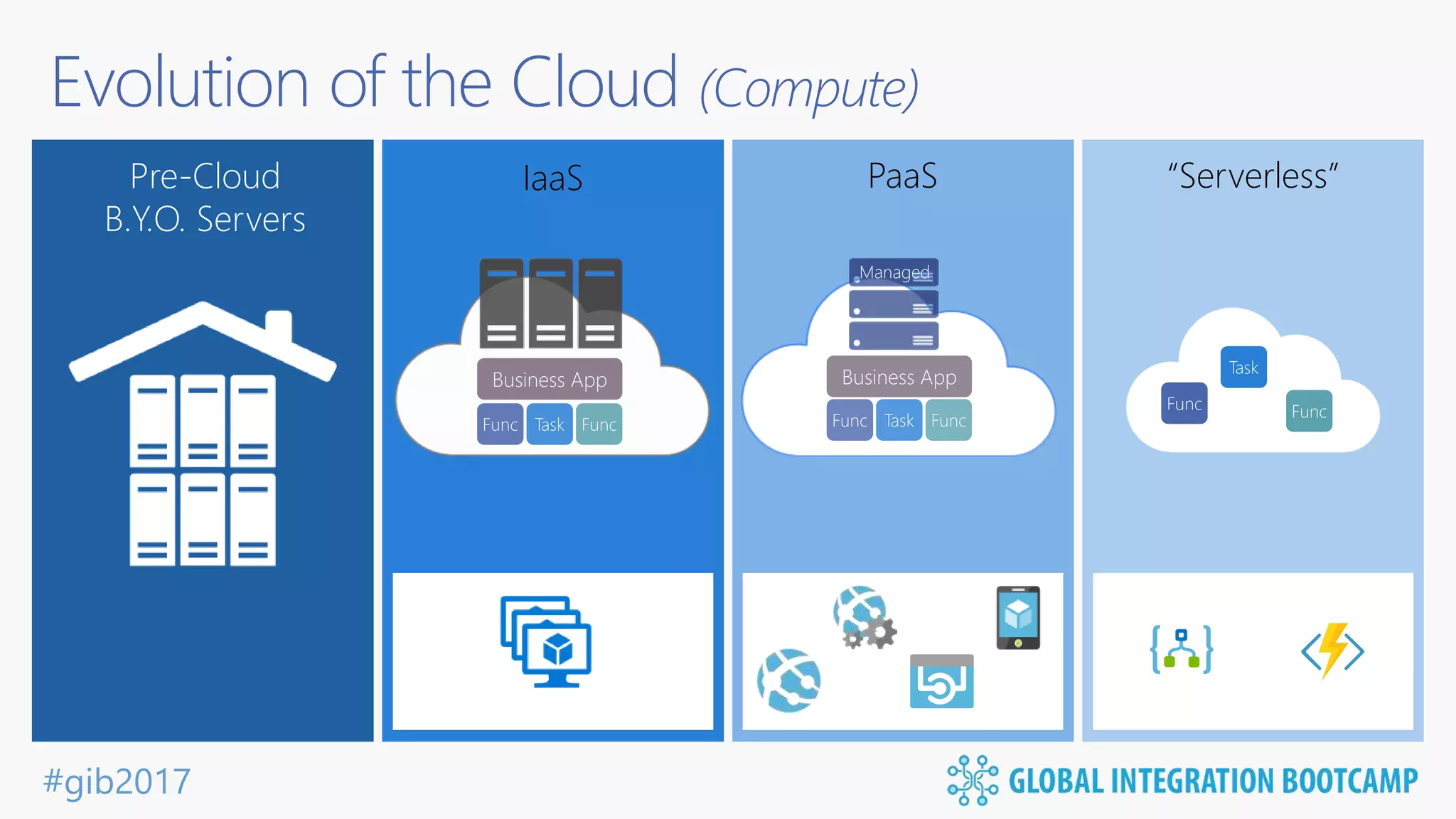
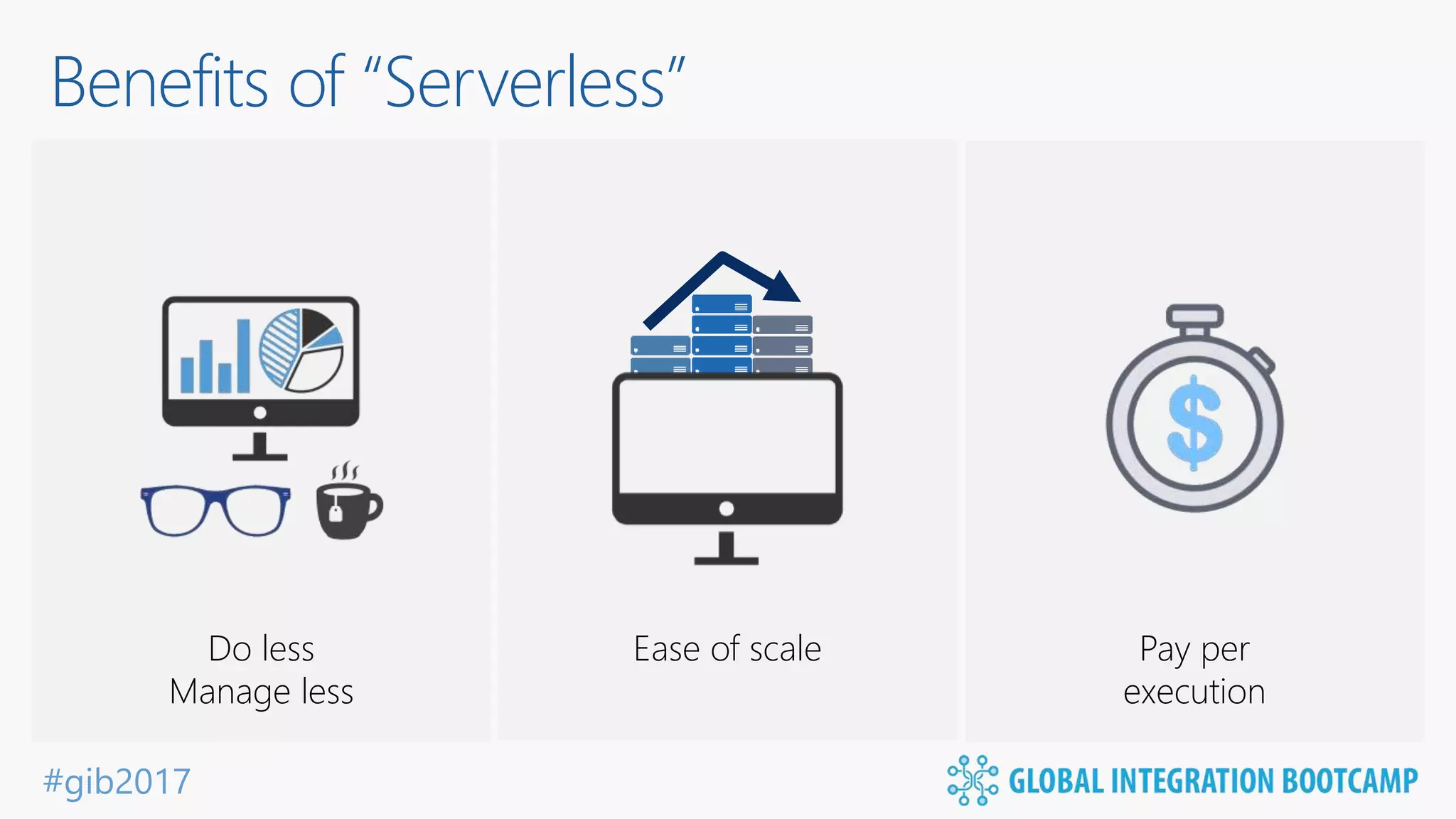
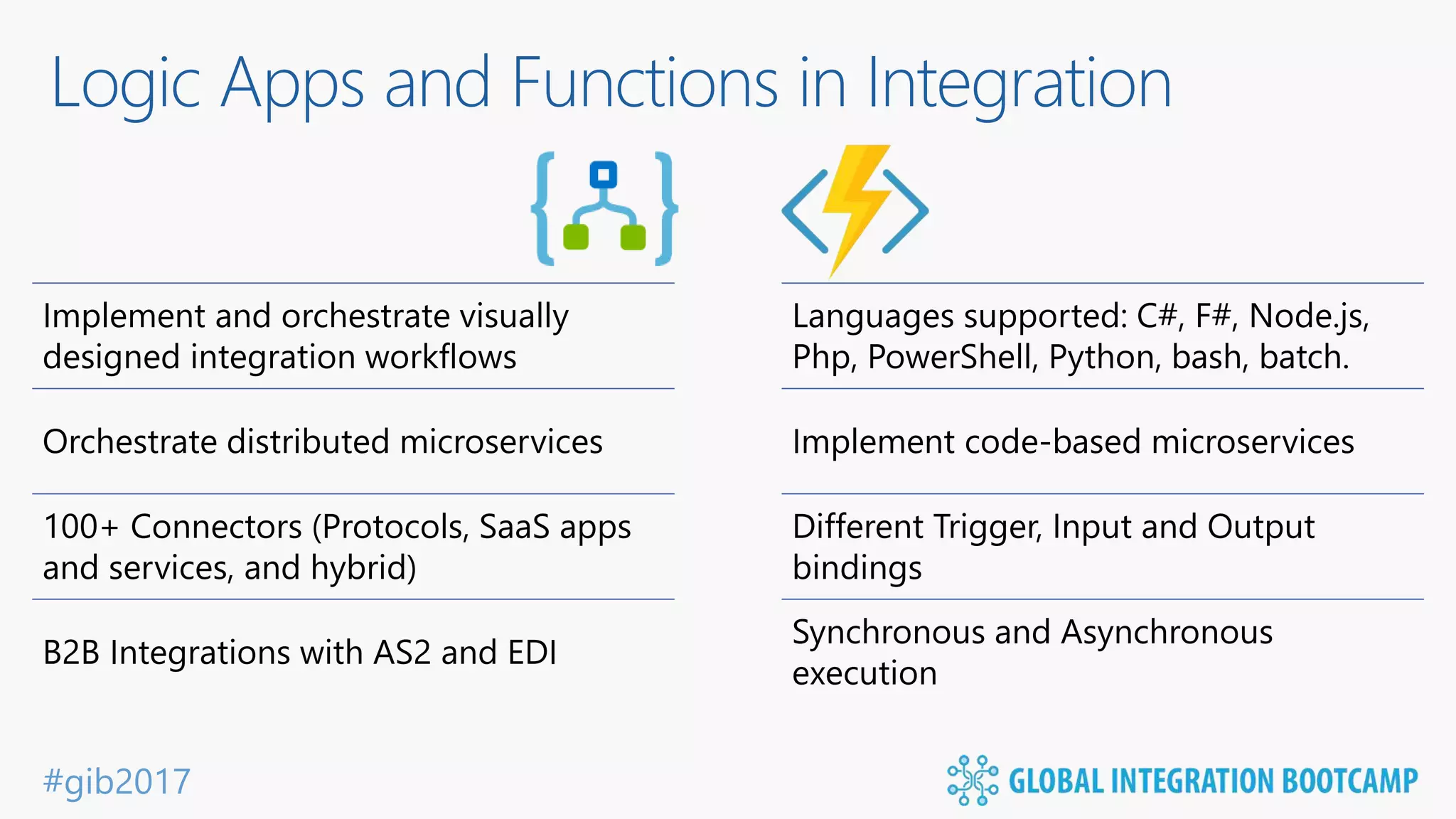
