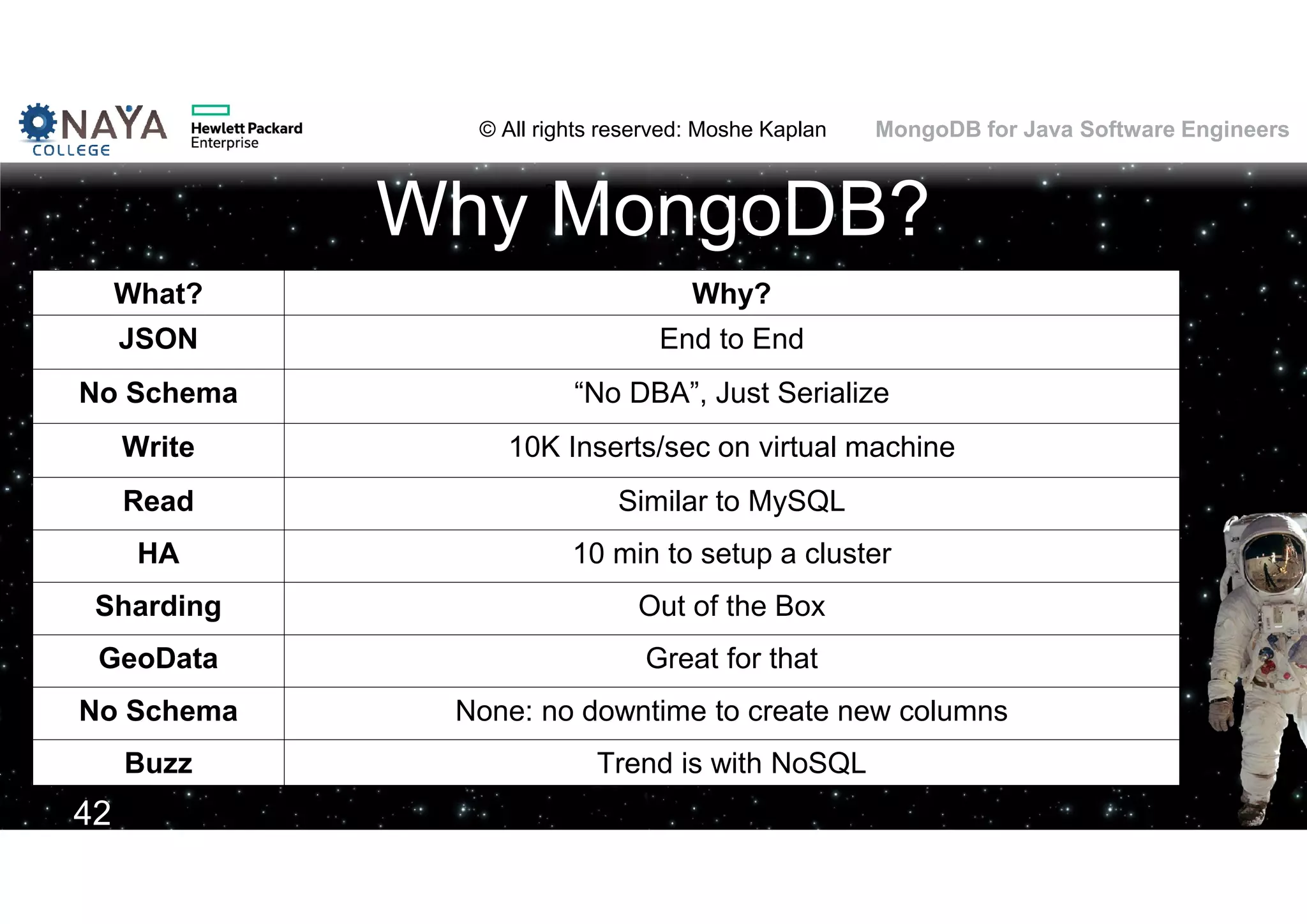
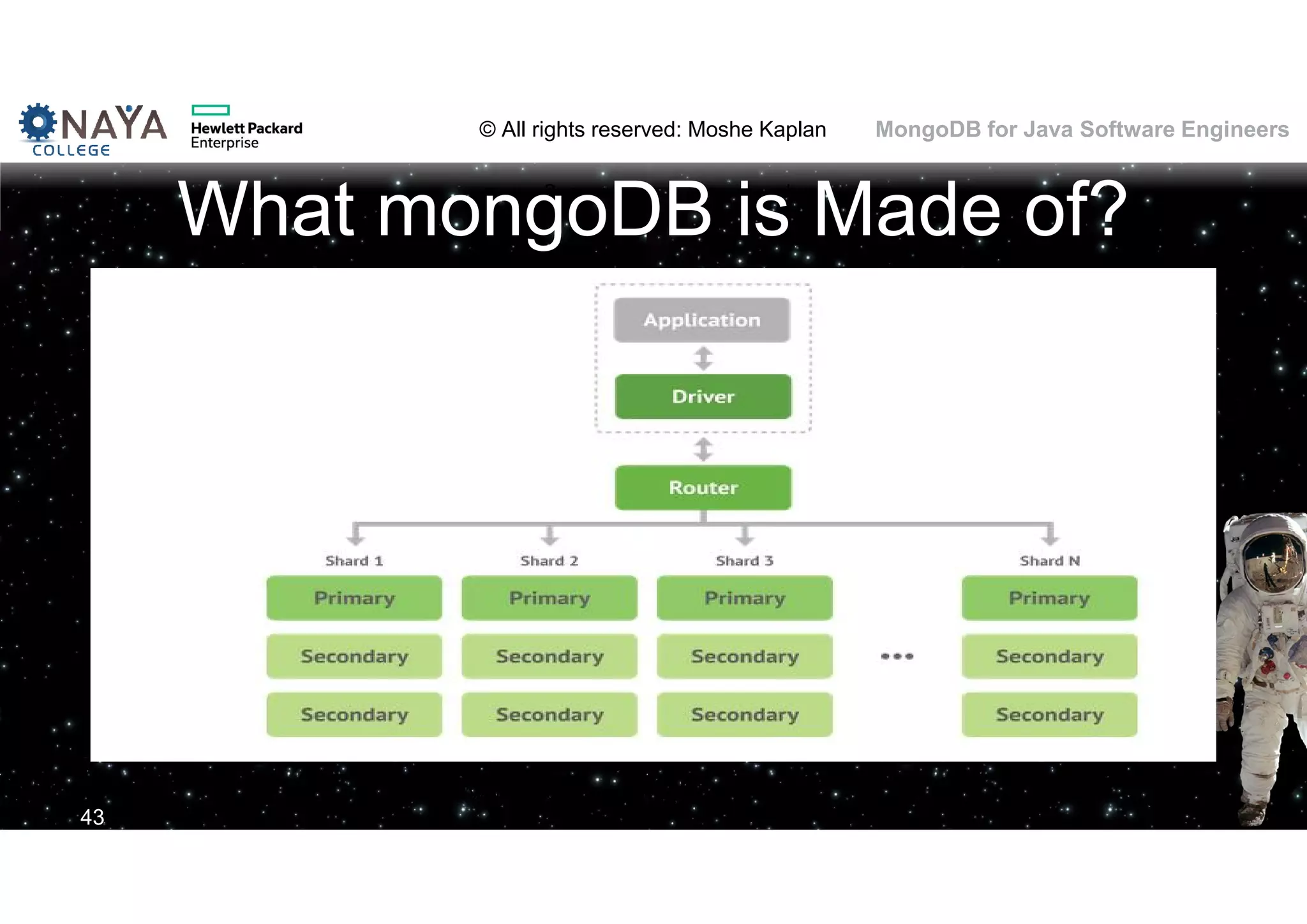
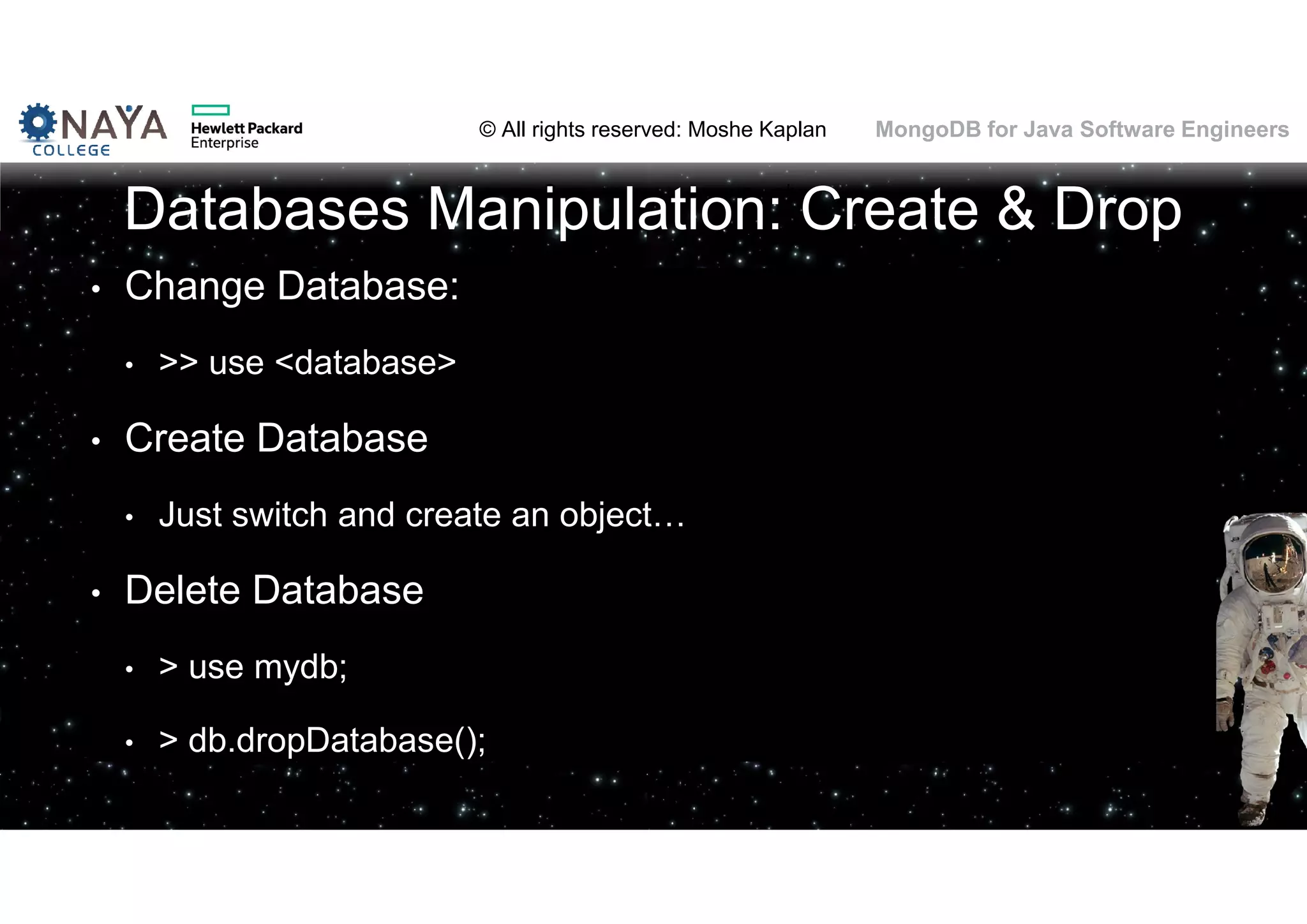
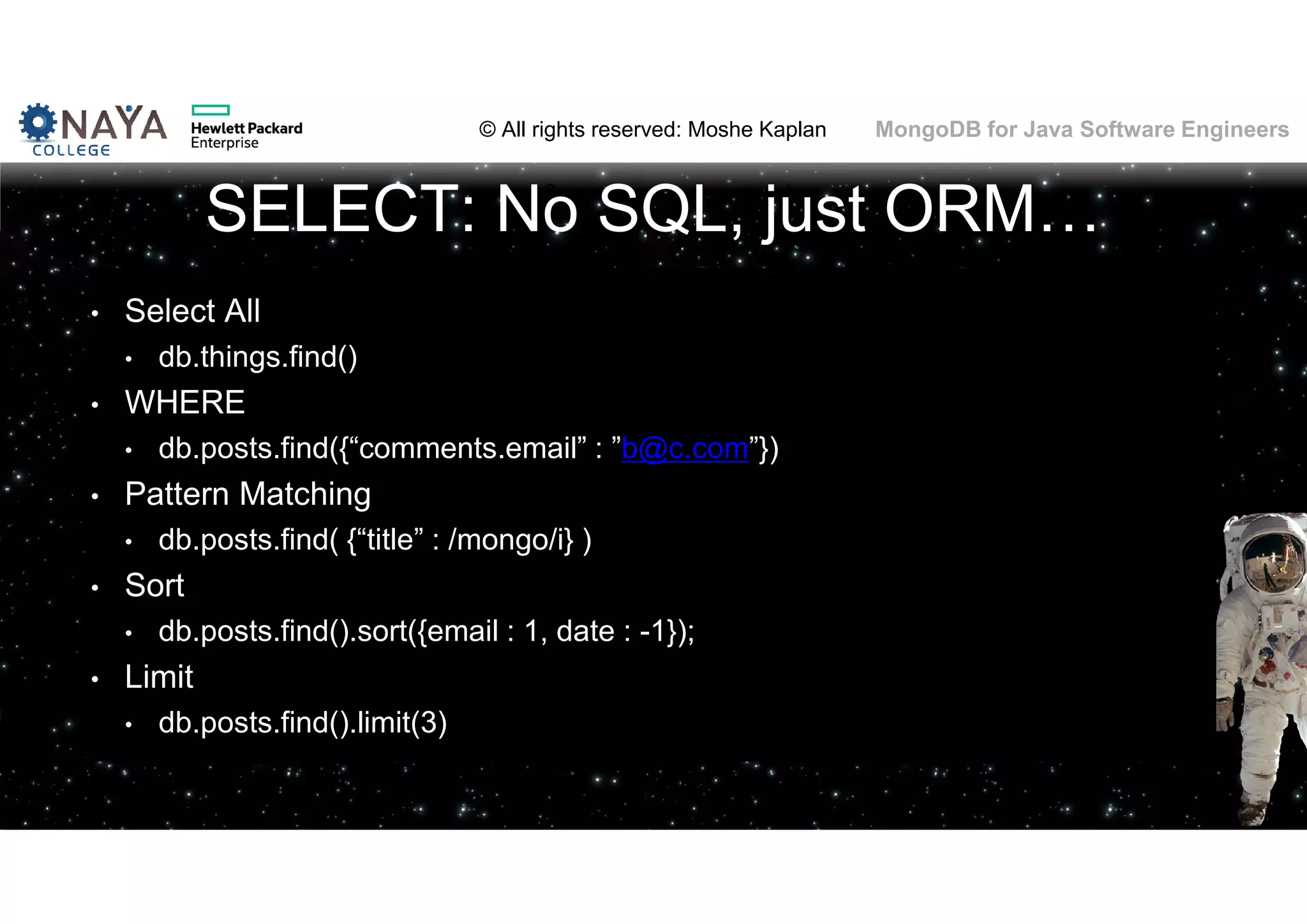
This document discusses MongoDB and its usage for Java software engineers. It begins with an introduction to MongoDB and discusses how it provides a document-oriented database that scales well for applications. Several examples of companies using MongoDB are also provided, such as Moovit and MediSafe. The document then covers various topics related to using MongoDB such as installation, querying data, data modeling differences from relational databases, migration from SQL to MongoDB, and challenges of MongoDB's schemaless design.














