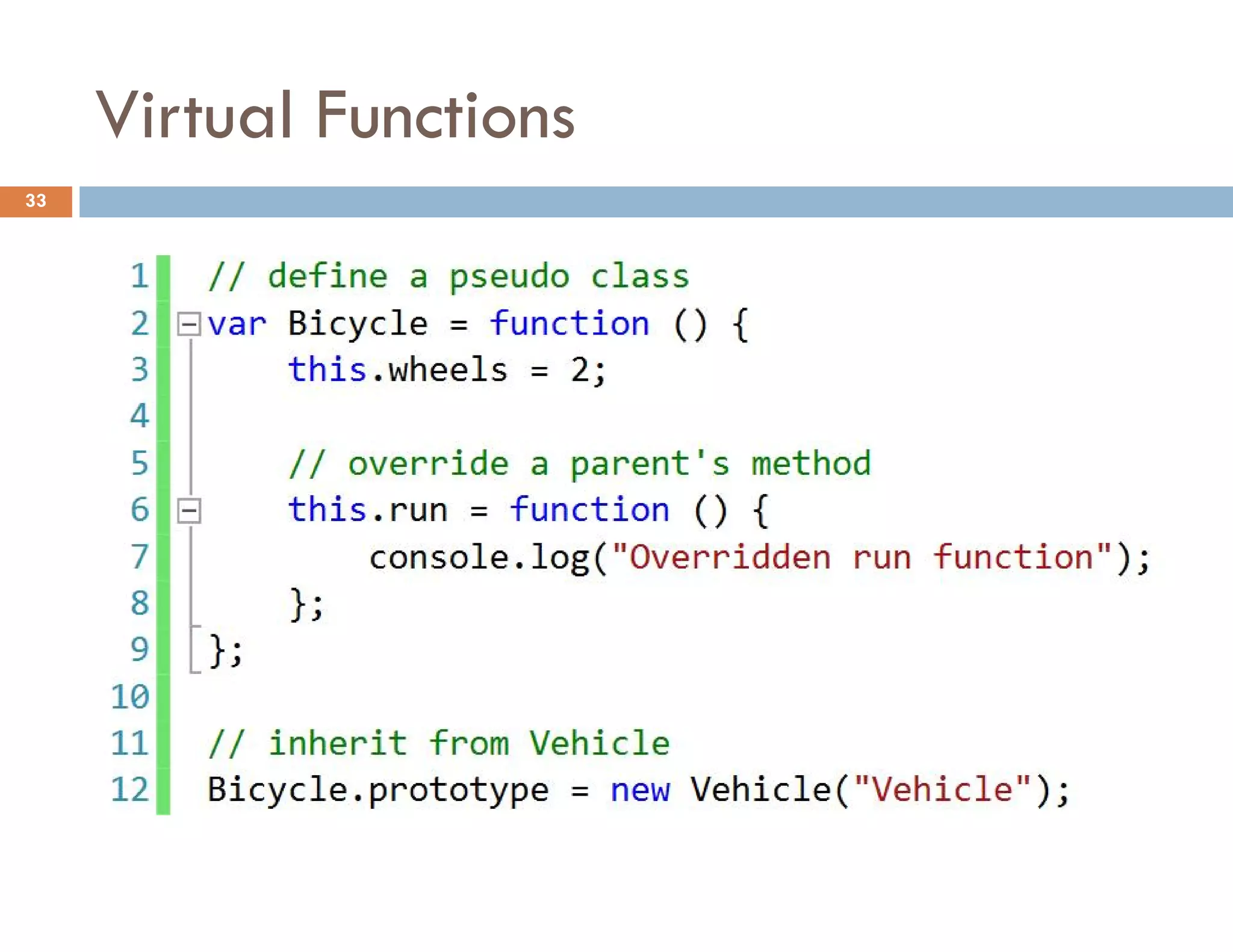
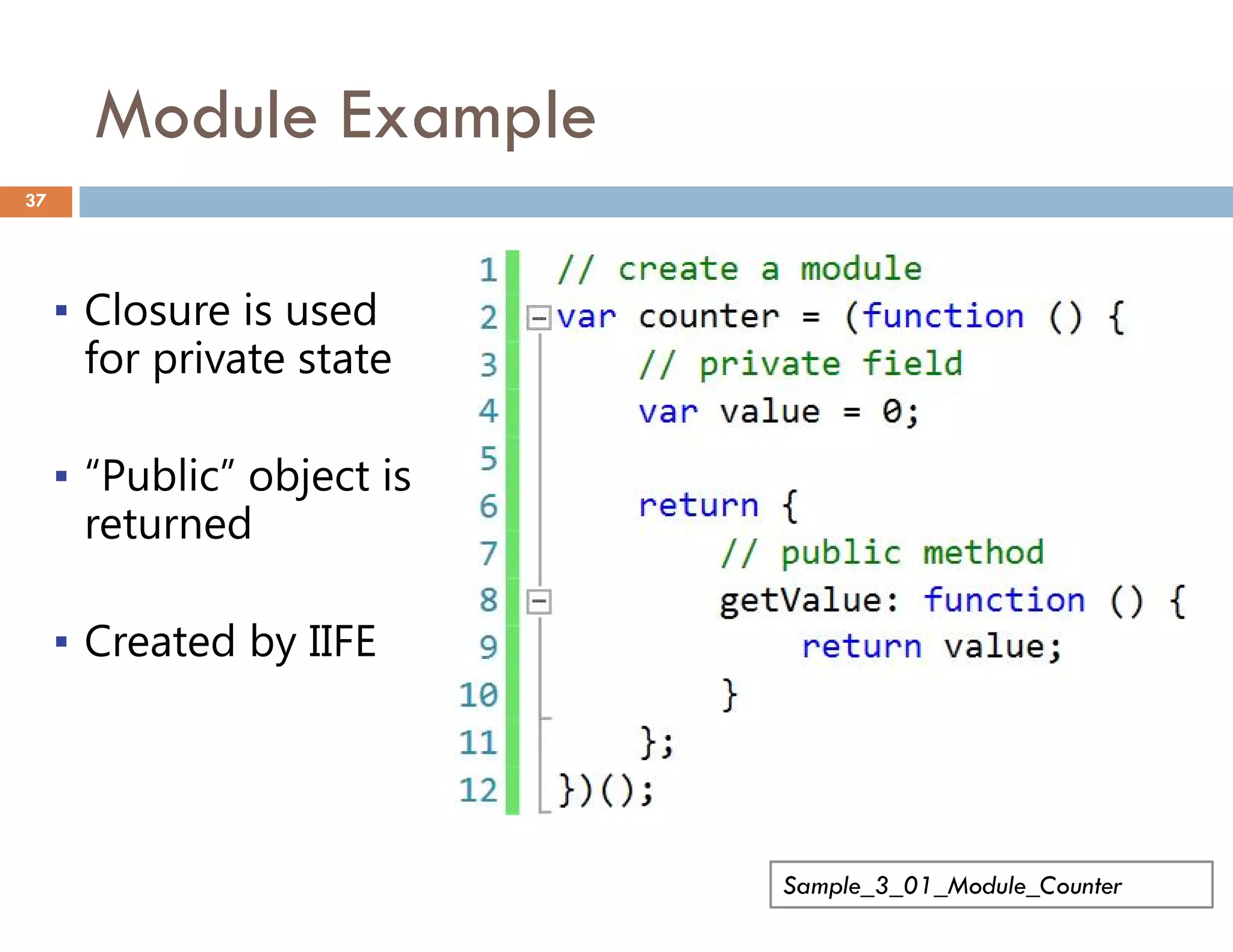
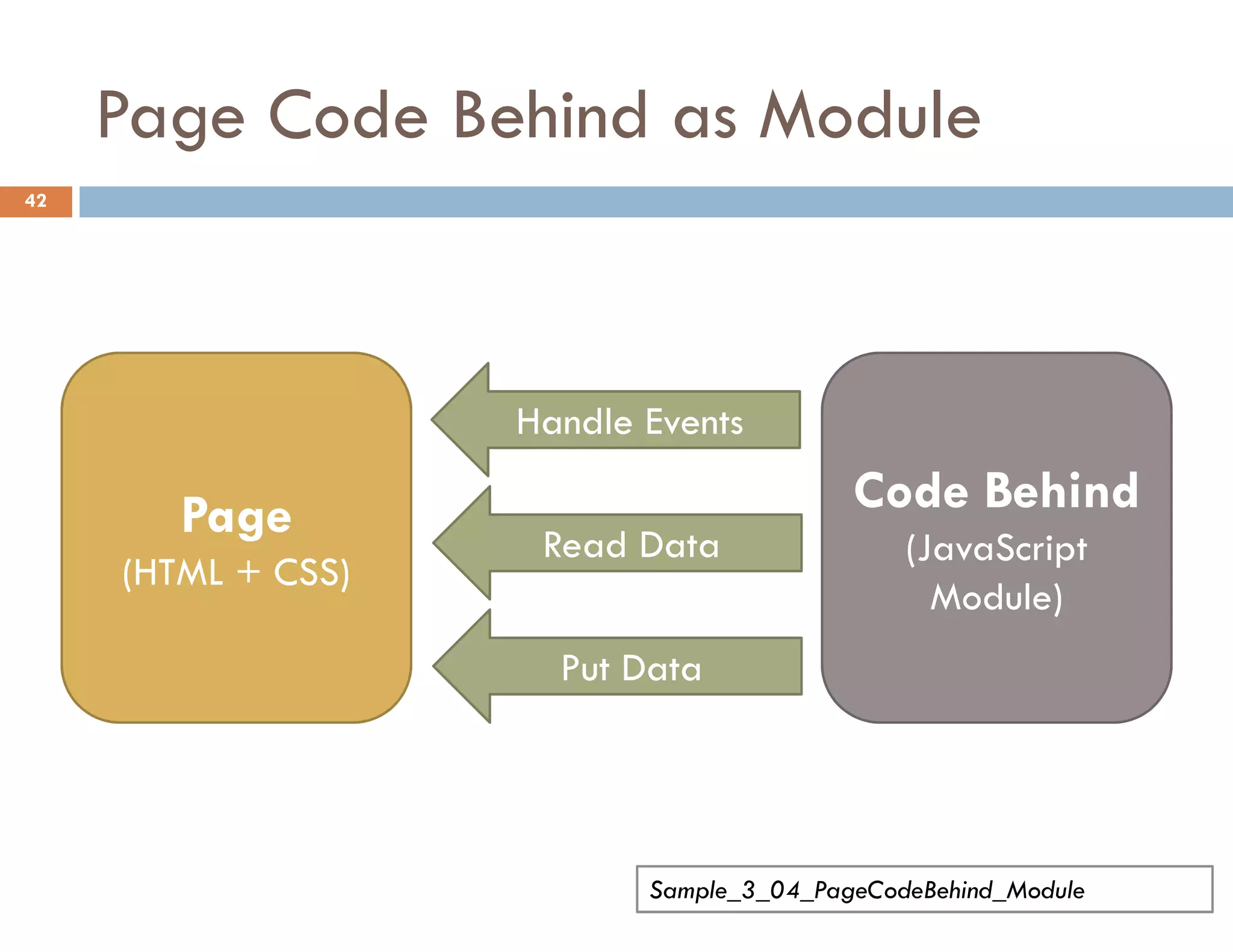
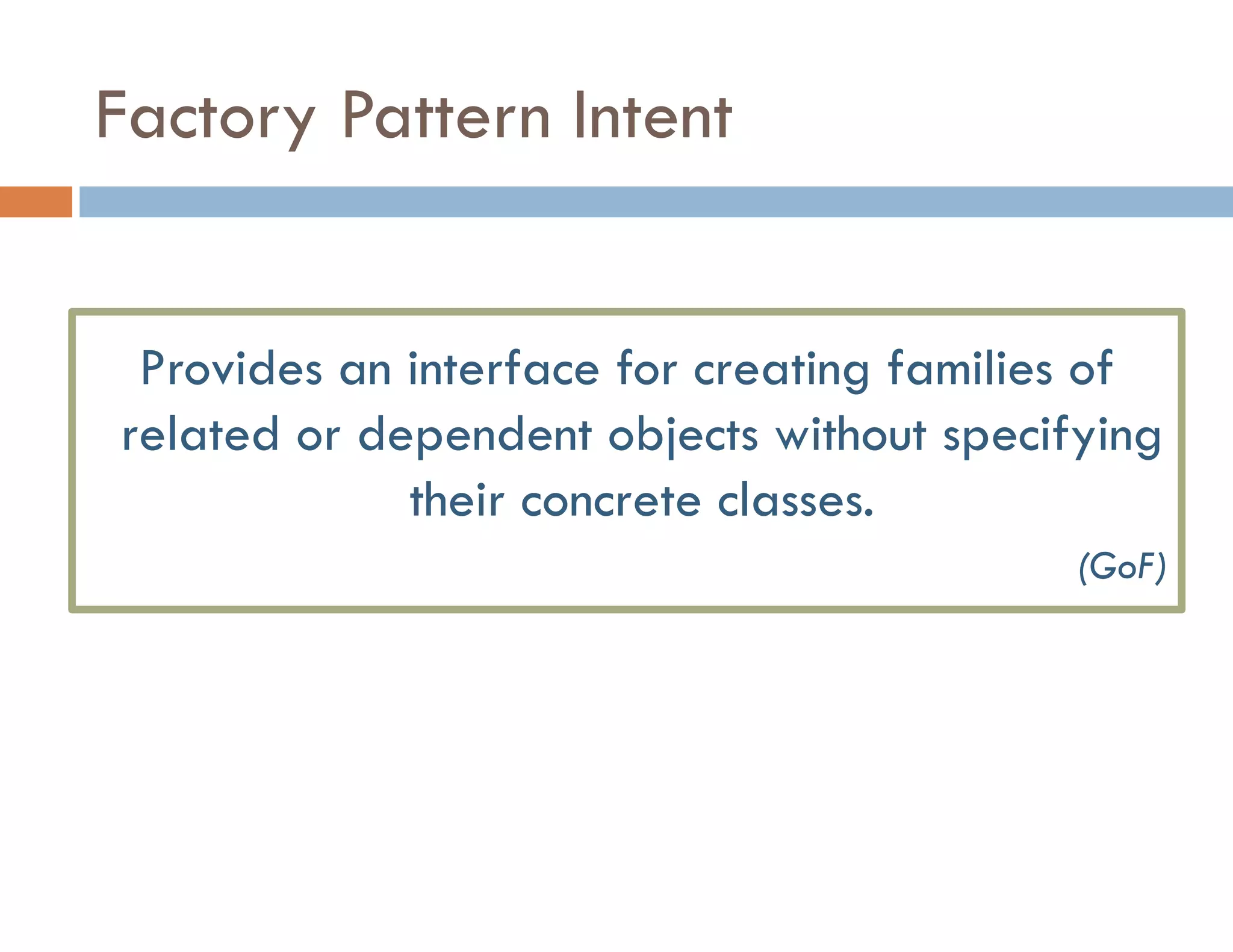
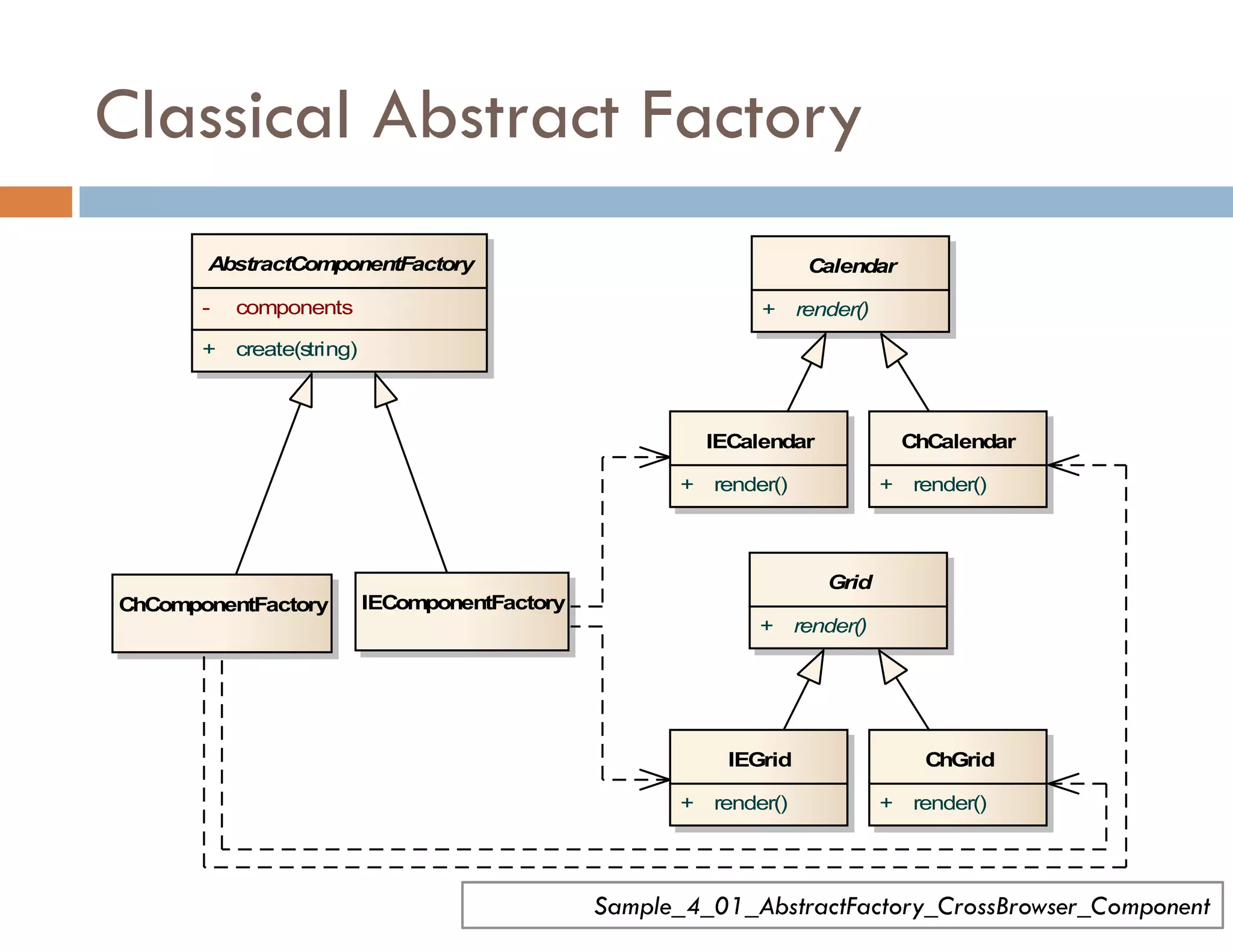
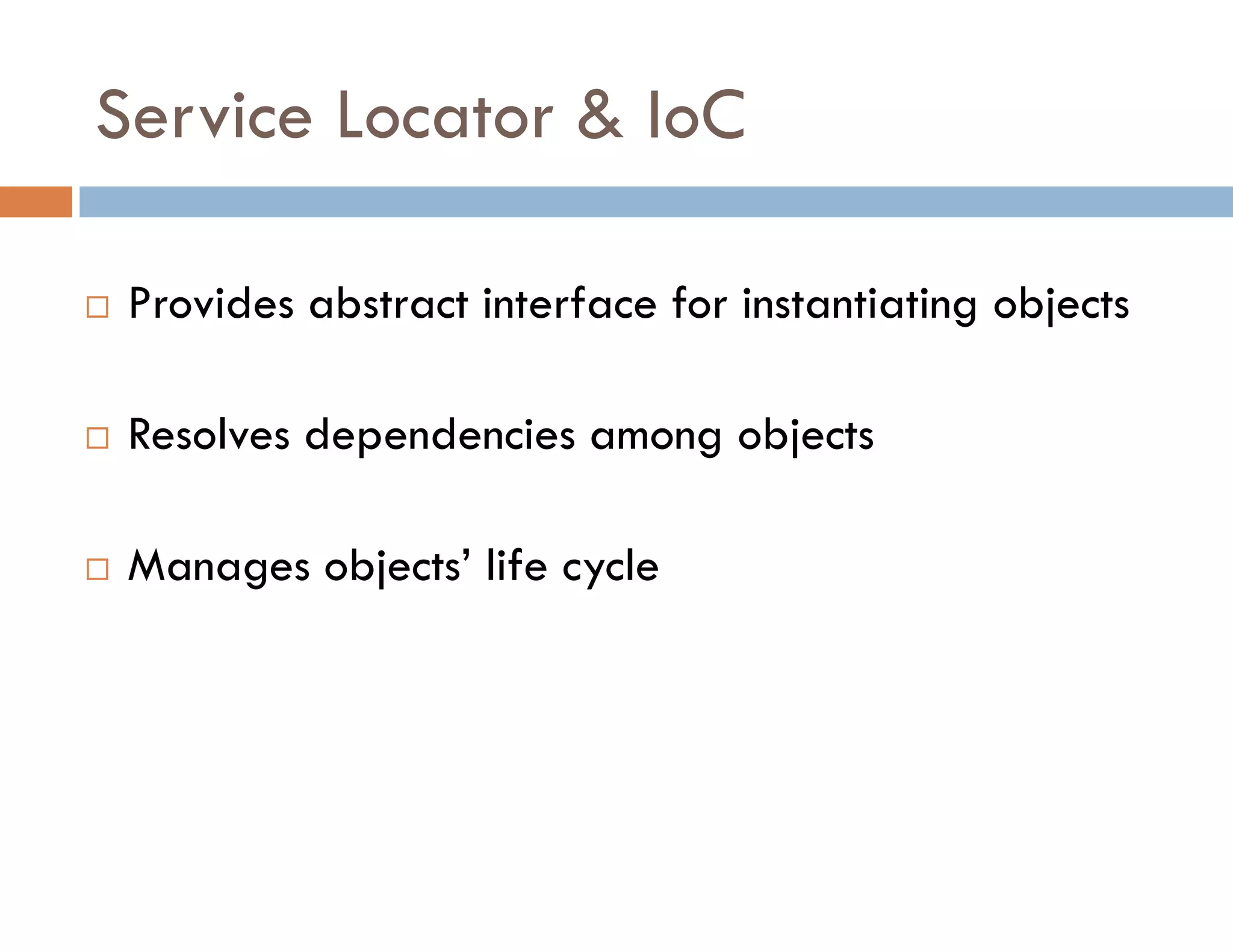
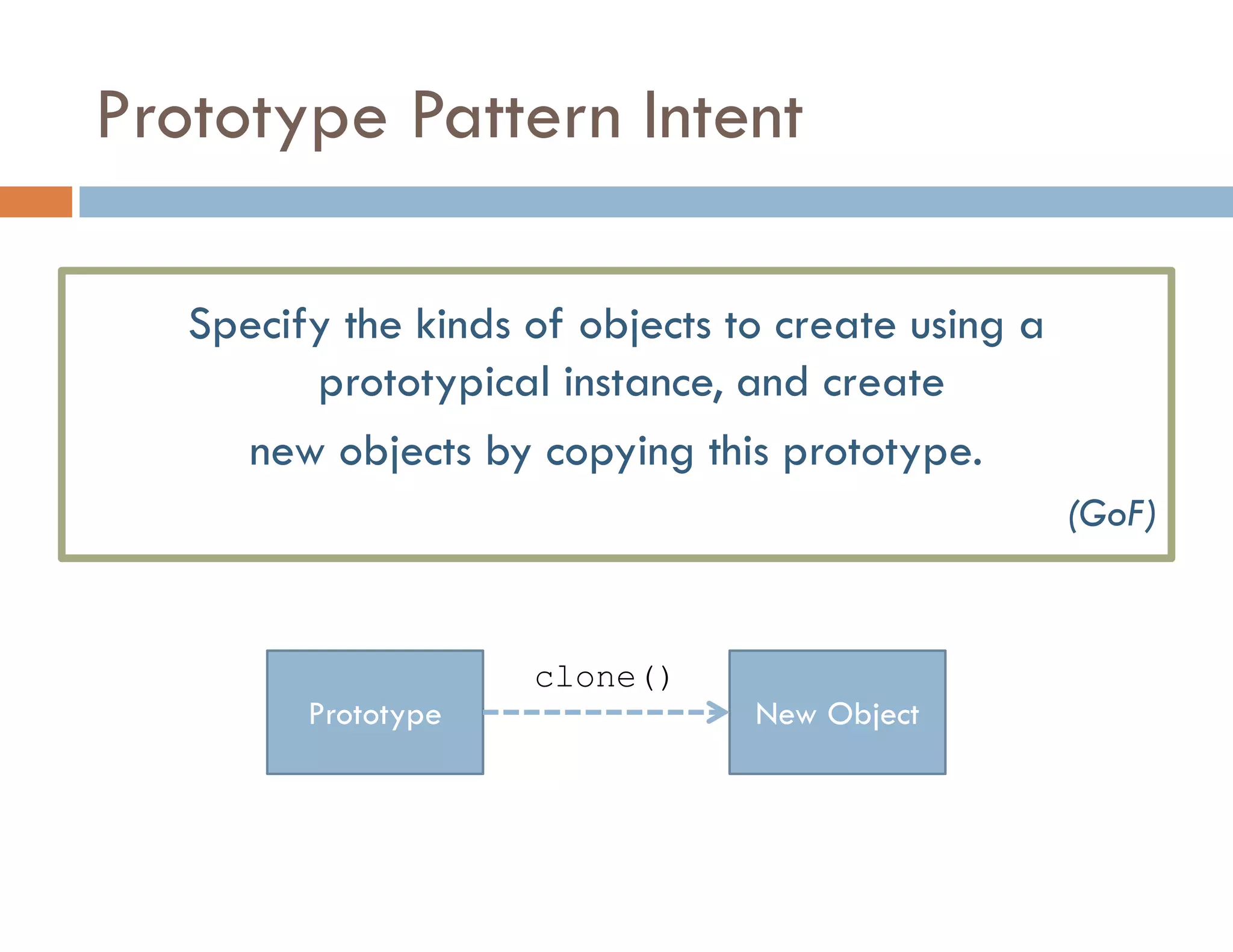
