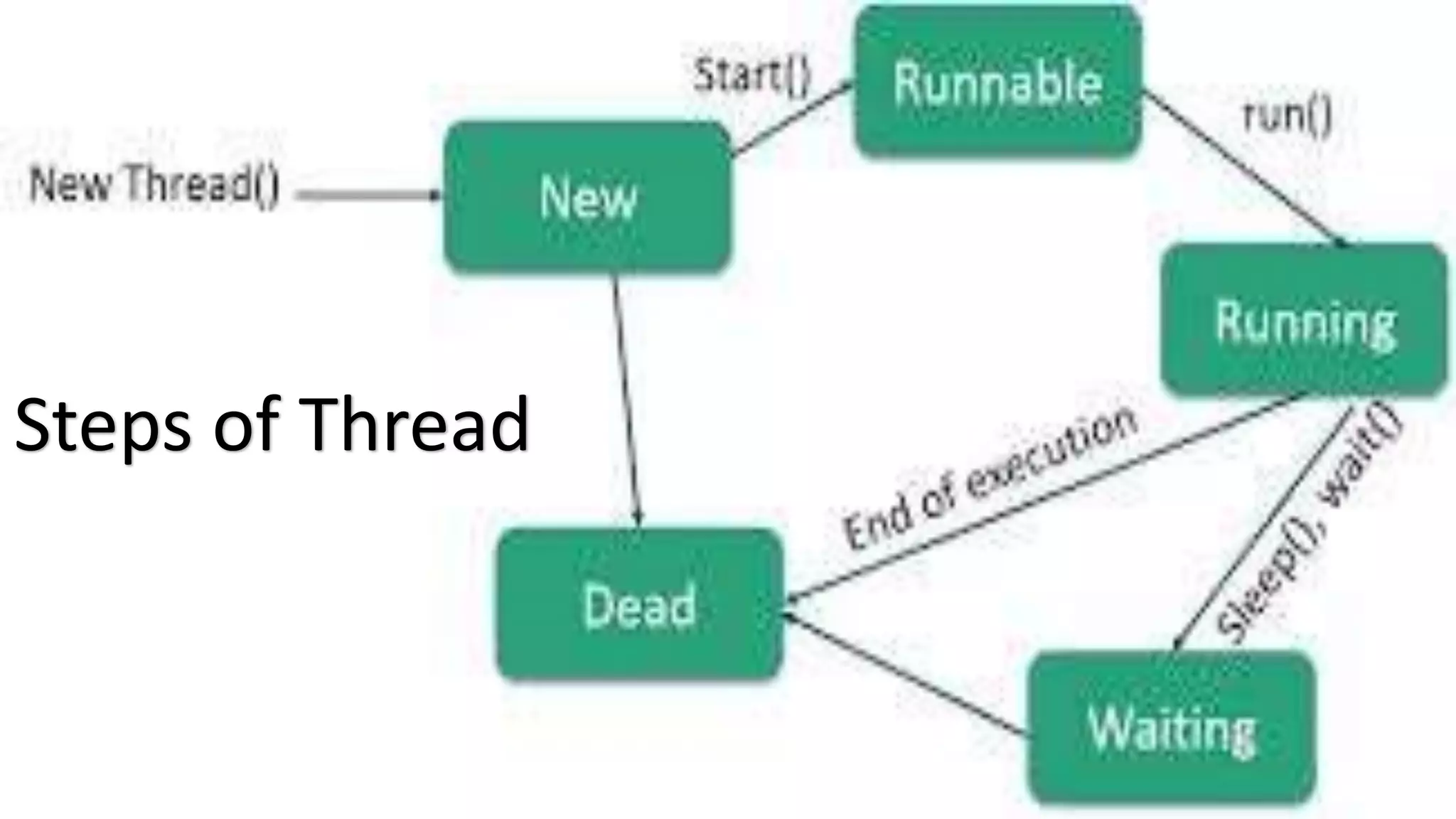
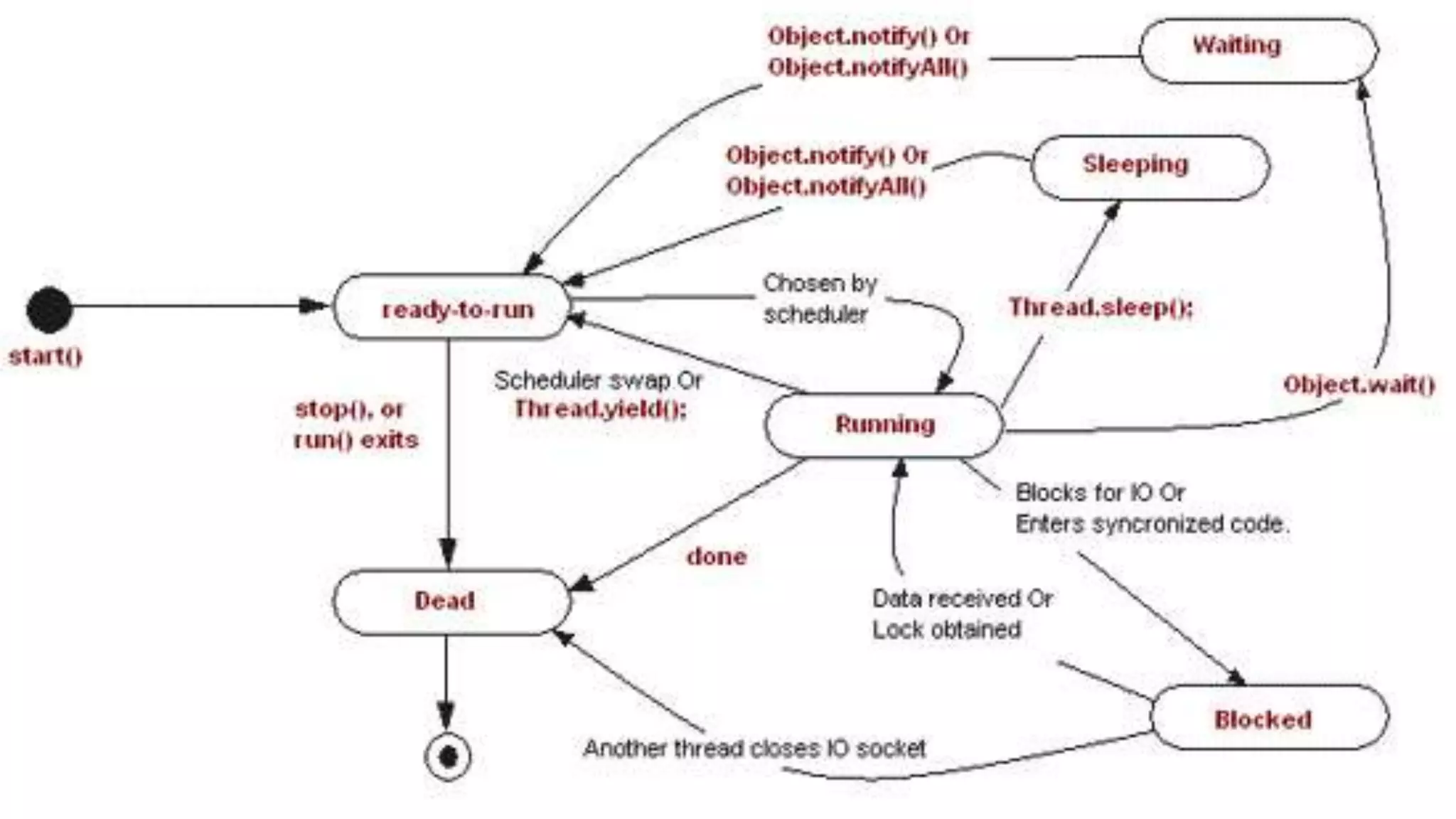
This document discusses multithreading in Java. It begins by defining a process as a program in execution that may contain multiple concurrently executing threads. It then defines a thread as the smallest unit of processing that can run independently within a process. The document goes on to compare threads and processes, discuss how to create multithreads in Java by extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface, provide examples of multithreading code, and list advantages of multithreading like enabling multiple concurrent tasks and improved performance.










![Method 1: Thread creation by extending Thread class class MultithreadingDemo implements Runnable { public void run() { System.out.println("My thread is in running state."); } public static void main(String args[]) { MultithreadingDemo obj=new MultithreadingDemo(); Thread objt1 = new Thread(obj); objt1.start(); } } Output: My thread is in running state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-in-java-171103045939/75/Multithreading-in-java-21-2048.jpg)
![Method 2: Thread creation by implementing Runnable Interface class MultithreadingDemo implements Runnable { public void run() { System.out.println("My thread is in running state."); } public static void main(String args[]) { MultithreadingDemo obj=new MultithreadingDemo(); Thread tobj =new Thread(obj); tobj.start(); } } A Simple Example Output: My thread is in running state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multithreading-in-java-171103045939/75/Multithreading-in-java-22-2048.jpg)


