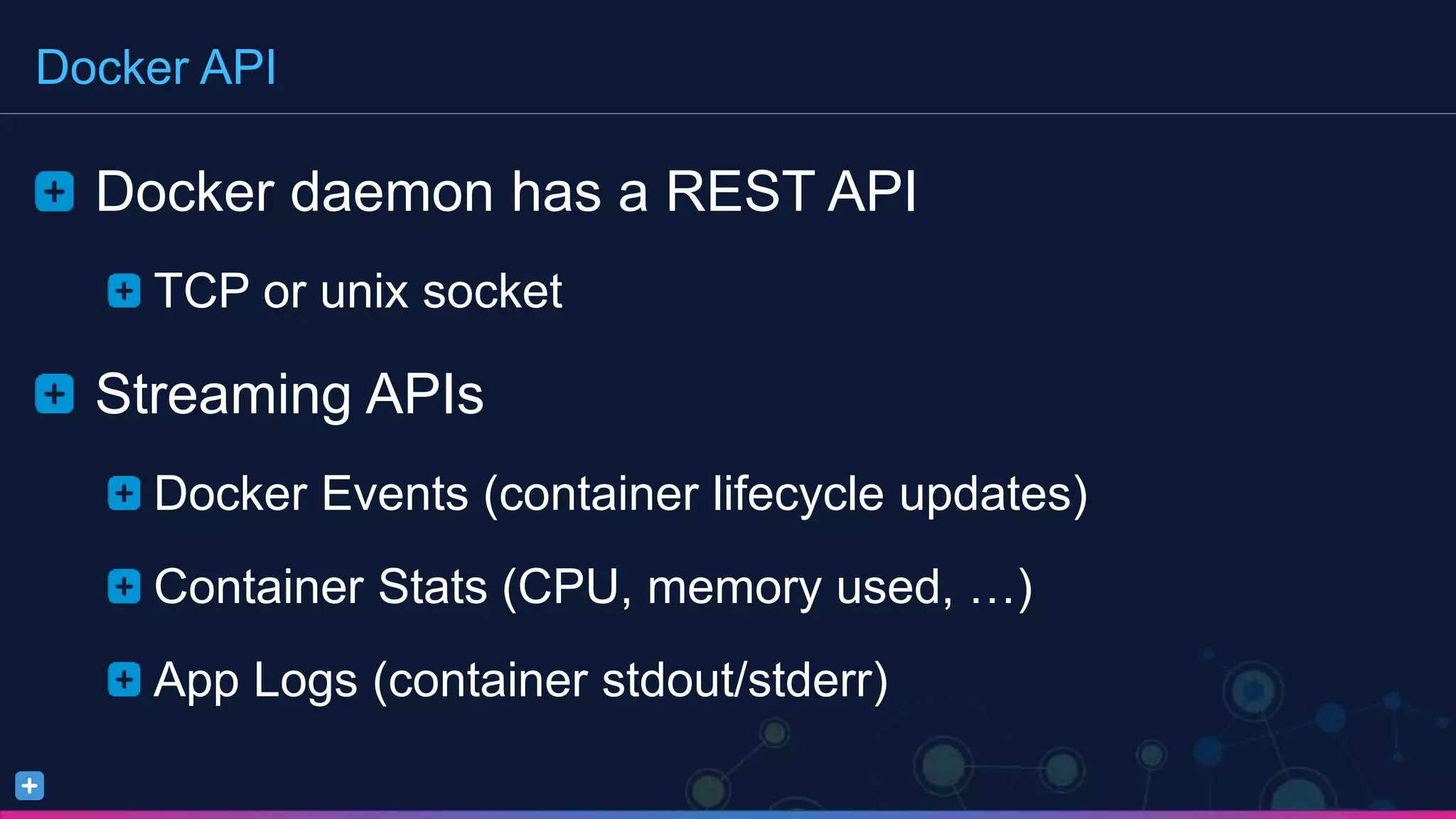
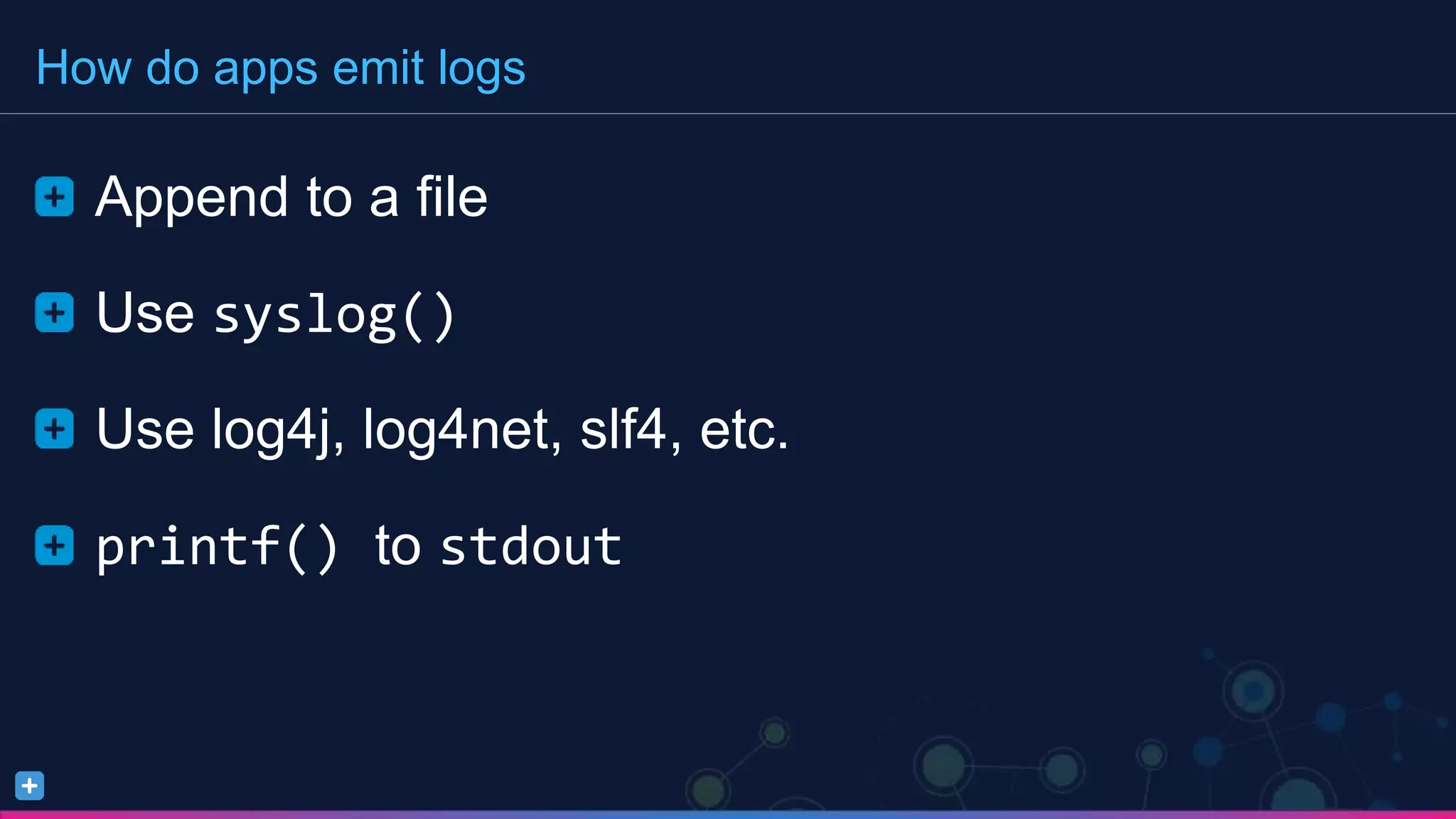
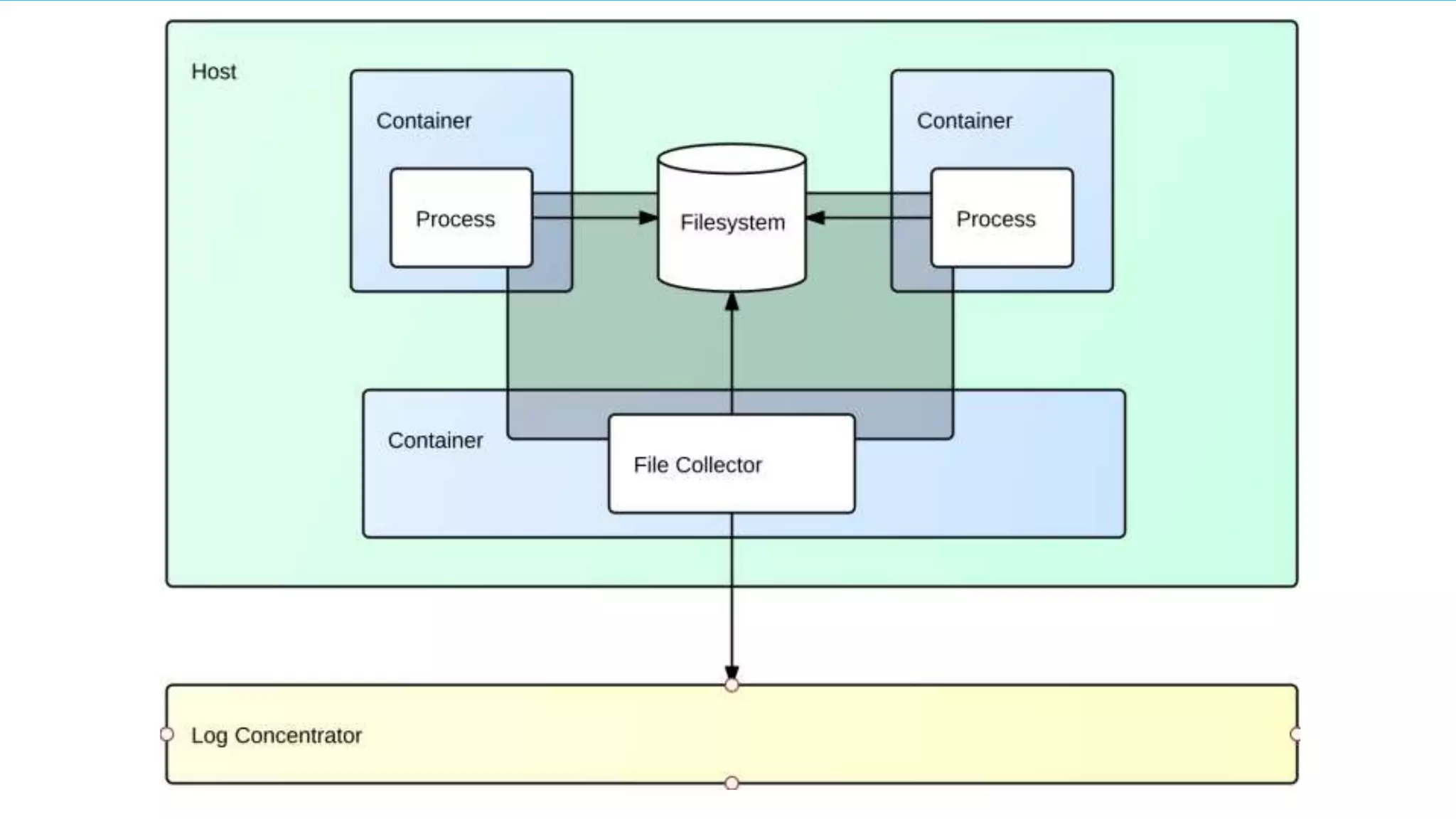
The document discusses a comprehensive monitoring solution for logging and metrics in Docker environments, highlighting challenges such as managing logs from multiple containerized applications. It details various methods for emitting logs, including using syslog, Docker logging drivers, and frameworks, and emphasizes the need for centralized log management. Additionally, it introduces the Sumo Logic Docker source as a solution for effective log collection and monitoring.