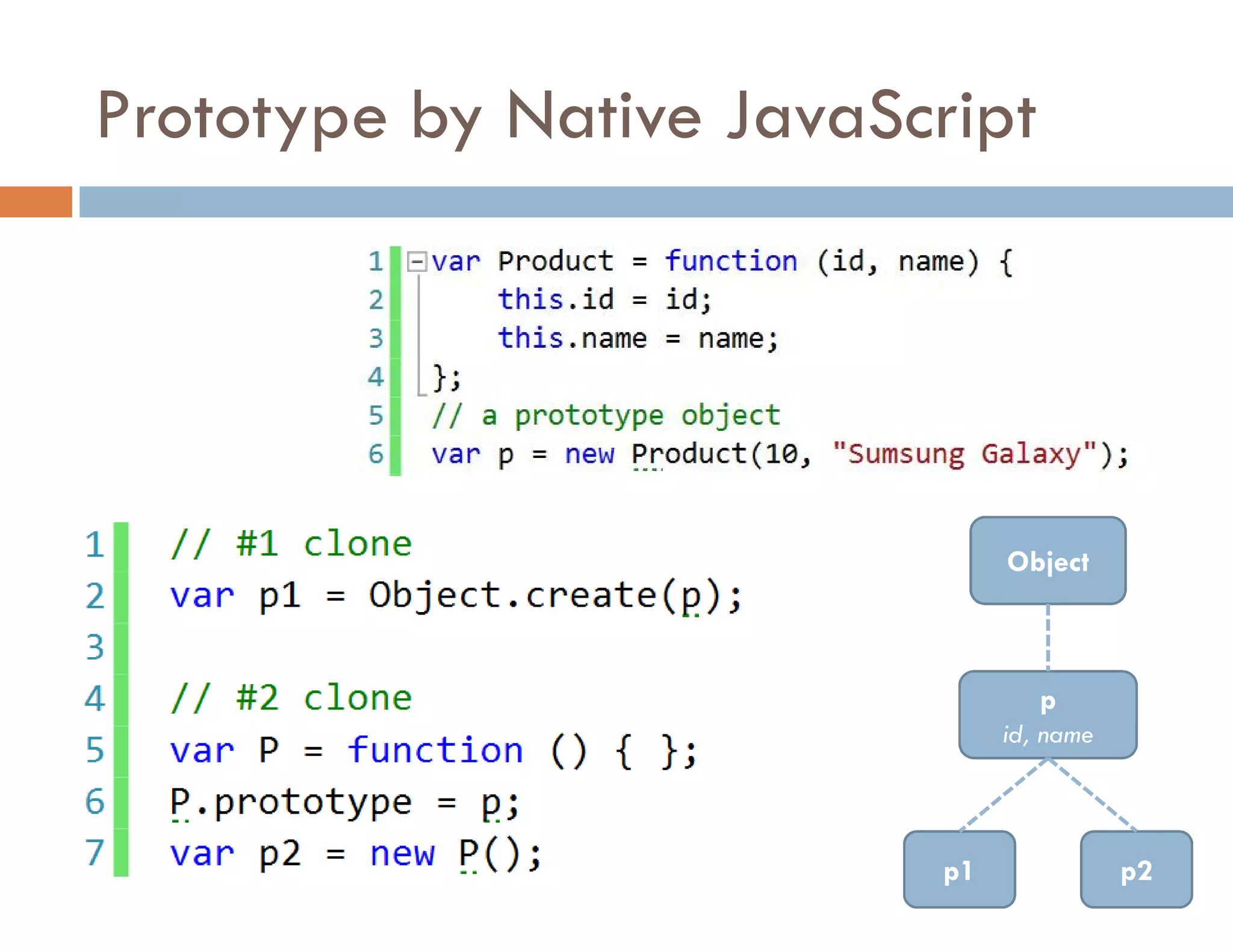
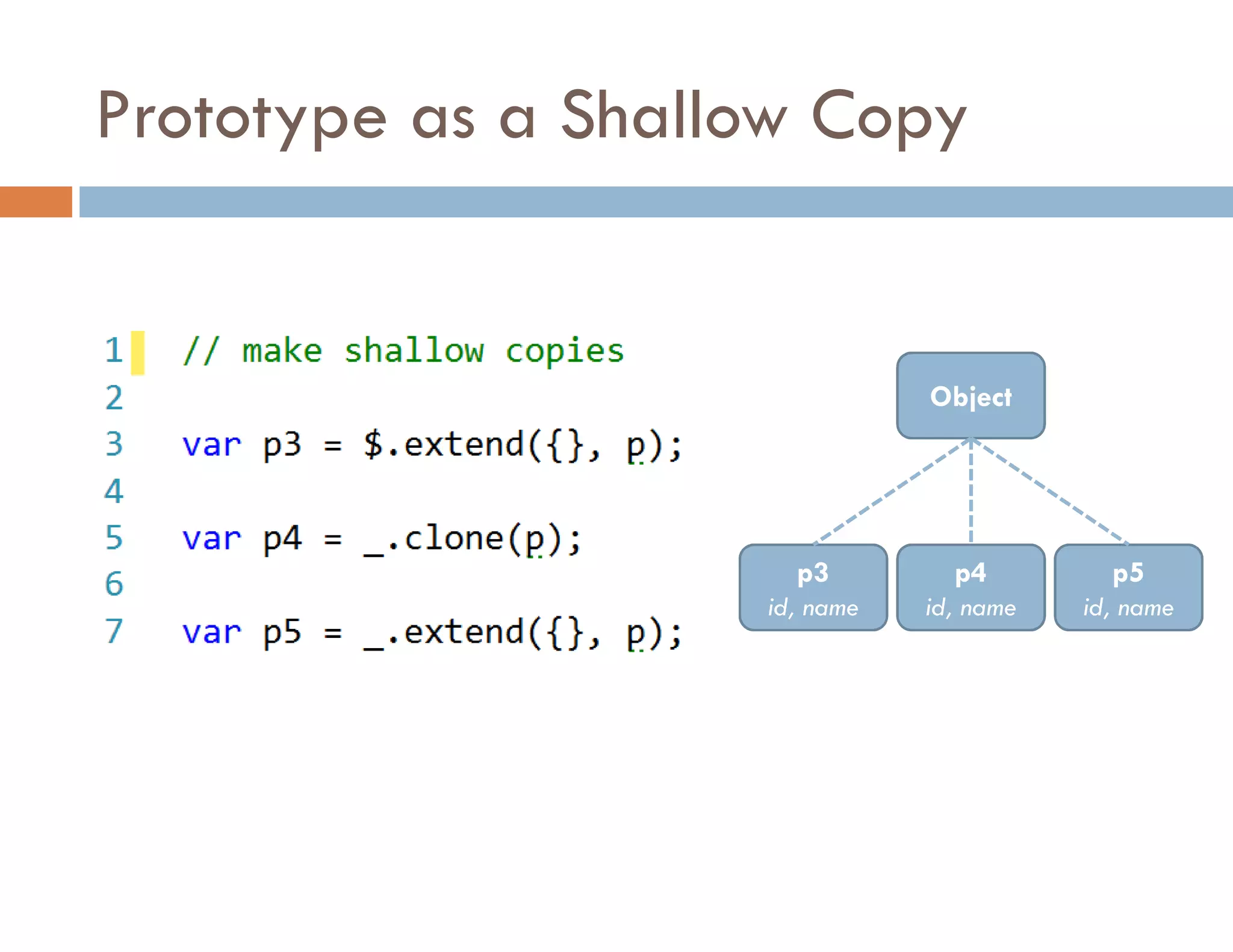
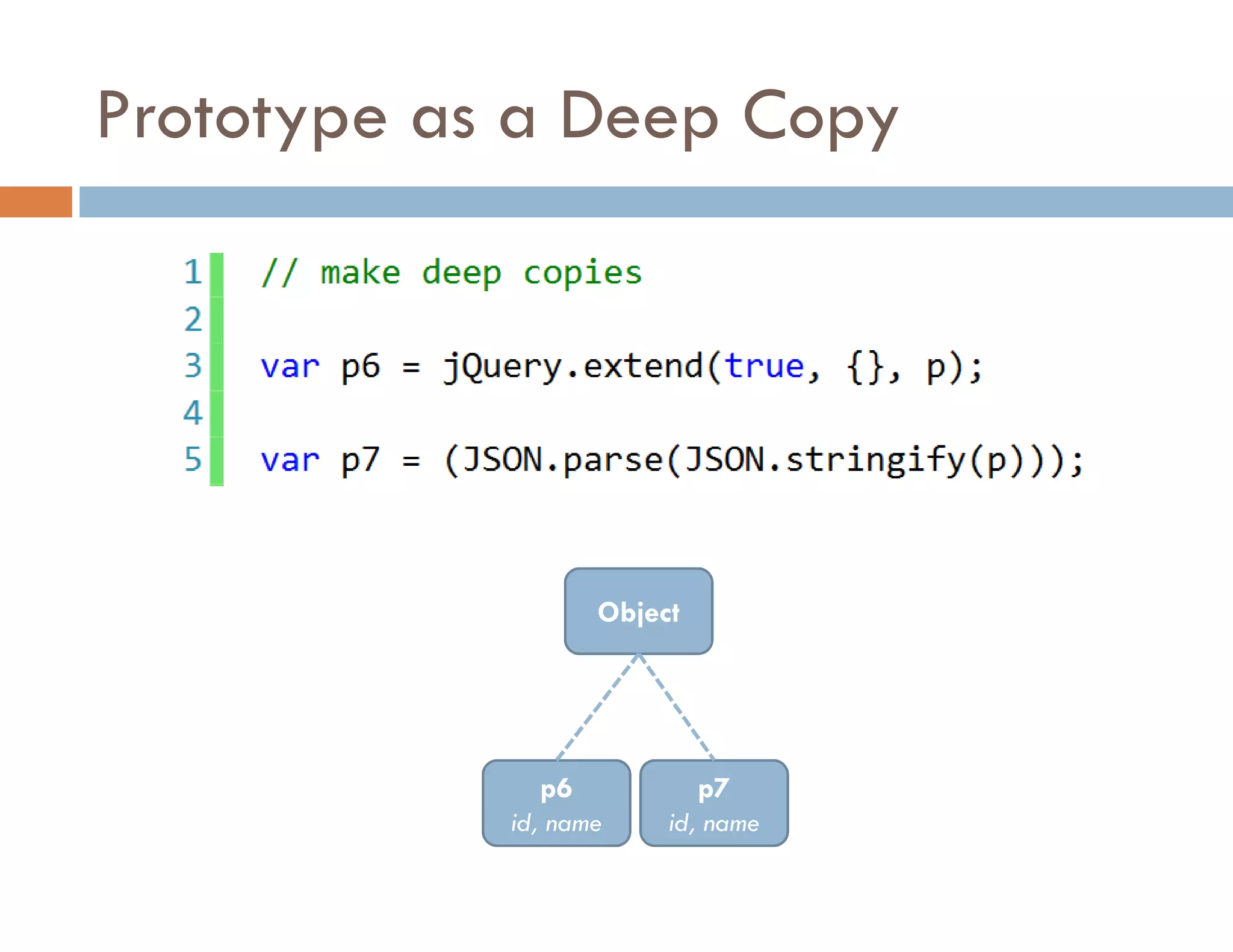
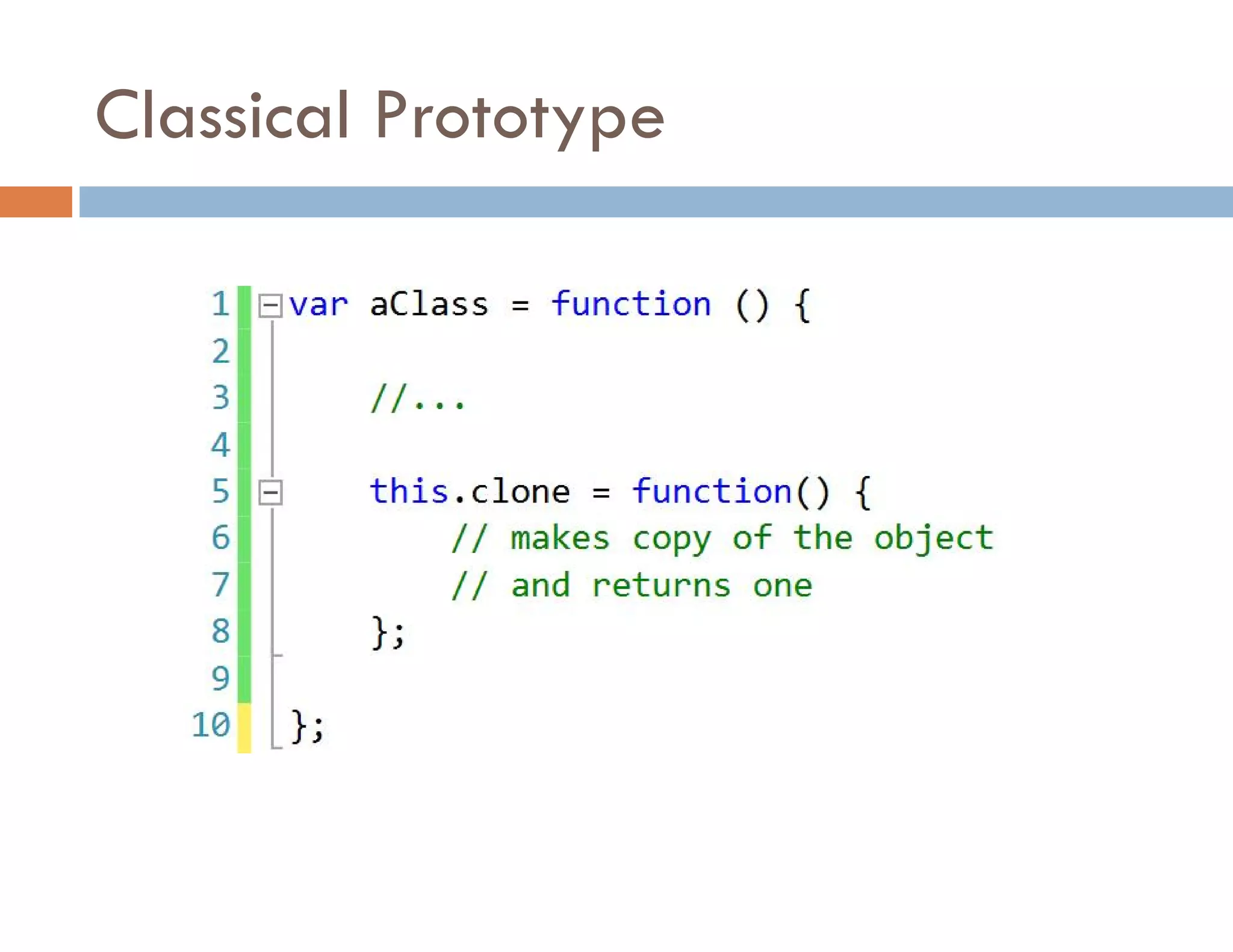
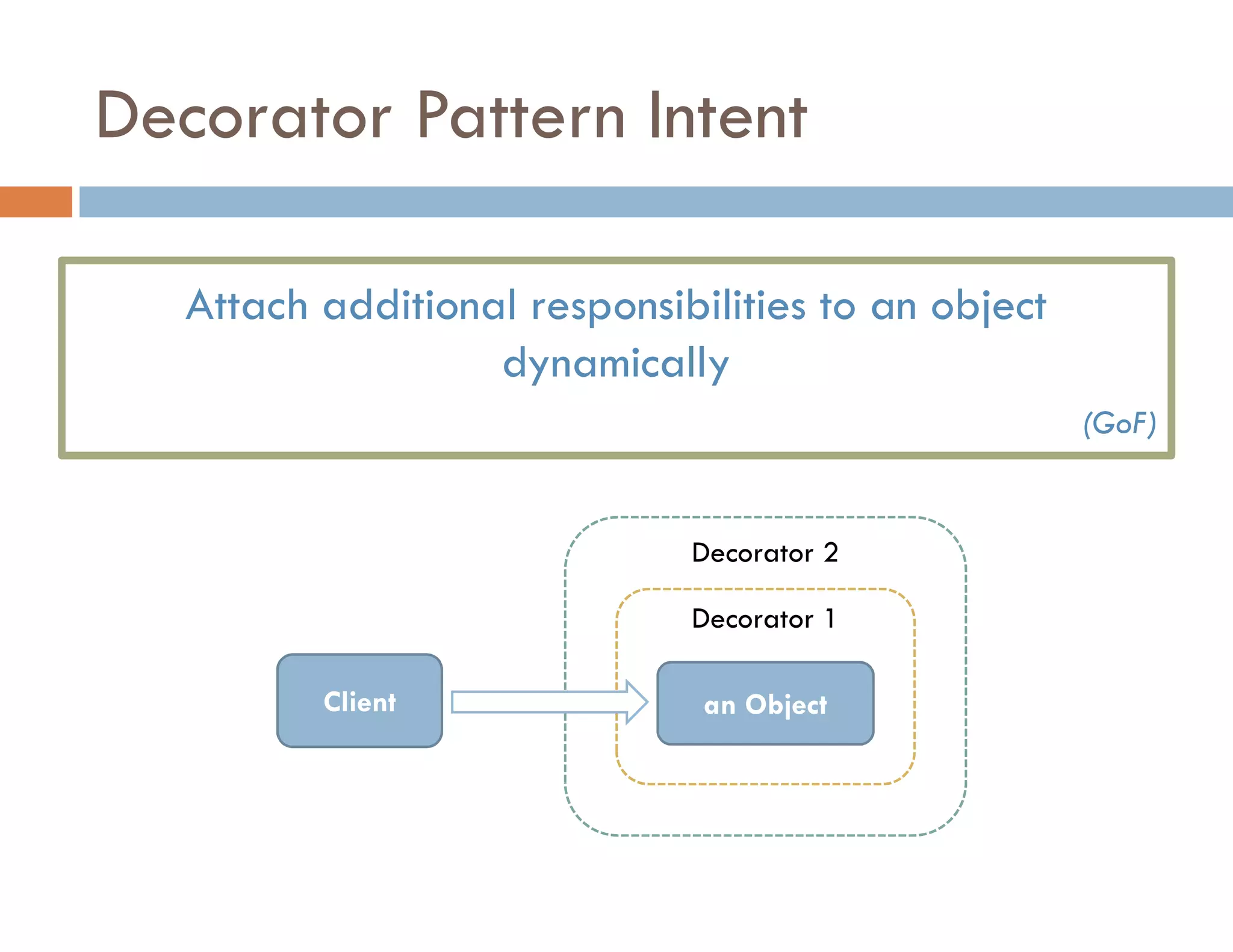
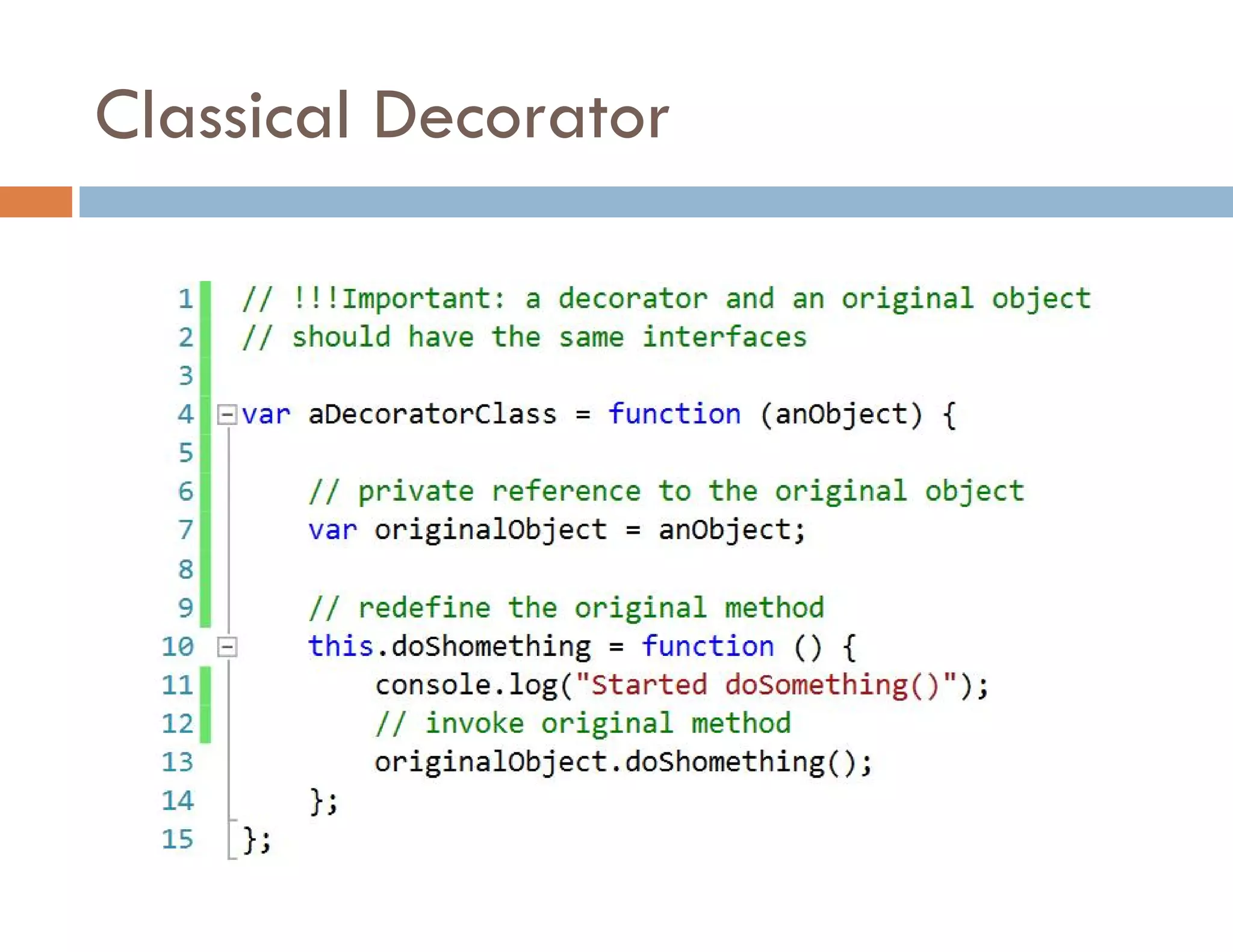
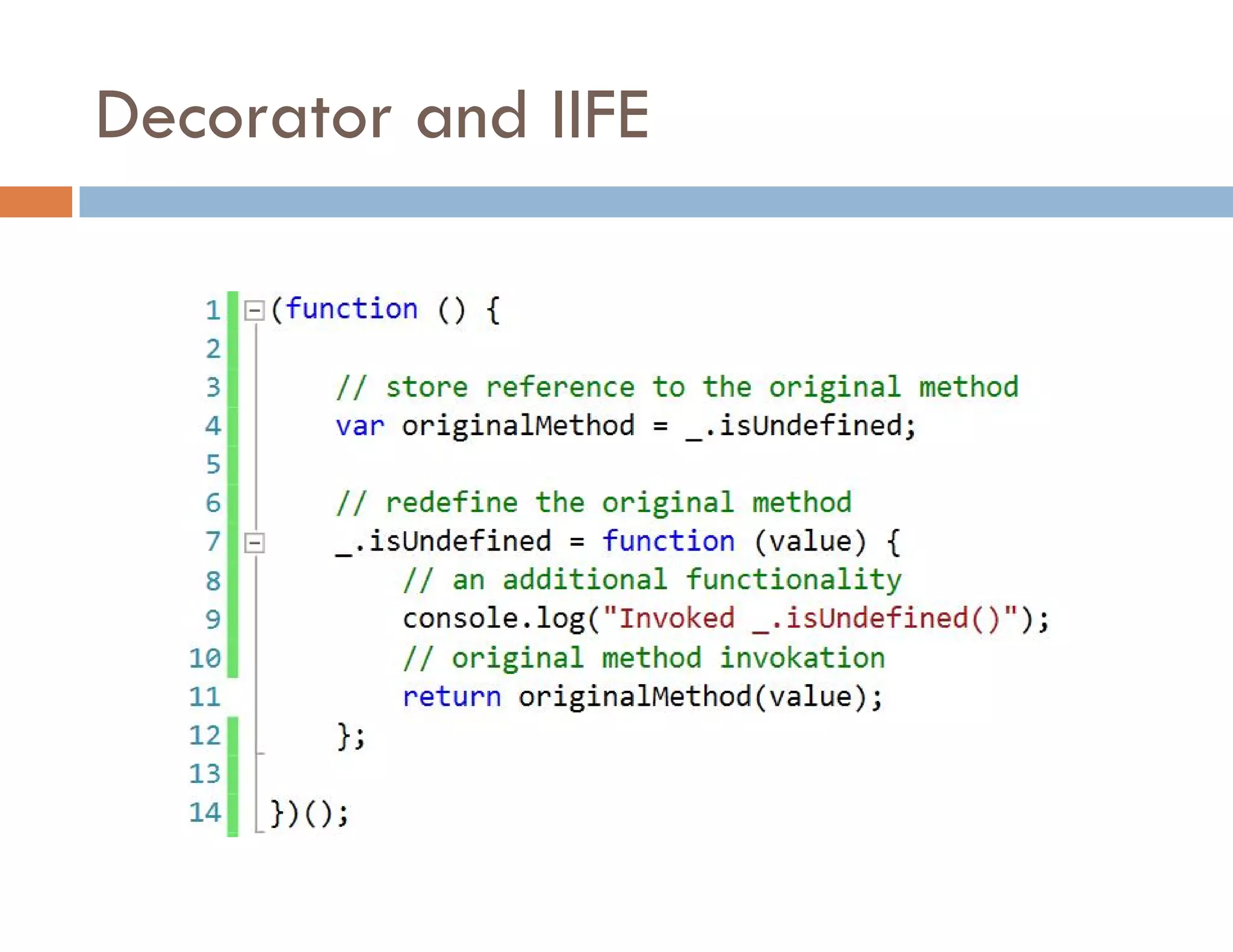
