This study introduces the mossa-ba algorithm, a novel multi-objective salp swarm optimization protocol designed to enhance energy-efficient routing in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks (WSNs). By integrating the artificial bee colony strategy with the salp swarm algorithm, it demonstrates significant improvements in load balancing and energy savings—over 34% in medium areas and more than 22% in larger areas—while facilitating better data transmission speed and accuracy compared to traditional protocols. The findings indicate that these advanced protocols outperform existing heterogeneous routing methods, contributing to the longevity and efficiency of sensor networks.
![MULTI OBJECTIVE SALP SWARM BASED ENERGY EFFICIENT ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR HETEROGENEOUS WIRELESS NETWORKS Salima Nebti1 and Mohammed Redjimi2 1 Department of Communication, Emir Abdelkader University, Constantine, Algeria 2 Department of Computer Science, 20 Août 1955 University, Skikda, Algeria ABSTRACT Routing is a persistent concern in wireless sensor networks (WSNs), as getting data from sources to destinations can be a tricky task. Challenges include safeguarding the data being transferred, ensuring network longevity, and preserving energy in harsh environmental conditions. Consequently, this study delves into the suitability of using multi-objective swarm optimization to route heterogeneous WSNs in the hope of mitigating these issues while boosting the speed and accuracy of data transmission. In order to achieve better performance in terms of load balancing and reducing energy expenditure, the MOSSA-BA algorithm was developed. This algorithm combines the Multi-Objective Salp Swarm Algorithm (MOSSA) with the exploiting strategy of the artificial bee colony (BA) in the neighbourhood of Salps. Inspired by the SEP and EDEEC protocols, the integrated solutions of MOSSA-BA were used to route two and three levels of heterogeneous networks. The embedded solutions provided outstanding performance in regards to FND, HND, LND, percentage of remaining energy, and the number of packages delivered to the base station. Compared to SEP, EDEEC, and other competitors based on MOSSA and a modified multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO), the MOSSA-BA-based protocols demonstrated energy-saving percentages of more than 34% in medium-sized areas of interest and over 22% in large-sized areas of detection. KEYWORDS Salp swarm algorithm, Artificial bees colony optimization, multi objective optimization, Enhanced Distributed Energy Efficient Clustering Protocol, Stable Election Protocol, heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. 1. INTRODUCTION In the world of IoT, wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are quickly becoming a crucial aspect of remote monitoring. These networks consist of low-power sensors that are strategically placed throughout a designated area to gather various physical readings, including temperature, humidity, pressure, luminosity, and speed. Once the data is gathered, it is subsequently conveyed to a base station for two main purposes: either for analysis or for interfacing with the environment. Although wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are still a relatively new innovation, their potential for enabling remote monitoring is being more widely acknowledged and appreciated [1]. Numerous practical applications of WSNs exist, ranging from predicting traffic accidents and monitoring water quality to managing smart homes and tracking weather patterns. In addition, WSNs are instrumental in detecting forest fires, remote patient monitoring, and managing military battlefields [2]. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 DOI: 10.5121/ijcnc.2023.15505 73](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-1-2048.jpg)
![Creating a sensor network involves careful consideration of several factors, including complete coverage of the targeted area, sustained communication links between nodes and the base station, self-reconfiguration capabilities for nodes, minimal energy expenditure, and instantaneous packet delivery to avert potential damage. Robust recovery mechanisms must also be in place to tackle any security breach [3]. Effective routing tactics become crucial for self-adapting wireless networks. Particularly for large WSNs where sensors' self-reconfiguration is a challenging undertaking because of the network topology's constant changes. This research delves into the use of swarm intelligence-based routing protocols as a solution for refining the energy consumption of nodes in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. By introducing modified versions of MOSSA and MOPSO, improved performance was actively observed during the utilization of the proposed MOSSA-BA, specifically in the enhancement of the SEP and EDEEC protocols. This document is divided into distinct sections. Beginning with an overview of comparable research studies, the SEP and EDEEC protocols are then outlined. From there, we delve into suggested routing protocols that emphasize swarm intelligence and the experimental results that accompany them. The conclusion ties everything together, summarizing key findings and analysing potential future opportunities. 