![docker run -v /tmp/clogs:/tmp/clogs -d --name="sumo-logic-collector" sumologic/collector:latest-file [Access ID] [Access key]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kansascitydevopseventsv1-150714104046-lva1-app6891/75/Logging-Metrics-with-Docker-10-2048.jpg)
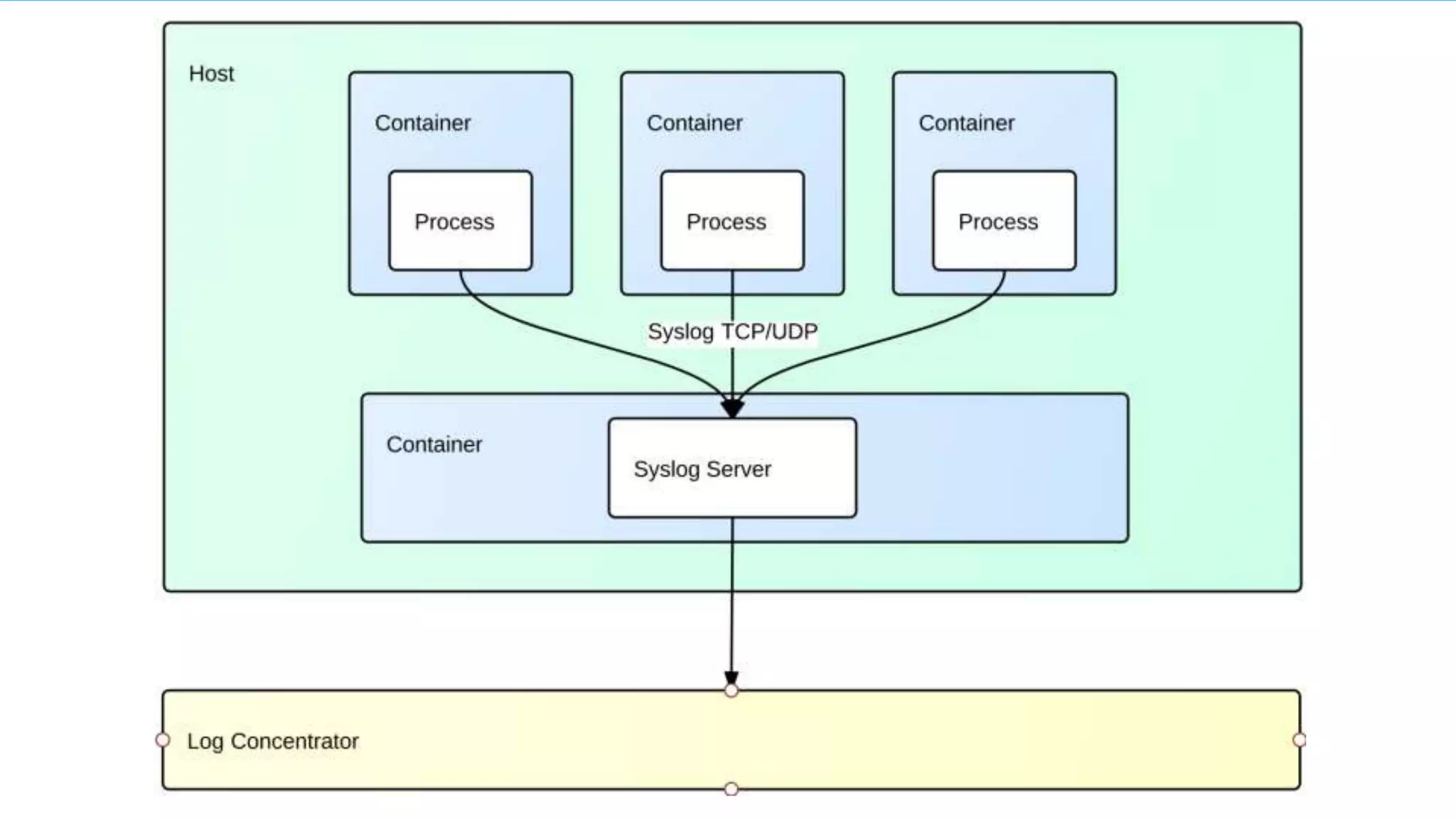
![docker run -d -p 514:514 -p 514:514/udp --name="sumo-logic-collector” sumologic/collector:latest-syslog [Access ID] [Access