Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times

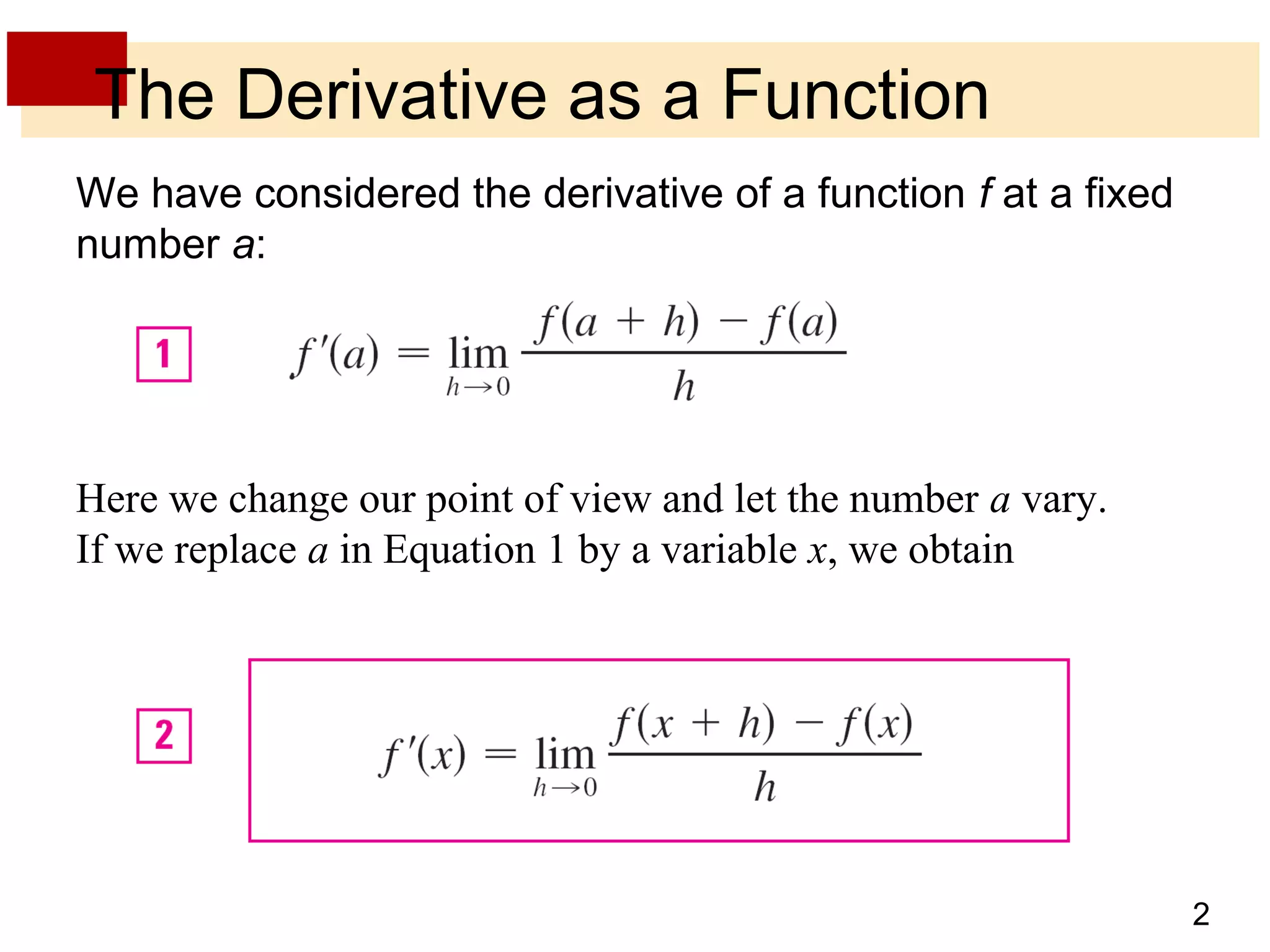
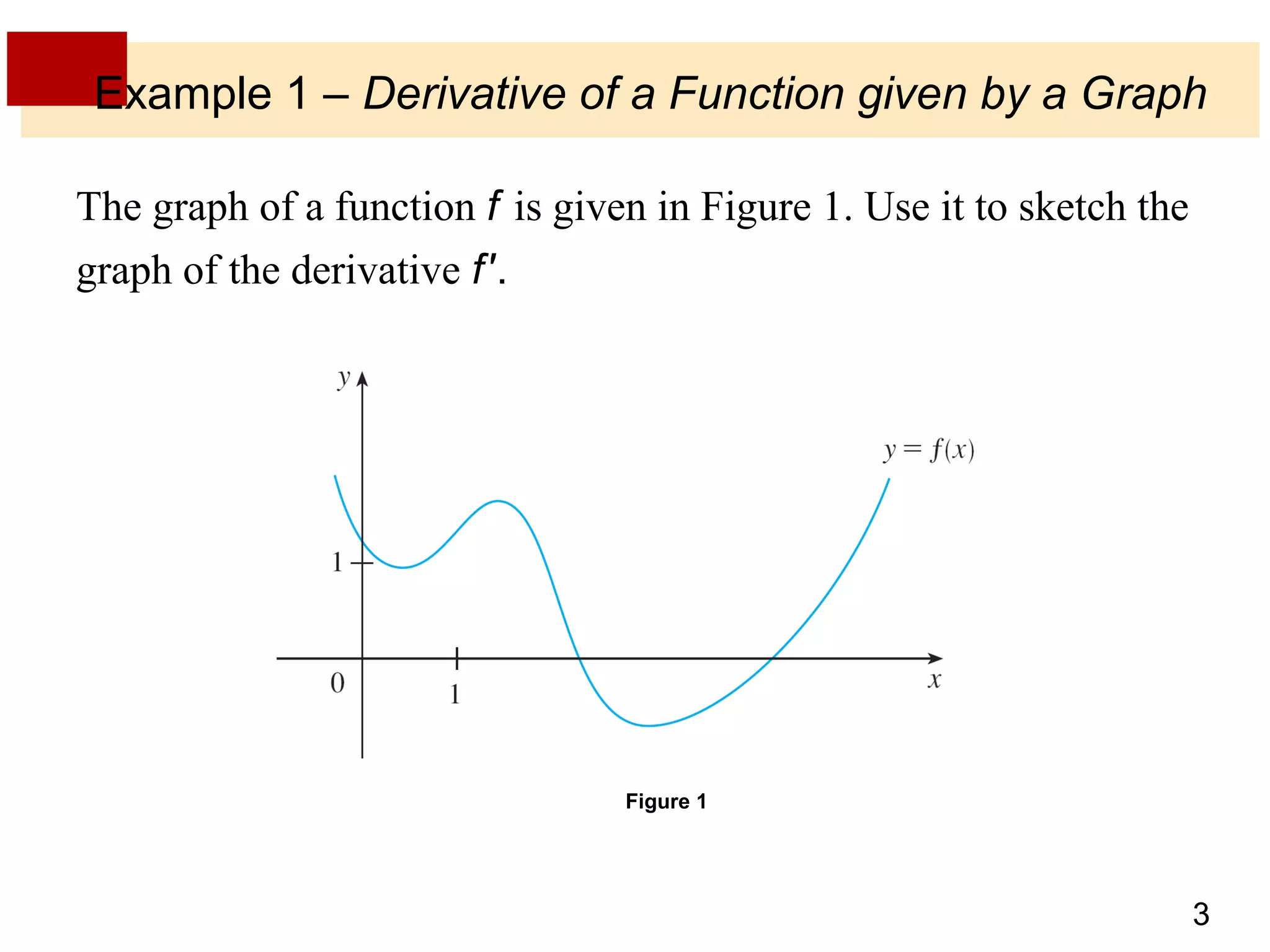