2. RELATED WORKS Wireless sensor networks consist of nodes that have a limited energy source and are frequently placed in harsh or unreachable locations, making it challenging to replace them. As a result, the network must have the longest possible lifespan. Numerous investigations have been conducted with the goal of achieving an extended lifespan for sensor networks. These explorations include cognitive radio, schemes for radio sleep and wake-up, data aggregation, and routing algorithms that include sink mobility, multipath routing, clustering-based protocols, heterogeneity incorporation, swarm-based protocols, and multi-objective-based protocols [5]. Energy-efficient routing protocols are increasingly gaining popularity in the research community due to their effectiveness and affordability. Clustering-based protocols have been developed to uphold connectivity in vast networks [5]. These routing algorithms serve as the cornerstone of contemporary research efforts owing to their capacity to expand, save energy, and automatically configure themselves by choosing alternate CHs in case of any unforeseen failures. The LEACH protocol, one of the oldest protocols, was developed to address the issue of remote nodes that cannot directly communicate with the base station [4]. To streamline data transfer, the protocol segregates nodes into clusters, assigning a specific cluster head to oversee data processing within each. By doing so, data routes are minimized. Moreover, to prevent uneven battery drain, nodes take turns as the CH role is rotated periodically. Nonetheless, LEACH's CH selection process overlooks the remaining energy levels of nodes, resulting in a network failure if a low-energy node is selected as CH. [6]. Various enhancements have then been suggested to improve LEACH's energy-saving capabilities, including LEACH-C [6], HEED [7], IEE-LEACH [11], BCE-LEACH [9], SRDC-LEACH [8], and HEER [10], etc. Moreover, a more advanced approach based on sensor heterogeneity has resulted in longer periods of stability and increased the lifespan of the network. The most commonly used heterogeneous protocols are SEP, DEEC, DDEEC, EDEEC, EDDEEC, and BEENISH [6]. To select a CH in the SEP protocol, it is essential to have complete knowledge about each sensor’s initial energy. The DEEC model has taken into account the remnant energy of cluster heads during their selection process, whereas the DDEEC protocol further implements a threshold that is dependent on the residual energy of individual nodes to prevent penalizing the advanced nodes. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 74](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-2-2048.jpg)
![The concept of heterogeneity was then expanded upon by EDEEC, which introduced a third level. EDDEEC established a three-level threshold for heterogeneity to prevent advanced nodes from being penalized. Additionally, BEENISH brought in a fourth level of heterogeneity to improve the overall stability of the network [12]. According to recent research, employing single-objective optimization methods can help prolong the lifespan of wireless sensor networks (WSNs). One such instance is the study conducted by Hasnat et al., who utilized the Artificial Bee Colony (ABC) algorithm during the CHs selection phase of the DEEC protocol to enhance both the longevity and throughput of WSNs [13]. Pawar suggested an improved SEP that relies on the PSO algorithm [14], while Abood et al. put forward a fuzzy stable election protocol (FSEP) that also uses the PSO approach to determine the most suitable path connecting a source node to the base station [15]. Meanwhile, Çelik came up with an ACO-based routing protocol for MANET, which aims to establish the most efficient route in regards to transmission delay and successful delivery of packets [22]. Although the studies mentioned above are aimed at prolonging the lifespan of networks, they do not guarantee balanced energy usage to prevent the premature depletion of sensors. Recently, researchers have become fascinated by the concept of multi-objective optimization in the context of wireless network routing, with the goal of achieving a better load balance between nodes. This approach entails optimizing multiple objectives simultaneously, such as energy efficiency, coverage, reliability, and connectivity. Among such researchers, Nabavi created a routing protocol that utilizes the multi-objective whale optimization algorithm (MOWOA), which has proven to be very effective. Maximizing the remaining energy of cluster heads (CHs) and the number of their neighbouring nodes were the primary considerations when implementing the MOWOA method for CH selection [16]. In order to improve coverage and save energy, Özdemir et al. suggested a multi-objective approach [17]. Meanwhile, Liu et al. focused on maximizing accuracy in spectrum detection and conserving energy [18]. Sheela et al. investigated a multi-objective model that aimed to extend network lifetime and maintain connectivity while ensuring coverage through the use of PSO [19]. In their research for secure routing and prolonged network lifespan, Yao et al. implemented a multi-objective technique in wireless sensor networks (WSNs). Their approach factored in three key objectives: remaining energy, trust ratings, and distance to the sink [20]. In a similar manner, Enan et al. proposed the Stable Aware Evolutionary Routing Protocol (SAERP) for enhancing stability duration in both homogeneous and heterogeneous WSNs. SAERP utilizes an effective evolutionary strategy to select cluster heads, outperforming LEACH and SEP protocols in terms of stability [24]. This work considered network heterogeneity to create a robust routing protocol that can maintain stability for a longer period of time. Additionally, a multi-objective scheme was implemented to improve the balancing of network loads. Despite being a powerful optimization tool for intricate issues, MOSSA has limitations in successfully resolving certain NP-hard problems like establishing data routes in wireless networks. Consequently, the artificial bee colony optimizer's bees' neighbourhood search strategy was integrated into MOSSA to enrich solution diversity. Several optimized protocols that rely on the principles of SEP and EDEEC, which involve two and three levels of heterogeneity, have been developed. These protocols have been further enhanced with the use of MOSSA, MOSSA-BA, and MOPSO. The contributions made in this regard are quite specific and include the following aspects: International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 75](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-3-2048.jpg)