![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers Document Databases var mydoc = { _id: ObjectId("5099803df3f4948bd2f98391"), name: { first: "Alan", last: "Turing" }, birth: new Date('Jun 23, 1912'), death: new Date('Jun 07, 1954'), contribs: [ "Turing machine", "Turing test", "Turingery" ], views : NumberLong(1250000) } 35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-35-2048.jpg)


![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers Installation: Give Yourself 5min • Add to /etc/yum.repos.d/10gen.repo • [10gen] • name=10gen Repository • baseurl=http://downloads-distro.mongodb.org/repo/redhat/os/x86_64 • gpgcheck=0 • enabled=1 • yum –y install mongo-10gen mongo-10gen-server • The Packages: • mongo-10gen: tools • mongo-10gen-server: mongod and mongos](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-44-2048.jpg)

![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers Installation w/ Authentication • /etc/mongod.conf • > mongo • use admin db.createUser( { user: "siteUserAdmin", pwd: “Pss0rdxxx", roles: [ { role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" } ] } )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-46-2048.jpg)



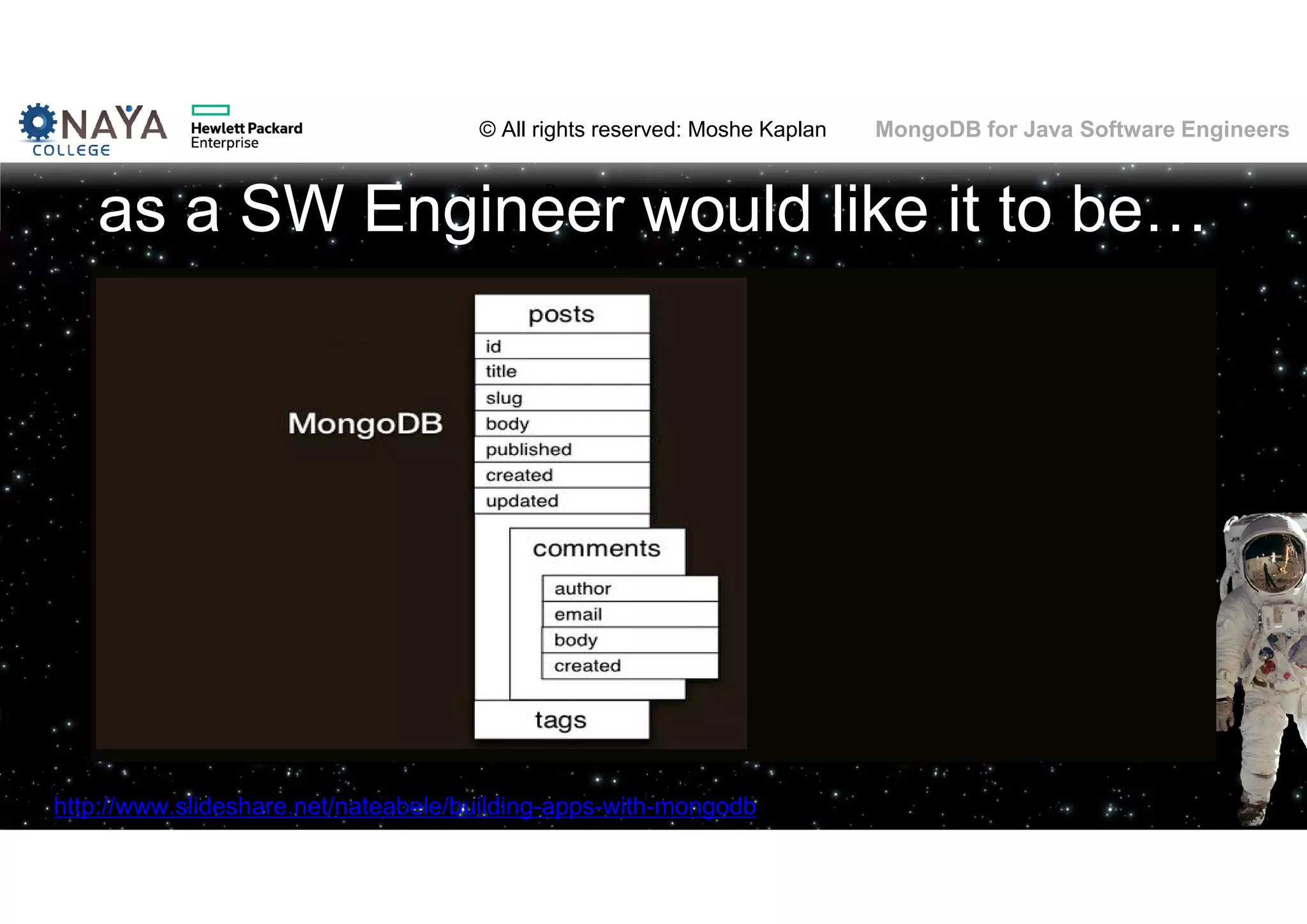

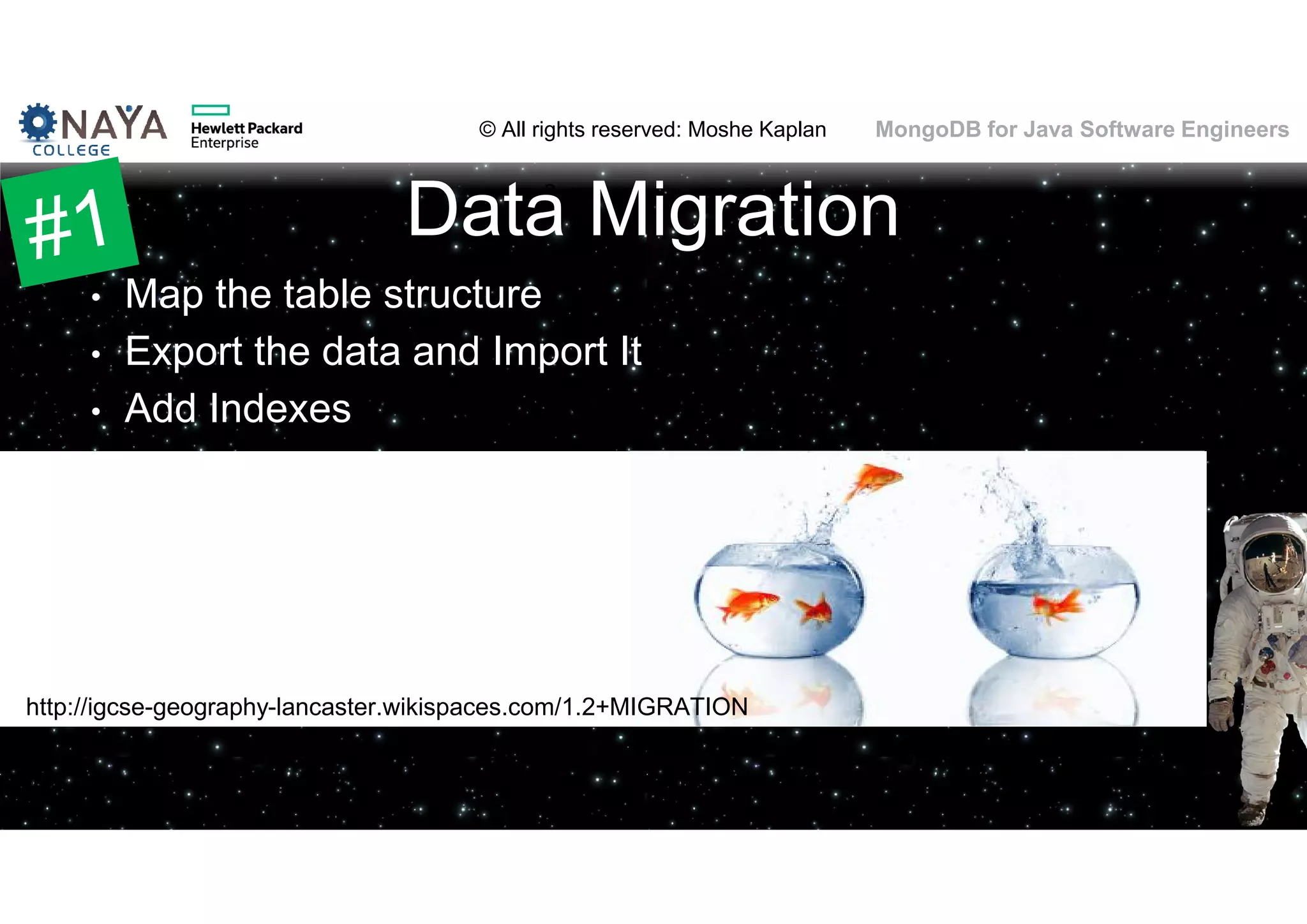
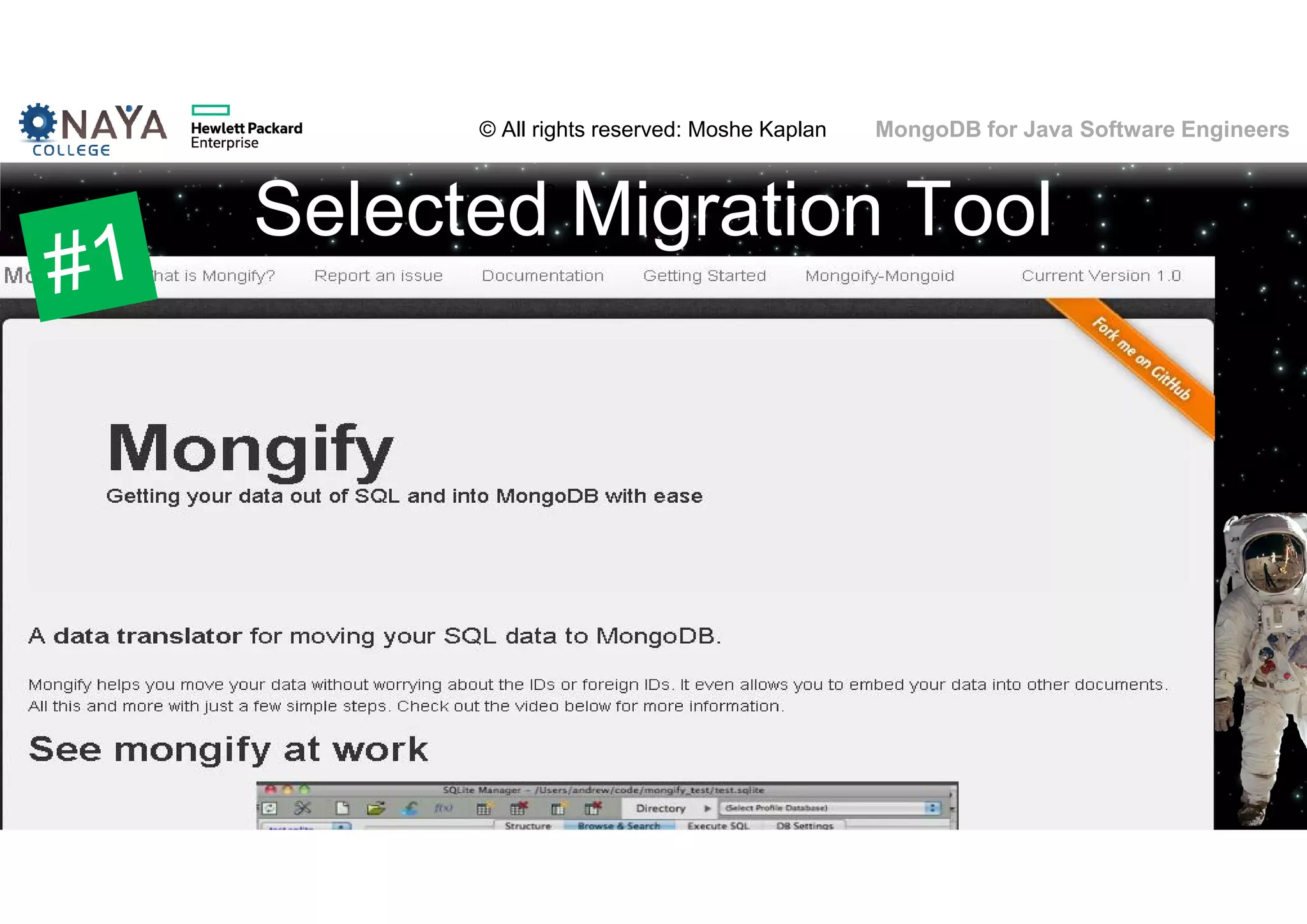
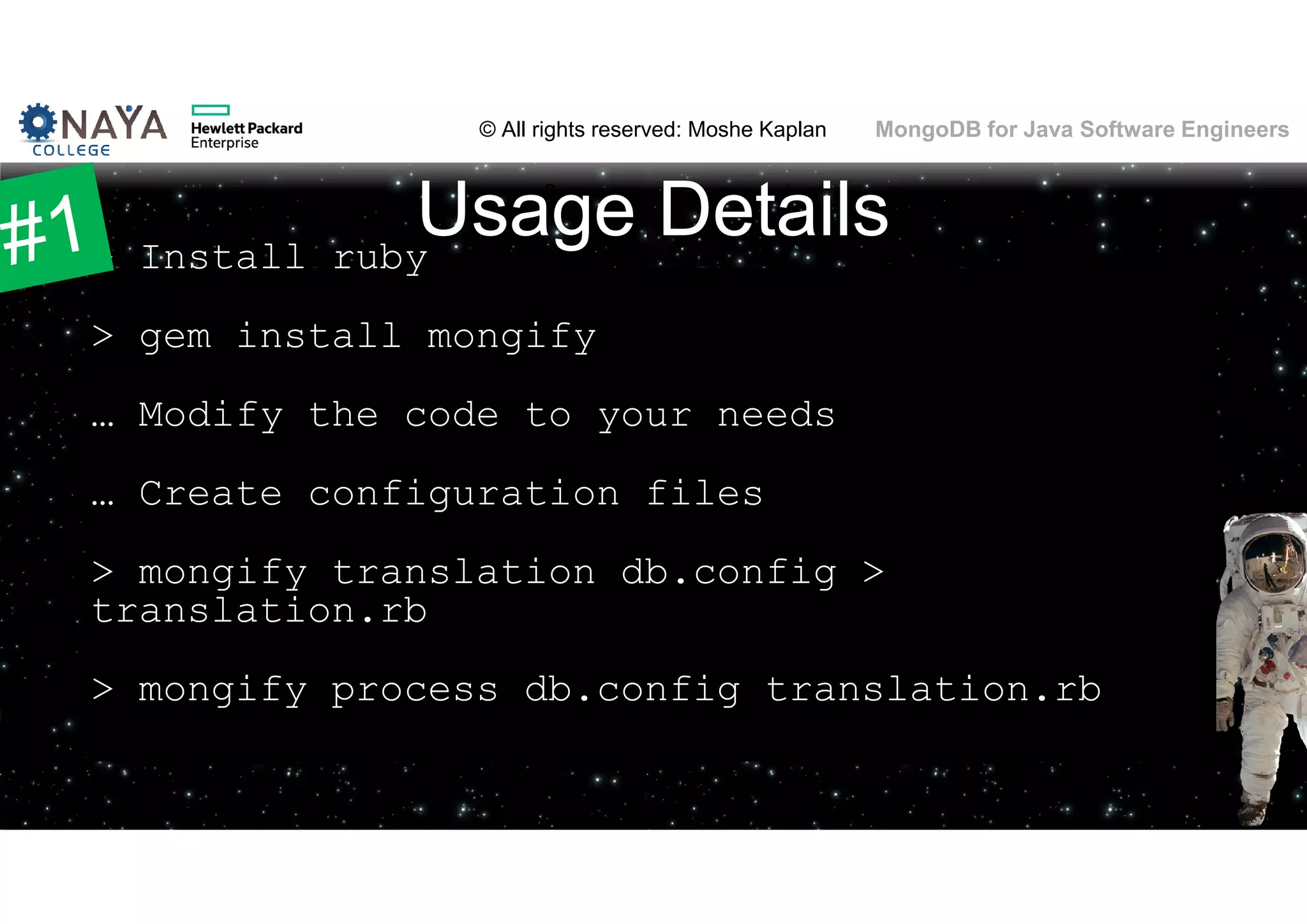