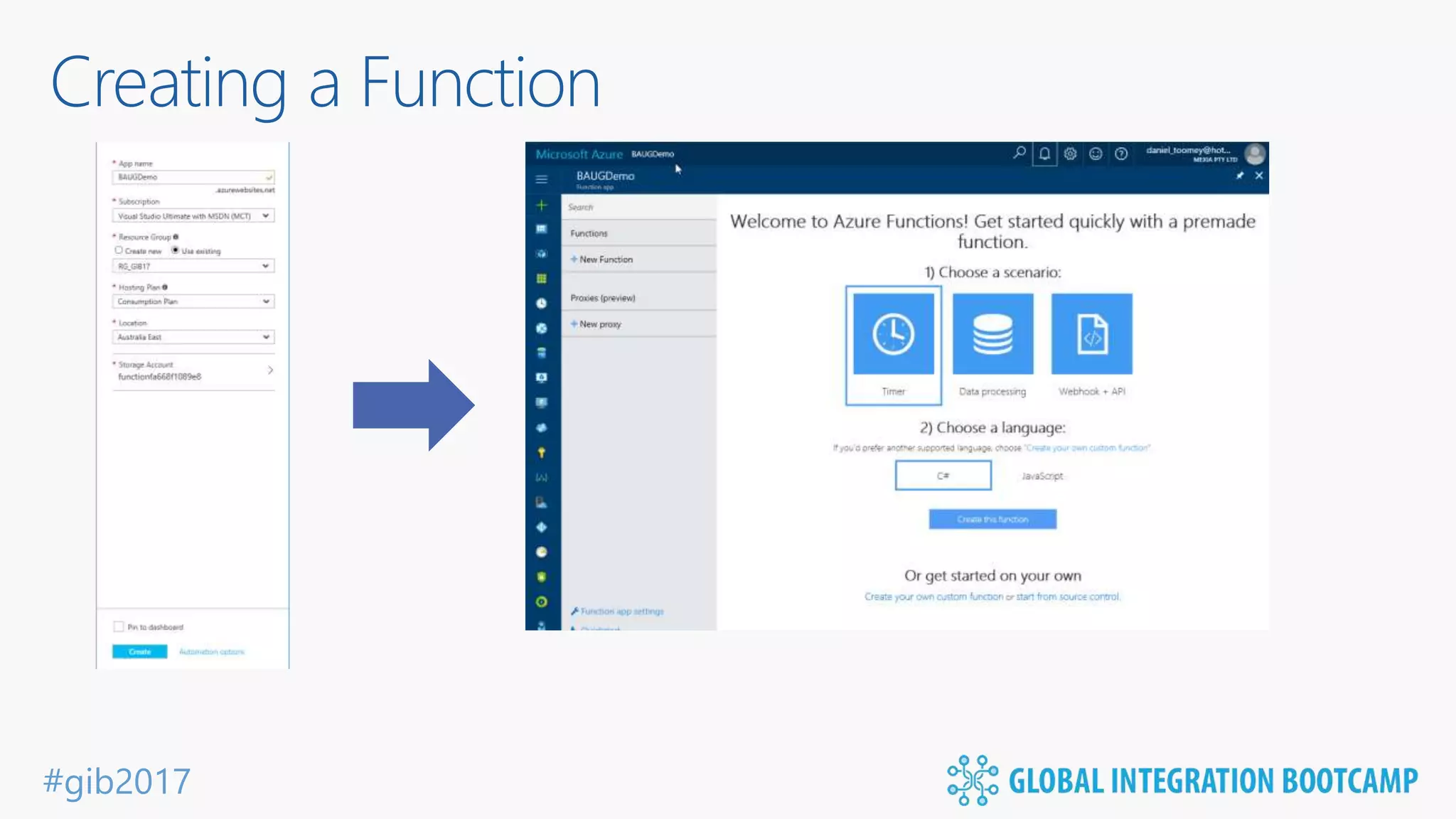
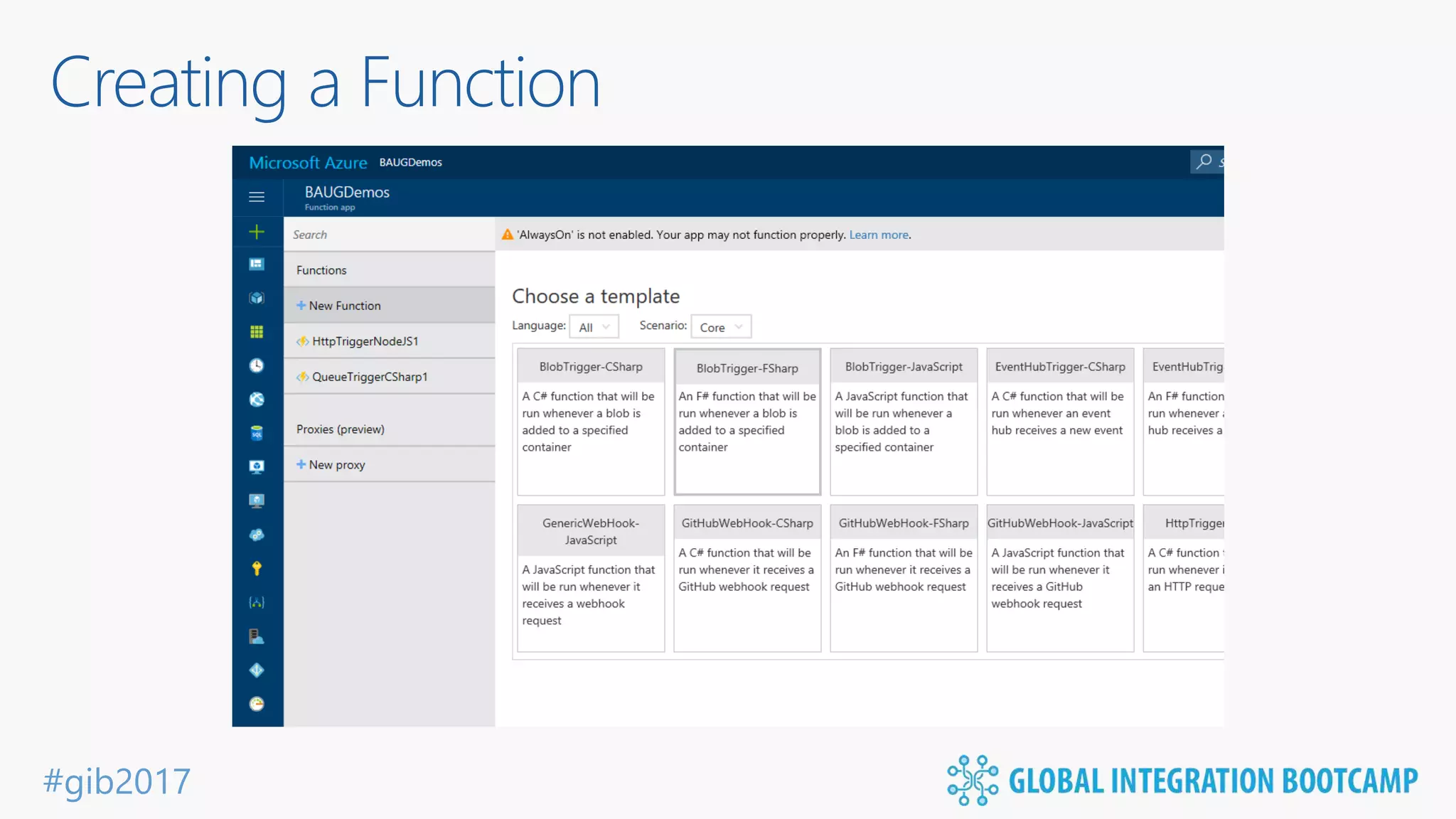
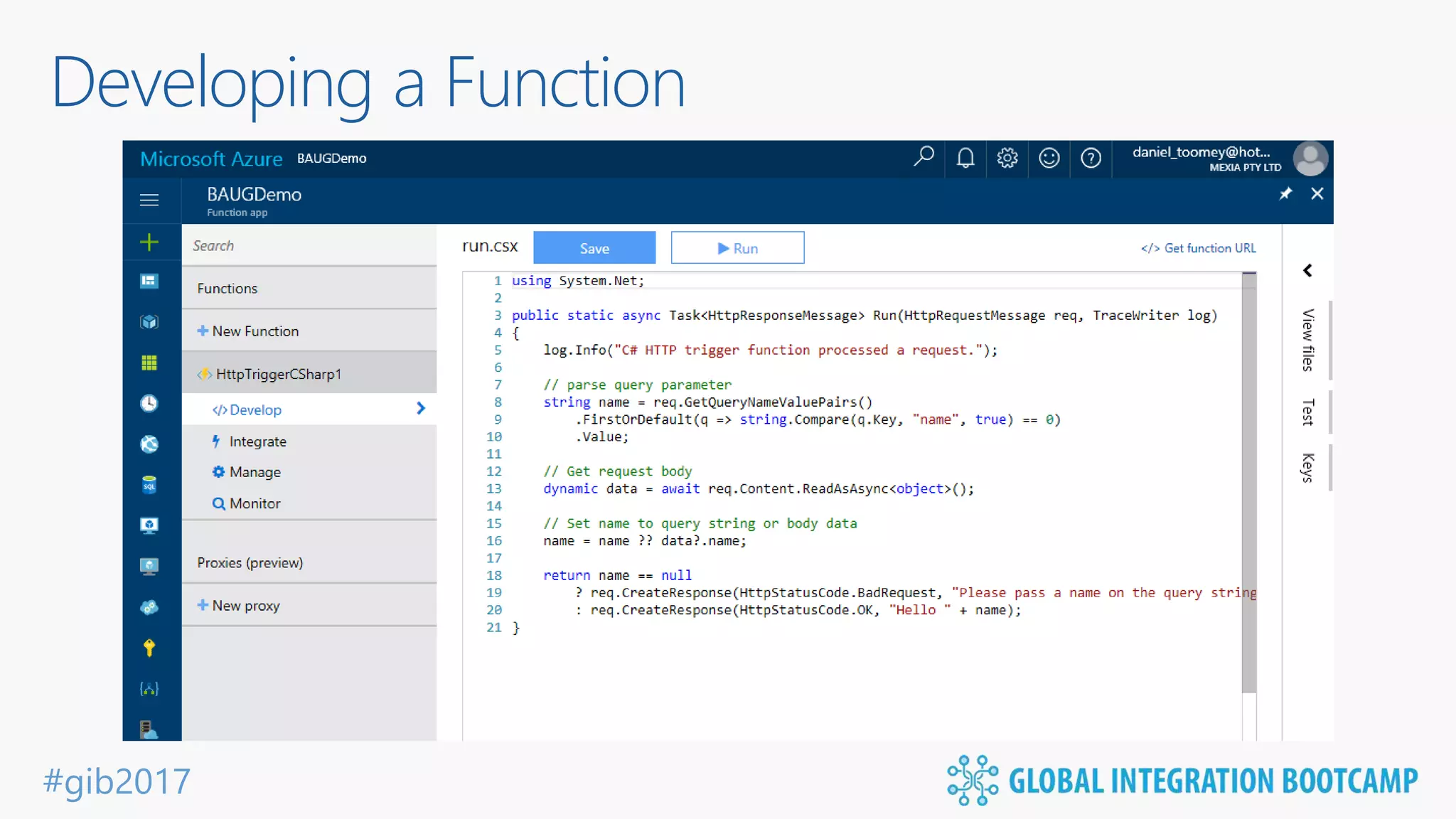