![•Firstly, the routing problem was solved by improving the basic MOSSA: the incorporation of the neighbourhood search strategy of ABC has made it more efficient in local exploitation, and the introduction of a ranking process based on the dominance concept has increased its flexibility. •The routing problem of wireless networks has been effectively resolved through the successful application of MOPSO, MOSSA, and MOSSA-BA (a modified version of MOSSA). • Investigating several criteria and selecting those that are simplified and effective in terms of energy savings and time consumption. •Optimization of two and three-level heterogeneous networks using the aforementioned algorithms. •Using these algorithms to optimize heterogeneous networks, the protocols that were implemented yielded better results than the standard heterogeneous protocols SEP and EDEEC. 2.1. SEP-Stable Election Protocol In order to rotate the roles of cluster heads (CHs) among nodes, heterogeneous protocols utilize a probability-based method. This method considers both the target percentage of CHs and the frequency of node selection as a CH. During each round, a node will produce a random number ranging from 0 to 1. If this value falls below the threshold function 𝑇(𝑆𝑖), then the node 𝑆𝑖 will be assigned as a CH [12]. { 𝑇(𝑆𝑖) = 𝑝 1 − 𝑝 ∗ 𝑟 𝑚𝑜𝑑( 1 𝑝) 𝑆𝑖 ∈ 𝐺 𝑇(𝑆𝑖) = 0 𝑜𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑤𝑖𝑠𝑒 (1) ” 𝑝 " is the desired percentage of CHs, "𝑟"is the current round, and "𝐺" is the set of nodes not elected as CHs in 1/ 𝑝 rounds. Therefore, the CHs are probabilistically determined based on equation (1), which favours the unelected nodes for 1/ 𝑝 rounds. SEP consists of two node categories, namely normal and advanced nodes. The former is initially endowed with a set amount of energy "E0", whereas the latter is given a larger amount of energy equal to "E0 × (1 + μ)". The probability of a node being elected as a CH is based on its initial energy level according to the formula [12]: Pi n = P 1 + μ. m (2) Pi a = P 1 + μ. m × (1 + μ) (3) m: is the proportion of advanced nodes During each round, every node "i" creates a random number ranging from 0 to 1. If the number is lower than the corresponding threshold, the node will operate as CH for that round. 2.2. EDEEC-Enhanced Distributed Energy Efficient Clustering Protocol The EDEEC protocol is a three-level heterogeneous protocol that selects nodes as CHs based on their initial and residual energy. The nodes are categorized into three energy levels: normal, intermediate, and super nodes, denoted by, E0, (E0. μ) and (E0. φ) respectively. Based on these levels, the selection probabilities for nodes to become CHs are given below [33]. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 76](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-4-2048.jpg)
![Pi n = P. ER(r) (1 + μ + φ). ET ̅̅̅(r) Pi a = P. ER(r). μ (1 + μ + φ). ET ̅̅̅(r) (4) Pi s = P. ER(r). φ (1 + μ + φ). ET ̅̅̅(r) The calculation of ET ̅̅̅(r), which represents the network average energy at round r, involves the residual energy of node i, denoted as ER(r), and the desired percentage of CH, represented by P: ET ̅̅̅(r) = 1 N . Etotal (1 − r R ) (5) "N" is the number of nodes and 𝑅 is the network lifetime calculated as below [32]: R = Etotal Eround (6) The calculation of Eround is explained in [33]. Essentially, nodes generate a random number range of 0-1. When this number falls below the specified threshold from equation (1), which utilizes 𝑃𝑖 from equation (4), the node takes on the role of CH. 3. MULTI-OBJECTIVE BASED HETEROGENEOUS PROTOCOLS 3.1 The Setup Phase The selection of CHs in SEP or EDEEC is determined through a random process that relies on a probability function considering the initial energy of nodes in SEP or the initial and remaining energy of nodes in EDEEC. As a result, routing problems in heterogeneous networks can be enhanced through the use of swarm intelligence-based optimization techniques such as ACO, PSO, ABC, BFO, and others. In this research, the selection of CHs during the initial phase of SEP or EDEEC has been investigated as a bi-objective optimization challenge. To simulate the process, the network is created with varying energy levels, similarly to SEP or EDEEC. In addition, MOSSA, MOSSA- BA, or MOPSO are utilized to optimize the CH set. During the setup phase, nodes transmit both initial and residual energy to the base station. The MOSSA, MOSSA-BA, or MOPSO algorithms scrutinize this data and determine the strongest cluster heads (CHs). Nodes with greater initial and residual energy are given priority during the selection process, using specific criteria. The newly appointed CHs are then announced to all nodes by the base station. In WSNs, the dominant communication model is that the sensor nodes transmit the collected data to one or a number of sinks via a multi-hop path. This pattern of communication creates an inequitable distribution of traffic load, as nodes that are in close proximity to a sink will experience a high traffic load. Therefore, this unbalanced distribution of traffic load can lead to the rapid death of nodes close to sinks, thus rendering the rest of the network inoperable. To mitigate this damage resulting from an unequal distribution of traffic, numerous researchers have tackled the issue of load balancing by developing novel routing algorithms that rely on gauging the remaining energy reserves and other path capacity metrics [35]. In this work, to avoid congested links within node clusters, traffic loads are aggregated and redundancy is eliminated. Additionally, access to the radio channel connecting the member nodes with their cluster heads is planned according to the TDMA protocol, and the Carrier-Sense Multiple Access (CSMA) protocol is employed to connect nodes with their nearest CHs [26]. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 77](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-5-2048.jpg)
