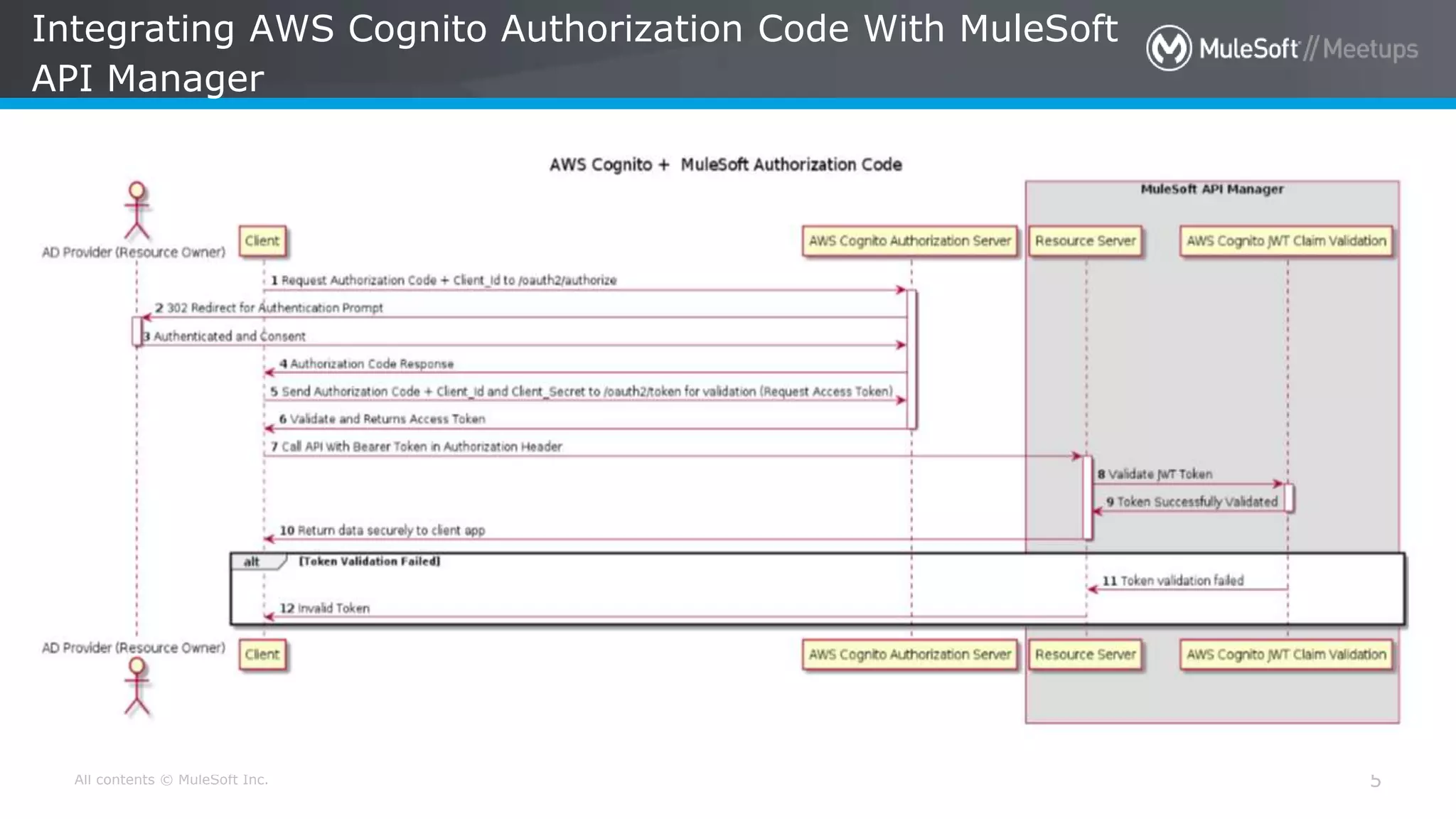
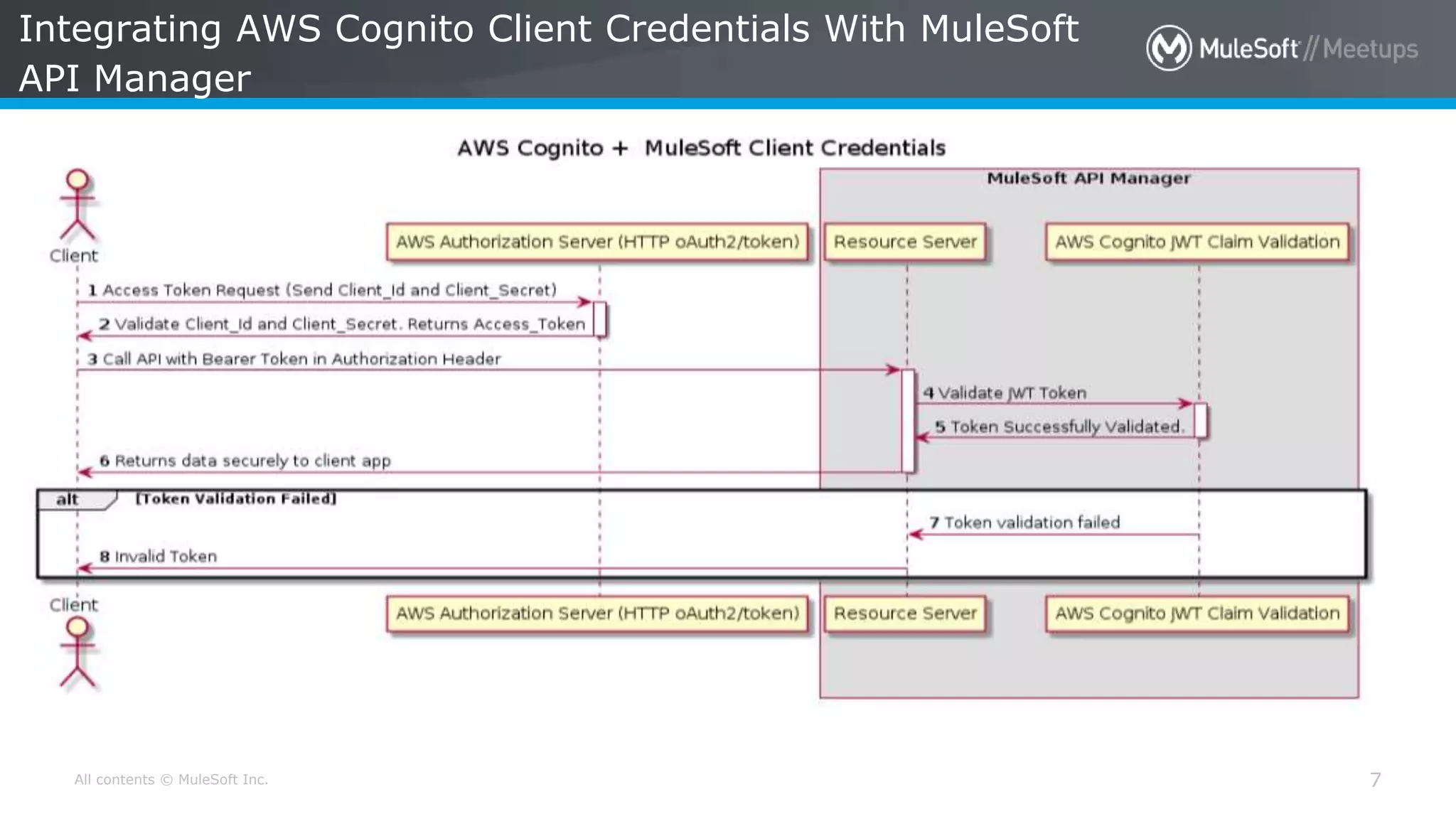
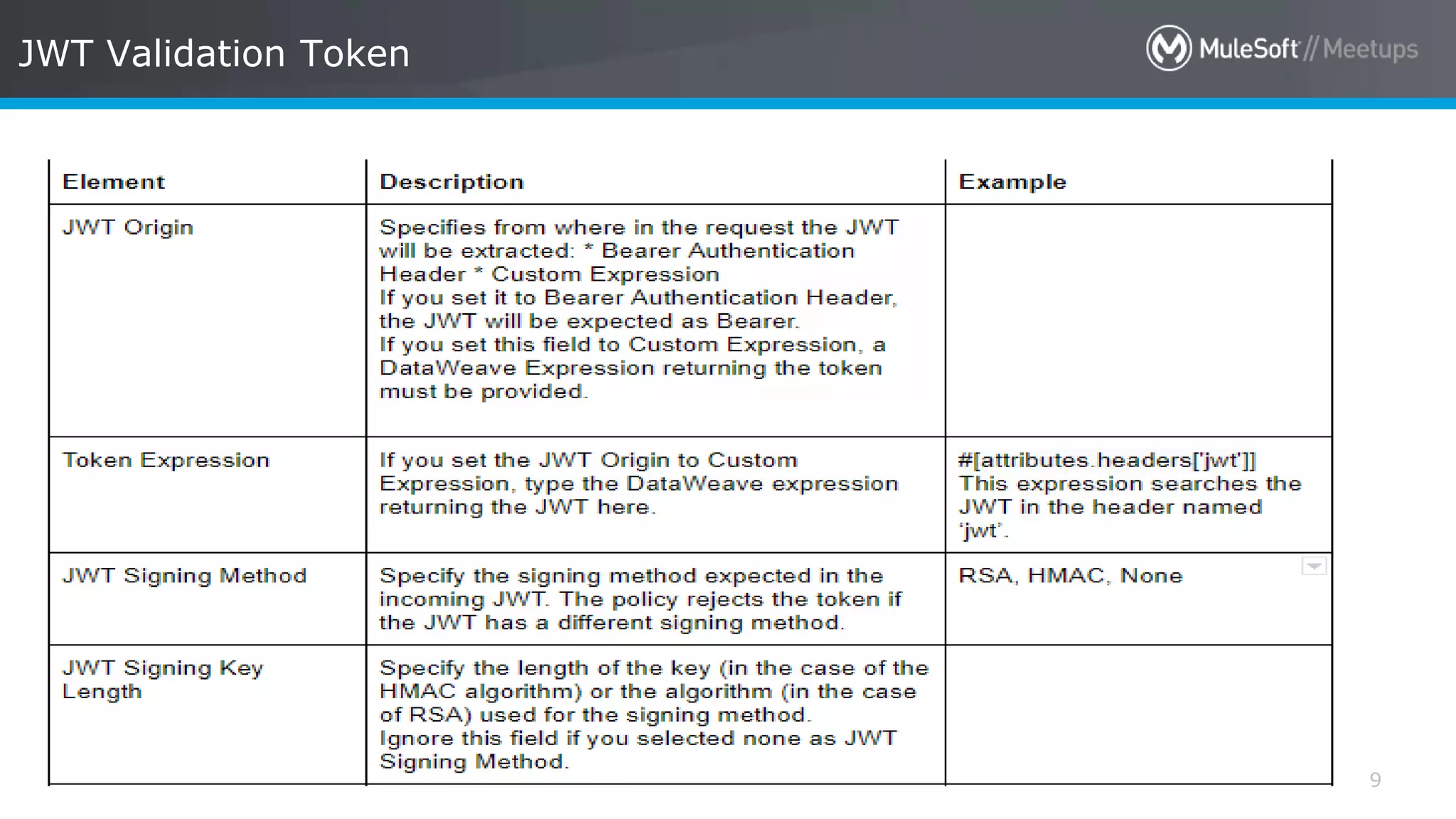
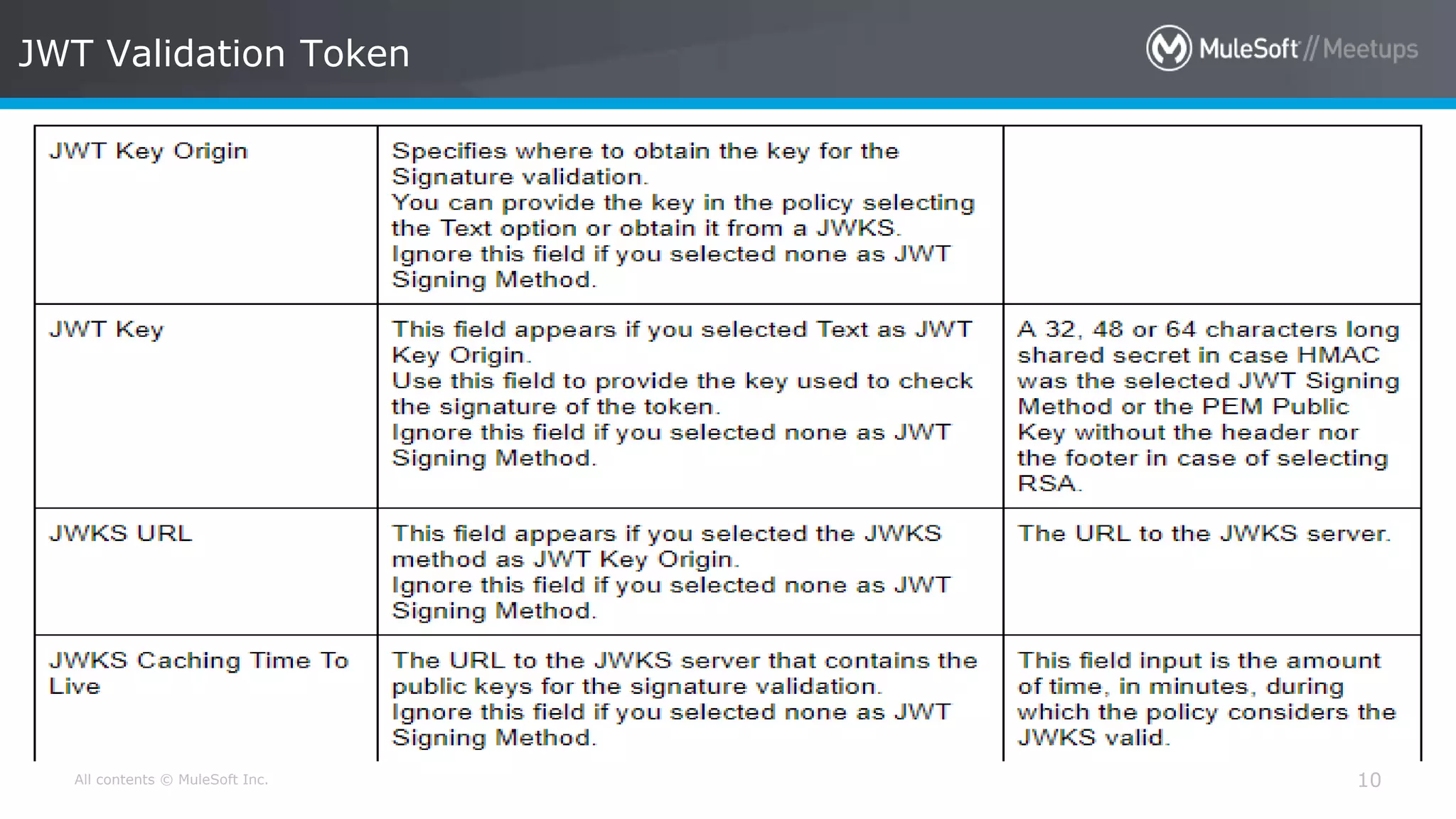