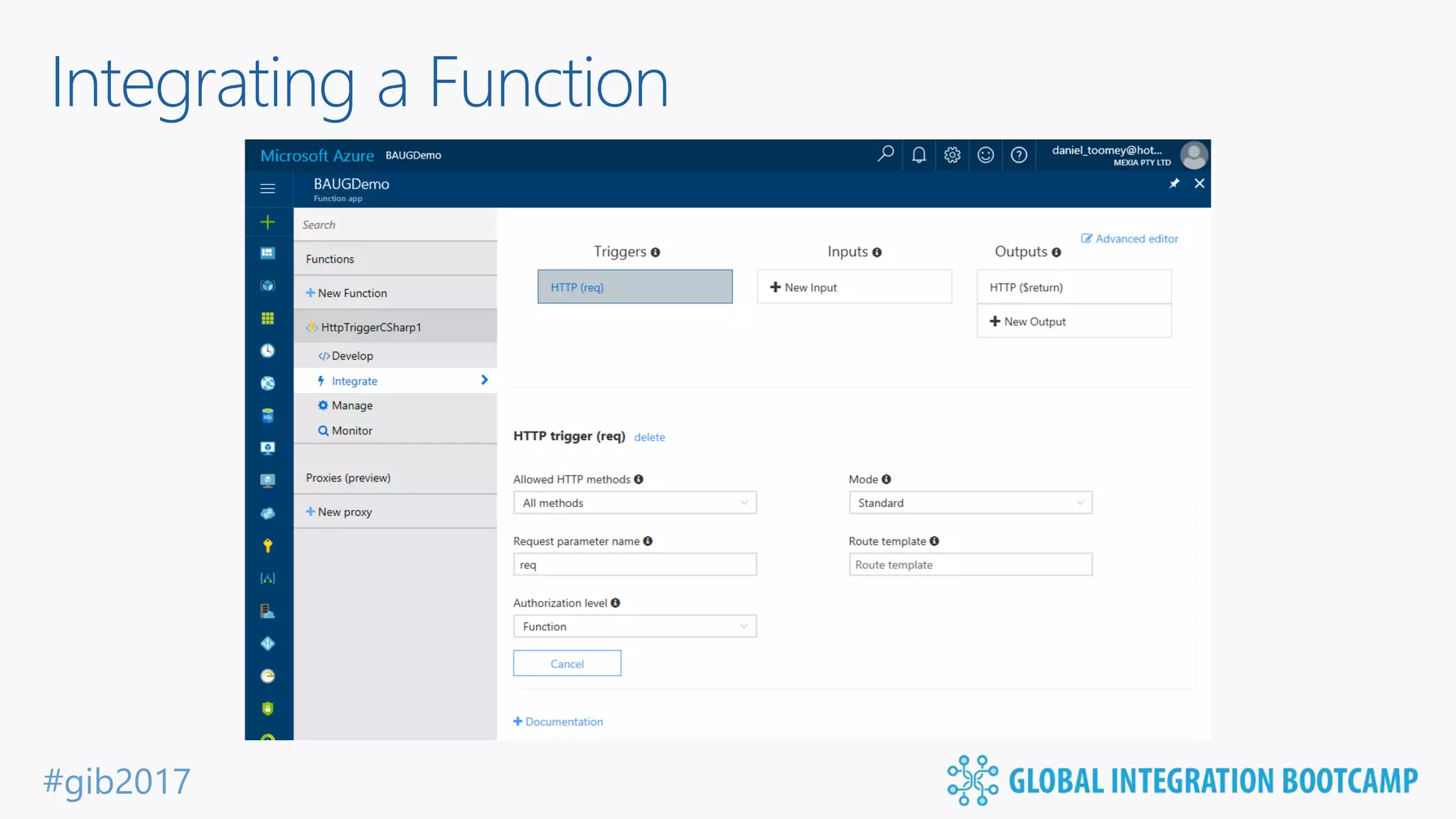
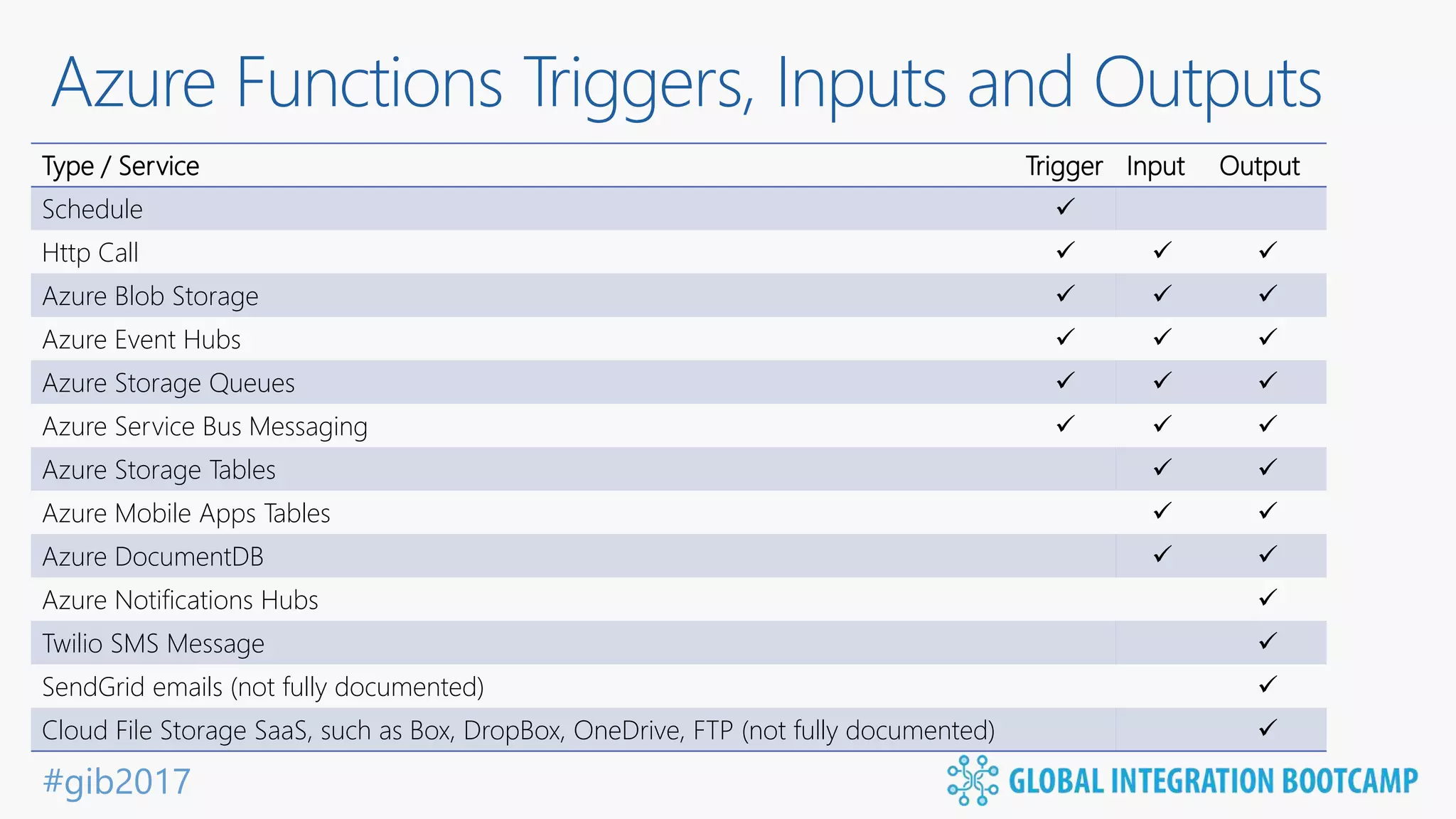
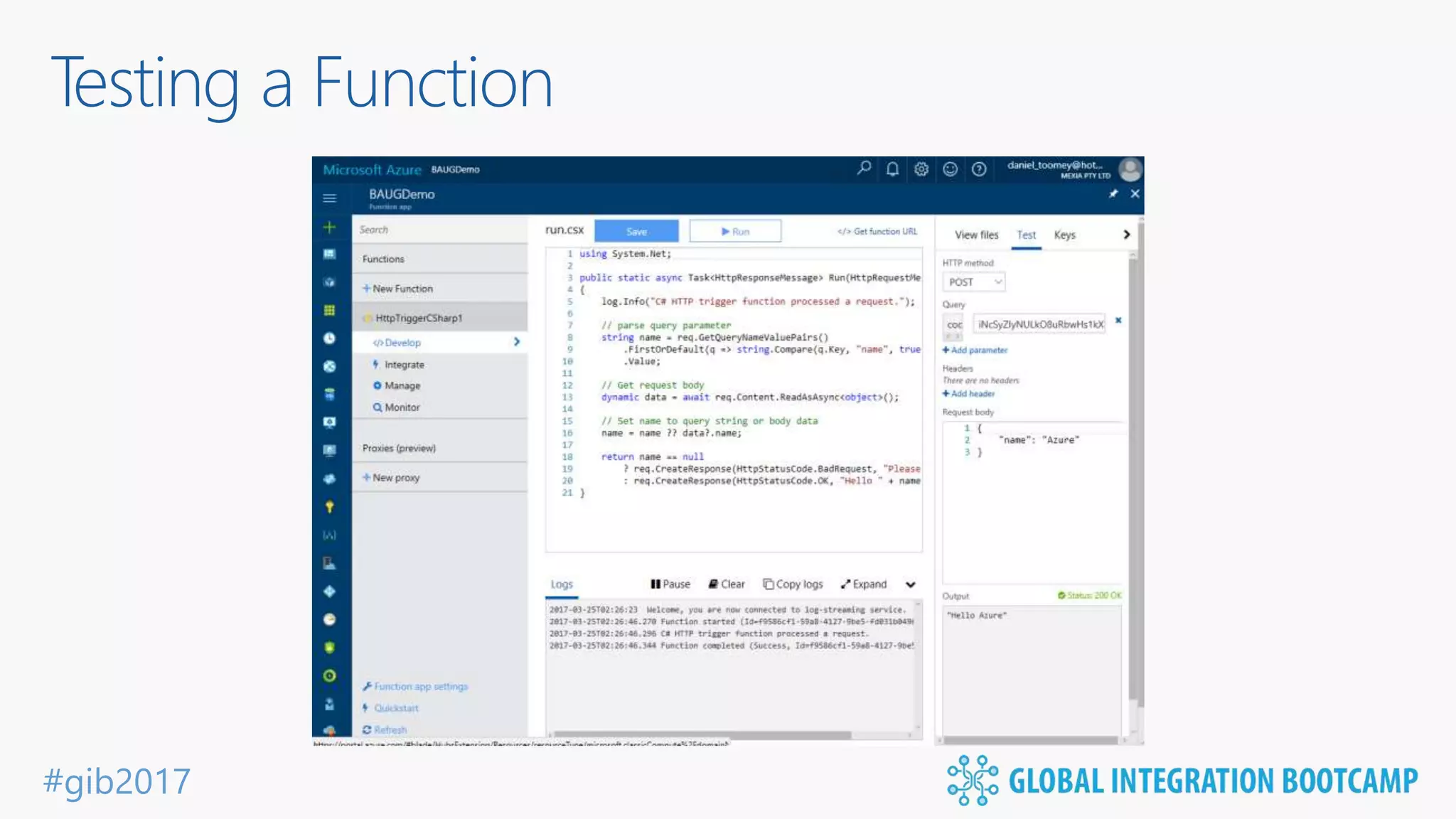