![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers Date Functions • Year(), Month()… function included • … buy only in the JavaScript engine • Solution: New fields! • [original field] • [original field]_[year part] • [original field]_[month part] • [original field]_[day part] • [original field]_[hour part] 61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-61-2048.jpg)









![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers WHERE • != “A” { $ne: "A" } • > 25 { $gt: 25 } • > 25 AND <= 50 { $gt: 25, $lte: 50 } • Like ‘bc%’ /^bc/ • < 25 OR >= 50 { $or : [ { $lt: 25 }, { $gte : 50 } ] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-78-2048.jpg)








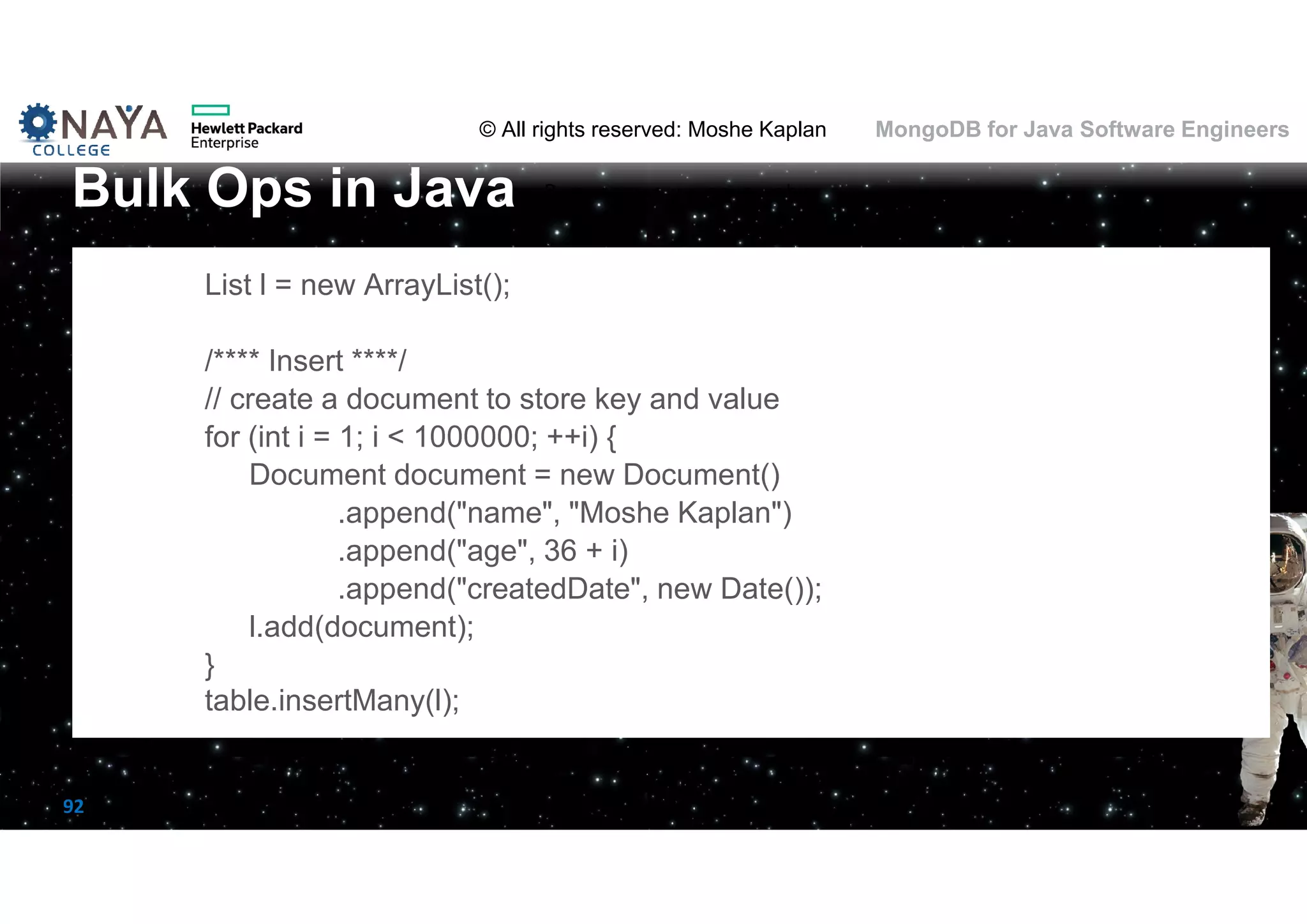
![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers 93 List<String> continentList = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"Africa", "Europe", "Asia"}); DBObject match = new BasicDBObject("$match", new BasicDBObject("continent.name", new BasicDBObject("$in", continentList))); DBObject projectFields = new BasicDBObject("continent.name", 1); projectFields.put("area", 1); projectFields.put("_id", 0); DBObject project = new BasicDBObject("$project", projectFields ); DBObject groupFields = new BasicDBObject( "_id", "$continent.name"); groupFields.put("average", new BasicDBObject( "$avg", "$area")); DBObject group = new BasicDBObject("$group", groupFields); List agList = new ArrayList(); agList.add(match); agList.add(project); agList.add(group); MongoCursor<Document> cursor = countries.aggregate(agList).iterator(); while (cursor.hasNext()) { System.out.println(cursor.next()); } Aggregation Framework in Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-93-2048.jpg)