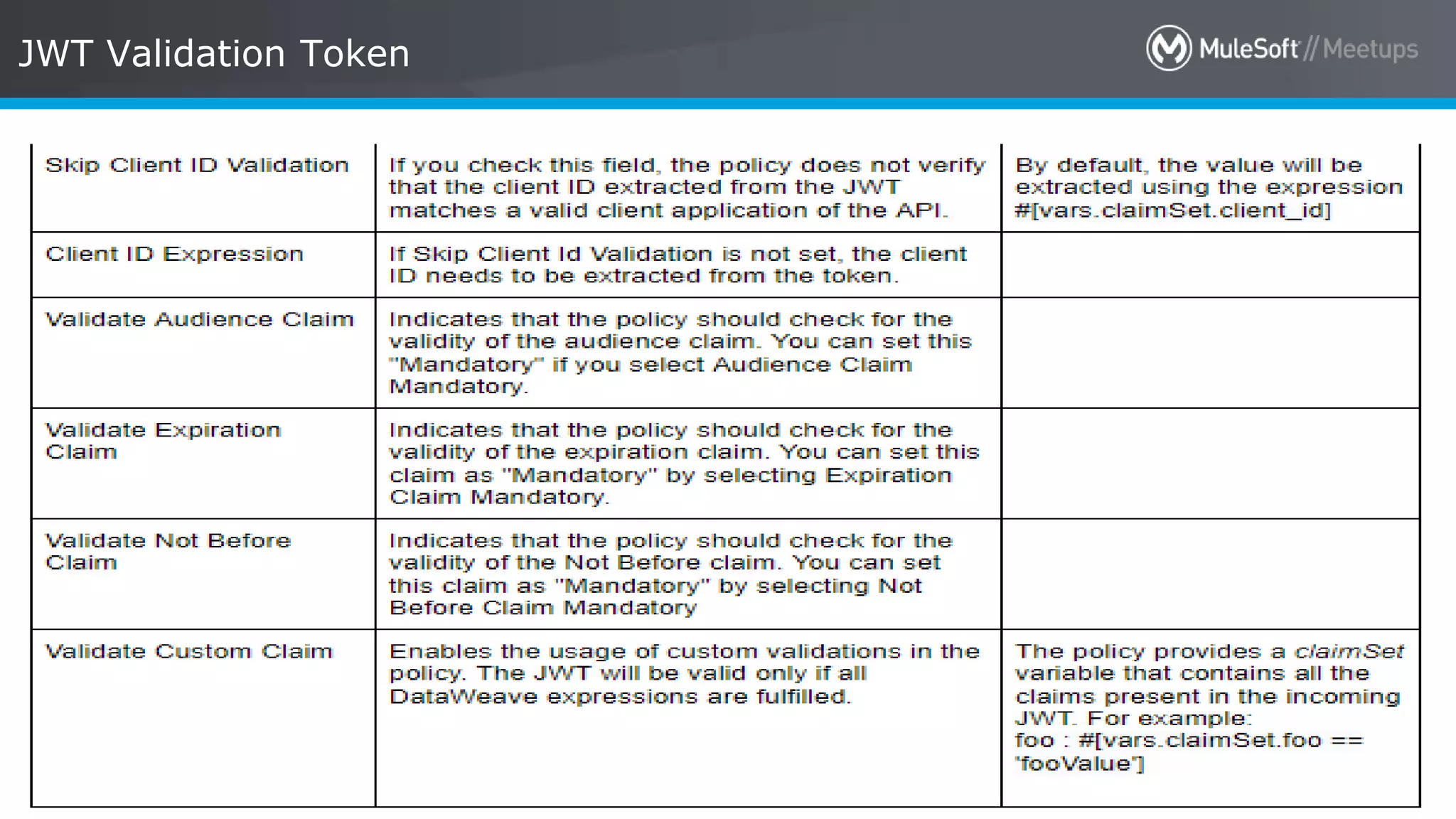
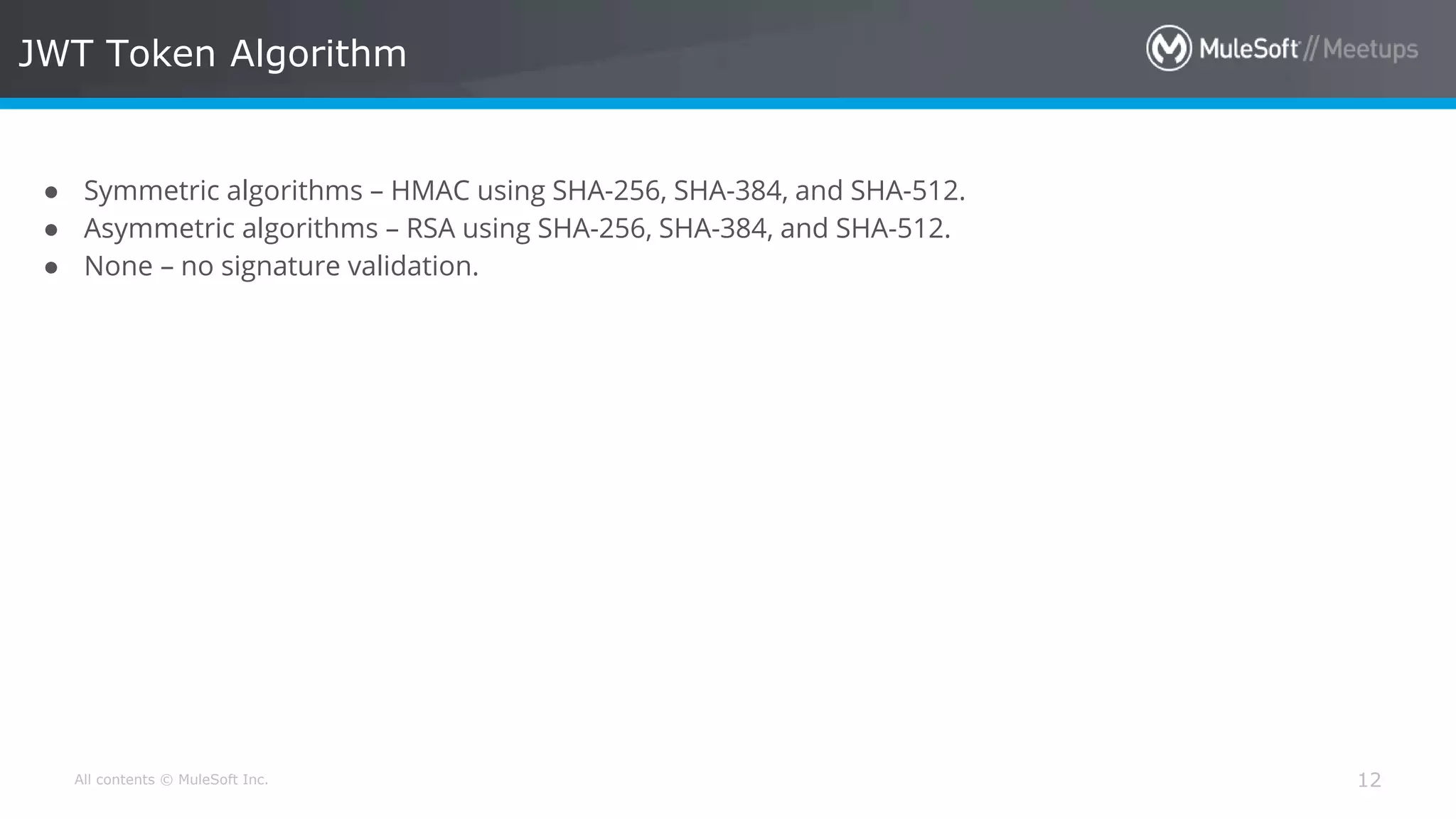
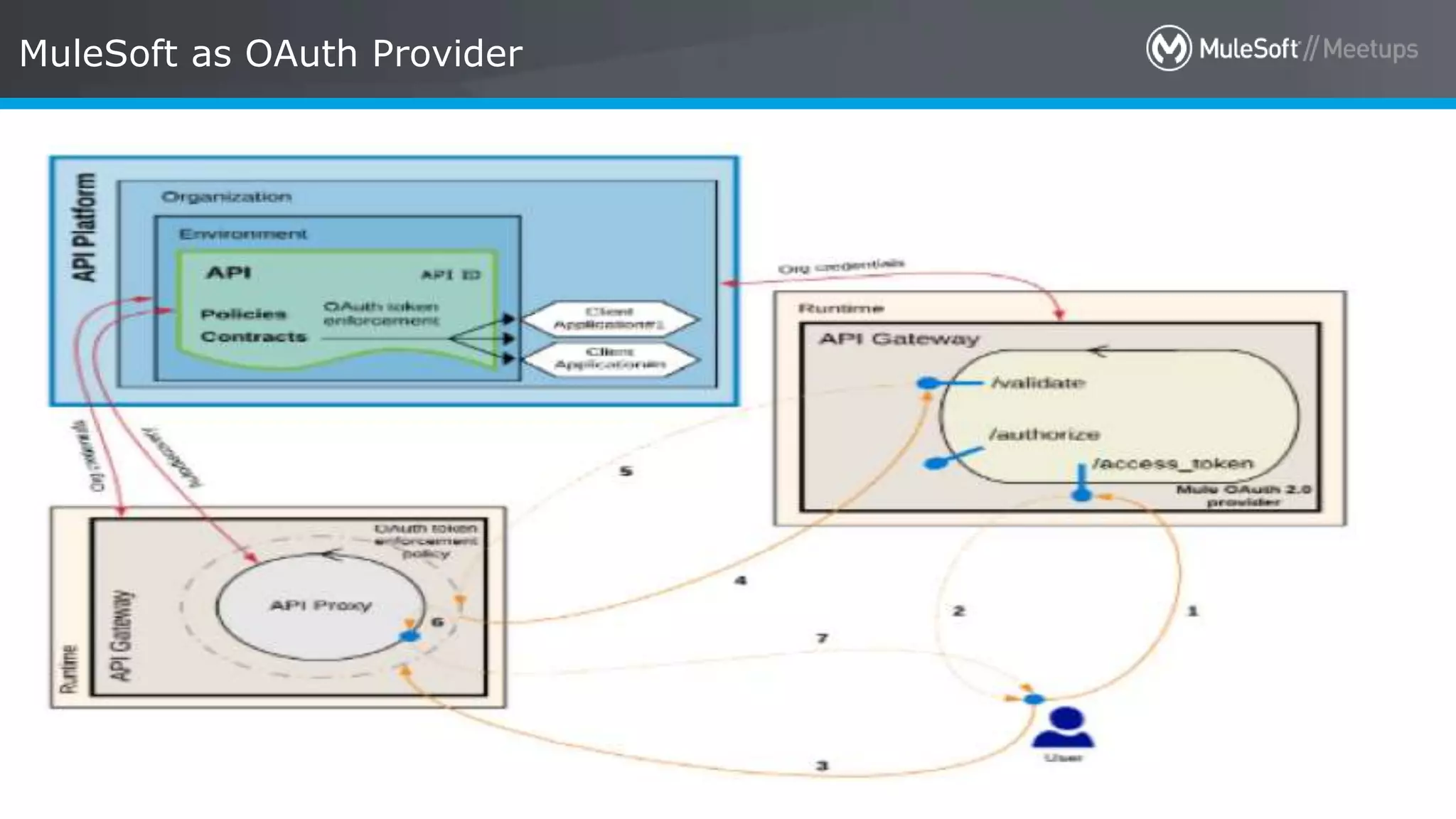
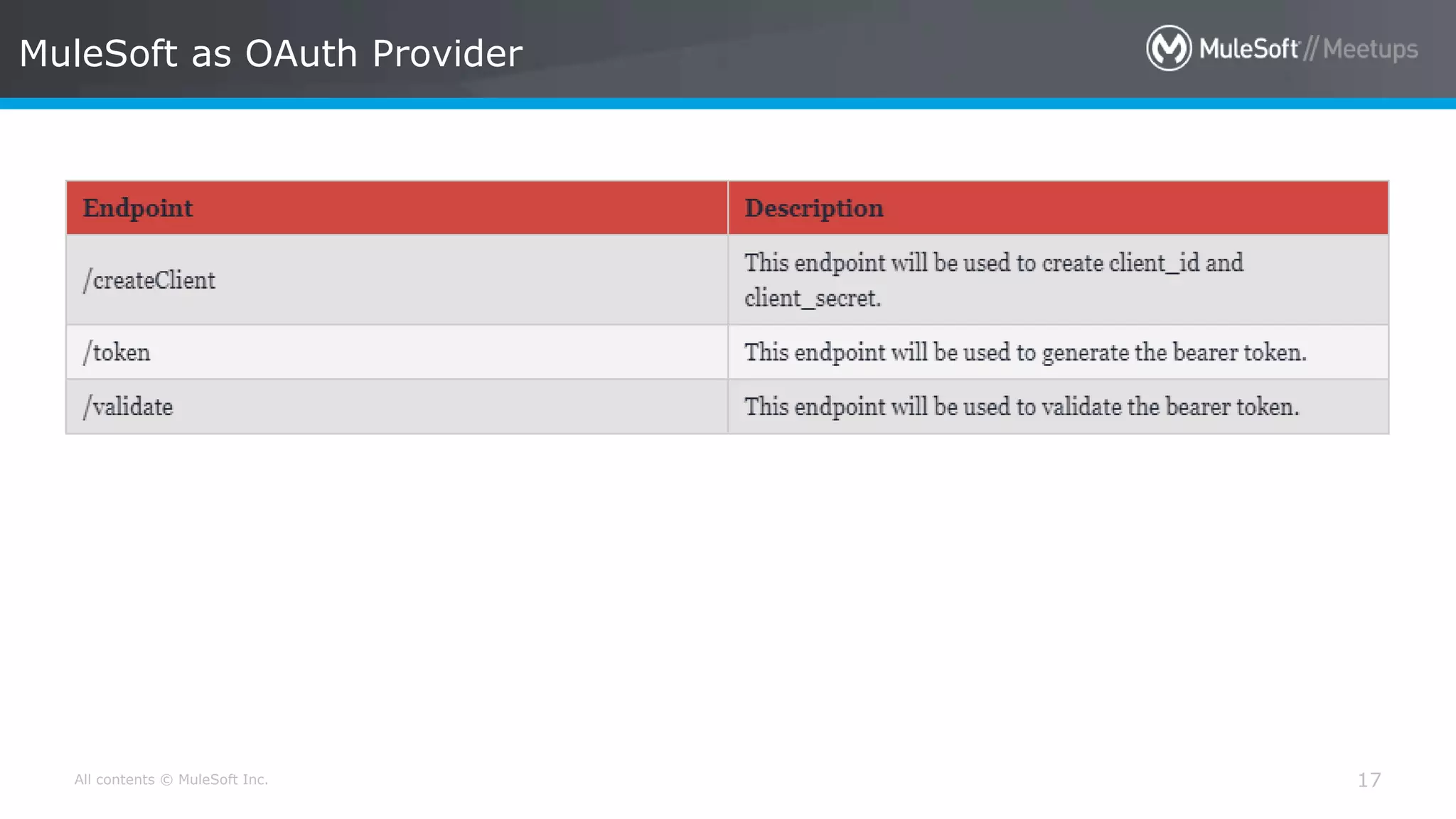