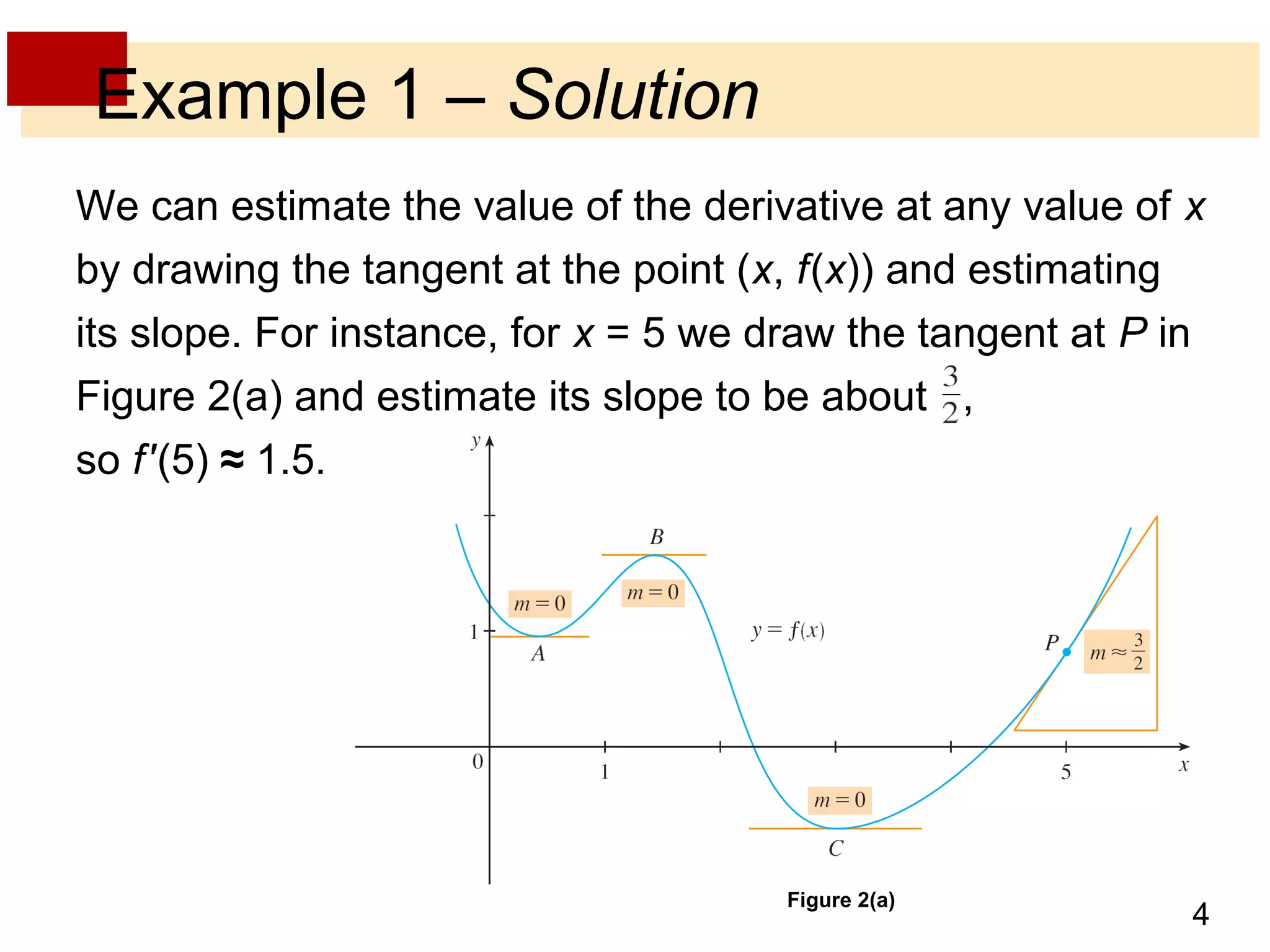
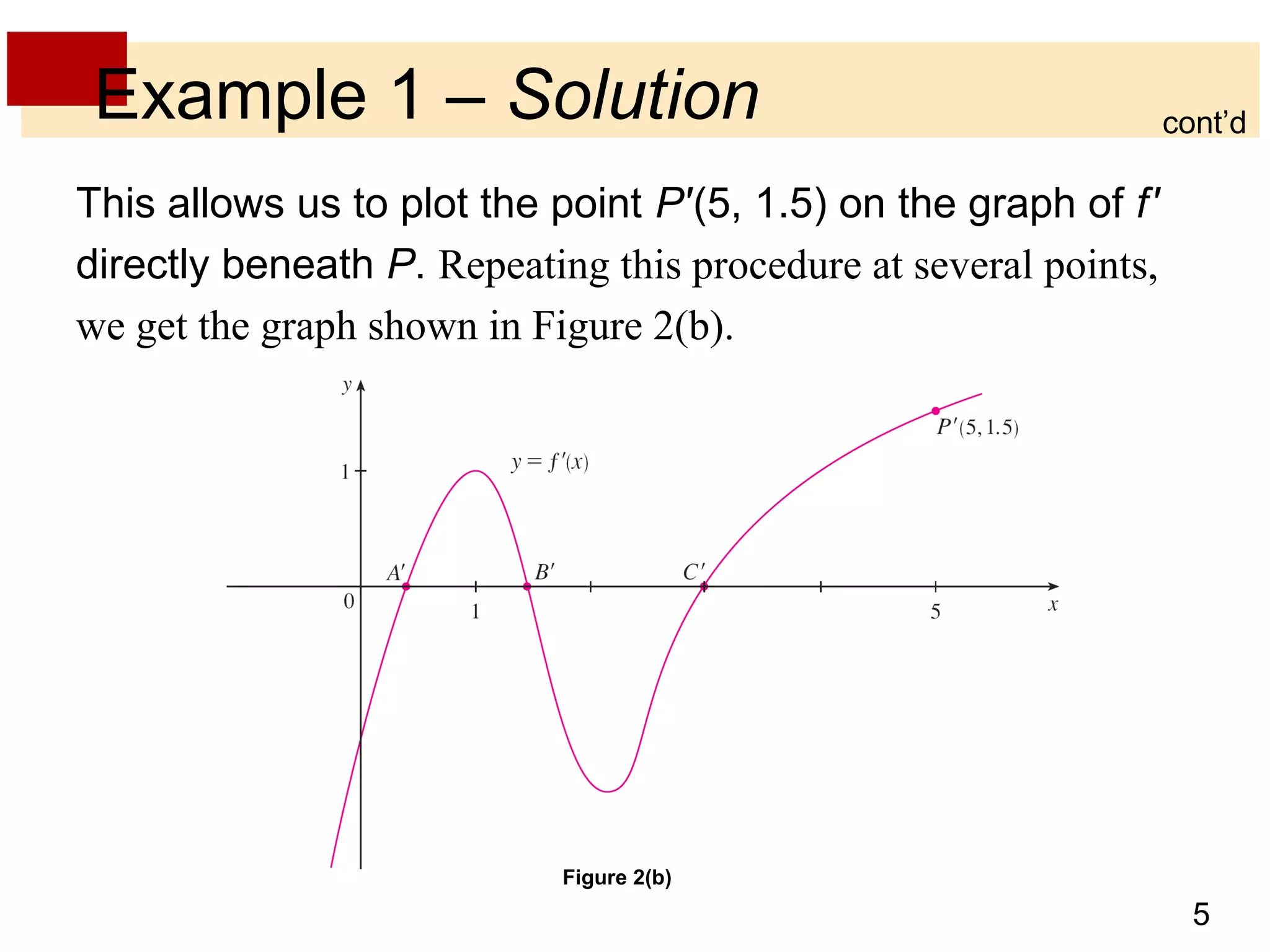
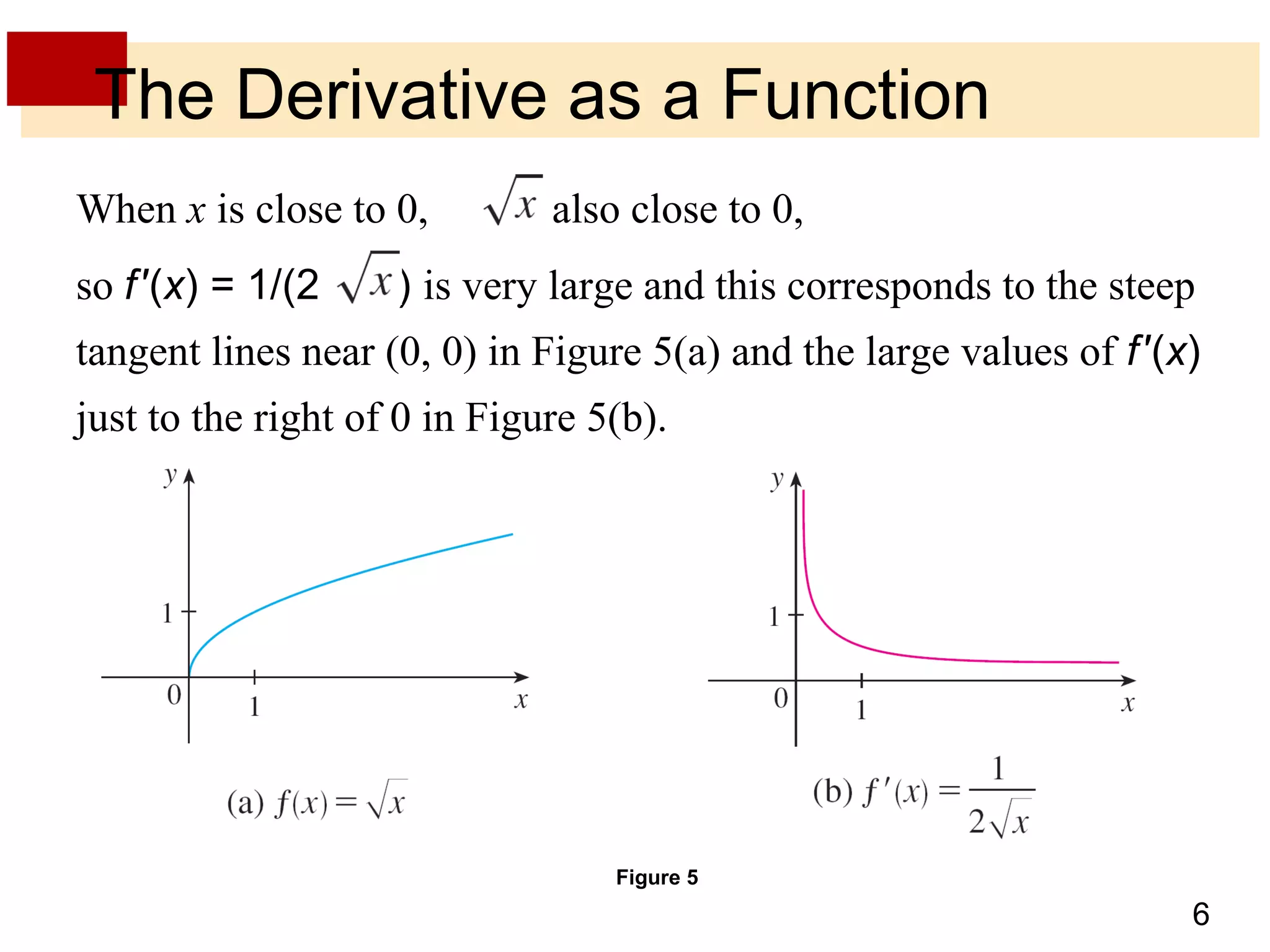

