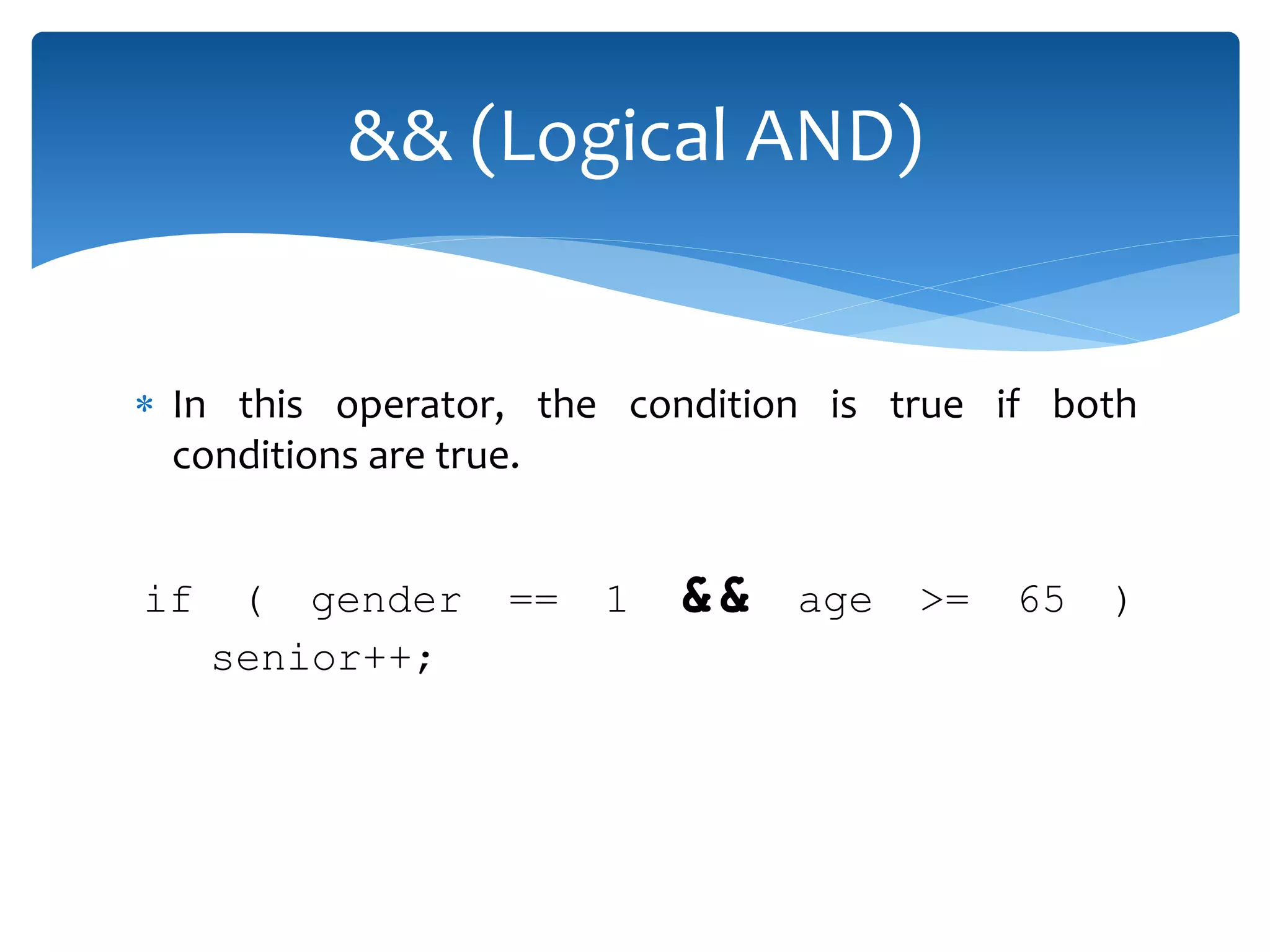
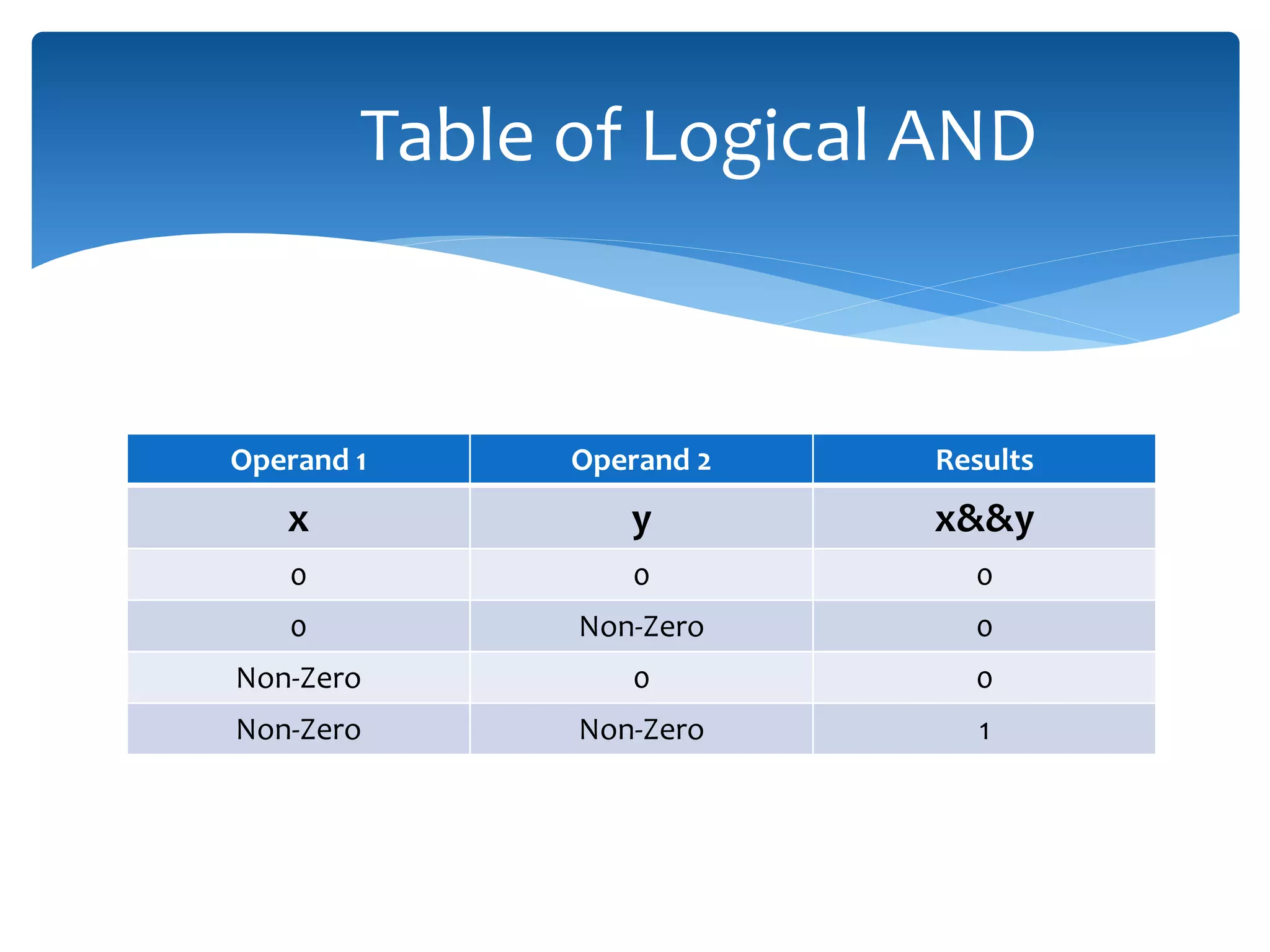
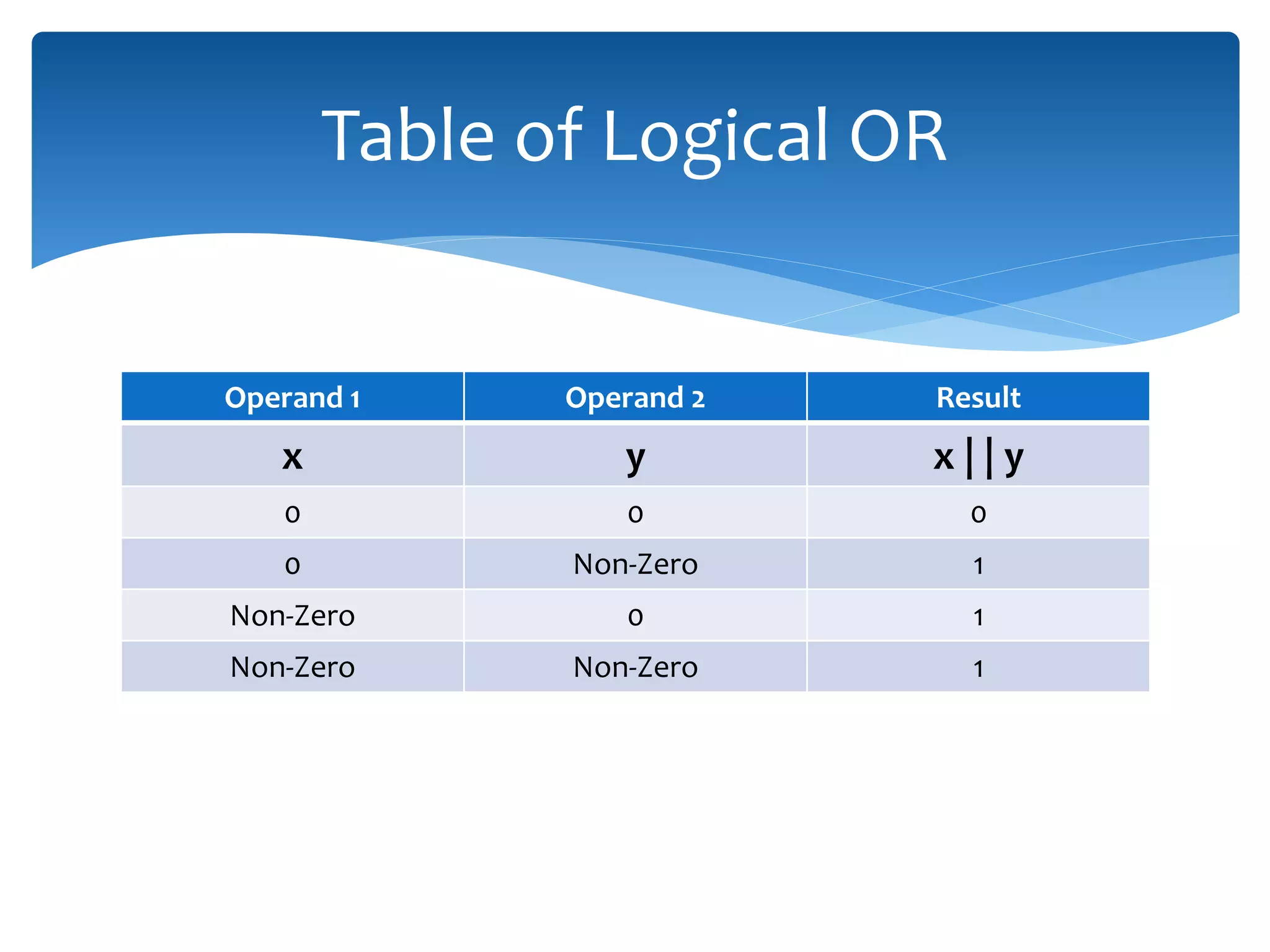