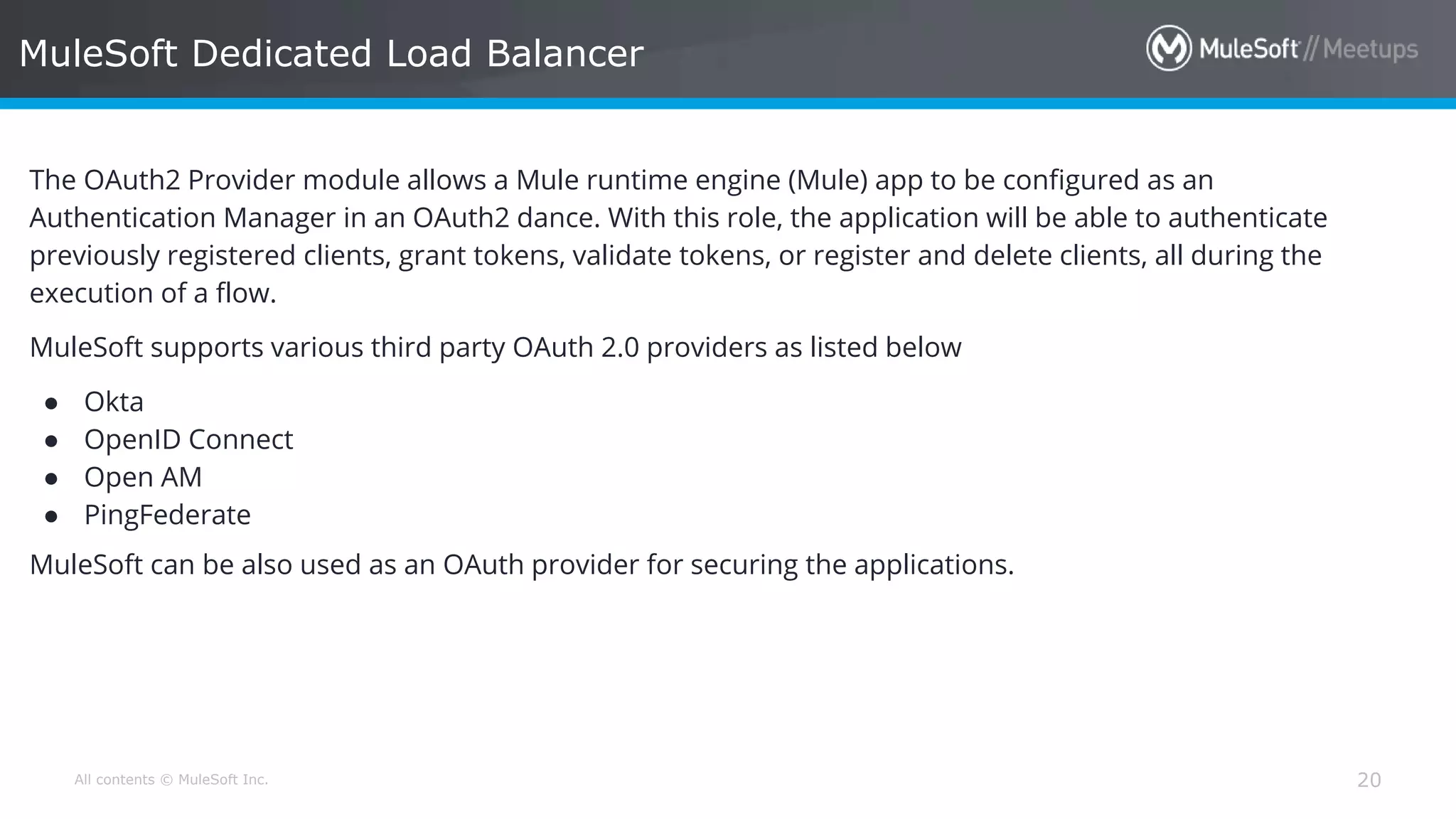
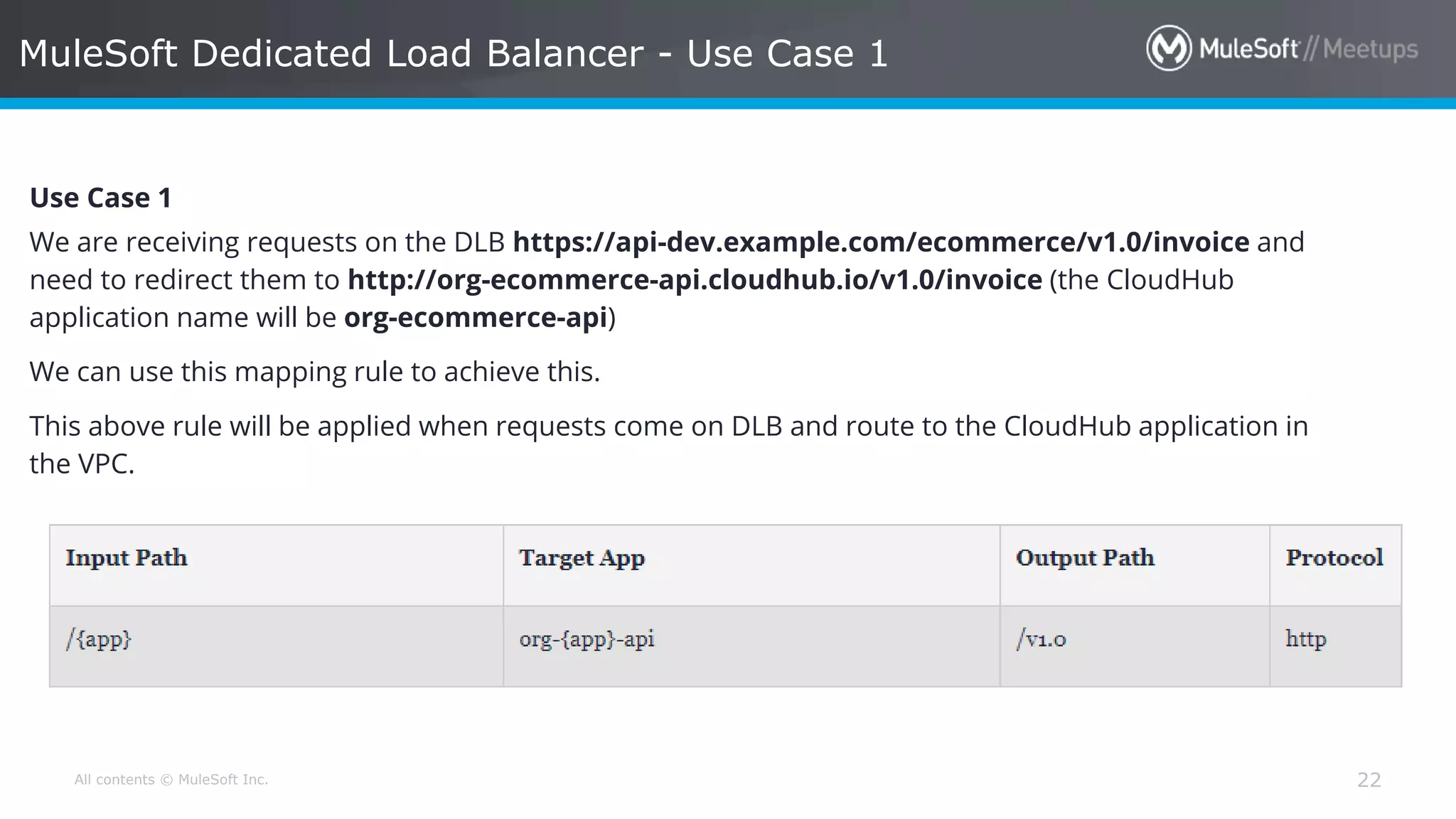
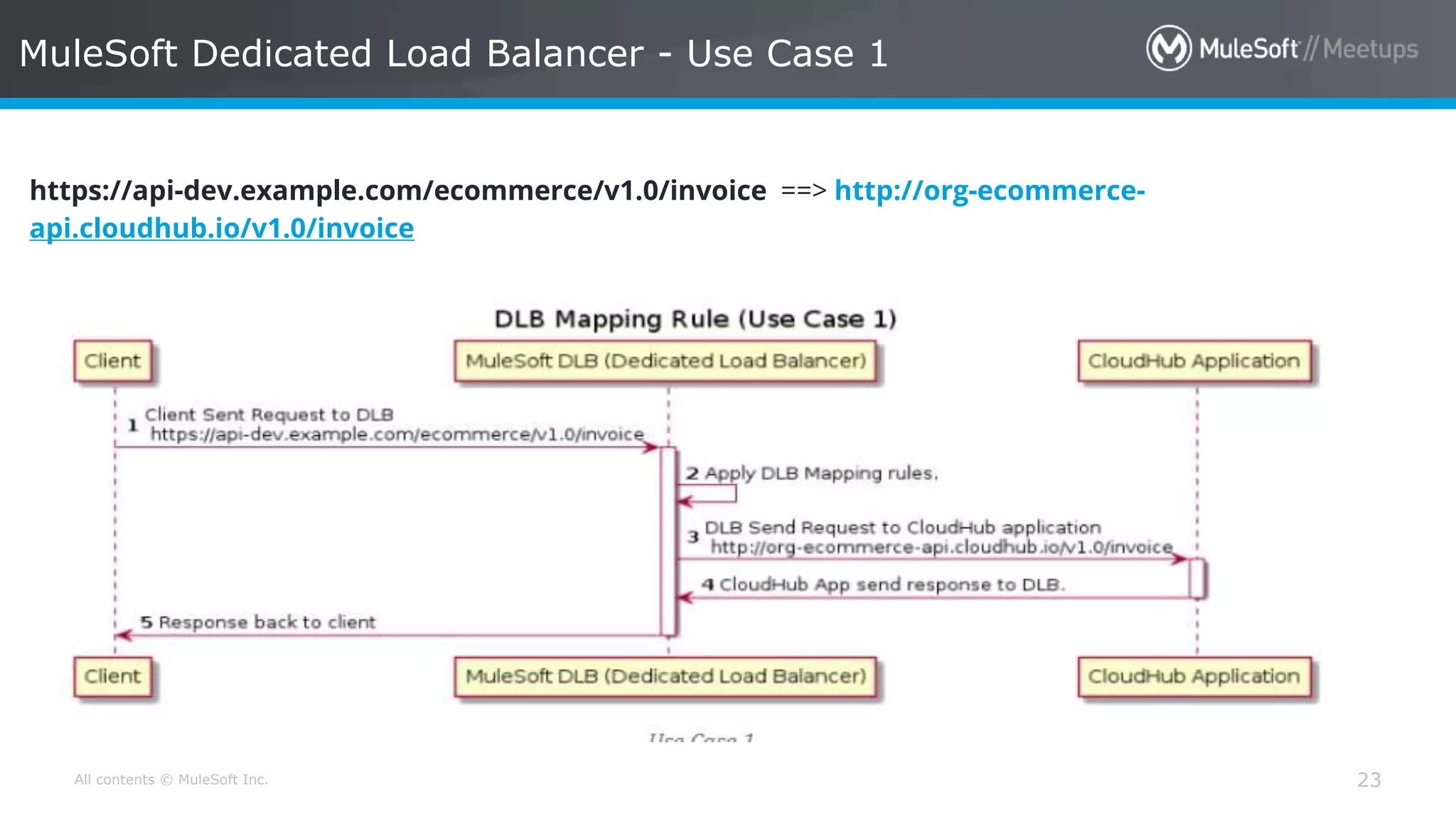
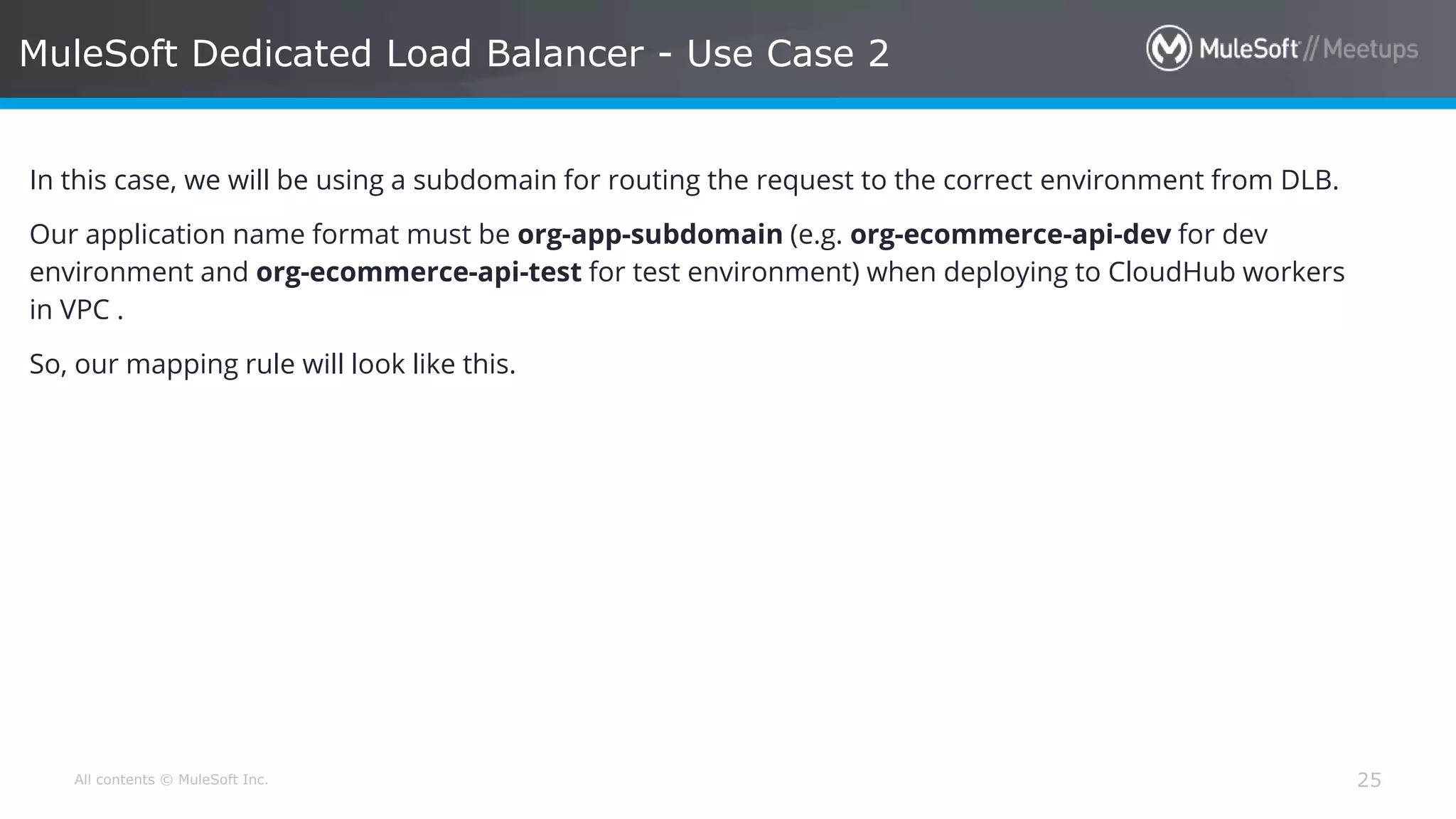