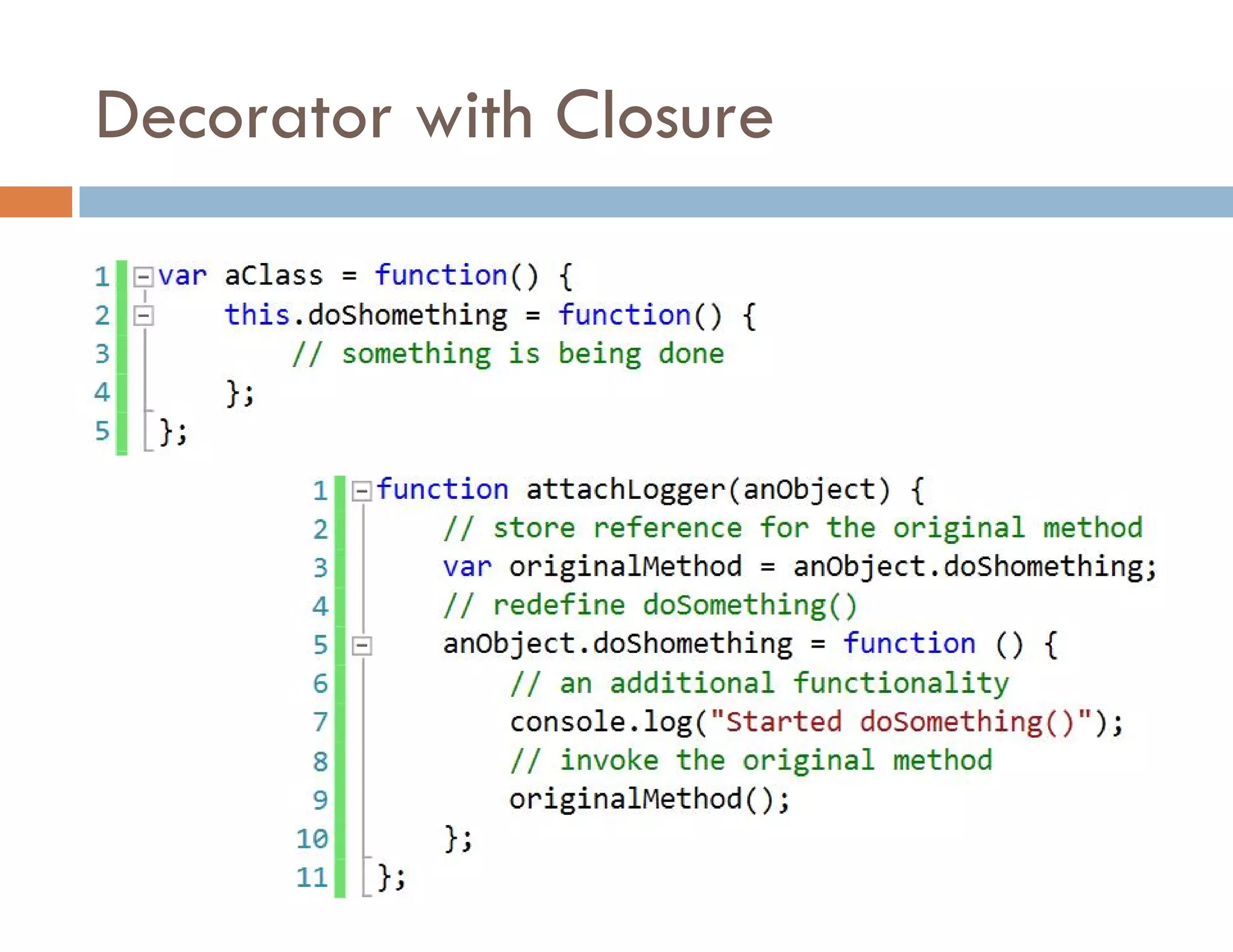
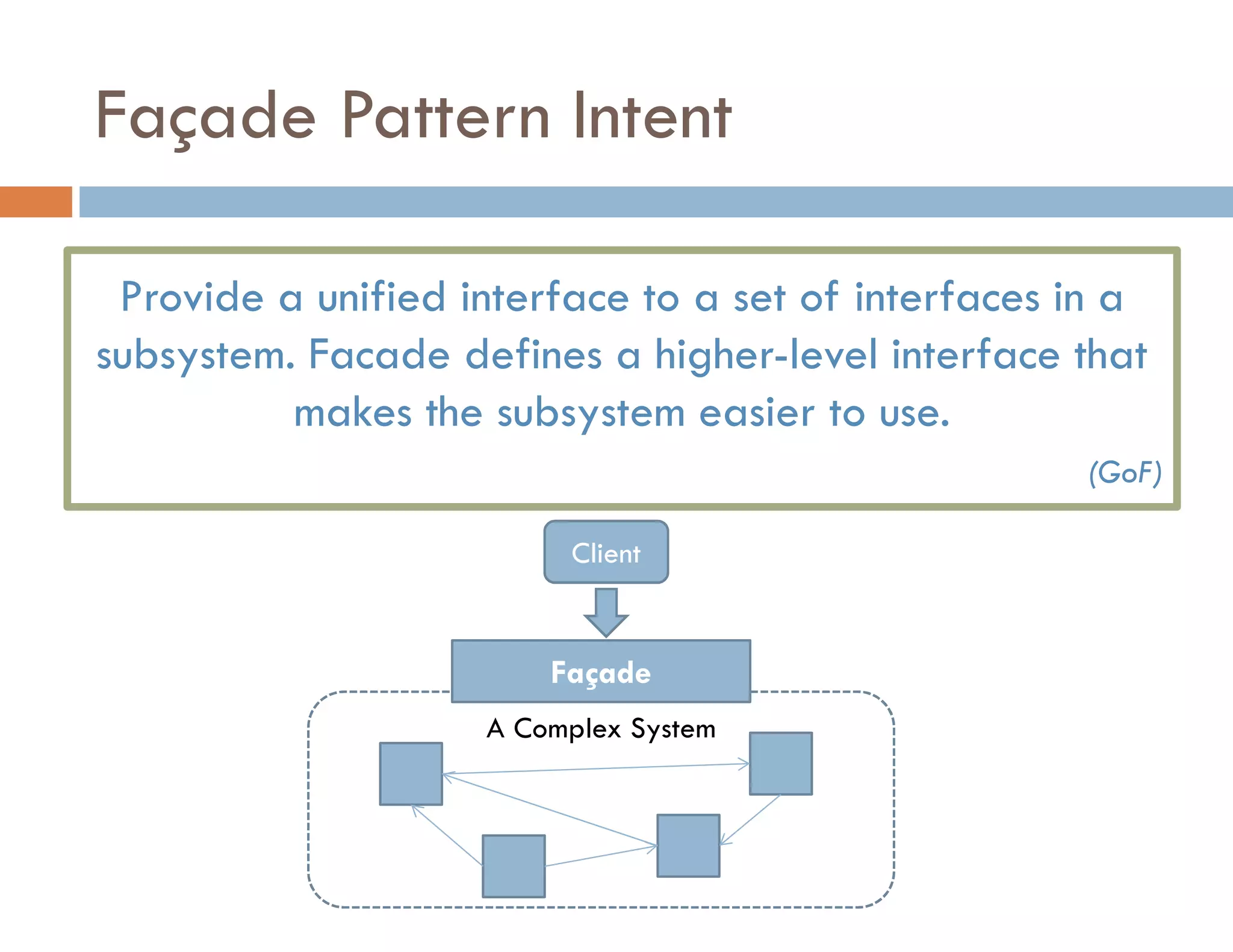
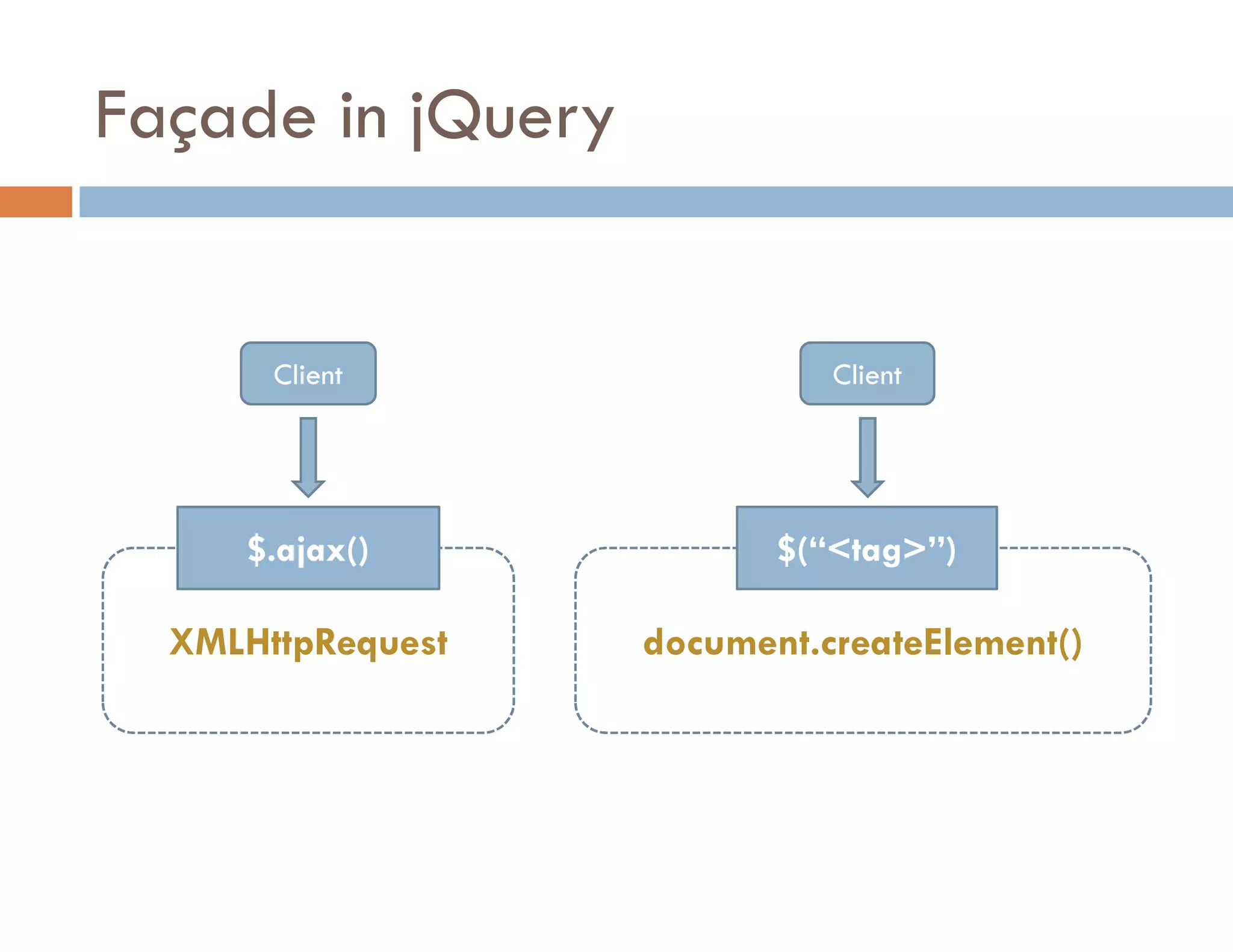
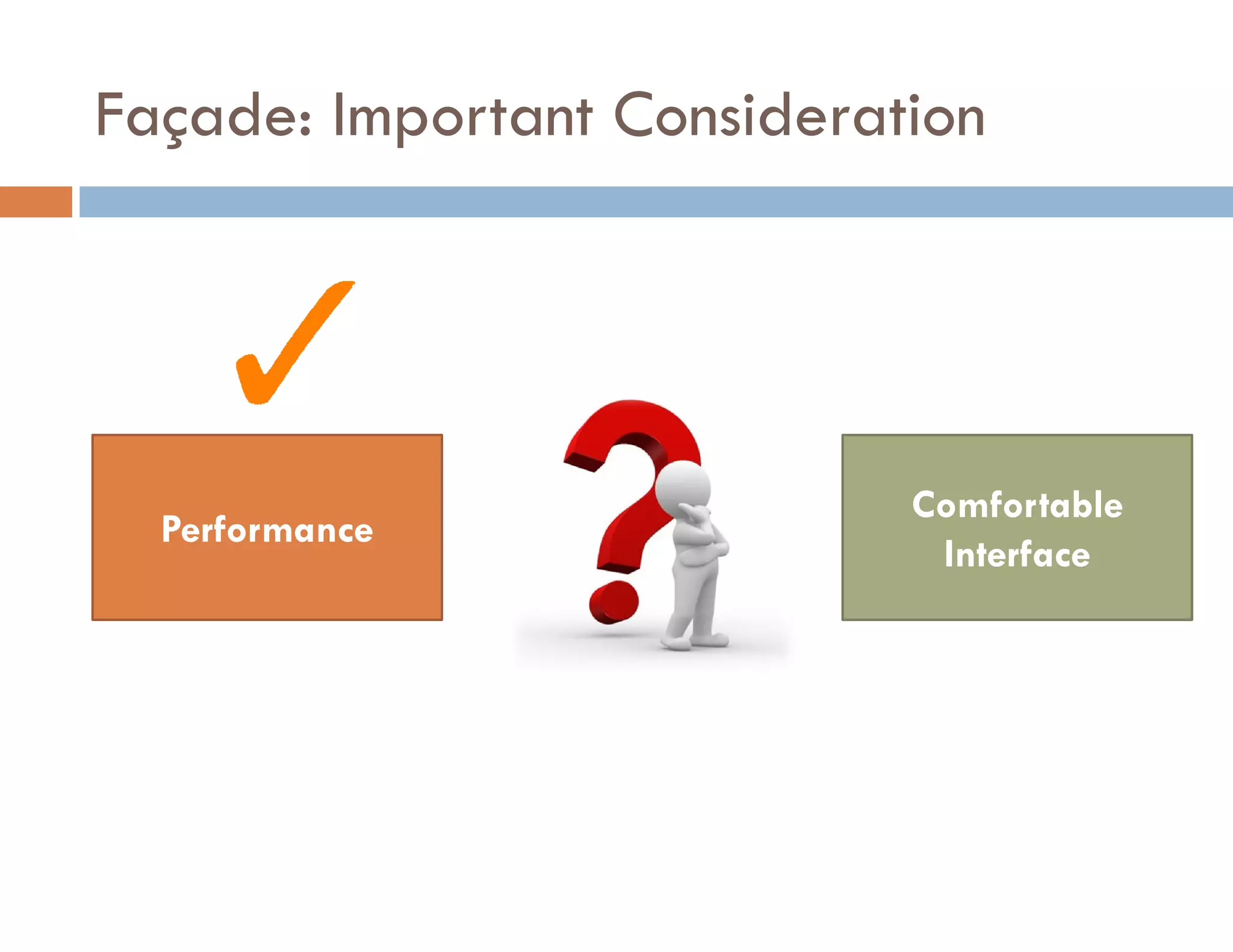
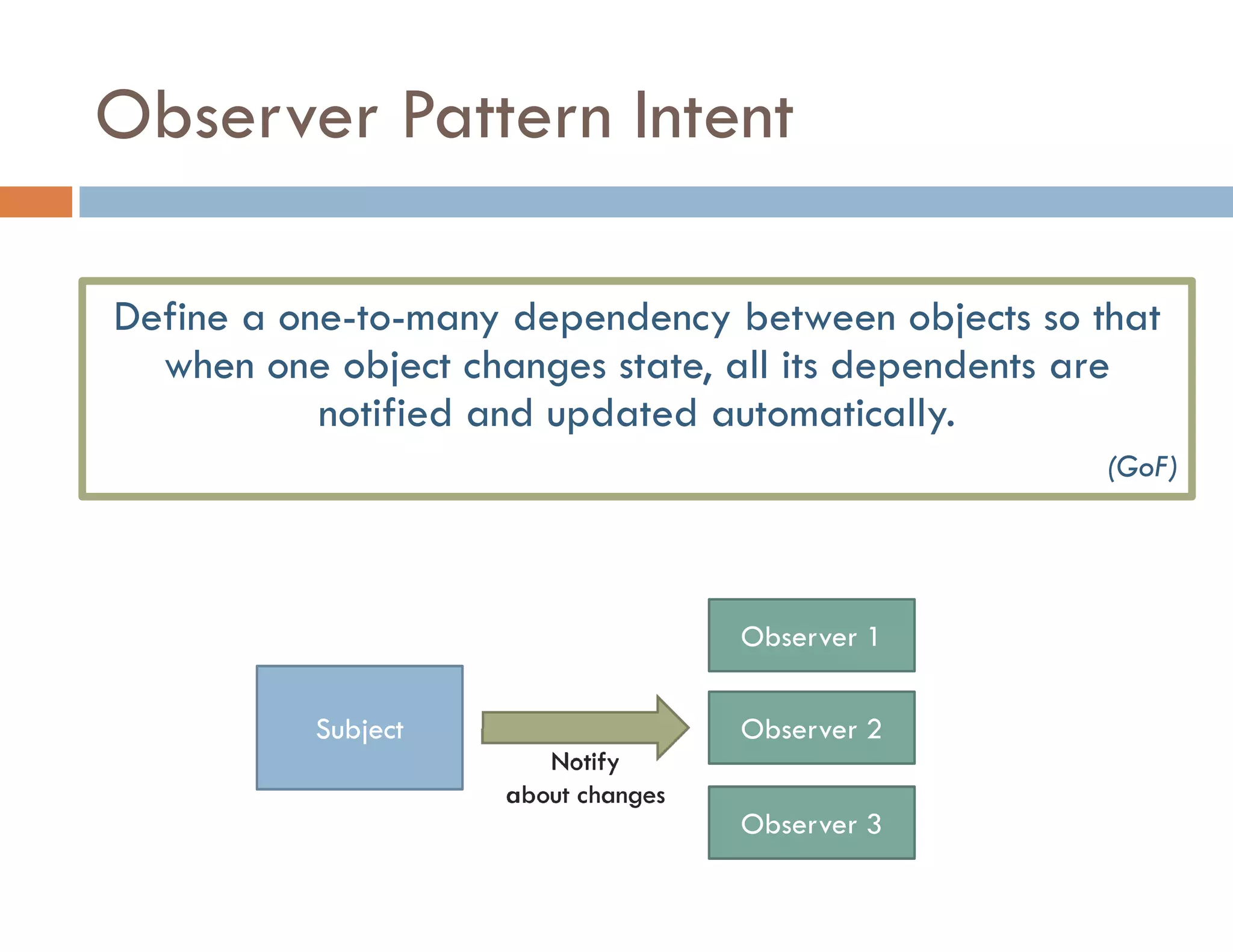
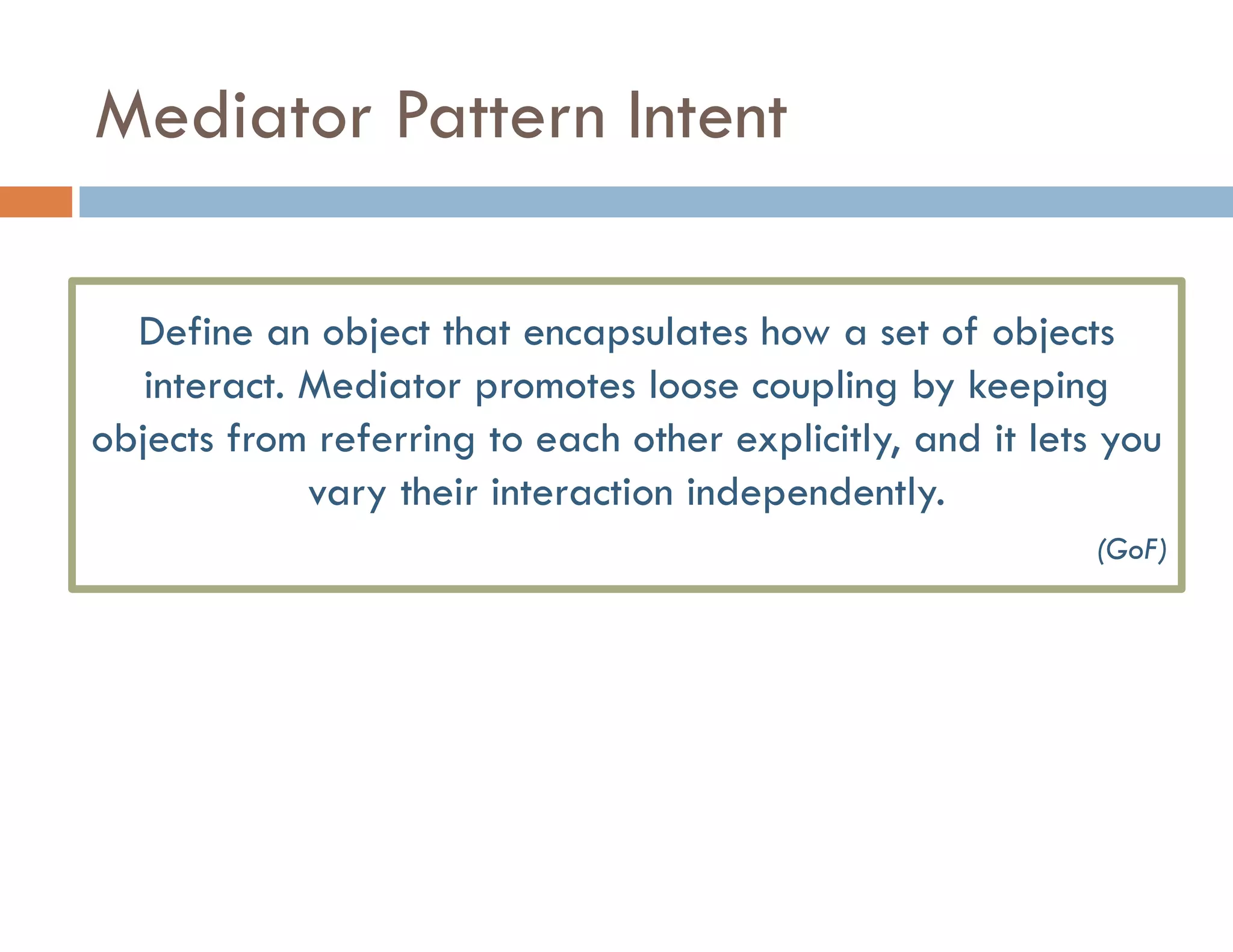
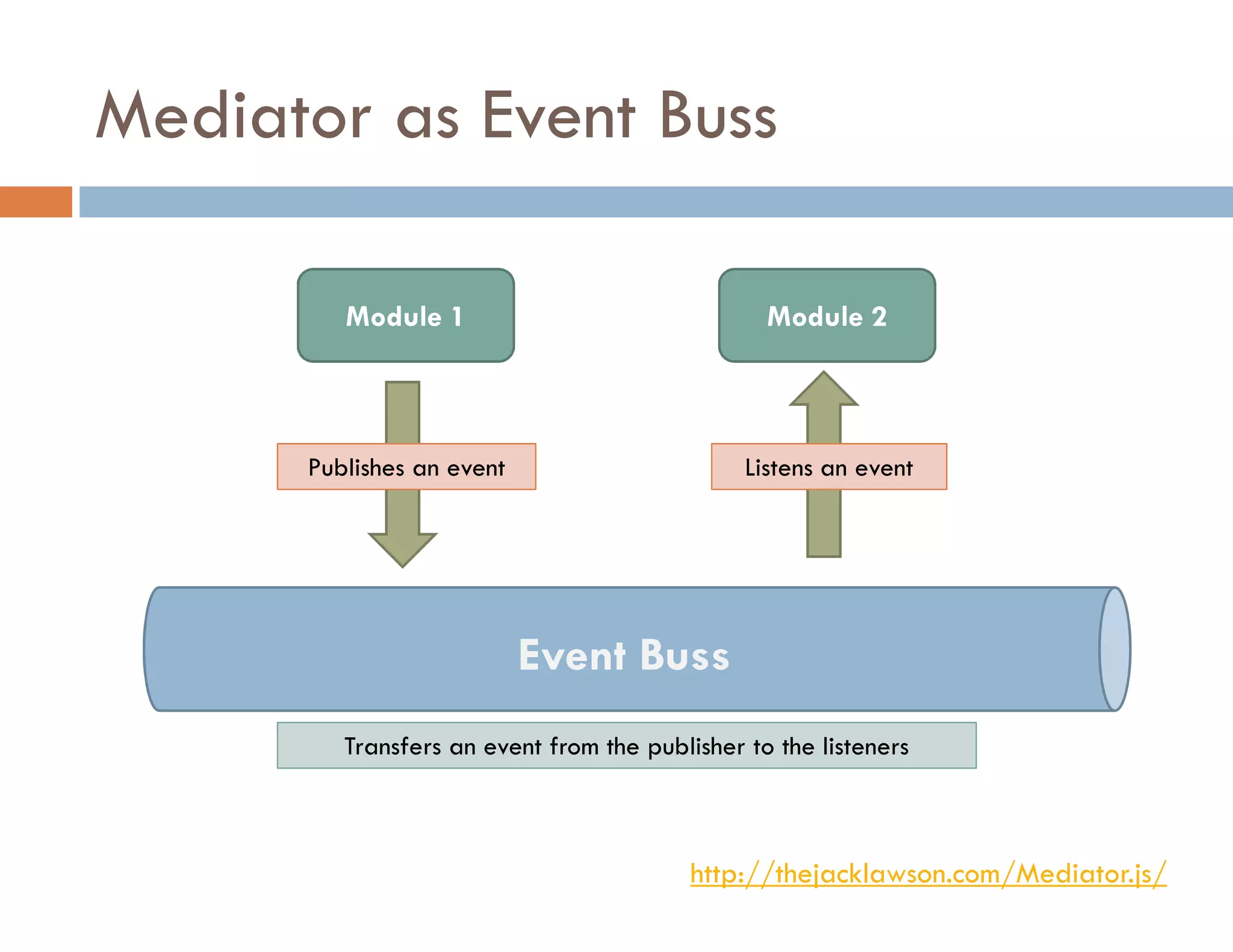
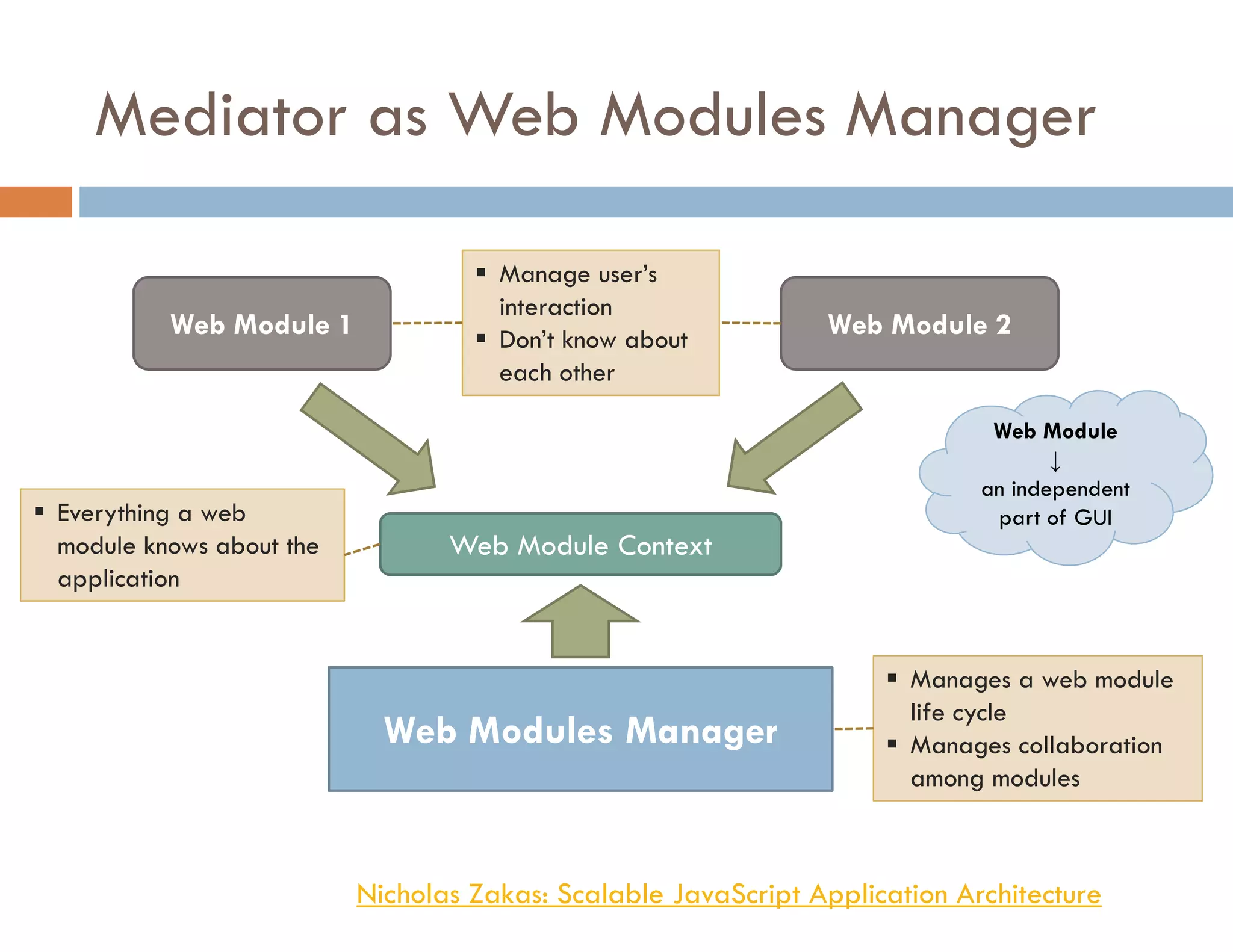
