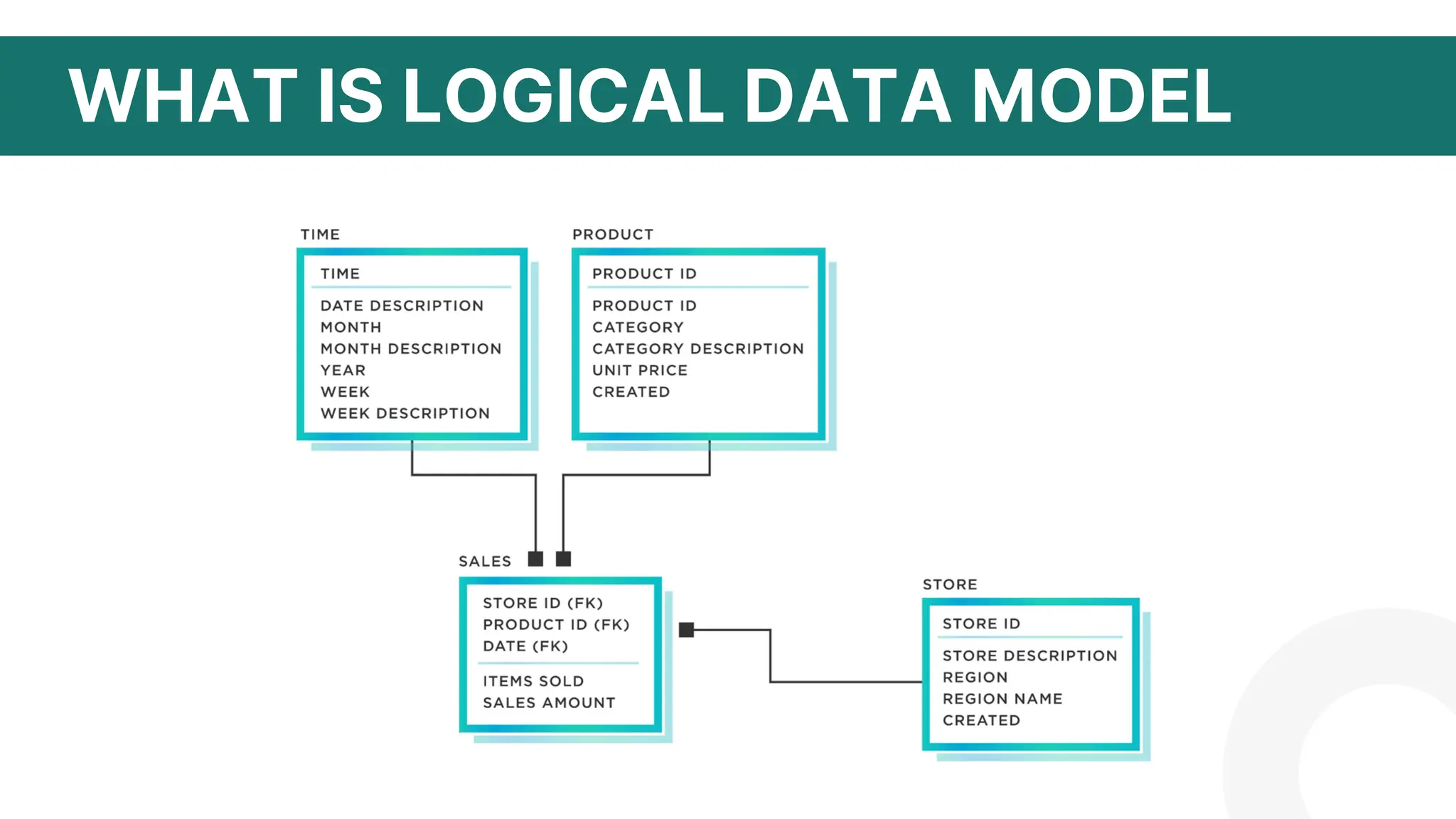
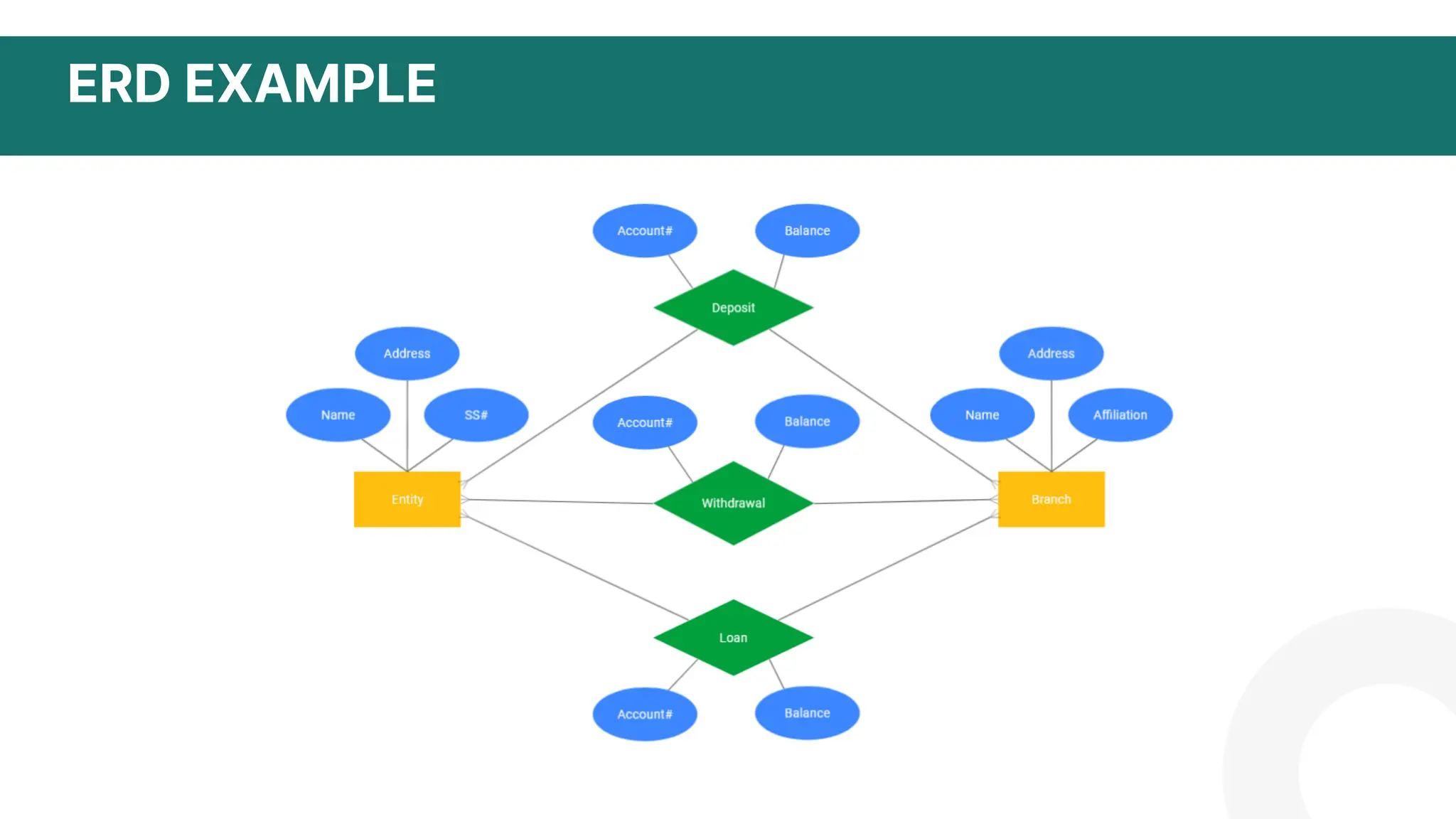
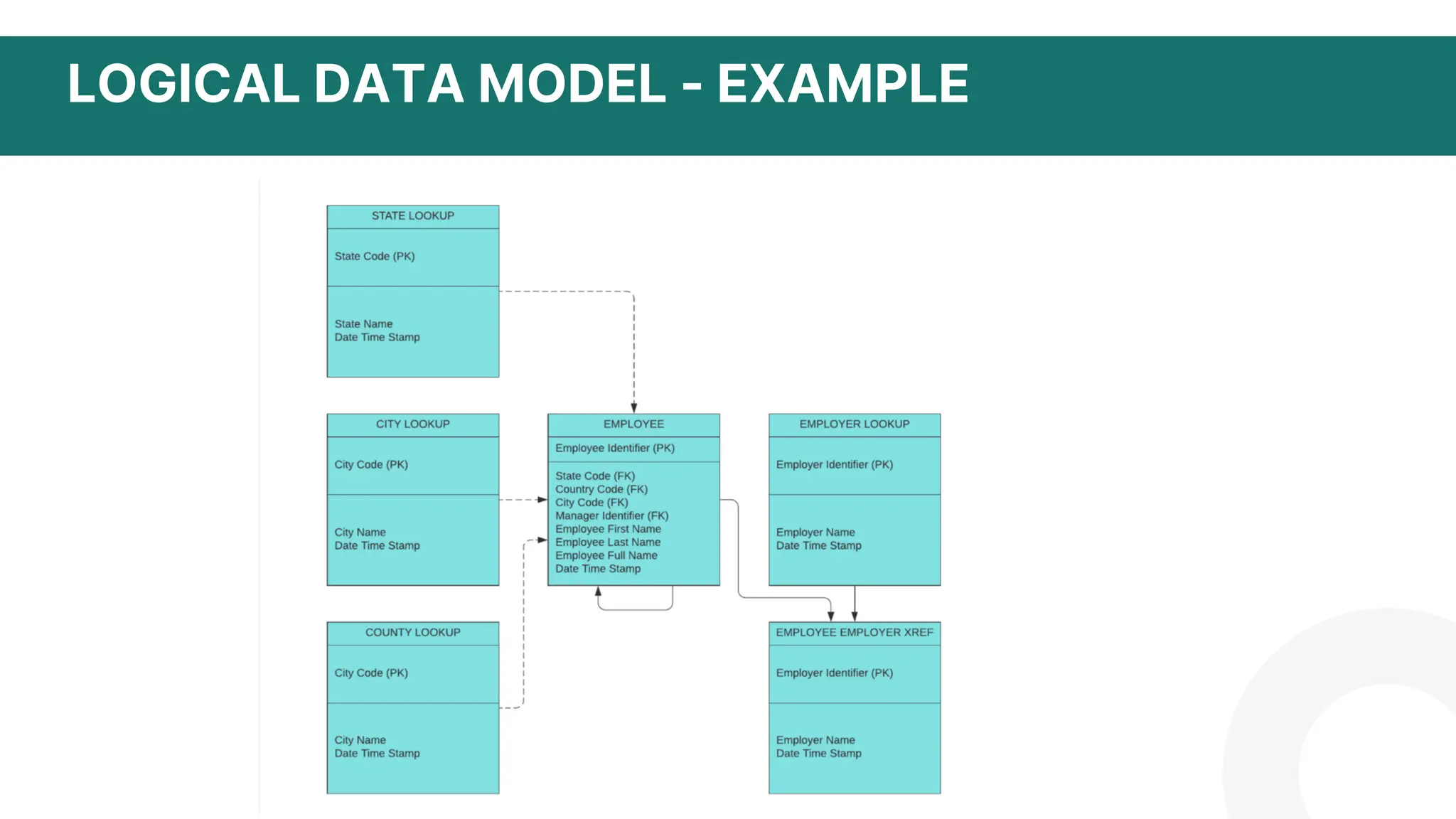
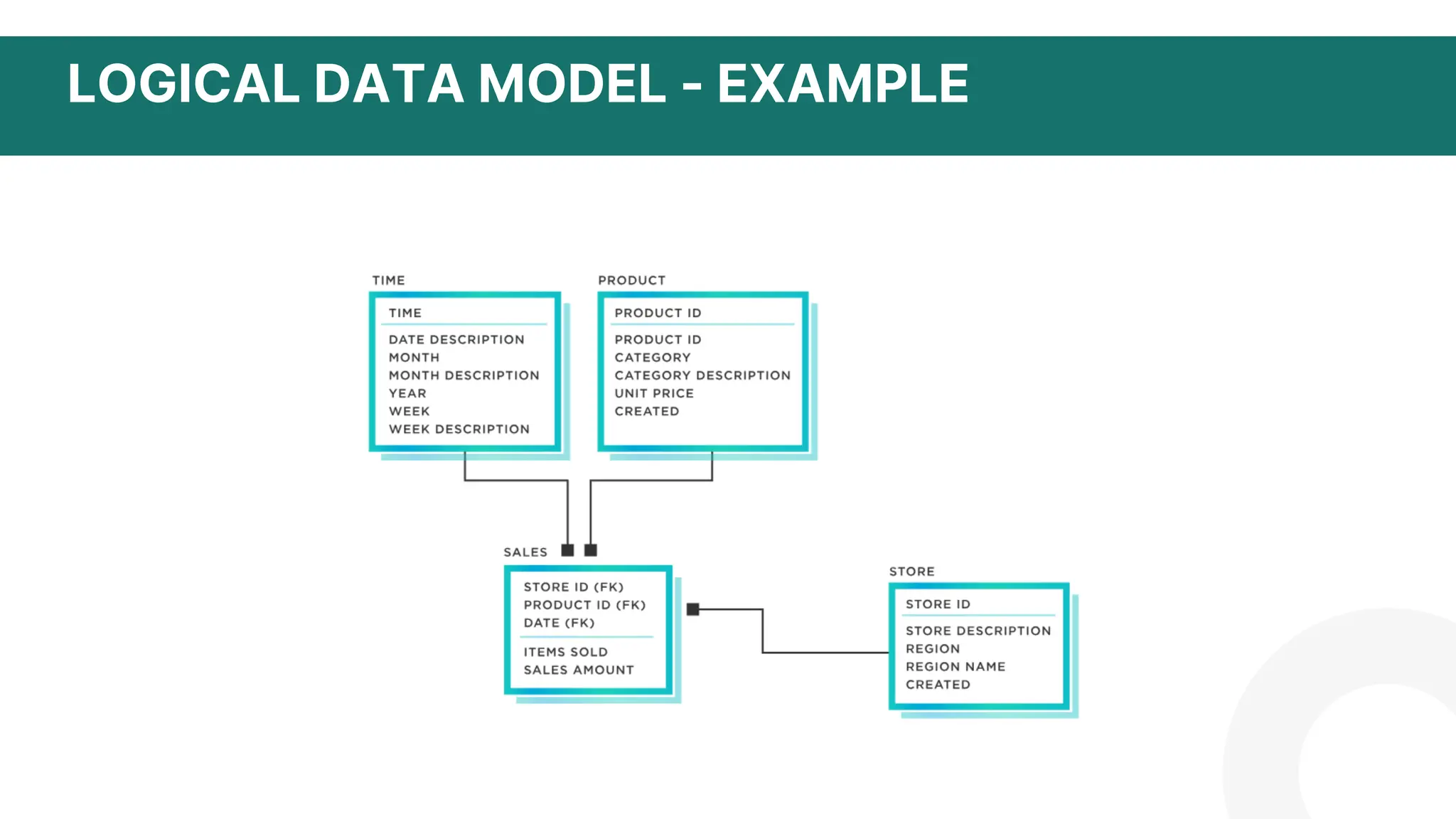