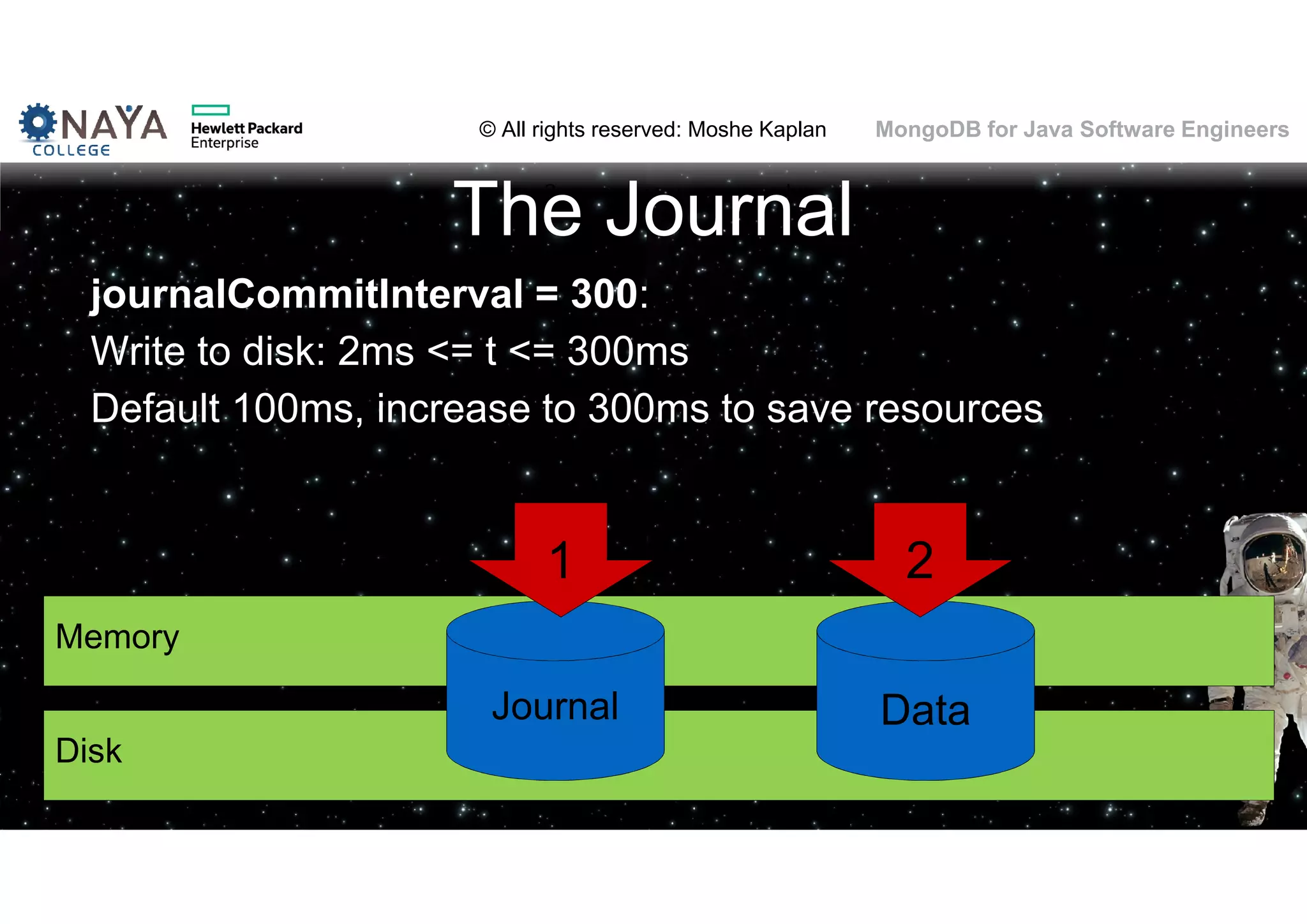
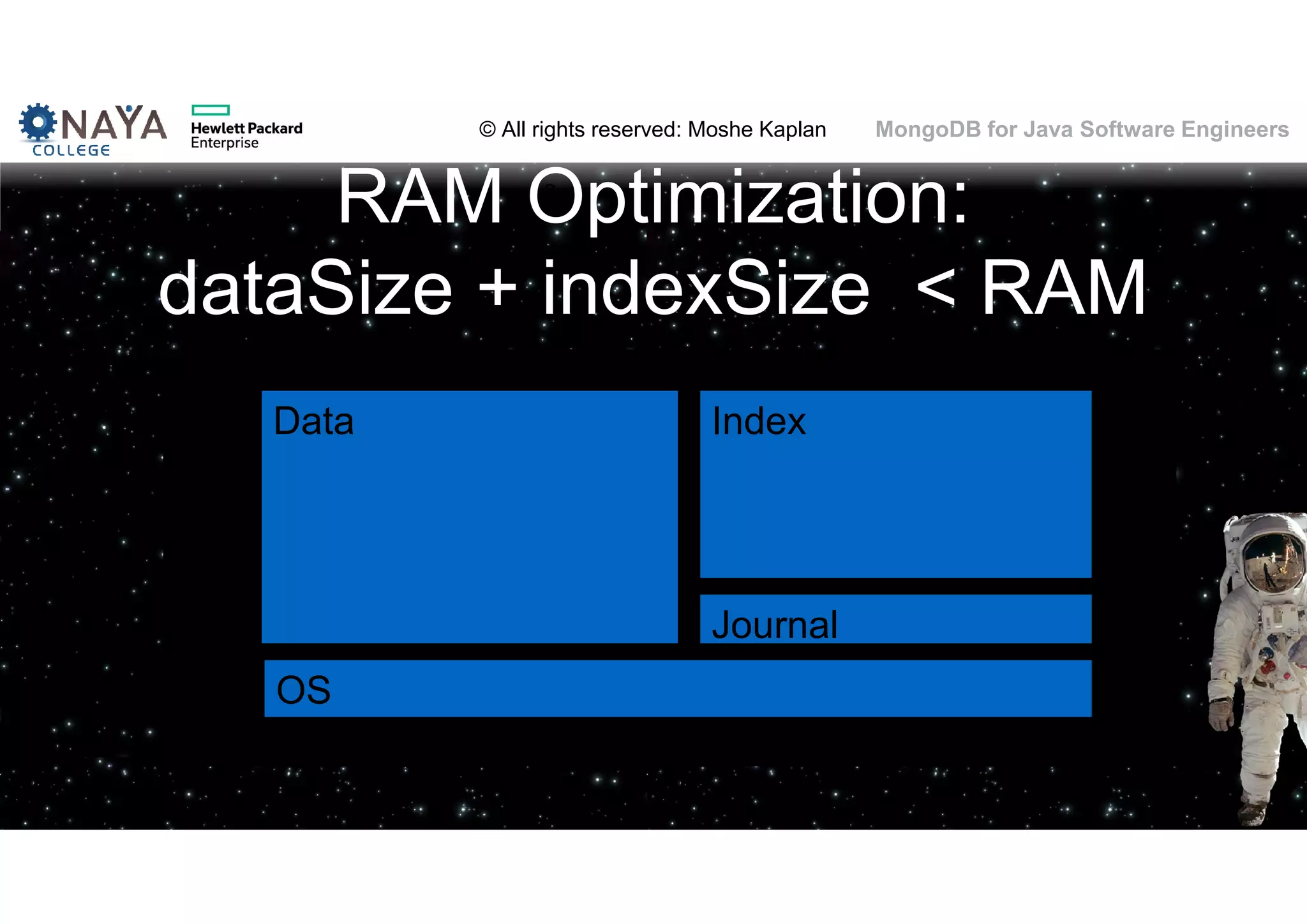
![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers Profiling Configuration • Enable: • mongod --profile=1 --slowms=15 • db.setProfilingLevel([level] , [time]) • How much: • 0 (none) 1 (slow queries only) 2 (all) • 100ms: default • Where: • system.profile collection @ local db 99](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-99-2048.jpg)



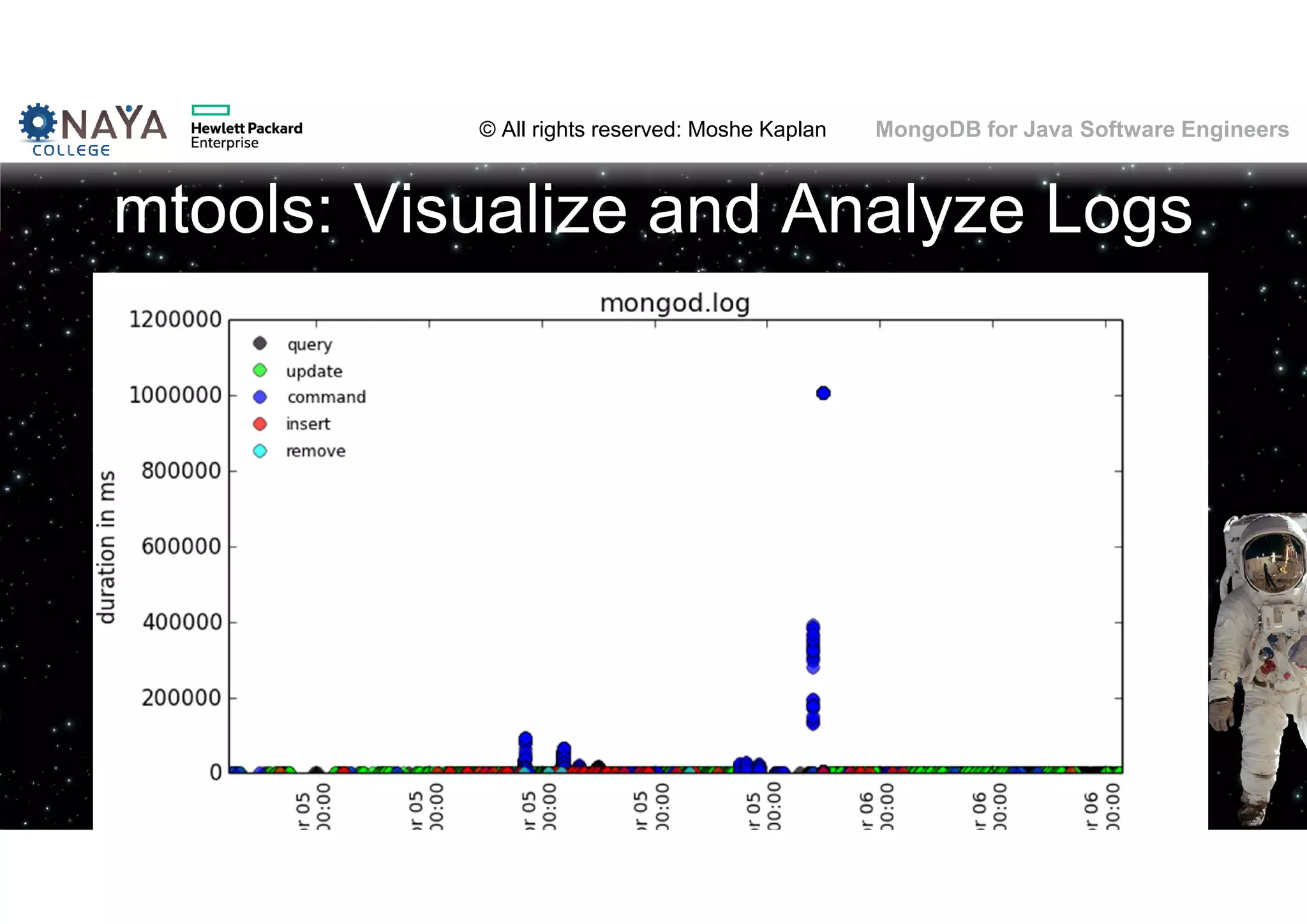
![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers Dex: The Index Analyzer • Installation: • sudo apt-get -y install python-pip sudo pip install dex • Running: • dex [mongodb_uri] (-f <logfile_path> | -p) [<options>] • dex -w -p -n "testdb.*" mongodb://127.0.0.1/testdb -f /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-105-2048.jpg)