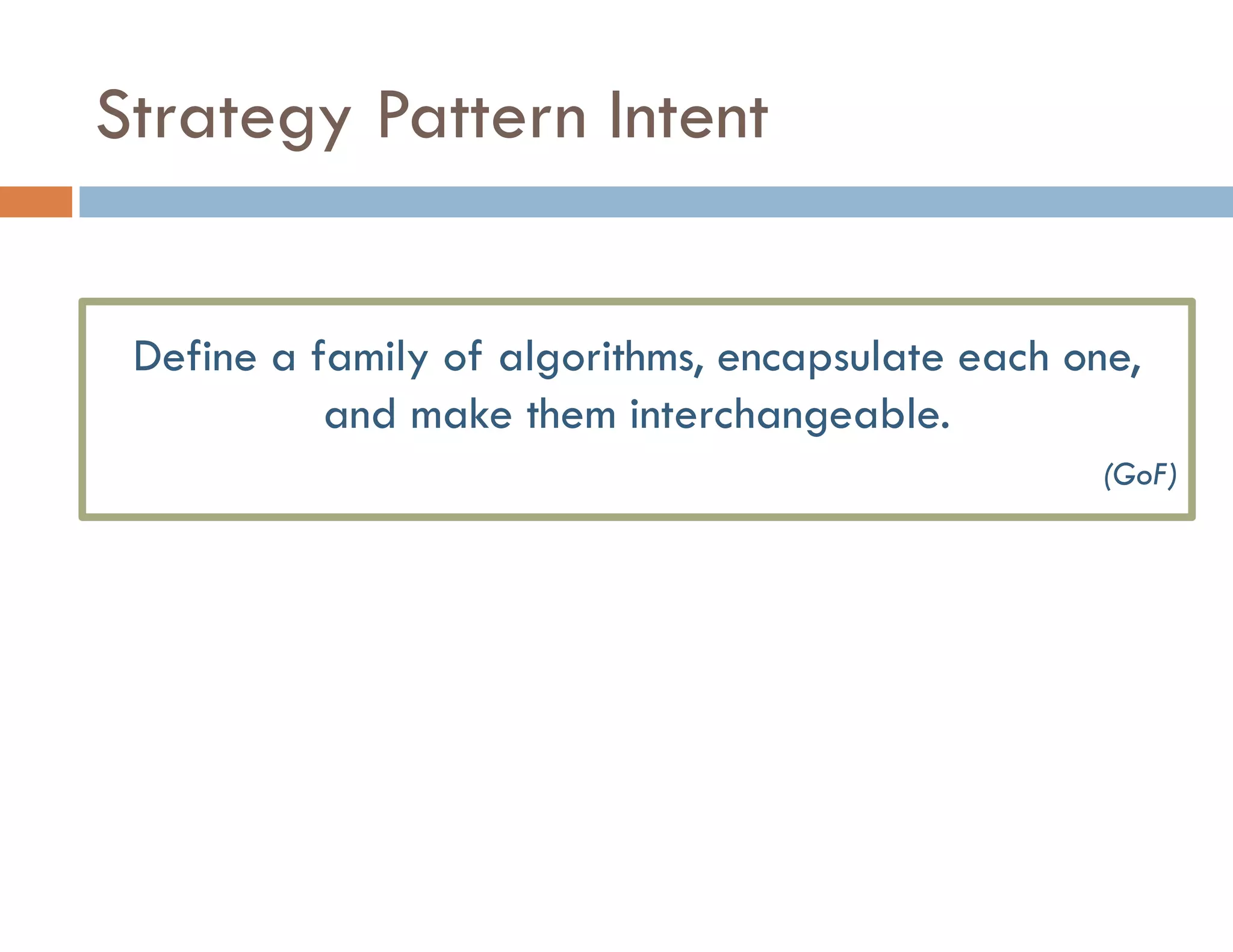
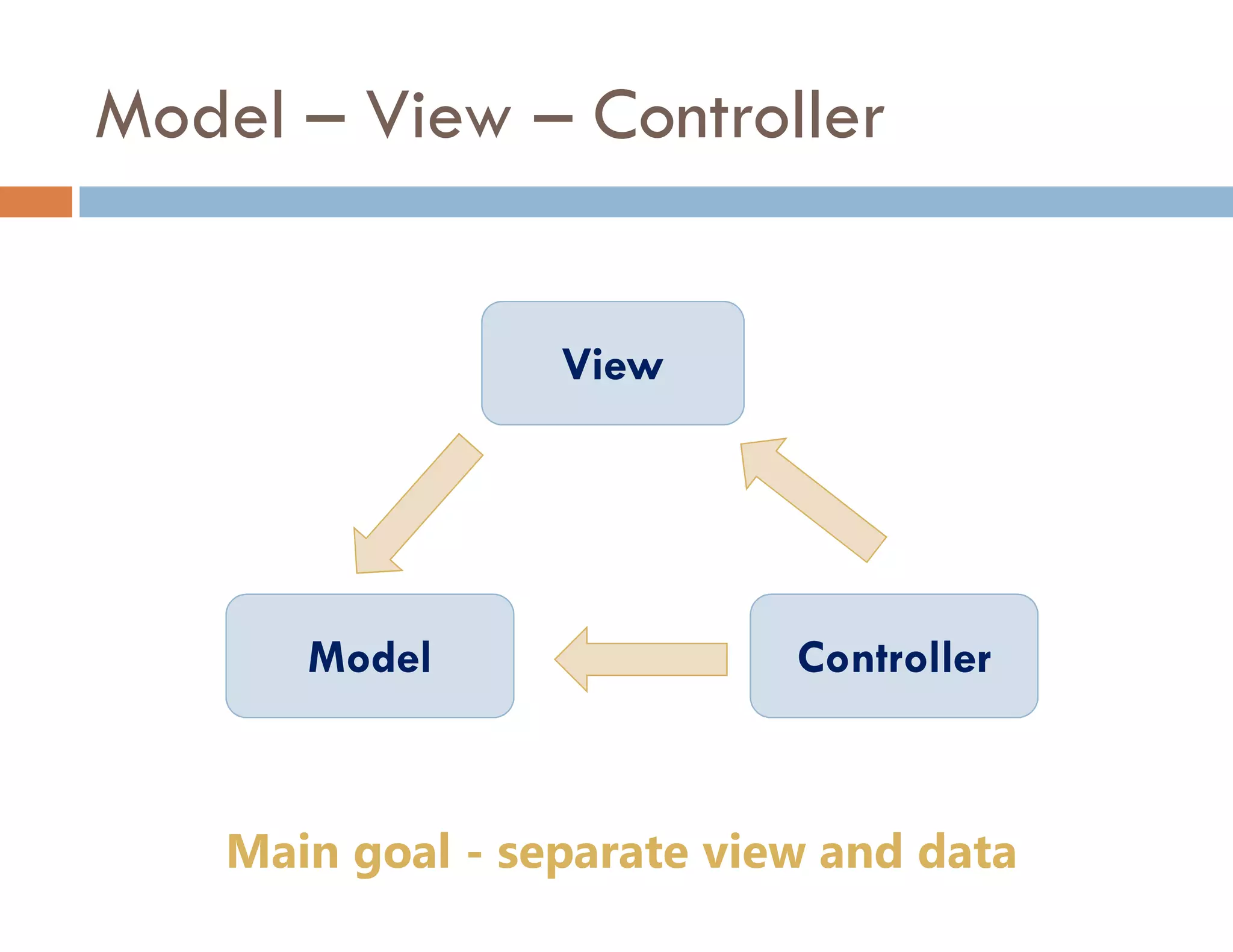
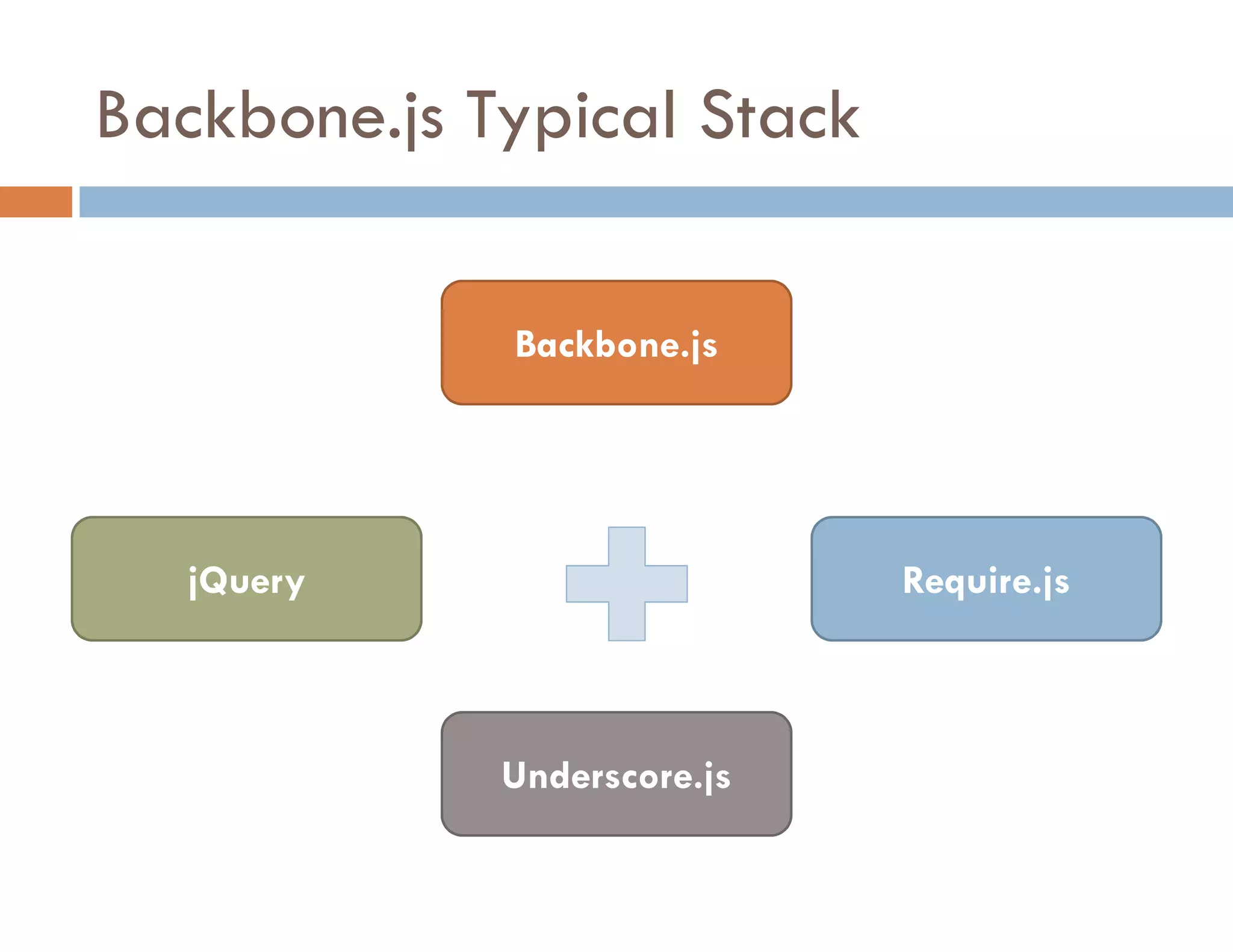
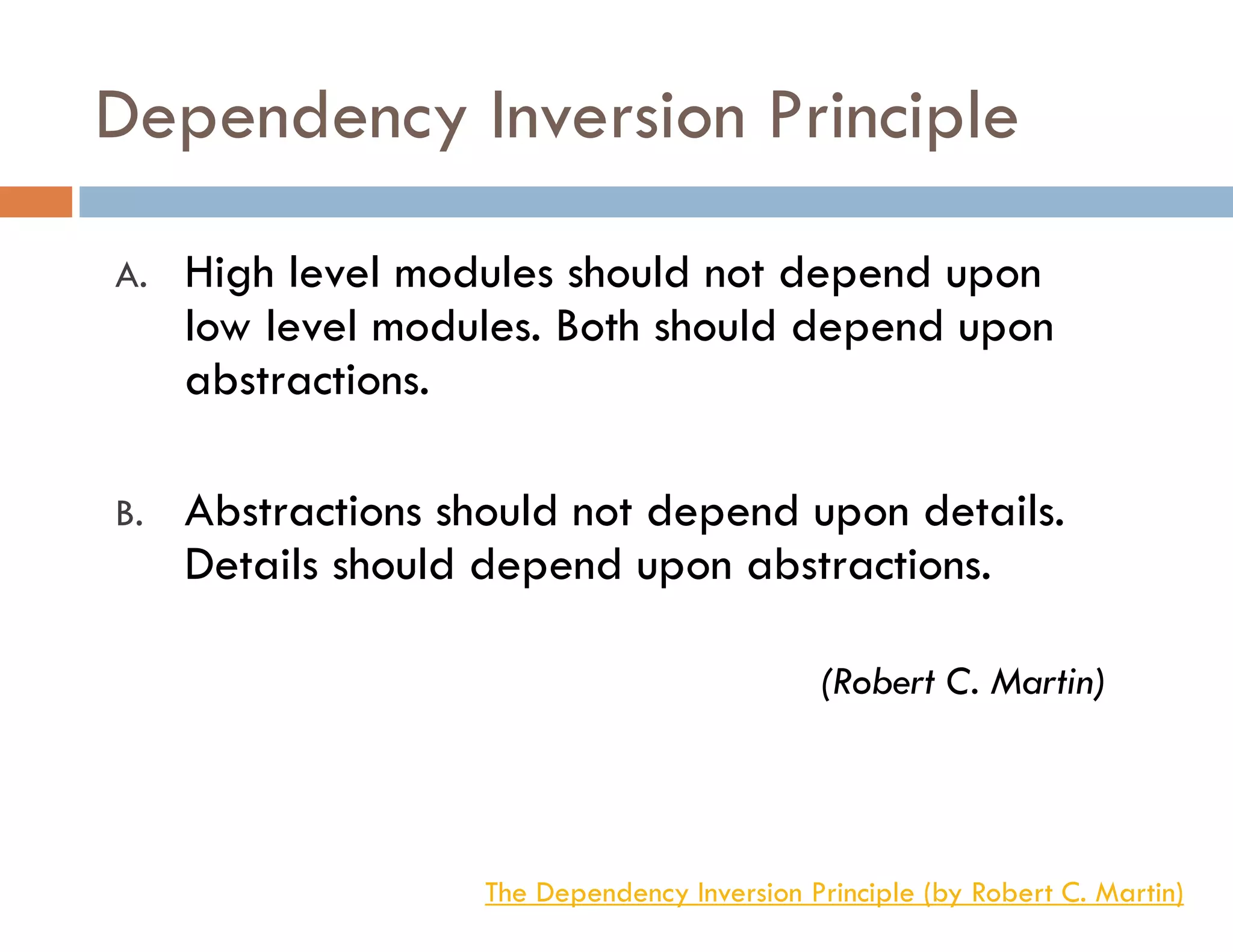
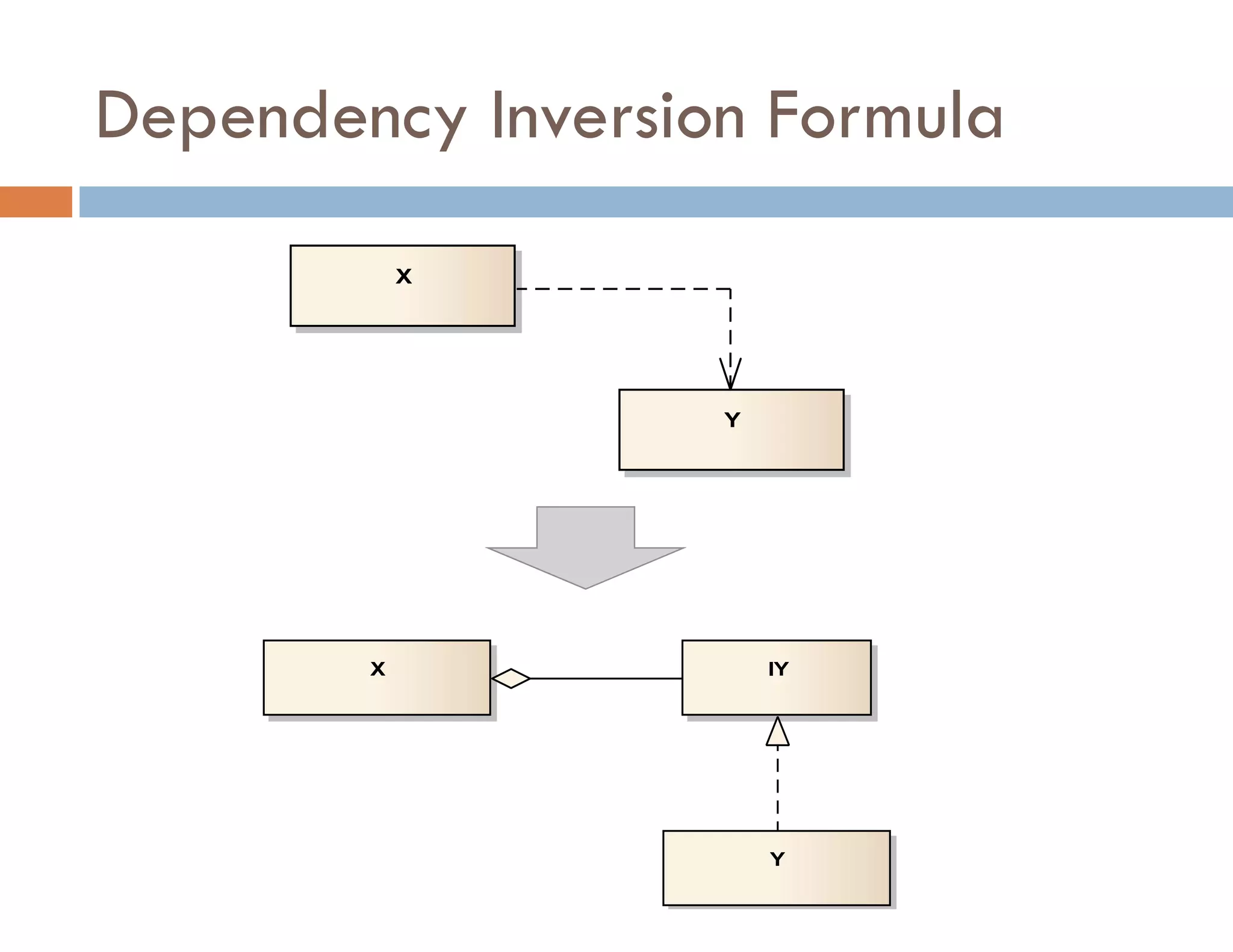
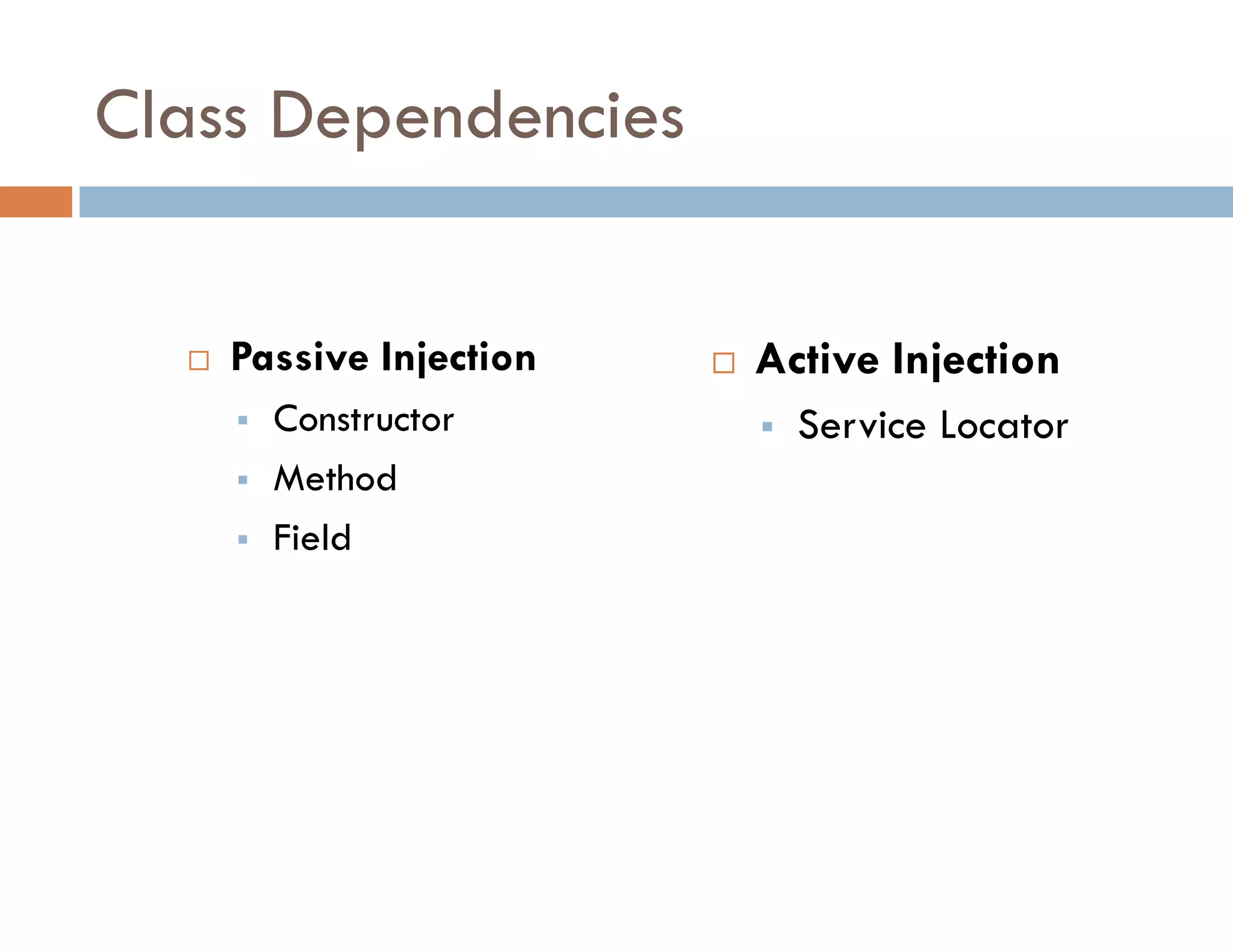
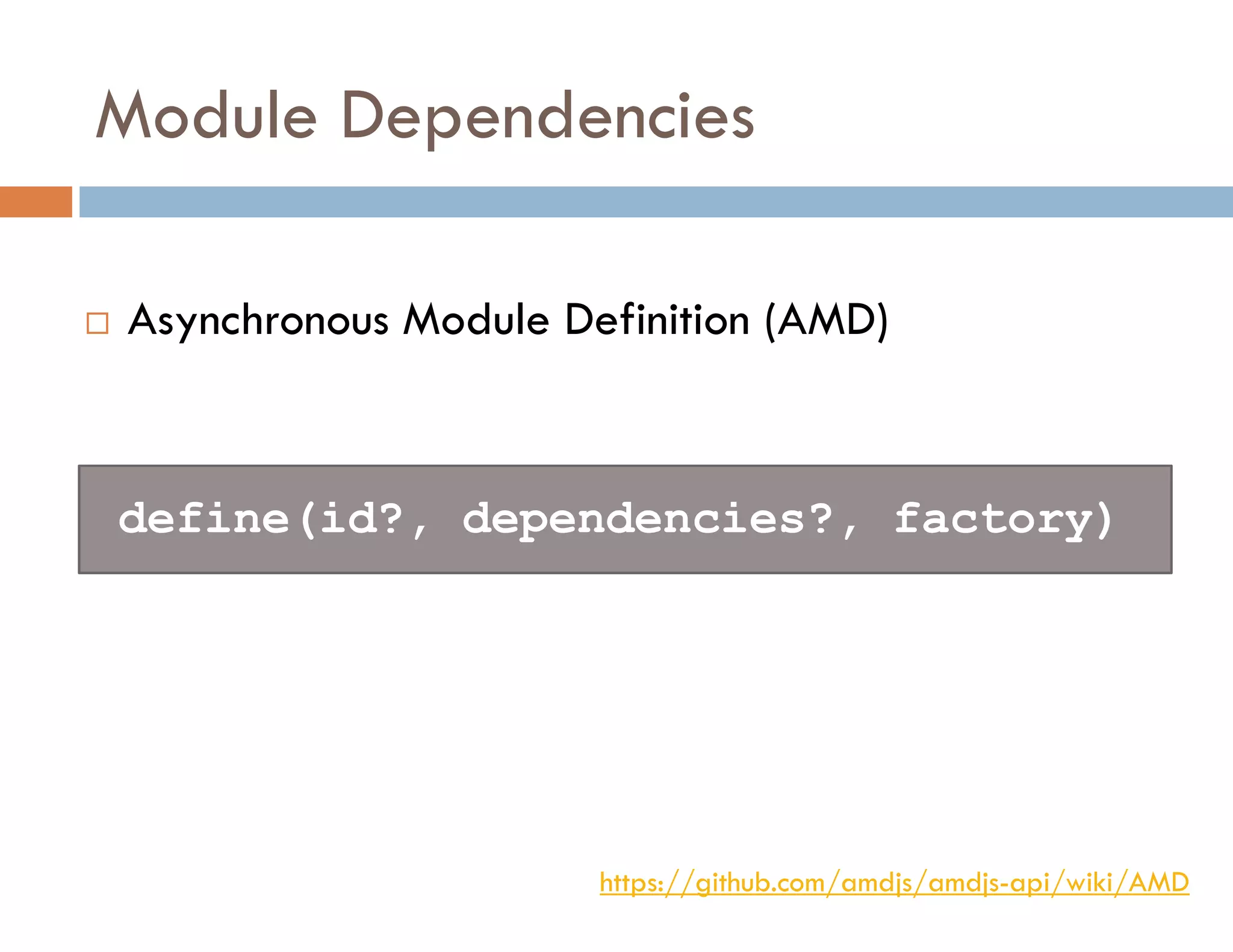