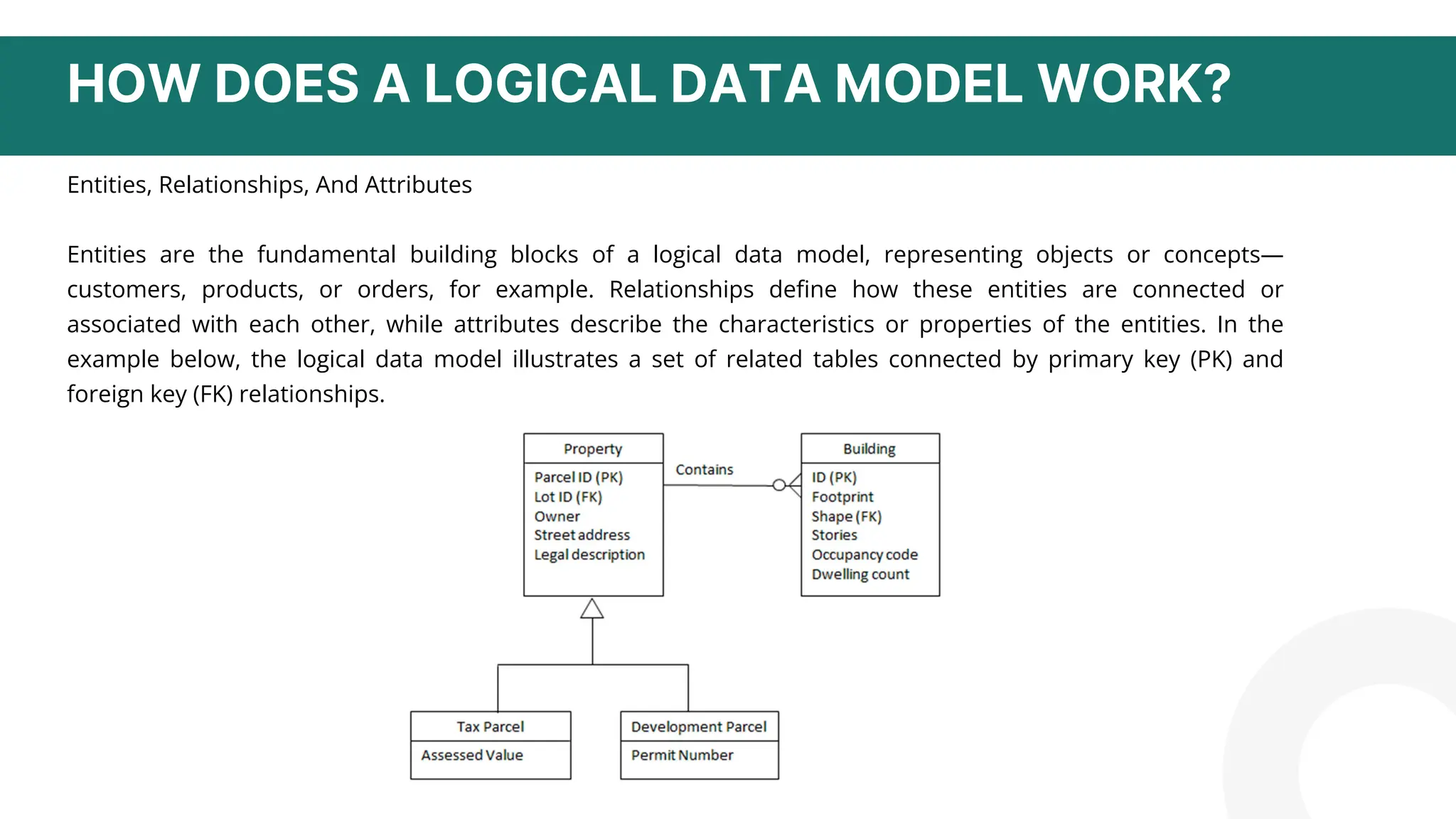
The document discusses logical data modeling. It defines a logical data model as establishing the structure of data elements and relationships independent of physical implementation. It notes logical data models serve as a blueprint for used data. The document outlines key components of logical data models including entities, relationships, and attributes. It also discusses characteristics such as being independent of database systems and modeling business requirements. Overall, the summary provides a high-level overview of the key topics and purpose of logical data modeling covered in the document.