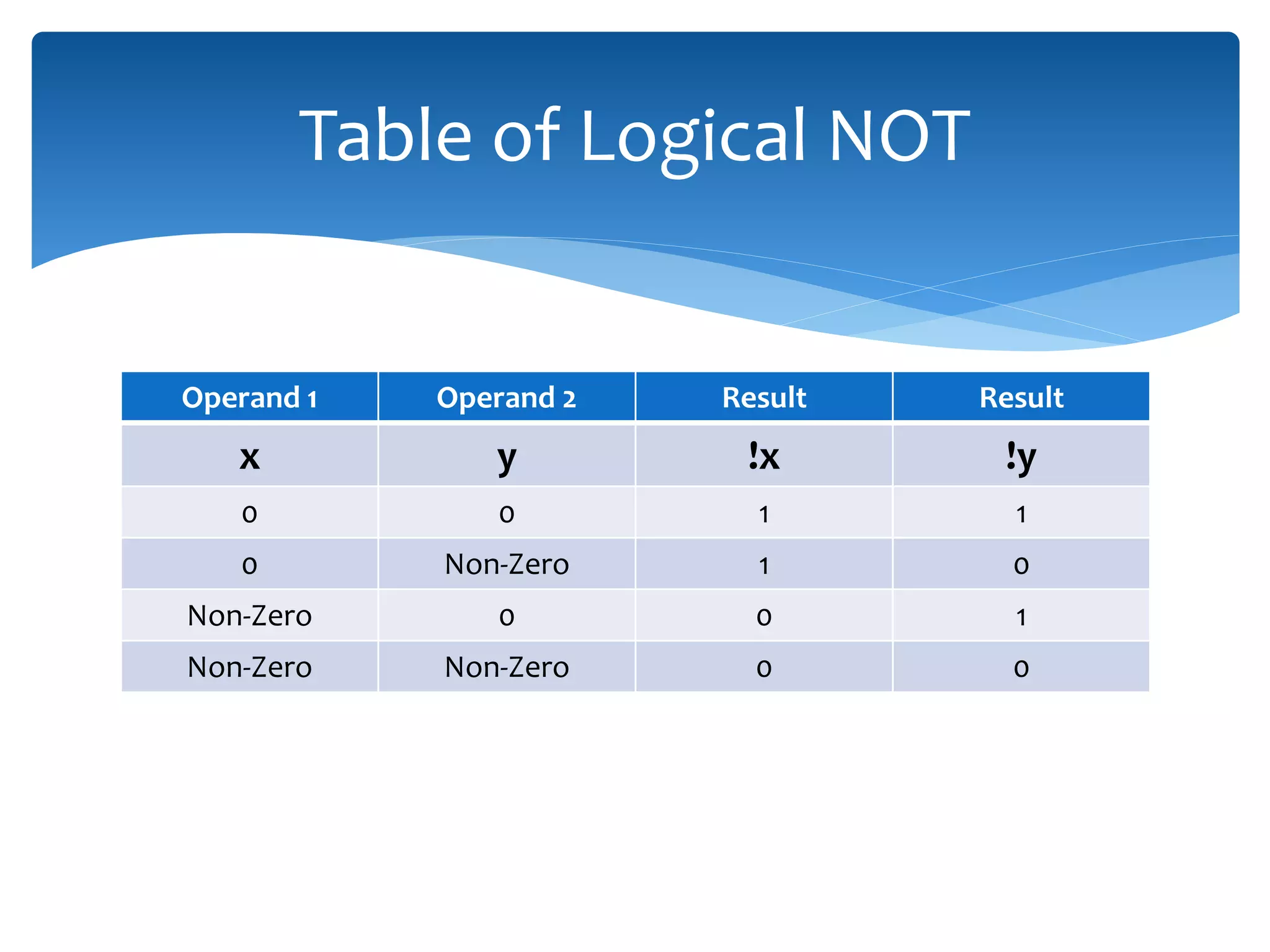
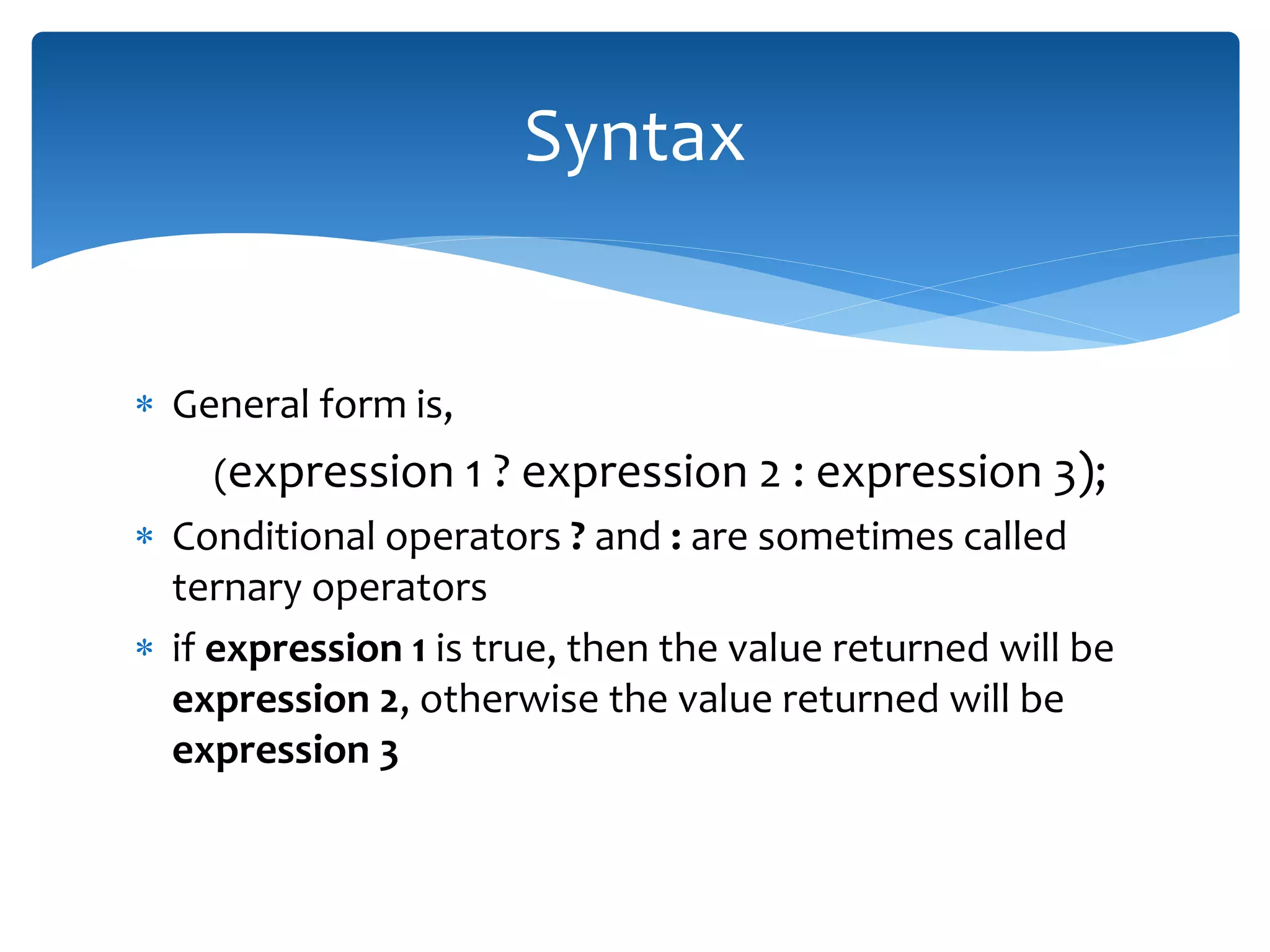
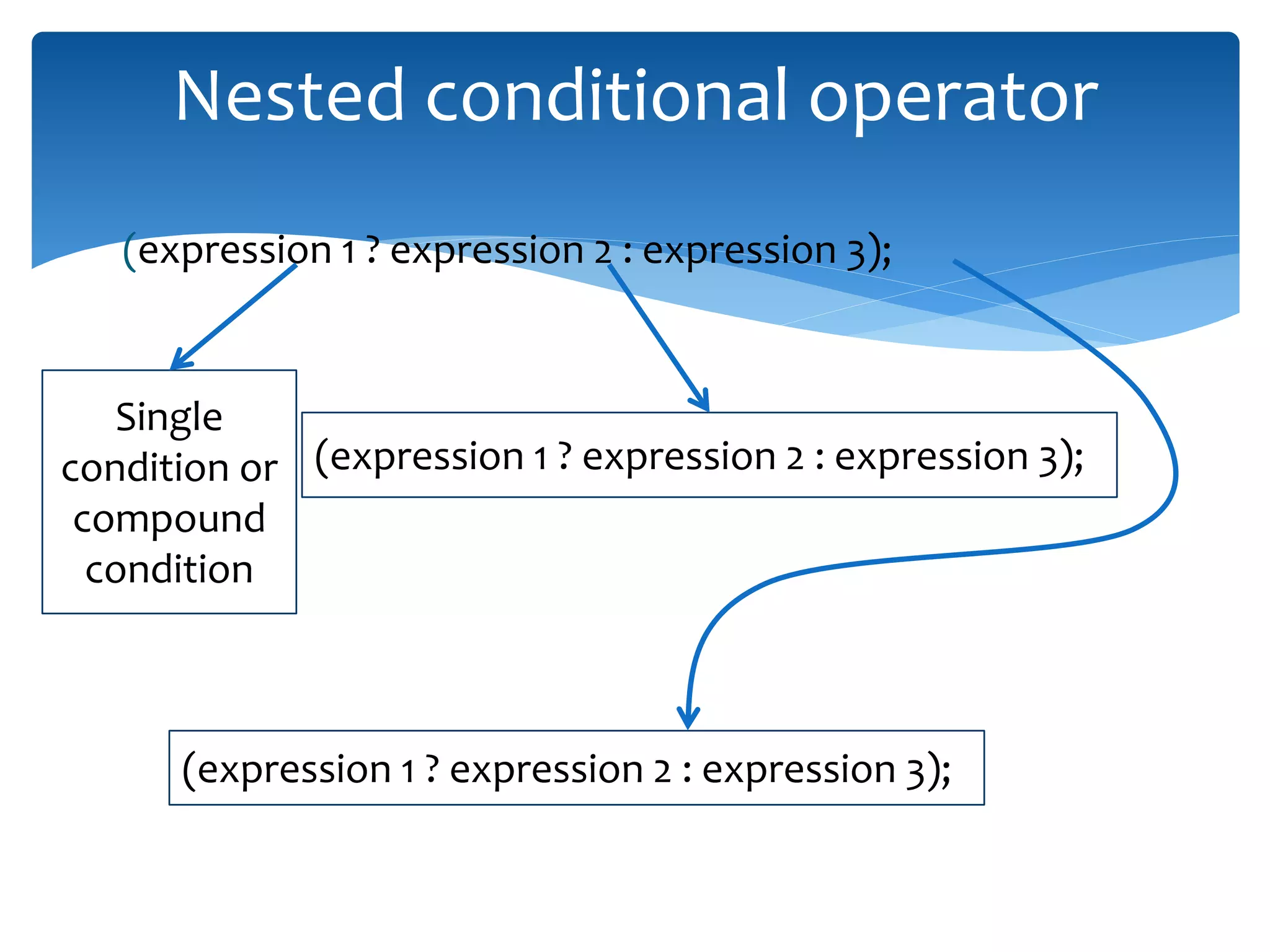
The document discusses logical operators (&&, ||, !) and conditional operators. It defines each operator, provides truth tables to illustrate how they work, and gives examples of code using each one. The && operator returns true only if both conditions are true. The || operator returns true if either condition is true. The ! operator inverts the value of a condition. The conditional operator ?: is like an if/else statement written in a single line and can be nested to evaluate multiple conditions.