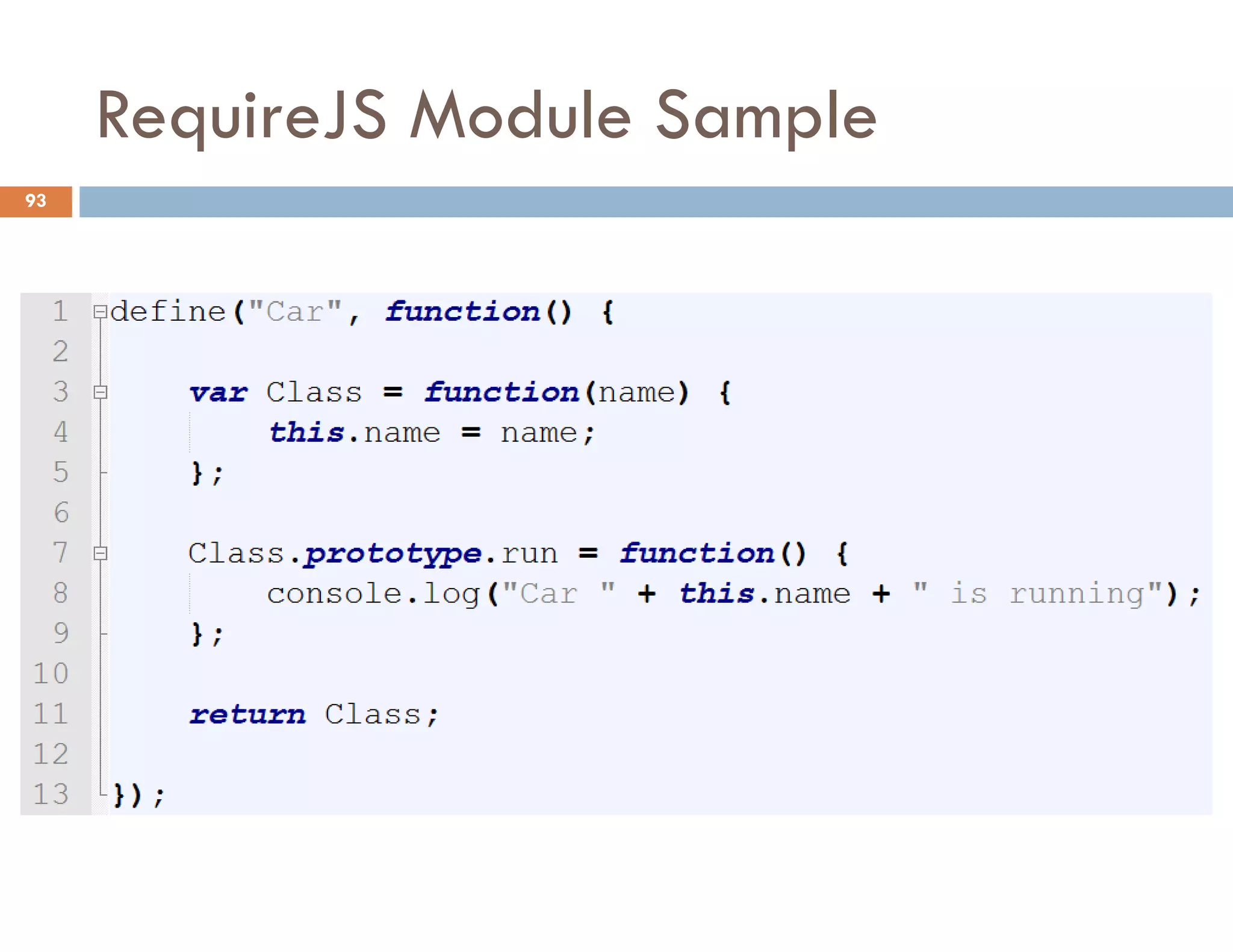
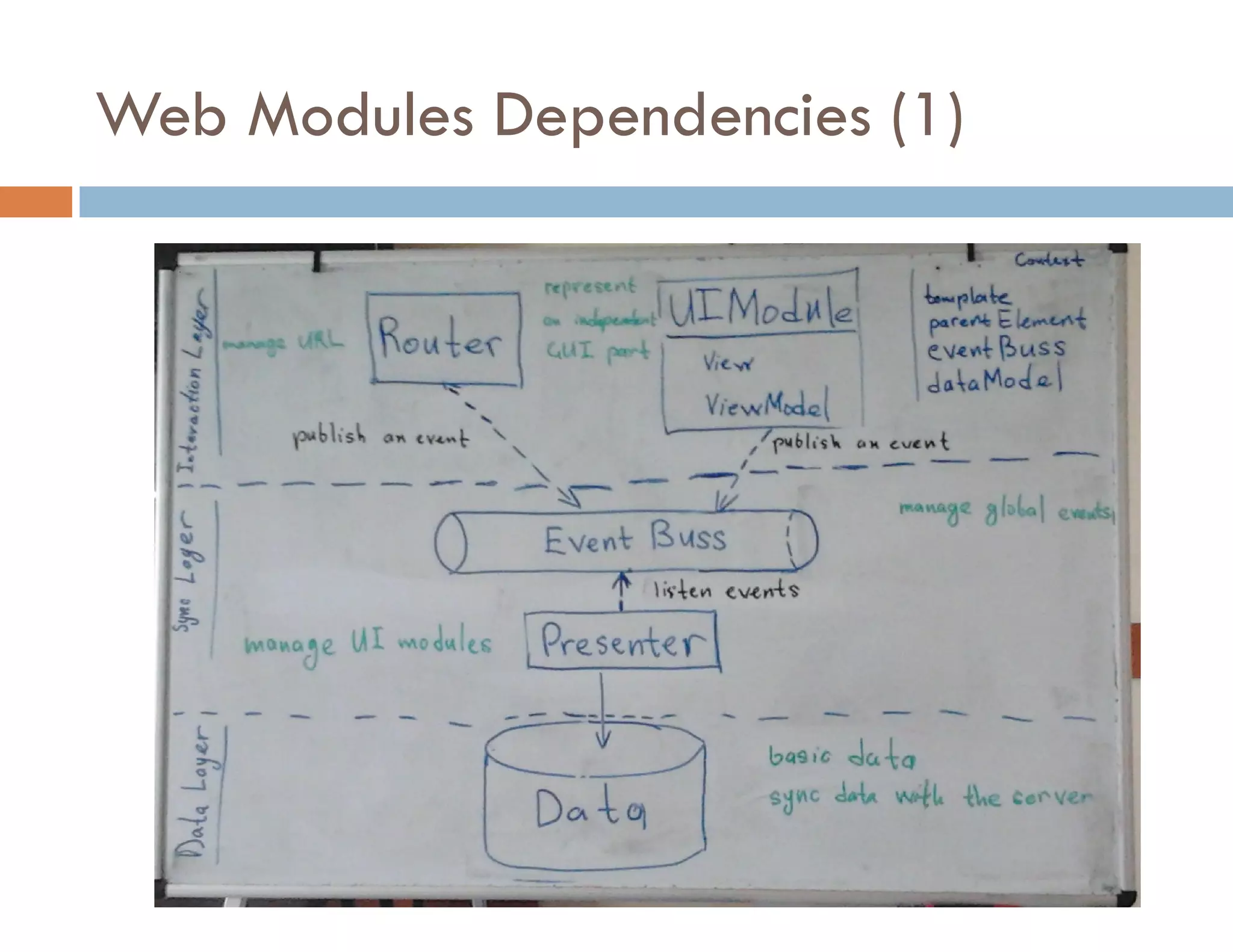
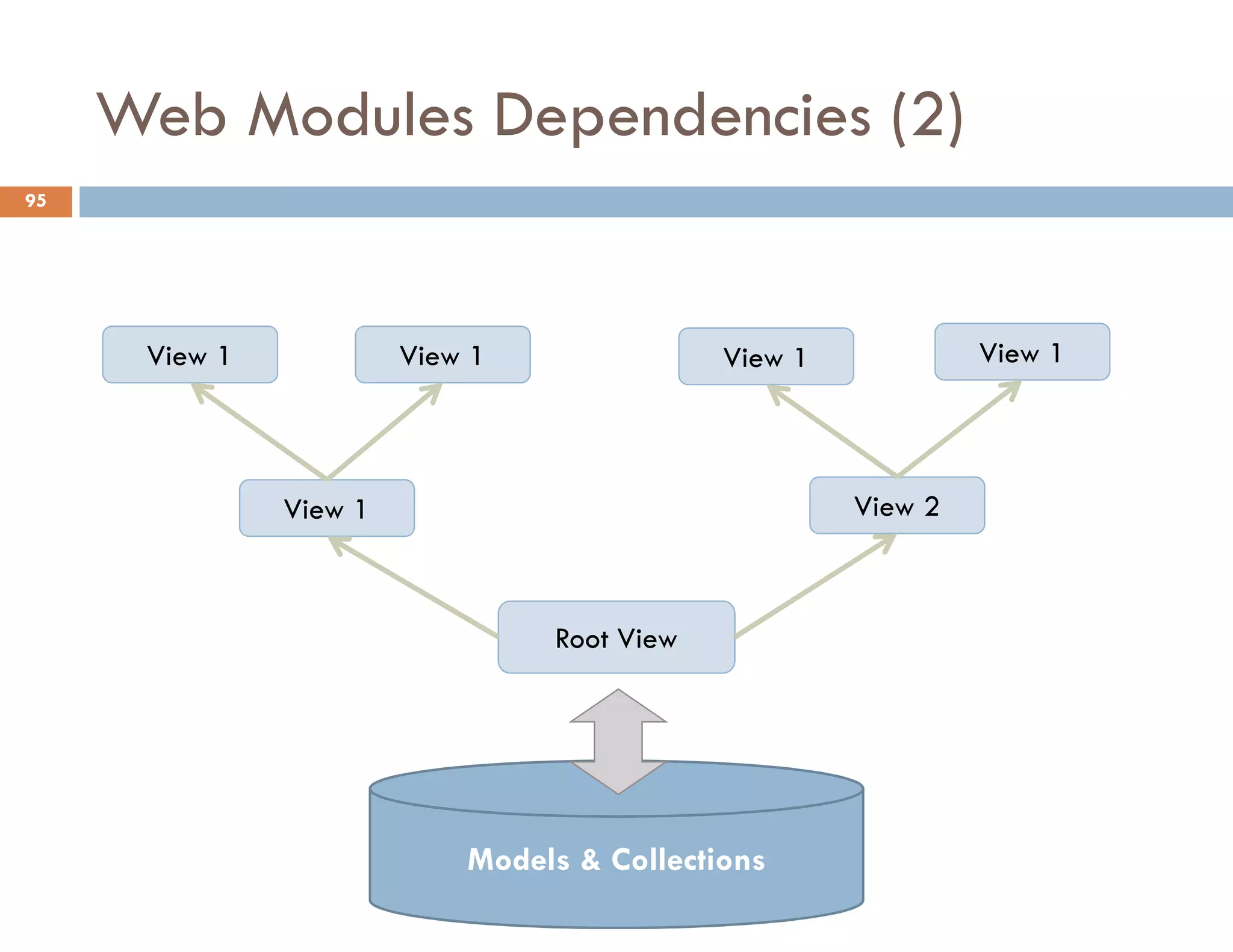
The document covers modern JavaScript application development, focusing on achieving well-structured code through various methods such as object-oriented programming, module