key]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kansascitydevopseventsv1-150714104046-lva1-app6891/75/Logging-Metrics-with-Docker-13-2048.jpg)


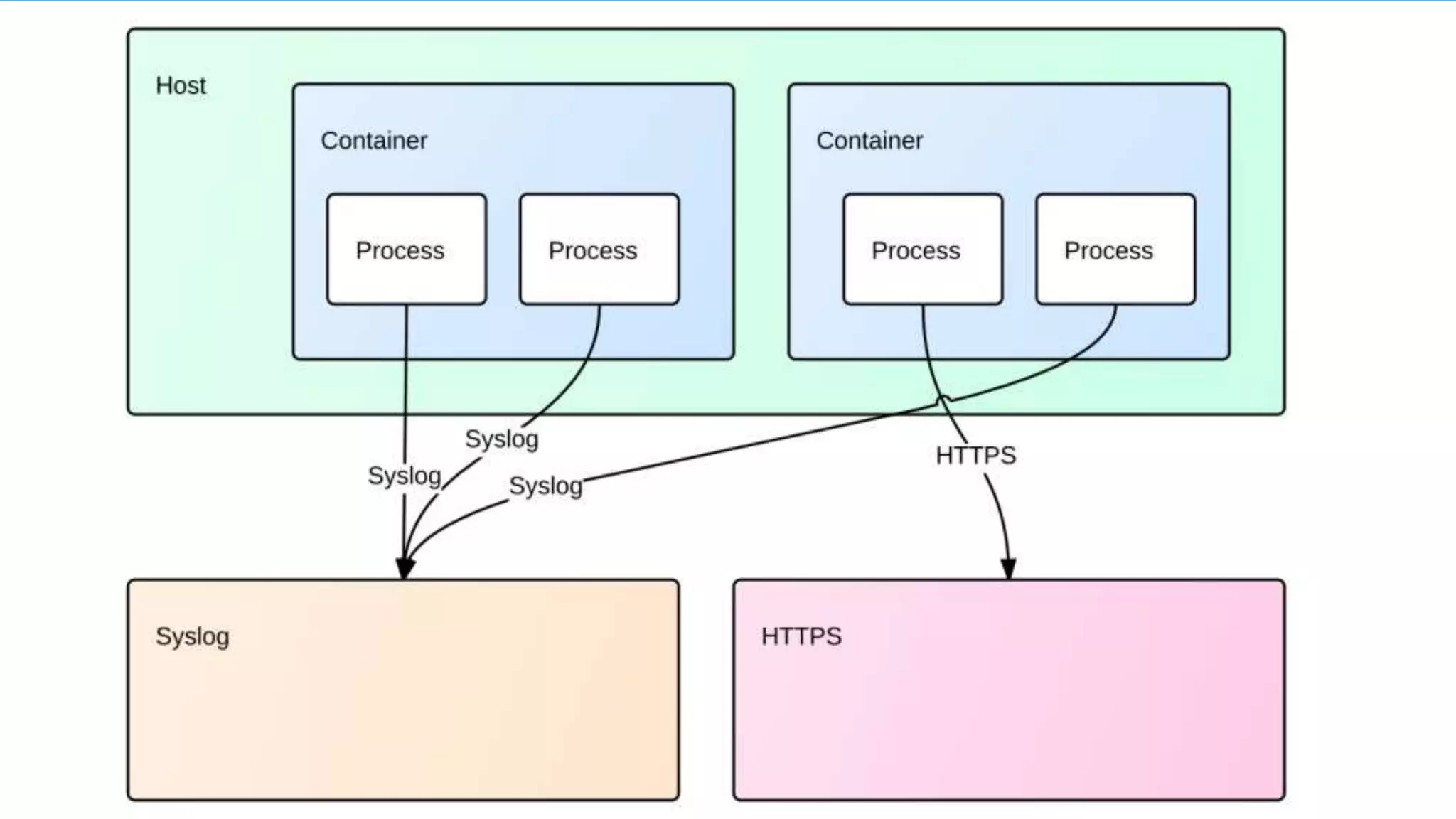


![What Docker provides Captures stdout/stderr Feeds it to logging drivers docker logs command Returns the entire log every time Works with json-file driver only Can tail logs docker logs –tf –-tail 0 [ID]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kansascitydevopseventsv1-150714104046-lva1-app6891/75/Logging-Metrics-with-Docker-20-2048.jpg)