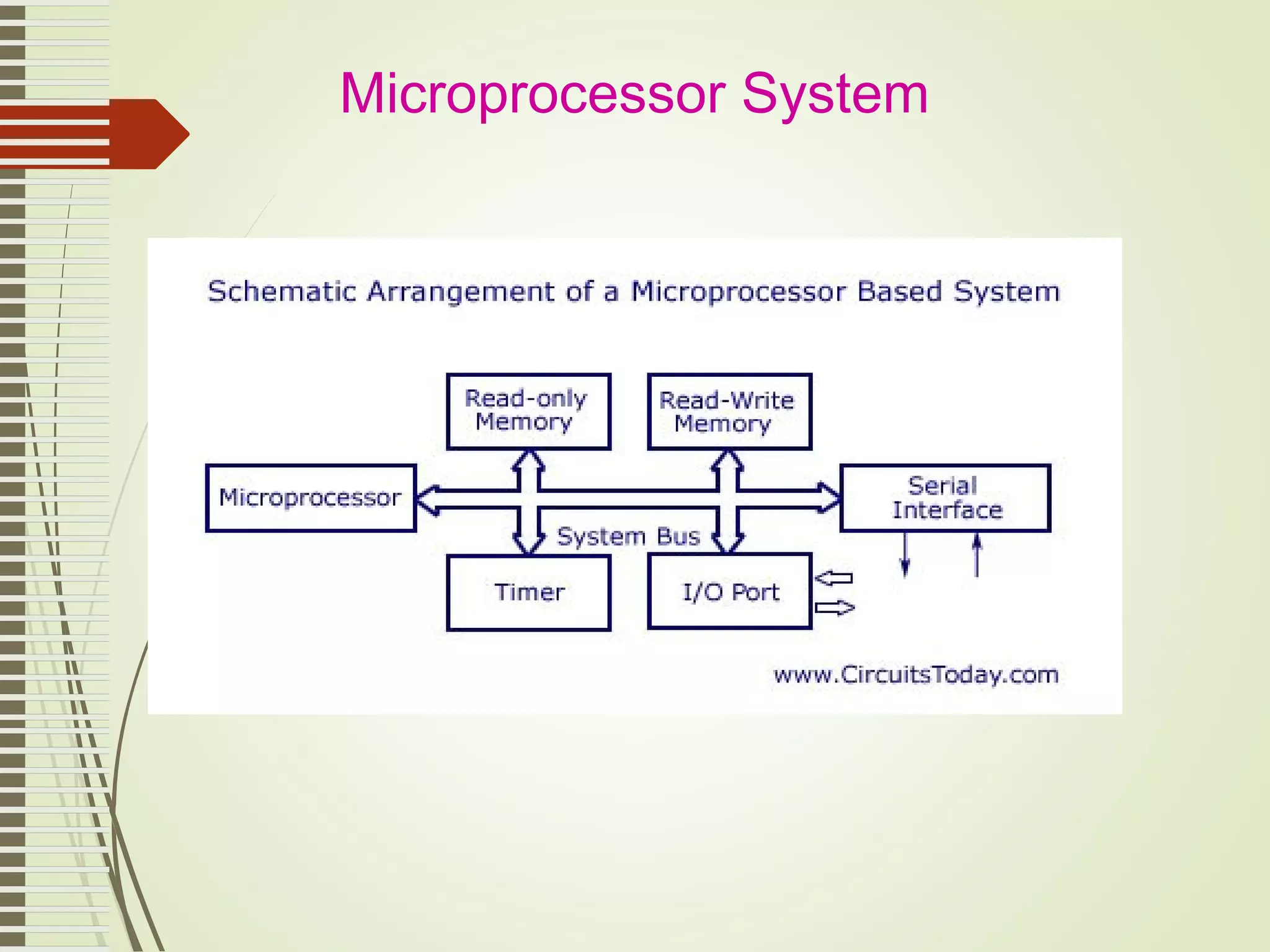
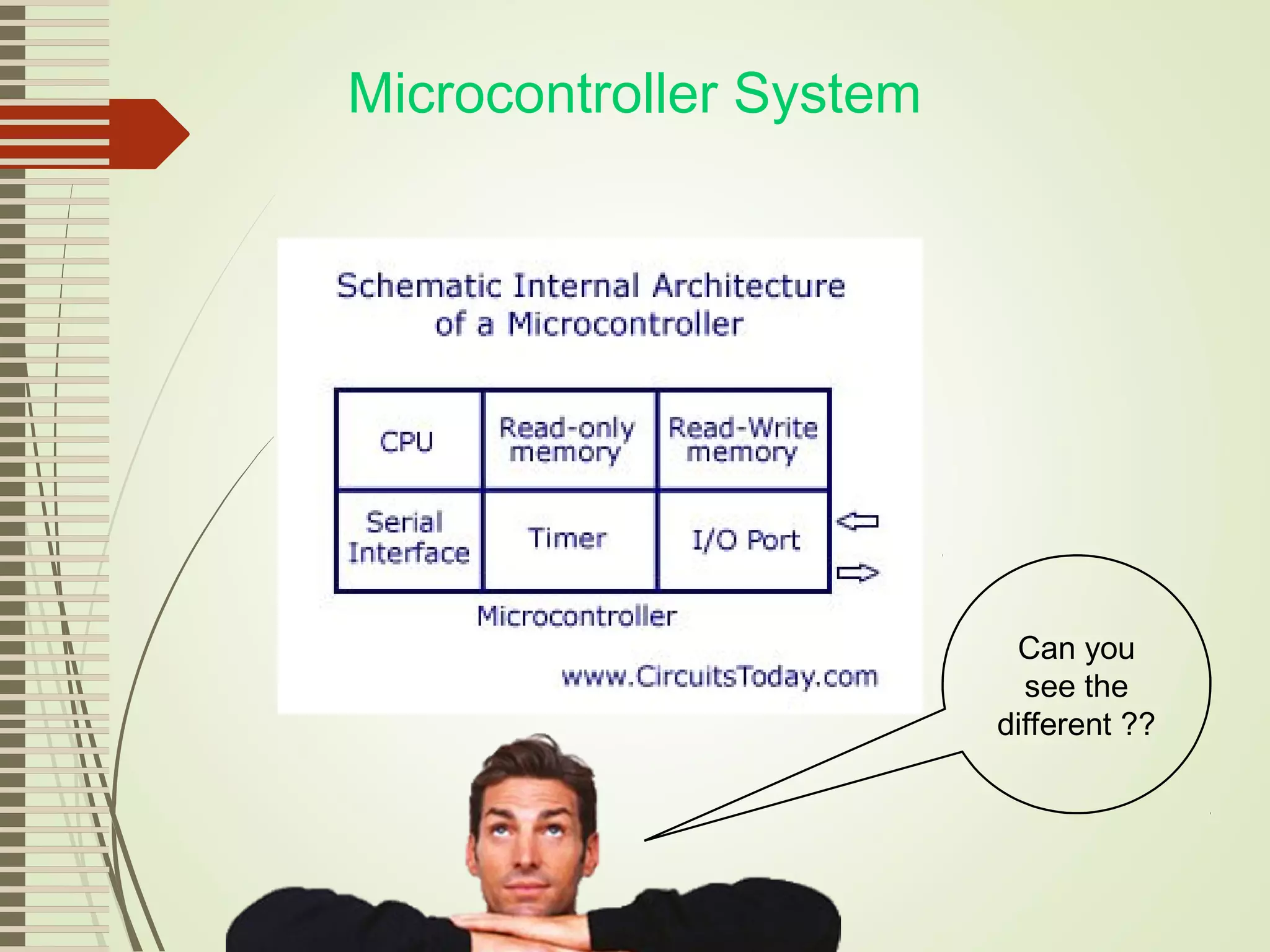
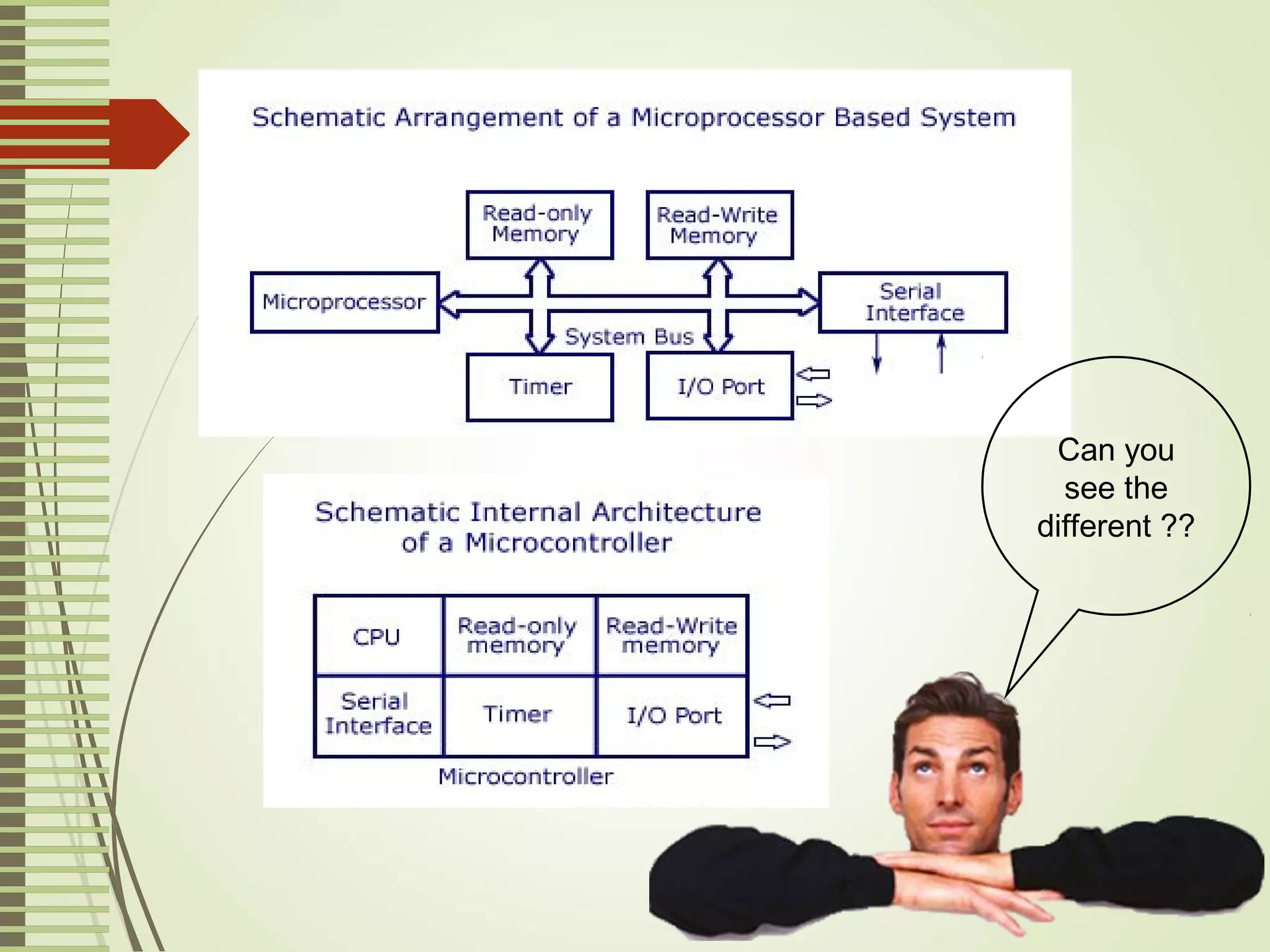
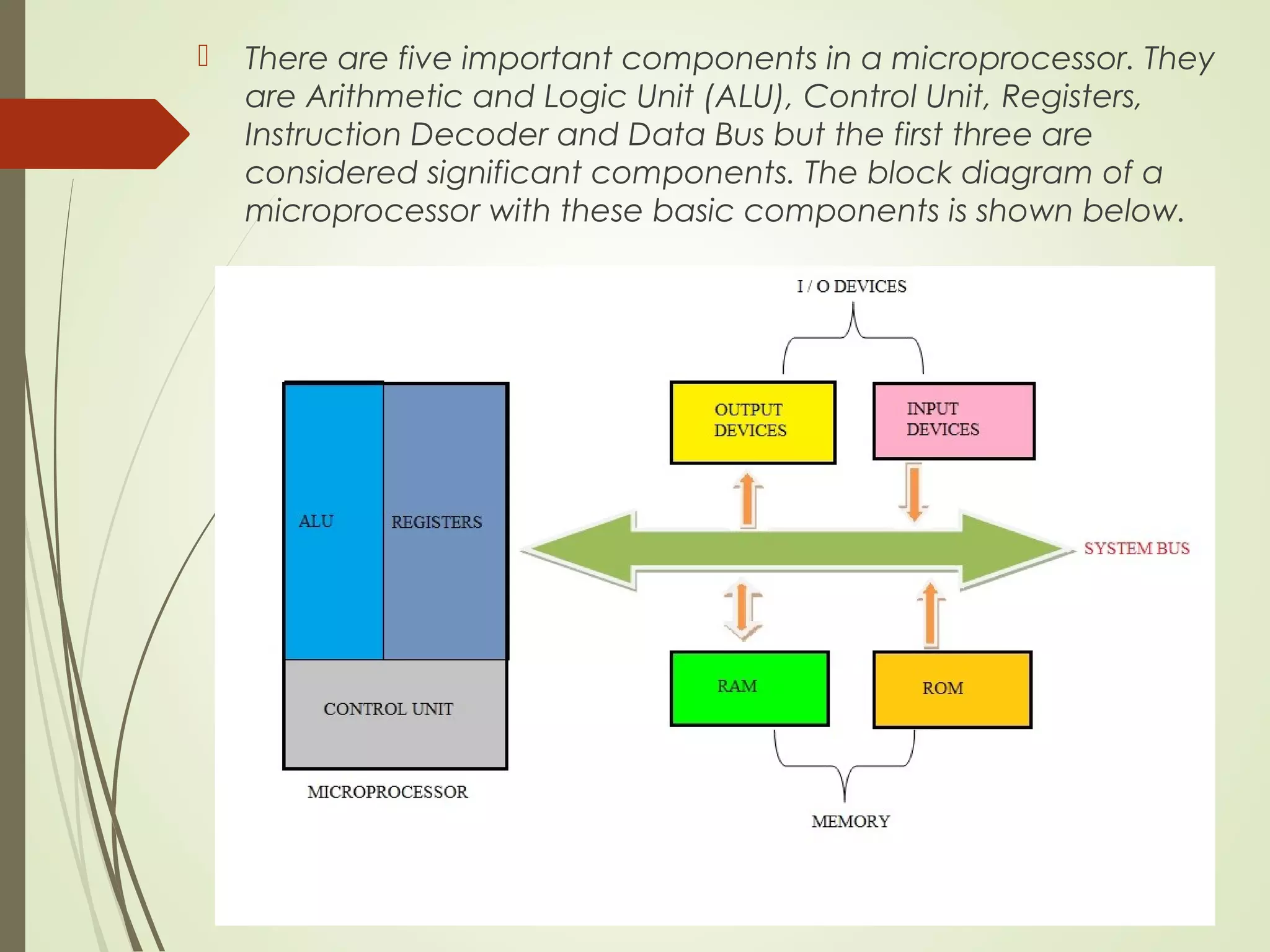