patterns, and MVC frameworks. It discusses key principles like dependency management, design patterns, and the importance of separating concerns in code structure while highlighting patterns for creating scalable and maintainable applications. Additionally, the document provides practical examples and references for further reading to support learning and application of these concepts.





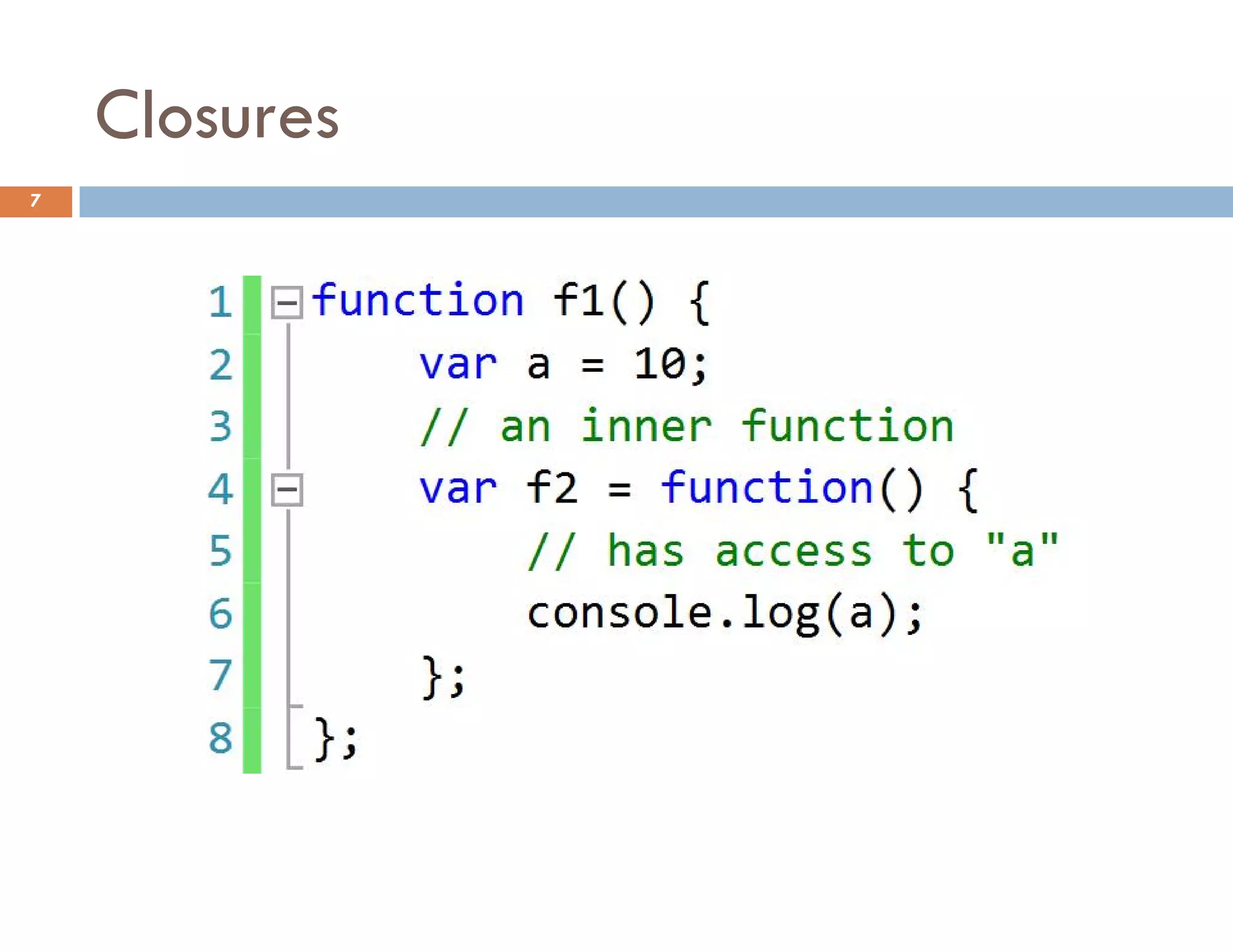

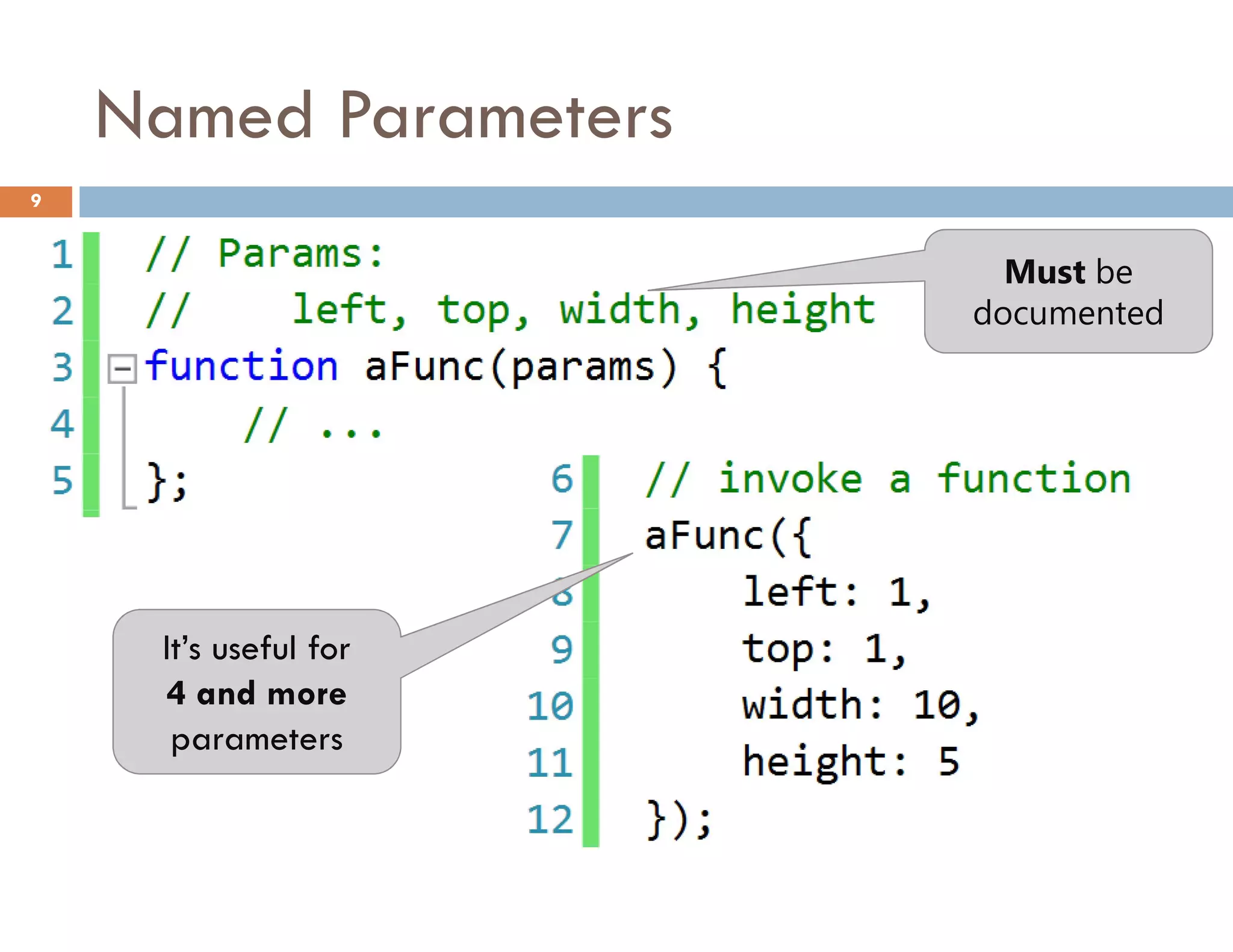



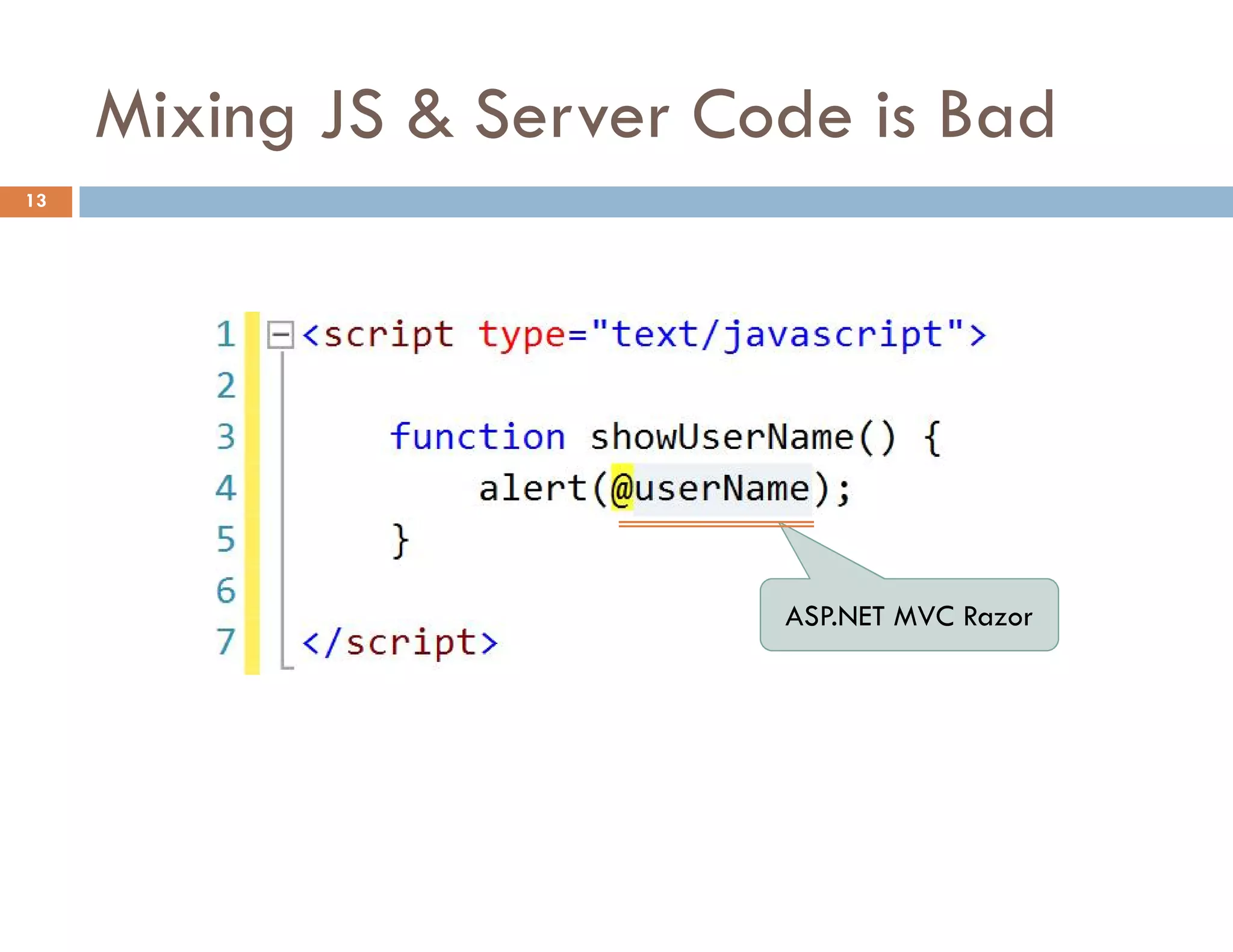
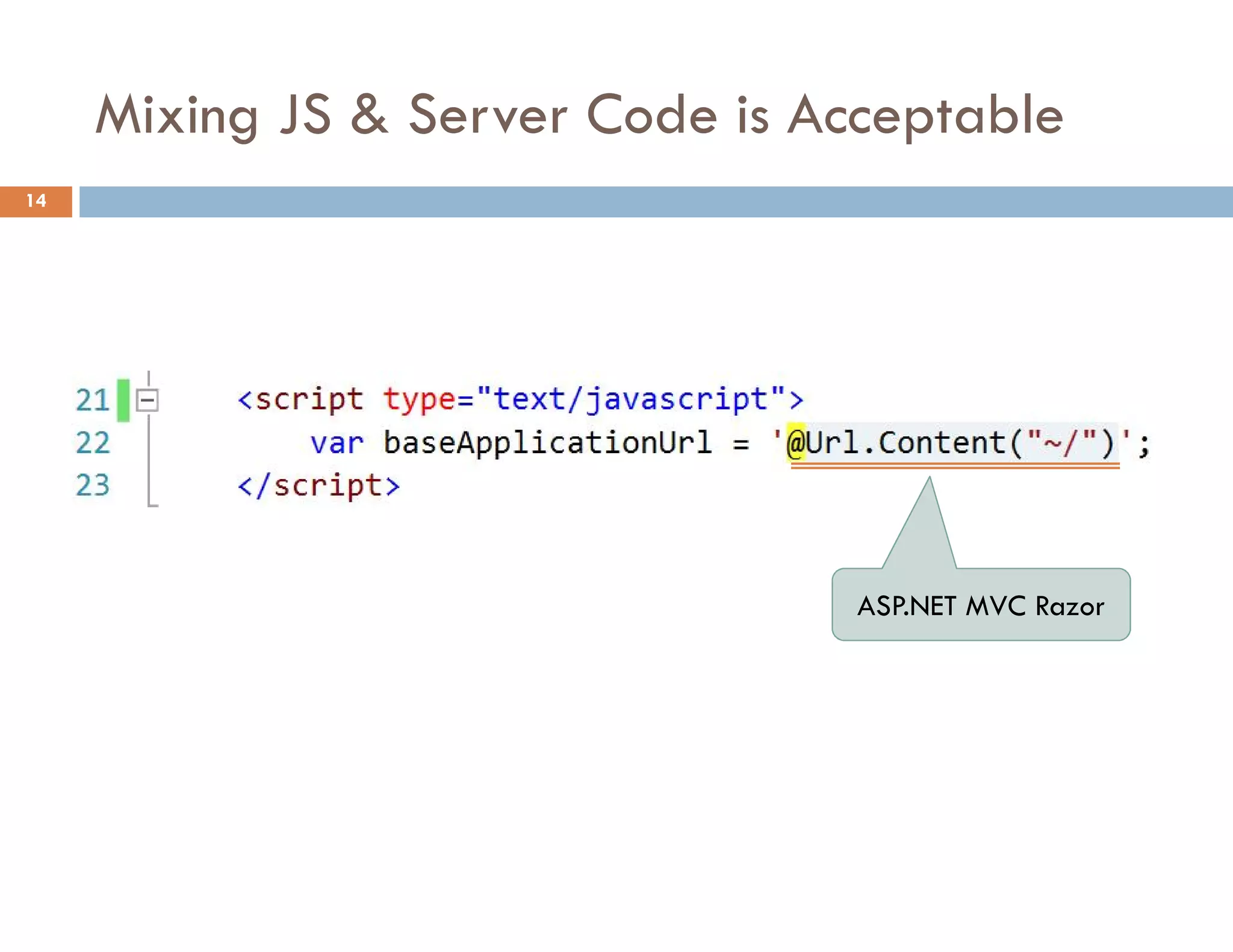



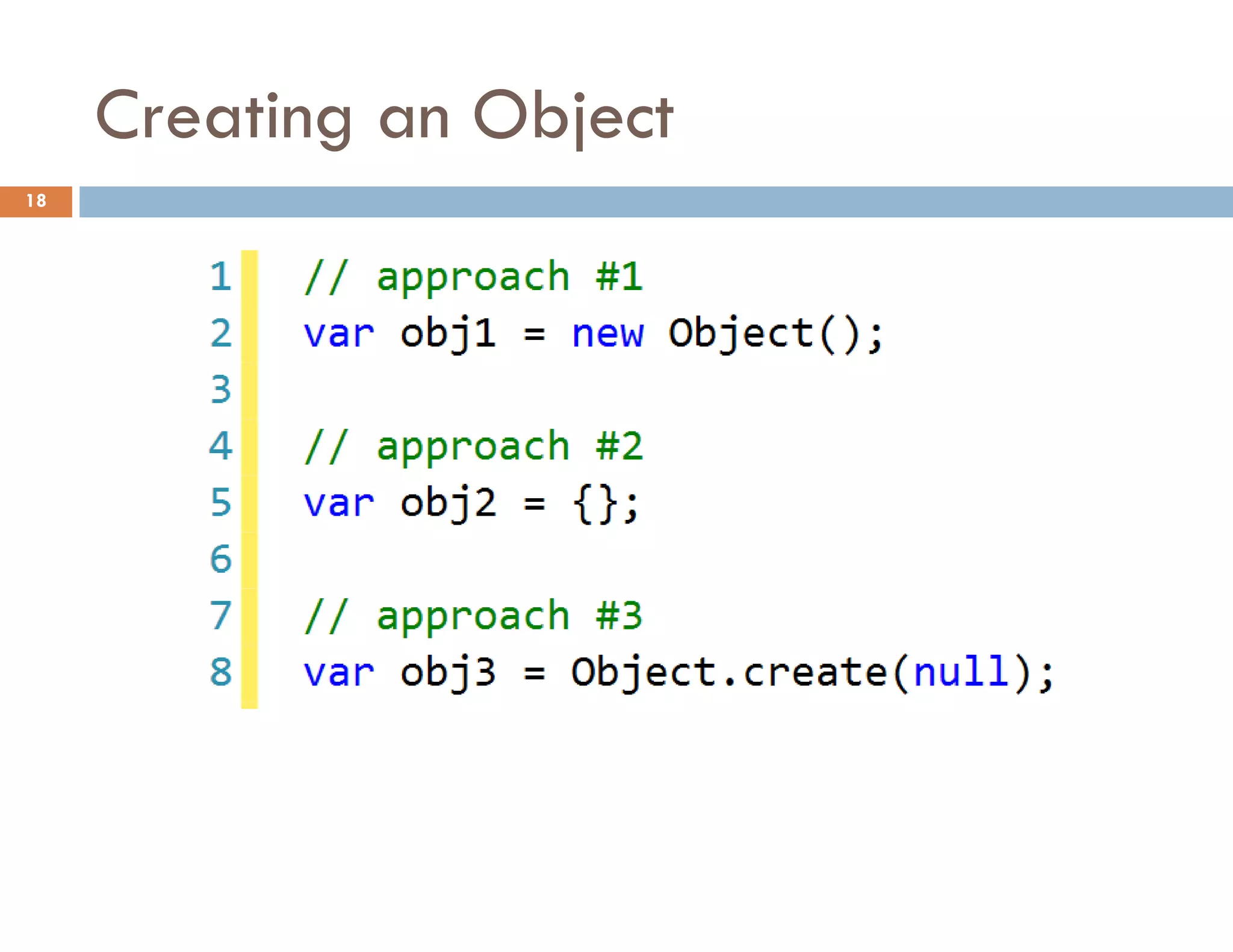