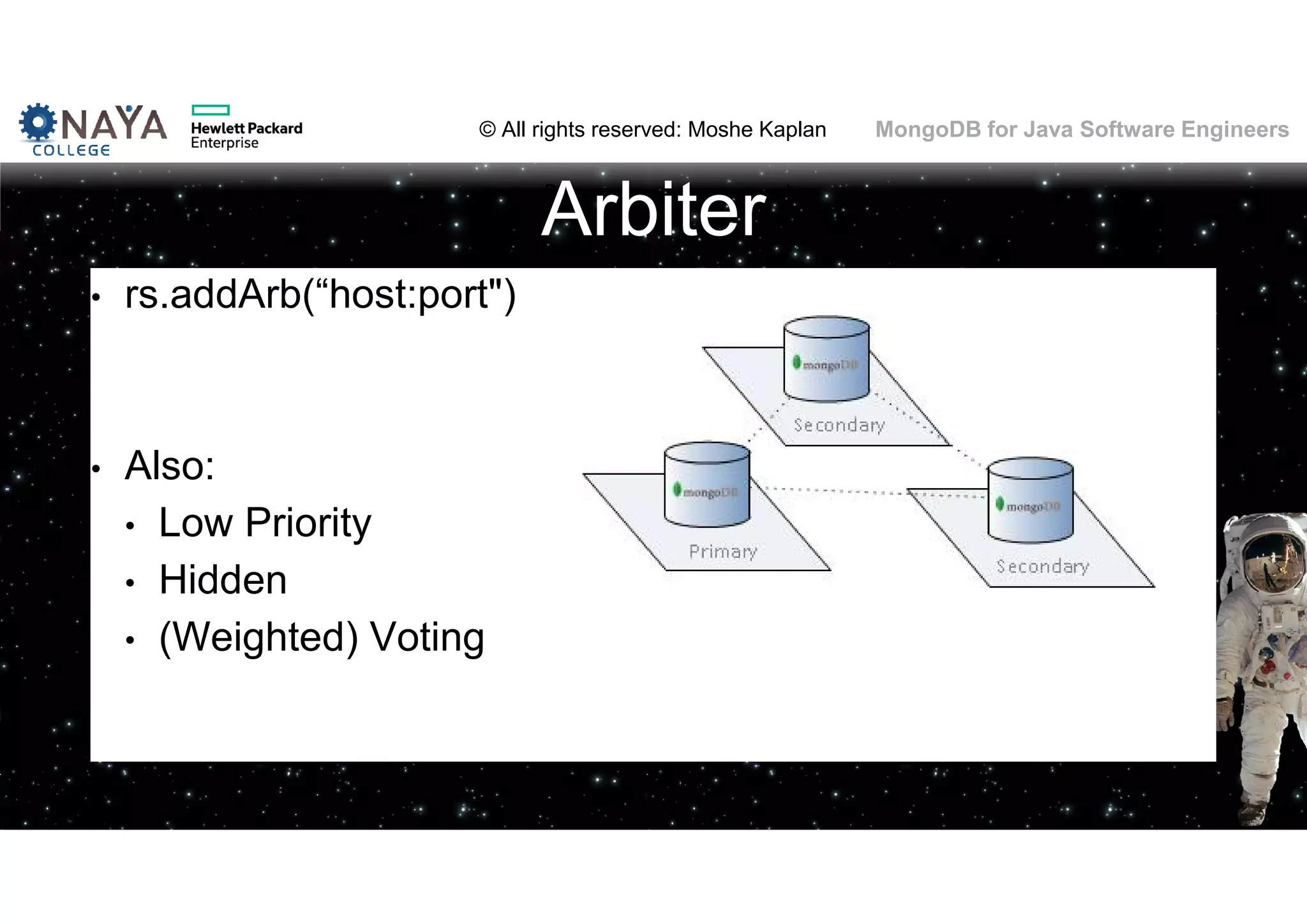
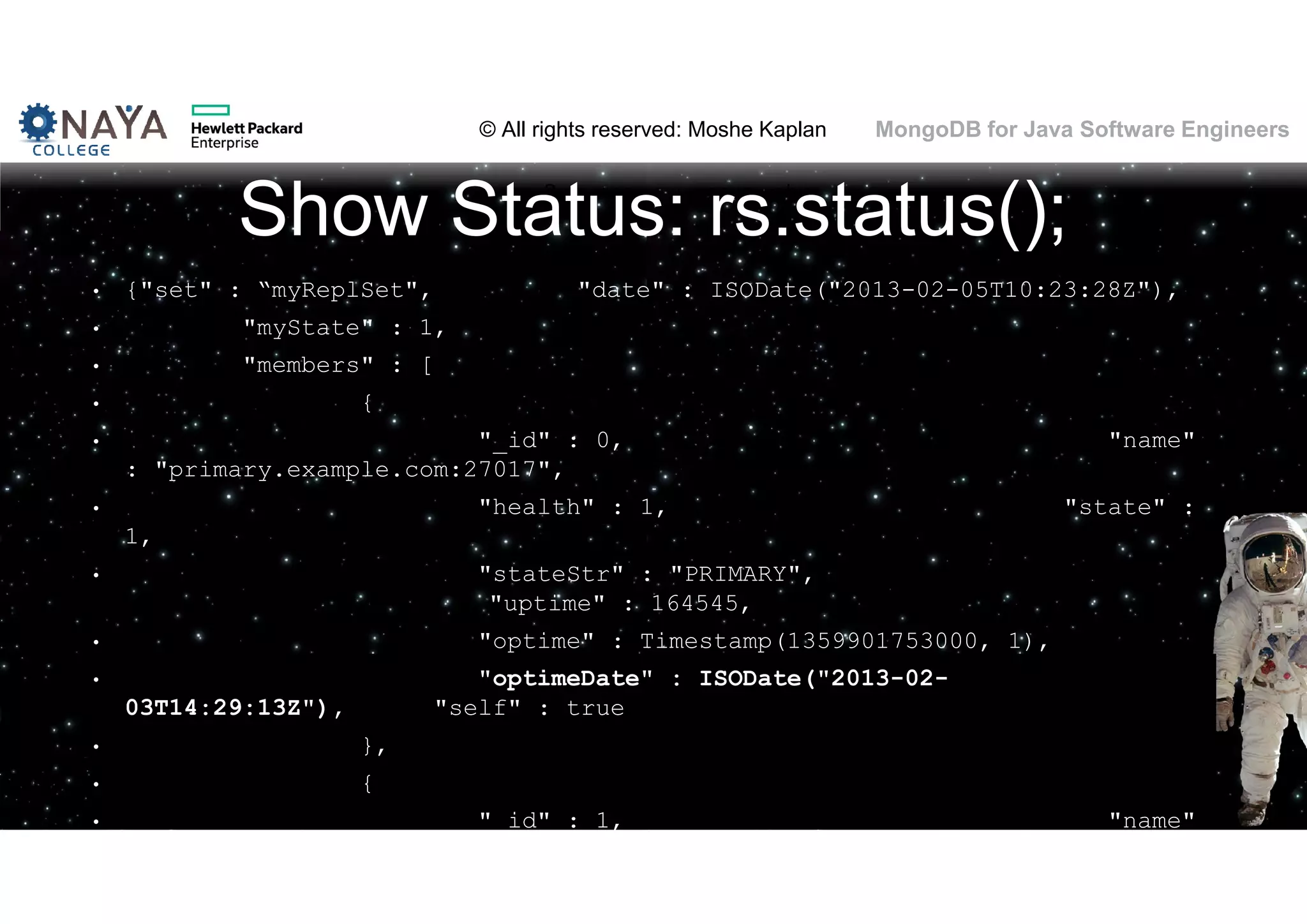