![Moreover, to prevent collisions and overhearing within each cluster, data transfer from nodes to CHs is carried out using the TDMA protocol. This latter ensures the effective distribution of transmission slots among sensor nodes, with the objective of decreasing power consumption [21]. Under the TDMA protocol, a cluster head (CH) will establish a transmission schedule for each member of its cluster. Nodes will then activate their radio antennas exclusively during their designated time slots. This eliminates the energy waste and resource depletion that result from nodes remaining idle or "overhearing" by entering the inactive nodes into sleep mode [30]. To avoid potential communication collisions between CHs and the base station, the CSMA/CA or CSMA/CD protocol is commonly used. This adaptable protocol is capable of accommodating changes in scale and topology, but it requires medium monitoring before every transmission, which can increase energy consumption. Consequently, it is mainly employed for communications between CHs and the BS [31]. Furthermore, the proposed routing algorithm optimizes the selection of cluster heads (CHs) based on their remaining energy and alternates the CH role between nodes to balance the traffic load. To minimize the energy consumed by nodes per round, this approach involves the selection of a large number of CH nodes, as modeled by equations (7) and (8) in subsection 3.1.2. 3.1.1 Salps Representation In this study, the network size, which is determined by the number of nodes, is used as the size of each salp (particle). To select the CHs (cluster heads) using multi-objective optimization methods, the salps are randomly initialized within the range of -3 to 3. Once initialized, the salps are converted to binary, where only positive values are set to 1 and negative values are set to 0. This binary representation indicates which nodes are elected as CHs (with a value of 1) and which nodes belong to the nearest cluster (with a value of 0). The range of -3 to 3 is chosen to ensure that around half of the nodes are selected as CHs and to avoid having an empty set of CHs. An illustration of the adopted representation is below: Figure 1. A solution representing a network comprising 6 nodes The node consists of various variables that convey its state, such as whether it is a CH, its energy level, and whether it is depleted. The salps are initiated with random values ranging from -3 to 3, with only positive values being considered and negative values being set to zero. The number of CHs is still significant, so a second criterion is employed to control their selection, which is incorporated into the objective functions presented in the subsequent section. 3.1.2 The Objective Functions Both the SEP and EDEEC protocols operate on a fundamental principle that establishes the criteria for each. While the SEP protocol endeavours to maximize the total initial energy of cluster heads (CHs), the EDEEC protocol strives to maximize the sum of CHs' residual energy divided by the average energy of the rth round, as specified in equation (5). Nonetheless, in bi-objective optimization, it was determined that focusing solely on residual energy produced more favourable experimental outcomes. Salp -3 1.9 -2.8 1.6 0.5 -1.3 Nodes IDs 1 2 3 4 5 6 Binary Salp 0 1 0 1 1 0 International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 78](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-6-2048.jpg)
![FSEP (CHi) = max ( ∑ ECHi Nb (CHi) i=1 , Nb (CHi)) (7) FEDEEC(CHi) = max( ∑ ER i(r) Nb (CHi) i=1 , Nb (CHi) ) (8) ECHi is the initial energy of cluster head i at round r, Nb (CHi) is the number of cluster heads, and ER i(r) is the residual energy of cluster head i at round r. A crucial aspect of multi-objective optimization is the dominance concept, which is utilized to compare and assess potential solutions. To be considered superior, solution S1 must either perform strictly better or equally well in all objectives than solution S2 and also outperform S2 in at least one objective. The Pareto-optimal set is a collection of non-dominated solutions that are preserved in a separate archive. This archive is governed by strict regulations, which require the inclusion of any non-dominated solution that is not inferior to any other archive item as well as the exclusion of any dominated archive item by a non-dominated solution. These rules are intended to ensure the excellence of the solutions within the archive [28]. When multiple objectives are optimized, the results are presented as a Pareto set that showcases non-dominated solutions. To determine the best non-dominated solution, decision-making techniques like multi-attribute decision-making (MADM) are commonly employed. The outcome of the MOSSA or MOSSA-BA algorithms is represented by the most optimal food source discovered, while the modified MOPSO algorithm generates the most recent non-dominated solution added to the archive. 3.1.3. MOSSA-Multi-Objective Salp Swarm Algorithm The Salp Swarm Algorithm (SSA) is an optimized technique that imitates the swimming behaviour of salps when looking for food sources in the ocean. In a spiral pattern, semi-translucent salps follow a leader salp to locate the most fitting food source [28]. Through this process, the leader guides the group of followers to locate the best food source. Figure 2. Salps motion To solve a d-dimensional problem, the salps positions can be specified by a two-dimensional matrix Xi j(i = 1 … N, j = 1 … d),with N the number of salps as shown below [34]: X = [ x11 x21 x12 x22 … x1d … x2d ⋮ ⋮ … ⋮ xN1 xN2 … xNd ] Leader International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 79](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-7-2048.jpg)