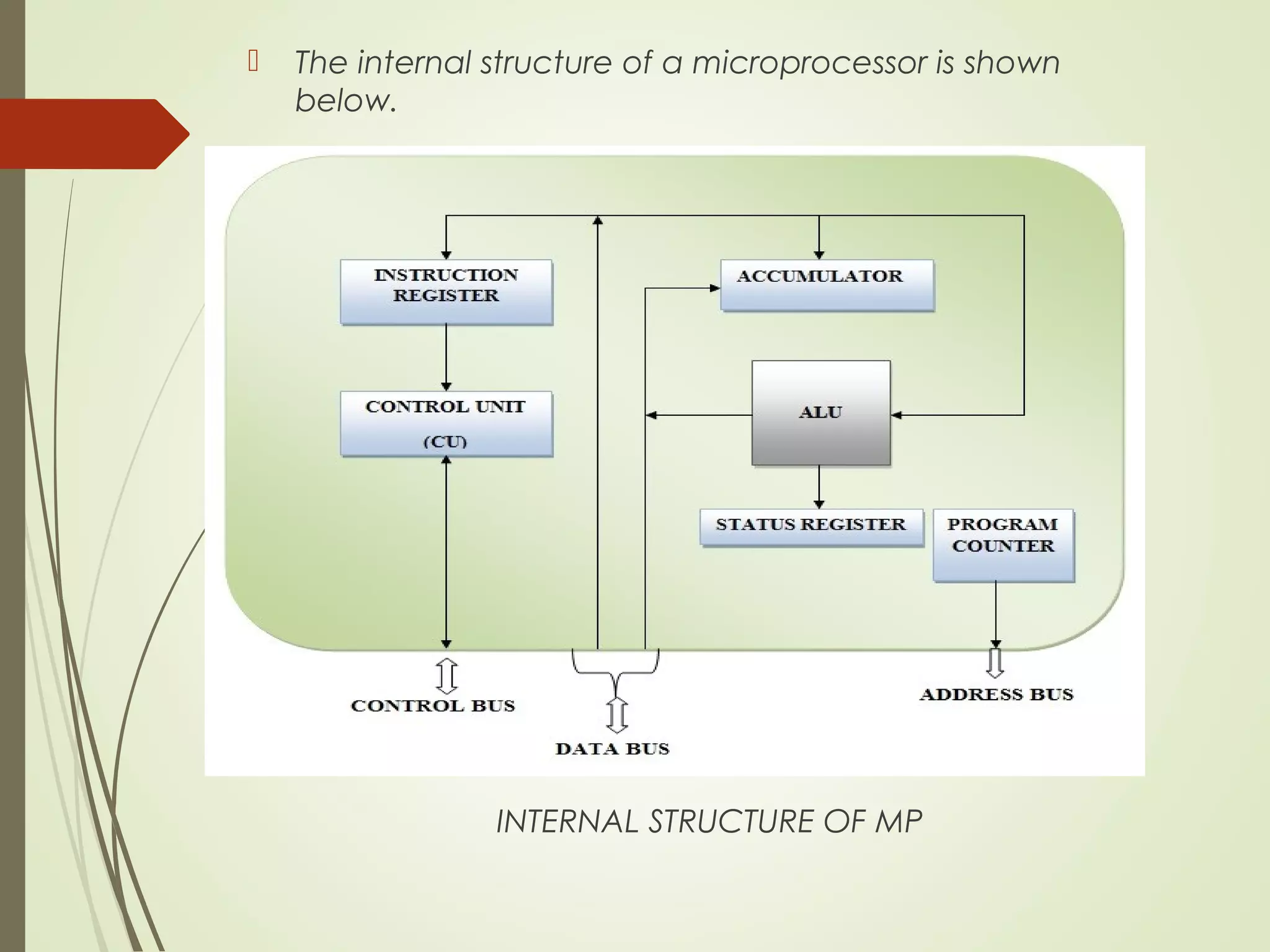
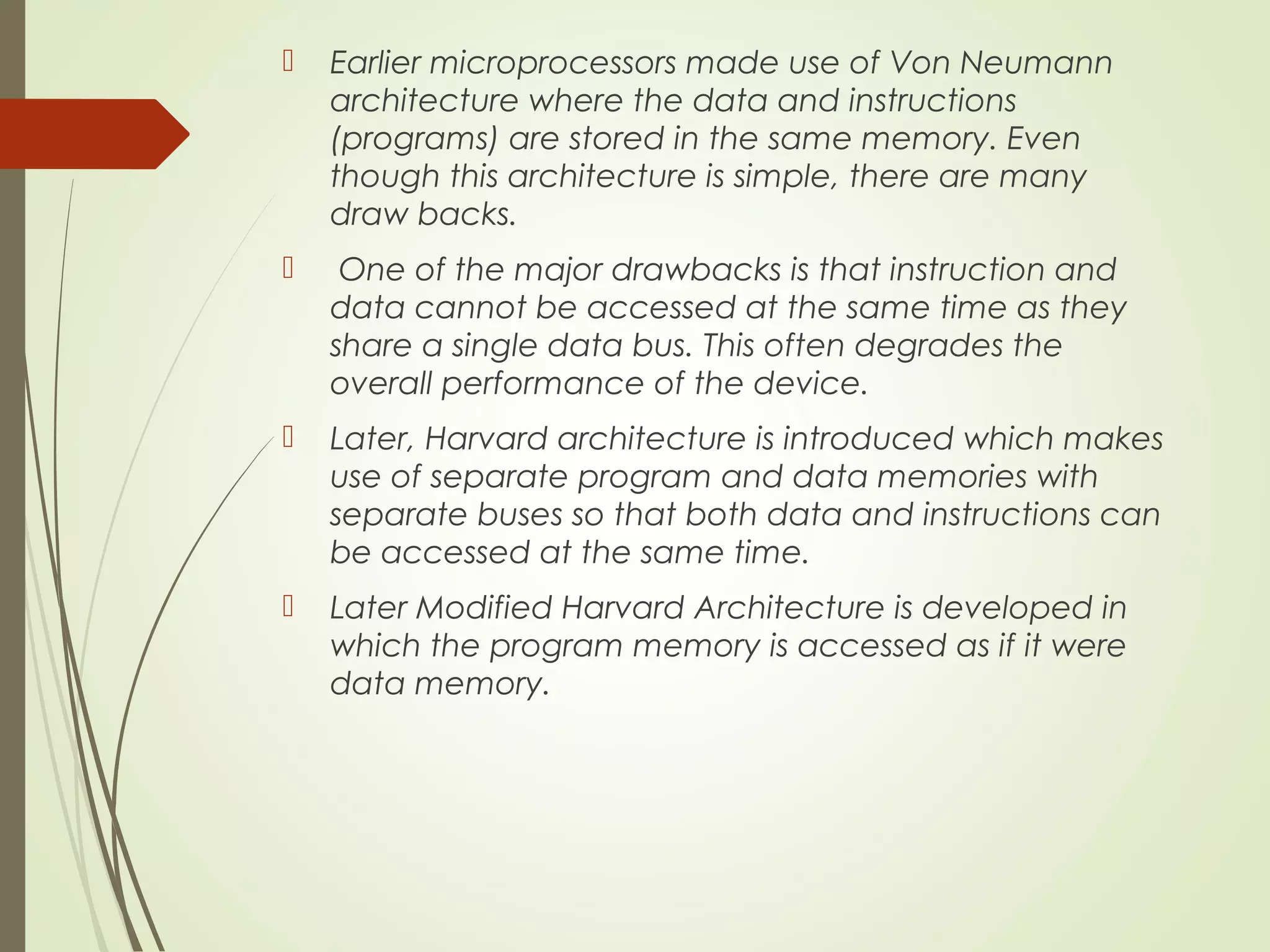
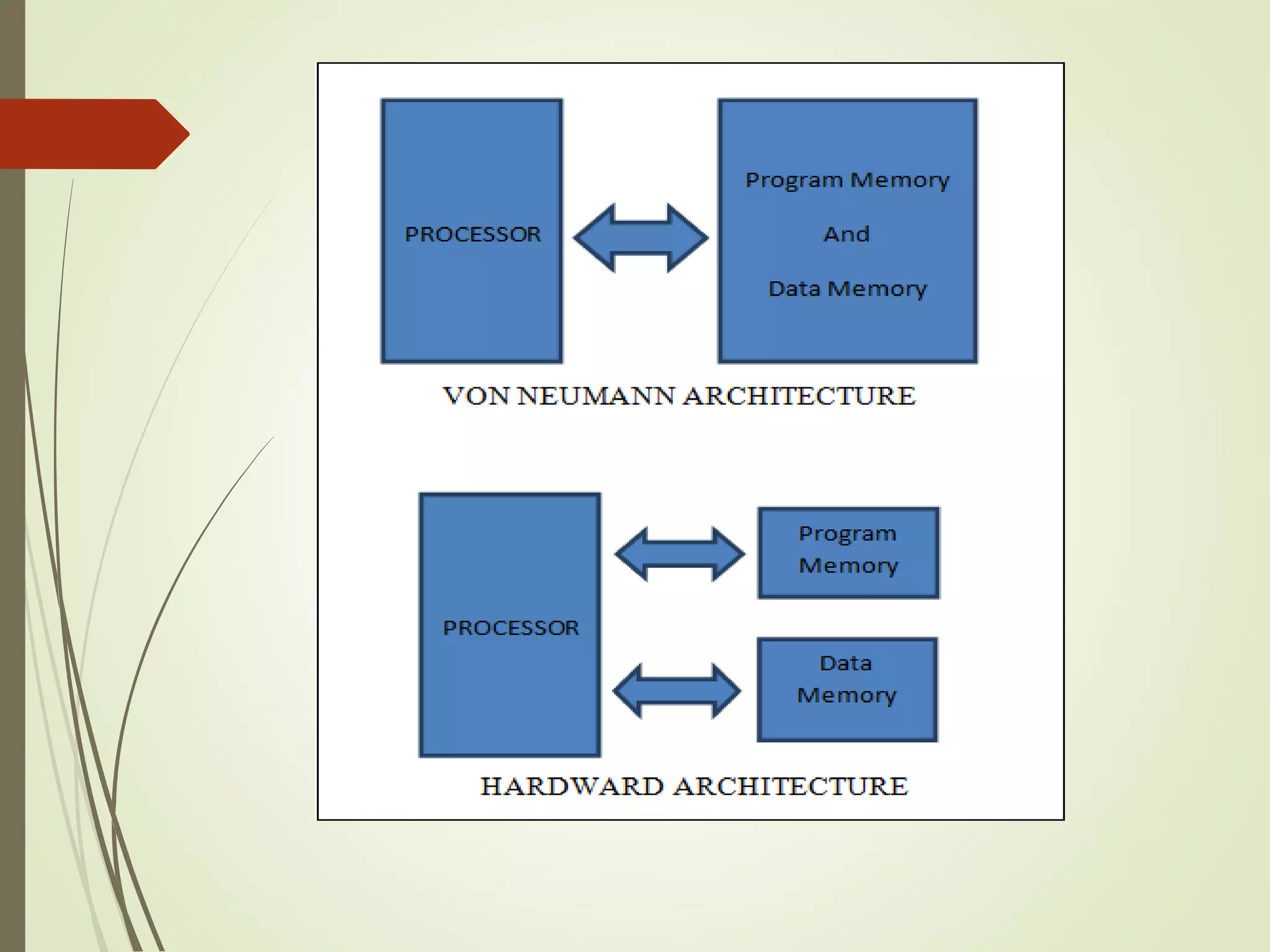