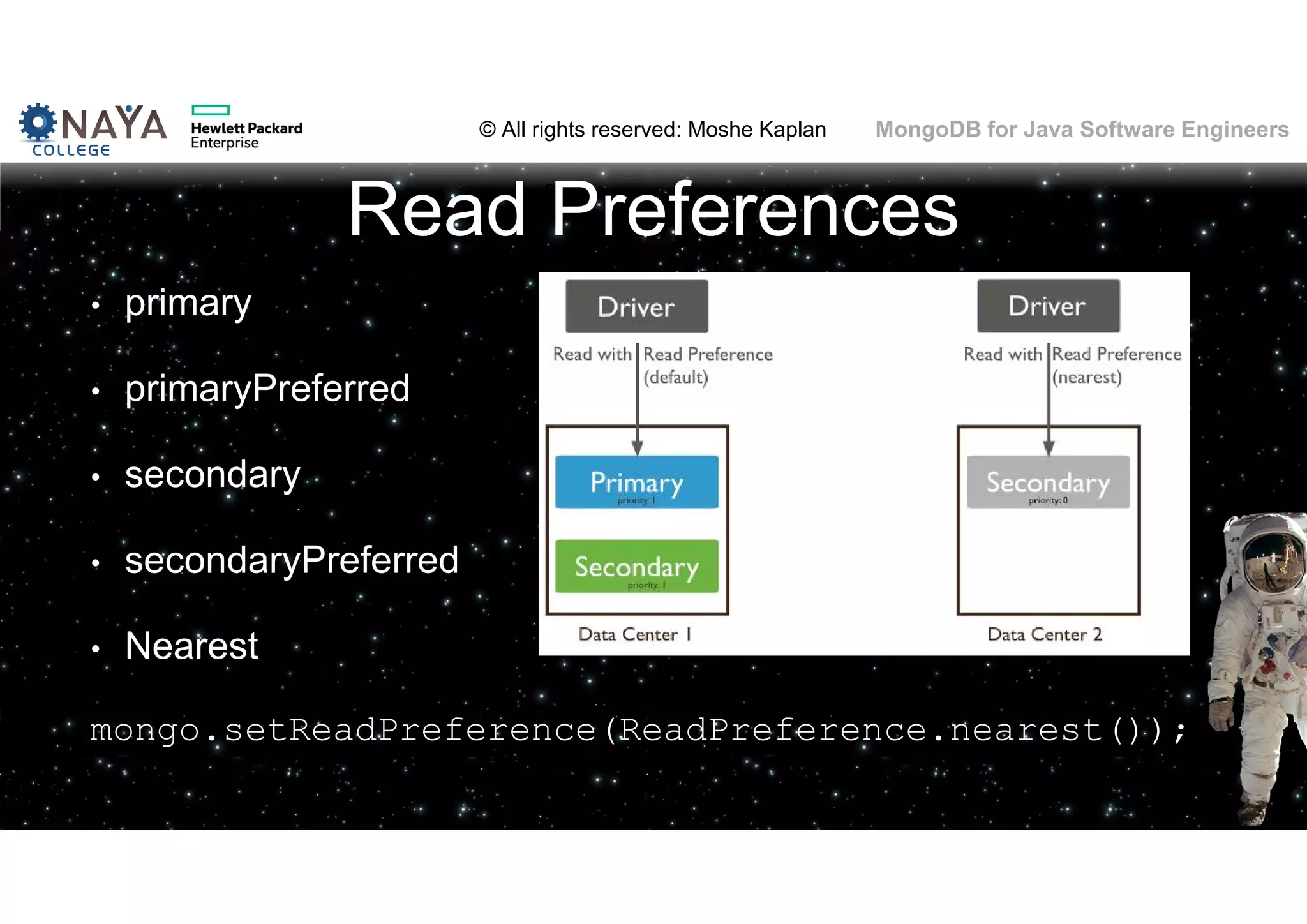
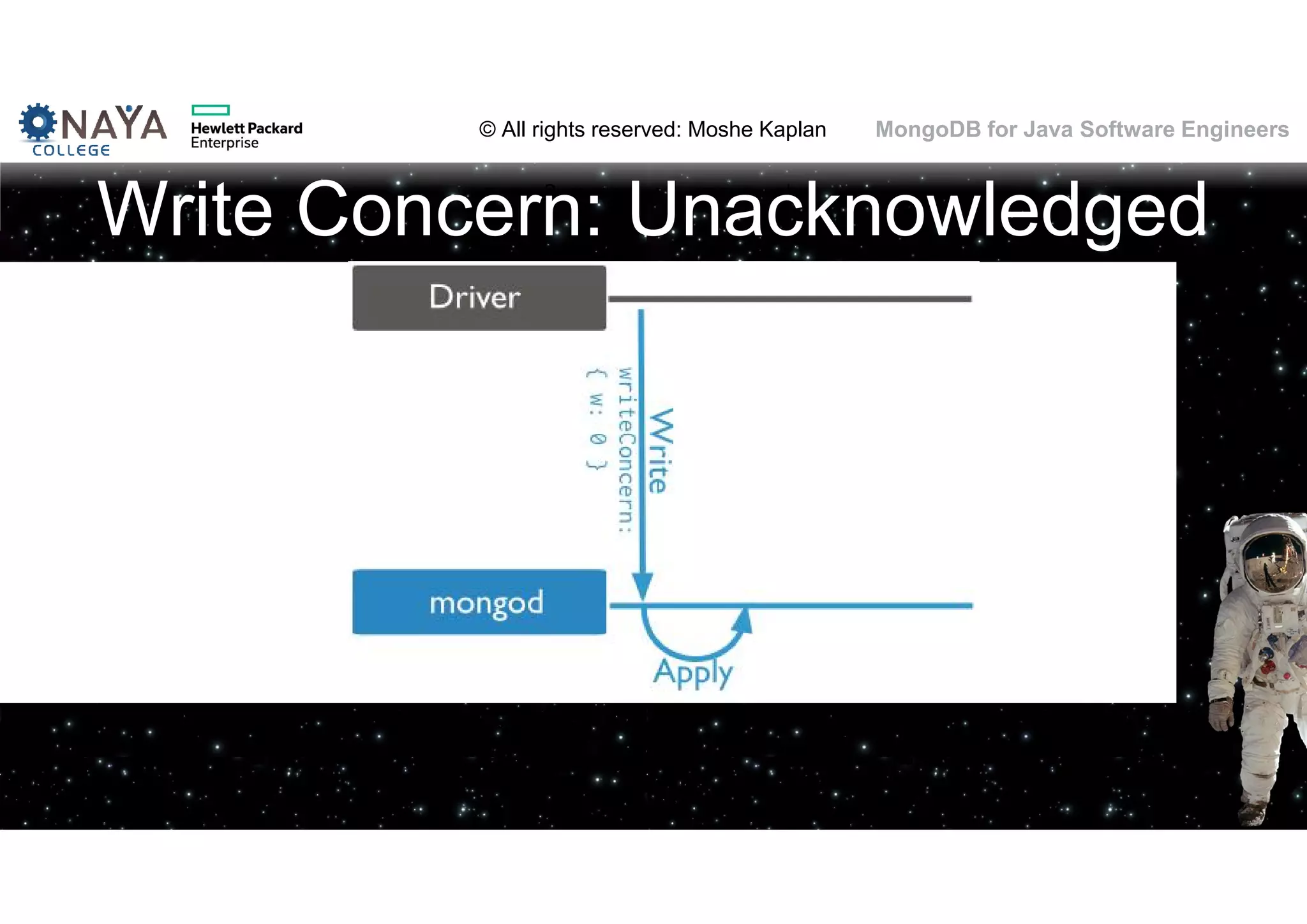
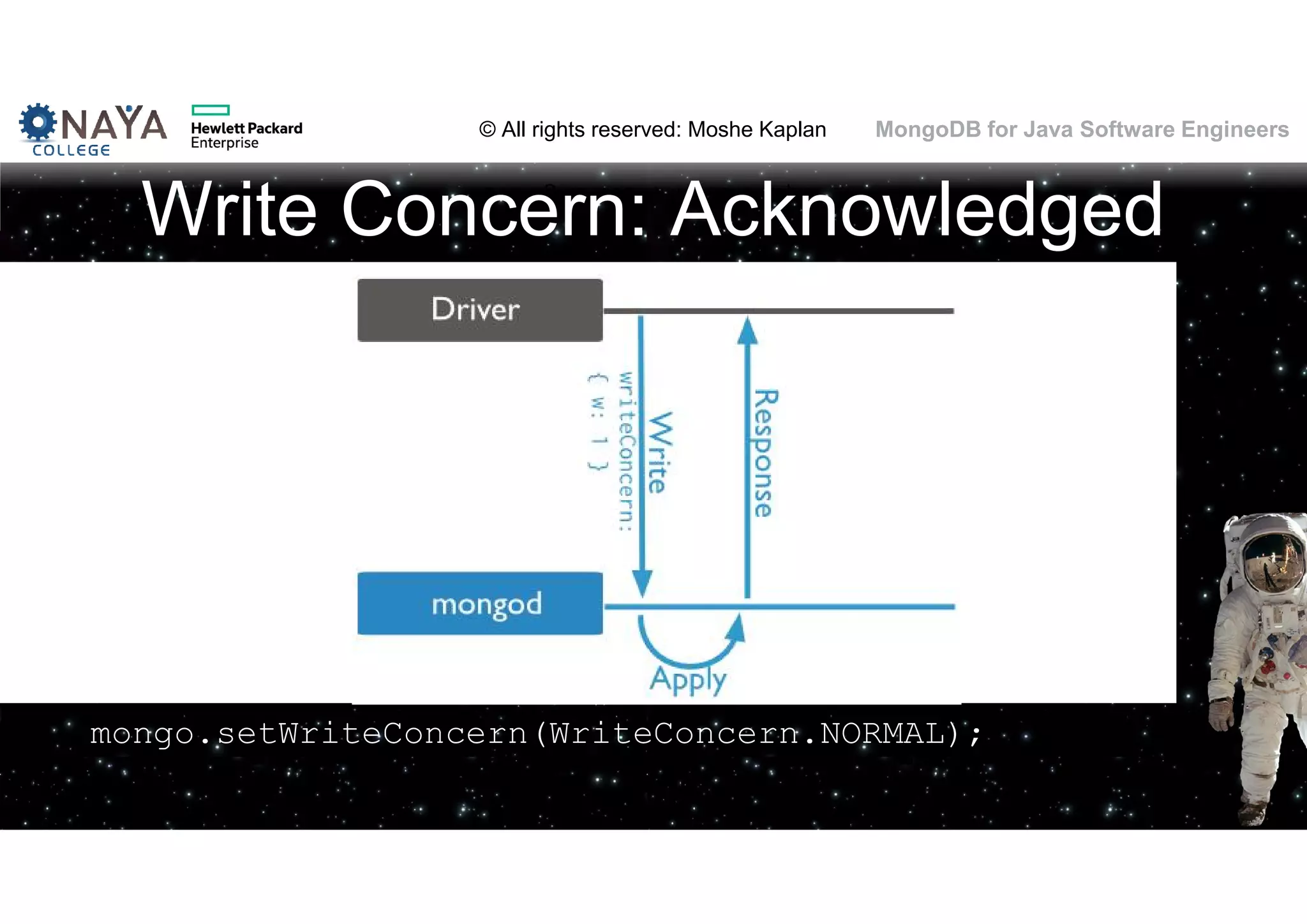
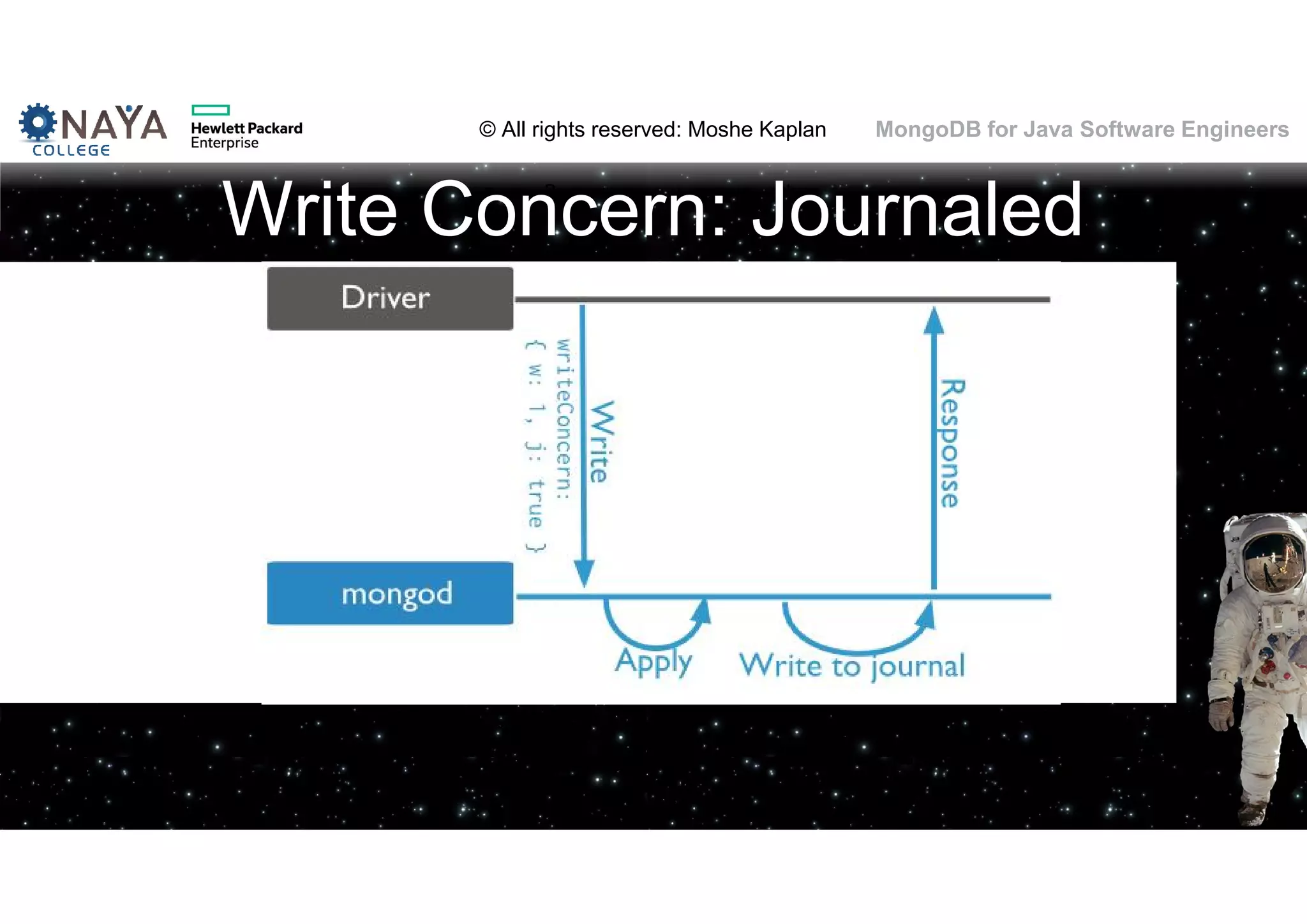
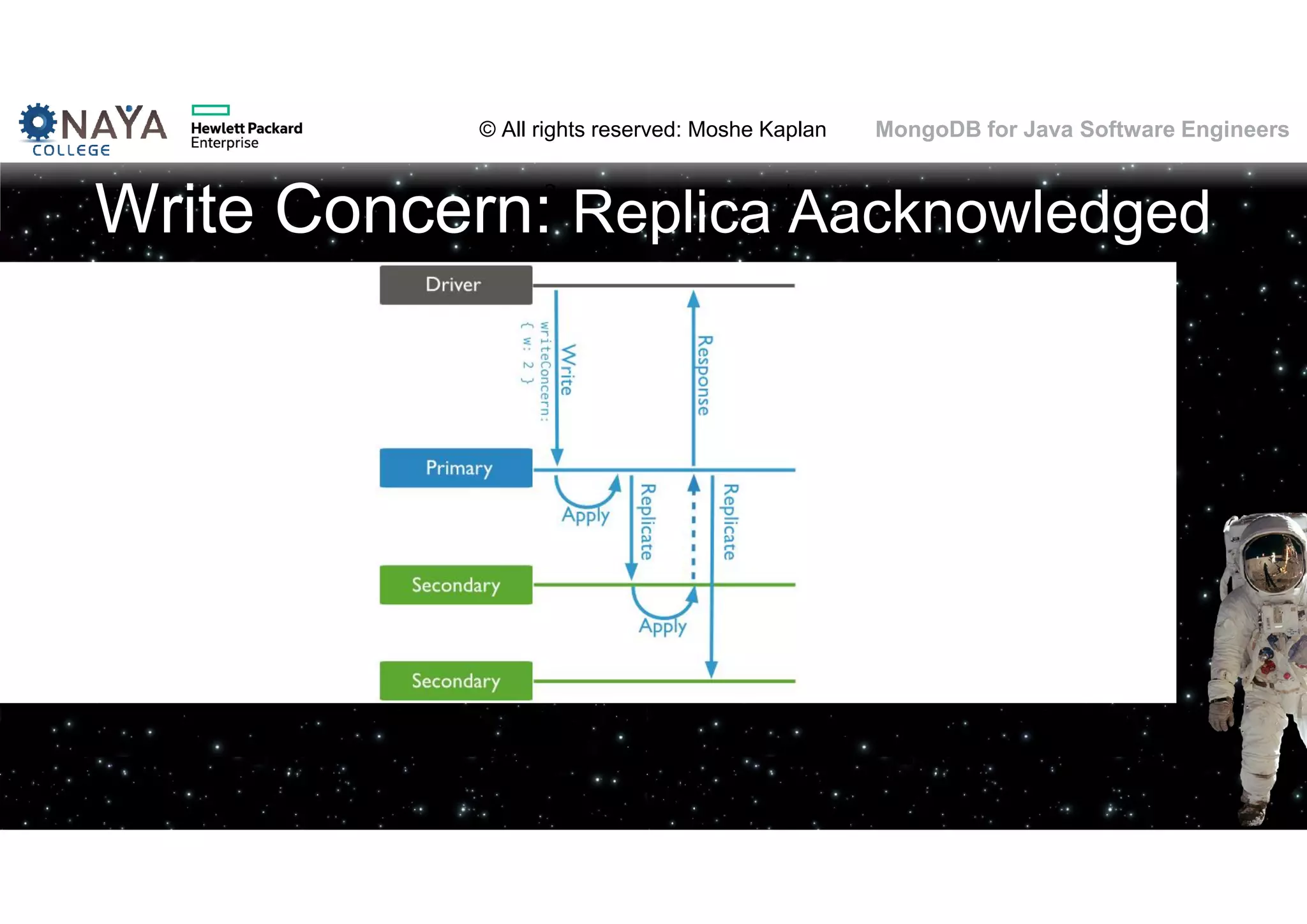