![In our study, to minimize delay and achieve lower latency, we opted for a limited number of solutions. Specifically, we set the number of salps, or potential solutions, to 20 and the number of iterations to 30. Additionally, we adapted the SSA algorithm to the routing problem by setting the problem's dimension (d) equal to the number of nodes in the network. The Newtonian displacement process of the salp colony was modelled by the SSA algorithm using the formulation below. The process involves determining the fitness of salps, identifying the optimal food position Fj, and then having the leading Salp X1j move towards it using equation (9) [34]. X1j = { Fj + c1. r1(Ubj − Lbj) + c1. Lbj, r2 ≥ 0 Fj − c1. r1(Ubj − Lbj) + c1. Lbj, r2 < 0 (9) c1 = 2. e −( 4 it maxit ) 2 (10) ″ it‶ is the current iteration and ″maxit‶ is the maximum number of iterations. Ubj and Lbj are respectively the upper and lower bounds of the j th dimension. r1 & r2 are random values between 0 and 1. The follower salps change their positions according to: Xij = 1 2 (Xij + X(i−1)j) (11) The followers’ positions are then constricted in the range [Lbj, Ubj ]. SSA steps 1. Salps Initialization Repeat 2. Salps evaluation 3. Determination of the best food source (the best salp) 4. Update the leader position 5. Update the followers’ positions 6. Constriction of leader & followers’ position within their initial range. Until a maximum number of iterations The leader Salp employs equation (9) to approach the best food source, while the first follower trails the leader Salp by utilizing equation (11). Subsequently, each successive follower adjusts its position closer to the previous one, imitating the Newtonian motion of Salps. This iterative algorithm continues with periodic assessments of salps and food source replacement until the maximum iteration limit is achieved. To tackle the complexity of multi-objective challenges, the SSA devised an external archive strictly for preserving non-dominated solutions. As the algorithm progresses, each salp is evaluated against the archive's contents. If a Salp surpasses any of the archive's solutions, the latter is replaced. To maintain a balance, an element from the most crowded area of the archive is removed when it becomes too large. To complete this task, the roulette wheel method is employed. This involves selecting an item located within the most densely populated area of the objective space within the archive. A score is assigned to each element within the archive based on the number of neighbouring items it possesses. This is calculated using a specific distance threshold within the objective space, as explained below [34]. Th(k) = max(F(k)) − min(F(k)) archive size (12) International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 80](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-8-2048.jpg)
![k =1,...,to number of objective functions, and max(F(k)) and min(F(k)) are the vectors of the maximum and minimum values of each objective function. In order to evaluate archive elements, the MOSSA algorithm measures their distance from other solutions within the archive. If an element's distance falls below a predetermined threshold (represented as "th" in equation 12), its rank is incremented. The selection of an archive element is done through a roulette selection process, with each solution's rank serving as its probability of being chosen. P(S) = Nb (Neighbours) (13) In the archive, the element that stands the greatest chance of being eliminated is the one that possesses the most nearby solutions in the objective space. In order to promote diversity, the MOSSA algorithm picks its food source from the least crowded area of the archive. As a result, the solution with the lowest rank is more likely to be chosen. The probability of choosing an element "S" as the food source is calculated by means of the formula below: P(S) = 1 Nb (Neighbours) (14) The MOSSA can be summarized in the following steps: The MOSSA steps 1. Salps Initialization Repeat 2. Salps evaluation 3. Determination of non-dominated salps 4.Archive Update If the archive is full ⎯ Remove a resident solution in the densest region of the repository objective space ⎯ add the non-dominated salp to the archive end if 3. Select a resident food source in the less dense region of the archive objective space 4. Update the leader position using equation (9) 5. Update the followers’ positions using equation (11) 6. Constriction of leader & followers’ position within their initial range. Until a maximum number of iterations 3.1.4. Hybrid MOSSA-BA For CH Selection The MOSSA in its basic form, involves a group of followers moving in spiral chains and being led by a single leader. However, if the leader becomes stuck on a less-than-ideal solution, the followers will also converge on that limited solution. In order to maximize the algorithm's efficacy, one potential solution is to employ multiple leaders who guide multiple chains of followers. This approach can lead to a slight improvement in the algorithm's performance. To address this issue, the MOSSA-BA was introduced. This approach integrates the neighbourhood search strategy of artificial bee colony optimization to boost the MOSSA's exploitation capabilities. Instead of using equation (11) that forces Salps to converge with the leader's solution, the MOSSA-BA method employs equation (15) below to update the follower Salps [29]. Newsalp = salp(i) + α. φ. (salp(i) − salp (k)) (15) International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 81](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-9-2048.jpg)