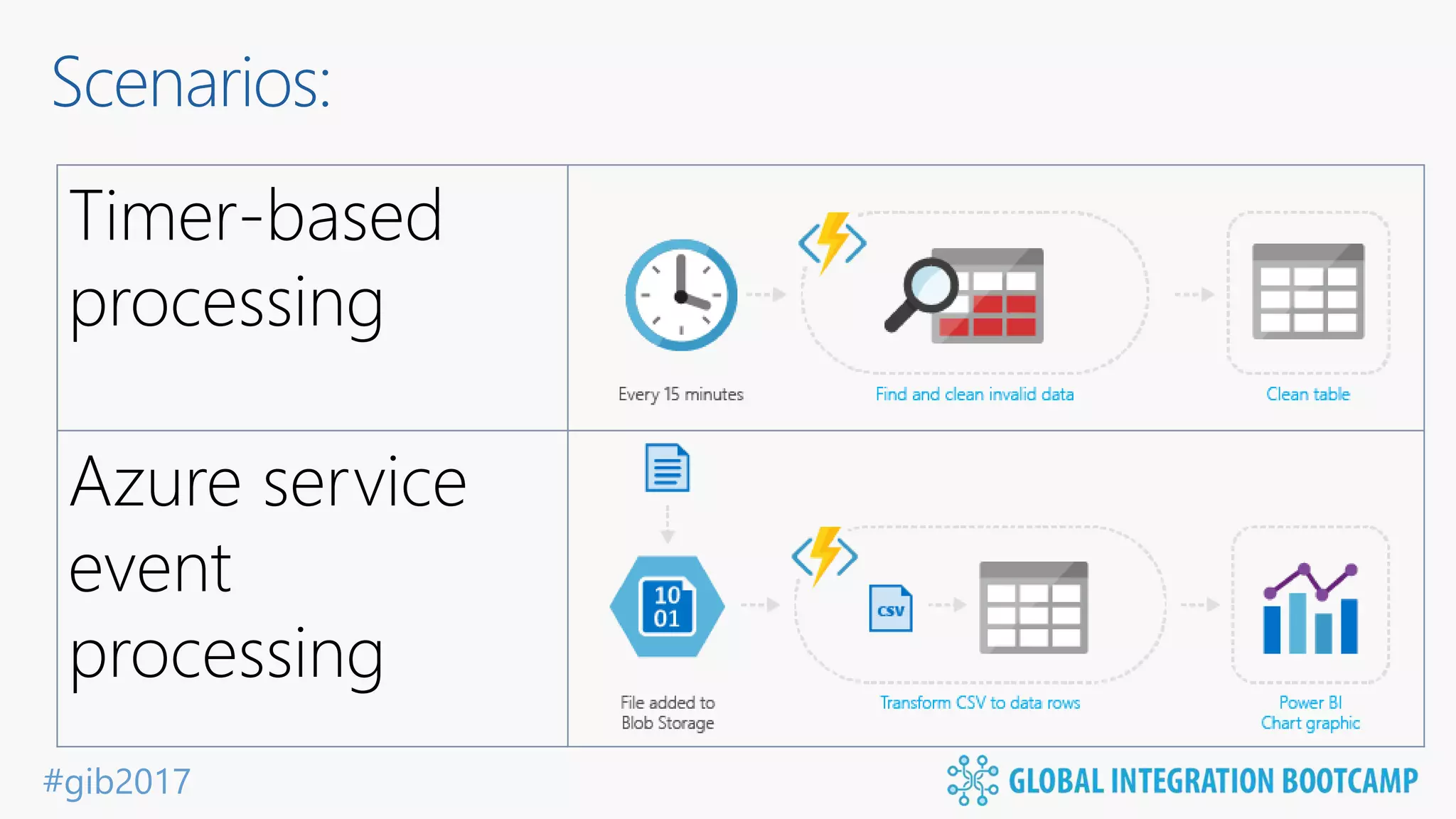
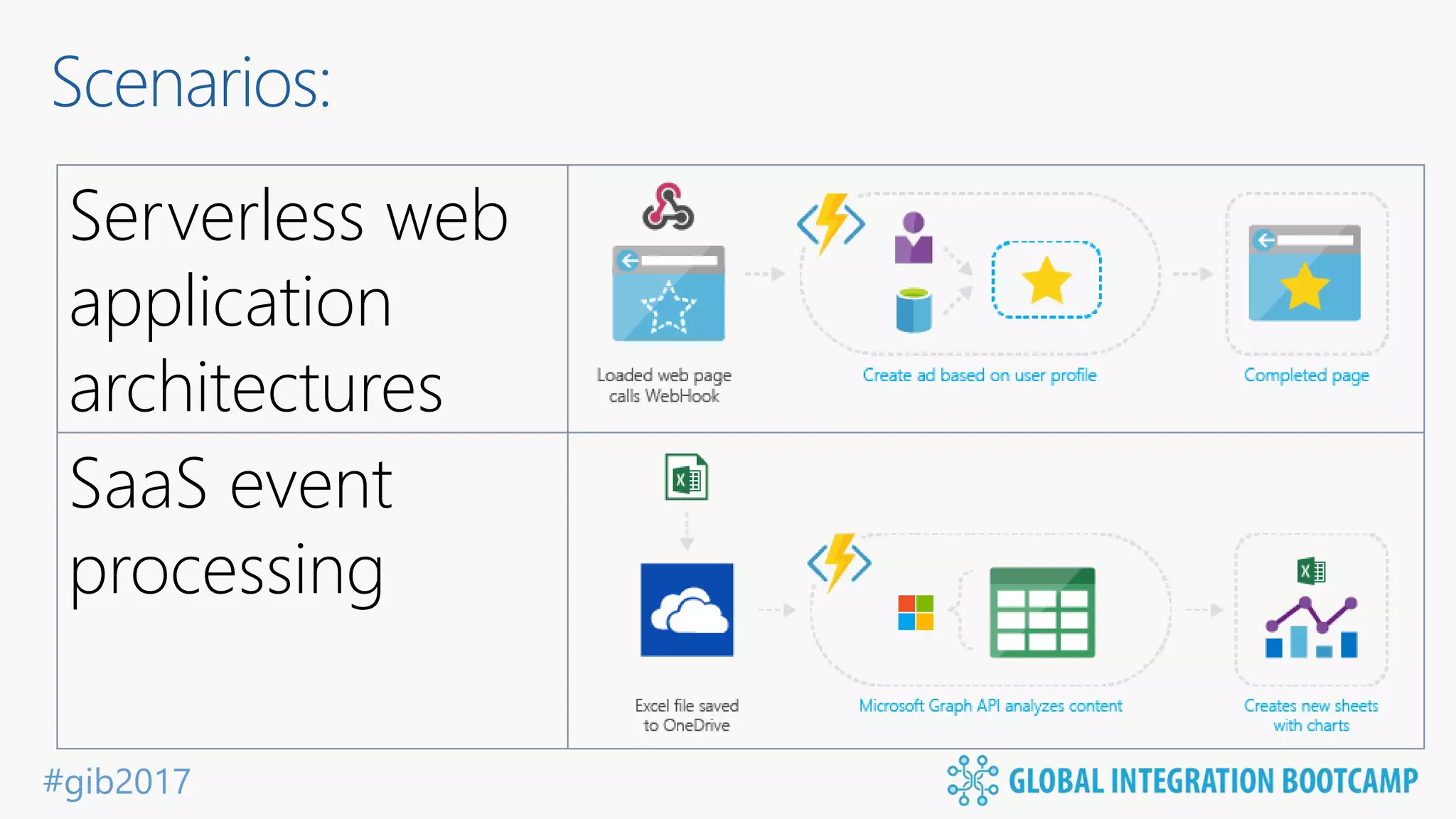
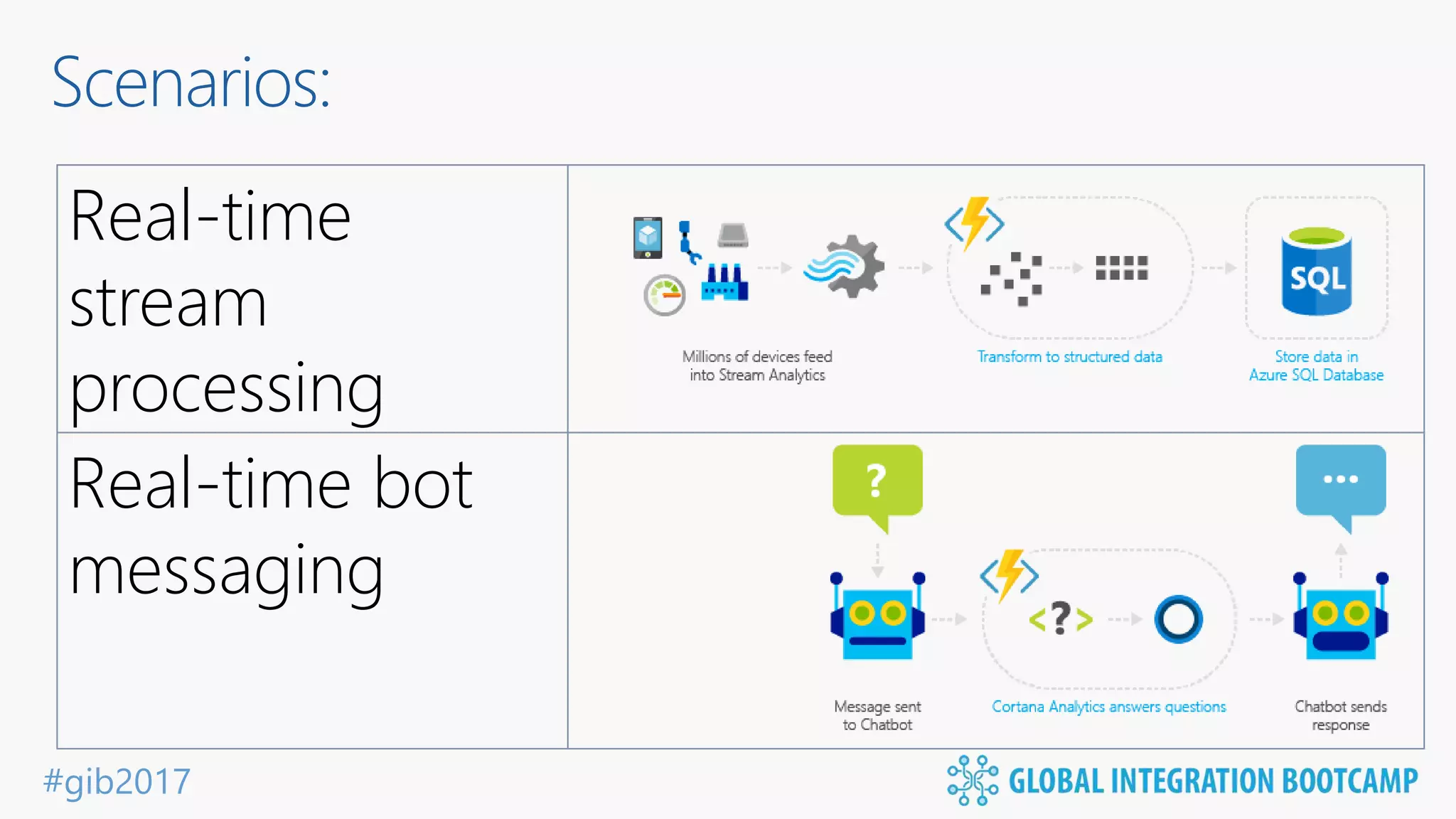