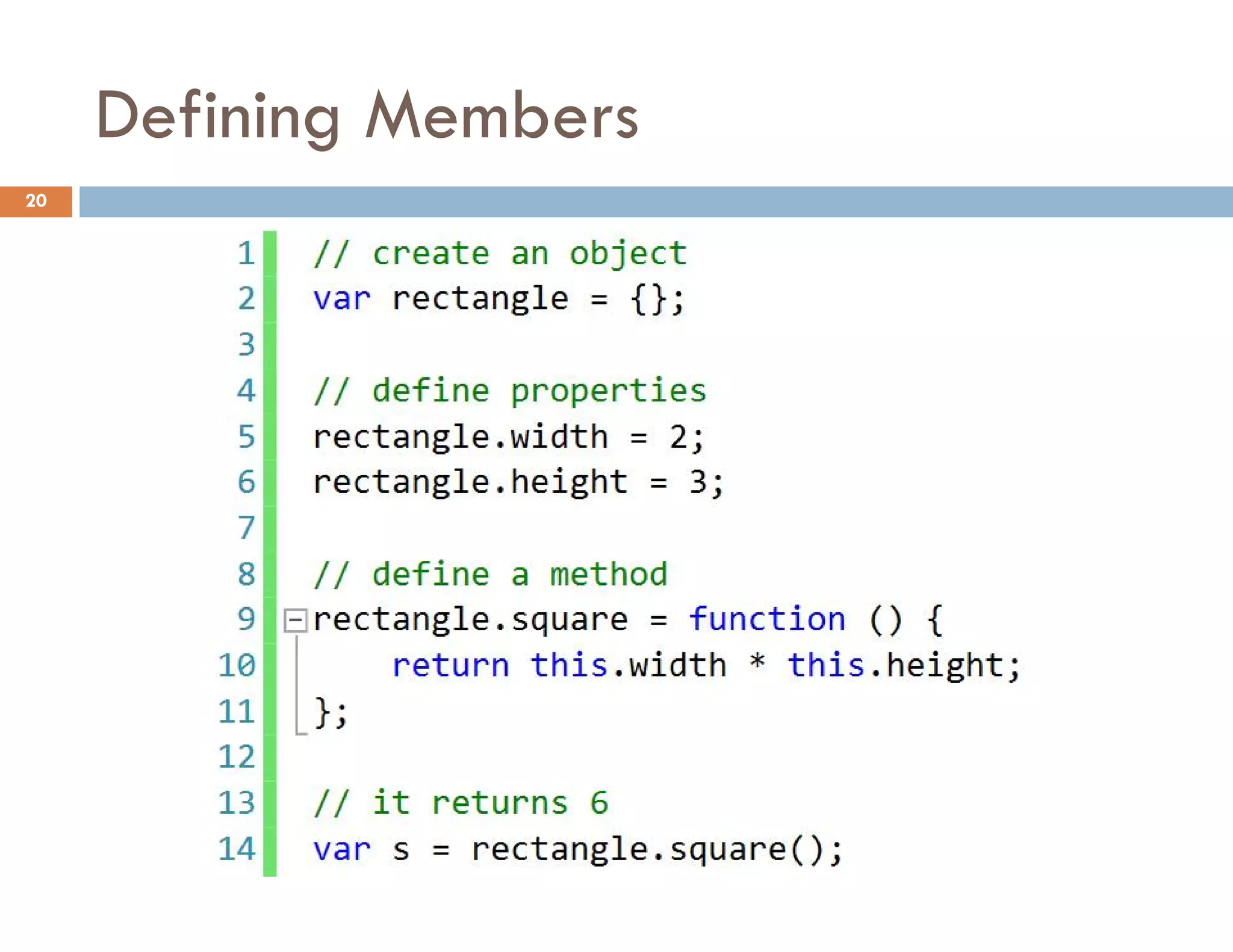



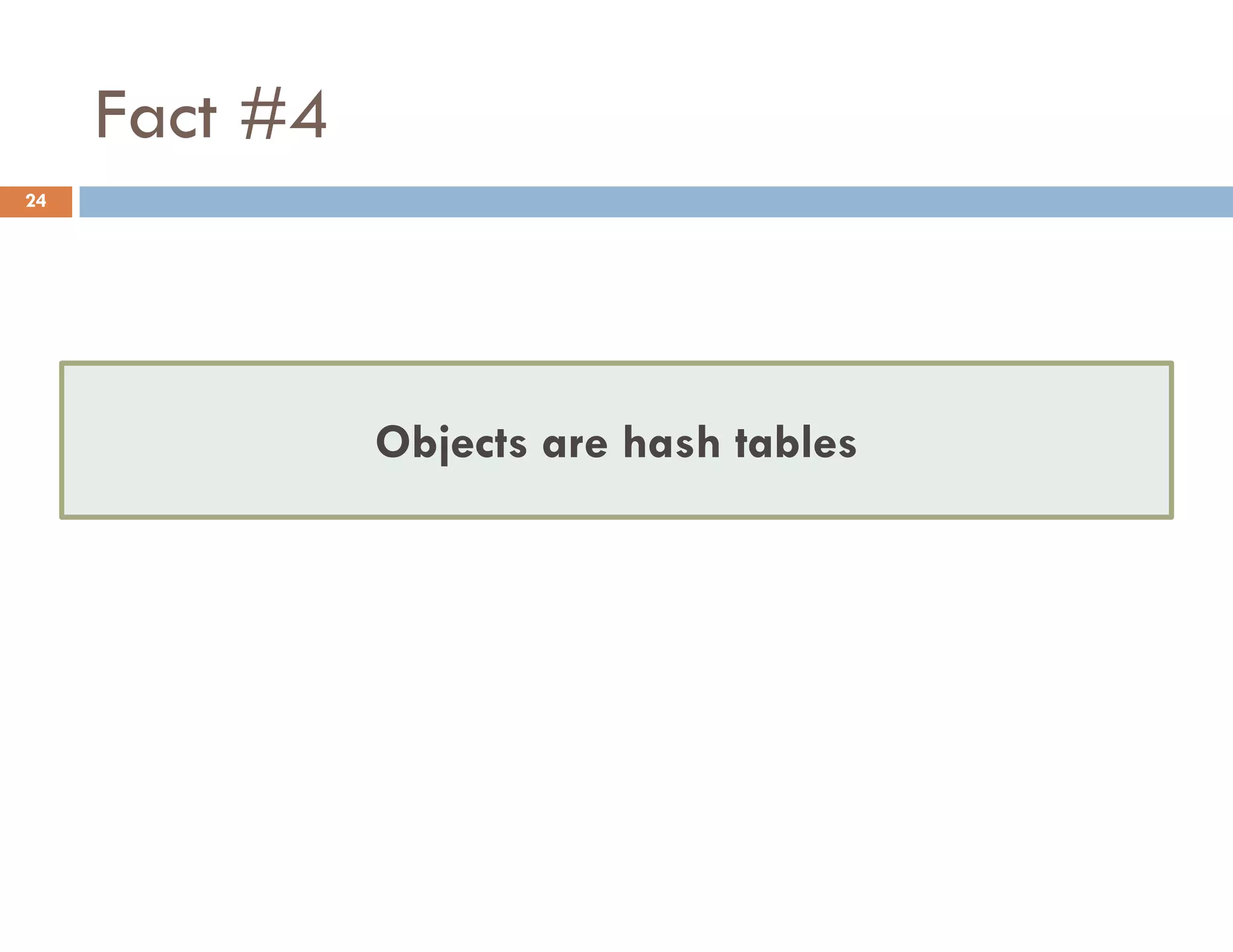
![Access to a Property with [] 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modernjavascriptapplications-140430115446-phpapp02/75/Modern-JavaScript-Applications-Design-Patterns-25-2048.jpg)