![α = 6, φ ∈ [−1,1], and k is a random salp different from i. In the event that the newly produced Salp dominates over its old one in terms of Pareto efficiency, it replaces the latter. Afterwards, a fresh inventory of non-dominated Salps is generated, and the archive is revised with each element being assigned a rank that reflects its density with the dominated Salps. This rank is calculated by the formula proposed by Coello et al. [27]: rank(S) = C Nb (dominated salps) (16) "C" is a constant, and Nb (dominated salps) is the number of salps dominated by salp “S”. The process of choosing the salp residing in the area with the highest concentration of salps is determined by using a roulette wheel that takes into account the probabilities assigned to each salp. prob (S) = rank(S) ∑ rank(i) nb i=1 (17) prob(S) is the selection probability of the salp “S”, and nb is the number of archive elements. The best food source is the archive element residing in the densest region of dominated solutions. To locate the best food source, the leader is directed to move according to equation (9), while the remaining Salps explore their neighbourhood using equation (15). Every Salp records the most superior position it discovers based on Pareto dominance. Salps that are not productive in finding improved positions in their neighbourhood for a number of cycles will be reset at random to promote diversity. MOSSA-BA is an improved version of MOSSA that incorporates ABC exploitation strategies and the MOPSO ranking process. These enhancements aim to enhance its efficiency and flexibility in addressing routing issues in WSNs. Below is an adaptation of MOSSA-BA for CH selection in the setup phase of SEP (EDEEC) protocols: The MOSSA-BA based SEP (EDEEC) protocol 1.Network initialization 2. Randomly initialize two-level nodes in the SEP-based protocol 3. Randomly initialize three-level nodes in the EDEEC-based protocol. 4. Initialize the sink node in the middle of the area of Interest. %The setup phase 5. For each round do 6. Salps initialization 7. Initialize salps randomly in the range [-3,3]. 8. Repeat 9. Update the position of each salp using equation (15). 10. Replace the old salp with the better new one in terms of Pareto dominance 11. Otherwise, increase its ineffectiveness counter 12. Determination of non-dominated salps 13. For each non dominated salp do 14. If the archive is full 15. Remove a resident solution in the densest region of the repository objective space 16. Add the non-dominated salp to the repository 17. else 18. Add the non-dominated salp to the repository International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 82](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-10-2048.jpg)
![19. end if 20. end for 21. Select a resident food source in the less dense region of the repository objective space. 22. Update the leader position using equation (9) 23. Update each follower position using equation (15). 24. Replace each old follower with the better new one in terms of Pareto dominance 25. Otherwise, increase its ineffectiveness counter 26. Reset the ineffective salps in the range [-3,3]. 27. Until a maximum number of iterations %Clustering 28. Transform the best-found food source into binary 29. Select the associated nodes with value 1 in the best food source as cluster heads (CHs). 30. Join each non-CH node to the closest CH using CSMA Protocol via a (Join-Request) message. %The steady-state phase 31. Transmit data from nodes to CHs using TDMA protocol. 32. Transmit received data from CHs to base station using CSMA protocol. 33. end for each round 3.2. The Steady-State Phase Once MOSSA or MOSSA-BA has completed the optimization process, the base station selects the most optimal food source found and uses it to broadcast CHs IDs across the network. The nodes in turn connect to their nearest CH via the Carrier Sense Multiple Access protocol (CSMA) based on their radio signal strength (RSSI). In each cluster, the CH coordinates access to the medium with the TDMA protocol and transmits the collected data to the base station. The CHs maintain their communication with the base station using the CSMA protocol [25]. In this study, the radio energy model is used to simulate the nodes energy consumption. According to the radio energy model, each node loses energy 𝐸𝑇𝑟𝑆 (𝑝, 𝑑) for each packet transmission and loses 𝐸𝑅𝑐𝑝𝑡(𝑝)for each packet reception [26]: 𝐸𝑇𝑟𝑆 (𝑝, 𝑑) = { 𝑝 × 𝐸𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐 + 𝑝 × 𝑒𝑓𝑠 × 𝑑2 𝑖𝑓 𝑑 < 𝑑0 𝑝 × 𝐸𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐 + 𝑝 × 𝑒𝑚𝑝 × 𝑑4 𝑖𝑓 𝑑 > 𝑑0 (18) 𝐸𝑅𝑐𝑝𝑡(𝑝) = 𝑝 × (𝐸𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐 + 𝐸𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑔) (19) 𝑑0 is a distance threshold: 𝑑0 = √𝑒𝑓𝑠/𝑒𝑚𝑝 𝑑: is the distance between two communicating nodes. 𝐸𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐 refers to the energy consumed by the electronic circuit. 𝑒𝑚𝑝 represents the energy utilized by the amplifier in free space. 𝑒𝑓𝑠 denotes the energy required by the amplifier in a fading space with multiple paths. 𝐸𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑔: is the needed energy for data aggregation. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 83](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-11-2048.jpg)