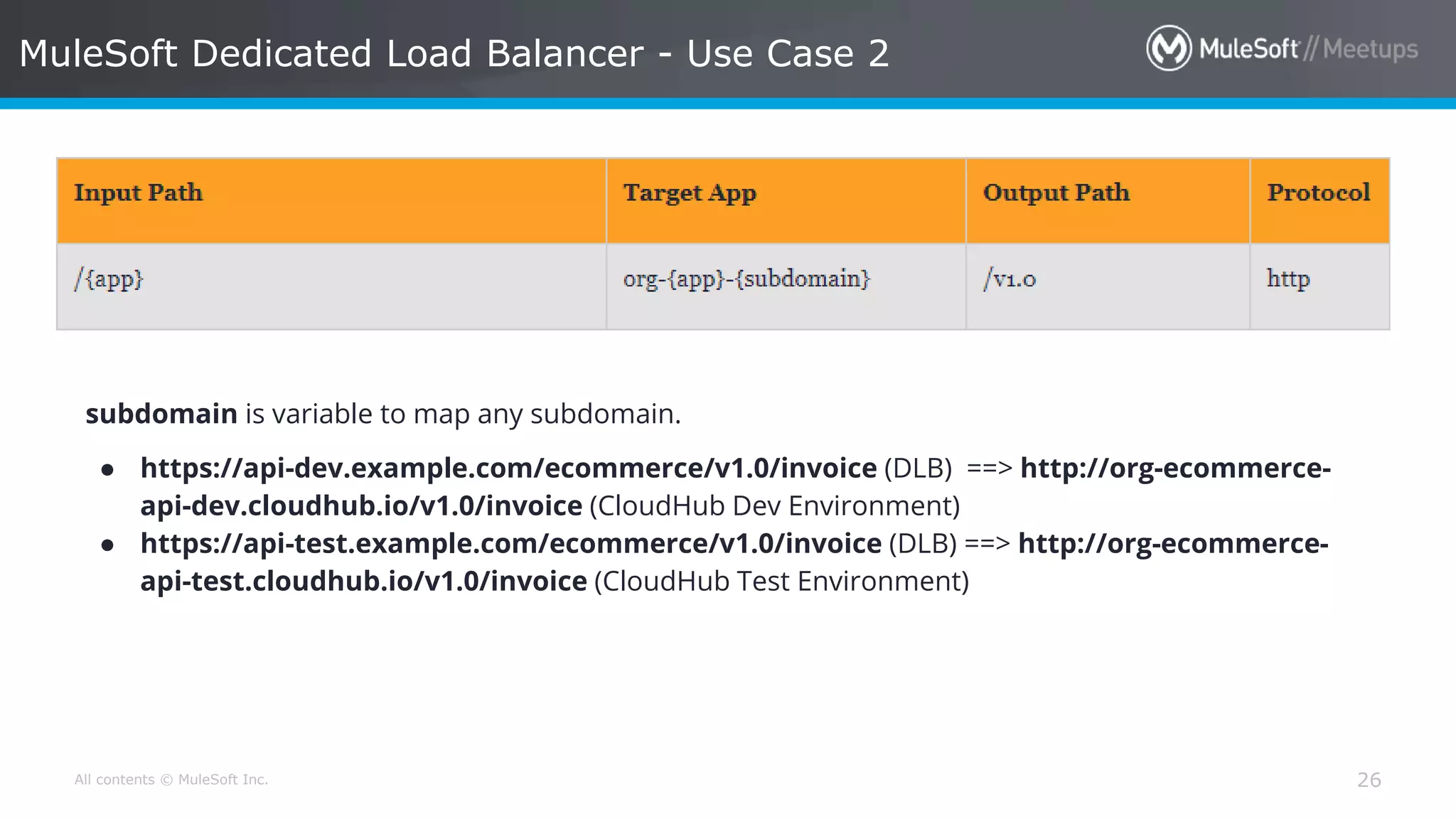
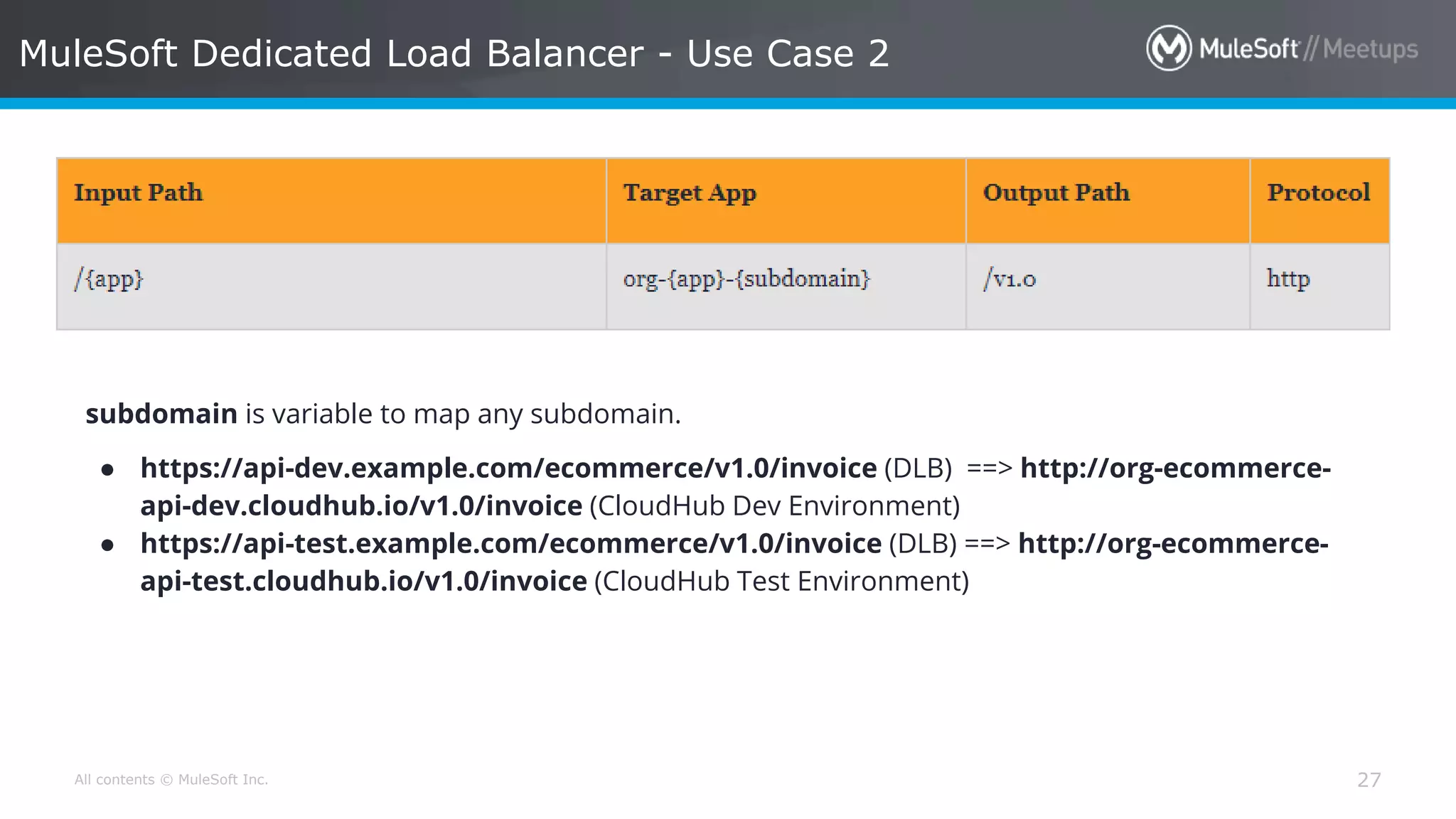
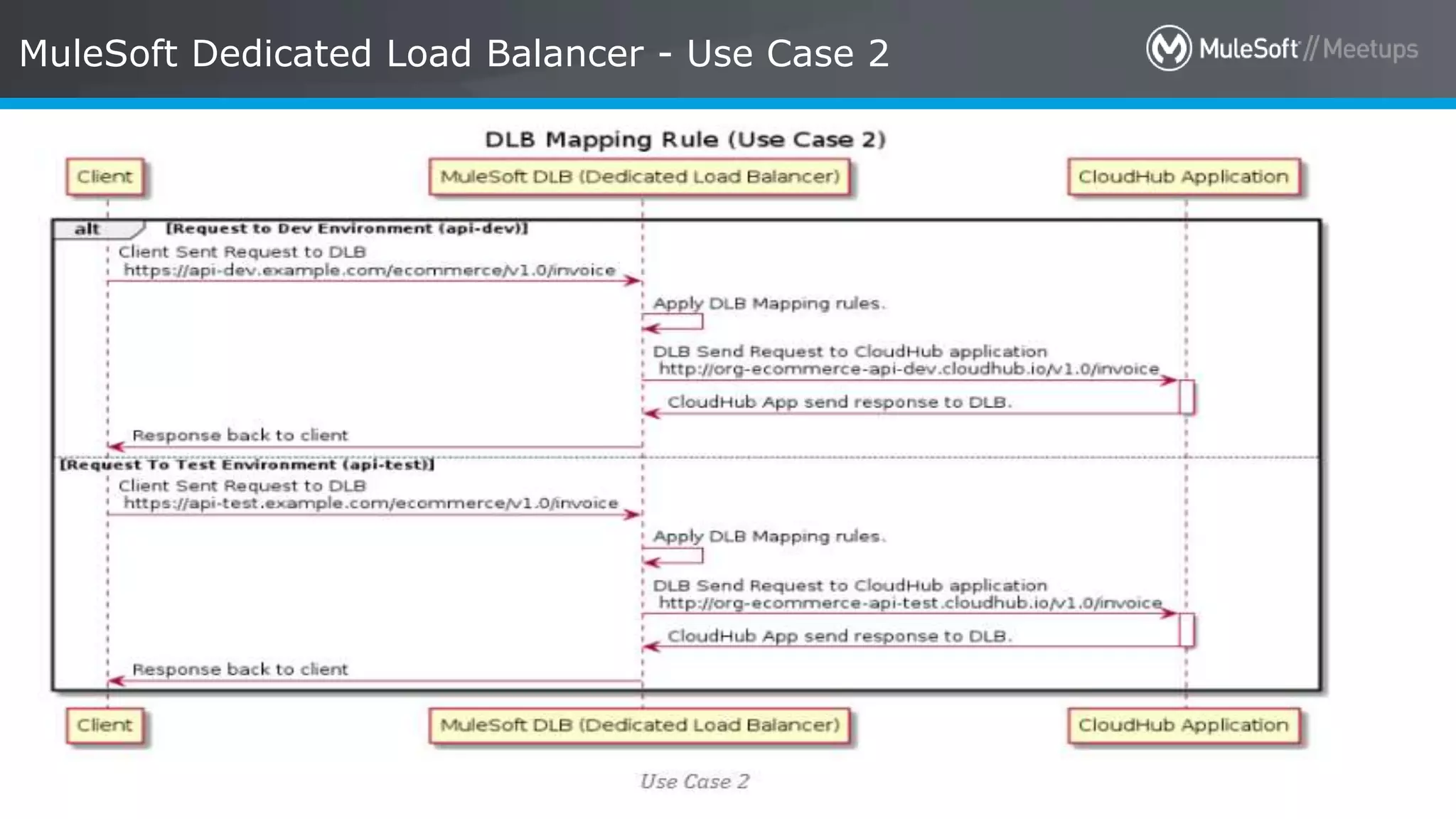
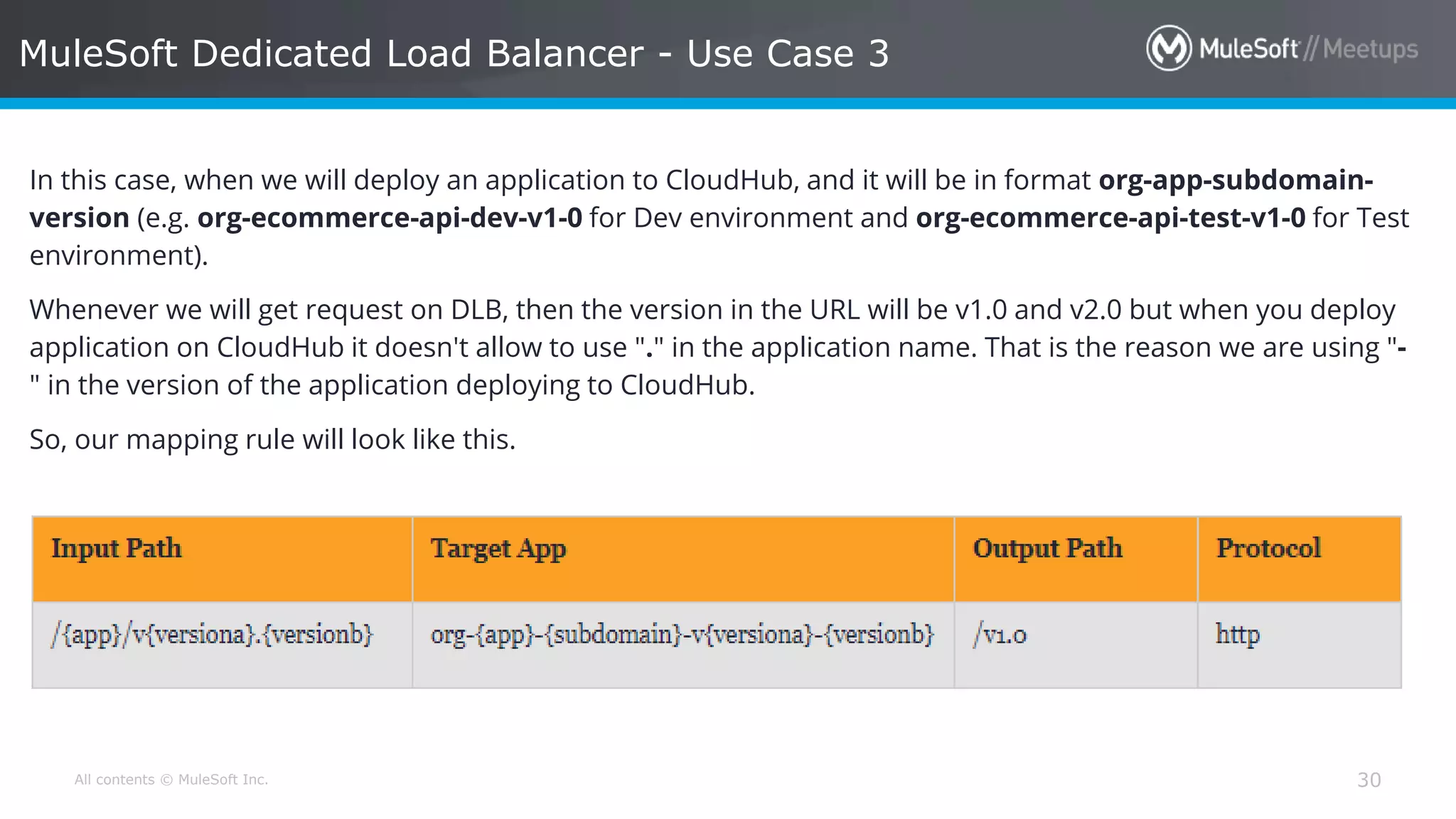