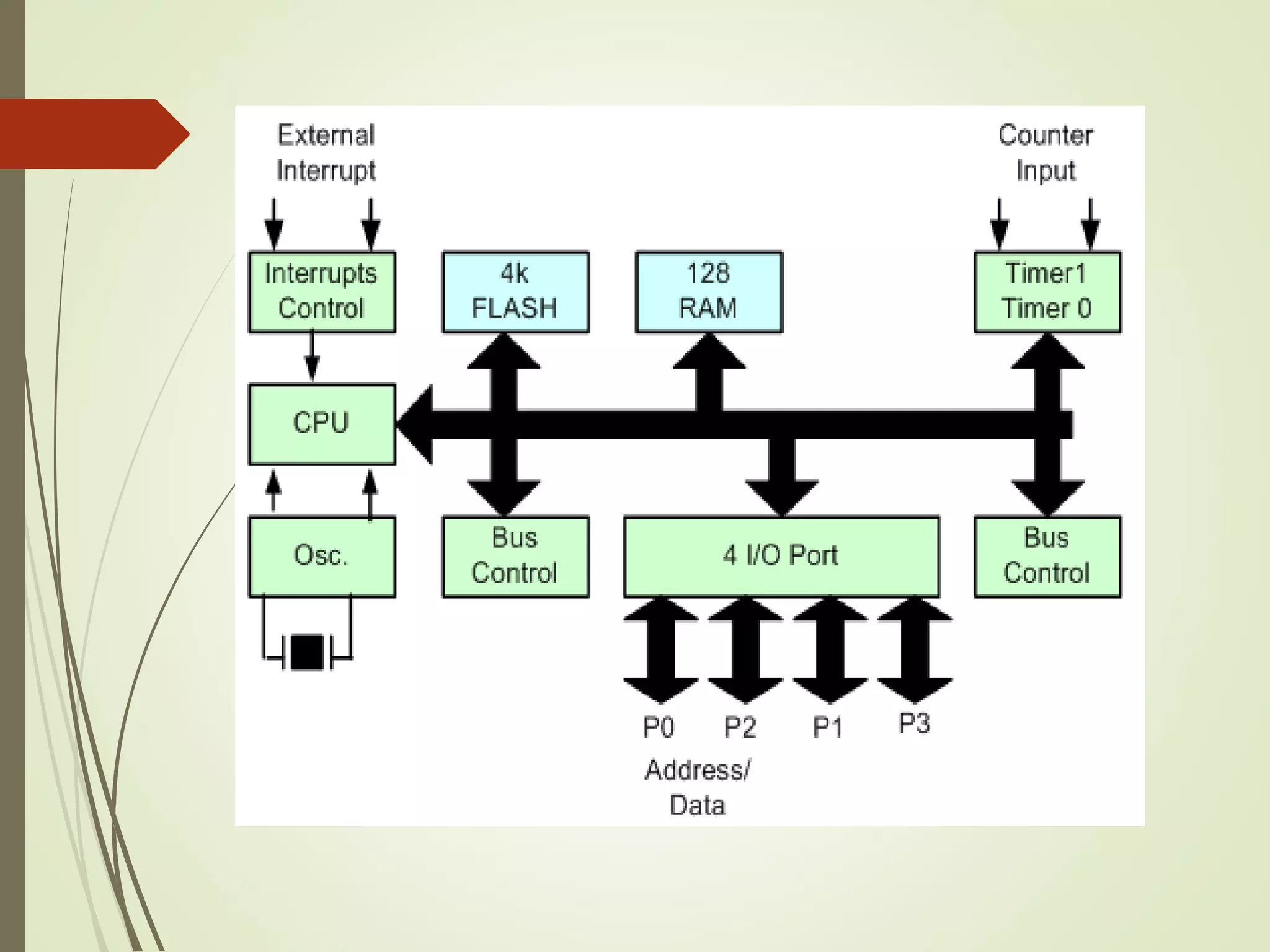
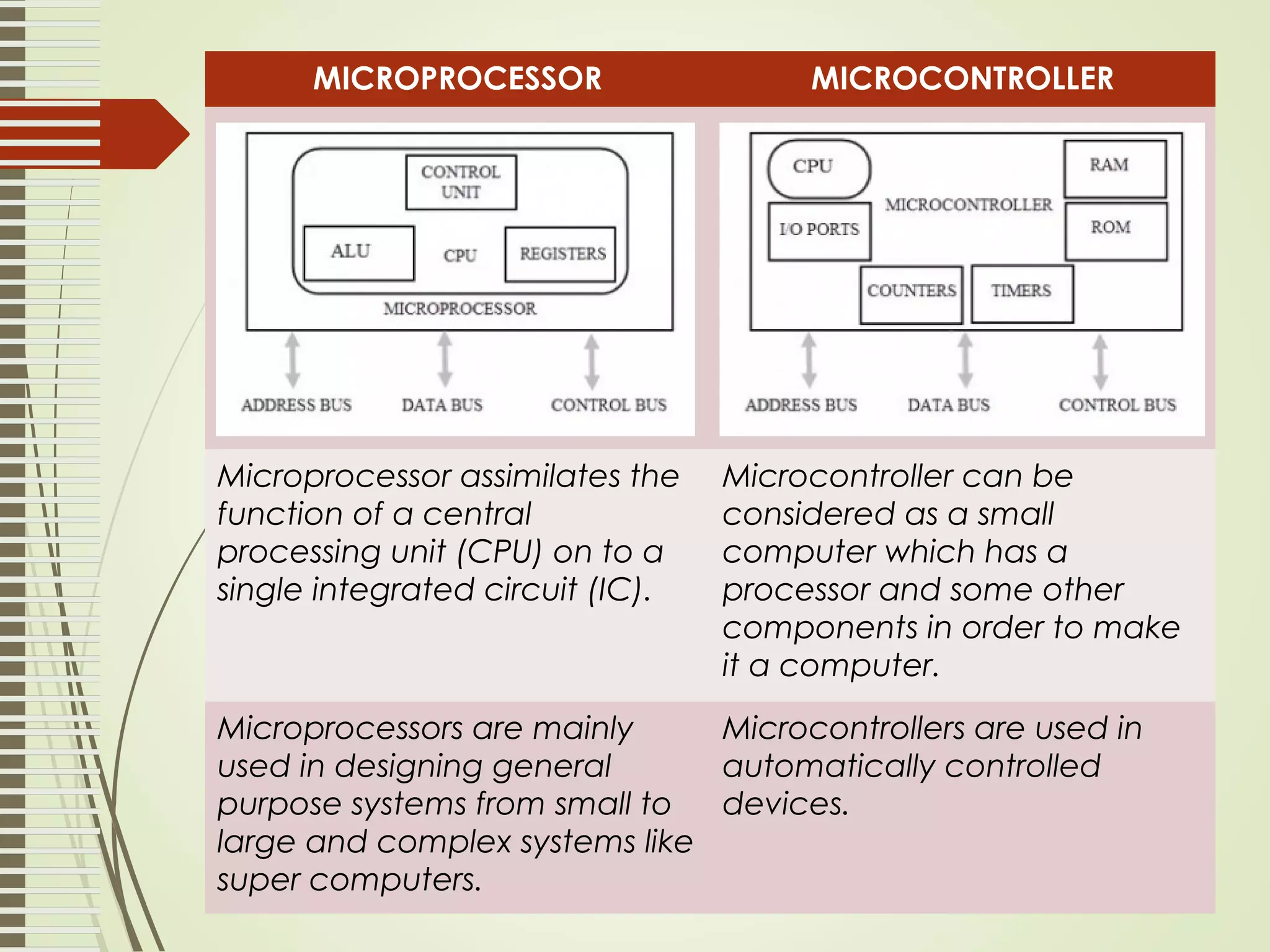
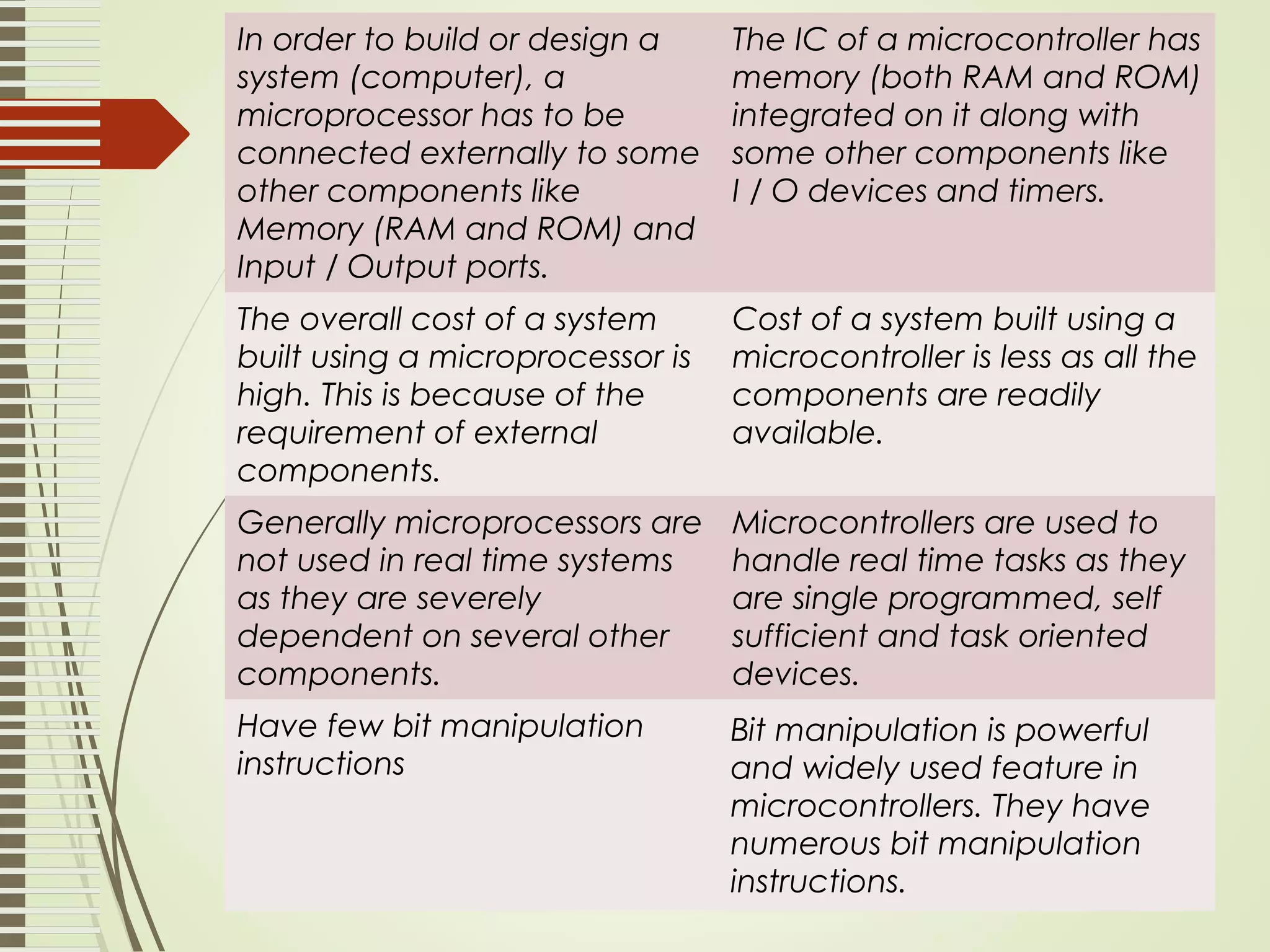
Microprocessors and microcontrollers are both integrated circuits that contain a processor, memory, and input/output peripherals on a single chip. Microprocessors are general purpose CPUs used to build computer systems, while microcontrollers are self-contained systems that control embedded devices. Microcontrollers contain additional components like timers and analog-to-digital converters that make them suitable for real-time control applications in devices and appliances. Common applications of microcontrollers include industrial control systems, home appliances, automotive engine control systems, and consumer electronics. Microprocessors are used to build more complex computer systems for applications like desktop PCs, servers, communication equipment, and industrial instrumentation.