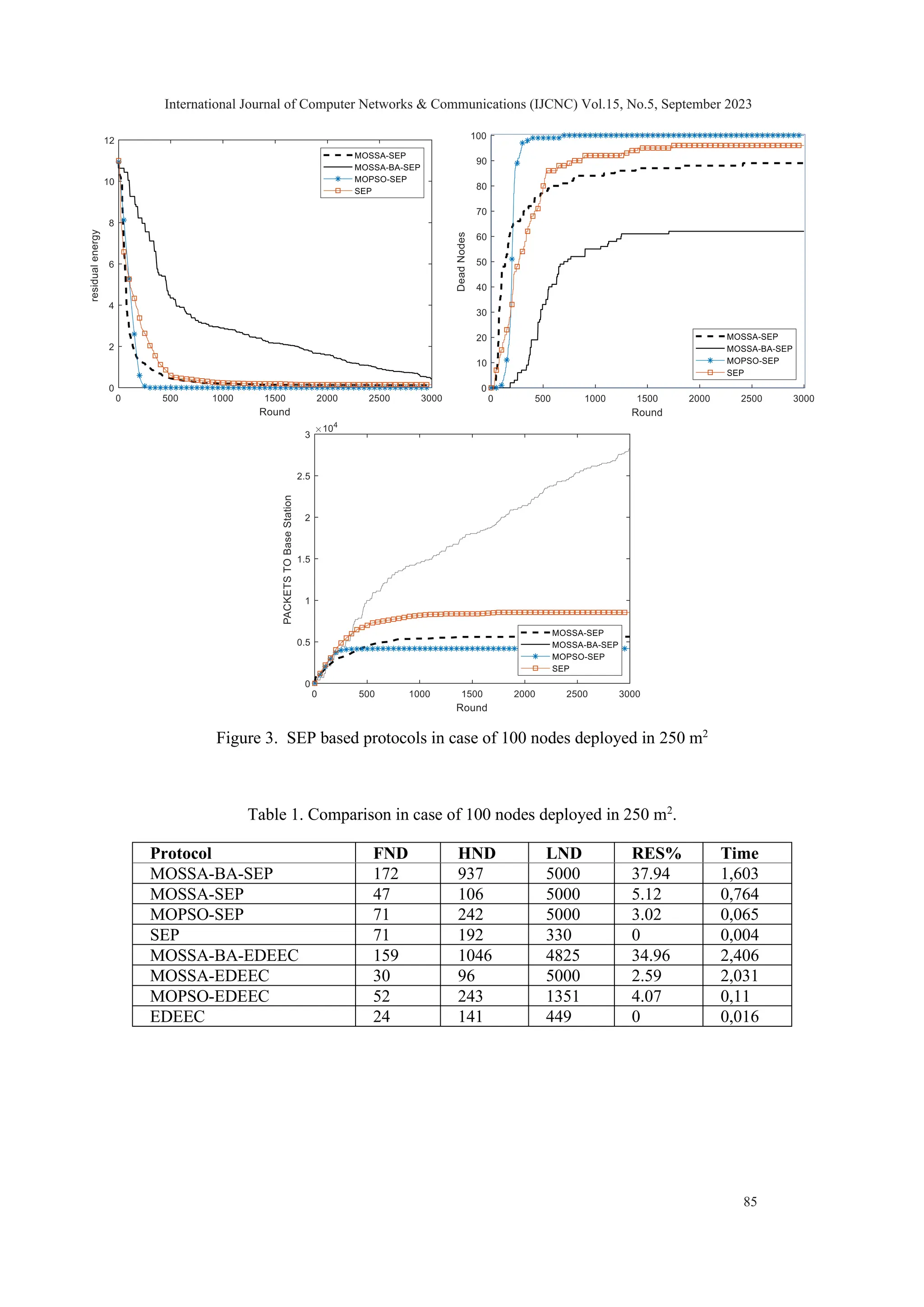
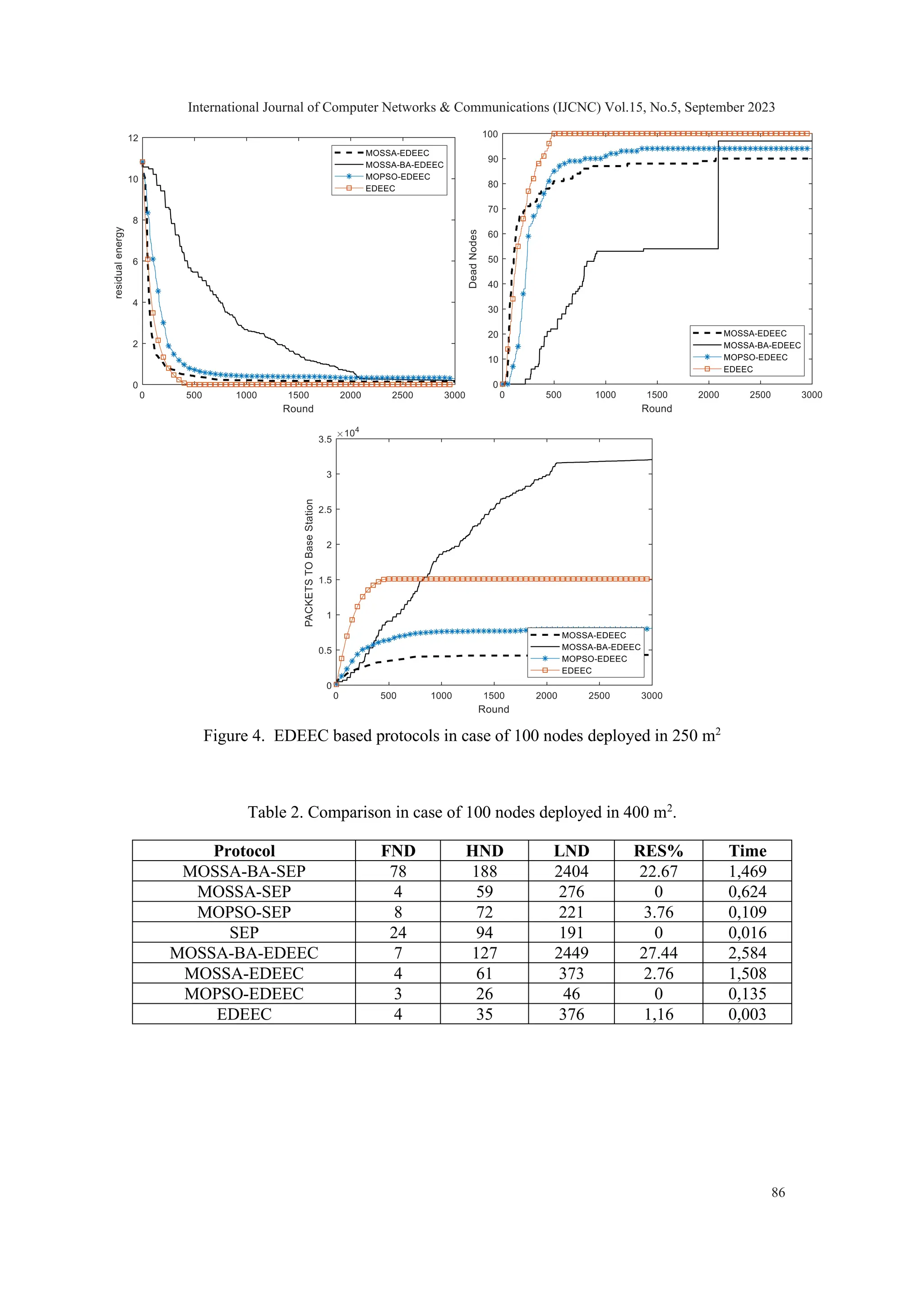
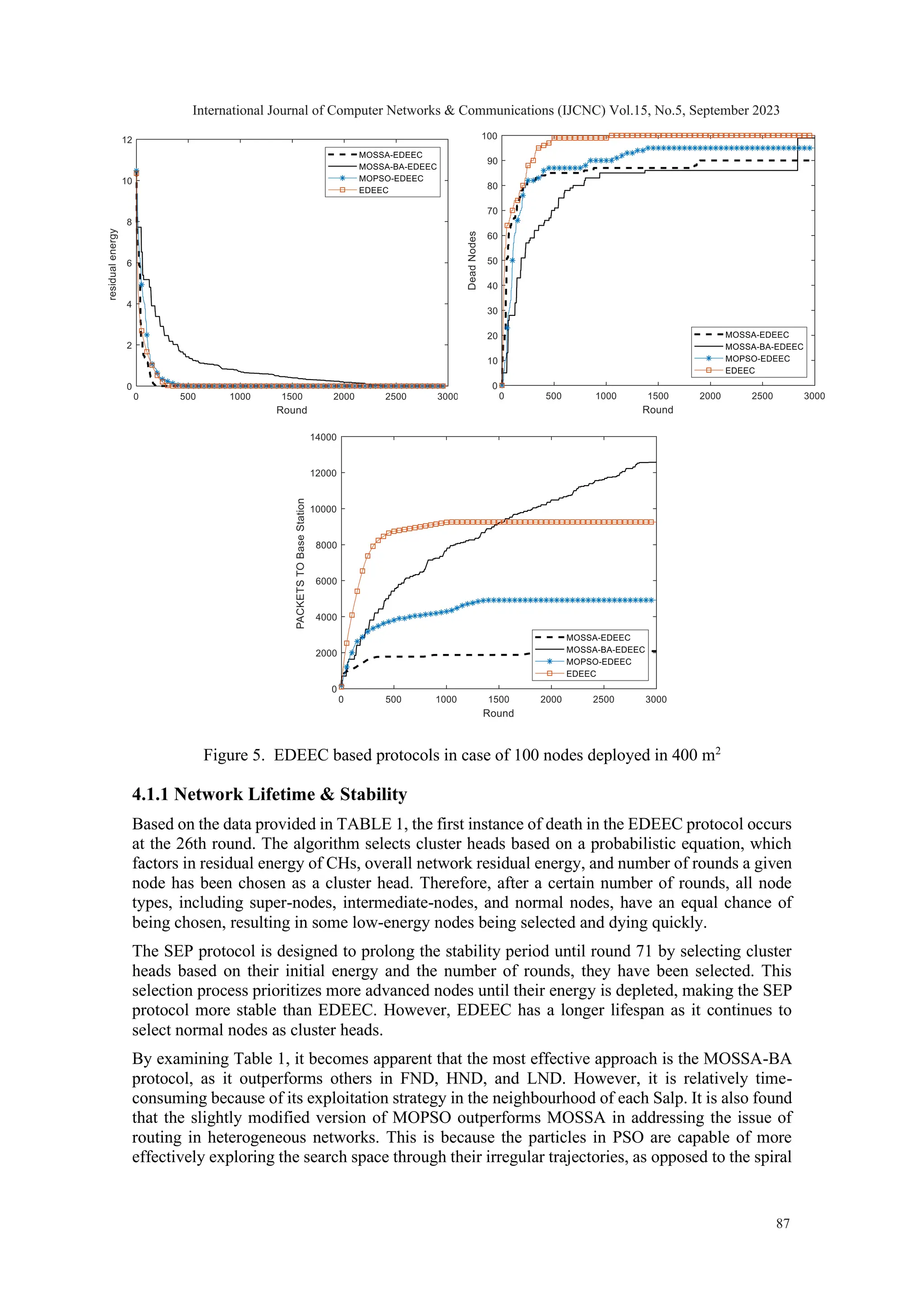
![4. RESULTS ANALYSIS & DISCUSSION An assessment and comparison analysis of various algorithms' efficiency are presented in this section, featuring MOSSA, MOSSA-BA, and MOPSO with SEP or EDEEC protocols. The MOPSO applied here is a modified version of the algorithm from [27], with the latest solution appended to the archive being deemed the global leader instead of a solution picked at random from the most densely populated area in the archive. To ensure a fair comparison, MATLAB 2018 was used to conduct experiments with identical parameters. The sensors were randomly placed in the area of interest and were given 0.1 joules as initial energy, while the sink had an unlimited energy supply. The values for 𝐸𝑒𝑙𝑒𝑐, emp, and 𝐸𝑃𝑟𝑜𝑐𝑒𝑠𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑔 were respectively 50 nanojoules, 100 picojoules, and 5 nanojoules, and the size of the data packet used was 4000 bits. The percentage of super and intermediate nodes is, respectively, m = 0.1 and mo = 0.2. Their correspondent energy factors are, respectively, 𝜑=1.25 and 𝜇=1. The network topology is ad hoc, which means that the sensor nodes communicate solely through the wireless channel using radio propagation without the need for any intermediary infrastructure devices like a wireless access point (AP). 4.1 Evaluation Numerous evaluations have been conducted to assess the efficacy of the proposed algorithms. The experiments made adjustments to network parameters, such as network size, to determine the impact of density on network performance. The results were quantified by measuring the number of rounds before the first node death (FND), the death of half-nodes (HND), or the death of the last node (LND), as well as the percentage of remaining energy (RES%) and time expended per round. The initial test entails the haphazard placement of 100 nodes throughout a detection zone spanning 250 by 250 square meters. For the second option, we expanded the area of interest to encompass 400 m2 . In order to evaluate the efficacy of the suggested algorithms, we took into account the subsequent metrics [36]: 1. Stability period and network lifetime: i.e., the duration of network operation until the first death of a node and the period of network operation until the complete death of all nodes 2. Reliability, i.e., the rate of successful packet delivery to the base station 3. Scaling: the network's ability to handle large-scale networks in an effective manner 4. Network density, i.e., the concentration of nodes in the area of interest 5. Energy saving, i.e., the proportion of residual energy in the overall network per round The behaviour of the algorithms analysed can be observed in the following figures, which depict the changes in response to variations in the size of the area of interest. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 84](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-12-2048.jpg)


![connectivity, security, delay, and coverage in applications that mirror real-world scenarios. Additionally, it would be beneficial to incorporate novel swarm intelligence-based algorithms and assess their effectiveness in comparison to these methods, such as Rao and GOW. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCES [1] Hong, Y., Wang, S., Kang, H., & Hu, Y. (2022). Iterative Virtual Force Localization Based on Anchor Selection for Three-Dimensional Wireless Sensor Networks. Tehnički vjesnik, 29(3), 1048-1058. [2] Premkumar, M., Sundararajan, T. V. P., & Mohanbabu, G. (2022). Dynamic Defense Mechanism for DoS Attacks in Wireless Environments Using Hybrid Intrusion Detection System and Statistical Approaches. Tehnički vjesnik, 29(3), 965-970. [3] McDermott, C. D., & Petrovski, A. (2017). Investigation of computational intelligence techniques for intrusion detection in wireless sensor networks. International journal of computer networks and communications, 9(4). [4] Heinzelman, W. R., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000, January). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd annual Hawaii international conference on system sciences (pp. 10-pp). IEEE. [5] Akkari, W., Bouhdid, B., & Belghith, A. (2015). LEATCH: Low energy adaptive tier clustering hierarchy. Procedia Computer Science, 52, 365-372. [6] Dhawan, H., & Waraich, S. (2014). A comparative study on LEACH routing protocol and its variants in wireless sensor networks: a survey. International Journal of Computer Applications, 95(8). [7] Kour, H., & Sharma, A. K. (2010). Hybrid energy efficient distributed protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor network. International journal of computer applications, 4(6), 1-5. [8] Hamdoon Shuker, O.N., Increasing The Lifetime of Wireless Sensor Networks using LEACH Protocol, Middle East University Amman, Jordan, Master thesis. 2014. [9] Daanoune, I., Baghdad, A., & Ballouk, A. (2020). Extending the Lifetime of Wireless Sensor Networks using an Improved Clustering Protocol. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE) ISSN, 2277-3878. [10] Yi, D., & Yang, H. (2016). HEER–A delay-aware and energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Computer Networks, 104, 155-173. [11] Liu, Y., Wu, Q., Zhao, T., Tie, Y., Bai, F., & Jin, M. (2019). An improved energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Sensors, 19(20), 4579. [12] Singh, A., & Rana, S. B. (2015). Heterogeneous routing protocols in wireless sensor network: A survey. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 2(03), 1014-1019. [13] Hasnat, M. A., Akbar, M., Iqbal, Z., Khan, Z. A., Qasim, U., & Javaid, N. (2015, February). Bio inspired distributed energy efficient clustering for Wireless Sensor Networks. In 2015 5th National Symposium on Information Technology: Towards New Smart World (NSITNSW) (pp. 1-7). IEEE. [14] Pawar, K. (2015), Optimization of Stable Election Protocol through Genetic Algorithm & Particle Swarm Optimization in clustered wireless sensor network, International Journal of Digital Application & Contemporary research, (Vol 4, Issue 04). pp. 1–5. [15] Abood, B., & Al-Rikabi, Y. K. (2019). Lifetime enhancement for clustering protocols in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 14(3), 1305-1314. [16] Nabavi, S. R. (2021). An optimal routing protocol using multi-objective whale optimization algorithm for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Smart Electrical Engineering, 10(02), 77-86. [17] Özdemir, S., Attea, B. A. A., & Khalil, Ö. A. (2013). Multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition for energy efficient coverage in wireless sensor networks. Wireless personal communications, 71, 195-215. International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 90](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-18-2048.jpg)
![[18] Liu, W., Qin, G., Li, S., He, J., & Zhang, X. (2015). A multiobjective evolutionary algorithm for energy-efficient cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio sensor network. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 11(5), 581589. [19] Rani, K. S. S., & Devarajan, N. (2012). Multiobjective sensor node deployment in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 4(4), 1262-1266. [20] Yao, X., & Zheng, X. (2008, December). A secure routing scheme based on multi-objective optimization in wireless sensor networks. In 2008 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security (Vol. 1, pp. 436-441). IEEE. [21] Nguyen, V., & Hong, C. S. (2018). Adaptive TDMA and CSMA-Based MAC Protocols for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks: A Survey. In AETA 2017-Recent Advances in Electrical Engineering and Related Sciences: Theory and Application (pp. 163-171). Springer International Publishing. [22] Çelik, F. (2015). ACO-based load balancing scheme for manets. Tehnički vjesnik, 22(5), 1165- 1169. [23] Veerabadrappa, K., & Lingareddy, S. C. (2022). Secure Routing using Multi-Objective Trust Aware Hybrid Optimization for Wireless Sensor Networks. International Journal of Intelligent Engineering and Systems, 15(1), 540-548. [24] Khalil, Enan. A., & Attea, B. A. A. (2013). Stable-aware evolutionary routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 69, 1799-1817. [25] Padmanabhan, K., Kamalakkannan, P. (2011). “A study on energy efficient routing protocols in wireless sensor networks,” European Journal of Scientific Research, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 517–529, doi: 10.5121/ijdps.2012.3326. [26] Heinzelman, W. B., Chandrakasan, A. P., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on wireless communications, 1(4), 660-670. [27] Coello, C. A. C., Pulido, G. T., & Lechuga, M. S. (2004). Handling multiple objectives with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Transactions on evolutionary computation, 8(3), 256-279. [28] Špoljarić, T., Pavić, I., & Alinjak, T. (2022). Performance Comparison of No-preference and Weighted Sum Objective Methods in Multi-Objective Optimization of AVR-PSS Tuning in Multi- machine Power System. Tehnički vjesnik, 29(6), 1931-1940. [29] Karaboga, D., & Basturk, B. (2007). Artificial bee colony (ABC) optimization algorithm for solving constrained optimization problems. In Foundations of Fuzzy Logic and Soft Computing: 12th International Fuzzy Systems Association World Congress, IFSA 2007, Cancun, Mexico, June 18-21, 2007. Proceedings 12 (pp. 789-798). Springer Berlin Heidelberg. [30] Kaur, T., & Kumar, D. (2016). TDMA-based MAC protocols for wireless sensor networks: A survey and comparative analysis. In 2016 5th international conference on wireless networks and embedded systems (WECON) (pp. 1-6). IEEE. [31] Rambabu, C., Prasad, V. V. K. D. V., & Prasad, K. S. (2020). Multipath cluster-based hybrid MAC protocol for wireless sensor networks. Wireless and Microwave Technologies, 1, 1-16. [32] Vançin, S., & Erdem, E. (2018). Threshold balanced sampled DEEC model for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Wireless communications and mobile computing, 2018, 1-12. [33] MRIU, F. (2016). An Enhanced Distributed Energy-Efficient Clustering (DEEC) Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking, 9(11), 49-58. [34] Khajehzadeh, M., Iraji, A., Majdi, A., Keawsawasvong, S., & Nehdi, M. L. (2022). Adaptive Salp Swarm Algorithm for Optimization of Geotechnical Structures. Applied Sciences, 12(13), 6749. [35] Wang, Q. (2010). Traffic Analysis & Modeling in Wireless Sensor Networks and Their Applications on Network Optimization and Anomaly Detection. Netw. Protoc. Algorithms, 2(1), 74-92. [36] Al-Salti, F., Alzeidi, N., Day, K., & Touzene, A. (2023). PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF ERGR-EMHC ROUTING PROTOCOL USING LSWTS AND 3DUL LOCALIZATION SCHEMES IN UWSNS. International Journal of Computer Networks and Communications, 15(2). International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC) Vol.15, No.5, September 2023 91](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15523cnc05-231108044143-0ed24041/75/Multi-Objective-Salp-Swarm-based-Energy-Efficient-Routing-Protocol-for-Heterogeneous-Wireless-Networks-19-2048.jpg)