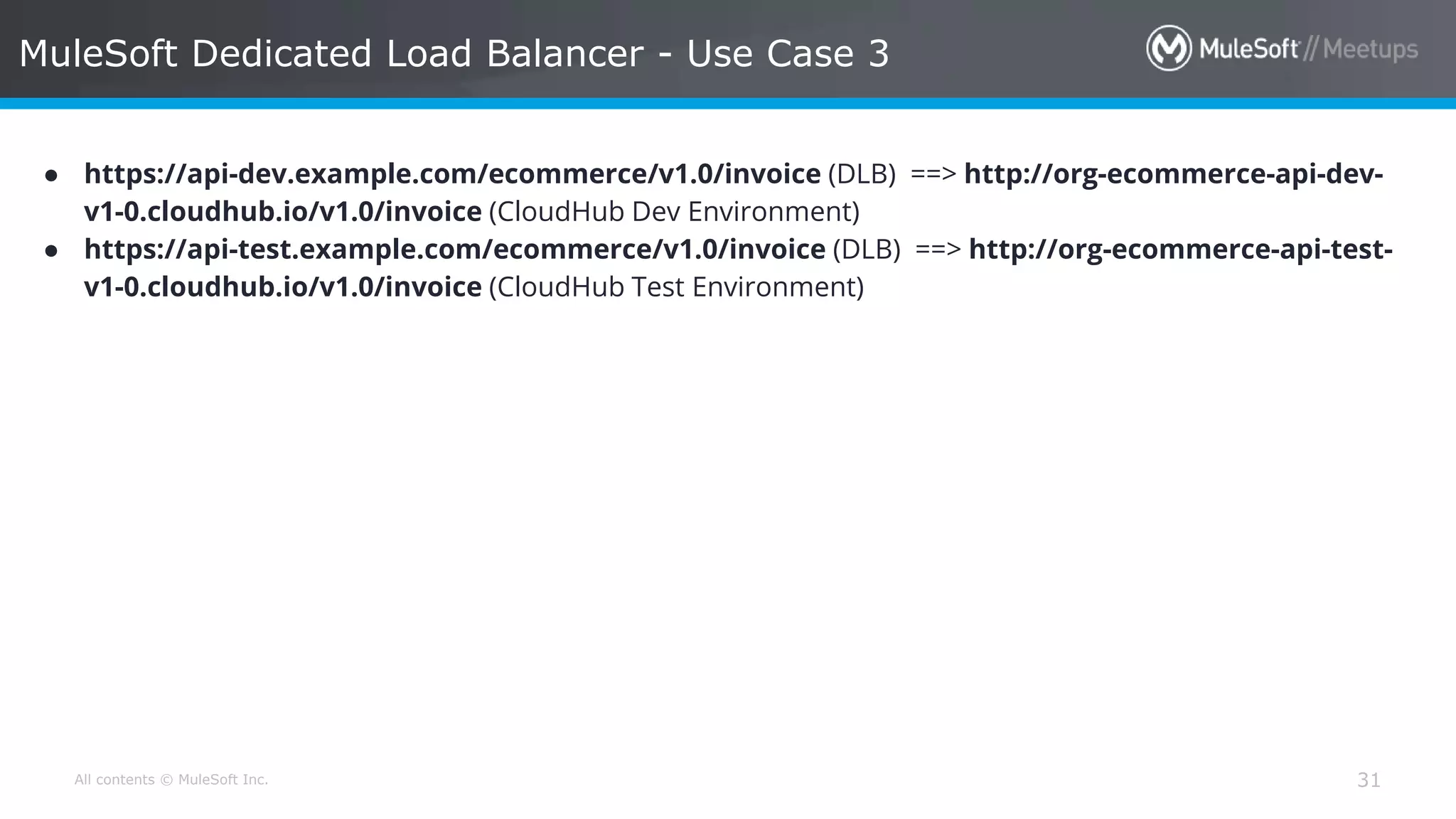
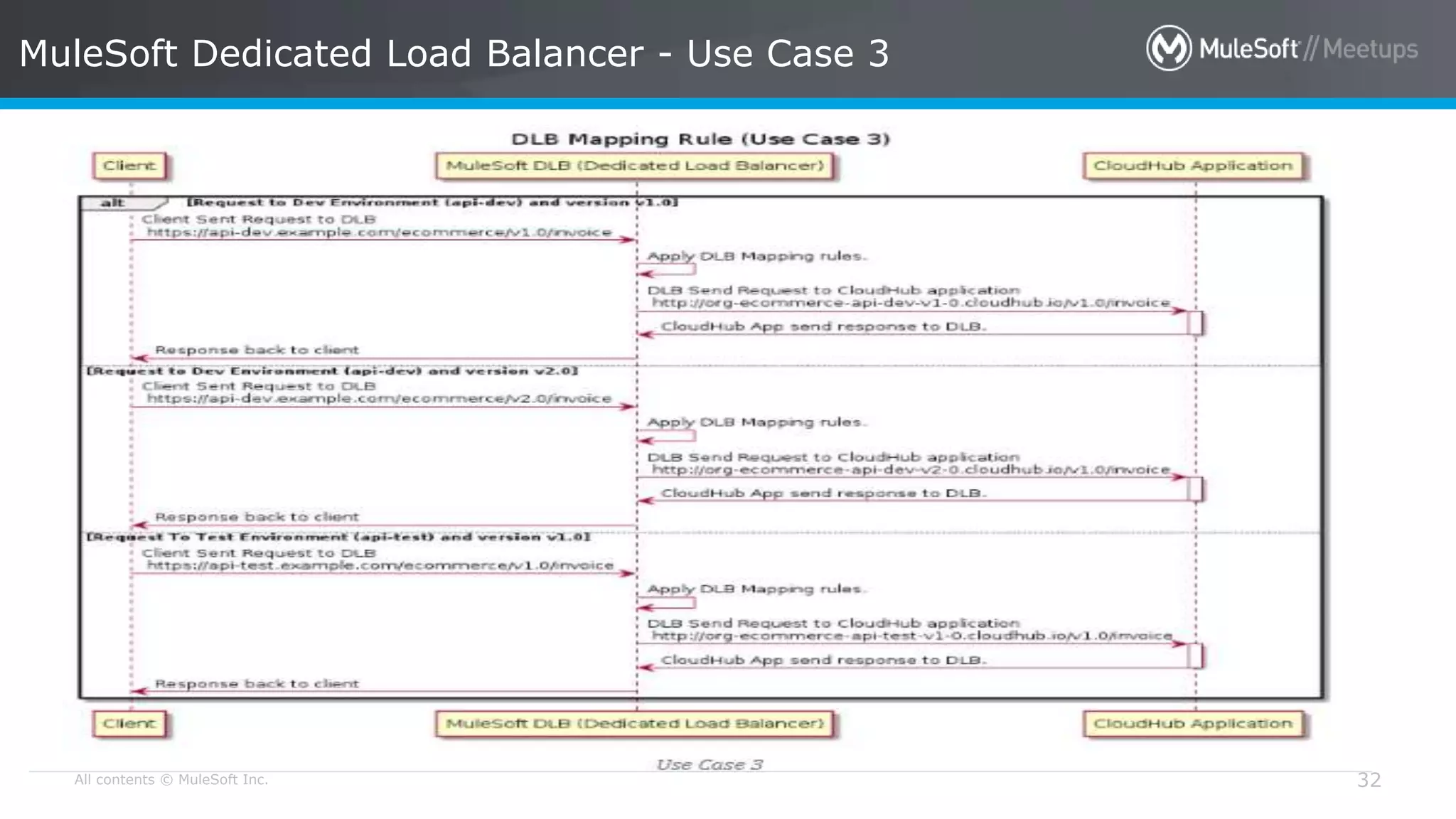
The document discusses AWS Cognito, a user identity and data synchronization service that allows the management of app data across devices, supporting both authenticated users and guests. It explains authorization methods, including authorization code and client credentials grants, and highlights JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for secure communication. Additionally, it outlines the use of MuleSoft as an OAuth provider and describes mapping rules for routing requests in dedicated load balancers for development and testing environments.