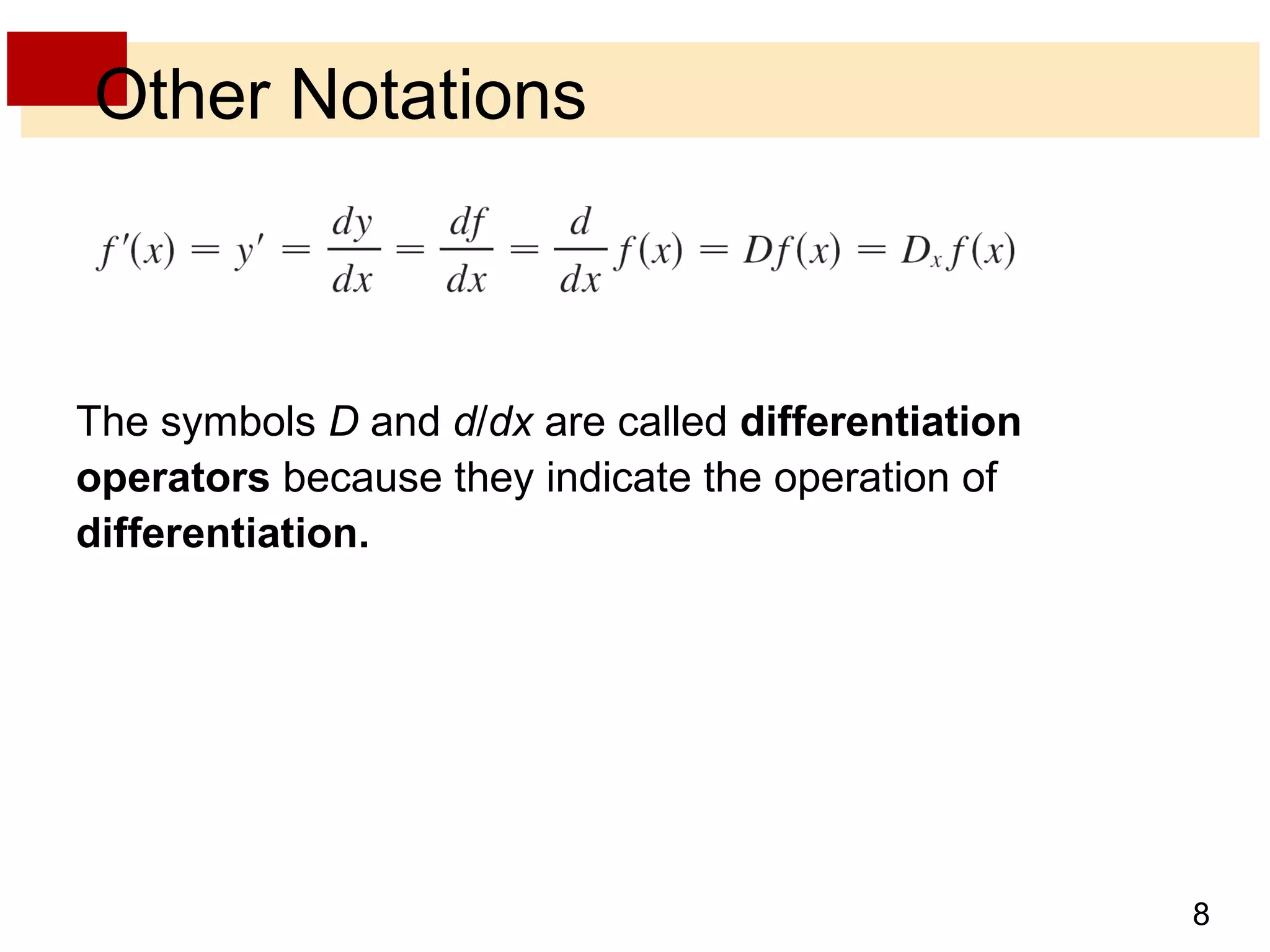
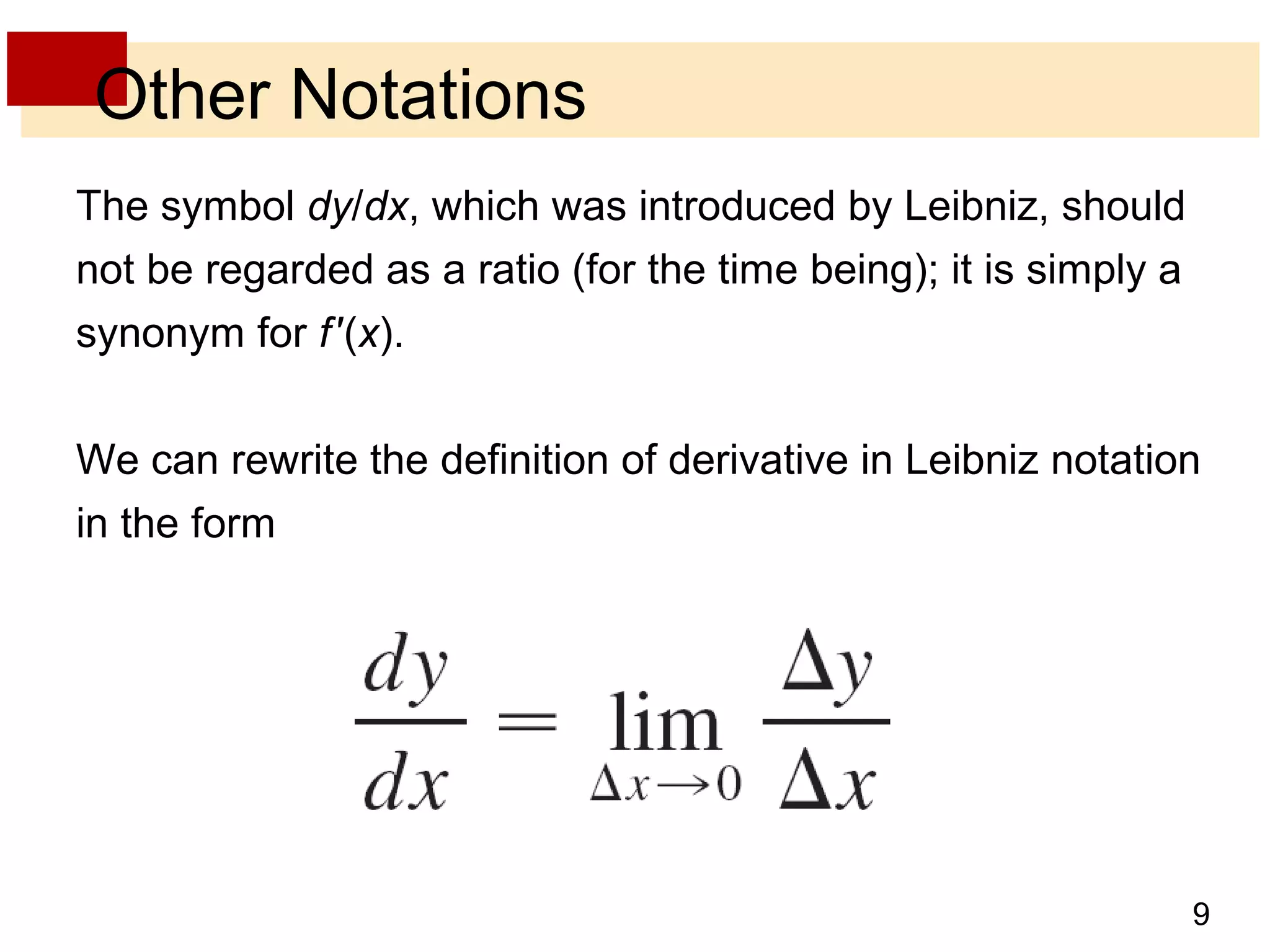
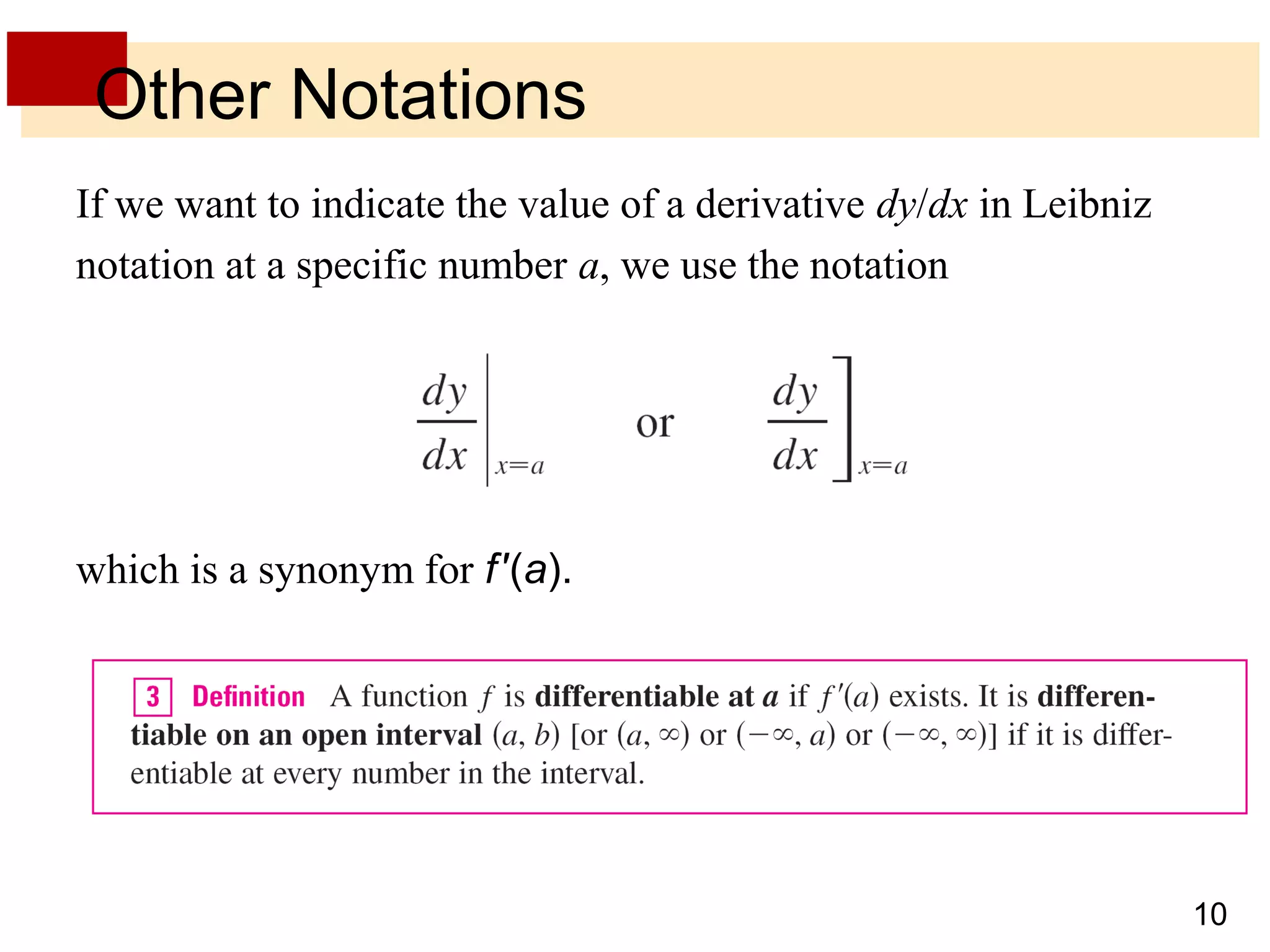
The document discusses the derivative as a function. It explains that the derivative of a function f at a number a can be written as an equation with a as a variable x, yielding the derivative as a function f'(x). It provides an example of using the graph of a function f to sketch the graph of its derivative f' by estimating the slope of tangents at various points on f and plotting corresponding points on f'. The derivative approaches very large values as x approaches 0 if f'(x) = 1/(2√x) and becomes very small as x becomes large, corresponding to flatter tangents on f and a horizontal asymptote for f'. It also discusses other notations for the derivative such as D, d