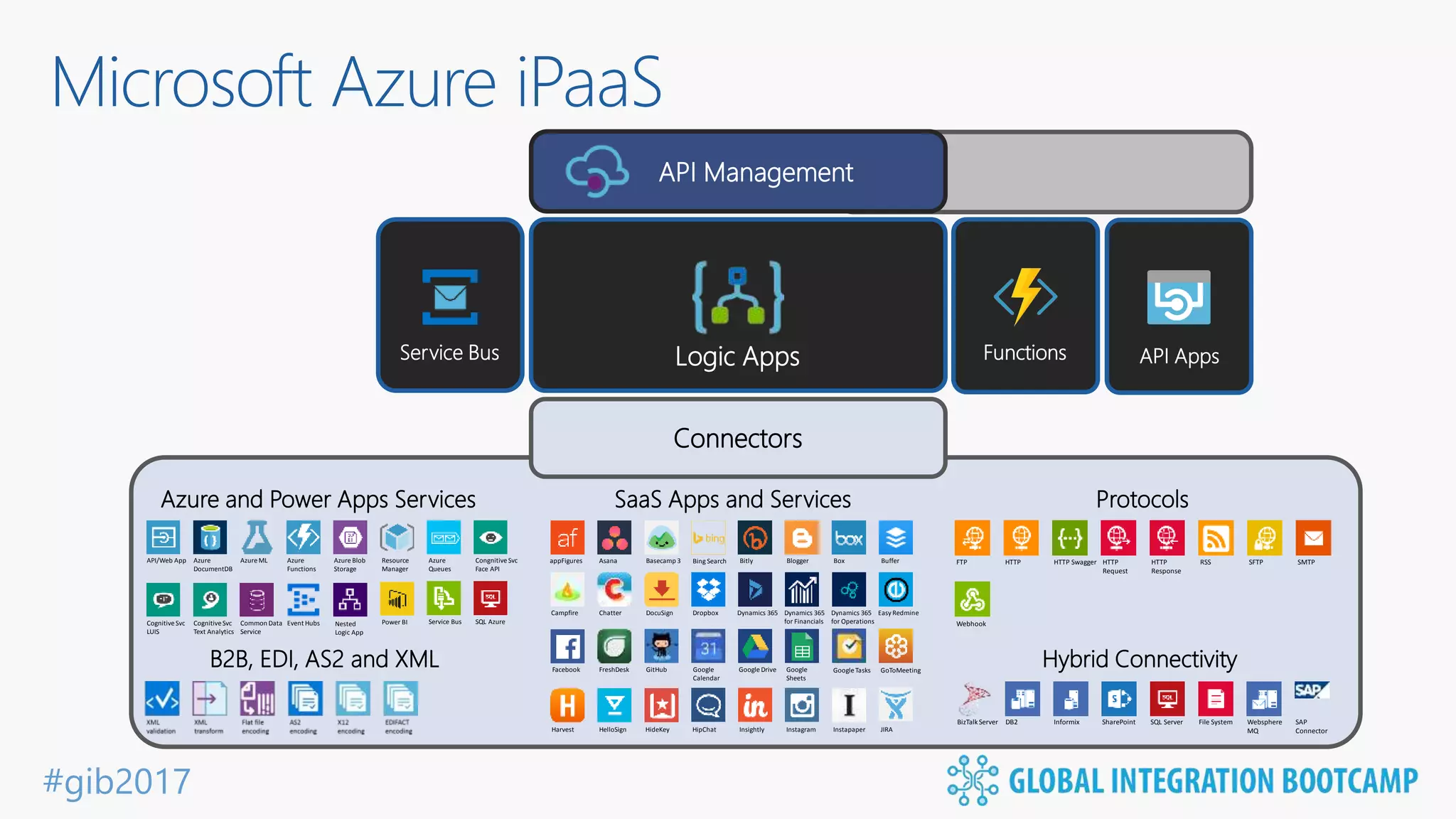
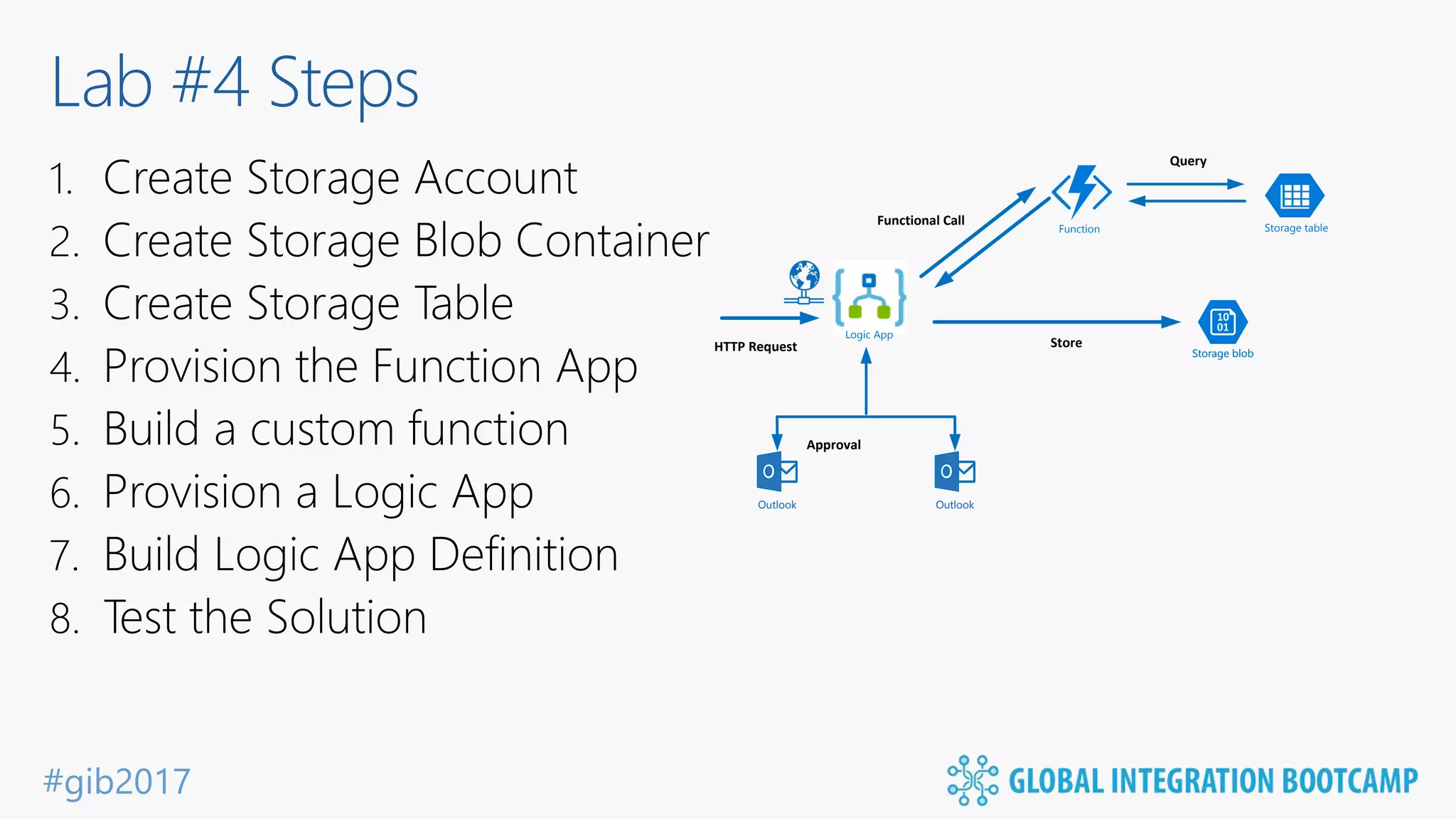
The document discusses the evolution and benefits of 'serverless' computing, focusing on Microsoft Azure's Logic Apps and Azure Functions. It highlights the ease of integration, event-driven architecture, and the ability to focus on code and deployment without managing underlying infrastructure. Additionally, it provides an overview of the various connectors and triggers available for integrating Azure services and third-party applications.