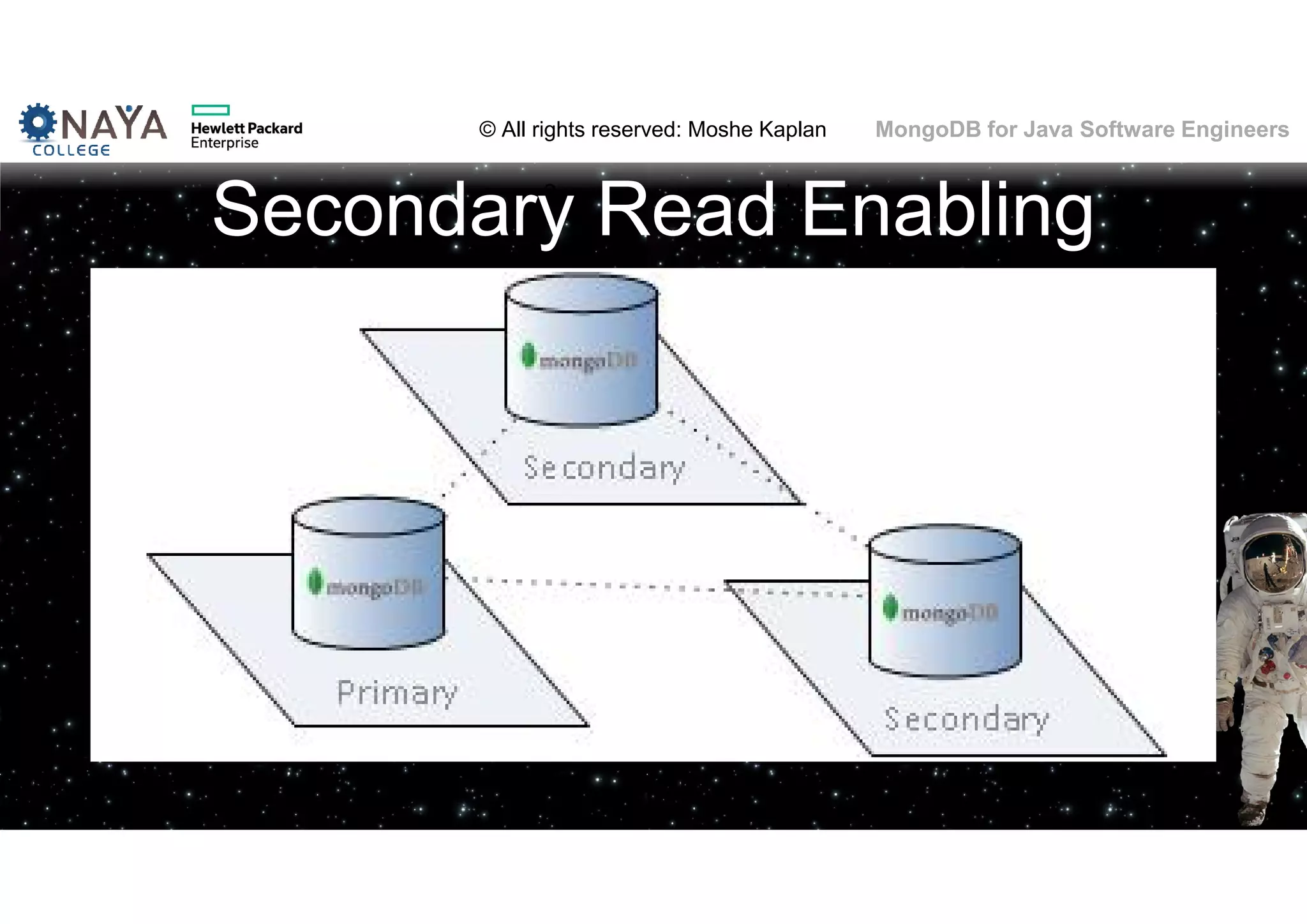



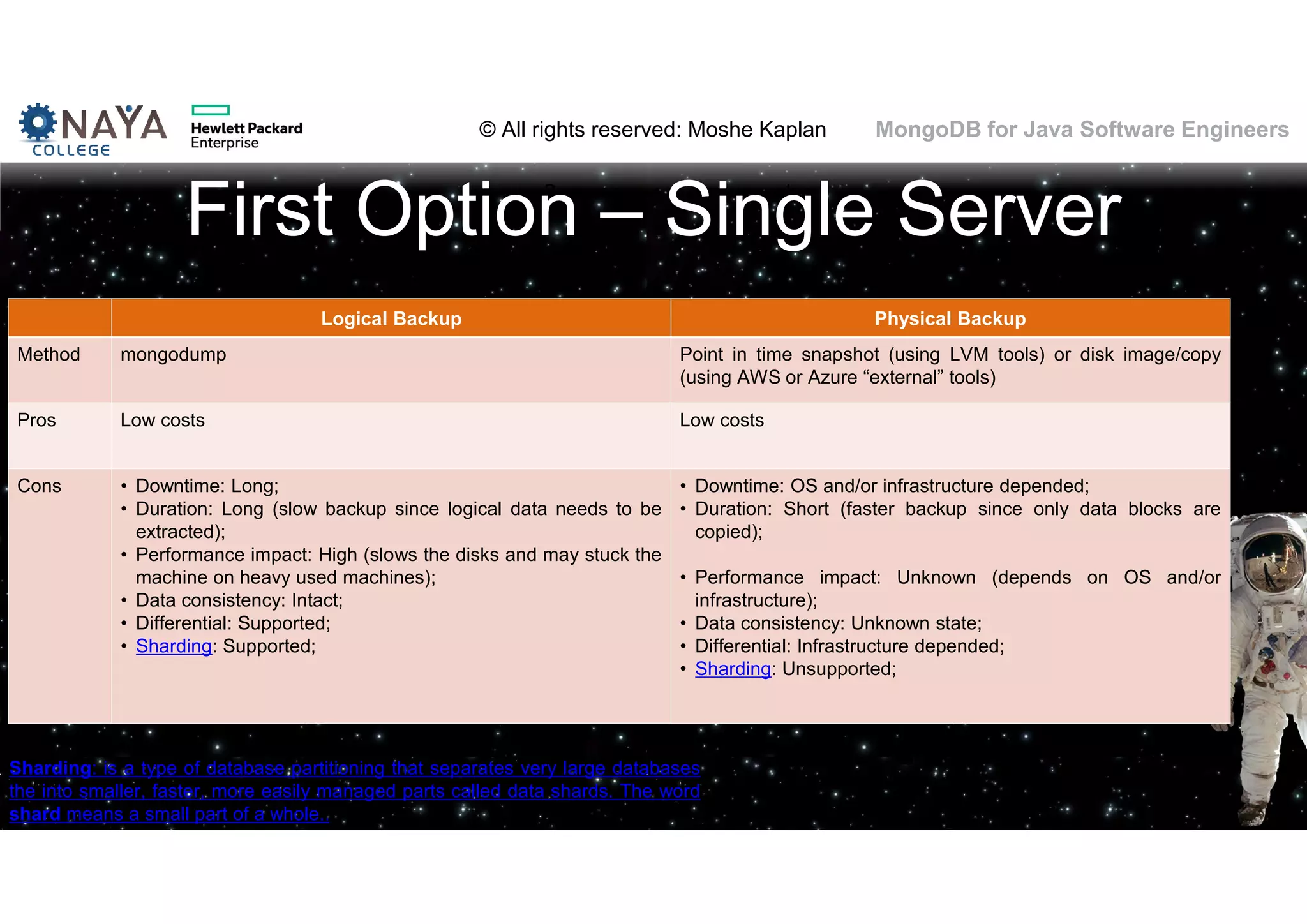

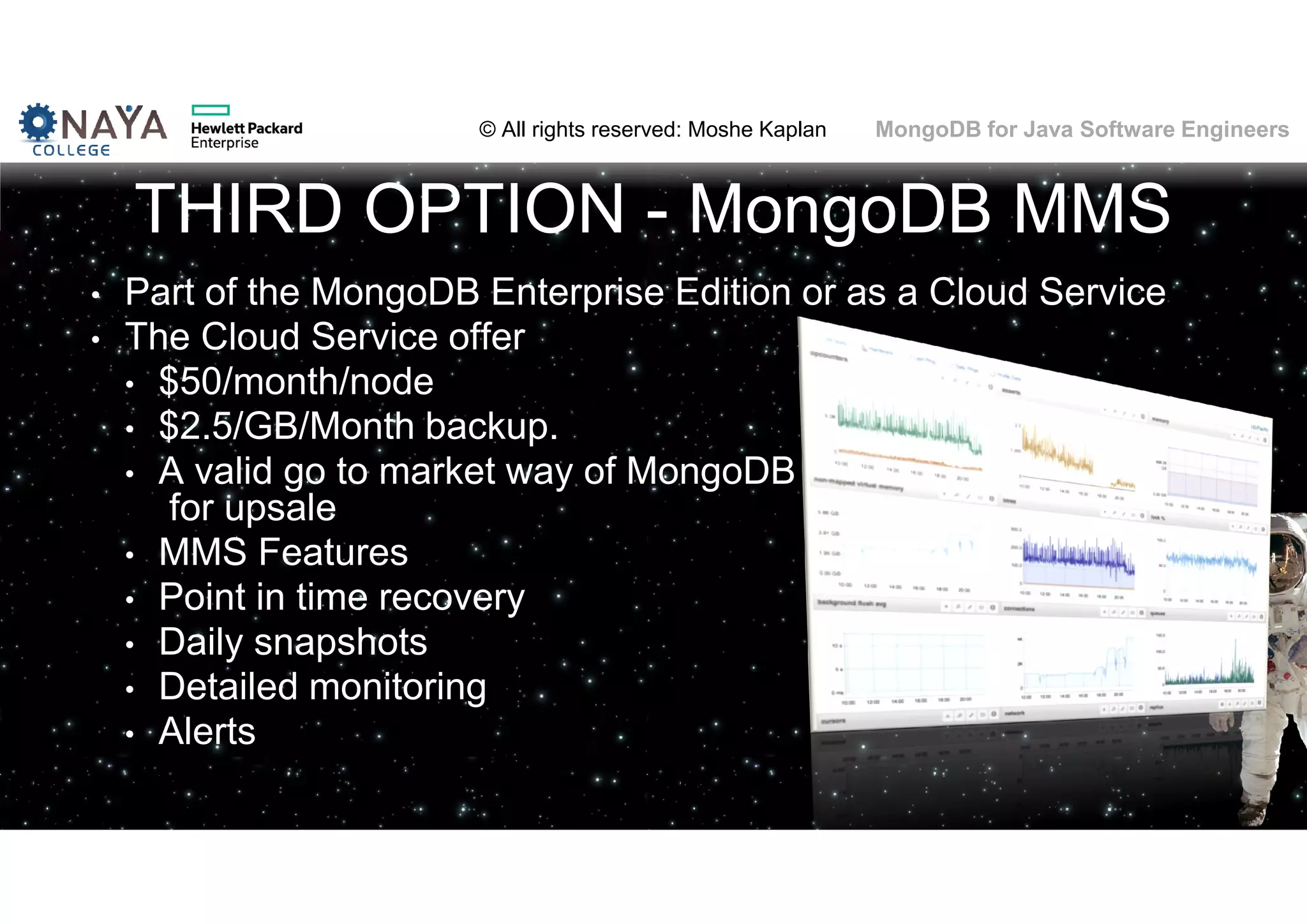

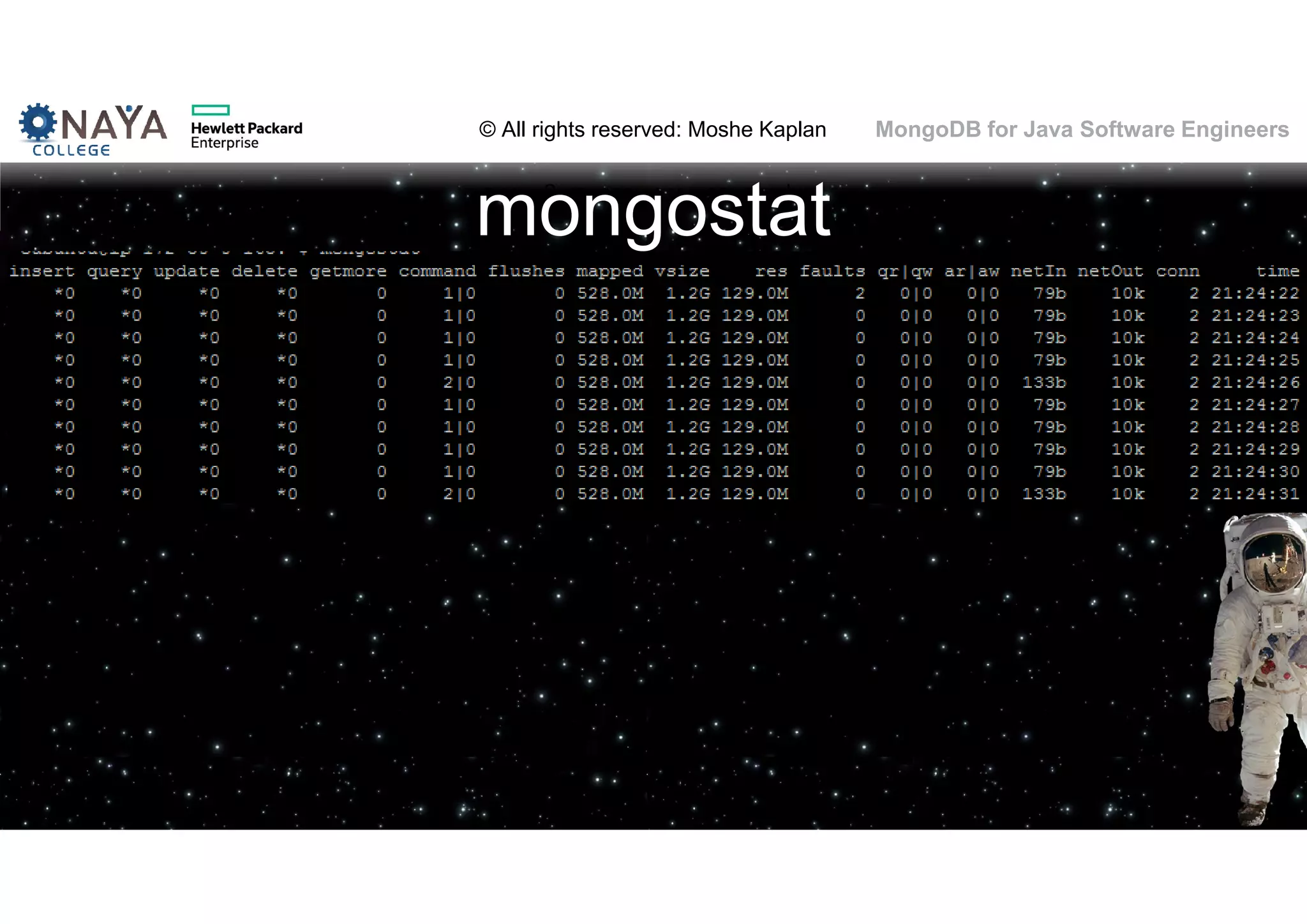
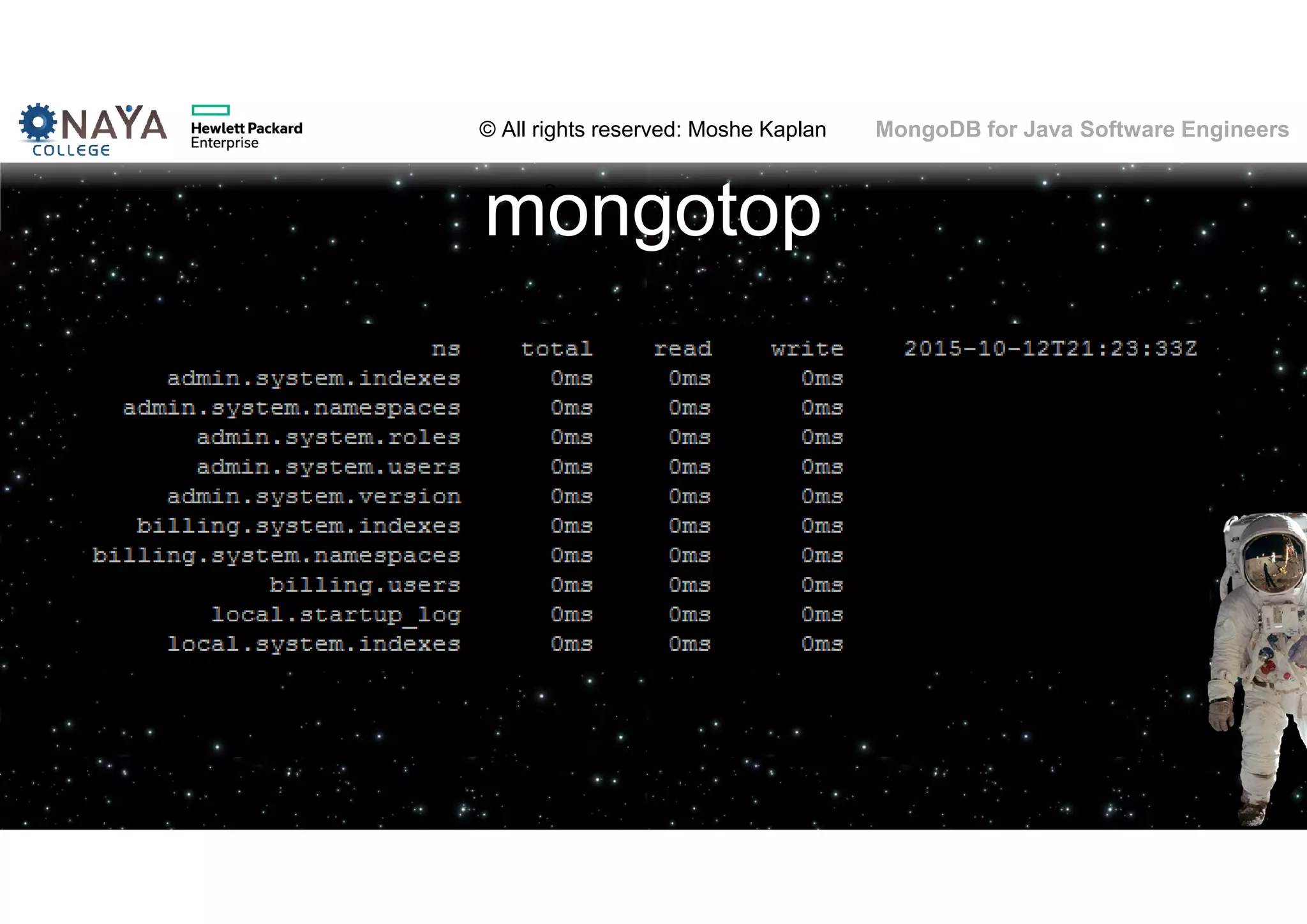


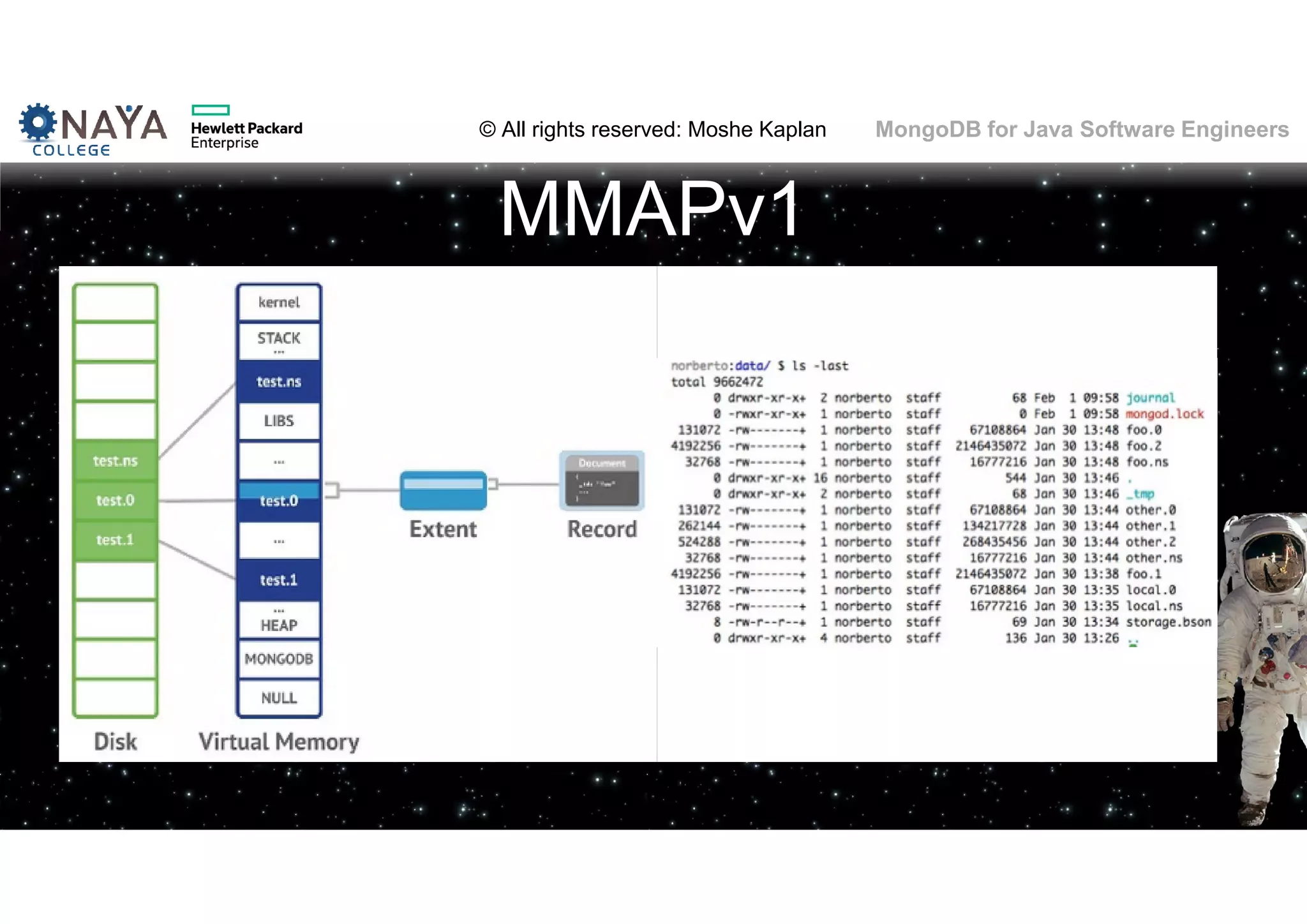

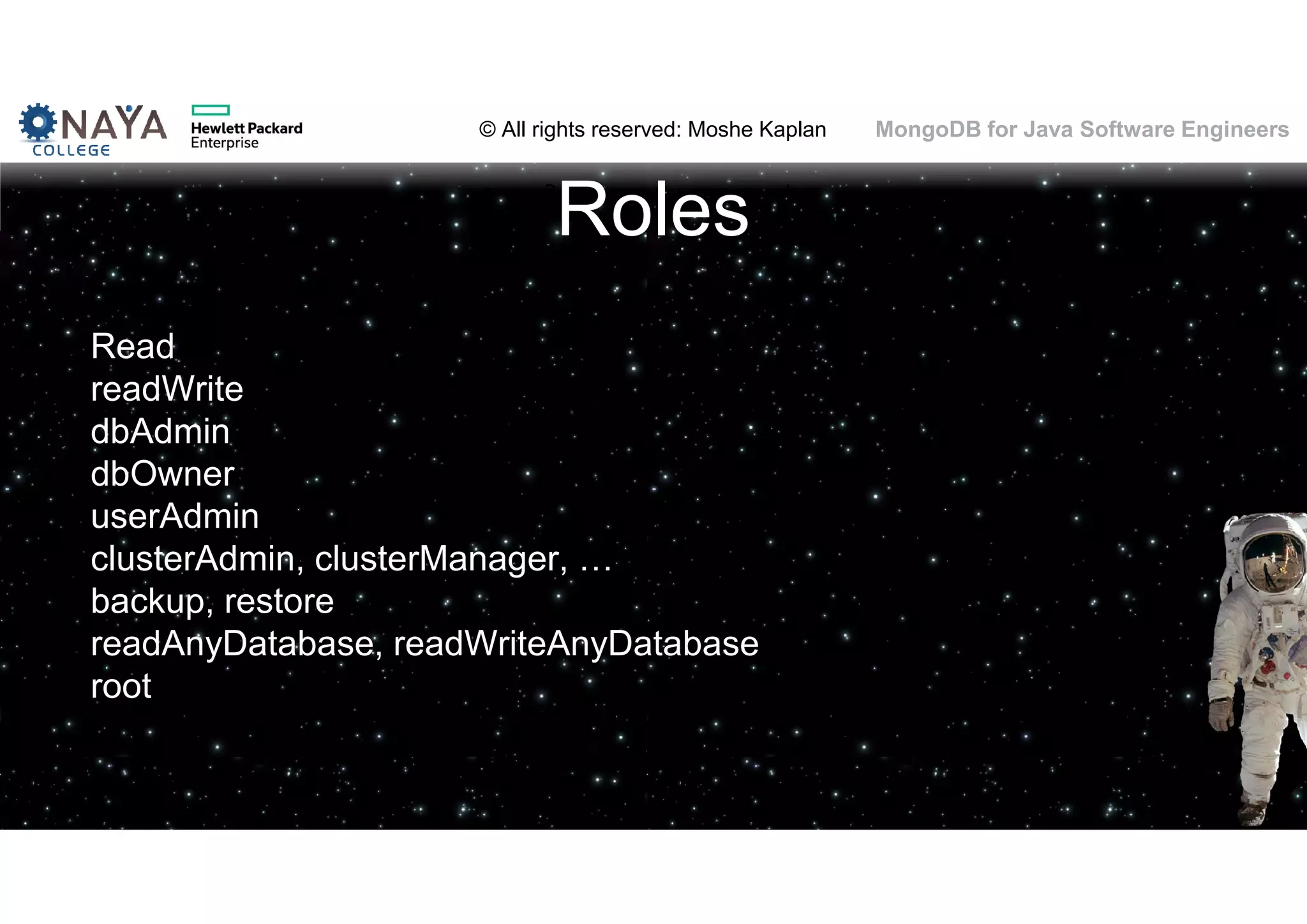
![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers Providing Permissions • use admin db.createUser( { user: "siteUserAdmin", pwd: "password", roles: [ { role: "userAdminAnyDatabase", db: "admin" } ] } ) • use records db.createUser( { user: "recordsUserAdmin", pwd: "password", roles: [ { role: "userAdmin", db: "records" } ] } )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-150-2048.jpg)
![© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan© All rights reserved: Moshe Kaplan MongoDB for Java Software Engineers Granular Actions use admin db.createRole( role: "manageOpRole", privileges: [ { resource: { cluster: true }, actions: [ "killop", "inprog" ] }, { resource: { db: "", collection: "" }, actions: [ "killCursors" ] } ], roles: [] } )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtrainingforjavasoftwareengineers-151124080500-lva1-app6892/75/MongoDB-training-for-java-software-engineers-152-2048.jpg)
